Texas Instruments CY74FCT163H501CPVC, CY74FCT163H501CPAC, CY74FCT163501CPVCT, CY74FCT163501CPVC, CY74FCT163501CPACT Datasheet
...
Data sheet acquired from Cypress Semiconductor Corporation.
Data sheet modified to remove devices not offered.
CY74FCT163501
CY74FCT163H501
SCCS047 - January 1998 - Revised March 2000
Features
• Low power, pin-compatible replacement for LCX and LPT families
• 5V tolerant inputs and outputs
• 24 mA balanced drive outputs
• Power-off disable outputs permits live insertion
• Edge-rate control circuitry for reduced noise
• FCT-C speed at 4.6 ns
• Latch-up performance exceeds JEDEC standard no. 17
• ESD > 2000V per MIL-STD-883D, Method 3015
• Typical output skew < 250ps
• Industrial temperature range of –40˚C to +85˚C
• TSSOP (19.6-mil pitch) or SSOP (25-mil pitch)
• Typical V (ground bounce) performance exceeds Mil olp
Std 883D
• VCC = 2.7V to 3.6V
CY74FCT163501 Features:
•Balanced output drivers: 24 mA
•Reduced system switching noise
• Typical V |
(ground bounce) <0.6V at V |
CC |
= 3.3V, |
OLP |
|
|
TA= 25˚C
CY74FCT163H501 Features:
•Bus hold retains the last active state
•Devices with bus hold are not recommended for translating rail-to-rail CMOS signals to 3.3V logic levels
18-Bit Registered Transceivers
• Eliminates the need for external pull-up or pull-down resistors
Functional Description
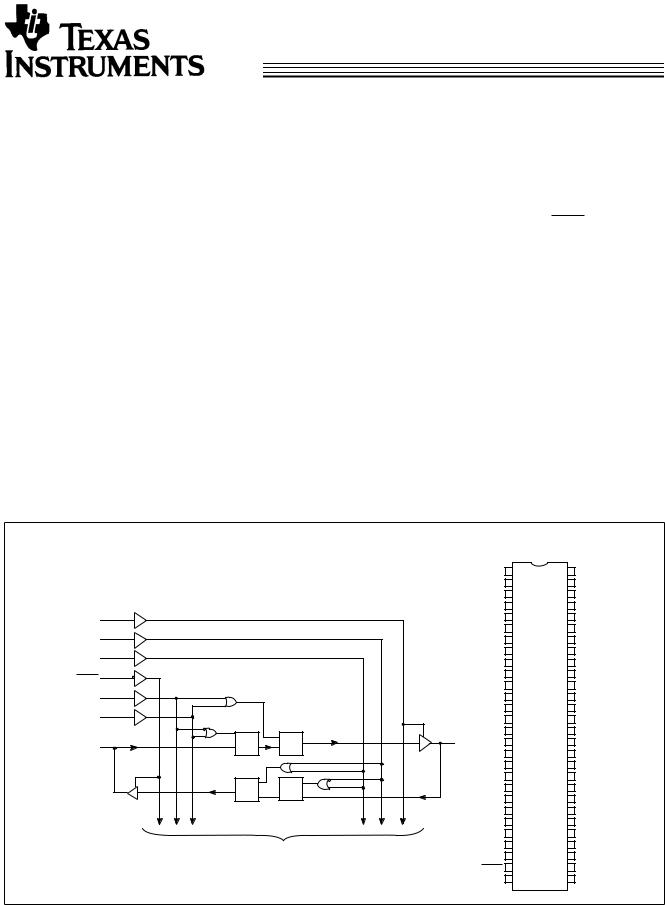
These 18-bit universal bus transceivers can be operated in transparent, latched or clock modes by combining D-type latches and D-type flip-flops. Data flow in each direction is controlled by output enable (OEAB and OEBA), latch enable (LEAB and LEBA), and clock inputs (CLKAB and CLKBA). For A-to-B data flow, the device operates in transparent mode when LEAB is HIGH. When LEAB is LOW, the A data is latched if CLKAB is held at a HIGH or LOW logic level. If LEAB is LOW, the A bus data is stored in the latch/flip-flop on the LOW-to-HIGH transition of CLKAB. OEAB performs the output enable function on the B port. Data flow from B-to-A is similar to that of A-to-B and is controlled by OEBA, LEBA, and CLKBA. The output buffers are designed with a power-off disable feature to allow live insertion of boards.
THE CY74FCT163501 has 24-mA balanced output drivers with current limiting resistors in the outputs. This reduces the need for external terminating resistors, as well as provides for minimal undershoot and reduced ground bounce. The CY74FCT163501 is ideal for driving transmission lines.
The CY74FCT163H501 is a 24-mA balanced output part, that has “bus hold” on the data inputs. The device retains the input’s last state whenever the input goes to high impedance. This eliminates the need for pull-up/down resistors and prevents floating inputs.
Functional Block Diagram; CY74FCT163501, CY74FCT163H501 |
Pin Configuration |
|||||||
|
SSOP/TSSOP |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Top View |
|
||
|
|
|
|
OEAB |
1 |
56 |
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
LEAB |
2 |
55 |
CLKAB |
|
|
|
|
|
A1 |
3 |
54 |
B1 |
|
|
|
|
|
GND |
4 |
53 |
GND |
|
OEAB |
|
|
|
A2 |
5 |
52 |
B2 |
|
|
|
|
|
A3 |
6 |
51 |
B3 |
|
CLKBA |
|
|
|
VCC |
7 |
50 |
VCC |
|
LEBA |
|
|
|
A4 |
8 |
49 |
B4 |
|
|
|
|
A5 |
9 |
48 |
B5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
OEBA |
|
|
|
A6 |
10 |
47 |
B6 |
|
|
|
|
GND |
11 |
46 |
GND |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
CLKAB |
|
|
|
A7 |
12 |
45 |
B7 |
|
LEAB |
|
|
|
A8 |
13 |
44 |
B8 |
|
|
|
|
A9 |
14 |
43 |
B9 |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
C |
C |
|
A10 |
15 |
42 |
B10 |
|
|
B1 |
A11 |
16 |
41 |
B11 |
|||
A 1 |
D |
D |
||||||
|
A12 |
17 |
40 |
B12 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
GND |
18 |
39 |
GND |
|
|
C |
C |
|
A13 |
19 |
38 |
B13 |
|
|
|
A14 |
20 |
37 |
B14 |
|||
|
D |
D |
|
|||||
|
|
A15 |
21 |
36 |
B15 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
VCC |
22 |
35 |
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
A 16 |
23 |
34 |
B16 |
|
|
|
|
|
A 17 |
24 |
33 |
B17 |
|
|
TO 17 OTHER CHANNELS |
FCT163501-1 |
GND |
25 |
32 |
GND |
||
|
A 18 |
26 |
31 |
B18 |
||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
OEBA |
27 |
30 |
CLKBA |
|
|
|
|
|
LEBA |
28 |
29 |
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FCT163501-2 |
|
Copyright © 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated

CY74FCT163501
CY74FCT163H501
Pin Description
|
Name |
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OEAB |
A-to-B Output Enable Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B-to-A Output Enable Input (Active LOW) |
|
OEBA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
LEAB |
A-to-B Latch Enable Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LEBA |
B-to-A Latch Enable Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLKAB |
A-to-B Clock Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLKBA |
B-to-A Clock Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
A-to-B Data Inputs or B-to-A Three-State |
|
|
|
|
Outputs[1] |
|
B |
B-to-A Data Inputs or A-to-B Three-State |
|
|
|
|
Outputs[1] |
Maximum Ratings[6, 7]
(Above which the useful life may be impaired. For user guidelines, not tested.)
Storage Temperature ..................................... |
−55°C to +125°C |
Ambient Temperature with |
−55°C to +125°C |
Power Applied .................................................. |
|
DC Input Voltage ................................................. |
−0.5V to +7.0V |
DC Output Voltage .............................................. |
−0.5V to +7.0V |
DC Output Current |
−60 to +120 mA |
(Maximum Sink Current/Pin) ........................... |
|
Power Dissipation .......................................................... |
1.0W |
Static Discharge Voltage............................................ |
>2001V |
(per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015) |
|
Function Table[2, 3]
|
Inputs |
|
Outputs |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
OEAB |
LEAB |
CLKAB |
A |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
X |
X |
X |
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
H |
X |
L |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
H |
X |
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
L |
|
|
L |
L |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
L |
|
|
H |
H |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
L |
L |
X |
B[4] |
|
H |
L |
H |
X |
B[5] |
|
Operating Range
|
Ambient |
|
Range |
Temperature |
VCC |
Industrial |
−40°C to +85°C |
2.7V to 3.6V |
|
|
|
1.On the 74FCT163H501 these pins have bus hold.
2.A-to-B data flow is shown. B-to-A data flow is similar but uses OEBA, LEBA, and CLKBA.
3.H = HIGH Voltage Level L = LOW Voltage Level X = Don’t Care
Z = High-impedance
 = LOW-to-HIGH Transition
= LOW-to-HIGH Transition
4.Output level before the indicated steady-state input conditions were established.
5.Output level before the indicated steady-state input conditions were established, provided that CLKAB was HIGH before LEAB went LOW.
6.Operation beyond the limits set forth may impair the useful life of the device. Unless otherwise noted, these limits are over the operating free-air temperature range.
7.Unused inputs must always be connected to an appropriate logic voltage level, preferably either VCC or ground.
2

CY74FCT163501
CY74FCT163H501
Electrical Characteristics for Non Bus Hold Devices Over the Operating Range VCC = 2.7V to 3.6V
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
|
Test Conditions |
Min. |
Typ.[8] |
Max. |
Unit |
|
VIH |
Input HIGH Voltage |
All Inputs |
|
2.0 |
|
5.5 |
V |
|||
VIL |
Input LOW Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.8 |
V |
|
VH |
Input Hysteresis[9] |
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
mV |
|
VIK |
Input Clamp Diode Voltage |
VCC=Min., IIN=–18 mA |
|
–0.7 |
–1.2 |
V |
||||
IIH |
Input HIGH Current |
VCC=Max., VI=5.5 |
|
|
|
±1 |
µA |
|||
IIL |
Input LOW Current |
VCC=Max., VI=GND |
|
|
±1 |
µA |
||||
IOZH |
High Impedance Output Current |
VCC=Max., VOUT=5.5V |
|
|
±1 |
µA |
||||
|
|
(Three-State Output pins) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
IOZL |
High Impedance Output Current |
VCC=Max., VOUT=GND |
|
|
±1 |
µA |
||||
|
|
(Three-State Output pins) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
OS |
Short Circuit Current[10] |
V |
CC |
=Max., V =GND |
–60 |
–135 |
–240 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
OUT |
|
|
|
|
|
||
IOFF |
Power-Off Disable |
VCC=0V, VOUT≤4.5V |
|
|
±100 |
µA |
||||
ICC |
Quiescent Power Supply Current |
VIN≤0.2V, |
VCC=Max. |
|
0.1 |
10 |
µA |
|||
|
|
|
VIN>VCC–0.2V |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
ICC |
Quiescent Power Supply Current |
VIN=VCC–0.6V[11] |
VCC=Max. |
|
2.0 |
30 |
µA |
||
|
|
(TTL inputs HIGH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.Typical values are at VCC=3.3V, TA = +25˚C ambient.
9.This parameter is specified but not tested.
10.Not more than one output should be shorted at a time. Duration of short should not exceed one second. The use of high-speed test apparatus and/or sample and hold techniques are preferable in order to minimize internal chip heating and more accurately reflect operational values. Otherwise prolonged shorting of a high output may raise the chip temperature well above normal and thereby cause invalid readings in other parametric tests. In any sequence of parameter tests, IOS tests should be performed last.
11.Per TTL driven input (VIN=3.4V); all other inputs at VCC or GND.
3
 Loading...
Loading...