Analog Devices AD9218BST-80, AD9218BST-65, AD9218BST-40, AD9218BST-105, AD9218-65PCB Datasheet
...
a |
10-Bit, 40/65/80/105 MSPS |
|
3 V Dual A/D Converter |
||
|
|
|
|
|
AD9218 |
|
|
|
FEATURES
Dual 10-Bit, 40 MSPS, 65 MSPS, 80 MSPS, and 105 MSPS ADC
Low Power: 275 mW at 105 MSPS per Channel On-Chip Reference and Track/Holds
300 MHz Analog Bandwidth Each Channel SNR = 57 dB @ 41 MHz, Encode = 80 MSPS
1 V p-p or 2 V p-p Analog Input Range Each Channel Single 3.0 V Supply Operation (2.7 V–3.6 V) Power-Down Mode for Single Channel Operation Two’s Complement or Offset Binary Output Mode Output Data Alignment Mode
Pin-Compatible with 8-Bit AD9288 –75 dBc Crosstalk between Channels
APPLICATIONS
Battery-Powered Instruments
Hand-Held Scopemeters
Low Cost Digital Oscilloscopes
I and Q Communications
Ultrasound Equipment
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
ENCODE A |
TIMING |
AD9218 |
|
|
||
AINA |
T/H |
ADC |
OUTPUT |
|
D9A–D0A |
|
|
REGISTER |
|||||
AINA |
|
10 |
10 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
USER |
|
REFINA |
|
|
|
|
SELECT #1 |
|
|
|
|
|
USER |
||
REFOUT |
|
REF |
|
|
||
|
|
|
SELECT #2 |
|||
REFINB |
|
|
|
|
DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
FORMAT/ |
|
AINB |
|
|
|
|
GAIN |
|
T/H |
ADC |
OUTPUT |
|
D9B–D0B |
||
A B |
REGISTER |
|||||
|
10 |
10 |
||||
IN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENCODE B |
TIMING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VD |
GND |
VDD |
||
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9218 is a dual 10-bit monolithic sampling analog-to- digital converter with on-chip track-and-hold circuits and is optimized for low cost, low power, small size and ease of use. The product operates at a 105 MSPS conversion rate with outstanding dynamic performance over its full operating range. Each channel can be operated independently.
The ADC requires only a single 3.0 V (2.7 V to 3.6 V) power supply and an encode clock for full operation. No external reference or driver components are required for many applications. The digital outputs are TTL/CMOS-compatible and a separate output power supply pin supports interfacing with 3.3 V or 2.5 V logic.
The clock input is TTL/CMOS-compatible and the 10-bit digital outputs can be operated from 3.0 V (2.5 V to 3.6 V) supplies. User-selectable options are available to offer a combination of power-down modes, digital data formats and digital data timing schemes. In power-down mode, the digital outputs are driven to a high-impedance state.
Fabricated on an advanced CMOS process, the AD9218 is available in a 48-lead surface-mount plastic package (7 × 7 mm LQFP) specified over the industrial temperature range (–40°C to +85°C).
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
Low Power—Just 275 mW power dissipation per channel at 105 MSPS. Other speed grade proportionally scaled down while maintaining high ac performance.
Pin Compatibility Upgrade—Allows easy migration from 8-bit to 10-bit. Pin-compatible with the 8-bit AD9288 dual ADC.
Ease of Use—On-chip reference and user controls provide flexibility in system design.
High Performance—Maintain 54 dB SNR at 105 MSPS with a Nyquist input.
Channel Crosstalk—Very low at –75 dBc.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 |
www.analog.com |
Fax: 781/326-8703 |
© Analog Devices, Inc., 2001 |
AD9218–SPECIFICATIONS
DC SPECIFICATIONS (VDD = 3.0 V, VD = 3.0 V; external reference, unless otherwise noted.)
|
|
Test |
AD9218BST-40/-65 |
AD9218BST-80/-105 |
|
|
|||
Parameter |
Temp |
Level |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESOLUTION |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
10 |
|
Bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACCURACY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No Missing Codes1 |
Full |
VI |
|
GNT |
|
|
GNT |
|
|
Offset Error2 |
25°C |
I |
–18 |
2 |
18 |
–18 |
2 |
18 |
LSB |
Gain Error2 |
25°C |
I |
–2 |
3 |
8 |
–2 |
3.5 |
8 |
% FS |
Differential Nonlinearity |
25°C |
I |
–1 |
±0.3/± 0.6 |
1/1.3 |
–1 |
±0.5/± 0.8 |
1.2/1.7 |
LSB |
(DNL) |
|
|
|
±0.8 |
|
|
±0.6/± 0.9 |
|
|
|
Full |
VI |
|
|
|
|
LSB |
||
Integral Nonlinearity (INL) |
25°C |
I |
–1/–1.6 |
±0.3/± 1 |
1/1.6 |
–1.35/–2.7 |
±0.75/± 2 |
1.35/2.7 |
LSB |
|
Full |
VI |
|
± 1 |
|
|
±1/±2.3 |
|
LSB |
TEMPERATURE DRIFT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ppm/°C |
Offset Error |
Full |
V |
|
10 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
Gain Error2 |
Full |
V |
|
80 |
|
|
100 |
|
ppm/°C |
Reference |
Full |
V |
|
40 |
|
|
40 |
|
ppm/°C |
REFERENCE |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal Reference Voltage |
I |
1.18 |
1.24 |
1.28 |
1.18 |
1.24 |
1.28 |
V |
|
(REFOUT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
kΩ |
Input Resistance (REFIN A, B) |
Full |
V |
9 |
11 |
13 |
9 |
11 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANALOG INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Differential Input Voltage |
Full |
V |
|
1 or 2 |
|
|
1 |
|
V |
Range (AIN, AIN)3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common-Mode Voltage |
Full |
V |
|
VD/3 |
|
|
VD/3 |
|
V |
Input Resistance |
Full |
VI |
8 |
10 |
14 |
8 |
10 |
14 |
kΩ |
Input Capacitance |
25°C |
V |
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
pF |
POWER SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VD |
Full |
IV |
2.7 |
3 |
3.6 |
2.7 |
3 |
3.6 |
V |
VDD |
Full |
IV |
2.7 |
3 |
3.6 |
2.7 |
3 |
3.6 |
V |
Supply Currents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IVD (VD = 3.0 V)4 |
Full |
VI |
|
108/117 |
113/122 |
|
172/183 |
175/188 |
mA |
IVDD (VDD = 3.0 V)4 |
25°C |
V |
|
7/11 |
|
|
13/17 |
|
mA |
Power Dissipation DC5 |
Full |
VI |
|
325/350 |
340/365 |
|
515/550 |
525/565 |
mW |
IVD Power-Down Current6 |
Full |
VI |
|
20 |
|
|
22 |
|
mA |
Power Supply Rejection Ratio |
25°C |
I |
|
± 1 |
|
|
± 1 |
|
mV/V |
NOTES
1No Missing Codes across industrial temperature range guaranteed for -40 MSPS, -65 MSPS, and -80 MSPS grades. No missing codes at room temperature guaranteed for -105 grade.
2Gain error and gain temperature coefficients are based on the ADC only (with a fixed 1.25 V external reference) -65 Grade in 2 V p-p range, -40, -85, -105 Grades in 1 V p-p range.
3(AIN – AIN) = ± 0.5 V in 1 V range (full scale), (AIN – AIN) = ± 1 V in 2 V range (full scale).
4AC Power Dissipation measured with rated encode and a 10.3 MHz analog input @ 0.5 dBFS, C LOAD = 5 pF. 5DC Power Dissipation measured with rated encode and a dc analog input (Outputs Static, IV DD = 0)
6In power-down state IVDD = ± 10 A typical (all grades).
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2– |
REV. 0 |
AD9218
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS (VDD = 3.0 V, VD = 3.0 V; external reference, unless otherwise noted.)
|
|
Test |
AD9218BST-40/-65 |
AD9218BST-80/-105 |
|
||||
Parameter |
Temp |
Level |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIGITAL INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Encode Input Common Mode |
Full |
V |
|
VD/2 |
|
|
VD/2 |
|
V |
Encode “1” Voltage |
Full |
VI |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
V |
Encode “0” Voltage |
Full |
VI |
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
0.8 |
V |
Encode Input Resistance |
Full |
VI |
1.8 |
2.0 |
2.3 |
1.8 |
2.0 |
2.3 |
kΩ |
Logic “1” Voltage—S1, S2, DFS |
Full |
VI |
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
V |
Logic “0” Voltage—S1, S2, DFS |
Full |
VI |
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
0.8 |
V |
Logic “1” Current—S1 |
Full |
VI |
–50 |
± 10 |
+50 |
–50 |
± 10 |
+50 |
µA |
Logic “0” Current—S1 |
Full |
VI |
–400 |
–230 |
–50 |
–400 |
–230 |
–50 |
µA |
Logic “1” Current—S2 |
Full |
VI |
50 |
230 |
400 |
50 |
230 |
400 |
µA |
Logic “0” Current—S2 |
Full |
VI |
–50 |
± 10 |
+50 |
–50 |
± 10 |
+50 |
µA |
Logic “1” Current—DFS |
Full |
VI |
30 |
100 |
200 |
30 |
100 |
200 |
µA |
Logic “0” Current—DFS |
Full |
VI |
–400 |
–230 |
–50 |
–400 |
–230 |
–50 |
µA |
Input Capacitance—S1, S2, Encode Inputs |
25°C |
V |
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
pF |
Input Capacitance DFS |
25°C |
V |
|
4.5 |
|
|
4.5 |
|
pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIGITAL OUTPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Logic “1” Voltage |
Full |
VI |
2.45 |
|
|
2.45 |
|
|
V |
Logic “0” Voltage |
Full |
VI |
|
|
0.05 |
|
|
0.05 |
V |
Output Coding |
|
|
Two’s Comp. or Offset Binary |
Two’s Comp. or Offset Binary |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specifications subject to change without notice.
AC SPECIFICATIONS (VDD = 3.0 V, VD = 3.0 V; external reference, unless otherwise noted.)
|
|
Test |
AD9218BST-40/-65 |
AD9218BST-80/-105 |
|
||||
Parameter |
Temp |
Level |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Without Harmonics) |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN = 10.3 MHz |
I |
58/55 |
59/57 |
|
57/53 |
58/55 |
|
dB |
|
fIN = Nyquist2 |
25°C |
I |
-/54 |
59/56 |
|
55/52 |
57/54 |
|
dB |
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SINAD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(With Harmonics) |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN = 10.3 MHz |
I |
58/54 |
59/56 |
|
56/52 |
58/53 |
|
dB |
|
fIN = Nyquist2 |
25°C |
I |
-/53 |
59/55 |
|
55/51 |
57/53 |
|
dB |
Effective Number of Bits |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN = 10.3 MHz |
I |
9.4/8.8 |
9.6/9.1 |
|
9.1/8.4 |
9.4/8.6 |
|
Bits |
|
fIN = Nyquist2 |
25°C |
I |
-/8.6 |
9.6/8.9 |
|
9/8.3 |
9.3/8.6 |
|
Bits |
Second Harmonic Distortion |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN = 10.3 MHz |
I |
–72/–66 |
–89/–77 |
|
–69/–60 |
–77/–68 |
|
dBc |
|
fIN = Nyquist2 |
25°C |
I |
-/–63 |
–89/–72 |
|
–65/–57 |
–76/–66 |
|
dBc |
Third Harmonic Distortion |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN = 10.3 MHz |
I |
–68/–62 |
–79/–68 |
|
–62/–57 |
–71/–63 |
|
dBc |
|
fIN = Nyquist2 |
25°C |
I |
-/–60 |
–78/–64 |
|
–63/–57 |
–73/–69 |
|
dBc |
Spurious Free Dynamic Range SFDR |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN = 10.3 MHz |
I |
–68/–62 |
–79/–67 |
|
–62/–57 |
–69/–62 |
|
dBc |
|
fIN = Nyquist2 |
25°C |
I |
-/–60 |
–78/–64 |
|
–63/–57 |
–70/–63 |
|
dBc |
Two-Tone Intermod Distortion (IMD) |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN1 = 10 MHz, fIN2 = 11 MHz |
V |
|
–74/–73 |
|
|
|
|
dBc |
|
at –7 dBFS |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fIN1 = 30 MHz, fIN2 = 31 MHz |
V |
|
–73/–73 |
|
|
–77/–67 |
|
dBc |
|
at –7 dBFS |
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Bandwidth, Full Power |
V |
|
300 |
|
|
300 |
|
MHz |
|
Crosstalk |
25°C |
V |
|
–75 |
|
|
–75 |
|
dBc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES
1AC specs based on an analog input voltage of –0.5 dBFS at 10.3 MHz unless otherwise noted. AC specs for -40, -80, -105 grades are tested in 1 V p-p range and driven differentially. AC specs for -65 grade are tested in 2 V p-p range and driven differentially.
2The -65, -80, and -105 grades are tested close to Nyquist for that grade: 31 MHz, 39 MHz, and 51 MHz for the -65, -80, and -105 grades respectively.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. 0 |
–3– |

AD9218–SPECIFICATIONS
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS (VDD = 3.0 V, VD = 3.0 V; external reference, unless otherwise noted.)
|
|
Test |
AD9218BST-40/-65 |
AD9218BST-80/-105 |
|
||
Parameter |
Temp |
Level |
Min Typ |
Max |
Min Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENCODE INPUT PARAMETERS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Encode Rate |
Full |
VI |
40/65 |
|
80/105 |
|
MSPS |
Minimum Encode Rate |
Full |
IV |
|
20/20 |
|
20/20 |
MSPS |
Encode Pulsewidth High (tEH) |
Full |
IV |
7/6 |
|
5/3.8 |
|
ns |
Encode Pulsewidth Low (tEL) |
Full |
IV |
7/6 |
|
5/3.8 |
|
ns |
Aperture Delay (tA) |
25°C |
V |
2 |
|
2 |
|
ns |
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) |
25°C |
V |
3 |
|
3 |
|
ps rms |
DIGITAL OUTPUT PARAMETERS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Valid Time (tV)* |
Full |
VI |
3 |
|
3 |
|
ns |
Output Propagation Delay (tPD)* |
Full |
VI |
4.5 |
7 |
4.5 |
6 |
ns |
Output Rise Time (tR) |
25°C |
V |
1 |
|
1.0 |
|
ns |
Output Fall Time (tF) |
25°C |
V |
1.2 |
|
1.2 |
|
ns |
Out of Range Recovery Time |
25°C |
V |
5 |
|
5 |
|
ns |
Transient Response Time |
25°C |
V |
5 |
|
5 |
|
ns |
Recovery Time from Power-Down |
25°C |
V |
10 |
|
10 |
|
Cycles |
Pipeline Delay |
Full |
IV |
5 |
|
5 |
|
Cycles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES
*tV and tPD are measured from the 1.5 level of the ENCODE input to the 50%/50% levels of the digital outputs swing. The digital output load during test is not to exceed an ac load of 5 pF or a dc current of ± 40 A. Rise and fall times measured from 10% to 90%.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
SAMPLE N |
SAMPLE |
|
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
|
N+1 |
|
N+5 |
N+6 |
AINA, |
|
|
|
|
AINB |
|
|
|
|
tA |
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
|
N+2 |
N+3 |
N+4 |
|
|
tEH |
tEL |
|
|
|
1/fS |
|
|
|
ENCODE
A&B
|
|
|
|
|
tPD |
tV |
D9A–D0A |
DATA N–5 |
DATA N–4 |
DATA N–3 |
DATA N–2 |
DATA N–1 |
DATA N |
D9B–D0B |
DATA N–5 |
DATA N–4 |
DATA N–3 |
DATA N–2 |
DATA N–1 |
DATA N |
Figure 1. Normal Operation, Same Clock (S1 = 1, S2 = 0) Channel Timing
–4– |
REV. 0 |
AD9218
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
|
N |
N+1 |
N+2 |
|
|
|
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
N+7 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N+8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AINA, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AINB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tA |
|
SAMPLE |
|
SAMPLE SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
tEL |
N+3 |
|
N+4 |
N+5 |
N+6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
tEH |
1/fS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
ENCODE A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tPD |
|
|
tV |
ENCODE B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D9A–D0A |
DATA N–10 |
DATA N–8 |
DATA N–6 |
DATA N–4 |
DATA N–2 |
DATA N |
DATA N+2 |
||||
D9B–D0B |
DATA N–9 |
DATA N–7 |
DATA N–5 |
DATA N–3 |
DATA N–1 |
DATA N+1 |
|||||
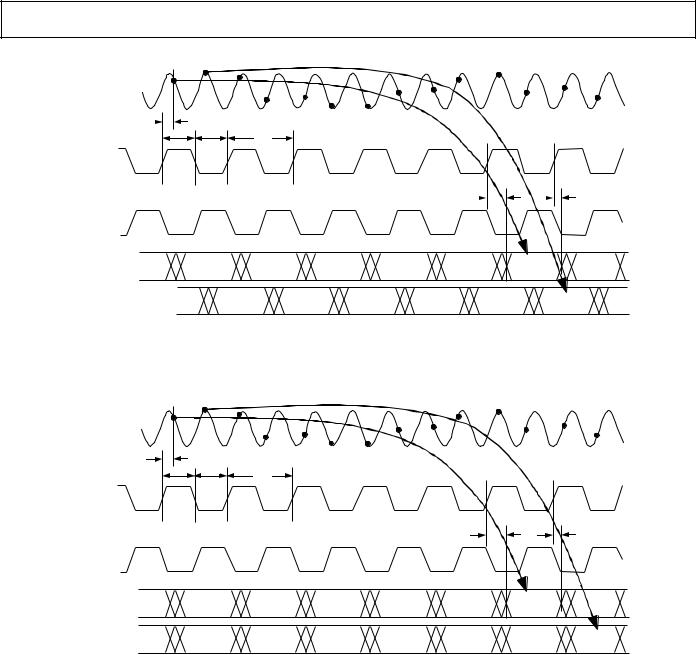
Figure 2. Normal Operation with Two Clock Sources (S1 = 1, S2 = 0) Channel Timing
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE SAMPLE |
|
|
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
N |
N+1 |
N+2 |
|
|
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
|
N+7 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
N+8 |
|
|
AINA, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AINB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tA |
|
SAMPLE |
SAMPLE SAMPLE |
SAMPLE |
|
|
|
|
tEL |
N+3 |
N+4 |
N+5 |
N+6 |
|
|
|
|
tEH |
1/fS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
ENCODE A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tPD |
|
tV |
ENCODE B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D9A–D0A |
DATA N–10 |
DATA N–8 |
|
DATA N–6 |
DATA N–4 |
DATA N–2 |
DATA N |
DATA N+2 |
D9B–D0B |
DATA N–11 |
DATA N–9 |
|
DATA N–7 |
DATA N–5 |
DATA N–3 |
DATA N–1 |
DATA N+1 |
Figure 3. Data Align with Two Clock Sources (S1 = 1, S2 = 1) Channel Timing
REV. 0 |
–5– |

AD9218
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS1 |
|
|
VD, VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 V |
|
Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
–0.5 V to VD + 0.5 |
V |
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
–0.5 V to VDD + 0.5 |
V |
REFIN Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
–0.5 V to VD + 0.5 |
V |
Digital Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . 20 mA |
|
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . –55°C to +125°C |
|
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . –65°C to +150°C |
|
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . 150°C |
|
Maximum Case Temperature . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . 150°C |
|
θJA2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . 57°C/W |
|
NOTES
1Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions outside of those indicated in the operation sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2Measured on a four-layer board with solid ground plane.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test Level
I 100% production tested.
II100% production tested at 25°C and sample tested at specified temperatures.
III Sample tested only.
IV Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization testing.
V Parameter is a typical value only.
VI 100% production tested at 25°C; guaranteed by design and characterization testing for industrial temperature range; 100% production tested at temperature extremes for military devices.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD9218 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
ORDERING GUIDE
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
|
|
Temperature |
|
|
|
Package |
||
Model |
|
Range |
|
|
Package Description |
Option |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD9218BST-40, -65, -80, -105 |
|
–40°C to +85°C |
|
Metric Quad Flat Pack (1.4 mm thick: LQFP) |
ST-48 |
|||
AD9218-65PCB |
|
25°C |
|
|
Evaluation Board (Supports -40/-65 Grade) |
|
||
AD9218-105PCB |
|
25°C |
|
|
Evaluation Board (Supports -80/-105 Grade) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Table I. User Select Modes |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
S1 |
S2 |
User Select Options |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
0 |
Power-Down Both Channel A and B. |
|
||||
0 |
|
1 |
Power-Down Channel B Only. |
|
||||
1 |
|
0 |
Normal Operation (Data Align Disabled). |
|
||||
1 |
|
1 |
Data Align Enabled (data from both channels |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
available on rising edge of Clock A. Channel B |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
data is delayed by a 1/2 clock cycle.) |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–6– |
REV. 0 |

AD9218
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Pin No. |
Mnemonic |
|
|
|
|
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1, 12, 16, 27, 29, 32, 34, 45 |
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
Ground |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
2 |
AINA |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Input for Channel A |
|
|
|||||||||||||
3 |
AINA |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Input for Channel A (Complementary) |
|||||||||||||||
4 |
DFS/GAIN |
|
|
|
|
Data Format Select and Analog Input Gain Mode. (Low = offset binary out- |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
put available, 1 V p-p supported; high = two’s complement output available, |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 V p-p supported; floating = offset binary output available, 2 V p-p supported; |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Set to VREF = two’s complement output available, 2 V p-p supported.) |
|||||||||||||
5 |
REFINA |
|
|
|
|
|
Reference Voltage Input for Channel A |
|||||||||||||||
6 |
REFOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
Internal Reference Voltage |
|
|
|||||||||||||
7 |
REFINB |
|
|
|
|
|
Reference Voltage Input for Channel B |
|||||||||||||||
8 |
S1 |
|
|
|
|
|
User Select #1 (Refer to Table I) |
|||||||||||||||
9 |
S2 |
|
|
|
|
|
User Select #2 (Refer to Table I) |
|||||||||||||||
10 |
AINB |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Input for Channel B (Complementary) |
|||||||||||||||
11 |
AINB |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Input for Channel B |
|
|
|||||||||||||
13, 30, 31, 48 |
VD |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Supply (3 V) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
14 |
ENCB |
|
|
|
|
|
Clock Input for Channel B |
|
|
|||||||||||||
15, 28, 33, 46 |
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Supply (2.5 V to 3.6 V) |
|
||||||||||||||
17–26 |
D9B–D0B |
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Output for Channel B (D9B = MSB) |
|||||||||||||||
35–44 |
D0A–D9A |
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Output for Channel A (D9A = MSB) |
|||||||||||||||
47 |
ENCA |
|
|
|
|
|
Clock Input for Channel A |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIN CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
A |
V |
GND |
(MSB) |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENC |
D9 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
DD |
|
A |
A |
A |
A |
A |
A |
A |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
47 |
46 |
45 |
44 |
43 |
42 |
41 |
40 |
39 |
38 |
37 |
|
|
||
|
GND |
1 |
|
PIN 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
D1A |
|||||||
|
AINA |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
IDENTIFIER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
D0A |
|||||||||||
|
|
AINA |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
GND |
|||||
|
DFS/GAIN |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
VDD |
||||||
|
REFINA |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
AD9218 |
|
|
|
32 |
GND |
|||||||||
|
REFOUT |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
VD |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOP VIEW |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
REF |
IN |
B |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
V |
D |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Not to Scale) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
S1 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
GND |
|||
|
|
|
|
S2 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
VDD |
|||
|
|
AINB |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
GND |
|||||
|
AINB 11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
D0B |
||||||||
|
GND 12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
D1B |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
ENC |
V |
GND |
(MSB)D9 |
D8 |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
B |
DD |
|
B |
B |
B |
B |
B |
B |
B |
B |
|
|
|
REV. 0 |
–7– |

AD9218
TERMINOLOGY
Analog Bandwidth
The analog input frequency at which the spectral power of the fundamental frequency (as determined by the FFT analysis) is reduced by 3 dB.
Aperture Delay
The delay between the 50% point of the rising edge of the ENCODE command and the instant at which the analog input is sampled.
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter)
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay.
Crosstalk
Coupling onto one channel being driven by a low level (–40 dBFS) signal when the adjacent interfering channel is driven by a full-scale signal.
Differential Analog Input Resistance, Differential Analog Input Capacitance and Differential Analog Input Impedance
The real and complex impedances measured at each analog input port. The resistance is measured statically and the capacitance and differential input impedances are measured with a network analyzer.
Differential Analog Input Voltage Range
The peak-to-peak differential voltage that must be applied to the converter to generate a full-scale response. Peak differential voltage is computed by observing the voltage on a single pin and subtracting the voltage from the other pin, which is 180 degrees out of phase. Peak-to-peak differential is computed by rotating the inputs phase 180 degrees and again taking the peak measurement. The difference is then computed between both peak measurements.
Differential Nonlinearity
The deviation of any code width from an ideal 1 LSB step.
Effective Number of Bits
The effective number of bits (ENOB) is calculated from the measured SNR based on the equation:
ENOB = SNRMEASURED – 1.76 dB
6.02
ENCODE Pulsewidth/Duty Cycle
Pulsewidth high is the minimum amount of time that the ENCODE pulse should be left in Logic 1 state to achieve rated performance; pulsewidth low is the minimum time ENCODE pulse should be left in low state. See timing implications of changing tENCH in text. At a given clock rate, these specifications define an acceptable ENCODE duty cycle.
Full-Scale Input Power
Expressed in dBm. Computed using the following equation:
|
V 2 Full −Scale rms |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZINPUT |
||||
PowerFull −Scale |
= 10 log |
|
|
|
|
|
0.001 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gain Error
Gain error is the difference between the measured and ideal full scale input voltage range of the ADC.
Harmonic Distortion, Second
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the second harmonic component, reported in dBc.
Harmonic Distortion, Third
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the third harmonic component, reported in dBc.
Integral Nonlinearity
The deviation of the transfer function from a reference line measured in fractions of 1 LSB using a “best straight line” determined by a least square curve fit.
Minimum Conversion Rate
The encode rate at which the SNR of the lowest analog signal frequency drops by no more than 3 dB below the guaranteed limit.
Maximum Conversion Rate
The encode rate at which parametric testing is performed.
Output Propagation Delay
The delay between a differential crossing of ENCODE and ENCODE and the time when all output data bits are within valid logic levels.
Noise (for Any Range within the ADC)
|
|
FSdBm −SNRdBc −SignaldBFS |
|
VNOISE = |
|
|
|
|
|||
Z 0.001 10 |
10 |
|
|
Where Z is the input impedance, FS is the full scale of the device for the frequency in question, SNR is the value for the particular input level, and Signal is the signal level within the ADC reported in dB below full scale. This value includes both thermal and quantization noise.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
The ratio of a change in input offset voltage to a change in power supply voltage.
Signal-to-Noise-and-Distortion (SINAD)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set 1 dB below full scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components, including harmonics but excluding dc.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (without Harmonics)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components, excluding the first five harmonics and dc.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the peak spurious spectral component. The peak spurious component may or may not be a harmonic. May be reported in dBc (i.e., degrades as signal level is lowered), or dBFS (always related back to converter full scale).
Two-Tone Intermodulation Distortion Rejection
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value of the worst third order intermodulation product; reported in dBc.
Two-Tone SFDR
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value of the peak spurious component. The peak spurious component may or may not be an IMD product. May be reported in dBc (i.e., degrades as signal level is lowered), or in dBFS (always related back to converter full scale).
–8– |
REV. 0 |
 Loading...
Loading...