MOTOROLA MC10E211FN, MC10E211FNR2, MC100E211FNR2 Datasheet
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
1:6 Differential Clock
Distribution Chip
The MC10E/100E211 is a low skew 1:6 fanout device designed explicitly for low skew clock distribution applications. The device can be driven by either a differential or single-ended ECL or, if positive power supplies are used, PECL input signal (PECL is an acronym for Positive ECL, PECL levels are ECL levels referenced to +5V rather than ground). If a single-ended input is to be used the VBB pin should be connected to the CLK input and bypassed to ground via a 0.01μF capacitor. The VBB supply is designed to act as the switching reference for the input of the E211 under single-ended input conditions, as a result this pin can only source/sink up to 0.5mA of current.
•Guaranteed Low Skew Specification
•Synchronous Enabling/Disabling
•Multiplexed Clock Inputs
•VBB Output for Single-Ended Use
•Internal 75kΩ Input Pulldown Resistors
•Common and Individual Enable/Disable Control
•High Bandwidth Output Transistors
•Extended 100E VEE Range of ±4.2V to ±5.46V
The E211 features a multiplexed clock input to allow for the distribution of a lower speed scan or test clock along with the high speed system clock. When LOW (or left open in which case it will be pulled LOW by the input pulldown resistor) the SEL pin will select the differential clock input.
MC10E211
MC100E211
1:6 DIFFERENTIAL
CLOCK DISTRIBUTION CHIP
FN SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 776-02
Both a common enable and individual output enables are provided. When asserted the positive output will go LOW on the next negative transition of the CLK (or SCLK) input. The enabling function is synchronous so that the outputs will only be enabled/disabled when the outputs are already in the LOW state. In this way the problem of runt pulse generation during the disable operation is avoided. Note that the internal flip flop is clocked on the falling edge of the input clock edge, therefore all associated specifications are referenced to the negative edge of the CLK input.
The output transitions of the E211 are faster than the standard ECLinPS edge rates. This feature provides a means of distributing higher frequency signals than capable with the E111 device. Because of these edge rates and the tight skew limits guaranteed in the specification, there are certain termination guidelines which must be followed. For more details on the recommended termination schemes please refer to the applications information section of this data sheet.
FUNCTION TABLE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLK |
SCLK |
SEL |
|
ENx |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H/L |
X |
L |
|
L |
CLK |
|
X |
H/L |
H |
|
L |
SCLK |
|
Z* |
Z* |
X |
|
H |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Z = Negative transition of CLK or SCLK
ECLinPS is a trademark of Motorola Inc.
5/95
Motorola, Inc. 1996 |
2±1 |
REV 3 |
MC10E211 MC100E211
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EN4 |
|
EN5 |
VCC0 |
Q5 |
|
Q5 |
|
Q4 |
|
Q4 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
24 |
|
23 |
|
22 |
|
21 |
|
20 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
EN3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q3 |
||||||||||
|
|
SEL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
Q3 |
||||||
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
SCLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
VCC |
||||||||
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
VEE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q2 |
|||||||||||
|
CLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
Q2 |
|||||||
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
CLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q1 |
||||||||||
VBB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
Q1 |
||||||||
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
10 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC0 |
Q0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CEN |
EN2 |
|
EN1 |
|
EN0 |
|
|
Q0 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
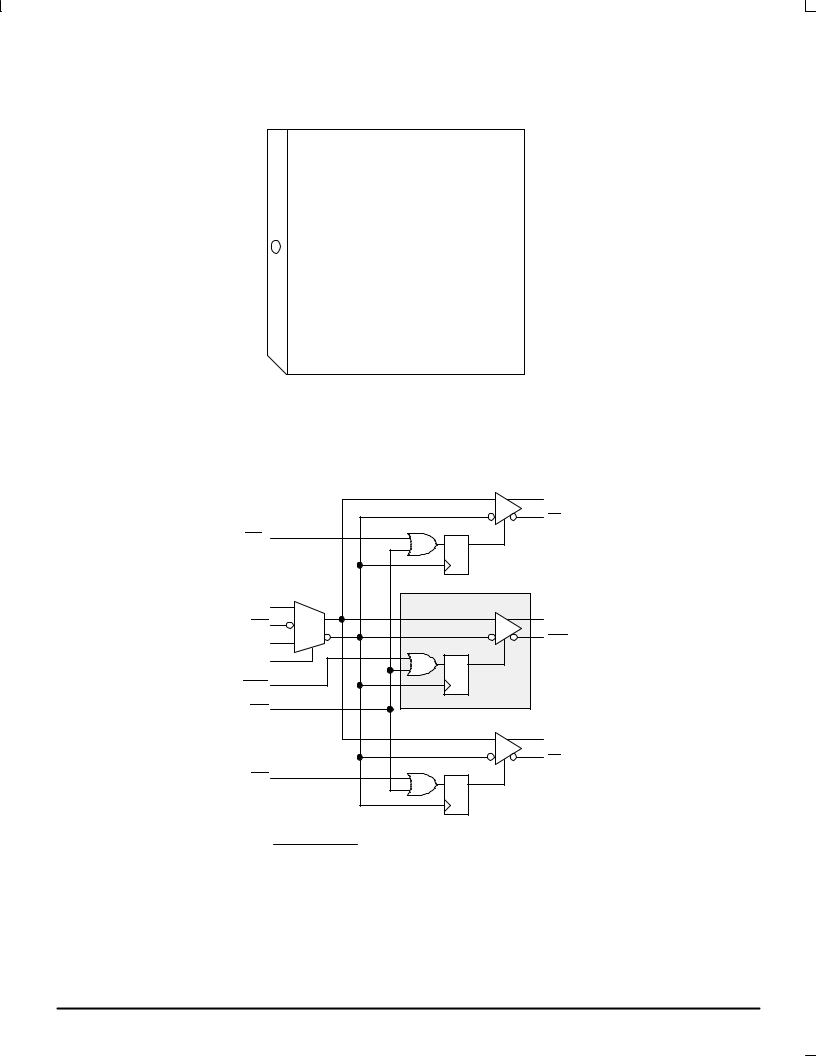
Pinout: 28-Lead PLCC (Top View)
|
|
Q0 |
|
|
|
Q0 |
|
EN0 |
|
DQ |
|
|
|
||
CLK |
0 |
BITS 1-4 |
|
Q1-4 |
|||
CLK |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
SCLK |
1 |
Q1-4 |
|
|
|
||
SEL |
|
DQ |
|
EN1-4 |
|
|
|
CEN |
|
|
|
|
|
Q5 |
|
|
|
Q5 |
|
EN5 |
|
DQ |
|
|
|
VBB 
Logic Diagram
MOTOROLA |
2±2 |
ECLinPS and ECLinPS Lite |
DL140 Ð Rev 4

MC10E211 MC100E211
DC CHARACTERISTICS (VEE = VEE(min) to VEE(max); VCC = VCCO = GND)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0°C |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
Condition |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Reference Voltage |
VBB |
±1.38 |
|
±1.27 |
±1.35 |
|
±1.25 |
±1.31 |
|
±1.19 |
V |
|
|||||||
|
10E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
100E |
|
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
±1.38 |
|
±1.26 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input High Current |
IIH |
|
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
μA |
|
|||||||
Power Supply Current |
IEE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mA |
|
|||||||
|
10E |
|
|
119 |
160 |
|
119 |
160 |
|
119 |
160 |
|
|
||||||
|
100E |
|
|
119 |
160 |
|
119 |
160 |
|
137 |
164 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC CHARACTERISTICS (VEE = VEE(min) to VEE(max); VCC = VCCO = GND) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0°C |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
Condition |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Propagation Delay to Output |
tPLH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|||||||
|
CLK to Q (Diff) |
tPHL |
795 |
930 |
1065 |
805 |
940 |
1075 |
825 |
960 |
1095 |
|
|
||||||
|
CLK to Q (SE) |
|
745 |
930 |
1115 |
755 |
940 |
1125 |
775 |
960 |
1145 |
|
|
||||||
|
SCLK to Q |
|
650 |
900 |
1085 |
650 |
910 |
1095 |
650 |
930 |
1115 |
|
|
||||||
|
SEL to Q |
|
745 |
970 |
1195 |
755 |
980 |
1205 |
775 |
1000 |
1225 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable Time |
tPHL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|||||||
|
CLK or SCLK to Q |
|
|
600 |
800 |
|
600 |
800 |
|
600 |
800 |
|
2 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part±to±Part Skew |
tskew |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|||||||
|
CLK (Diff) to Q |
|
|
|
270 |
|
|
270 |
|
|
270 |
|
|
||||||
|
CLK (SE), SCLK to Q |
|
|
|
370 |
|
|
370 |
|
|
370 |
|
|
||||||
|
Within-Device Skew |
|
|
50 |
75 |
|
50 |
75 |
|
|
75 |
|
1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Setup Time |
ts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|||||||
|
EN |
x to CLK |
|
200 |
±100 |
|
200 |
±100 |
|
200 |
±100 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
CEN |
to CLK |
|
200 |
0 |
|
200 |
0 |
|
200 |
0 |
|
|
2 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Hold Time |
th |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|||||||
|
CLK to |
|
|
|
|
|
900 |
600 |
|
900 |
160 |
|
900 |
600 |
|
|
2 |
||
|
ENx, CEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Minimum Input Swing (CLK) |
VPP |
0.25 |
|
1.0 |
0.25 |
|
1.0 |
0.25 |
|
1.0 |
V |
3 |
|||||||
Com. Mode Range (CLK) |
VCMR |
±0.4 |
|
Note |
±0.4 |
|
Note |
±0.4 |
|
Note |
V |
4 |
|||||||
Rise/Fall Times |
tr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ps |
|
|||||||
20 ± 80% |
|
|
|
tf |
150 |
|
400 |
150 |
|
400 |
150 |
|
400 |
|
|
||||
1.Within-Device skew is defined for identical transitions on similar paths through a device.
2.Setup, Hold and Disable times are all relative to a falling edge on CLK or SCLK.
3.Minimum input swing for which AC parameters are guaranteed. Full DC ECL output swings will be generated with only 50mV input swings.
4.The range in which the high level of the input swing must fall while meeting the VPP spec. The lower end of the range is VEE dependent and can be calculated as VEE + 2.4V.
ECLinPS and ECLinPS Lite |
2±3 |
MOTOROLA |
DL140 Ð Rev 4 |
|
|
 Loading...
Loading...