Analog Devices AD811AR-16-REEL7, AD811AR-16-REEL, AD811AR-16, AD811AN, AD811ACHIPS Datasheet
...
a |
High Performance |
Video Op Amp |
FEATURES
High Speed
140 MHz Bandwidth (3 dB, G = +1)
120 MHz Bandwidth (3 dB, G = +2)
35 MHz Bandwidth (0.1 dB, G = +2)
2500 V/ms Slew Rate
25 ns Settling Time to 0.1% (For a 2 V Step) 65 ns Settling Time to 0.01% (For a 10 V Step)
Excellent Video Performance (RL =150 V)
0.01% Differential Gain, 0.018 Differential Phase
Voltage Noise of 1.9 nV√Hz
Low Distortion: THD = –74 dB @ 10 MHz Excellent DC Precision
3 mV max Input Offset Voltage Flexible Operation
Specified for 65 V and 615 V Operation
62.3 V Output Swing into a 75 V Load (VS = 65 V)
APPLICATIONS
Video Crosspoint Switchers, Multimedia Broadcast
Systems
HDTV Compatible Systems
Video Line Drivers, Distribution Amplifiers
ADC/DAC Buffers
DC Restoration Circuits
Medical—Ultrasound, PET, Gamma and Counter
Applications
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD811 is a wideband current-feedback operational amplifier, optimized for broadcast quality video systems. The –3 dB bandwidth of 120 MHz at a gain of +2 and differential gain and phase of 0.01% and 0.01° (RL = 150 Ω) make the AD811 an excellent choice for all video systems. The AD811 is designed to meet a stringent 0.1 dB gain flatness specification to a bandwidth of 35 MHz (G = +2) in addition to the low differential gain and phase errors. This performance is achieved whether driving one or two back terminated 75 Ω cables, with a low power supply current of 16.5 mA. Furthermore, the AD811 is specified over a power supply range of ± 4.5 V to ± 18 V.
|
0.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.20 |
|
|
0.09 |
|
|
|
|
RF = 649V |
|
|
|
0.18 |
– Degrees |
|
–% |
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
FC = 3.58MHz |
|
|
0.16 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
100 IRE |
|
|
|
|
|||
0.07 |
|
|
|
|
MODULATED RAMP |
|
0.14 |
|||||
DIFFERENTIAL GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
DIFFERENTIAL PHASE |
||||||
0.06 |
|
|
|
|
RL = 150V |
|
|
|
0.12 |
|||
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.10 |
||
0.04 |
|
PHASE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.08 |
|||
0.03 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.06 |
||
0.02 |
GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.04 |
||
|
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.02 |
|
|
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
|
SUPPLY VOLTAGE –6Volts
REV. D
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
AD811
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
8-Lead Plastic (N-8) 20-Lead LCC (E-20A) Package
Cerdip (Q-8)
SOIC (SO-8) Packages |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC NC |
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
20 19 |
NC |
|
|
|
NC |
|
NC 4 |
|
|
18 NC |
||
1 |
|
8 |
|
NC 5 |
|
AD811 |
17 NC |
||||
|
|
2 |
|
|
+V S |
|
|
||||
–IN |
|
|
7 |
|
–IN 6 |
|
|
16 +VS |
|||
+IN |
|
3 |
|
6 |
OUTPUT |
NC 7 |
|
|
15 NC |
||
|
|
+IN 8 |
|
|
14 OUTPUT |
||||||
–VS |
4 |
AD811 |
5 |
NC |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
NC = NO CONNECT |
|
|
|
9 |
10 11 12 13 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
S |
NC NC NC NC |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC = NO CONNECT |
|
|
|
16-Lead SOIC (R-16) Package |
20-Lead SOIC (R-20) Package |
||||||||||
NC |
1 |
|
|
|
16 NC |
NC |
1 |
|
20 NC |
||
NC |
2 |
|
|
|
15 NC |
NC |
2 |
|
19 |
NC |
|
–IN |
3 |
|
|
14 +V S |
NC |
3 |
|
18 |
NC |
||
NC |
4 |
|
|
|
13 NC |
–IN |
4 |
|
17 +V S |
||
+IN |
5 |
|
|
|
12 OUTPUT |
NC |
5 |
|
16 NC |
||
NC |
6 |
|
|
|
11 NC |
+IN |
6 |
|
15 OUTPUT |
||
–VS |
7 |
|
AD811 |
|
10 |
NC |
NC |
7 |
|
14 NC |
|
NC |
8 |
|
|
9 |
NC |
–VS |
8 |
|
13 |
NC |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
NC = NO CONNECT |
|
NC |
9 |
AD811 |
12 |
NC |
||||
|
|
NC 10 |
11 NC |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC = NO CONNECT |
|
||
The AD811 is also excellent for pulsed applications where transient response is critical. It can achieve a maximum slew rate of greater than 2500 V/µs with a settling time of less than 25 ns to 0.1% on a 2 volt step and 65 ns to 0.01% on a 10 volt step.
The AD811 is ideal as an ADC or DAC buffer in data acquisition systems due to its low distortion up to 10 MHz and its wide unity gain bandwidth. Because the AD811 is a current feedback amplifier, this bandwidth can be maintained over a wide range of gains. The AD811 also offers low voltage and current noise of 1.9 nV/√Hz and 20 pA/√Hz, respectively, and excellent dc accuracy for wide dynamic range applications.
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
G = +2 |
|
|
|
9 |
RL |
= 150V |
615V |
|
|
VS = |
||
|
|
RG = RFB |
|
|
– dB |
6 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 65V |
||
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
–3 |
|
|
|
|
–6 |
|
|
|
|
1M |
|
10 M |
100 M |
FREQUENCY – Hz
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 |
World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com |
Fax: 781/326-8703 |
© Analog Devices, Inc., 1999 |
AD811–SPECIFICATIONS (@ TA = +258C and VS = 615 V dc, RLOAD = 150 Ω unless otherwise noted)
|
|
|
|
|
AD811J/A1 |
|
|
AD811S2 |
|
|
Model |
Conditions |
VS |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Small Signal Bandwidth (No Peaking) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–3 dB |
RFB = 562 Ω |
± 15 V |
|
140 |
|
|
140 |
|
MHz |
|
G = +1 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
G = +2 |
RFB = 649 Ω |
± 15 V |
|
120 |
|
|
120 |
|
MHz |
|
G = +2 |
RFB = 562 Ω |
± 5 V |
|
80 |
|
|
80 |
|
MHz |
|
G = +10 |
RFB = 511 Ω |
± 15 V |
|
100 |
|
|
100 |
|
MHz |
|
0.1 dB Flat |
RFB = 562 Ω |
± 5 V |
|
25 |
|
|
25 |
|
MHz |
|
G = +2 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
RFB = 649 Ω |
± 15 V |
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
MHz |
|
Full Power Bandwidth3 |
VOUT = 20 V p-p |
± 15 V |
|
40 |
|
|
40 |
|
MHz |
|
Slew Rate |
VOUT = 4 V p-p |
± 5 V |
|
400 |
|
|
400 |
|
V/µs |
|
|
VOUT = 20 V p-p |
± 15 V |
|
2500 |
|
|
2500 |
|
V/µs |
|
Settling Time to 0.1% |
10 V Step, |
AV = –1 |
± 15 V |
|
50 |
|
|
50 |
|
ns |
Settling Time to 0.01% |
|
|
± 5 V |
|
65 |
|
|
65 |
|
ns |
Settling Time to 0.1% |
2 V Step, |
AV = –1 |
|
25 |
|
|
25 |
|
ns |
|
Rise Time, Fall Time |
RFB = 649, AV = +2 |
± 15 V |
|
3.5 |
|
|
3.5 |
|
ns |
|
Differential Gain |
f = 3.58 MHz |
± 15 V |
|
0.01 |
|
|
0.01 |
|
% |
|
Differential Phase |
f = 3.58 MHz |
± 15 V |
|
0.01 |
|
|
0.01 |
|
Degree |
|
THD @ fC = 10 MHz |
VOUT = 2 V p-p, AV = +2 |
± 15 V |
|
–74 |
|
|
–74 |
|
dBc |
|
Third Order Intercept4 |
@ fC = 10 MHz |
± 5 V |
|
36 |
|
|
36 |
|
dBm |
|
|
|
|
± 15 V |
|
43 |
|
|
43 |
|
dBm |
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE |
|
|
± 5 V, ± 15 V |
|
0.5 |
3 |
|
0.5 |
3 |
mV |
|
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
5 |
mV |
|
Offset Voltage Drift |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
5 |
|
µV/°C |
INPUT BIAS CURRENT |
|
|
± 5 V, ± 15 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
µA |
–Input |
|
|
|
2 |
5 |
|
2 |
5 |
||
|
TMIN to TMAX |
± 5 V, ± 15 V |
|
|
15 |
|
|
30 |
µA |
|
+Input |
|
|
|
2 |
10 |
|
2 |
10 |
µA |
|
|
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
25 |
µA |
|
TRANSRESISTANCE |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOUT = ± 10 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = ∞ |
± 15 V |
0.75 |
1.5 |
|
0.75 |
1.5 |
|
MΩ |
|
|
RL = 200 Ω |
± 15 V |
0.5 |
0.75 |
|
0.5 |
0.75 |
|
MΩ |
|
|
VOUT = ± 2.5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 150 Ω |
± 5 V |
0.25 |
0.4 |
|
0.125 |
0.4 |
|
MΩ |
|
COMMON-MODE REJECTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOS (vs. Common Mode) |
VCM = ± 2.5 |
± 5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMIN to TMAX |
56 |
60 |
|
50 |
60 |
|
dB |
|||
TMIN to TMAX |
VCM = ± 10 V |
± 15 V |
60 |
66 |
|
56 |
66 |
|
dB |
|
Input Current (vs. Common Mode) |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
1 |
3 |
|
1 |
3 |
µA/V |
|
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION |
VS = ± 4.5 V to ± 18 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOS |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
60 |
70 |
|
60 |
70 |
|
dB |
|
+Input Current |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
0.3 |
2 |
|
0.3 |
2 |
µA/V |
|
–Input Current |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
0.4 |
2 |
|
0.4 |
2 |
µA/V |
|
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE |
f = 1 kHz |
|
|
|
1.9 |
|
|
1.9 |
|
nV/√Hz |
INPUT CURRENT NOISE |
f = 1 kHz |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
20 |
|
pA/√Hz |
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
± 5 V |
|
± 2.9 |
|
|
± 2.9 |
|
|
Voltage Swing, Useful Operating Range5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|||
|
TJ = +25°C |
± 15 V |
|
± 12 |
|
|
± 12 |
|
V |
|
Output Current |
|
|
100 |
|
|
100 |
|
mA |
||
Short-Circuit Current |
|
|
|
|
150 |
|
|
150 |
|
mA |
Output Resistance |
(Open Loop @ 5 MHz) |
|
|
9 |
|
|
9 |
|
Ω |
|
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MΩ |
+Input Resistance |
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
–Input Resistance |
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
14 |
|
Ω |
Input Capacitance |
+Input |
|
|
|
7.5 |
|
|
7.5 |
|
pF |
Common-Mode Voltage Range |
|
|
± 5 V |
|
± 3 |
|
|
± 3 |
|
V |
|
|
|
± 15 V |
|
± 13 |
|
|
± 13 |
|
V |
POWER SUPPLY |
|
|
|
± 4.5 |
|
± 18 |
± 4.5 |
|
± 18 |
|
Operating Range |
|
|
± 5 V |
|
|
V |
||||
Quiescent Current |
|
|
|
14.5 |
16.0 |
|
14.5 |
16.0 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
± 15 V |
|
16.5 |
18.0 |
|
16.5 |
18.0 |
mA |
TRANSISTOR COUNT |
# of Transistors |
|
|
40 |
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES
1The AD811JR is specified with ± 5 V power supplies only, with operation up to ± 12 volts. 2See Analog Devices’ military data sheet for 883B tested specifications.
3FPBW = slew rate/(2 π VPEAK).
4Output power level, tested at a closed loop gain of two.
5Useful operating range is defined as the output voltage at which linearity begins to degrade.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2– |
REV. D |

AD811
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS1 |
±18 |
|
|
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
V |
|
AD811JR Grade Only . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . .±12 |
V |
Internal Power Dissipation2 . . . |
. . . . . Observe Derating Curves |
||
Output Short Circuit Duration |
. . . . . Observe Derating Curves |
||
Common-Mode Input Voltage |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . ± VS |
|
Differential Input Voltage . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . .± 6 |
V |
Storage Temperature Range (Q, E) . . . . . . . . |
–65°C to +150°C |
||
Storage Temperature Range (N, R) . . . . . . . . |
–65°C to +125°C |
||
Operating Temperature Range |
|
0°C to +70°C |
|
AD811J . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
||
AD811A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
. –40°C to +85°C |
|
AD811S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . |
. . . . . . . +300°C |
||
NOTES
1Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
28-Lead Plastic Package: θJA = 90°C/W 8-Lead Cerdip Package: θJA = 110°C/W 8-Lead SOIC Package: θJA = 155°C/W 16-Lead SOIC Package: θJA = 85°C/W 20-Lead SOIC Package: θJA = 80°C/W 20-Lead LCC Package: θJA = 70°C/W
ORDERING GUIDE
|
Temperature |
Package |
Model |
Range |
Option* |
AD811AN |
–40°C to +85°C |
N-8 |
AD811AR-16 |
–40°C to +85°C |
R-16 |
AD811AR-20 |
–40°C to +85°C |
R-20 |
AD811JR |
0°C to +70°C |
SO-8 |
AD811SQ/883B |
–55°C to +125°C |
Q-8 |
5962-9313101MPA |
–55°C to +125°C |
Q-8 |
AD811SE/883B |
–55°C to +125°C |
E-20A |
5962-9313101M2A |
–55°C to +125°C |
E-20A |
AD811JR-REEL |
0°C to +70°C |
SO-8 |
AD811JR-REEL7 |
0°C to +70°C |
SO-8 |
AD811AR-16-REEL |
–40°C to +85°C |
R-16 |
AD811AR-16-REEL7 |
–40°C to +85°C |
R-16 |
AD811AR-20-REEL |
–40°C to +85°C |
R-20 |
AD811ACHIPS |
–40°C to +85°C |
Die |
AD811SCHIPS |
–55°C to +125°C |
Die |
*E = Ceramic Leadless Chip Carrier; N = Plastic DIP; Q = Cerdip; SO (R) = Small Outline IC (SOIC).
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum power that can be safely dissipated by the AD811 is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature. For the plastic packages, the maximum safe junction temperature is +145°C. For the cerdip and LCC packages, the maximum junction temperature is +175°C. If these maximums are exceeded momentarily, proper circuit operation will be restored as soon as the die temperature is reduced. Leaving the device in the “overheated” condition for an extended period can result in device burnout. To ensure proper operation, it is important to observe the derating curves in Figures 17 and 18.
While the AD811 is internally short circuit protected, this may not be sufficient to guarantee that the maximum junction temperature is not exceeded under all conditions. One important example is when the amplifier is driving a reverse terminated 75 Ω cable and the cable’s far end is shorted to a power supply. With power supplies of ± 12 volts (or less) at an ambient temperature of +25°C or less, if the cable is shorted to a supply rail, then the amplifier will not be destroyed, even if this condition persists for an extended period.
ESD SUSCEPTIBILITY
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 volts, which readily accumulate on the human body and on test equipment, can discharge without detection. Although the AD811 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may still occur on these devices if they are subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid any performance degradation or loss of functionality.
METALIZATION PHOTOGRAPH
Contact Factory for Latest Dimensions.
Dimensions Shown in Inches and (mm).
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD811 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. D |
–3– |

AD811–Typical Performance Characteristics
6Volts– |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = +258C |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
RANGE |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-COMMONMODE |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLY VOLTAGE –6Volts |
|
|
|
|
|
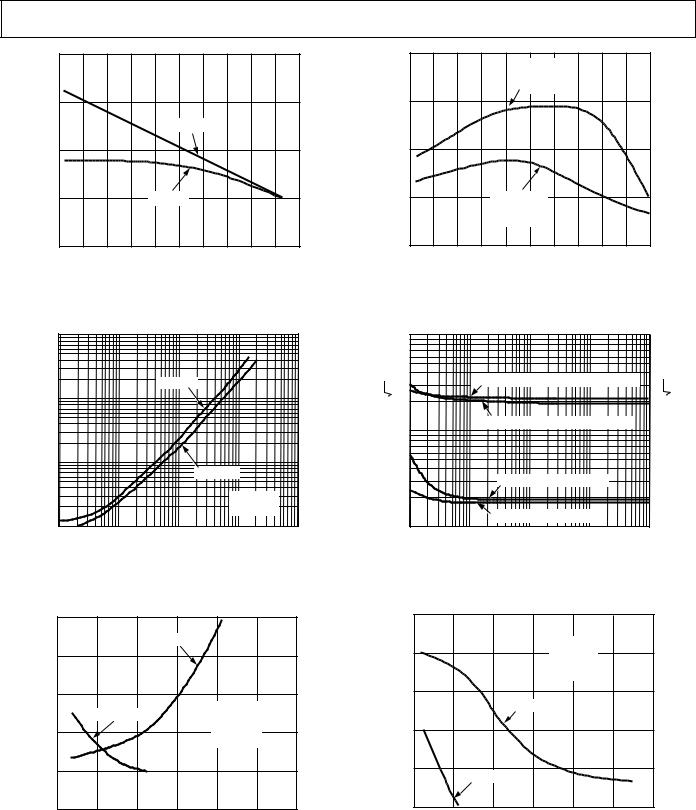
Figure 1. Input Common-Mode Voltage Range vs. Supply
MAGNITUDE OF THE OUTPUT VOLTAGE –6 Volts
20
TA = +258C
15
NO LOAD
10
RL = 150V
5
0
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
|
|
SUPPLY VOLTAGE –6 Volts |
|
|
Figure 4. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply
|
35 |
|
|
|
p–p |
30 |
|
|
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|
– Volts |
25 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
10 |
|
VS = 65V |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
100 |
1k |
10k |
LOAD RESISTANCE –V
Figure 2. Output Voltage Swing vs. Resistive Load
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NONINVERTING INPUT |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
65 TO 615V |
|
|
|
|
|
–mA |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 65V |
|
||
INPUT BIAS CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
INVERTING |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
–10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–20 |
|
|
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|||
|
–30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–60 –40 |
–20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
120 |
140 |
|
|
|
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
|
|
||||
Figure 3. Input Bias Current vs. Junction Temperature
mA |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 65V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
QUIESCENT |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–60 |
–40 |
–20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
120 |
140 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Figure 5. Quiescent Supply Current vs. Junction
Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mV |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 65V |
|
|
|
|
– |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OFFSET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–4 |
|
|
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|
|
||
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
–6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–60 |
–40 |
–20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
120 |
140 |
|
|
|
|
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
|
|
||||
Figure 6. Input Offset Voltage vs. Junction Temperature
–4– |
REV. D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD811 |
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|
|
|
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 200V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOUT = 610V |
|
|
|
|
||
SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT – |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRANSRESISTANCE – MV |
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
100 |
|
|
|
VS = 65V |
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
VS = 65V |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 150V |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOUT = 62.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–60 |
–40 |
–20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
120 |
140 |
|
–60 –40 |
–20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
100 |
120 |
140 |
|
|
|
|
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
JUNCTION TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
|
|
||||||||
Figure 7. Short Circuit Current vs. Junction Temperature |
Figure 10. Transresistance vs. Junction Temperature |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
–V |
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT RESISTANCE |
|
|
VS = 65V |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLOSED-LOOP |
0.1 |
|
|
VS = 615V |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
GAIN = +2 |
|
|
|
|
|
RFB = 649V |
|
|
|
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
10k |
100k |
1M |
10M |
100M |
FREQUENCY – Hz
Figure 8. Closed-Loop Output Resistance vs. Frequency
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RISE TIME |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
OVERSHOOT – % |
|
OVERSHOOT |
|
VS = 615V |
|
|||
|
|
VO |
= 1V p–p |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
4 |
|
|
|
RL = 150V |
20 |
||
RISETIMEns– |
|
|
|
GAIN = +2 |
|
||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
600 |
800 |
1.0k |
1.2k |
1.4k |
1.6k |
|
|
VALUE OF FEEDBACK RESISTOR (RFB) –V |
|
|
||||
Figure 9. Rise Time and Overshoot vs. Value of Feedback Resistor, RFB
|
100 |
|
|
|
100 |
Hz |
|
NONINVERTING CURRENT VS = 65 TO 15V |
Hz |
||
|
|
|
|
||
– nV/ |
|
|
INVERTING CURRENT VS = 65 TO 15V |
– pA/ |
|
NOISE VOLTAGE |
10 |
|
10 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
VOLTAGE NOISE VS = 615V |
NOISECURRENT |
||
|
1 |
|
VOLTAGE NOISE VS = 65V |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
10 |
100 |
1k |
10k |
100k |
|
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz |
|
|
Figure 11. Input Noise vs. Frequency
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VO = 1V p–p |
|
|
|
MHz |
160 |
|
|
|
VS= 615V |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
RL= 150V |
|
|
|
|
–3dB BANDWIDTH – |
|
|
|
|
GAIN = +2 |
|
|
PEAKING – dB |
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
BANDWIDTH |
|
|
|||
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
40 |
|
PEAKING |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
400 |
600 |
800 |
1.0k |
1.2k |
1.4k |
1.6k |
|
|
|
VALUE OF FEEDBACK RESISTOR (RFB) –V |
|
|
||||
Figure 12. 3 dB Bandwidth and Peaking vs. Value of RFB
REV. D |
–5– |
 Loading...
Loading...