Motorola MC10E116FN, MC10E116FNR2, MC100E116FNR2, MC100E116FN Datasheet

MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Quint Differential Line
Receiver
The MC10E/100E116 is a quint differential line receiver with emitter-follower outputs. An internally generated reference supply (VBB) is available for single-ended reception.
•500ps Max. Propagation Delay
•VBB Supply Output
•Dedicated VCCO Pin for Each Receiver
•Extended 100E VEE Range of ± 4.2V to ± 5.46V
•75kΩ Input Pulldown Resistors
MC10E116
MC100E116
QUINT DIFFERENTIAL
LINE RECEIVER
Active current sources plus a deep collector feature of the MOSAIC III process provide the receivers with excellent common-mode noise rejection. Each receiver has a dedicated VCCO supply lead, providing optimum symmetry and stability.
The receiver design features clamp circuitry to cause a defined state if both the inverting and non-inverting inputs are left open; in this case the Q output goes LOW, while the Q output goes HIGH. This feature makes the device ideal for twisted pair applications.
If both inverting and non-inverting inputs are at an equal potential of > ±2.5V, the receiver does not go to a defined state, but rather current-shares in normal differential amplifier fashion, producing output voltage levels midway between HIGH and LOW, or the device may even oscillate.
FN SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 776-02
The device VBB output is intended for use as a reference voltage for single-ended reception of ECL signals to that device only. When using for this purpose, it is recommended that VBB is decoupled to VCC via a 0.01μF capacitor. Please refer to the interface section of the design guide for information on using the E116 in specialized applications.
The E116 features input pull-down resistors, as does the rest of the ECLinPS family. For applications which require bandwidths greater than that of the E116, the E416 device may be of interest.
Pinout: 28-Lead PLCC (Top View)
PIN NAMES
Pin |
Function |
||
|
|
|
|
D0, D0 ± D4, |
D4 |
|
Differential Input Pairs |
Q0, Q0 ± Q4, Q4 |
Differential Output Pairs |
||
VBB |
Reference Voltage Output. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
D3 |
|
D4 |
|
D4 |
VCCO |
Q4 |
|
Q4 |
VCCO |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
24 |
|
23 |
|
22 |
|
|
21 |
|
20 |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
D3 |
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
Q3 |
|||||
|
D2 |
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
Q3 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC |
||||||
|
D2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|||
VEE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q2 |
||||||||
VBB |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
Q2 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
D0 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
VCCO |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
Q1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
5 |
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D1 |
|
D1 |
VCCO |
|
Q0 |
|
Q0 |
VCCO |
|
Q1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
* All VCC and VCCO pins are tied together on the die. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5/95
Motorola, Inc. 1996 |
REV 3 |
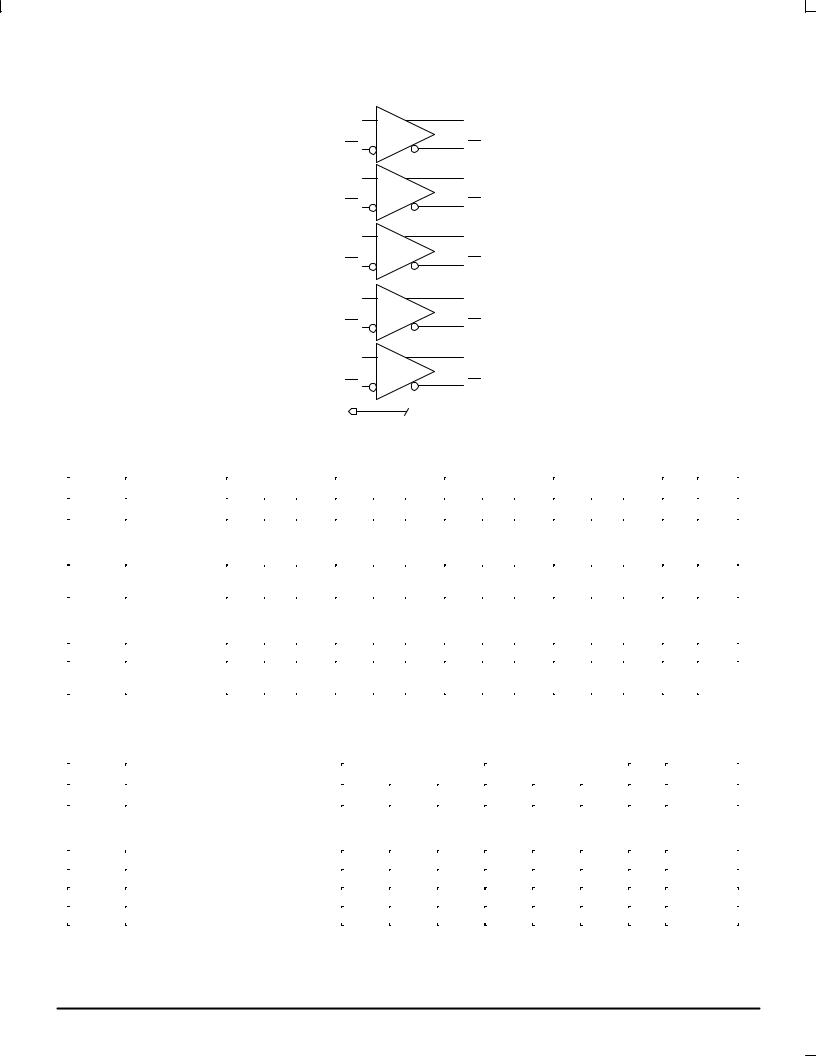
MC10E116 MC100E116
|
LOGIC DIAGRAM |
D0 |
Q0 |
D0 |
Q0 |
D1 |
Q1 |
D1 |
Q1 |
D2 |
Q2 |
D2 |
Q2 |
D3 |
Q3 |
D3 |
Q3 |
D4 |
Q4 |
D4 |
Q4 |
VBB
DC CHARACTERISTICS (VEE = VEE(min) to VEE(max); VCC = VCCO = GND)
|
|
|
|
±40°C |
|
|
0°C |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Symbol |
Characteristic |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
Cond |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VBB |
Output Reference |
±1.43 |
|
±1.30 |
±1.38 |
|
±1.27 |
±1.35 |
|
±1.25 |
±1.31 |
|
±1.19 |
V |
|
|
|
Voltage |
10E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
100E |
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IIH |
Input HIGH |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
200 |
|
|
200 |
|
|
200 |
μA |
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IEE |
Power Supply |
|
29 |
35 |
|
29 |
35 |
|
29 |
35 |
|
29 |
35 |
mA |
|
|
|
Current |
10E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
100E |
|
29 |
35 |
|
29 |
35 |
|
29 |
35 |
|
29 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VPP(DC) |
Input Sensitivity |
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
mV |
1 |
|
VCMR |
Commom Mode |
±2.0 |
|
±0.6 |
±2.0 |
|
±0.6 |
±2.0 |
|
±0.6 |
±2.0 |
|
±0.6 |
V |
2 |
|
|
Range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.Differential input voltage required to obtain a full ECL swing on the outputs.
2.VCMR is defined as the range within which the VIH level may vary, with the device still meeting the propagation delay specification. The VIL level must be such that the peak to peak voltage is less than 1.0 V and greater than or equal to VPP(min).
AC CHARACTERISTICS (VEE = VEE (min) to VEE (max); VCC = VCCO = GND)
|
|
|
|
±40°C |
|
|
0°C to 85°C |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Symbol |
Characteristic |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
|
Typ |
|
Max |
Unit |
Condition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tPLH |
Propagation Delay to Output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|
tPHL |
|
D (Differential) |
150 |
300 |
500 |
200 |
|
300 |
|
450 |
|
|
|
|
D (Single-Ended) |
150 |
300 |
550 |
150 |
|
300 |
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tskew |
Within-Device Skew |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
ps |
1 |
tskew |
Duty Cycle Skew |
tPLH ± tPHL |
|
±10 |
|
|
|
±10 |
|
|
ps |
2 |
VPP(AC) |
Minimum Input Swing |
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
|
mV |
3 |
tr/tf |
Rise/Fall Time |
|
250 |
375 |
625 |
275 |
|
375 |
|
575 |
ps |
20±80% |
1.Within-device skew is defined as identical transitions on similar paths through a device.
2.Duty cycle skew is defined only for differential operation when the delays are measured from the cross point of the inputs to the cross point of the outputs.
3.Minimum input swing for which AC parameters are guaranteed.
MOTOROLA |
2±2 |
 Loading...
Loading...