Texas Instruments TPS5210PWPR, TPS5210PWP, TPS5210EVM-126, TPS5210EVM-119, TPS5210EVM-116 Datasheet
...
TPS5210 PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS-BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
D ±1% Reference Over Full Operating |
|
|
DW OR PWP PACKAGE |
|
|||||
|
Temperature Range |
|
|
|
|
(TOP VIEW) |
|
||
D Synchronous Rectifier Driver for Greater |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IOUT |
|
|
1 |
28 |
|
|
PWRGD |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Than 90% Efficiency |
DROOP |
|
|
2 |
27 |
|
|
VID0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
D Programmable Reference Voltage Range of |
OCP |
|
|
3 |
26 |
|
|
VID1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
1.3 V to 3.5 V |
VHYST |
|
|
4 |
25 |
|
|
VID2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
D User±Selectable Hysteretic Type Control |
VREFB |
|
|
5 |
24 |
|
|
VID3 |
|
VSENSE |
|
|
6 |
23 |
|
|
VID4 |
||
D Droop Compensation for Improved Load |
|
|
|
|
|||||
ANAGND |
|
|
7 |
22 |
|
|
INHIBIT |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Transient Regulation |
SLOWST |
|
|
8 |
21 |
|
|
IOUTLO |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
D |
Adjustable Overcurrent Protection |
BIAS |
|
|
9 |
20 |
|
|
LOSENSE |
|
|
|
|
||||||
D |
Programmable Softstart |
LODRV |
|
|
10 |
19 |
|
|
HISENSE |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
D |
Overvoltage Protection |
LOHIB |
|
|
11 |
18 |
|
|
BOOTLO |
DRVGND |
|
|
12 |
17 |
|
|
HIGHDR |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Active Deadtime Control |
|
|
|
|
||||
D |
LOWDR |
|
|
13 |
16 |
|
|
BOOT |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
D |
Power Good Output |
DRV |
|
|
14 |
15 |
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
DInternal Bootstrap Schottky Diode
DLow Supply Current . . . 3-mA Typ
description
The TPS5210 is a synchronous-buck regulator controller which provides an accurate, programmable supply voltage to microprocessors. An internal 5-bit DAC is used to program the reference voltage to within a range of 1.3 V to 3.5 V. The output voltage can be set to be equal to the reference voltage or to some multiple of the reference voltage. A hysteretic controller with user-selectable hysteresis and programmable droop compensation is used to dramatically reduce overshoot and undershoot caused by load transients. Propagation delay from the comparator inputs to the output drivers is less than 250 ns. Overcurrent shutdown and crossover protection for the output drivers combine to eliminate destructive faults in the output FETs. The softstart current source is proportional to the reference voltage, thereby eliminating variation of the softstart timing when changes are made to the output voltage. PWRGD monitors the output voltage and pulls the open-collector output low when the output drops 7% below the nominal output voltage. An overvoltage circuit disables the output drivers if the output voltage rises 15% above the nominal value. The inhibit pin can be used to control power sequencing. Inhibit and undervoltage lockout assures the 12-V supply voltage and system supply voltage (5 V or 3.3 V) are within proper operating limits before the controller starts. Single-supply (12 V) operation is easily accomplished using a low-current divider for the required 5-V signals. The output driver circuits include 2-A drivers with internal 8-V gate-voltage regulators. The high-side driver can be configured either as a ground-referenced driver or as a floating bootstrap driver. The TPS5210 is available in a 28-pin SOIC package and a 28-pin TSSOP PowerPAD package. It operates over a junction temperature range of 0°C to 125°C.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
|
|
PACKAGES |
|
TJ |
|
|
|
SOIC |
|
TSSOP |
|
|
(DW) |
|
(PWP) |
|
|
|
|
0°C to 125°C |
TPS5210DW |
|
TPS5210PWPR |
The DW package is available taped and reeled. Add R suffix to device type (e.g., TPS5210DWR).
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright 1999, Texas Instruments Incorporated
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
1 |
2
75265 TEXAS DALLAS, •655303 BOX OFFICE POST
INHIBIT |
|
|
|
|
|
VCC |
ANAGND |
|
PWRGD |
LOSENSE |
IOUTLO |
HISENSE |
IOUT |
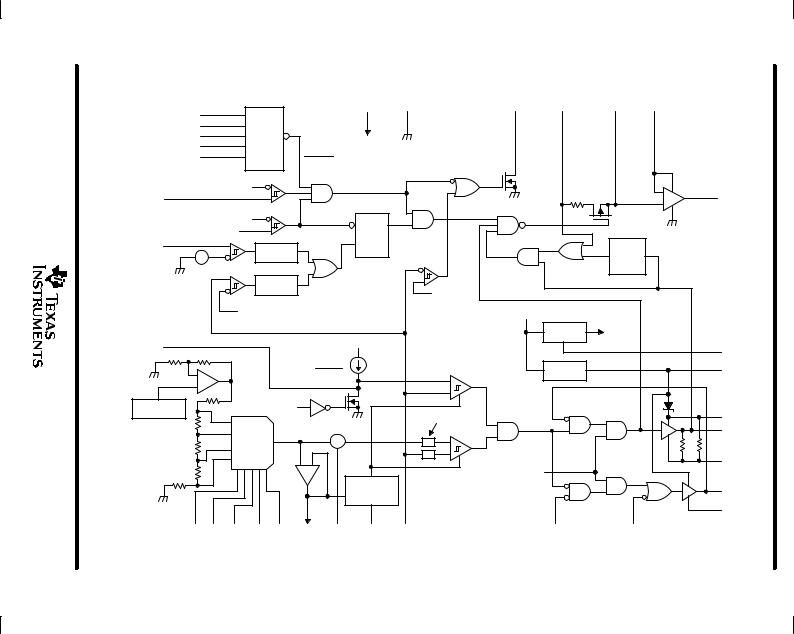
diagramblockfunctional |
REVISED±1998SEPTEMBER± SLVS171A |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
VID0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
7 |
|
28 |
20 |
21 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
VID1 |
|
|
11111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID4 |
|
|
|
NOCPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
22 |
|
2 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
UVLO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
2x |
|
|
MAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shutdown |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
10 V |
|
|
S |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
VCC |
|
|
|
Fault |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 |
|||
3 |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
OCP |
|
|
Deglitch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rising |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Edge |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Deglitch |
|
|
|
|
VPGD |
|
|
|
|
HIGHDR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HIGHIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
VOVP |
|
|
|
|
|
0.93 Vref |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1.15 Vref |
|
VSENSE |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PREREG |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bias |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Bias |
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
SLOWST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BIAS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IVREFB |
|
|
|
Slowstart |
DRV REG |
|
|
14 |
DRV |
|
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
Comp |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bandgap |
|
|
Shutdown |
|
|
|
CM Filters |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOOT |
|
|
|||
|
|
VID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
HIGHDR |
|
|
|
|
|
VREF |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
MUX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Σ |
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
200 kΩ |
|
|
|||||
|
|
and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
± |
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Decoder |
|
|
|
|
Hysteresis |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOOTLO |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
+ |
± |
|
|
|
|
Comp |
|
|
|
200 kΩ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shutdown |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VREFB |
|
Hysteresis |
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
LOWDR |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DRVGND |
|
|
27 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
23 |
5 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
|
|
11 |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
VID0 VID1 VID2 |
VID3 VID4 VREFB DROOP VHYST |
VSENSE |
|
|
LOHIB |
LODRV |
|
|
|
|
|||||||

|
|
|
TPS5210 |
|
|
|
|
PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER |
|
|
|
|
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Terminal Functions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TERMINAL |
I/O |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
||
NAME |
NO. |
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
ANAGND |
7 |
|
Analog ground |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BIAS |
9 |
O |
Analog BIAS pin. A 1-mF ceramic capacitor should be connected from BIAS to ANAGND. |
|
BOOT |
16 |
I |
Bootstrap. Connect a 1-mF low-ESR capacitor from BOOT to BOOTLO. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOOTLO |
18 |
O |
Bootstrap low. Connect BOOTLO to the junction of the high-side and low-side FETs for floating drive |
|
|
|
|
configuration. Connect BOOTLO to PGND for ground reference drive configuration. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DROOP |
2 |
I |
Droop voltage. Voltage input used to set the amount of output-voltage set-point droop as a function of load |
|
|
|
|
current. The amount of droop compensation is set with a resistor divider between IOUT and ANAGND. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DRV |
14 |
O |
Drive regulator for the FET drivers. A 1-mF ceramic capacitor should be connected from DRV to DRVGND. |
|
DRVGND |
12 |
|
Drive ground. Ground for FET drivers. Connect to FET PWRGND. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HIGHDR |
17 |
O |
High drive. Output drive to high-side power switching FETs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HISENSE |
19 |
I |
High current sense. For current sensing across high-side FETs, connect to the drain of the high-side FETs; for |
|
|
|
|
optional resistor sensing scheme, connect to power supply side of current-sense resistor placed in series with |
|
|
|
|
high-side FET drain. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
INHIBIT |
22 |
I |
Disables the drive signals to the MOSFET drivers. Can also serve as UVLO for system logic supply (either 3.3 V |
|
|
|
|
or 5 V). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IOUT |
1 |
O |
Current out. Output voltage on this pin is proportional to the load current as measured across the Rds(on) of the |
|
|
|
|
high-side FETs. The voltage on this pin equals 2×Rds(on)×IOUT. In applications where very accurate current |
|
|
|
|
sensing is required, a sense resistor should be connected between the input supply and the drain of the high-side |
|
|
|
|
FETs. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IOUTLO |
21 |
O |
Current sense low output. This is the voltage on the LOSENSE pin when the high-side FETs are on. A ceramic |
|
|
|
|
capacitor should be connected from IOUTLO to HISENSE to hold the sensed voltage while the high-side FETs |
|
|
|
|
are off. Capacitance range should be between 0.033 mF and 0.1 mF. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LODRV |
10 |
I |
Low drive enable. Normally tied to 5 V. To activate the low-side FETs as a crowbar, pull LODRV low. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOHIB |
11 |
I |
Low side inhibit. Connect to the junction of the high and low side FETs to control the anti-cross-conduction and |
|
|
|
|
eliminate shoot-through current. Disabled when configured in crowbar mode. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOSENSE |
20 |
I |
Low current sense. For current sensing across high-side FETs, connect to the source of the high-side FETs; for |
|
|
|
|
optional resistor sensing scheme, connect to high-side FET drain side of current-sense resistor placed in series |
|
|
|
|
with high-side FET drain. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOWDR |
13 |
O |
Low drive. Output drive to synchronous rectifier FETs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCP |
3 |
I |
Over current protection. Current limit trip point is set with a resistor divider between IOUT and ANAGND. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PWRGD |
28 |
O |
Power good. Power Good signal goes high when output voltage is within 7% of voltage set by VID pins. |
|
|
|
|
Open-drain output. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLOWST |
8 |
O |
Slow Start (soft start). A capacitor from SLOWST to ANAGND sets the slowstart time. |
|
|
|
|
Slowstart current = IVREFB/5 |
|
VCC |
15 |
|
12-V supply. A 1-mF ceramic capacitor should be connected from VCC to DRVGND. |
|
VHYST |
4 |
I |
HYSTERESIS set pin. The hysteresis is set with a resistor divider from VREFB to ANAGND. |
|
|
|
|
The hysteresis window = 2 ×(VREFB ± VHYST) |
|
VID0 |
27 |
I |
Voltage Identification input 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID1 |
26 |
I |
Voltage Identification input 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID2 |
25 |
I |
Voltage Identification input 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID3 |
24 |
I |
Voltage Identification input 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VID4 |
23 |
I |
Voltage Identification input 4. Digital inputs that set the output voltage of the converter. The code pattern for |
|
|
|
|
setting the output voltage is located in Table 1. Internally pulled up to 5 V with a resistor divider biased from VCC. |
|
VREFB |
5 |
O |
Buffered reference voltage from VID network |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSENSE |
6 |
I |
Voltage sense Input. To be connected to converter output voltage bus to sense and control output voltage. It is |
|
|
|
|
recommended an RC low pass filter be connected at this pin to filter noise. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
3 |

TPS5210
PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
detailed description
VREF
The reference/voltage identification (VID) section consists of a temperature-compensated bandgap reference and a 5-bit voltage selection network. The 5 VID terminals are inputs to the VID selection network and are TTL-compatible inputs internally pulled up to 5 V by a resistor divider connected to VCC. The VID codes conform to the Intel VRM 8.3 DC-DC Converter Specification for voltage settings between 1.8 V and 3.5 V, and they are decremented by 50 mV, down to 1.3 V, for the lower VID settings. Voltages higher than VREF can be implemented using an external divider. Refer to Table 1 for the VID code settings. The output voltage of the VID network, VREF, is within ±1% of the nominal setting over the VID range of 1.3 V to 2.5 V, including a junction temperature range of 5°C to +125°C, and a VCC supply voltage range of 11.4 V to 12.6 V. The output of the reference/VID network
is indirectly brought out through a buffer to the VREFB pin. The voltage on this pin will be within 2% of VREF. It is not recommended to drive loads with VREFB, other than setting the hysteresis of the hysteretic comparator,
because the current drawn from VREFB sets the charging current for the slowstart capacitor. Refer to the slowstart section for additional information.
hysteretic comparator
The hysteretic comparator regulates the output voltage of the synchronous-buck converter. The hysteresis is
set by 2 external resistors and is centered on VREF. The 2 external resistors form a resistor divider from VREFB to ANAGND, with the output voltage connecting to the VHYST pin. The hysteresis of the comparator will be equal to twice the voltage difference between the VREFB and VHYST pins. The propagation delay from the comparator
inputs to the driver outputs is 250 ns (maximum). The maximum hysteresis setting is 60 mV.
low-side driver
The low-side driver is designed to drive low-Rds(on) n-channel MOSFETs. The current rating of the driver is 2 A, source and sink. The bias to the low-side driver is internally connected to the DRV regulator.
high-side driver
The high-side driver is designed to drive low-Rds(on) n-channel MOSFETs. The current rating of the driver is 2 A, source and sink. The high-side driver can be configured either as a ground-referenced driver or as a floating bootstrap driver. When configured as a floating driver, the bias voltage to the driver is developed from the DRV regulator. The internal bootstrap diode, connected between the DRV and BOOT pins, is a Schottky for improved drive efficiency. The maximum voltage that can be applied between BOOT and DRVGND is 30 V. The driver can be referenced to ground by connecting BOOTLO to DRVGND, and connecting BOOT to either DRV or VCC.
deadtime control
Deadtime control prevents shoot-through current from flowing through the main power FETs during switching transitions by actively controlling the turn-on times of the MOSFET drivers. The high-side driver is not allowed to turn on until the gate-drive voltage to the low-side FETs is below 2 V; the low-side driver is not allowed to turn on until the voltage at the junction of the high-side and low-side FETs (Vphase) is below 2 V.
current sensing
Current sensing is achieved by sampling and holding the voltage across the high-side power FETs while the high-side FETs are on. The sampling network consists of an internal 60-Ω switch and an external ceramic hold capacitor. Recommended value of the hold capacitor is between 0.033 μF and 0.1 μF. Internal logic controls the turn-on and turn-off of the sample/hold switch such that the switch does not turn on until the Vphase voltage transitions high, and the switch turns off when the input to the high-side driver goes low. The sampling will occur only when the high-side FETs are conducting current. The voltage on the IOUT pin equals 2 times the sensed high-side voltage. In applications where a higher accuracy in current sensing is required, a sense resistor can be placed in series with the high-side FETs, and the voltage across the sense resistor can be sampled by the current sensing circuit.
4 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TPS5210 PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
detailed description (continued)
droop compensation
The droop compensation network reduces the load transient overshoot/undershoot on VO, relative to VREF . VO is programmed to a voltage greater than VREF by an external resistor divider from VO to VSENSE to reduce the undershoot on VO during a low-to-high load transient. The overshoot during a high-to-low load transient is reduced by subtracting the voltage on DROOP from VREF. The voltage on IOUT is divided with an external resistor divider, and connected to DROOP.
inhibit
INHIBIT is a TTL-compatible digital input used to enable the controller. When INHIBIT is low, the output drivers are low and the slowstart capacitor is discharged. When INHIBIT goes high, the short across the slowstart capacitor is released and normal converter operation begins. When the system-logic supply is connected to INHIBIT, it also controls power sequencing by locking out controller operation until the system-logic supply exceeds the input threshold voltage of the inhibit circuit. The 12-V supply and the system logic supply (either 5 V or 3.3 V) must be above UVLO thresholds before the controller is allowed to start up. The start threshold is 2.1 V and the hysteresis is 100 mV for the INHIBIT comparator.
VCC undervoltage lockout (UVLO)
The undervoltage lockout circuit disables the controller while the VCC supply is below the 10-V start threshold during power up. When the controller is disabled, the output drivers will be low and the slowstart capacitor is discharged. When VCC exceeds the start threshold, the short across the slowstart capacitor is released and normal converter operation begins. There is a 2-V hysteresis in the undervoltage lockout circuit for noise immunity.
slowstart
The slowstart circuit controls the rate at which VO powers up. A capacitor is connected between SLOWST and ANAGND and is charged by an internal current source. The current source is proportional to the reference
voltage, so that the charging rate of Cslowst is proportional to the reference voltage. By making the charging current proportional to VREF, the power-up time for VO will be independent of VREF. Thus, CSLOWST can remain the same value for all VID settings. The slowstart charging current is determined by the following equation:
Islowstart = I(VREFB) / 5 (amps)
Where I(VREFB) is the current flowing out of VREFB.
It is recommended that no additional loads be connected to VREFB, other than the resistor divider for setting the
hysteresis voltage. The maximum current that can be sourced by the VREFB circuit is 500 mA. The equation for setting the slowstart time is:
tSLOWST = 5 ×CSLOWST × RVREFB (seconds)
Where RVREFB is the total external resistance from VREFB to ANAGND.
power good
The power-good circuit monitors for an undervoltage condition on VO. If VO is 7% below VREF, then the PWRGD pin is pulled low. PWRGD is an open-drain output.
overvoltage protection
The overvoltage protection (OVP) circuit monitors VO for an overvoltage condition. If VO is 15% above VREF, then a fault latch is set and both output drivers are turned off. The latch will remain set until VCC goes below the undervoltage lockout value. A 3-ms deglitch timer is included for noise immunity. Refer to the LODRV section for information on how to protect the microprocessor against overvoltages due to a shorted fault across the high-side power FET.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
5 |

TPS5210
PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
detailed description (continued)
overcurrent protection
The overcurrent protection (OCP) circuit monitors the current through the high-side FET. The overcurrent threshold is adjustable with an external resistor divider between IOUT and ANAGND, with the divider voltage connected to the OCP pin. If the voltage on OCP exceeds 100 mV, then a fault latch is set and the output drivers are turned off. The latch will remain set until VCC goes below the undervoltage lockout value. A 3-μs deglitch timer is included for noise immunity. The OCP circuit is also designed to protect the high-side power FET against a short-to-ground fault on the terminal common to both power FETs.
drive regulator
The drive regulator provides drive voltage to the output drivers. The minimum drive voltage is 7 V. The minimum short circuit current is 100 mA. Connect a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from DRV to DRVGND.
LODRV
The LODRV circuit is designed to protect the microprocessor against overvoltages that can occur if the high-side power FETs become shorted. External components to sense an overvoltage condition are required to use this feature. When an overvoltage fault occurs, the low-side FETs are used as a crowbar. LODRV is pulled low and the low-side FET will be turned on, overriding all control signals inside the TPS5210 controller. The crowbar action will short the input supply to ground through the faulted high-side FETs and the low-side FETs. A fuse in series with Vin should be added to disconnect the short-circuit.
Table 1. Voltage Identification Codes
|
|
|
VID TERMINALS |
|
|
VREF |
|
||
|
|
(0 = GND, 1 = floating or pull-up to 5 V) |
|
|
|||||
|
VID4 |
VID3 |
|
VID2 |
|
VID1 |
VID0 |
(Vdc) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
1.35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
1.40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
1.45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
1.50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
1.65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1.70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
1.75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
1.85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
1.90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
2.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
No CPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
2.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
2.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
2.40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
2.50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
2.60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TPS5210 PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
Table 1. Voltage Identification Codes (Continued)
|
|
VID TERMINALS |
|
|
VREF |
||
|
(0 = GND, 1 = floating or pull-up to 5 V) |
|
|||||
VID4 |
VID3 |
|
VID2 |
|
VID1 |
VID0 |
(Vdc) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
2.70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
2.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
2.90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
3.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
3.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
3.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
3.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
3.40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
3.50 |
absolute maximum ratings over operating virtual junction temperature (unless otherwise noted)²
Supply voltage range, VCC (see Note1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 14 V |
Input voltage range: BOOT to DRVGND (High-side Driver ON) . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 30 V |
BOOT to HIGHDRV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 15 V |
BOOT to BOOTLO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 15 V |
INHIBIT, VIDx, LODRV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 7.3 V |
PWRGD, OCP, DROOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 7 V |
LOHIB, LOSENSE, IOUTLO, HISENSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 14 V |
VSENSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V to 5 V |
Voltage difference between ANAGND and DRVGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.5 V |
Output current, VREFB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 mA |
Short circuit duration, DRV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Continuous |
Continuous total power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
See Dissipation Rating Table |
Operating virtual junction temperature range, TJ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to 125°C |
Storage temperature range, Tstg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . ±65°C to 150°C |
Lead temperature soldering 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260°C |
²Stresses beyond those listed under ªabsolute maximum ratingsº may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under ªrecommended operating conditionsº is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: Unless otherwise specified, all voltages are with respect to ANAGND.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE |
TA ≤ 25°C |
DERATING FACTOR |
TA = 70°C |
TA = 85°C |
|
POWER RATING |
ABOVE TA = 25°C |
POWER RATING |
POWER RATING |
||
|
|||||
DW |
1200 mW |
12 mW/°C |
660 mW |
480 mW |
|
PWP |
1150 mW |
11.5 mW/°C |
630 mW |
460 mW |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
7 |

TPS5210
PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
recommended operating conditions
|
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage, VCC |
11.4 |
13 |
V |
Input voltage, BOOT to DRVGND |
0 |
28 |
V |
|
|
|
|
Input voltage, BOOT to BOOTLO |
0 |
13 |
V |
|
|
|
|
Input voltage, INHIBIT, VIDx, LODRV, PWRGD, OCP, DROOP |
0 |
6 |
V |
|
|
|
|
Input voltage, LOHIB, LOSENSE, IOUTLO, HISENSE |
0 |
13 |
V |
|
|
|
|
Input voltage, VSENSE |
0 |
4.5 |
V |
|
|
|
|
Voltage difference between ANAGND and DRVGND |
0 |
±0.2 |
V |
|
|
|
|
Output current, VREFB² |
0 |
0.4 |
mA |
² Not recommended to load VREFB other than to set hystersis since IVREFB sets slowstart time. |
|
|
|
electrical characteristics over recommended operating virtual junction temperature range, VCC = 12 V, IDRV = 0 A (unless otherwise noted)
reference/voltage identification
|
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, 1.3 V ≤ VREF ≤ 2.5 V |
±0.01 |
|
0.01 |
V/V |
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 2.6 V |
±0.0104 |
|
0.0104 |
V/V |
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 2.7 V |
±0.0108 |
|
0.0108 |
V/V |
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 2.8 V |
±0.0112 |
|
0.0112 |
V/V |
|
Reference voltage accuracy, (Includes |
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 2.9 V |
±0.0116 |
|
0.0116 |
V/V |
|
offset of droop compensation net- |
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 3 V |
±0.0120 |
|
0.0120 |
V/V |
|
work) |
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 3.1 V |
±0.0124 |
|
0.0124 |
V/V |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 3.2 V |
±0.0128 |
|
0.0128 |
V/V |
V |
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 3.3 V |
±0.0132 |
|
0.0132 |
V/V |
REF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 3.4 V |
±0.0136 |
|
0.0136 |
V/V |
|
|
VCC = 11.4 to 12.6 V, VREF = 3.5 V |
±0.0140 |
|
0.0140 |
V/V |
|
|
VREF = 1.3 V, Hysteresis window = 30 mV |
±0.011 |
|
0.011 |
|
|
|
VREF =1.3 V, Hysteresis, |
±0.008 |
|
0.008 |
|
|
|
TJ = 60°C window = 30 mV (see Note 3) |
|
|
||
|
Cumulative reference accuracy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VREF = 1.9 Vv, Hysteresis, |
|
|
|
V/V |
|
|
(see Note 2) |
±0.0090 |
|
0.0090 |
||
|
|
TJ = 60°C window = 30 mV (see Note 3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VREF = 3.5 V, Hysteresis, |
±0.0115 |
|
0.0115 |
|
|
|
TJ = 60°C window = 30 mV (see Note 3) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIDx |
High-level input voltage |
|
2.25 |
|
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIDx |
Low-level input voltage |
|
|
|
1 |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VREFB |
Output voltage |
IVREFB = 50 μA |
VREF±2% |
VREF |
VREF+2% |
V |
Output regulation |
10 μA ≤ IO ≤ 500 μA |
|
2 |
|
mV |
|
|
|
|
||||
VIDx |
Input resistance |
VIDx = 0 V |
36 |
73 |
95 |
kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input pull-up voltage divider |
|
4.8 |
4.9 |
5 |
V |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES: 2. Cumulative reference accuracy is the combined accuracy of the reference voltage and the input offset voltage of the hysteretic comparator. Cumulative accuracy equals the average of the high-level and low-level thresholds of the hysteretic comparator.
3. This parameter is ensured by design and is not production tested.
8 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TPS5210 PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRONOUS BUCK REGULATOR CONTROLLER
SLVS171A ± SEPTEMBER 1998 ± REVISED MAY 1999
electrical characteristics over recommended operating virtual junction temperature range, VCC = 12 V, IDRV = 0 A (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
power good
|
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Undervoltage trip threshold |
|
90 |
93 |
95 |
%VREF |
VOL |
Low-level output voltage |
IO = 5 mA |
|
0.5 |
0.75 |
V |
IOH |
High-level input current |
VPWRGD = 6 V |
|
1 |
|
μA |
Vhys |
Hysteresis voltage |
|
1.3 |
2.9 |
4.5 |
%VREF |
slowstart
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
|
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge current |
VSLOWST = 0.5 V, VVREFB |
= 1.3 V, |
10.4 |
13 |
15.6 |
μA |
IVREFB = 65 μA |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discharge current |
VSLOWST = 1 V |
|
|
3 |
|
mA |
Comparator input offset voltage |
|
|
|
|
10 |
mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparator input bias current |
See Note 3 |
|
|
10 |
100 |
nA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comparator hysteresis |
|
|
±7.5 |
|
7.5 |
mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE 3: This parameter is ensured by design and is not production tested. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
hysteretic comparator
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
Input offset voltage |
VDROOP = 0 V (see Note 3) |
±2.5 |
2.5 |
mV |
Input bias current |
See Note 3 |
|
500 |
nA |
|
|
|
|
|
Hysteresis accuracy |
VREFB ± VHYST = 15 mV |
±3.5 |
3.5 |
mV |
|
(Hysteresis window = 30 mV) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum hysteresis setting |
VREFB ± VHYST = 30 mV |
|
60 |
mV |
NOTE 3: This parameter is ensured by design and is not production tested.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
9 |
 Loading...
Loading...