Texas Instruments TLC3702MJGB, TLC3702MJG, TLC3702MFKB, TLC3702MDR, TLC3702MD Datasheet
...
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TLC3702 |
||
|
VOLTAGE COMPARATORS |
||||||||
|
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
D Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive |
D, JG, OR P PACKAGE |
||||||||
Loads Without Pullup Resistor, |
|
|
|
|
(TOP VIEW) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IO = ± 8 mA |
1OUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
|
|
|
|
1 |
8 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
D Very Low Power . . . 100 μW Typ at 5 V |
|
|
|
|
|||||
1IN ± |
|
|
2 |
7 |
|
2OUT |
|||
D Fast Response Time . . . tPLH = 2.7 μs Typ |
|
|
|||||||
1IN + |
|
|
|
3 |
6 |
|
2IN ± |
||
With 5-mV Overdrive |
GND |
|
|
|
4 |
5 |
|
2IN + |
|
D Single-Supply Operation . . . 3 V to 16 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TLC3702M . . . 4 V to 16 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D On-Chip ESD Protection |
|
FK PACKAGE |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
(TOP VIEW) |
|
|
||||
description
The TLC3702 consists of two independent micropower voltage comparators designed to operate from a single supply and be compatible with modern HCMOS logic systems. They are functionally similar to the LM339 but use onetwentieth of the power for similar response times. The push-pull CMOS output stage drives capacitive loads directly without a powerconsuming pullup resistor to achieve the stated response time. Eliminating the pullup resistor not only reduces power dissipation, but also saves board space and component cost. The output stage is also fully compatible with TTL requirements.
Texas Instruments LinCMOS process offers superior analog performance to standard CMOS processes. Along with the standard CMOS advantages of low power without sacrificing speed, high input impedance, and low bias currents, the LinCMOS process offers extremely stable input offset voltages with large differential input voltages. This characteristic makes it possible to build reliable CMOS comparators.
|
NC |
1OUT |
NC |
V |
NC |
|
|
|
|
|
DD |
|
|
NC |
3 |
2 |
1 |
20 19 |
NC |
|
4 |
|
|
|
18 |
||
1IN ± |
5 |
|
|
|
17 |
2OUT |
NC |
6 |
|
|
|
16 |
NC |
1IN + |
7 |
|
|
|
15 |
2IN ± |
NC |
8 |
|
|
|
14 |
NC |
|
9 |
10 11 12 13 |
|
|||
|
NC |
GND |
NC |
2IN+ |
NC |
|
NC ± No internal connection |
|
|||||
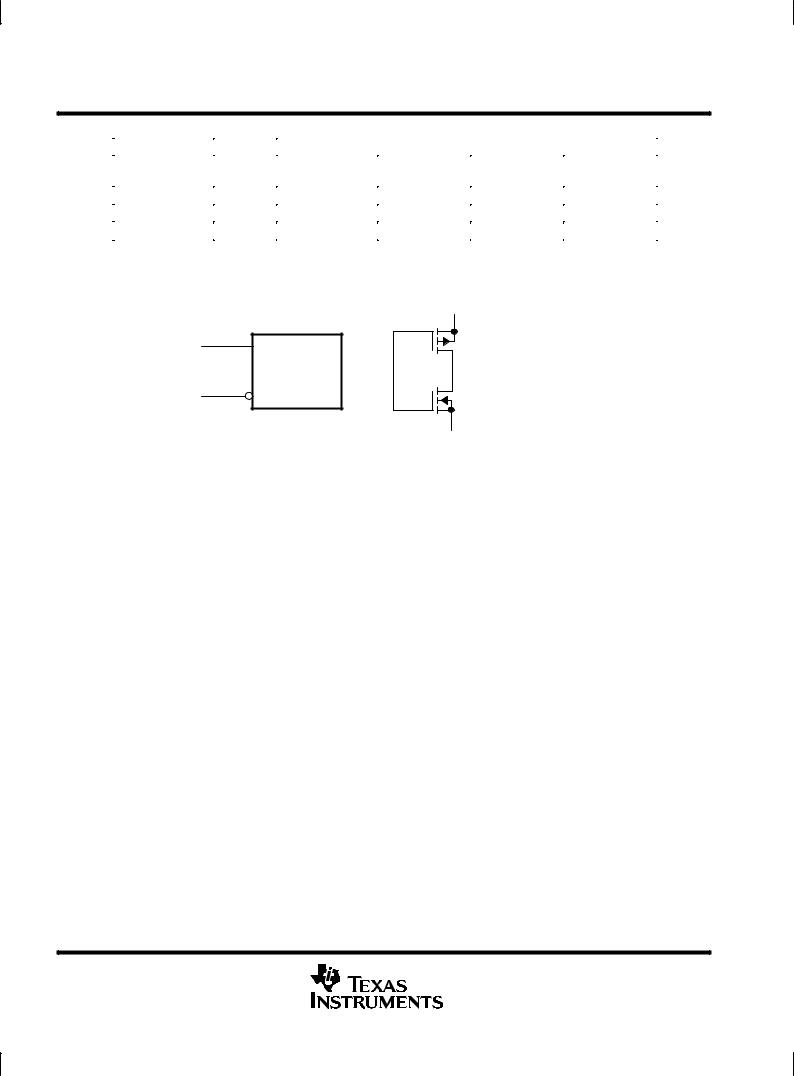
symbol (each comparator)
IN +
OUT
IN ±
The TLC3702C is characterized for operation over the commercial temperature range of 0°C to 70°C. The TLC3702I is characterized for operation over the extended industrial temperature range of ±40°C to 85°C. The TLC3702M is characterized for operation over the full military temperature range of ±55°C to 125°C.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
LinCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright 1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
1 |
TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
|
VIOmax |
|
PACKAGES |
|
||
TA |
|
|
|
|
||
SMALL OUTLINE |
CERAMIC |
CERAMIC DIP |
PLASTIC DIP |
|||
at 25°C |
||||||
|
|
(D) |
(FK) |
(JG) |
(P) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0°C to 70°C |
5 mV |
TLC3702CD |
Ð |
Ð |
TLC3702CP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C to 85°C |
5 mV |
TLC3702ID |
Ð |
Ð |
TLC3702IP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±55°C to 125°C |
5 mV |
TLC3702MD |
TLC3702MFK |
TLC3702MJG |
Ð |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The D package is available taped and reeled. Add R suffix to the device type (e.g., TLC3702CDR).
functional block diagram (each comparator)
VDD
IN+
Differential
Input 
 OUT
OUT
Circuits
IN±
GND
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)²
Supply voltage range, VDD (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
±0.3 V to 18 V |
Differential input voltage, VID (see Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . ±18 V |
Input voltage range, VI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
±0.3 V to VDD |
Output voltage range, VO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
± 0.3 V to VDD |
Input current, II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . ±5 mA |
Output current, IO (each output) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . ±20 mA |
Total supply current into VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . 40 mA |
Total current out of GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . 40 mA |
Continuous total power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
See Dissipation Rating Table |
|
Operating free-air temperature range, TA: TLC3702C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . 0°C to 70°C |
TLC3702I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
±40°C to 85°C |
TLC3702M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
±55°C to 125°C |
Storage temperature range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
±65°C to 150°C |
Case temperature for 60 seconds: FK package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . 260°C |
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds: D or P package . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . 260°C |
|
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 60 seconds: JG package . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . 300°C |
² Stresses beyond those listed under ªabsolute maximum ratingsº may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under ªrecommended operating conditionsº is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. All voltage values, except differential voltages, are with respect to network ground. 2. Differential voltages are at IN+ with respect to IN ±.
2 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE |
TA ≤ 25°C |
DERATING FACTOR |
TA = 70°C |
TA = 85°C |
TA = 125°C |
|
POWER RATING |
ABOVE TA = 25°C |
POWER RATING |
POWER RATING |
POWER RATING |
||
|
||||||
D |
725 mW |
5.8 mW/°C |
464 mW |
377 mW |
145 mW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FK |
1375 mW |
11.0 mW/°C |
880 mW |
715 mW |
275 mW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
JG |
1050 mW |
8.4 mW/°C |
672 mW |
546 mW |
210 mW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
1000 mW |
8.0 mW/°C |
640 mW |
520 mW |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
recommended operating conditions
|
|
TLC3702C |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIN |
NOM |
MAX |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage, VDD |
3 |
5 |
16 |
V |
Common-mode input voltage, VIC |
± 0.2 |
|
VDD ± 1.5 |
V |
High-level output current, IOH |
|
|
±20 |
mA |
Low-level output current, IOL |
|
|
20 |
mA |
Operating free-air temperature, TA |
0 |
|
70 |
°C |
electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, VDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
|
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS² |
T |
TLC3702C |
|
UNIT |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
A |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
V = 5 V to 10 V, |
° |
|
1.2 |
5 |
|
||
VIO |
Input offset voltage |
|
DD |
25 C |
|
mV |
|||
VIC = VICRmin, |
|
|
|
|
|||||
0°C to 70°C |
|
|
6.5 |
||||||
|
|
See Note 3 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IIO |
Input offset current |
VIC = 2.5 V |
25°C |
|
1 |
|
pA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
70°C |
|
|
0.3 |
nA |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IIB |
Input bias current |
VIC = 2.5 V |
25°C |
|
5 |
|
pA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
70°C |
|
|
0.6 |
nA |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VICR |
Common-mode input voltage range |
|
|
|
25°C |
0 to VDD ± 1 |
|
|
V |
|
|
|
0°C to 70°C |
0 to VDD ± 1.5 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CMRR |
Common-mode rejection ratio |
VIC = VICRmin |
70°C |
|
84 |
|
dB |
||
|
|
|
|
|
0°C |
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
kSVR |
Supply-voltage rejection ratio |
VDD = 5 V to 10 V |
70°C |
|
85 |
|
dB |
||
|
|
|
|
|
0°C |
|
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOH |
High-level output voltage |
VID = 1 V, |
25°C |
4.5 |
4.7 |
|
V |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
I |
OH |
= ± 4 mA |
° |
4.3 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
70 C |
|
|
|
||
VOL |
Low-level output voltage |
VID = ±1 V, |
25°C |
|
210 |
300 |
mV |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
I |
OH |
= 4 mA |
° |
|
|
375 |
|||
|
|
|
|
70 C |
|
|
|
||
IDD |
Supply current (both comparators) |
Outputs low, No load |
25°C |
|
18 |
40 |
μA |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
0°C to 70°C |
|
|
50 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
² All characteristics are measured with zero common-mode voltage unless otherwise noted.
NOTE 3: The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4.5 V or down to 0.3 V.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
3 |

TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
recommended operating conditions
|
|
TLC3702I |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIN |
NOM |
MAX |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage, VDD |
3 |
5 |
16 |
V |
Common-mode input voltage, VIC |
±0.2 |
|
VDD ± 1.5 |
V |
High-level output current, IOH |
|
|
±20 |
mA |
Low-level output current, IOL |
|
|
20 |
mA |
Operating free-air temperature, TA |
±40 |
|
85 |
°C |
electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, VDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
|
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS² |
T |
|
TLC3702I |
|
UNIT |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
VIO |
Input offset voltage |
VDD = 5 V to 10 V, |
25°C |
|
|
1.2 |
5 |
mV |
|||
V = V |
ICR |
min, See Note 3 |
° |
° |
|
|
7 |
||||
|
|
IC |
|
|
±40 C to 85 C |
|
|
|
|||
IIO |
Input offset current |
VIC = 2.5 V |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
1 |
|
pA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
1 |
nA |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IIB |
Input bias current |
VIC = 2.5 V |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
5 |
|
pA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
85°C |
|
|
|
2 |
nA |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
0 to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD ± 1 |
|
|
|
|
VICR |
Common-mode input voltage range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C to 85°C |
0 to |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD ± 1.5 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
CMRR |
Common-mode rejection ratio |
VIC = VICRmin |
85°C |
|
|
84 |
|
dB |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C |
|
|
83 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
kSVR |
Supply-voltage rejection ratio |
VDD = 5 V to 10 V |
85°C |
|
|
85 |
|
dB |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C |
|
|
83 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOH |
High-level output voltage |
VID = 1 V, |
|
IOH = ±4 mA |
25°C |
|
4.5 |
4.7 |
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
85°C |
|
4.3 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOL |
Low-level output voltage |
VID = ±1 V, |
|
IOH = ±4 mA |
25°C |
|
|
210 |
300 |
mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
85°C |
|
|
|
400 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IDD |
Supply current (both comparators) |
Outputs low, |
No load |
25°C |
|
|
18 |
40 |
μA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
±40°C to 85°C |
|
|
65 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
² All characteristics are measured with zero common-mode voltage unless otherwise noted.
NOTE 3. The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4.5 V or down to 0.3 V.
4 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
recommended operating conditions
|
|
TLC3702M |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIN |
NOM |
MAX |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage, VDD |
4 |
5 |
16 |
V |
Common-mode input voltage, VIC |
0 |
|
VDD ± 1.5 |
V |
High-level output current, IOH |
|
|
± 20 |
mA |
Low-level output current, IOL |
|
|
20 |
mA |
Operating free-air temperature, TA |
± 55 |
|
125 |
°C |
electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, VDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
|
PARAMETER |
|
TEST CONDITIONS² |
TA |
|
TLC3702M |
|
UNIT |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
VIO |
Input offset voltage |
VDD = 5 V to 10 V, |
25°C |
|
|
1.2 |
5 |
mV |
|||||
V |
IC |
= V |
ICR |
min, See Note 3 |
° |
° |
|
|
10 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
±55 C to 125 C |
|
|
|
||||
IIO |
Input offset current |
VIC = 2.5 V |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
1 |
|
pA |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
125°C |
|
|
|
15 |
nA |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IIB |
Input bias current |
VIC = 2.5 V |
|
|
25°C |
|
|
5 |
|
pA |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
125°C |
|
|
|
30 |
nA |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
0 to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD ± 1 |
|
|
|
|
VICR |
Common-mode input voltage range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±55°C to 125°C |
0 to |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD ± 1.5 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
CMRR |
Common-mode rejection ratio |
VIC = VICRmin |
125°C |
|
|
83 |
|
dB |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±55°C |
|
|
82 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
kSVR |
Supply-voltage rejection ratio |
VDD = 5 V to 10 V |
125°C |
|
|
85 |
|
dB |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
± 55°C |
|
|
82 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOH |
High-level output voltage |
VID = 1 V, |
|
IOH = ±4 mA |
25°C |
|
4.5 |
4.7 |
|
V |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
125°C |
|
4.2 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOL |
Low-level output voltage |
VID = ±1 V, |
|
IOH = ±4 mA |
25°C |
|
|
210 |
300 |
mV |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
125°C |
|
|
|
500 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IDD |
Supply current (both comparators) |
Outputs low, |
No load |
25°C |
|
|
18 |
40 |
μA |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
±55°C to 125°C |
|
|
90 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
² All characteristics are measured with zero common-mode voltage unless otherwise noted.
NOTE 3. The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4.5 V or down to 0.3 V.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
5 |

TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
switching characteristics, VDD = 5 V, TA = 25°C
|
|
|
|
|
TLC3702C, TLC3702I |
|
||
|
PARAMETER |
|
TEST CONDITIONS |
TLC3702M |
|
UNIT |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overdrive = 2 mV |
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 10 kHz, |
Overdrive = 5 mV |
|
2.7 |
|
|
|
t |
Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output² |
|
|
|
|
μs |
||
Overdrive = 10 mV |
|
1.9 |
|
|||||
PLH |
|
CL |
= 50 pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overdrive = 20 mV |
|
1.4 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overdrive = 40 mV |
|
1.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VI = 1.4 V step at IN+ |
|
1.1 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Overdrive = 2 mV |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 10 kHz, |
Overdrive = 5 mV |
|
2.3 |
|
|
|
t |
Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output² |
|
|
|
|
μs |
||
Overdrive = 10 mV |
|
1.5 |
|
|||||
PHL |
|
CL |
= 50 pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overdrive = 20 mV |
|
0.95 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overdrive = 40 mV |
|
0.65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VI = 1.4 V step at IN+ |
|
0.15 |
|
|
||
tf |
Fall time |
f = 10 kHz, |
Overdrive = 50 mV |
|
50 |
|
ns |
|
CL |
= 50 pF |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
tr |
Rise time |
f = 10 kHz, |
Overdrive = 50 mV |
|
125 |
|
ns |
|
CL |
= 50 pF |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
² Simultaneous switching of inputs causes degradation in output response.
6 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
LinCMOS process
The LinCMOS process is a linear polysilicon-gate CMOS process. Primarily designed for single-supply applications, LinCMOS products facilitate the design of a wide range of high-performance analog functions from operational amplifiers to complex mixed-mode converters.
While digital designers are experienced with CMOS, MOS technologies are relatively new for analog designers. This short guide is intended to answer the most frequently asked questions related to the quality and reliability of LinCMOS products. Further questions should be directed to the nearest TI field sales office.
electrostatic discharge
CMOS circuits are prone to gate oxide breakdown when exposed to high voltages even if the exposure is only for very short periods of time. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is one of the most common causes of damage to CMOS devices. It can occur when a device is handled without proper consideration for environmental electrostatic charges, e.g., during board assembly. If a circuit in which one amplifier from a dual op amp is being used and the unused pins are left open, high voltages tend to develop. If there is no provision for ESD protection, these voltages may eventually punch through the gate oxide and cause the device to fail. To prevent voltage buildup, each pin is protected by internal circuitry.
Standard ESD-protection circuits safely shunt the ESD current by providing a mechanism whereby one or more transistors break down at voltages higher than the normal operating voltages but lower than the breakdown voltage of the input gate. This type of protection scheme is limited by leakage currents which flow through the shunting transistors during normal operation after an ESD voltage has occurred. Although these currents are small, on the order of tens of nanoamps, CMOS amplifiers are often specified to draw input currents as low as tens of picoamps.
To overcome this limitation, TI design engineers developed the patented ESD-protection circuit shown in Figure 1. This circuit can withstand several successive 2-kV ESD pulses, while reducing or eliminating leakage currents that may be drawn through the input pins. A more detailed discussion of the operation of the TI ESD-protection circuit is presented on the next page.
All input and output pins on LinCMOS and Advanced LinCMOS products have associated ESD-protection circuitry that undergoes qualification testing to withstand 2000 V discharged from a 100-pF capacitor through a 1500-Ω resistor (human body model) and 200 V from a 100-pF capacitor with no current-limiting resistor (charged device model). These tests simulate both operator and machine handling of devices during normal test and assembly operations.
VDD
R1 |
|
Input |
|
|
R2 |
Q1 |
Q2 |
|
|
D1 |
D2 |
GND |
|
To Protect Circuit
D3
Figure 1. LinCMOS ESD-Protection Schematic
LinCMOS and Advanced LinCMOS are trademarks of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
7 |

TLC3702
DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
SLCS013D ± NOVEMBER 1986 ± REVISED NOVEMBER 1998
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
input protection circuit operation
Texas Instruments patented protection circuitry allows for both positiveand negative-going ESD transients. These transients are characterized by extremely fast rise times and usually low energies, and can occur both when the device has all pins open and when it is installed in a circuit.
positive ESD transients
Initial positive charged energy is shunted through Q1 to VSS. Q1 turns on when the voltage at the input rises above the voltage on the VDD pin by a value equal to the VBE of Q1. The base current increases through R2 with input current as Q1 saturates. The base current through R2 forces the voltage at the drain and gate of Q2 to exceed its threshold level (VT 22 to 26 V) and turn Q2 on. The shunted input current through Q1 to VSS is now shunted through the n-channel enhancement-type MOSFET Q2 to VSS. If the voltage on the input pin continues to rise, the breakdown voltage of the zener diode D3 is exceeded and all remaining energy is dissipated in R1 and D3. The breakdown voltage of D3 is designed to be 24 V to 27 V, which is well below the gate-oxide voltage of the circuit to be protected.
negative ESD transients
The negative charged ESD transients are shunted directly through D1. Additional energy is dissipated in R1 and D2 as D2 becomes forward biased. The voltage seen by the protected circuit is ±0.3 V to ±1 V (the forward voltage of D1 and D2).
circuit-design considerations
LinCMOS products are being used in actual circuit environments that have input voltages that exceed the recommended common-mode input voltage range and activate the input protection circuit. Even under normal operation, these conditions occur during circuit power up or power down, and in many cases, when the device is being used for a signal conditioning function. The input voltages can exceed VICR and not damage the device only if the inputs are current limited. The recommended current limit shown on most product data sheets is
±5 mA. Figure 2 and Figure 3 show typical characteristics for input voltage versus input current.
Normal operation and correct output state can be expected even when the input voltage exceeds the positive supply voltage. Again, the input current should be externally limited even though internal positive current limiting is achieved in the input protection circuit by the action of Q1. When Q1 is on, it saturates and limits the current to approximately 5-mA collector current by design. When saturated, Q1 base current increases with input current. This base current is forced into the VDD pin and into the device IDD or the VDD supply through R2 producing the current limiting effects shown in Figure 2. This internal limiting lasts only as long as the input voltage is below the VT of Q2.
When the input voltage exceeds the negative supply voltage, normal operation is affected and output voltage states may not be correct. Also, the isolation between channels of multiple devices (duals and quads) can be severely affected. External current limiting must be used since this current is directly shunted by D1 and D2 and no internal limiting is achieved. If normal output voltage states are required, an external input voltage clamp is required (see Figure 4).
8 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
 Loading...
Loading...