Analog Devices AD641AP, AD641AN, AD641-EB, 5962-9559801MRA Datasheet

a |
250 MHz Demodulating |
Logarithmic Amplifier |
FEATURES
Logarithmic Amplifier Performance
Usable to 250 MHz
44 dB Dynamic Range
62.0 dB Log Conformance
37.5 mV/dB Voltage Output
Stable Slope and Intercepts
2.0 nV/√Hz Input Noise Voltage
50 mV Input Offset Voltage
Low Power
65 V Supply Operation
9 mA (+VS), 35 mA (–VS) Quiescent Current
Onboard Resistors
Onboard 103 Attenuator
Dual Polarity Current Outputs
Direct Coupled Differential Signal Path
APPLICATIONS
IF/RF Signal Processing
Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
High Speed Signal Compression
High Speed Spectrum Analyzer
ECM/Radar
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD641 is a 250 MHz, demodulating logarithmic amplifier with an accuracy of ±2.0 dB and 44 dB dynamic range. The AD641 uses a successive detection architecture to provide an output current that is logarithmically proportional to its input voltage. The output current can be converted to a voltage using one of several on-chip resistors to select the slope. A single AD641 provides up to 44 dB of dynamic range at speeds up to 250 MHz, and two cascaded AD641s together can provide 58 dB of dynamic range at speeds up to 250 MHz. The AD641 is fully stable and well characterized over either the industrial or military temperature ranges.
The AD641 is not a logarithmic building block, but rather a complete logarithmic solution for compressing and measuring wide dynamic range signals. The AD641 is comprised of five stages and each stage has a full wave rectifier, whose current depends on the absolute value of its input voltage. The output of these stages are summed together to provide the demodulated output current scaled at 1 mA per decade (50 µA/dB).
Without utilizing the 10× input attenuator, log conformance of 2.0 dB is maintained over the input range –44 dBm to 0 dBm. The attenuator offers the most flexibility without significantly impacting performance.
REV. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
AD641
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
20-Lead Plastic DIP (N)
20-Lead Cerdip (Q)
–INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
+INPUT |
|
1 |
|
|
|
20 |
|||
ATN LO |
|
|
|
|
|
ATN OUT |
|
2 |
|
|
|
19 |
|||
ATN COM |
|
|
|
|
|
CKT COM |
|
3 |
|
|
|
18 |
|||
ATN COM |
|
|
|
|
|
RG1 |
|
4 |
|
|
|
17 |
|||
ATN IN |
|
AD641 |
|
RG0 |
|||
5 |
16 |
||||||
BL1 |
|
TOP VIEW |
|
RG2 |
|||
6 |
15 |
||||||
(Not to Scale) |
|||||||
–V |
|
|
LOG OUT |
||||
7 |
|
|
|
14 |
|||
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITC |
|
|
|
|
|
LOG COM |
|
8 |
|
|
|
13 |
|||
BL2 |
|
|
|
|
|
+VS |
|
9 |
|
|
|
12 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
+OUTPUT |
|
–OUTPUT |
10 |
|
|
|
11 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20-Lead PLCC (P)
|
|
|
ATN COM |
|
ATN LO |
–INPUT |
|
+INPUT |
ATN OUT |
|
|
|||
|
3 |
2 |
|
1 |
20 |
|
19 |
|
|
|
||||
ATN COM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIN 1 |
|
|
18 |
CKT COM |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IDENTIFIER |
|
|
||||
ATN IN |
5 |
|
|
|
AD641 |
|
|
17 |
RG1 |
|||||
BL1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
RG0 |
||||||
|
|
|
TOP VIEW |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
–V |
7 |
|
|
(Not to Scale) |
15 |
RG2 |
||||||||
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITC |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
LOG OUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
12 |
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BL2 |
–OUTSIG |
+OUTSIG |
|
+V |
LOGCOM |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
The 250 MHz bandwidth and temperature stability make this product ideal for high speed signal power measurement in RF/ IF systems. ECM/Radar and Communication applications are routinely in the 100 MHz–180 MHz range for power measurement. The bandwidth and accuracy, as well as dynamic range, make this part ideal for high speed, wide dynamic range signals.
The AD641 is offered in industrial (–40°C to +85°C) and military (–55°C to +125°C) package temperature ranges. Industrial versions are available in plastic DIP and PLCC; MIL versions are packaged in cerdip.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 |
World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com |
Fax: 781/326-8703 |
© Analog Devices, Inc., 1999 |
AD641–SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (VS = 65 V; TA = +258C, unless otherwise noted)
|
|
|
AD641A |
|
AD641S |
|
|
||
Parameter |
Conditions |
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
TRANSFER FUNCTION1 |
|
(IOUT = IY LOG |VIN/VX|for VIN = 0.75 mV to ±200 mV dc) |
|
||||||
LOG AMPLIFIER PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 dB Bandwidth |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
250 |
|
MHz |
Voltage Compliance Range |
|
|
–0.3 |
|
+VS – 1 |
–0.3 |
|
+VS – 1 |
V |
Slope Current, IY |
|
|
0.98 |
1.00 |
1.02 |
0.98 |
1.00 |
1.02 |
mA |
Accuracy vs. Temperature |
|
|
|
0.002 |
|
|
0.002 |
|
%/°C |
Over Temperature |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
|
0.98 |
|
1.02 |
mA |
Intercept dBm |
250 MHz |
|
–40.84 |
–40.43 |
–39.96 |
–40.84 |
–40.43 |
–39.96 |
dBm |
Over Temperature |
TMIN to TMAX, 250 MHz |
|
|
|
|
–40.59 |
|
–39.47 |
dBm |
Zero Signal Output Current2 |
|
|
|
–0.2 |
|
|
–0.2 |
|
mA |
ITC Disabled |
Pin 8 to COM |
|
|
–0.27 |
|
|
–0.27 |
|
mA |
Maximum Output Current |
|
|
|
|
2.3 |
|
|
2.3 |
mA |
DYNAMIC RANGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single Configuration |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
44 |
|
dB |
Over Temperature |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
40 |
|
|
38 |
|
dB |
Dual Configuration |
|
|
|
58 |
|
|
58 |
|
dB |
Over Temperature |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
52 |
|
|
52 |
|
dB |
LOG CONFORMANCE |
f = 250 MHz |
|
|
± 0.5 |
± 2.0 |
|
± 0.5 |
± 2.0 |
|
Single Configuration |
–44 dBm to 0 dBm |
|
|
|
dB |
||||
Over Temperature |
–42 dBm to –4 dBm; TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
±1.0 |
±2.5 |
|
±1.0 |
±2.5 |
dB |
|
–42 dBm to –2 dBm, TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
± 0.5 |
± 2.0 |
|
||
Dual Configuration |
S: –60 dBm to –2 dBm; |
|
|
± 0.5 |
± 2.0 |
|
dB |
||
Over Temperature |
A: –56 dBm to –4 dBm, TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
±1.0 |
±2.5 |
|
±1.0 |
±2.5 |
dB |
LIMITER CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
± 1.6 |
|
|
± 1.6 |
|
|
Flatness |
–44 dBm to 0 dBm @ 10.7 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
dB |
||
Phase Variation |
–44 dBm to 0 dBm @ 10.7 MHz |
|
|
± 2.0 |
|
|
± 2.0 |
|
Degrees |
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
kΩ |
Input Resistance |
Differential |
|
|
500 |
|
|
500 |
|
|
Input Offset Voltage |
Differential |
|
|
50 |
200 |
|
50 |
200 |
µV |
vs. Temperature |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
0.8 |
|
µV/°C |
Over Temperature |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
µV |
vs. Supply |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
µV/V |
Input Bias Current |
|
|
|
7 |
25 |
|
7 |
25 |
µA |
Input Bias Offset |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
µA |
Common Mode Input Range |
|
|
–2 |
|
+0.3 |
–2 |
|
+0.3 |
V |
SIGNAL INPUT (Pins 1, 20) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input Capacitance |
Either Pin to COM |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
pF |
Noise Spectral Density |
1 kHz to 10 MHz |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
nV/√Hz |
Tangential Sensitivity |
BW = 100 MHz |
|
|
–72 |
|
|
–72 |
|
dBm |
INPUT ATTENUATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Pins 2, 3, 4, 5 & 19) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Attenuation3 |
Pins 5 to Pin 19 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
20 |
|
dB |
Input Resistance |
Pins 5 to 3/4 |
|
|
300 |
|
|
300 |
|
Ω |
APPLICATION RESISTORS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
kΩ |
(Pins 15, 16, 17) |
|
|
0.995 |
1.000 |
1.005 |
0.995 |
1.000 |
1.005 |
|
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Pins 10, 11) |
|
|
|
± 180 |
|
|
± 180 |
|
|
Peak Differential Output4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
mV |
||
Output Resistance |
Either Pin to COM |
|
|
75 |
|
|
75 |
|
Ω |
Quiescent Output Voltage |
Either Pin to COM |
|
|
–90 |
|
|
–90 |
|
mV |
POWER SUPPLY |
|
|
± 4.5 |
|
± 7.5 |
± 4.5 |
|
± 7.5 |
|
Voltage Supply Range |
|
|
|
|
V |
||||
Quiescent Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+VS (Pin 12) |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
9 |
15 |
|
9 |
15 |
mA |
–VS (Pin 7) |
TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
35 |
60 |
|
35 |
60 |
mA |
NOTES
1Logarithms to base 10 are used throughout. The response is independent of the sign of VIN.
2The zero-signal current is a function of temperature unless internal temperature compensation (ITC) pin is grounded. 3Attenuation ratio trimmed to calibrate intercept to 10 mV when in use. It has a temperature coefficient of +0.3%/°C. 4The fully limited signal output will appear to be a square wave; its amplitude is proportional to absolute temperature.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2– |
REV. C |

AD641
ORDERING GUIDE
|
|
Temperature |
Package |
Package |
|||
Model |
|
Range |
|
Description |
Option |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD641AN |
|
–40°C to |
+85°C |
Plastic DIP |
N-20 |
||
AD641AP |
|
–40°C to |
+85°C |
PLCC |
P-20A |
||
5962-9559801MRA |
–55°C to |
+125°C |
Cerdip |
Q-20 |
|||
AD641-EB |
|
|
|
Evaluation Board |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
uJC |
|
uJA |
|
|
|
|
|
(8C/W) |
|
(8C/W) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
20-Lead Plastic DIP Package (N) |
|
24 |
|
61 |
|||
20-Lead Cerdip Package (Q) |
|
|
25 |
|
85 |
||
20-Lead Plastic Leadless Chip Carrier (P) |
28 |
|
75 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS* |
±7.5 V |
Supply Voltages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
Input Voltage (Pin 1 or Pin 20 to COM) . . . |
–3 V to +300 mV |
Attenuator Input Voltage (Pin 5 to Pin 3/4) . . |
. . . . . . . . . ±4 V |
Storage Temperature Range, Q . . . . . . . . . . |
–65°C to +150°C |
Storage Temperature Range, N, P . . . . . . . . |
–65°C to +125°C |
Ambient Temperature Range, Rated Performance |
|
Industrial, AD641A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
–40°C to +85°C |
Military, AD641S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
–55°C to +125°C |
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . |
. . . . . . . +300°C |
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may adversely affect device reliability.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD641 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. C |
–3– |
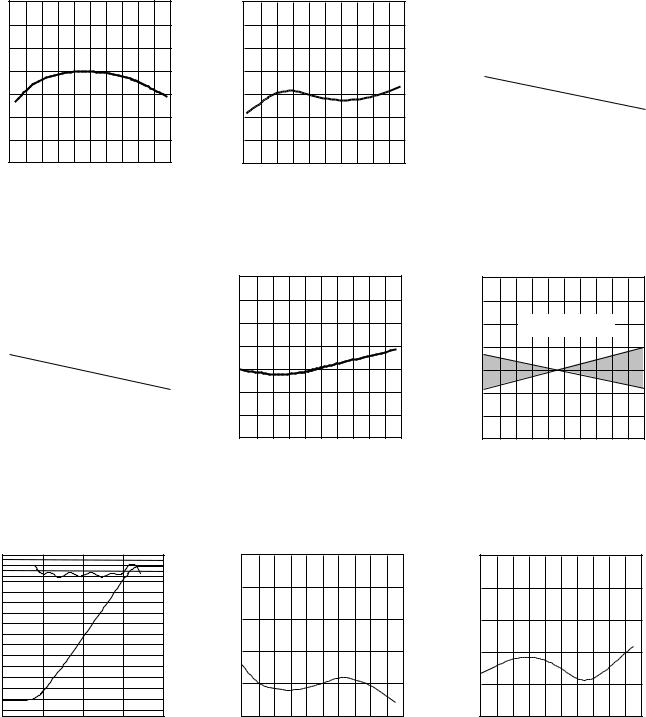
AD641–Typical DC Performance Characteristics
|
1.015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.010 |
|
|
|
|
|
mA |
1.005 |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.995 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLOPE |
0.990 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.985 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.980 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 100 120 140 |
|
–60 –40 –20 |
|||||
|
TEMPERATURE –8C |
|||||
Figure 1. Slope Current, IY, vs. Temperature
|
1.015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– mV |
1.010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1.005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1.000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERCEPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.990 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.995 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.985 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
5.5 |
6.0 |
6.5 |
7.0 |
7.5 |
|||||||
|
4.5 |
|||||||||||||
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGES –6 Volts
Figure 4. Intercept Voltage, VX, vs. Supply Voltages
|
2.4 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
– mA |
|
|
|
|
|
1.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT CURRENT |
1.4 |
|
|
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
ERROR – dB |
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
||
0.8 |
|
|
|
||
0.6 |
|
|
|
||
0.4 |
|
|
|
||
0.2 |
|
|
|
||
0 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
–0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
1.0 |
10.0 |
100.0 |
1000.0 |
INPUT VOLTAGE – mV (EITHER SIGN)
Figure 7. DC Logarithmic Transfer Function and Error Curve for Single AD641
|
1.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– mV |
1.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERCEPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–60 |
–40 –20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 100 120 140 |
|
|
TEMPERATURE –8C |
|||||
Figure 2. Intercept Voltage, VX, vs. Temperature
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
– mV |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERCEPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–60 –40 –20 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 100 120 140 |
|
TEMPERATURE –8C |
|||||
Figure 5. Intercept Voltage (Using Attenuator) vs. Temperature
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
– dB |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ERROR |
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ABSOLUTE |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 100 120 140 |
|
–60 –40 –20 |
|||||
|
TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
||||
Figure 8. Absolute Error vs. Temperature, VIN = ±1 mV to ±100 mV
|
1.006 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– mV |
1.004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1.002 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CURRENT |
1.000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLOPE |
0.998 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.996 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.994 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
5.5 |
6.0 |
6.5 |
7.0 |
7.5 |
|||||||
|
4.5 |
|||||||||||||
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGES –6 Volts
Figure 3. Slope Current, IY, vs. Supply Voltages
mV |
+0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
+0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+0.2 |
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE |
|||||
|
DEVIATION WILL BE WITHIN |
||||||
OFFSET |
|
SHADED AREA. |
|
|
|||
+0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DEVIATION |
–0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–0.3 |
|
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 100 120 140 |
|
–60 –40 –20 |
||||||
|
|
TEMPERATURE –8C |
|||||
Figure 6. Input Offset Voltage Deviation vs. Temperature
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
– dB |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ERROR |
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ABSOLUTE |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 100 120 140 |
|
–60 –40 –20 |
|||||
|
TEMPERATURE –8C |
|
||||
Figure 9. Absolute Error vs. Temperature, Using Attenuator. VIN = ±10 mV to ±1 V, Pin 8 Grounded to Disable ITC Bias
–4– |
REV. C |
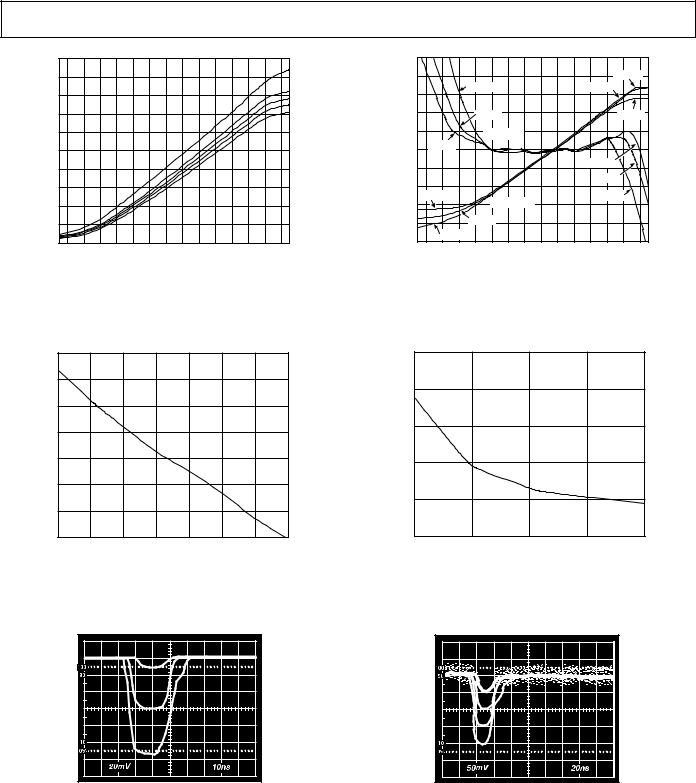
Typical AC Performance Characteristics–AD641
|
–2.25 |
|
|
–2.00 |
50MHz |
|
|
|
|
–1.75 |
150MHz |
|
190MHz |
|
mA |
|
210MHz |
–1.50 |
250MHz |
|
– |
–1.25 |
|
CURRENT |
|
|
–1.00 |
|
|
–0.75 |
|
|
OUTPUT |
|
|
–0.50 |
|
|
–0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.00 |
|
|
0.25 |
0 |
|
–52–48 –44–40 –36 –32 –28 –24 –20 –16 –12–4–8 2 |
INPUT LEVEL – dBm
Figure 10. AC Response at 50 MHz, 150 MHz, 190 MHz, 210 MHz at 250 MHz, vs. dBm Input (Sinusoidal Input)
|
87.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dBm |
82.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LEVEL |
80.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERCEPT |
77.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
72.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
100 |
150 |
170 |
190 |
210 |
230 |
250 |
|
|
|
INPUT FREQUENCY – MHz |
|
|
|||
Figure 11. Intercept Level (dBm) vs. Frequency (Cascaded AD641s—Sinusoidal Input)
|
–2.00 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
–1.75 |
|
+1258C |
4 |
|
|
–1.50 |
+1258C |
+258C |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
OUTPUT– mA |
–1.25 |
+258C |
–558C |
2 |
INERROR– dB |
–1.00 |
ERROR |
|
1 |
||
–0.75 |
–558C |
|
0 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
–0.50 |
|
+1258C |
–1 |
|
|
|
+258C |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
–0.25 |
+1258C |
|
–558C |
–2 |
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
|
|
||
|
–0.00 |
|
|
–3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0.25 |
+258C |
|
|
–4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0.50 |
–558C |
|
|
–5 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
||
|
–52–48 –44–40 –36 –32 –28 –24 –20 –16 –12–4–8 2 |
|||||
|
|
|
INPUT LEVEL – dBm |
|
|
|
Figure 13. Logarithmic Response and Linearity at |
|
|||||
200 MHz, TA for TA = –55°C, +25°C, +125°C |
|
|
||||
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
– mA |
0.95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
0.90 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.85 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLOPE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
150 |
190 |
210 |
250 |
|
INPUT FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 14. Slope Current, IY, vs. Input Frequency
5µs |
5µs |
100 |
|
90 |
|
10 |
|
0% |
|
20mV |
20mV |
Figure 12. Baseband Pulse Response of Single AD641, |
Figure 15. Baseband Pulse Response of Cascaded AD641s |
Inputs of 1 mV, 10 mV and 100 mV |
at Inputs of 0.2 mV, 2 mV, 20 mV and 200 mV |
REV. C |
–5– |
 Loading...
Loading...