Analog Devices AD532SH, AD532SD, AD532SCHIPS, AD532KH, AD532KD Datasheet
...
a |
Internally Trimmed |
Integrated Circuit Multiplier |
FEATURES
Pretrimmed to 1.0% (AD532K)
No External Components Required
Guaranteed 1.0% max 4-Quadrant Error (AD532K)
Diff Inputs for (X1 – X2) (Y1 – Y2)/10 V Transfer Function Monolithic Construction, Low Cost
APPLICATIONS
Multiplication, Division, Squaring, Square Rooting
Algebraic Computation
Power Measurements
Instrumentation Applications
Available in Chip Form
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD532 is the first pretrimmed single chip monolithic multiplier/divider. It guarantees a maximum multiplying error of
± 1.0% and a ± 10 V output voltage without the need for any external trimming resistors or output op amp. Because the AD532 is internally trimmed, its simplicity of use provides design engineers with an attractive alternative to modular multipliers, and its monolithic construction provides significant advantages in size, reliability and economy. Further, the AD532 can be used as a direct replacement for other IC multipliers that require external trim networks.
FLEXIBILITY OF OPERATION
The AD532 multiplies in four quadrants with a transfer function of (X1 – X2)(Y1 – Y2)/10 V, divides in two quadrants with a 10 V Z/(X1 – X2) transfer function, and square roots in one quadrant with a transfer function of ±√ 10 V Z. In addition to these basic functions, the differential X and Y inputs provide significant operating flexibility both for algebraic computation and transducer instrumentation applications. Transfer functions, such as XY/10 V, (X2 – Y2)/10 V, ±X2/10 V, and 10 V Z/(X1 – X2), are easily attained and are extremely useful in many modulation and function generation applications, as well as in trigonometric calculations for airborne navigation and guidance applications, where the monolithic construction and small size of the AD532 offer considerable system advantages. In addition, the high CMRR (75 dB) of the differential inputs makes the AD532 especially well qualified for instrumentation applications, as it can provide an output signal that is the product of two transducergenerated input signals.
REV. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
AD532
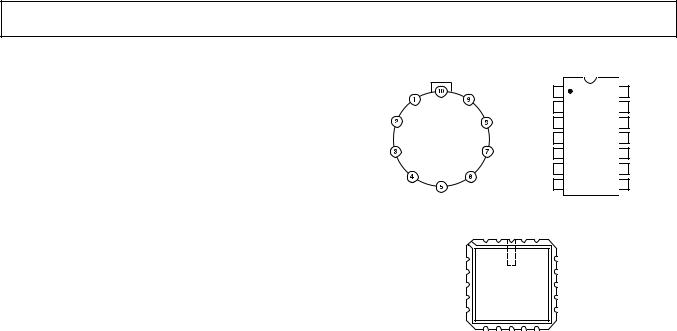
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
|
Y2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y1 |
|
VOS |
|
|
|
Z |
1 |
|
14 |
+VS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
2 |
|
13 |
Y1 |
+VS |
AD532 |
|
GND |
|
–VS |
3 |
|
12 |
Y2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
|
|
AD532 |
VOS |
|
|
TOP VIEW |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
TOP VIEW 11 |
||
Z |
(Not to Scale) |
|
X2 |
|
|
NC |
5 |
(Not to Scale) 10 |
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
6 |
|
9 |
X2 |
OUT |
|
X1 |
|
|
|
X1 |
7 |
|
8 |
NC |
|
–VS |
OUT |
|
NC |
+V |
|
NC = NO CONNECT |
|
||
|
|
Z |
Y |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
S |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
20 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
–VS 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
Y2 |
|
|
|
NC 5 |
|
AD532 |
|
17 |
NC |
|
|||
|
NC 6 |
|
|
16 |
VOS |
|
||||
|
|
TOP VIEW |
|
|
||||||
|
NC 7 |
(Not to Scale) |
15 |
NC |
|
|||||
|
NC 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
GND |
|
|
|
|
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
1 |
NC |
NC |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
|||
NC = NO CONNECT
GUARANTEED PERFORMANCE OVER TEMPERATURE
The AD532J and AD532K are specified for maximum multiplying errors of ± 2% and ± 1% of full scale, respectively at 25°C, and are rated for operation from 0°C to 70°C. The AD532S has a maximum multiplying error of ± 1% of full scale at 25°C; it is also 100% tested to guarantee a maximum error of ± 4% at the extended operating temperature limits of –55°C and +125°C. All devices are available in either the hermetically-sealed TO-100 metal can, TO-116 ceramic DIP or LCC packages. J, K, and S grade chips are also available.
ADVANTAGES OF ON-THE-CHIP TRIMMING OF THE MONOLITHIC AD532
1.True ratiometric trim for improved power supply rejection.
2.Reduced power requirements since no networks across supplies are required.
3.More reliable since standard monolithic assembly techniques can be used rather than more complex hybrid approaches.
4.High impedance X and Y inputs with negligible circuit loading.
5.Differential X and Y inputs for noise rejection and additional computational flexibility.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 |
World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com |
Fax: 781/326-8703 |
© Analog Devices, Inc., 2001 |
AD532–SPECIFICATIONS (@ 25 C, VS = 15 V, R ≥ 2 k VOS grounded, unless otherwise noted.)
|
|
|
|
AD532J |
|
|
|
|
|
AD532K |
|
|
|
|
|
AD532S |
|
|
|
||||||
Model |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
|
Typ |
Max |
Min |
|
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|||||||||||||
MULTIPLIER PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transfer Function |
|
(X1 – X2 )(Y1 – Y2 ) |
|
(X1 – X2 )(Y1 – Y2 ) |
|
(X1 – X2 )(Y1 – Y2 ) |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
10V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10V |
|
|
|
|||||
Total Error (–10 V ≤ X, Y ≤ +10 V) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
±1.5 |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
± |
0.7 |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
±0.5 |
1.0 |
% |
|||||||
TA = Min to Max |
|
|
|
±2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±0.01 |
4.0 |
% |
||||
Total Error vs. Temperature |
|
|
|
±0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
0.03 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.04 |
%/°C |
|||||
Supply Rejection (±15 V ± 10%) |
|
|
|
±0.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±0.05 |
|
|
%/% |
|||
Nonlinearity, X (X = 20 V p-p, Y = 10 V) |
|
|
|
±0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±0.5 |
|
|
% |
|||
Nonlinearity, Y (Y = 20 V p-p, X = 10 V) |
|
|
|
±0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±0.2 |
|
|
% |
|||
Feedthrough, X (Y Nulled, |
|
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|||
X = 20 V p-p 50 Hz) |
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
30 |
mV |
||||||||||
Feedthrough, Y (X Nulled, |
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|||
Y = 20 V p-p 50 Hz) |
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
mV |
||||||||||
Feedthrough vs. Temperature |
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
mV p-p/°C |
||||
Feedthrough vs. Power Supply |
|
|
|
±0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±0.25 |
|
|
mV/% |
|||
DYNAMICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Small Signal BW (VOUT = 0.1 rms) |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
MHz |
|||
1% Amplitude Error |
|
|
|
75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
|
|
kHz |
||||
Slew Rate (VOUT 20 p-p) |
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
V/µs |
||||
Settling Time (to 2%, ∆VOUT = 20 V) |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
µs |
|||
NOISE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wideband Noise f = 5 Hz to 10 kHz |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
mV (rms) |
||||
f = 5 Hz to 5 MHz |
|
|
|
3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.0 |
|
|
mV (rms) |
||||
OUTPUT |
±10 |
±13 |
|
|
±10 |
|
± |
|
|
|
±10 |
|
±13 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
Output Voltage Swing |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|||||||||||||||
Output Impedance (f ≤ 1 kHz) |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
Ω |
|||
Output Offset Voltage |
|
|
|
±40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
mV |
|||
Output Offset Voltage vs. Temperature |
|
|
|
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
mV/°C |
||||
Output Offset Voltage vs. Supply |
|
|
|
±2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±2.5 |
|
|
mV/% |
|||
INPUT AMPLIFIERS (X, Y, and Z) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Signal Voltage Range (Diff. or CM |
|
|
|
±10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±10 |
|
|
|
|||
Operating Diff) |
40 |
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
V |
|||||||||
CMRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dB |
||||||
Input Bias Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
µA |
X, Y Inputs |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.5 |
|
|||||||
X, Y Inputs TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
µA |
|||
Z Input |
|
|
|
±10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
5 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
±5 |
15 |
µA |
|||||
Z Input TMIN to TMAX |
|
|
|
±30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±25 |
|
|
µA |
|||
Offset Current |
|
|
|
±0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±0.1 |
|
|
µA |
|||
Differential Resistance |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
MΩ |
||||
DIVIDER PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transfer Function (Xl > X2) |
|
|
10 V Z/(X1 – X2) |
|
10 V Z/(X1 – X2) |
|
|
|
|
10 V Z/(X1 – X2) |
|
||||||||||||||
Total Error |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(VX = –10 V, –10 V ≤ VZ ≤ +10 V) |
|
|
|
±2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±1 |
|
|
% |
|||
(VX = –1 V, –10 V ≤ VZ ≤ +10 V) |
|
|
|
±4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±3 |
|
|
% |
|||
SQUARE PERFORMANCE |
(X1 – X2 )2 |
|
|
(X1 – X2 )2 |
|
|
|
(X1 – X2 )2 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
Transfer Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10V |
±0.8 |
|
|
|
10V |
± |
|
|
|
|
10V |
±0.4 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
Total Error |
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
% |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
SQUARE ROOTER PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
–√10 V Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–√10 V Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–√10 V Z |
|
|
|
||||
Transfer Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Total Error (0 V ≤ VZ ≤ 10 V) |
|
|
|
±1.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
±1.0 |
|
|
% |
|||
POWER SUPPLY SPECIFICATIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply Voltage |
|
|
|
±15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±15 |
|
|
|
|||
Rated Performance |
±10 |
18 |
±10 |
|
15 |
18 |
±10 |
|
±22 |
V |
|||||||||||||||
Operating |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|||||||||||||||
Supply Current |
|
|
|
4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
6 |
|
|
|||
Quiescent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mA |
|||||||||
PACKAGE OPTIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO-116 (D-14) |
AD532JD |
|
|
AD532KD |
|
|
|
AD532SD |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
TO-100 (H-10A) |
AD532JH |
|
|
AD532KH |
|
|
|
AD532SH |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
LCC (E-20A) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532SE/883B |
|
|
|
|||||
Specifications subject to change without notice.
Specifications shown in boldface are tested on all production units at final electrical test. Results from those tests are used to calculate outgoing quality levels. All min and max specifications are guaranteed, although only those shown in boldface are tested on all production units.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
H-10A: θJC = 25°C/W; θJA = 150°C/W E-20A: θJC = 22°C/W; θJA = 85°C/W D-14: θJC = 22°C/W; θJA = 85°C/W
–2– |
REV. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
ORDERING GUIDE |
|
|
|
CHIP DIMENSIONS AND BONDING DIAGRAM |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contact factory for latest dimensions. |
||||||||||
|
Temperature |
|
Package |
|
Package |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dimensions shown in inches and (mm). |
||||||||||||||
Model |
Ranges |
|
Descriptions |
|
Options |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532JD |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532JD/+ |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.107 |
VS |
OUTPUT |
||||
AD532KD |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2.718) |
||||||
AD532KD/+ |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532JH |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Header |
|
H-10A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532KH |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Header |
|
H-10A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
AD532JCHIPS |
0°C to 70°C |
|
Chip |
|
|
|
X1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
AD532SD |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
0.062 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1.575) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
AD532SD/883B |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS |
|
JM38510/13903BCA |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Side Brazed DIP |
|
D-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y1 |
|
AD532SE/883B |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
LCC |
|
E-20A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
AD532SH |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Header |
|
H-10A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532SH/883B |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Header |
|
H-10A |
|
|
|
|
|
X2 |
GND |
VOS |
Y2 |
||||||
JM38510/13903BIA |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Header |
|
H-10A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AD532SCHIPS |
–55°C to +125°C |
|
Chip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
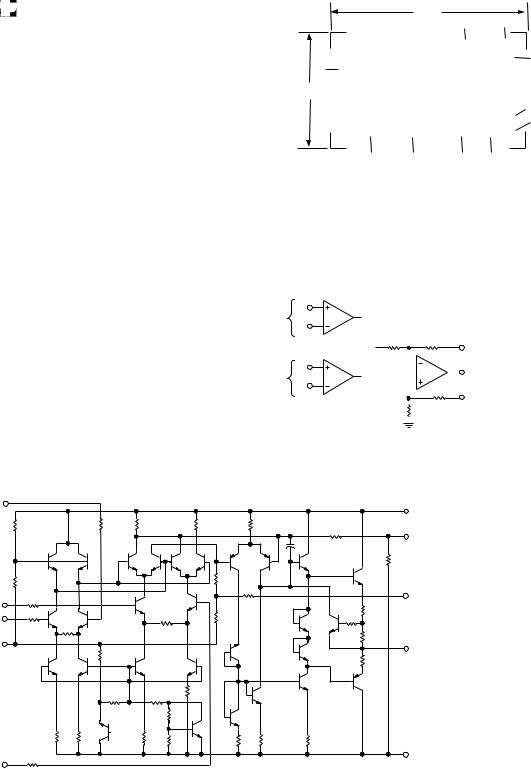
The functional block diagram for the AD532 is shown in Figure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1, and the complete schematic in Figure 2. In the multiplying |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
and squaring modes, Z is connected to the output to close the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
feedback around the output op amp. (In the divide mode, it is |
|
|
|
X1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
used as an input terminal.) |
|
|
|
|
VX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
X2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
The X and Y inputs are fed to high impedance differential |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|||||
amplifiers featuring low distortion and good common-mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
rejection. The amplifier voltage offsets are actively laser trimmed |
|
|
|
Y1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
to zero during production. The product of the two inputs is |
|
|
VY |
Y2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
resolved in the multiplier cell using Gilbert’s linearized trans- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10R |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOS |
|||||||
conductance technique. The cell is laser trimmed to obtain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
(X1 – X2) (Y1 – Y2) |
|
R |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
VOUT = (X1 – X2)(Y1 – Y2)/10 volts. The built-in op amp is used |
|
|
|
VOUT = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
10V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
to obtain low output impedance and make possible self-contained |
(WITH Z TIED TO OUTPUT) |
|
|
||
operation. The residual output voltage offset can be zeroed at |
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram |
|
VOS in critical applications . . . otherwise the VOS pin should |
||
|
||
be grounded. |
|
X2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R2 |
R6 |
R8 |
|
R16 |
R23 |
|
R27 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C1 |
Z |
|
Q1 |
Q2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q7 |
Q8 |
|
Q14 Q15 |
Q16 Q17 |
Q21 |
R33 |
|
|
R34 |
|
|
|
|
|
R20 |
|
|
Q25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOS |
|
Y1 |
R9 |
|
Q9 |
|
Q10 |
|
|
|
||
R1 |
|
|
|
|
|
R30 |
||||
X1 |
Q4 |
|
R13 |
|
R21 |
|
|
|||
Q3 |
|
|
|
Q22 |
R31 |
|||||
|
R3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q18 |
|
Q23 |
OUTPUT |
|
|
|
R10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R29 |
|||
|
Q5 |
Q6 |
Q11 |
|
Q12 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q24 |
Q27 |
|
|
R32 |
|
R11 |
|
R19 |
Q20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
R14 |
Q19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R4 |
Q28 |
|
R12 |
|
Q13 |
|
|
|
|
|
R5 |
|
R15 |
R24 |
R25 |
R26 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Y2 |
R18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS CAN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram
REV. C |
–3– |
 Loading...
Loading...