HEIDENHAIN iTNC 530 Service Manual

Service Manual
iTNC 530
May 2006

Contents |
1 |
Safety Precautions |
9 |
|
|
||||
|
2 |
Using the Service Manual ................................................................................................... |
11 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
About this Manual ......................................................................................................... |
11 |
|
|
2.2 |
Further Service Manuals................................................................................................ |
11 |
|
|
2.3 |
Other Documentation:................................................................................................... |
12 |
|
|
2.4 Support .......................................................................................................................... |
12 |
|
|
|
2.5 |
Service Training Seminars ............................................................................................. |
12 |
|
|
2.6 |
Safety ............................................................................................................................ |
12 |
3 Code Numbers ..................................................................................................................... |
13 |
|
3.1 |
Introduction ................................................................................................................... |
13 |
3.2 |
Overview ....................................................................................................................... |
13 |
3.3 Notes on Entering the Code Numbers .......................................................................... |
14 |
|
4 Error Messages .................................................................................................................... |
17 |
|
4.1 |
Introduction ................................................................................................................... |
17 |
4.2 |
HELP Key....................................................................................................................... |
19 |
4.3 |
ERR Key ........................................................................................................................ |
20 |
4.4 |
CE Key .......................................................................................................................... |
21 |
4.5 |
List of NC Error Messages ............................................................................................ |
22 |
5 Errors..................................................................................................................................... |
23 |
|
5.1 |
Introduction ................................................................................................................... |
23 |
5.2 |
Notes and Tips............................................................................................................... |
23 |
5.3 |
Overview of Possible Errors .......................................................................................... |
26 |
5.4 Important Notes on the |
|
|
|
Use of HEIDENHAIN Interface Boards in SIMODRIVE System.................................... |
29 |
6 Log |
......................................................................................................................................... |
35 |
6.1 .......................................................................................................................... |
General |
35 |
6.2 ............................................................................................................... |
Calling the Log |
36 |
6.3 ................................................................................................ |
Overview of Log Entries |
37 |
6.4 ................................................................................................. |
Example of a Log Entry |
40 |
7 Integrated Diagnosis Functions.......................................................................................... |
41 |
|
7.1 |
Introduction ................................................................................................................... |
41 |
7.2 |
Meanings of the Signals under “DSP”.......................................................................... |
43 |
7.3 |
Electronic ID Label......................................................................................................... |
47 |
8 Integrated Oscilloscope....................................................................................................... |
49 |
|
8.1 |
General .......................................................................................................................... |
49 |
8.2 |
Setup ............................................................................................................................. |
50 |
8.3 |
Saving and Loading Recordings..................................................................................... |
53 |
8.4 |
Circular Interpolation Test.............................................................................................. |
54 |
9 Monitoring Functions .......................................................................................................... |
55 |
|
9.1 |
Introduction ................................................................................................................... |
55 |
9.2 |
During Booting............................................................................................................... |
55 |
9.3 |
During Operation ........................................................................................................... |
57 |
|
9.3.1 Position or Servo Lag Monitoring ........................................................................ |
58 |
|
9.3.2 Nominal Speed Value ........................................................................................... |
60 |
|
9.3.3 Movement Monitoring ......................................................................................... |
61 |
|
9.3.4 Standstill Monitoring ............................................................................................ |
62 |
|
9.3.5 Positioning Window ............................................................................................. |
62 |
|
9.3.6 Monitoring of the Power Supply Unit .................................................................. |
64 |
|
9.3.7 Temperature Monitoring ...................................................................................... |
65 |
|
9.3.8 I2t Monitoring ....................................................................................................... |
66 |
July 2002 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

9.3.9 Current Utilization of the Drive Motors ................................................................ |
67 |
|
9.3.10 Status of HEIDENHAIN Inverters ...................................................................... |
68 |
|
9.3.11 Control of Motor Brakes .................................................................................... |
70 |
|
9.3.12 EMERGENCY STOP Monitoring During Operation ............................................ |
72 |
|
10 PLC Diagnosis..................................................................................................................... |
73 |
|
10.1 |
General ........................................................................................................................ |
73 |
10.2 |
Service Diagnosis in PLC Mode .................................................................................. |
76 |
10.2.1 The TABLE Function .......................................................................................... |
76 |
|
10.2.2 The LOGIC Diagram .......................................................................................... |
82 |
|
10.2.3 The TRACE Function ......................................................................................... |
84 |
|
10.2.4 The WATCH LIST Function ................................................................................ |
85 |
|
10.2.5 The I/O-FORCE LIST .......................................................................................... |
87 |
|
10.3 |
The COMPILE Function............................................................................................... |
89 |
10.4 |
Calling the PLC Error Table for Diagnosis.................................................................... |
91 |
10.5 |
Nonvolatile PLC Markers and Words .......................................................................... |
93 |
10.6 |
Overviews ................................................................................................................... |
95 |
10.7 |
Specifications ............................................................................................................ |
106 |
10.7.1 PLC Inputs ....................................................................................................... |
106 |
|
10.7.2 Analog Inputs ................................................................................................... |
107 |
|
10.7.3 Inputs for Thermistors ..................................................................................... |
107 |
|
10.7.4 PLC Outputs .................................................................................................... |
108 |
|
11 Principle of Operation of the iTNC 530 Control ............................................................ |
109 |
|
11.1 |
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
109 |
11.2 |
Block Diagrams with Short Explanations................................................................... |
109 |
11.3 |
Basic Circuit Diagrams ........................................................................................... |
116 |
11.4 |
Exchange Possibilities of the iTNC 530..................................................................... |
118 |
12 Important Features of HEIDENHAIN Components ....................................................... |
119 |
|
12.1 |
HEIDENHAIN Components in a Machine Tool.......................................................... |
119 |
12.2 |
Hardware Identification ............................................................................................. |
120 |
12.3 |
Display of System Information .................................................................................. |
130 |
13 Connector Designation and Layout .............................................................................. |
135 |
|
13.1 |
Important Note ......................................................................................................... |
135 |
13.2 MC and CC ................................................................................................................ |
135 |
|
13.2.1 Designation and Position of Connectors ......................................................... |
135 |
|
13.2.2 Pin Layouts on the MC and CC ....................................................................... |
142 |
|
13.3 |
Power Supply Units................................................................................................... |
173 |
13.3.1 UV 105 Power Supply Unit .............................................................................. |
174 |
|
13.3.2 UV 105 B Power Supply Unit ........................................................................... |
176 |
|
13.3.3 UV 106 (B) Power Supply Unit ......................................................................... |
178 |
|
13.4 |
Inverters and Motors................................................................................................. |
179 |
13.5 |
Interface boards for the SIMODRIVE system 611D.................................................. |
179 |
13.6 |
Encoders ................................................................................................................... |
180 |
13.6.1 Position encoders ............................................................................................ |
180 |
|
13.6.2 Speed encoders ............................................................................................... |
182 |
|
13.7 |
Touch Probe Systems ............................................................................................... |
182 |
13.8 |
Handwheels .............................................................................................................. |
183 |
13.8.1 HR 4xx Portable Handwheel ............................................................................ |
183 |
|
13.8.2 HR 130 Panel-Mounted Handwheel ................................................................ |
185 |
|
13.8.3 HRA 110 Handwheel Adapter ......................................................................... |
185 |
|
13.9 |
PLC Input/Output Units ............................................................................................. |
187 |
13.9.1 Designation and Position of Connectors ......................................................... |
187 |
|
13.9.2 PL 4xxB Pin Layouts ........................................................................................ |
190 |
|
13.9.3 Pin Layout PL 510 ............................................................................................ |
195 |
|
13.10 Machine Operating Panel ...................................................................................... |
199 |
|
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530

13.10.1 Designation and Position of Connectors on MB 420 ..................................... |
199 |
||
13.10.2 Pin Layouts on MB 420 ................................................................................. |
199 |
||
13.11 iTNC Keyboard......................................................................................................... |
200 |
||
13.11.1 Designation and Position of Connectors ........................................................ |
200 |
||
13.11.2 Pin layouts ..................................................................................................... |
201 |
||
13.12 Visual Display Units ................................................................................................. |
202 |
||
13.12.1 |
Designation and Position of Connectors ....................................................... |
202 |
|
13.12.2 |
Pin layouts .................................................................................................... |
203 |
|
13.13 BTS 1x0 Monitor/Keyboard Switch.......................................................................... |
204 |
||
14 Power Supply ................................................................................................................... |
205 |
||
14.1 |
Power Supply for the iTNC 530 ................................................................................. |
205 |
|
14.1.1 General ............................................................................................................ |
205 |
||
14.1.2 UV 105, UV 105 B ............................................................................................ |
210 |
||
14.1.3 UV 106, UV 106 B ............................................................................................ |
214 |
||
14.2 |
Power Supply for Control-Is-Ready Signal ................................................................. |
216 |
|
14.3 |
Buffer Battery ............................................................................................................ |
217 |
|
14.4 |
Info menu .................................................................................................................. |
220 |
|
14.5 |
Power Supply for the Display Units........................................................................... |
221 |
|
14.6 |
Power Supply for PLC Outputs ................................................................................. |
222 |
|
14.6.1 General ............................................................................................................ |
222 |
||
14.6.2 Supply Voltage for PLC Outputs on the MC .................................................... |
223 |
||
14.6.3 Supply Voltage for PLC Outputs on the PL 4xx B ............................................ |
225 |
||
14.6.4 Supply Voltage for PLC Outputs on the PL 510 ............................................... |
228 |
||
15 Hard Disk and File Manager of the iTNC 530................................................................. |
231 |
||
15.1 |
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
231 |
|
15.2 |
Structure of the Hard Disk......................................................................................... |
232 |
|
15.3 |
Hard Disk Test ......................................................................................................... |
233 |
|
15.4 |
Setting the System Time........................................................................................... |
237 |
|
15.5 |
File Management of TNC Partition (TNC:\) .............................................................. |
239 |
|
15.6 |
File Management PLC Partition (PLC:\) ..................................................................... |
241 |
|
16 Data Backup ..................................................................................................................... |
245 |
||
16.1 |
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
245 |
|
16.2 |
Connection Setup ...................................................................................................... |
247 |
|
16.2.1 Via Ethernet ..................................................................................................... |
247 |
||
16.2.2 Via Serial Interface RS 232/V.24 or RS 422/V.11 ............................................. |
256 |
||
16.3 |
Reading In and Out of Individual Files or Directories................................................. |
258 |
|
16.4 |
Backup.................................................................................................................... |
... |
261 |
16.5 |
Extracting files from the backup file .......................................................................... |
265 |
|
16.6 |
Restore |
...................................................................................................................... |
266 |
16.7 |
Data Interface Operating Modes ............................................................................... |
269 |
|
16.7.1 Overview of operating modes ......................................................................... |
269 |
||
16.7.2 Interface configuration and assignment of mode ............................................ |
270 |
||
16.8 |
Drive Symbols ........................................................................................................... |
271 |
|
16.9 |
Cable overview .......................................................................................................... |
272 |
|
16.9.1 Ethernet Interface RJ45 Connection ............................................................... |
272 |
||
16.9.2 RS-232-C/V.24 .................................................................................................. |
273 |
||
16.9.3 RS-422/V.11 .................................................................................................... |
278 |
||
17 Encoder Interface ............................................................................................................. |
279 |
||
17.1 |
Position encoders ...................................................................................................... |
279 |
|
17.1.1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... |
279 |
||
17.1.2 Possible Causes of Error .................................................................................. |
280 |
||
17.1.3 Service diagnosis ............................................................................................. |
281 |
||
July 2002 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

17.1.4 Additional Diagnosis Possibility on Encoders with EnDat Interface ................ |
283 |
|
17.1.5 Corrective action .............................................................................................. |
283 |
|
17.1.6 Re-Setting the Machine Datum ....................................................................... |
284 |
|
17.2 |
Speed encoders ........................................................................................................ |
286 |
17.2.1 Introduction .................................................................................................... |
286 |
|
17.2.2 Possible Causes of Error ................................................................................. |
287 |
|
17.2.3 Trouble Shooting on the CC 422 ..................................................................... |
287 |
|
17.2.4 Trouble Shooting on CC the 422 ..................................................................... |
289 |
|
17.2.5 Additional Diagnosis Possibility on Encoders with EnDat Interface ................ |
292 |
|
17.2.6 Corrective action .............................................................................................. |
292 |
|
17.2.7 Resetting the Spindle Orientation ................................................................... |
293 |
|
17.3 |
Error Code for Encoders with EnDat Interface.......................................................... |
294 |
17.4 |
Checking position and speed encoders..................................................................... |
295 |
17.5 |
Position Measurement with the Motor Encoder ...................................................... |
296 |
18 Referencing....................................................................................................................... |
301 |
|
18.1 |
Definition ................................................................................................................... |
301 |
18.2 |
Traversing the Reference Marks ............................................................................... |
302 |
18.3 |
Deselect Referencing for Axes ................................................................................. |
309 |
19 Checking the Enables on the iTNC................................................................................. |
311 |
|
19.1 |
General ...................................................................................................................... |
311 |
19.2 |
Examination............................................................................................................... |
313 |
19.2.1 Examination of the output Control-is-ready (X41/pin34) and input Control-is-ready |
||
|
signal acknowledgement I3 (X42/pin 4) .......................................................... |
314 |
19.2.2 Checking the global drive enable I32, connector X42 / pin 33 ......................... |
319 |
|
19.2.3 Checking the drive enabling for the axis groups via connector |
|
|
|
X150 and X151 (if wired) ................................................................................ |
321 |
19.2.4 Checking the readiness of the inverter system ............................................... |
322 |
|
19.2.5 Überprüfung von PLC-Modulen, Merkern und WörternChecking PLC |
|
|
|
modules, markers and words ......................................................................... |
325 |
20 Interface to the Drives ..................................................................................................... |
327 |
|
20.1 |
Digital Drives ............................................................................................................. |
327 |
20.1.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................... |
327 |
|
20.1.2 Possible Causes of Errors ................................................................................ |
328 |
|
20.1.3 Trouble Shooting: Exchanging PWM Outputs on the CC 422 ......................... |
329 |
|
20.1.4 Trouble Shooting: Exchanging PWM Outputs on the CC 424 ......................... |
333 |
|
20.1.5 Trouble Shooting: Exchanging Power Modules or Output Stages of the |
|
|
|
Same Type ...................................................................................................... |
337 |
20.1.6 Trouble Shooting: Exchanging the HEIDENHAIN Interface Boards for |
|
|
|
the SIMODRIVE 611 System .......................................................................... |
340 |
20.2 |
Analog Drives ............................................................................................................ |
341 |
20.2.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................... |
341 |
|
20.2.2 Possible Causes of Errors ................................................................................ |
341 |
|
20.2.3 Testing the analog nominal speed value interface ......................................... |
341 |
|
20.2.4 Adjusting the Electrical Offset (Drift Adjustment) ........................................... |
346 |
|
20.2.5 Speed Adjustment at Servo Amplifier (Tachometer Adjustment) .................... |
349 |
|
20.3 |
Switching the Position Display for Service Purposes ................................................ |
351 |
21 Visual Display Unit .......................................................................................................... |
353 |
|
21.1 |
General ...................................................................................................................... |
353 |
21.2 |
Possible Causes of Errors ......................................................................................... |
353 |
21.3 |
Fault diagnosis........................................................................................................... |
354 |
22 Keyboard Unit .................................................................................................................. |
357 |
|
22.1 |
General ...................................................................................................................... |
357 |
22.2 |
Front View of the Keyboard Units ............................................................................ |
357 |
22.3 |
Possible Causes of Error ........................................................................................... |
359 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530

22.4 |
Checking the Keys..................................................................................................... |
360 |
22.5 |
Checking the Potentiometers.................................................................................... |
364 |
22.6 |
Checking the Mouse Pad .......................................................................................... |
366 |
22.7 |
Key Matrix of the Keyboard Units.............................................................................. |
367 |
22.8 |
Key Matrix of the Keyboard Units.............................................................................. |
382 |
23 Machine Operating Panel................................................................................................ |
385 |
|
23.1 |
General ...................................................................................................................... |
385 |
23.2 |
Checking the Power Supply ...................................................................................... |
386 |
23.3 |
Checking the Keys..................................................................................................... |
387 |
23.4 |
Checking the Outputs................................................................................................ |
389 |
24 Handwheel........................................................................................................................ |
391 |
|
24.1 |
General information ................................................................................................... |
391 |
24.2 |
HR 420 Portable Handwheel with Display................................................................. |
393 |
24.2.1 Checking the Keys ........................................................................................... |
393 |
|
24.2.2 Checking the Potentiometers .......................................................................... |
393 |
|
24.3 |
HR 410 Portable Handwheel ..................................................................................... |
396 |
24.3.1 Checking the Keys ........................................................................................... |
396 |
|
24.4 |
HR 150 Panel-Mounted Handwheels with HRA 110 Handwheel Adapter ................ |
398 |
24.4.1 Checking the Switch ........................................................................................ |
398 |
|
25 Touch Probe ..................................................................................................................... |
401 |
|
25.1 |
General information ................................................................................................... |
401 |
25.2 |
Touch Trigger Probe with Cable Connection for Workpiece Setup and |
|
Measurement ............................................................................................................. |
403 |
|
25.3 |
Touch Trigger Probe with Infrared Transmission for Workpiece Setup |
|
|
and Measuring........................................................................................................... |
405 |
25.4 |
Triggering Touch Probe for Tool Measurement......................................................... |
408 |
26 Exchange of HEIDENHAIN Components........................................................................ |
411 |
|
26.1 |
Important Information................................................................................................ |
411 |
26.2 |
Exchanging the MC 422 ............................................................................................ |
418 |
26.3 |
Removing the Drive Assembly .................................................................................. |
425 |
26.4 |
Exchanging the MC 422 B or the MC 420................................................................. |
431 |
26.5 |
Exchanging the HDR ................................................................................................. |
433 |
26.6 |
Exchanging the CC .................................................................................................... |
441 |
26.7 |
Exchange of Further HEIDENHAIN Components...................................................... |
442 |
27 Loading of Service Packs ................................................................................................ |
443 |
|
27.1 |
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
443 |
27.2 |
Preparations and Execution up to NC Software 34049x-01 |
|
(Single and Dual-Processor Version)........................................................................... |
444 |
|
27.3 |
Preparations and Execution as of NC Software 34049x-02 |
|
(Single-Processor Version).......................................................................................... |
446 |
|
27.4 |
Preparations and Execution as of NC Software 34049x-02 |
|
(Dual-Processor Version) ............................................................................................ |
449 |
|
27.5 |
Service Packs on the Control's Hard Disk ................................................................. |
452 |
28 Activating the NC Software Used on the Machine....................................................... |
453 |
|
28.1 |
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
453 |
28.2 |
Execution................................................................................................................... |
453 |
29 Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment.................................................................. |
455 |
|
29.1 |
Important notes ......................................................................................................... |
455 |
29.2 |
Test Adapter, ID 375830-01 ...................................................................................... |
456 |
29.3 |
Universal Measuring Adapter, ID 255480-01............................................................. |
460 |
29.4 |
Encoder Diagnostic Set PWM 9, ID 512134-01 ....................................................... |
461 |
29.5 |
Mounting Help PWT 10/17/18 ................................................................................... |
463 |
29.6 |
IK 215 Adjustment and Testing Kit, ID 547858-01 ................................................... |
464 |
July 2002 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

30 Machine Parameters........................................................................................................ |
465 |
30.1 What is a Machine Parameter? ................................................................................. |
465 |
30.2 The Machine Parameter Editor.................................................................................. |
465 |
30.3 Meaning of the Machine Parameters........................................................................ |
473 |
30.4 List of Machine Parameters |
|
(excerpt from the Technical Manual of iTNC 530 of November 2005) ....................... |
474 |
30.4.1 Encoders and Machines .................................................................................. |
474 |
30.4.2 Positioning ....................................................................................................... |
480 |
30.4.3 Operation with velocity feedforward control ................................................... |
484 |
30.4.4 Operation with following error (servo lag) ....................................................... |
485 |
30.4.5 Integrated speed and current control .............................................................. |
486 |
30.4.6 Spindle ............................................................................................................. |
495 |
30.4.7 Integral PLC ..................................................................................................... |
498 |
30.4.8 Configuration of the Data Interface ................................................................. |
501 |
30.4.9 3-D touch probe ............................................................................................... |
503 |
30.4.10 Tool Measurement with TT ........................................................................... |
505 |
30.4.11 Tapping .......................................................................................................... |
509 |
30.4.12 Display and Operation ................................................................................... |
510 |
30.4.13 Color .............................................................................................................. |
517 |
30.4.14 Machining and program run ........................................................................... |
520 |
30.4.15 Hardware ....................................................................................................... |
527 |
30.4.16 Second spindle .............................................................................................. |
534 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530

1 Safety Precautions
DANGER
Ensure that the equipment grounding conductor is continuous!
Interruptions in the equipment grounding conductor may cause damage to persons or property.
DANGER
Ensure that the main switch of the control and units are switched off when you engage or disengage connecting elements or connection clamps.
Caution
In order to be able to judge the behavior of an NC controlled machine, you need to have fundamental knowledge about controls, encoders, drives, electronics and mechanics.
Inappropriate use may cause considerable damage to persons or property.
DANGER
Incorrect or not optimized input values may lead to malfunction of the machine and may thus cause damage to persons or property.
Machine parameters may only be changed by the machine manufacturer or after consulting the machine manufacturer!
Caution
Note the safety precautions on the machine (e.g., stickers, signs) and the safety precautions in the documentation of the machine manufacturer (e.g., operating instruction).
Caution
HEIDENHAIN does not accept any responsibility for indirect or direct damage caused to persons or property through incorrect use or operation of the machine!
DANGER
Technicians who work on the electricity of the machine must have the corresponding technical knowledge and competence!
DANGER
Always secure vertical axes from falling down before you perform tests on these axes!
DANGER
The interfaces for the PLC inputs/outputs, machine operating panel and PL expansion cards comply with the basic insulation in accordance with IEC 742 EN 50 178.
Only units that comply with the requirements of IEC 742 EN 50 178 for basic insulation may be connected, otherwise damage to persons or property may be caused.
The maximum dc voltage mean value of the PLC inputs is 31 V.
May 2006 |
1 – 9 |

Meaning of the symbols used in this manual
DANGER
Failure to comply with this information could result in most serious up to fatal injuries or in substantial material damage.
Caution
Failure to comply with this information could result in injuries and interruptions of operation up to material damage.
Note
These boxes contain important and useful information for servicing.
1 – 10 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

2 Using the Service Manual
2.1About this Manual
This service manual will assist service personnel in the diagnosis and correction of errors on TNC-controlled machine tools.
It includes:
Theoretical explanation of functions and their correlations
Details of possible error reasons
Descriptions of error diagnosis
Details of corrective action
The “Overview of Possible Errors” on page 26 often includes references to the descriptions of error diagnosis. You will find these descriptions in the chapters of the Service Manual structured according to topics.
The Service Manual does not provide commissioning support!
It comprises the service possibilities with the current hardware and software of the control at the editing date of this manual. The service possibilities of your units may differ from the manual. Hardware or software based differences in servicing are indicated in the corresponding descriptions.
This manual is valid for:
iTNC 530 single-processor with NC software 340420 / 421
iTNC 530 single-processor with NC software 340422 / 423
iTNC 530 dual-processor with NC software 340480 / 481
iTNC 530 single-processor with NC software 340490 / 491
iTNC 530 dual-processor with NC software 340492 / 493
It must be provided that …
The machine had been working perfectly before the error ocurred.
Only genuine spare parts are used!
|
|
Note |
|
|
Basic knowledge in Windows is required for some descriptions in this Service Manual |
|
|
concerning the handling of the dual-processor control iTNC 530 and the use of a service |
|
|
laptop or PC. |
|
|
|
Udpate service |
This Service Manual is updated only at irregular intervals. |
|
|
You find the current printable version on our website. |
|
|
(http://www.heidenhain.de/Services/...) |
|
|
A zip file can be downloaded. This zip file can be unzipped with a password. Your receive this |
|
|
password during a HEIDENHAIN service training course or upon telephoned request! |
|
Loose-leaf binders or ring binders are only provided in connection with a service training course.
2.2Further Service Manuals
Service Manual for Inverter Systems and Motors
May 2006 |
2 – 11 |

2.3Other Documentation
In the following documents your find further important information:
Machine documentation of the machine manufacturer
(circuit diagrams, wiring diagrams, machine operation manual, etc.)
HEIDENHAIN User's Manual for iTNC 530
TNCguide (DVD)
Mounting instructions by HEIDENHAIN
Brochures of the corresponding HEIDENHAIN units
Note
Current HEIDENHAIN documentation can be obtained fast from our website. --> www.heidenhain.de
2.4Support
Caution
The machine manufacturer must be contacted for error diagnosis on your machine tool!
However, support will also be provided by the Service Department of HEIDENHAIN Traunreut or by the nearest HEIDENHAIN agency.
You will find the necessary telephone and fax numbers, as well as relevant e-mail addresses, on the back cover of the Service Manual, or on the HEIDENHAIN website at http://www.heidenhain.de.
2.5Service Training Seminars
HEIDENHAIN Traunreut offers service training seminars in German. We recommend the HEIDENHAIN Service Training Seminars for iTNC 530 for the technician who works with this Service Manual.
Please inquire at HEIDENHAIN Traunreut or go to our website at www.heidenhain.de/Services/Training.
Note
If required, please inquire at the HEIDENHAIN subsidiary in your country whether Service Training Seminars are offered in your language.
2.6Safety
DANGER
It is extremely important to read also the general safety precautions in chapter 1!
See “Safety Precautions” on page 9.
2 – 12 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

3 Code Numbers
3.1Introduction
With code numbers …
Certain areas of the hard disk
Certain file types
Certain functions
... can be called.
DANGER
Code numbers may only be passed on and/or used by trained service technicians. Inexpert handling may result in the loss of important data, in a faulty machine performance and thus lead to damage or injury to property or persons.
3.2Overview
Code number |
Brief Description |
|
|
0 |
Delete the soft keys MP EDIT, PLC EDIT, OSCI, etc. |
|
|
123 |
Edit subset of machine parameters for the machine operator |
|
|
75368 |
Offset adjustment for analog axes, see page 1- 346 |
|
|
79513 |
Info menu (U[BATT], U[ACCU], U[VCC], TEMP, T[CPU1], see page 1- 220 |
|
|
95148 |
Call the active machine parameter list, see page 1- 468 |
|
|
531210 |
Reset non-volatile PLC markers and words in the RAM |
|
|
688379 |
Integrated oscilloskop, see page 1- 49 |
|
|
807667 |
Call the PLC area, see page 1- 241 |
|
|
857282 |
Reset the operating times |
|
|
LOGBOOK |
Call and save the internal log of the TNC, see page 1- 35 |
|
|
NET123 |
Network settings for the single-processor control, see page 1- 247 |
|
|
SIK |
Display of the number of the SIK system identification key and display of the |
|
enabled options, see page 1- 414 |
|
|
VERSION |
Create the file TNC:\Version.a |
|
System data is saved in this file for diagnostic purposes. |
|
The file can be read out for diagnosis. |
|
|
May 2006 |
3 – 13 |

3.3Notes on Entering the Code Numbers
Keep the code numbers in confidence!
Code numbers can only be entered in the Programming and Editing mode.
The screen must be blank or the file editor is displayed.
The program manager must not be open (pressing the MOD key would activate the interface settings screen).
Press MOD and enter the code number. Finish with ENTER.
Example of calling |
Select the Programming and Editing operating mode. |
the active machine |
|
parameter list |
Call window for code number |
|
Enter and confirm code number
Note
The machine manufacturer can define own MP and PLC code numbers. In this case the HEIDENHAIN code numbers do not function any longer. --> Contact your machine manufacturer.
As long as the machine parameter list is in the editor no further code number can be entered. I.e., first close the MP list when you want to enter a new code number
When certain code numbers are entered, new soft keys are displayed, e.g., MP EDIT, PLC EDIT, OSCI.
With these soft keys you can also change to the corresponding areas without having to enter the code number again.
After you have entered the code number for the machine parameters the PLC tree can be seen in the program manager. Only files with the ending .MP are displayed.
3 – 14 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

After you have entered the PLC code number, all files of the PLC tree can be seen and loaded into the editor. However, to edit machine parameters, the soft key MP EDIT needs to be pressed.
When you have finished your work do not forget to delete all code-number soft keys (MP EDIT, PLC EDIT, OSCI, etc.) --> Enter code number 0, confirm with ENTER and exit the codenumber page with END or reboot the control.
May 2006 |
3 – 15 |

3 – 16 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

4 Error Messages
4.1Introduction
Type of error message
iTNC 530 features a comprehensive integral monitoring system for the prevention of input or operation errors, as well as for identification and diagnosis of technical errors on the control and the connected units. The monitoring system is an integral component of the iTNC hardware and software and is active as long as the control is switched on. The presence of a technical fault or an operation error is made known through a plain-language message.
The machine manufacturer can also define specific PLC error messages.
PLC Error Messages
Machine-specific error messages
Are defined by the machine manufacturer (e.g., coolant pump defective, protective door open, etc.)
The machine manufacturer defines how the control reacts to a PLC error message (NC stop, EMERGENCY STOP, etc.).
The machine manufacturer defines whether the control can still be operated or has to be rebooted after a PLC error message.
If you have any questions, please contact your machine manufacturer.
NC Error Messages
Are part of the HEIDENHAIN NC software
Can be subdivided in error messages that result from operation, programming and machine applications and those that indicate a technical defect (units, electronical and mechanical parts, etc.).
DSP error messages are special NC error messages. Such error messages are preceded by a HEX code, e.g., "C300 track error". DSP errors may signalize defects in the CC 42x and/or connected units.
HEIDENHAIN defines how the control reacts to an NC error message (NC stop, EMERGENCY STOP, etc.).
HEIDENHAIN defines whether the control can still be operated or has to be rebooted after an NC error message.
If you have any questions, please contact your machine manufacturer and/or HEIDENHAIN.
Note
Is the displayed error message an NC or PLC error message?
If you cannot see this from the error text, press ERR --> See the Group column of the error list in the newly displayed window. PLC errors are marked as such, NC errors are again subdivided into subsections; See “ERR Key” on page 20.
A further possibility is to call the log. --> See “Log” on page 35. The NC error messages are there distinguished by a N-, PLC error messages by a P-.
There are no error numbers assigned to NC error messages that begin with N-1 .
Operating System Error Messages
Often show the note CHILD PROCESS ERROR
The control cannot be operated any more and has to be rebooted.
If you have any questions, please contact your machine manufacturer and/or HEIDENHAIN.
May 2006 |
4 – 17 |

Display of error message
Reaction of the control
All error messages that can be acknowledged with the CE key are …
Displayed in the headline (upper edge of display; normally in red color).
Are made known through a plain-language message.
(before some error messages there is an additional HEX code. It is used for identification purposes as so-called DSP error. These are errors in the control loop or errors that are recognized by the control-loop software.)
The machine manufacturer can display additional information on PLC error messages in the small PLC window (atop the soft-key row).
Error messages that require a rebooting of the control ...
Are displayed in a red window in the center of the screen.
Are made known through a plain-language message.
(before some error messages there is an additional HEX code. It is used for identification purposes as so-called DSP error. These are errors in the control loop or errors that are recognized by the control-loop software.)
Display Only
The machine does not react. Programs are not stopped.
NC Stop
The axes decelerate at the nominal-value characteristics; normally the contour of the workpiece is not damaged.
EMERGENCY STOP
Axes and spindle decelerate at the current limit; the machine should be stopped as fast as possible. The contour of the workpiece is not regarded and may be damaged.
4 – 18 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

4.2HELP Key
Display help texts for error messages
(if this key is pressed again, the window will be closed)
If the service technician presses the HELP key a window is shown that describes the cause of error and possibilities of corrective action in addition to the displayed error message. This support can also be realized for PLC error messages by the machine manufacturer!
Note
HELP texts cannot be displayed any more for error messages in red windows. The control is not in operating condition any more. It must be rebooted.
Information on these errors can be found in the list of NC error messages; See “List of NC Error Messages” on page 22.
May 2006 |
4 – 19 |
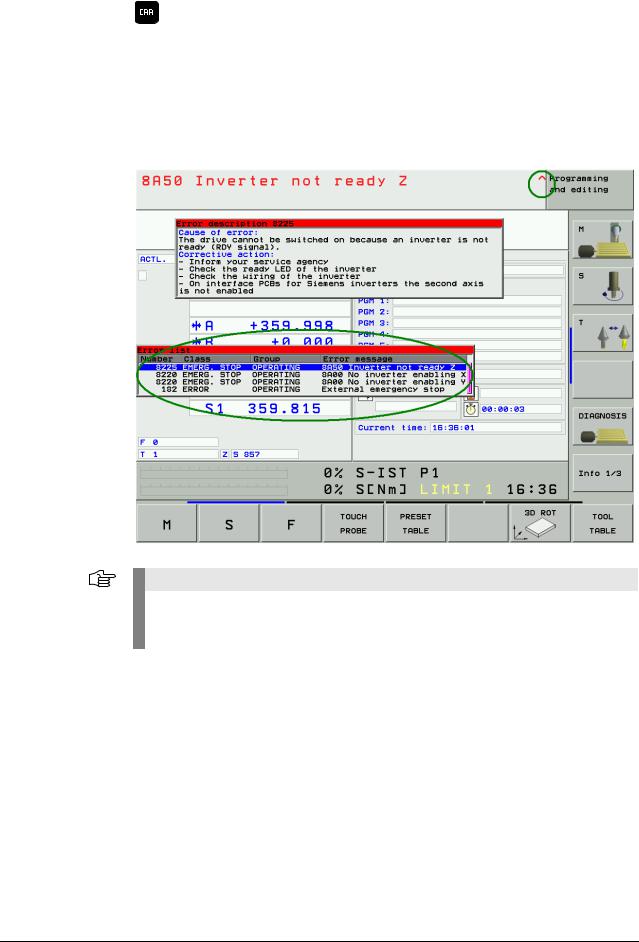
4.3ERR Key
Display all pending error messages
(if this key is pressed again, the window will be closed)
If there is an AND symbol (little red roof) in the header in addition to the error message, there is more than one pending error message.
The ERR key (ERROR) is located directly over the HELP key. If this key is pressed, an error list appears. All pending NC and PLC error messages of the control are displayed in an own window. In addition, the help window can be called with the HELP key.
Note
If there is no ERR key over the HELP key on your keyboard, press the corresponding space bar over the HELP key. --> If the NC software of the iTNC 530 supports the function of the ERR key, the ERR list can also be called!
4 – 20 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

The ERR window is described below:
Column |
Description |
Number |
Error number that was defined by HEIDENHAIN or the machine manufacturer |
|
(-1: No error number defined) |
|
|
Class |
Error class. Defines the reaction of the control: |
|
ERROR |
|
Program run is interrupted by the TNC (INTERNER STOP) |
|
FEED HOLD |
|
The feed rate enable is deleted |
|
PGM HOLD |
|
The program run is interrupted (control-in-operation symbol blinking) |
|
PGM ABORT |
|
The program run is aborted (INTERNER STOP) |
|
EMERG. STOP |
|
EMERGENCY STOP is generated |
|
RESET |
|
TNC executes a warm start |
|
WARNING |
|
Warning message, program run is continued |
|
INFO |
|
Info message, program run is continued |
|
|
Group |
Error source. |
|
GENERAL |
|
General error |
|
OPERATING |
|
Error during machining and machine traverse |
|
PROGRAMMING |
|
Error during programming |
|
PLC |
|
PLC error message of the machine manufacturer |
|
|
Error |
Displayed error text |
message |
|
|
|
The individual error messages can be selected with the cursor; the open help window shows the appertaining text.
4.4CE Key
Delete the error message
Displayed error messages can be acknowledged with the CE key.
If the error cause is still existing, the corresponding error message is displayed again. --> Eliminate the error!
Note
Messages regarding very fatal errors, cannot be confirmed with the CE key.
The control must be rebooted.--> Press the END key.
If this does not function ... --> Switch the power switch of the machine off and on again.
May 2006 |
4 – 21 |

4.5List of NC Error Messages
You can find the complete list of NC error messages (incl. operation errors) on the DVD TNCguide in several languages and sorted by error numbers. These TNCguide information can also be found on our website http://www.heidenhain.de/Services/...
Note
Where it is possible and makes sense, you may switch the control off and on again to observe whether the error message is generated again afterwards.
Note:
In the next version of this Service Manual the list of NC error messages will be filtered for error messages that indicate a technical defect.
Information and links to suitable routines for error diagnosis will be included!
4 – 22 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

5 Errors
5.1Introduction
Not all error conditions on the control or machine can be shown by error messages on the monitor.
Therefore, this chapter gives you an overview of errors with notes and tips how to proceed.
What is the cause of Ask the last operator or technician who has worked with or on the machine about the course the error? of events.
Have there been any particular incidences, such as …
Cleaning of the machine (humidity, etc.)
Thunderstorms
Modifications to the machine
NC software update
New machining program
Tool breakage
Collision
Power failure
Etc.
The error diagnosis will be easier for you by pointed questions and precise answers!
Static and nonstatic |
Errors can also be defined in the categories of static errors (e.g., interruption in the electrical |
errors |
cabinet, defective unit) and nonstatic errors (e.g., loose connection, shielding problems, |
|
interferences). |
|
Naturally, the error location of static errors is easier. |
Sporadic and |
Check whether you can reproduce a certain error on the machine at any time (nonsporadic error). |
nonsporadic |
This assists you in trouble shooting. |
errors |
The integrated log or the PLC logic diagram are some possibilities to investigate sporadic errors. |
5.2Notes and Tips
Comparison with |
If a dimensionally identical or similar machine is available, the functionality of this machine can |
functioning |
be compared with the defective machine. |
machines |
This can be very helpful for trouble shooting! |
Connectors and Observe the following during connecting and disconnecting:
females
D-Sub Connectors or Females
Connect and disconnect straightly! Otherwise, the spring contact in the D-sub connectors could be widened. This may result in contact problems!
Ribbon Connectors or Females
Connect carefully and straightly with constant pressure to prevent a deflection of the males.
Signal Socket at the Motor
Slide the nib of the connector into the notch of the signal socket and screw the connector straightly. Do not use force! Otherwise the males could be bent or even pressed into the socket.
May 2006 |
5 – 23 |

Low voltages |
All units connected to the control are also supplied by the control (encoders with long |
|
cables are maybe provided with voltage amplifiers). It is thus possible that defective connected |
|
units or also damaged cables have an influence on the low voltages in the control and generate |
|
a variety of error messages. |
|
Only the newer control hardware is equipped with the so-called polyfuses. These are electronic |
|
fuses that separate defective peripheral units from the low voltages in the control in case of an |
|
error. Polyfuses are equipped with a self-resetting function ("self-healing effect") |
|
Always disconnect suspicious units from the control for error diagnosis! |
|
If necessary, deactivate these units or the axis concerned in the machine parameter list. |
Note
It is not sufficient to deactivate a suspicious axis with machine parameter MP10 (without disconnecting suspicious units).
The corresponding units (e.g., position encoder for this axis) are not monitored any more but are still supplied with power. The defective scale can thus influence the low voltages of the control, for example!
Note
If you are not in a position/allowed to activate the axes with MP10, MP subfiles might be active and/or this is not permitted by the PLC program. --> Ask the machine manufacturer!
Switch on the control and check whether errors still occur.
Caution
For trouble shooting do not connect obviously defective controls (e.g., position encoder with short circuit after entering of humidity) to other input connectors (z.B. X1-X6, X35-X38) of the control.
Defective cables may result in interruptions but also in undefined conditions and direct error messages. Therefore, especially check possible worn and squeezed positions of the cables.
Shielding and |
Also defective shieldings and groundings can result in undefined errors or in a malfunction |
grounding |
of the machine (e.g., vibration of axes, poor surface of the workpiece). The reason are |
|
compensating currents that are caused by potential differences. |
|
Therefore, check the terminals, shielded cables (the shielding braid must not contact the 0 V |
|
conductor inside the cable), cover plates, grounding bars, contact plates, etc. |
Caution
If HEIDENHAIN expansion boards for the SIMODRIVE system are used, please check the mandatory grounding.
--> See “Important Notes on the Use of HEIDENHAIN Interface Boards in SIMODRIVE System” on page 29.
5 – 24 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

Sources of |
Also observe likely sources of interference that may have a negative effect on the connected |
interference |
units. |
|
Noise is mainly produced by capacitive and inductive coupling from electrical conductors or from |
|
device inputs/outputs, such as ... |
|
Strong magnetic fields from transformers or electric motors |
|
Relays, contactors and solenoid valves |
|
High-frequency equipment, pulse equipment and stray magnetic fields from switch-mode |
|
power supplies |
|
Power lines and leads to the above equipment |
Make sure that …
There is a minimum distance of 20 cm from the MC 42x(B), CC 42x and its leads to interfering equipment.
There is a minimum distance of 10 cm from the MC 42x(B), CC 42x and its leads to cables that carry interference signals. For cables in metallic ducting, adequate decoupling can be achieved by using a grounded separation shield.
The cross section of potential compensating lines is min. 6 mm2.
Contact the machine manufacturer if these conditions are not fulfilled!
|
|
|
|
Caution |
|
|
|
|
Only use original HEIDENHAIN cables, connectors and couplings as replacement! |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contamination |
Pay special attention to contaminated units (oil, grease, dust, etc.)! |
|||
|
|
What could be the reason for the contamination? |
||
|
|
Some examples: |
||
|
|
Machining of graphite |
||
|
|
Coolant or coolant vapor |
||
|
|
Defective filter system in the electrical cabinet (filter pads) |
||
|
|
Oil or oil vapor |
||
|
|
Oil in the compressed-air system |
||
Humidity |
Check whether humidity has entered the units! |
|||
|
|
What could be the reason? |
||
|
|
Some examples: |
||
|
|
Defective climate control unit in the electrical cabinet |
||
|
|
Coolant or coolant vapor |
||
|
|
Condensation of boards due to differences in temperature |
||
|
|
Defective tubes, sealings, etc. |
||
Shipping brace of |
Check whether the shipping brace of the hard disk of the mounted control has |
|||
the hard disk |
been removed. |
|||
May 2006 |
5 – 25 |

5.3Overview of Possible Errors
This table shows an overview of specific errors on the machine or control, possible causes of the errors as well as measures for correcting these errors.
The potential measures for correcting the errors are described in more detail in the corresponding chapters.
Note
Where it is possible and makes sense, you may switch the control off and on again to observe whether the error is generated again afterwards.
Error |
Possible Cause of Error |
Measures for Error Diagnosis and/ |
|
|
or Corrective action |
The iTNC monitor remains dark after the |
iTNC monitor defective |
Check the visual display unit; |
machine has been switched on. |
Power supply to monitor |
See “Visual Display Unit” on |
|
defective |
page 353 |
|
Check power supply of the MC; |
|
|
Power supply of the MC |
|
|
See “Power Supply” on page 205 |
|
|
defective |
|
|
Disconnect defective or suspicious |
|
|
Defective unit connected to the |
|
|
control (short circuit, etc.) |
units or cables, See “Low volta- |
|
ges” on page 24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The control does not boot completely (error |
Hard disk defective |
Exchange MC or HDR or drive |
messages regarding the boot process are |
|
assembly; See “Exchange of |
sometimes displayed). |
|
HEIDENHAIN Components” on |
|
|
page 411 |
|
|
|
The message "RELAY EXTERNAL DC |
EMERGENCY STOP chain |
Check output "Control is ready" and |
VOLTAGE MISSING" does not disappear |
interrupted |
acknowledgement I3; See |
although the key "Control voltage ON" is |
24 V power supply (connector) |
“Checking the Enables on the |
pressed. |
X34 missing |
iTNC” on page 311 |
|
||
|
MC defective |
|
|
|
|
When the machine is switched on, the error |
Wiring defective, contactors |
Check the related components; |
message "EMERGENCY STOP defective" |
defective or too slow |
See “Error message EMERGENCY |
|
MC defective |
STOP DEFECTIVE” on page 317 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
During switch-on or operation DSP errors |
Data loss on the hard disk in the |
Check the hard disk; See “Hard |
are generated. A mechanical reason or a |
range of the SYS partition. |
Disk Test” on page 233 |
defective unit can be ruled out. |
|
Activate the NC software again; |
|
|
See “Activating the NC Software |
|
|
Used on the Machine” on page 453 |
|
|
|
The "Power interrupted" message cannot |
The key gets caught |
See “Keyboard Unit” on page 357 |
be confirmed or the login password cannot |
|
|
be entered in a dual-processor control. |
|
|
|
|
|
The machine cannot be referenced after |
Interruption between the |
Eliminate the interruption, repair |
switch-on or the axes cannot be moved |
NC-stop key and control (the |
the key, etc. |
during operation or the spindle cannot be |
NC-stop signal is lowactive) |
See “Machine Operating Panel” on |
switched on during operation. |
|
page 385 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The machine is in the mode "Cross over |
Inverter system is not ready |
See “Checking the Readiness of |
reference points" which is neither possible |
for operation |
the Inverter System” on page 322 |
with the NC-START key nor with the axis |
|
|
direction keys. |
|
|
|
|
|
During reference run, the machine moves |
The trip dogs for the reversal |
See “Referencing” on page 301 |
to the limit switch. |
of direction during reference run |
|
|
are defective |
|
|
|
|
During reference run, the machine moves |
The machine was switched off |
Referencing with axis-direction |
to the mechanical stop (for machines |
at the wrong position |
keys (no automatic reference mark |
without limit stop). |
|
traverse)! |
An error message is sometimes displayed, |
|
|
e.g. "8640 I2T value of motor is too high ..." |
|
|
|
|
|
5 – 26 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

Error |
Possible Cause of Error |
Measures for Error Diagnosis and/ |
|
|
|
or Corrective action |
|
iTNC monitor is frozen. |
Power failure |
Check the primary supply (cables, |
|
The control has locked up. |
Failure of one or several phases |
fuses, terminals); |
|
The main switch has to be switched off and |
in the supply line |
See “Power Supply” on page 205 |
|
on again. |
The power supply voltage has |
Check the wiring of the inverter |
|
After reset of the control"Power fail |
fallen below the minimum value |
system, see circuit diagrams of the |
|
Interrupt!" is entered in the log of new |
Interruption in the electrical |
machine manufacturer |
|
software versions. |
Check the functioning of the |
||
cabinet |
|||
|
inverter system or the motor (see |
||
|
Inverter (power supply module) |
||
|
Service Manual for Inverter |
||
|
defective |
||
|
Systems and Motors) |
||
|
Short circuit of drives (drive |
||
|
|
||
|
modules, motors) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
STIB ("Control-in-operation = "*" in status |
Axis did not reach the posi- |
Carry out drift adjustment; |
|
display) remains in place even though |
tioning window |
See “Interface to the Drives” on |
|
positioning appears to be completed. |
Excessive drift of analog axes |
page 327 |
|
The next NC block is not executed in the |
Approach behavior of axis not |
Re-optimization or new |
|
automatic operating modes , the NC |
optimized |
optimization of the axis by the |
|
program gets caught. |
|
machine manufacturer |
|
|
|
|
|
"Vibrating" axes, sometimes connected |
Poor shielding or grounding |
Check the grounding of your |
|
with loud noises. |
Connectors on grounding termi- |
machine, refer to the machine |
|
|
nal X131 of infeed/regenerative |
manufacturer |
|
|
module (Simodrive 611D) not |
Ensure the grounding clamps are |
|
|
properly wired |
secure |
|
|
Grounding terminal X131 of |
Check the shielding or the covers |
|
|
power supply module |
|
|
|
(Simodrive 611D) or grounding |
|
|
|
connection damaged |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Servo lag is too high at standstill |
Electrical offset of analog axes |
Carry out offset adjustment; |
|
|
|
See “Adjusting the Electrical Offset |
|
|
|
(Drift Adjustment)” on page 346 |
|
|
|
|
|
Error messages regarding encoders or |
Probe or handwheel that were |
Disconnect the probe and |
|
other connected units are generated |
exposed to humidity (coolant, |
handwheel including the cables. |
|
although you find out that these do not |
etc.) or have been damaged. |
Screw the dummy plug |
|
cause the errors! |
--> Supply voltages (5 V, 12 V, |
(ID 271958-03) instead of the hand- |
|
15 V) are impaired. A variety of |
wheel or bridge the handwheel in |
||
|
|||
|
error messages are possible. |
the EMERGENCY STOP chain. |
|
|
|
Deactivate the handwheel in |
|
|
|
MP7640. Check whether the |
|
|
|
error messages are still generated. |
|
|
|
|
|
Various error messages are generated but |
Connection (short circuit) of |
Check the cables for damage. |
|
are not substantiated. |
shielding potential (chassis, |
Check the machine for correct |
|
|
cable shielding) with 0 V voltage |
shielding (ask the machine manu- |
|
|
potential of the NC power |
facturer). |
|
|
supply |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC functions do not function any more |
Data loss on the hard disk in the |
Check the hard disk; |
|
(There might be an information by the |
range of the SYS partition |
See “Hard Disk Test” on page 233 |
|
control that the corresponding files have |
|
Activate the NC software again; |
|
been deleted). |
|
See “Activating the NC Software |
|
|
|
Used on the Machine” on page 453 |
|
|
|
|
|
Bucking of the analog axis |
Carbon brushes for power |
Exchange the carbon brushes |
|
|
supply or tachometer measu- |
|
|
|
ring that have been abrided on |
|
|
|
one side or used up |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The axes cannot be traversed and the red |
Drive release missing |
See “Checking the Enables on the |
|
LEDs SH2 of all HEIDENHAIN drive |
|
iTNC” on page 311 |
|
modules light up (or the red LEDs SH2 or |
|
|
|
RESET of the HEIDENHAIN interface cards |
|
|
|
for the SIMODRIVE system) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
There are repeated hard disk errors |
Defects on the hard disk |
Check the hard disk; See “Hard |
|
|
Defective unit connected to the |
Disk Test” on page 233 |
|
|
|
||
|
control (short circuit, etc.) |
Disconnect suspicious units; |
|
|
|
See “Notes and Tips” on page 23 |
|
|
|
|
May 2006 |
5 – 27 |

Error |
Possible Cause of Error |
Measures for Error Diagnosis and/ |
|
|
or Corrective action |
During processing the motors run (axes, |
Defective braking resistor |
Check the primary supply (cables, |
spindle) down out of loop. |
(conversion of electrical energy |
fuses, terminals); |
|
to heat energy not possible) |
See “Power Supply” on page 205 |
|
Defective infeed/regenerative |
Check the functioning of the |
|
feedback module (energy |
inverter system or the braking |
|
recovery not possible) |
resistor; |
|
Interruption in the primary |
See Service Manual for Inverter |
|
Systems and Motors |
|
|
supply (fuses, wires, etc.; |
|
|
Check the wiring of the inverter |
|
|
energy recovery not possible) |
|
|
|
system, see circuit diagrams of the |
|
|
machine manufacturer |
|
|
|
An axis is to be traversed and an error |
Brake not released |
Check whether the brake is |
message is displayed, e.g. "8640 I2T value |
|
released |
of motor is too high ..." |
|
Check the wiring of the motor |
(or a similar error message that indicates an |
|
system; |
excessive load of the drive) |
|
See circuit diagrams of the |
|
|
machine manufacturer |
|
|
Some HEIDENHAIN inverters can |
|
|
control the motor brakes; |
|
|
See Service Manual for Inverter |
|
|
Systems and Motors |
|
|
|
5 – 28 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |

5.4Important Notes on the Use of HEIDENHAIN Interface Boards in SIMODRIVE System
Version with |
HEIDENHAIN interface boards for the SIMODRIVE system in the version with D-Sub connector |
D-Sub connector |
are available with or without metallic insulation of HEIDENHAIN PWM signals to the Siemens |
|
interface. |
Interface boards without metallic insulation are recognized as follows:
On the front panel there are the LEDs NB (not ready) and IF (pulse release).
There is no grounding screw on the front panel.
There is no transformer on the front panel.
These board have the Id.Nr. 291070-01, 324952-01, 02, 03 and 10 without index A.
Caution
The terminal X131 of the Siemens E/R module of boards without metallic insulation may not be connected to the central signal ground of the machine!
Note
The HEIDENHAIN interface boards of the first generation were built without metallic insulation.
May 2006 |
5 – 29 |

Interface boards with metallic insulation are distinguished as follows:
On the front panel there are the LEDs RESET X1, READY and RESET X2.
There is a grounding screw on the front panel.
There is no transformer on the front panel.
These boards have the ID 324952-10 with index
A, 11, 12, ...
Transformer component on the board
Grounding screw on the front panel
5 – 30 |
HEIDENHAIN Service Manual iTNC 530 |
 Loading...
Loading...