Analog Devices AD549SH-883B, AD549SH, AD549LH, AD549KH, AD549JH Datasheet
...
a |
Ultralow Input Bias Current |
|
Operational Amplifier |
||
|
|
AD549* |
FEATURES
Ultralow Bias Current: 60 fA max (AD549L) 250 fA max (AD549J)
Input Bias Current Guaranteed Over Common-Mode Voltage Range
Low Offset Voltage: 0.25 mV max (AD549K) 1.00 mV max (AD549J)
Low Offset Drift: 5 mV/8C max (AD549K) 20 mV/8C max (AD549J)
Low Power: 700 mA max Supply Current
Low Input Voltage Noise: 4 mV p-p 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
MIL-STD-883B Parts Available
APPLICATIONS Electrometer Amplifiers Photodiode Preamp
pH Electrode Buffer
Vacuum lon Gage Measurement
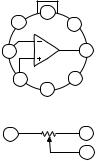
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
GUARD PIN, CONNECTED TO CASE
|
NC |
|
|
|
OFFSET NULL |
8 |
V+ |
|
|
1 |
AD549 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|||
INVERTING 2 |
|
6 |
OUTPUT |
|
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
5 |
|
|
NONINVERTING |
4 |
OFFSET |
||
NULL |
||||
INPUT |
V– |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
||
1 |
10kΩ |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
4 |
–15V |
|
|
VOS TRIM |
|
|
|
NC = NO CONNECTION |
|
|
||
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD549 is a monolithic electrometer operational amplifier with very low input bias current. Input offset voltage and input offset voltage drift are laser trimmed for precision performance. The AD549’s ultralow input current is achieved with “Topgate” JFET technology, a process development exclusive to Analog Devices. This technology allows the fabrication of extremely low input current JFETs compatible with a standard junctionisolated bipolar process. The 1015 Ω common-mode impedance, a result of the bootstrapped input stage, insures that the input current is essentially independent of common-mode voltage.
The AD549 is suited for applications requiring very low input current and low input offset voltage. It excels as a preamp for a wide variety of current output transducers such as photodiodes, photomultiplier tubes, or oxygen sensors. The AD549 can also be used as a precision integrator or low droop sample and hold. The AD549 is pin compatible with standard FET and electrometer op amps, allowing designers to upgrade the performance of present systems at little additional cost.
The AD549 is available in a TO-99 hermetic package. The case is connected to Pin 8 so that the metal case can be independently connected to a point at the same potential as the input terminals, minimizing stray leakage to the case.
*Protected by Patent No. 4,639,683.
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
The AD549 is available in four performance grades. The J, K, and L versions are rated over the commercial temperature range 0°C to +70°C. The S grade is specified over the military temperature range of –55°C to +125°C and is available processed to MIL-STD-883B, Rev C. Extended reliability PLUS screening is also available. Plus screening includes 168-hour burn-in, as well as other environmental and physical tests derived from MIL-STD-883B, Rev C.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1.The AD549’s input currents are specified, 100% tested and guaranteed after the device is warmed up. Input current is guaranteed over the entire common-mode input voltage range.
2.The AD549’s input offset voltage and drift are laser trimmed to 0.25 mV and 5 μV/°C (AD549K), 1 mV and 20 μV/°C (AD549J).
3.A maximum quiescent supply current of 700 μA minimizes heating effects on input current and offset voltage.
4.AC specifications include 1 MHz unity gain bandwidth and 3 V/μs slew rate. Settling time for a 10 V input step is 5 μs to 0.01%.
5.The AD549 is an improved replacement for the AD515, OPA104, and 3528.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
AD549–SPECIFICATIONS (@ +258C and VS = +15 V dc, unless otherwise noted)
Model |
|
AD549J |
|
|
AD549K |
|
|
AD549L |
|
|
AD549S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT BIAS CURRENT1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Either Input, VCM = 0 V |
|
150 |
250 |
|
75 |
100 |
|
40 |
60 |
|
75 |
100 |
fA |
|||||
Either Input, VCM = ±10 V |
|
150 |
250 |
|
75 |
100 |
|
40 |
60 |
|
75 |
100 |
fA |
|||||
Either Input at TMAX, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCM = 0 V |
|
11 |
|
|
4.2 |
|
|
2.8 |
|
|
420 |
|
pA |
|||||
Offset Current |
|
50 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
30 |
|
fA |
|||||
Offset Current at TMAX |
|
2.2 |
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
0.85 |
|
|
125 |
|
pA |
|||||
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Initial Offset |
|
0.5 |
1.0 |
|
0.15 |
0.25 |
|
0.3 |
0.5 |
|
0.3 |
0.5 |
mV |
|||||
Offset at TMAX |
|
|
1.9 |
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
0.9 |
|
|
2.0 |
mV |
|||||
vs. Temperature |
|
10 |
20 |
|
2 |
5 |
|
5 |
10 |
|
10 |
15 |
mV/°C |
|||||
vs. Supply |
|
32 |
100 |
|
10 |
32 |
|
10 |
32 |
|
10 |
32 |
mV/V |
|||||
vs. Supply, TMIN to TMAX |
|
32 |
100 |
|
10 |
32 |
|
10 |
32 |
|
32 |
50 |
mV/V |
|||||
Long-Term Offset Stability |
|
15 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
15 |
|
mV/Month |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
4 |
|
|
4 |
6 |
|
4 |
|
|
4 |
|
mV p-p |
|||||
f = 10 Hz |
|
90 |
|
|
90 |
|
|
90 |
|
|
90 |
|
nV/Ö |
Hz |
|
|||
f = 100 Hz |
|
60 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
60 |
|
nV/Ö |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hz |
||||||||||
f = 1 kHz |
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
nV/Ö |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hz |
||||||||||
f = 10 kHz |
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
|
35 |
|
nV/Ö |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hz |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT CURRENT NOISE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz |
|
0.7 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
0.36 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
fA rms |
|||||
f = 1 kHz |
|
0.22 |
|
|
0.16 |
|
|
0.11 |
|
|
0.16 |
|
fA/Ö |
Hz |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT IMPEDANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Differential |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDIFF = ±1 |
|
1013i1 |
|
|
1013i1 |
|
|
1013i1 |
|
|
1013i1 |
|
WipF |
|||||
Common Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCM = ±10 |
|
1015i0.8 |
|
|
1015i0.8 |
|
|
1015i0.8 |
|
|
1015i0.8 |
|
WipF |
|||||
OPEN-LOOP GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VO @ ±10 V, RL = 10 k |
300 |
1000 |
|
300 |
1000 |
|
300 |
1000 |
|
300 |
1000 |
|
V/mV |
|||||
VO @ ±10 V, RL = 10 k, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMIN to TMAX |
300 |
800 |
|
300 |
800 |
|
300 |
800 |
|
300 |
800 |
|
V/mV |
|||||
VO = ±10 V, RL = 2 k |
100 |
250 |
|
100 |
250 |
|
100 |
250 |
|
100 |
250 |
|
V/mV |
|||||
VO = ±10 V, RL = 2 k, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMIN to TMAX |
80 |
200 |
|
80 |
200 |
|
80 |
200 |
|
25 |
150 |
|
V/mV |
|||||
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Differential3 |
|
|
±20 |
|
|
±20 |
|
|
±20 |
|
|
±20 |
V |
|||||
Common-Mode Voltage |
–10 |
|
+10 |
–10 |
|
+10 |
–10 |
|
+10 |
–10 |
|
+10 |
V |
|||||
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V = +10 V, –10 V |
80 |
90 |
|
90 |
100 |
|
90 |
100 |
|
90 |
100 |
|
dB |
|||||
TMIN to TMAX |
76 |
80 |
|
80 |
90 |
|
80 |
90 |
|
80 |
90 |
|
dB |
|||||
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage @ RL = 10 k, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMIN to TMAX |
–12 |
|
+12 |
–12 |
|
+12 |
–12 |
|
+12 |
–12 |
|
+12 |
V |
|||||
Voltage @ RL = 2 k, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMIN to TMAX |
–10 |
|
+10 |
–10 |
|
+10 |
–10 |
|
+10 |
–10 |
|
+10 |
V |
|||||
Short Circuit Current |
15 |
20 |
35 |
15 |
20 |
35 |
15 |
20 |
35 |
15 |
20 |
35 |
mA |
|||||
TMIN to TMAX |
9 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
mA |
|||||
Load Capacitance Stability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G = +1 |
|
4000 |
|
|
4000 |
|
|
4000 |
|
|
4000 |
|
pF |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FREQUENCY RESPONSE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unity Gain, Small Signal |
0.7 |
1.0 |
|
0.7 |
1.0 |
|
0.7 |
1.0 |
|
0.7 |
1.0 |
|
MHz |
|||||
Full Power Response |
|
50 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
50 |
|
kHz |
|||||
Slew Rate |
2 |
3 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
2 |
3 |
|
V/ms |
|||||
Settling Time, 0.1% |
|
4.5 |
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
4.5 |
|
ms |
|||||
0.01% |
|
5 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
5 |
|
ms |
|||||
Overload Recovery, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50% Overdrive, G = –1 |
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
ms |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–2– |
REV. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD549 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Model |
|
AD549J |
|
|
AD549K |
|
|
AD549L |
|
AD549S |
|
|
|
|
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min Typ |
Max |
|
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
POWER SUPPLY |
|
±15 |
|
|
±15 |
|
|
±15 |
|
±15 |
|
|
|
|
Rated Performance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|||||
Operating |
65 |
|
618 |
65 |
|
618 |
65 |
|
618 |
65 |
618 |
|
V |
|
Quiescent Current |
|
0.60 |
0.70 |
|
0.60 |
0.70 |
|
0.60 |
0.70 |
0.60 |
0.70 |
|
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TEMPERATURE RANGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
°C |
|
Operating, Rated Performance |
0 |
|
+70 |
0 |
|
+70 |
0 |
|
+70 |
–55 |
+125 |
|
||
Storage |
–65 |
|
+150 |
–65 |
|
+150 |
–65 |
|
+150 |
–65 |
+150 |
|
°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PACKAGE OPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO-99 (H-08A) |
|
AD549JH |
|
|
AD549KH |
|
|
AD549LH |
|
AD549SH, AD549SH/883B |
|
|||
Chips |
|
AD549JChips |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES
1Bias current specifications are guaranteed after 5 minutes of operation at TA = +25°C. Bias current increases by a factor of 2.3 for every 10°C rise in temperature. 2Input offset voltage specifications are guaranteed after 5 minutes of operation at T A = +25°C.
3Defined as max continuous voltage between the inputs such that neither input exceeds ± 10 V from ground. Specifications subject to change without notice.
All min and max specifications are guaranteed. Specifications in boldface are tested on all production units at final electrical test. Results from those tests are used to calculate outgoing quality levels.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS1
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Internal Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .500 mW Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V2
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indefinite Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +VS and –VS Storage Temperature Range (H) . . . . . . . . . .–65°C to +125°C Operating Temperature Range
AD549J (K, L) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0°C to +70°C AD549S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . . . . . . . . +300°C
NOTES
1Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2For supply voltages less than ± 18 V, the absolute maximum input voltage is equal to the supply voltage.
METALIZATION PHOTOGRAPH
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm). Contact factory for latest dimensions.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD549 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. A |
–3– |
AD549–Typical Characteristics
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
± V |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+VIN |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
VOLTAGEINPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
–VIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
||||
|
0 |
||||||||
SUPPLY VOLTAGE ± V
Figure 1. Input Voltage Range vs. Supply Voltage
– µA |
800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
700 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QUIESCENT |
600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMPLIFIER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
||||
|
|
|
SUPPLY VOLTAGE ± V |
|
|
||||
Figure 4. Quiescent Current vs. Supply Voltage
– V/mV |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
-LOOP GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPEN |
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–55 |
–25 |
5 |
35 |
65 |
95 |
125 |
|||||||
TEMPERATURE – °C
Figure 7. Open-Loop Gain vs. Temperature
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+25°C |
|
|
|
|
+VOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 10k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
± V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–VOUT |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
VOLTAGE |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
||||||
|
0 |
||||||||||
SUPPLY VOLTAGE ± V
Figure 2. Output Voltage
Swing vs. Supply Voltage
|
120 |
– dB |
|
RATIO |
110 |
REJECTION |
100 |
|
|
-MODE |
90 |
COMMON |
80 |
|
|
|
70 |
–15 –10 0 +10 +15 INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE – V
Figure 5. CMRR vs. Input
Common-Mode Voltage
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| – µV |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
WARM-UP TIME – Minutes |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Figure 8. Change in Offset
Voltage vs. Warm-Up Time
p-p |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Volts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = ±15 VOLTS |
|
|
|
||||||
– |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
1k |
|
|
|
10k |
100k |
||||||||
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
LOAD RESISTANCE – Ω
Figure 3. Output Voltage
Swing vs. Load Resistance
– V/mV |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
-LOOP GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPEN |
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLY VOLTAGE ± V |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Figure 6. Open-Loop Gain vs. |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
Supply Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– fA |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–10 |
–5 |
0 |
|
5 |
|
10 |
|
||||||
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE ± V
Figure 9. Input Bias Current vs. Common-Mode Voltage
–4– |
REV. A |
 Loading...
Loading...