Texas Instruments TL16C750Y, TL16C750PM, TL16C750FNR, TL16C750IPM, TL16C750FN Datasheet

TL16C750 ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
DPin-to-Pin Compatible With the Existing TL16C550B/C
DProgrammable 16or 64-Byte FIFOs to Reduce CPU Interrupts
DProgrammable Auto-RTS and Auto-CTS
DIn Auto-CTS Mode, CTS Controls Transmitter
DIn Auto-RTS Mode, Receiver FIFO Contents and Threshold Control RTS
DSerial and Modem Control Outputs Drive a RJ11 Cable Directly When Equipment Is on the Same Power Drop
DCapable of Running With All Existing TL16C450 Software
DAfter Reset, All Registers Are Identical to the TL16C450 Register Set
DUp to 16-MHz Clock Rate for Up to 1-Mbaud Operation
DIn the TL16C450 Mode, Hold and Shift Registers Eliminate the Need for Precise Synchronization Between the CPU and Serial Data
DProgrammable Baud Rate Generator Allows
Division of Any Input Reference Clock by 1 to (216 ±1) and Generates an Internal 16 ×
Clock
DStandard Asynchronous Communication Bits (Start, Stop, and Parity) Added or Deleted to or From the Serial Data Stream
D5-V and 3-V Operation
description
DRegister Selectable Sleep Mode and Low-Power Mode
DIndependent Receiver Clock Input
DIndependently Controlled Transmit, Receive, Line Status, and Data Set Interrupts
DFully Programmable Serial Interface Characteristics:
±5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-Bit Characters
±Even-, Odd-, or No-Parity Bit Generation and Detection
±1-, 1 1/2-, or 2-Stop Bit Generation
±Baud Generation (DC to 1 Mbits Per Second)
DFalse Start Bit Detection
DComplete Status Reporting Capabilities
D3-State Output CMOS Drive Capabilities for Bidirectional Data Bus and Control Bus
DLine Break Generation and Detection
DInternal Diagnostic Capabilities:
±Loopback Controls for Communications Link Fault Isolation
±Break, Parity, Overrun, Framing Error Simulation
DFully Prioritized Interrupt System Controls
DModem Control Functions (CTS, RTS, DSR, DTR, RI, and DCD)
DAvailable in 44-Pin PLCC and 64-Pin SQFP
DIndustrial Temperature Range Available for 64-Pin SQFP
The TL16C750 is a functional upgrade of the TL16C550C asynchronous communications element (ACE), which in turn is a functional upgrade of the TL16C450. Functionally equivalent to the TL16C450 on power up (character or TL16C450 mode), the TL16C750, like the TL16C550C, can be placed in an alternate mode (FIFO mode). This relieves the CPU of excessive software overhead by buffering received and transmitted characters. The receiver and transmitter FIFOs store up to 64 bytes including three additional bits of error status per byte for the receiver FIFO. The user can choose between a 16-byte FIFO mode or an extended 64-byte FIFO mode. In the FIFO mode, there is a selectable autoflow control feature that can significantly reduce software overload and increase system efficiency by automatically controlling serial data flow through the RTS output and the CTS input signals (see Figure 1).
The TL16C750 performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data received from a peripheral device or modem and parallel-to-serial conversion on data received from its CPU. The CPU can read the ACE status at any time. The ACE includes complete modem control capability and a processor interrupt system that can be tailored to minimize software management of the communications link.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright 1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
1 |
TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
description (continued)
The TL16C750 ACE includes a programmable baud rate generator capable of dividing a reference clock by divisors from 1 to (216 ± 1) and producing a 16×reference clock for the internal transmitter logic. Provisions are also included to use this 16× clock for the receiver logic. The ACE accommodates a 1-Mbaud serial rate (16-MHz input clock) so a bit time is 1 ms and a typical character time is 10 ms (start bit, 8 data bits, stop bit).
Two of the TL16C450 terminal functions have been changed to TXRDY and RXRDY, which provide signaling to a direct memory access (DMA) controller.
FN PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D4 |
D3 |
|
D2 |
|
D1 |
D0 NC V RI DCD |
|
DSR |
|
CTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D5 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
44 43 42 41 40 |
|
|
|
|
|
MR |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D6 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
OUT1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D7 |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
DTR |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RCLK |
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
RTS |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SIN |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
OUT2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
NC |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOUT |
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
INTRPT |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS0 |
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
|
RXRDY |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS1 |
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
A0 |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS2 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
A1 |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
A2 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
BAUDOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XIN |
XOUT |
|
WR1 |
|
WR2 |
SS |
NC |
|
|
RD1 RD2 DDIS |
|
TXRDY |
|
ADS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PM PACKAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BAUDOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(TOP VIEW) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
|
CS2 |
|
CS1 |
NC |
|
CS0 |
|
SOUT |
NC |
NC |
|
|
|
SIN RCLK |
NC |
D7 |
D6 |
D5 NC |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
XIN |
|
|
64 |
63 62 61 |
|
60 59 58 57 56 55 54 |
53 52 |
51 50 49 |
|
|
|
|
D4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|||||||||||
XOUT |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
|
NC |
|||||||||||
|
|
NC |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
|
|
D3 |
|||||||||
|
WR1 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
D2 |
|||||||||
|
|
NC |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
NC |
|||||||||
|
WR2 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
|
D1 |
||||||||||
|
|
NC |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42 |
|
|
D0 |
|||||||||
|
|
VSS |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
|
NC |
|||||||||
|
|
RD1 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
VCC |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
RD2 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
NC |
||||||||||
|
|
NC |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
RI |
|
|
||||||||
DDIS |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
NC |
||||||||||||
TXRDY |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
DCD |
|||||||||||
|
|
NC |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
DSR |
|
|||||||||
|
|
ADS |
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
NC |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
NC |
|
|
16 |
18 19 20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
CTS |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
30 31 32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
A1 |
|
|
|
|
A0 |
|
RXRDY |
|
NC |
|
INTRPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC MR |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
|
|
|
|
NC |
OUT2 |
|
|
|
RTS NC |
DTR |
NC |
OUT1 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
NC ± No internal connection
2 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TL16C750 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997 |
|||
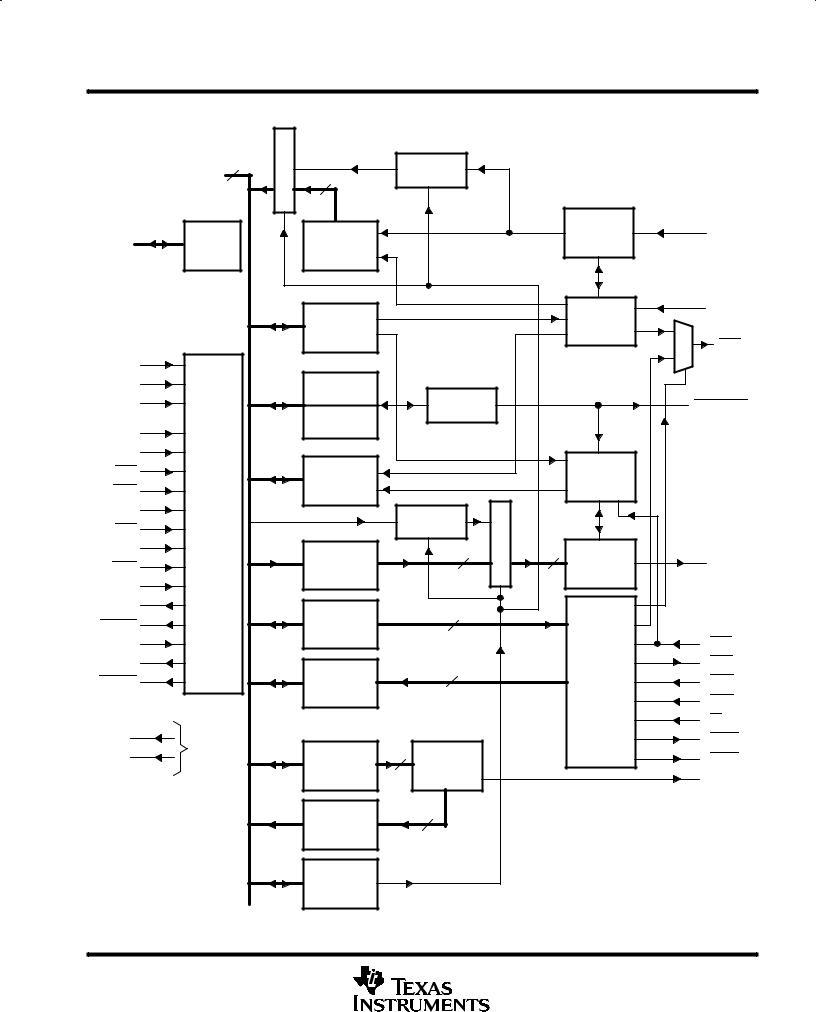
functional block diagram |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
8 |
l |
|
|
Receiver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
FIFO |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Data Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Receiver |
11 |
|
|
|
9 ± 2 |
Data |
|
|
Receiver |
|
|
|
|
Shift |
SIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
D(7 ± 0) |
|
|
Bus |
|
|
Buffer |
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
Buffer |
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Line |
|
|
|
|
Receiver |
10 |
RCLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timing and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
36 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A0 |
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 |
30 |
|
|
|
Divisor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
29 |
|
|
|
Latch (LS) |
|
Baud |
|
|
|
17 BAUDOUT |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Divisor |
|
Generator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CS0 |
|
|
|
Latch (MS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Autoflow |
|||
CS1 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
Line |
|
|
|
|
Transmitter |
Control |
|
CS2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timing and |
|||||
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
Status |
|
|
|
|
(AFE) |
|
|
ADS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
||||
Select |
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
MR |
39 |
|
|
Transmitter |
S |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
24 |
and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
RD1 |
Control |
|
|
|
FIFO |
e |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
RD2 |
25 |
Logic |
|
|
|
|
|
l |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transmitter |
|
8 |
e |
8 |
Transmitter |
13 |
|
|||
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
WR1 |
|
|
|
Holding |
|
|
c |
|
Shift |
|
SOUT |
||
WR2 |
21 |
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
t |
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
DDIS |
26 |
|
|
|
Modem |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
TXRDY |
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
||||
XIN |
18 |
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
CTS |
||
XOUT |
19 |
|
|
|
Modem |
|
8 |
|
|
Modem |
37 |
DTR |
|
RXRDY |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
DSR |
||||
|
|
|
Status |
|
|
|
Control |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
Logic |
42 |
DCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RI |
|
VCC |
44 |
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
OUT1 |
|
VSS |
22 |
|
|
Interrupt |
8 |
Interrupt |
|
|
|
35 |
|
||
Supply |
|
|
|
|
|
OUT2 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable |
|
Control |
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
Logic |
|
|
|
INTRPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupt |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FIFO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE A: Terminal numbers shown are for the FN package. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
3 |

TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Terminal Functions |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TERMINAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NAME |
NO. |
NO. |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|||||||
|
FN |
PM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A0 |
31 |
20 |
I |
Register select. A0 ± A2 are used during read and write operations to select the ACE register to read from |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
A1 |
30 |
18 |
|
or write to. Refer to Table 1 for register addresses and ADS signal description. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
A2 |
29 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
15 |
I |
Address strobe. When |
|
|
is active (low), the register select signals (A0, A1, and A2) and chip select signals |
|
|||||||||||
|
ADS |
|
|
|
|
ADS |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(CS0, CS1, CS2) drive the internal select logic directly; when ADS is high, the register select and chip select |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signals are held at the logic levels they were in when the low-to-high transition of ADS occurred. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
64 |
O |
Baud out. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
is a 16 ×clock signal for the transmitter section of the ACE. The clock rate is established |
|
|||||||
|
BAUDOUT |
BAUDOUT |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
by the reference oscillator frequency divided by a divisor specified by the baud generator divisor latches. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BAUDOUT can also be used for the receiver section by tying this output to RCLK. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
CS0 |
14 |
59 |
I |
Chip select. When CS0 and CS1 are high and |
|
is low, the ACE is selected. When any of these inputs |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
CS2 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CS1 |
15 |
61 |
|
are inactive, the ACE remains inactive. Refer to the ADS signal description. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
CS2 |
16 |
62 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
33 |
I |
Clear to send. |
|
|
|
is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 4 (CTS) of the |
|
||||||||||
|
CTS |
|
|
|
|
CTS |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
modem status register. Bit 0 (DCTS) of the modem status register indicates that CTS has changed states |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
since the last read from the modem status register. When the modem status interrupt is enabled, CTS |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
changes states, and the auto-CTS mode is not enabled, an interrupt is generated. CTS is also used in the |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
auto-CTS mode to control the transmitter. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
D0 |
2 |
42 |
I/O |
Data bus. Eight data lines with 3-state outputs provide a bidirectional path for data, control, and status |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
D1 |
3 |
43 |
|
information between the ACE and the CPU. As inputs, they use fail safe CMOS compatible input buffers. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
D2 |
4 |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
D3 |
5 |
46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
D4 |
6 |
48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
D5 |
7 |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
D6 |
8 |
51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
D7 |
9 |
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42 |
36 |
I |
Data carrier detect. |
|
|
|
|
is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 7 (DCD) of |
|
|||||||||
|
DCD |
|
|
DCD |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the modem status register. Bit 3 (DDCD) of the modem status register indicates that DCD has changed states |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
since the last read from the modem status register. When the modem status interrupt is enabled and DCD |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
changes state, an interrupt is generated. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
DDIS |
26 |
12 |
O |
Driver disable. DDIS is active (high) when the CPU is not reading data. When active, DDIS can disable an |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
external transceiver. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
35 |
I |
Data set ready. |
|
|
|
is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 5 (DSR) of the |
|
||||||||||
|
DSR |
|
|
DSR |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
modem status register. Bit 1 (DDSR) of the modem status register indicates DSR has changed states since |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the last read from the modem status register. When the modem status interrupt is enabled and the DSR |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
changes states, an interrupt is generated. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
28 |
O |
Data terminal ready. When active (low), |
|
informs a modem or data set that the ACE is ready to establish |
|
||||||||||||
|
DTR |
|
|
DTR |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
communication. DTR is placed in the active state by setting the DTR bit of the modem control register to one. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DTR is placed in the inactive condition either as a result of a master reset, during loop mode operation, or |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
clearing the DTR bit. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
INTRPT |
33 |
23 |
O |
Interrupt. When active (high), INTRPT informs the CPU that the ACE has an interrupt to be serviced. Four |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conditions that cause an interrupt to be issued are: a receiver error, received data that is available or timed |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
out (FIFO mode only), an empty transmitter holding register, or an enabled modem status interrupt. INTRPT |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is reset (deactivated) either when the interrupt is serviced or as a result of a master reset. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
MR |
39 |
32 |
I |
Master reset. When active (high), MR clears most ACE registers and sets the levels of various output signals |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(refer to Table 2). |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
30 |
O |
Outputs 1 and 2. These are user-designated output terminals that are set to their active (low) level by setting |
|
||||||||||||||
|
OUT1 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
OUT2 |
35 |
25 |
|
their respective modem control register (MCR) bits (OUT1 and OUT2). OUT1 and OUT2 are set to their |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
inactive (high) level as a result of master reset, during loop mode operations, or by clearing bit 2 (OUT1) or |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit 3 (OUT2) of the MCR. |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
RCLK |
10 |
54 |
I |
Receiver clock. RCLK is the 16× baud rate clock for the receiver section of the ACE. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TL16C750 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Terminal Functions (Continued) |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TERMINAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
NAME |
NO. |
NO. |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
||||||||||||
|
FN |
PM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
9 |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RD1 |
|
|
|
Read inputs. When either |
RD1 |
|
or RD2 is active (low or high respectively) while the ACE is selected, the CPU |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
RD2 |
25 |
10 |
|
is allowed to read status information or data from a selected ACE register. Only one of these inputs is required |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for the transfer of data during a read operation; the other input should be tied in its inactive state (i.e., RD2 tied |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
low or RD1 tied high). |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
38 |
I |
Ring indicator. |
|
|
is a modem status signal. Its condition can be checked by reading bit 6 (RI) of the modem |
|
||||||||||||
|
RI |
|
|
|
|
|
RI |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
status register. Bit 2 (TERI) of the modem status register indicates that RI has transitioned from a low to a high |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
level since the last read from the modem status register. If the modem status interrupt is enabled when this |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transition occurs, an interrupt is generated. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
26 |
O |
Request to send. When active, |
|
informs the modem or data set that the ACE is ready to receive data. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
RTS |
|
|
|
|
RTS |
RTS |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is set to its active level by setting the RTS MCR bit and is set to its inactive (high) level either as a result of a |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
master reset, during loop mode operations, or by clearing bit 1 (RTS) of the MCR. In the auto-RTS mode, |
RTS |
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is set to its inactive level by the receiver threshold control logic. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32 |
21 |
O |
Receiver ready. Receiver direct memory access (DMA) signalling is available with |
|
When operating |
|
|||||||||||||
|
RXRDY |
|
RXRDY. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in the FIFO mode, one of two types of DMA signalling can be selected through the FIFO control register bit |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 (FCR3). When operating in the TL16C450 mode, only DMA mode 0 is allowed. Mode 0 supports |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
single-transfer DMA in which a transfer is made between CPU bus cycles. Mode 1 supports multitransfer DMA |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in which multiple transfers are made continuously until the receiver FIFO has been emptied. In DMA mode 0 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(FCR0 = 0 or FCR0 = 1, FCR3 = 0), when there is at least one character in the receiver FIFO or receiver holding |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
register, RXRDY is active (low). When RXRDY has been active but there are no characters in the FIFO or |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
holding register, |
RXRDY |
goes inactive (high). In DMA mode 1 (FCR0 = 1, FCR3 = 1), when the trigger level |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
or the timeout has been reached, RXRDY goes active (low); when it has been active but there are no more |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
characters in the FIFO or holding register, it goes inactive (high). |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
SIN |
11 |
55 |
I |
Serial data. SIN is the input from a connected communications device. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
SOUT |
13 |
58 |
O |
Composite serial data output to a connected communication device. SOUT is set to the marking (high) level |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
as a result of master reset. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
13 |
O |
Transmitter ready. Transmitter DMA signalling is available with |
|
When operating in the FIFO mode, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
TXRDY |
|
TXRDY. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
one of two types of DMA signalling can be selected through FCR3. When operating in the TL16C450 mode, |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
only DMA mode 0 is allowed. Mode 0 supports single-transfer DMA in which a transfer is made between CPU |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bus cycles. Mode 1 supports multitransfer DMA in which multiple transfers are made continuously until the |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transmit FIFO has been filled. |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
VCC |
44 |
40 |
|
5-V supply voltage |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
VSS |
22 |
8 |
|
Supply common |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
4 |
I |
Write inputs. When either input is active (low or high respectively) and while the ACE is selected, the CPU is |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
WR1 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WR2 |
21 |
6 |
|
allowed to write control words or data into a selected ACE register. Only one of these inputs is required to |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transfer data during a write operation; the other input should be tied in its inactive state (i.e., WR2 tied low or |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WR1 tied high). |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
XIN |
18 |
1 |
I/O |
External clock. XIN and XOUT connect the ACE to the main timing reference (clock or crystal). |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
XOUT |
19 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
detailed description
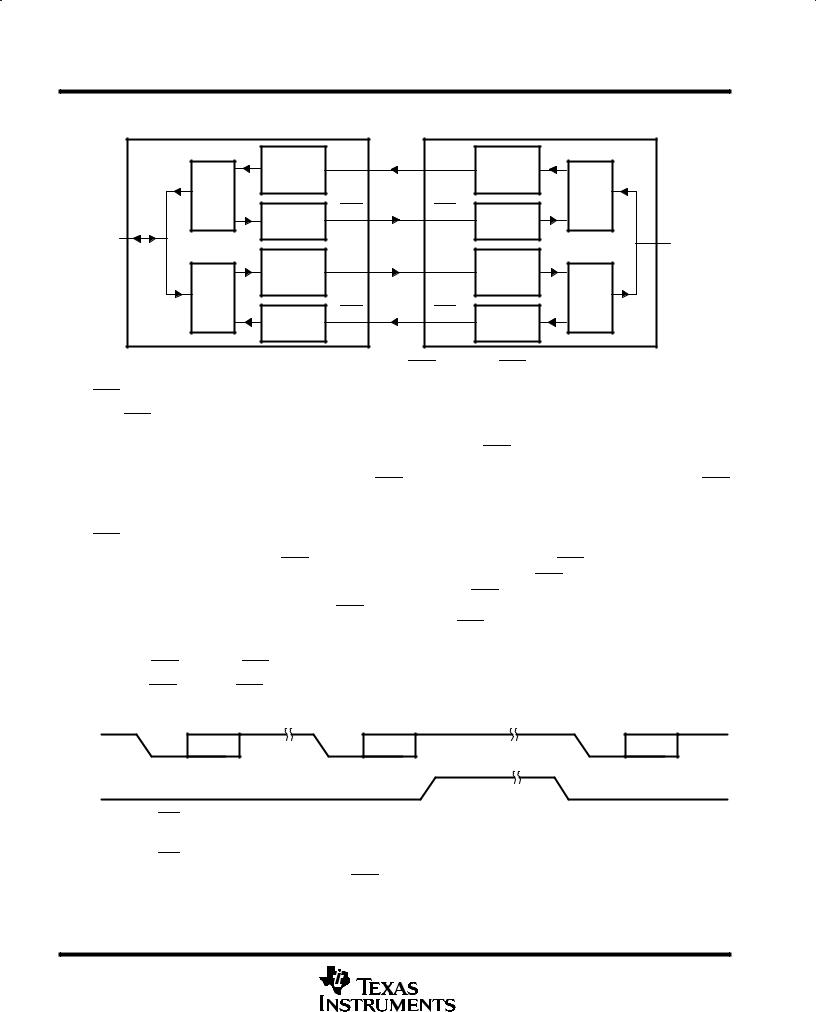
autoflow control
Auto-flow control is composed of auto-CTS and auto-RTS. With auto-CTS, CTS must be active before the transmit FIFO can emit data (see Figure 1). With auto-RTS, RTS becomes active when the receiver is empty or the threshold has not been reached. When RTS is connected to CTS, data transmission does not occur unless the receive FIFO has empty space. Thus, overrun errors are eliminated when ACE1 and ACE2 are TLC16C750s with enabled autoflow control. If not, overrun errors occur if the transmit data rate exceeds the receive FIFO read latency.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
5 |
TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
autoflow control (continued)
ACE1 |
|
|
ACE2 |
|
Serial to |
SIN |
SOUT |
Parallel |
|
Parallel |
|
|
to Serial |
|
RCV |
|
|
XMT |
|
FIFO |
RTS |
CTS |
FIFO |
|
Flow |
Flow |
|||
|
|
|||
Control |
|
|
Control |
|
D7± D0 |
|
|
D7± D0 |
|
|
|
|
||
Parallel |
SOUT |
SIN |
Serial to |
|
to Serial |
|
|
Parallel |
|
XMT |
|
|
RCV |
|
FIFO |
CTS |
RTS |
FIFO |
|
Flow |
Flow |
|||
|
|
|||
Control |
|
|
Control |
Figure 1. Autoflow Control (auto-RTS and auto-CTS) Example
auto-RTS (see Figure 1)
Auto-RTS data flow control originates in the receiver timing and control block (see functional block diagram) and is linked to the programmed receiver FIFO trigger level. When the receiver FIFO level reaches a trigger level of 1, 4, 8, or 14 in 16-byte mode or 1, 16, 32, or 56 in 64-byte mode, RTS is deasserted. The sending ACE may send an additional byte after the trigger level is reached (assuming the sending ACE has another byte to send) because it may not recognize the deassertion of RTS until after it has begun sending the additional byte. RTS is automatically reasserted once the receiver FIFO is emptied by reading the receiver buffer register. The reassertion signals the sending ACE to continue transmitting data.
auto-CTS (see Figure 1)
The transmitter circuitry checks CTS before sending the next data byte. When CTS is active, the transmitter sends the next byte. To stop the transmitter from sending the following byte, CTS must be released before the middle of the last stop bit that is currently being sent. The auto-CTS function reduces interrupts to the host system. When flow control is enabled, the CTS state changes and does not trigger host interrupts because the device automatically controls its own transmitter. Without auto-CTS, the transmitter sends any data present in the transmit FIFO and a receiver overrun error can result.
enabling auto-RTS and auto-CTS
The auto-RTS and auto-CTS modes of operation are activated by setting bit 5 of the modem control register (MCR) to 1 (see Figure 2).
SOUT |
Start Bits 0 ± 7 Stop |
|
Start Bits 0 ± 7 Stop |
|
|
|
Start Bits 0 ± 7 Stop |
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CTS
NOTES: A. When CTS is low, the transmitter keeps sending serial data out.
B.When CTS goes high before the middle of the last stop bit of the current byte, the transmitter finishes sending the current byte but it does not send the next byte.
C.When CTS goes from high to low, the transmitter begins sending data again.
Figure 2. CTS Functional Timing
6 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
enabling auto-RTS and auto-CTS (continued)
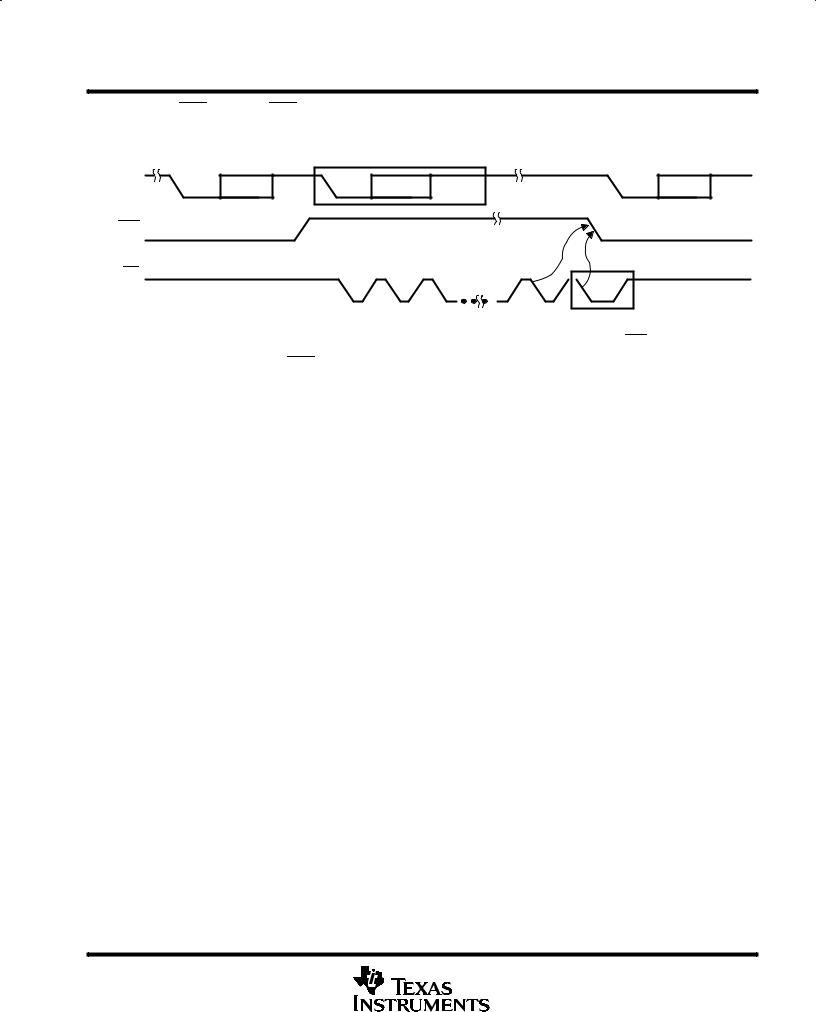
The receiver FIFO trigger level can be set to 1, 4, 8, or 14 bytes for the 16-byte mode and 1, 16, 32, or 56 bytes for 64-byte mode (see Figure 3).
SIN |
Start Byte N Stop |
Start |
Byte N+1 Stop |
|
Start |
Byte |
Stop |
RTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(RD RBR) |
|
1 |
2 |
N |
N+1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES: A. N = receiver FIFO trigger level
B. The two blocks in dashed lines cover the case where an additional byte is sent as described in auto-RTS.
Figure 3. RTS Functional Timing, Receiver FIFO Trigger Level
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)²
Supply voltage range, VCC (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . ±0.5 V to 6 V |
|
Input voltage range, VI: Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
±0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 |
V |
Fail safe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . ±0.5 V to 6.5 |
V |
Output voltage range, VO: Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
±0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 |
V |
Fail safe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . ±0.5 V to 6.5 |
V |
Input clamp current, IIK (VI < 0 or VI > VCC) (see Note 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ± 20 mA |
|
Output clamp current, IOK (VO < 0 or VO > VCC) (see Note 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . ± 20 mA |
|
Operating free-air temperature range, TA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . 0°C to 70°C |
|
Operating free-air temperature range, TA (TL16C750I) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . ±40°C to 85°C |
|
Storage temperature range, Tstg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . ±65°C to 150°C |
|
² Stresses beyond those listed under ªabsolute maximum ratingsº may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under ªrecommended operating conditionsº is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. This applies for external input and bidirectional buffers. VI > VCC does not apply to fail safe terminals. 2. This applies for external output and bidirectional buffers. VO > VCC does not apply to fail safe terminals.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
7 |

TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
recommended operating conditions low voltage (3.3 V nominal)
|
MIN |
NOM |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage, VCC |
3 |
3.3 |
3.6 |
V |
Input voltage, VI |
0 |
|
VCC |
V |
High-level input voltage, VIH (see Note 3) |
0.7 VCC |
|
|
V |
Low-level input voltage, VIL (see Note 3) |
|
|
0.3 VCC |
V |
Output voltage, VO (see Note 4) |
0 |
|
VCC |
V |
High-level output current, IOH (all outputs) |
|
|
1.8 |
mA |
Low-level output current, IOL (all outputs) |
|
|
3.2 |
mA |
Input capacitance, cI |
|
|
1 |
pF |
Operating free-air temperature, TA |
0 |
25 |
70 |
°C |
Junction temperature range, TJ (see Note 5) |
0 |
25 |
115 |
°C |
Oscillator/clock speed |
|
|
14 |
MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES: 3. Meets TTL levels, VIHmin = 2 V and VILmax = 0.8 V on nonhysteresis inputs |
|
|
|
|
4.Applies for external output buffers
5.These junction temperatures reflect simulated conditions. Absolute maximum junction temperature is 150°C. The customer is responsible for verifying junction temperature.
standard voltage (5 V nominal)
|
MIN |
NOM |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
Supply voltage, VCC |
4.75 |
5 |
5.25 |
V |
Input voltage, VI |
0 |
|
VCC |
V |
High-level input voltage, VIH |
0.7 VCC |
|
|
V |
Low-level input voltage, VIL |
|
|
0.2 VCC |
V |
Output voltage, VO (see Note 4) |
0 |
|
VCC |
V |
High-level output current, IOH (all outputs) |
|
|
4 |
mA |
Low-level output current, IOL (all outputs) |
|
|
4 |
mA |
Input capacitance, cI |
|
|
1 |
pF |
Operating free-air temperature, TA |
0 |
25 |
70 |
°C |
Junction temperature range, TJ (see Note 5) |
0 |
25 |
115 |
°C |
Oscillator/clock speed |
|
|
16 |
MHz |
NOTES: 4. Applies for external output buffers
5.These junction temperatures reflect simulated conditions. Absolute maximum junction temperature is 150°C. The customer is responsible for verifying junction temperature.
8 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
low voltage (3.3 V nominal)
|
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOH |
High-level output voltage² |
IOH = ± 1.8 mA |
VCC ± 0.55 |
|
V |
V |
Low-level output voltage² |
I = 3.2 mA |
|
0.5 |
V |
OL |
|
OL |
|
|
|
IOZ |
High-impedance 3-state output current (see Note 6) |
VI = VCC or GND |
|
± 10 |
μA |
IIL |
Low-level input current (see Note 7) |
VI = GND |
|
± 1 |
μA |
IIH |
High-level input current (see Note 8) |
VI = VCC |
|
1 |
μA |
² For all outputs except XOUT
NOTES: 6. The 3-state or open-drain output must be in the high-impedance state.
7.Specifications only apply with pullup termination turned off.
8.Specifications only apply with pulldown termination turned off.
standard voltage (5 V nominal)
|
PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOH |
High-level output voltage² |
IOH = ± 4 mA |
VCC ± 0.8 |
|
V |
VOL |
Low-level output voltage² |
IOL = 4 mA |
|
0.5 |
V |
IOZ |
High-impedance 3-state output current (see Note 6) |
VI = VCC or GND |
|
± 10 |
μA |
IIL |
Low-level input current (see Note 7) |
VI = GND |
|
± 1 |
μA |
IIH |
High-level input current (see Note 8) |
VI = VCC |
|
1 |
μA |
² For all outputs except XOUT
NOTES: 6. The 3-state or open-drain output must be in the high-impedance state.
7.Specifications only apply with pullup termination turned off.
8.Specifications only apply with pulldown termination turned off.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
9 |

TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997
system timing requirements over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature
|
|
|
PARAMETER |
ALT. SYMBOL |
FIGURE |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN MAX |
UNIT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tcR |
Cycle time, read (tw7 + td8 + td9) |
RC |
|
|
87 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tcW |
Cycle time, write (tw6 + td5 + td6) |
WC |
|
|
87 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tw1 |
Pulse duration, clock (XIN) high |
tXH |
4 |
f = 16 MHz maximum |
25 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tw2 |
Pulse duration, clock (XIN) low |
tXL |
4 |
f = 16 MHz maximum |
25 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tw5 |
Pulse duration, |
|
|
|
low |
tADS |
5, 6 |
|
9 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tw6 |
Pulse duration, write strobe |
tWR |
5 |
|
40 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tw7 |
Pulse duration, read strobe |
tRD |
6 |
|
40 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tw8 |
Pulse duration, MR |
tMR |
|
|
1 |
ms |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tsu1 |
Setup time, address valid before |
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ |
tAS |
5, 6 |
|
8 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tsu2 |
Setup time, CS valid before |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ |
tCS |
5, 6 |
|
8 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tsu3 |
Setup time, data valid before |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↓ or WR2↑ |
tDS |
5 |
|
15 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WR1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tsu4² |
Setup time, |
|
|
↑ before midpoint of stop bit |
|
16 |
|
10 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTS |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
th1 |
Hold time, address low after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ |
tAH |
5, 6 |
|
0 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
th2 |
Hold time, CS valid after |
ADS |
↑ |
tCH |
5, 6 |
|
0 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
th3 |
Hold time, CS valid after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ or WR2↓ |
tWCS |
5 |
|
10 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
WR1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
th4² |
Hold time, address valid after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ or WR2↓ |
tWA |
5 |
|
10 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WR1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
th5 |
Hold time, data valid after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ or WR2↓ |
tDH |
5 |
|
5 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
WR1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
th6 |
Hold time, CS valid after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ or RD2↓ |
tRCS |
6 |
|
10 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RD1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
th7² |
Hold time, address valid after |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ or RD2↓ |
tRA |
6 |
|
20 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RD1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td4² |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Delay time, CS valid before |
WR1 |
↓ or WR2↑ |
tCSW |
5 |
|
7 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td5 |
Delay time, address valid before |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↓ or WR2↑ |
tAW |
5 |
|
7 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WR1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td6² |
Delay time, write cycle, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑ or WR2↓ to |
|
|
↓ |
tWC |
5 |
|
40 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WR1 |
ADS |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td7² |
Delay time, CS valid to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
↓ or RD2↑ |
tCSR |
6 |
|
7 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RD1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td8² |
Delay time, address valid to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↓ or RD2↑ |
tAR |
6 |
|
7 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RD1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
↓ |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td9 |
Delay time, read cycle, |
RD1 |
↑ or RD2↓ to |
ADS |
tRC |
6 |
|
40 |
ns |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td10 |
Delay time, |
RD1 |
↓ or RD2↑ to data valid |
tRVD |
6 |
CL = 75 pF |
45 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
td11 |
Delay time, |
RD1 |
↑ or RD2↓ to floating data |
tHZ |
6 |
CL = 75 pF |
20 |
ns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
² Only applies when ADS is low
system switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (see Note 9)
PARAMETER |
ALT. SYMBOL |
FIGURE |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
tdis(R) Disable time, |
|
↓↑ or RD2↑↓ to DDIS↑↓ |
tRDD |
6 |
CL = 75 pF |
20 |
|
ns |
RD1 |
|
|||||||
NOTE 9: Charge and discharge times are determined by VOL, VOH, and external loading. |
|
|
|
|
||||
baud generator switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature, CL = 75 pF
|
PARAMETER |
ALT. SYMBOL |
FIGURE |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 16 MHz, CLK ÷2 |
|
|
|
|
||
tw3 |
Pulse duration, |
BAUDOUT |
low |
tLW |
4 |
50 |
|
ns |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 16 MHz, CLK ÷2 |
|
|
|
|
||
tw4 |
Pulse duration, |
BAUDOUT |
high |
tHW |
4 |
50 |
|
ns |
|
|||||
td1 |
Delay time, XIN↑ to |
|
|
|
↑ |
tBLD |
4 |
|
|
45 |
ns |
|
||
BAUDOUT |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
td2 |
Delay time, XIN↑↓ to |
BAUDOUT |
↓ |
tBHD |
4 |
|
|
45 |
ns |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

TL16C750
ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ELEMENT
WITH 64-BYTE FIFOs AND AUTOFLOW CONTROL
|
|
|
|
|
SLLS191C ± JANUARY 1995 ± REVISED DECEMBER 1997 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
commercial maximum switching characteristics, VCC = 4.75 V, TJ = 115°C |
|
|
|
||||||
PARAMETER |
FROM |
TO |
INTRINSIC |
DELTA |
|
DELAY (ns) |
|
|
|
DELAY |
DELAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(INPUT) |
(OUTPUT) |
CL = 15 pF |
CL = 50 pF |
CL = 85 pF |
CL = 100 pF |
|
|||
|
(ns) |
(ns/pF) |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
tPLH |
XIN |
XO |
± 0.92 |
0.571 |
7.65 |
27.66 |
47.66 |
56.23 |
|
tPHL |
± 0.79 |
0.312 |
3.89 |
14.83 |
25.76 |
30.45 |
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||
tr |
|
Output rise time, XO |
|
10.86 |
40.42 |
69.98 |
82.65 |
|
|
tf |
|
Output fall time, XO |
|
5.47 |
20.90 |
36.34 |
42.95 |
|
|
commercial maximum switching characteristics, VCC = 3 V, TJ = 115°C |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PARAMETER |
FROM |
TO |
INTRINSIC |
DELTA |
|
DELAY (ns) |
|
|
|
DELAY |
DELAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(INPUT) |
(OUTPUT) |
CL = 15 pF |
CL = 50 pF |
CL = 85 pF |
CL = 100 pF |
|
|||
|
(ns) |
(ns/pF) |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
tPLH |
XIN |
XO |
± 4.69 |
1.017 |
10.57 |
46.16 |
81.75 |
97.00 |
|
tPHL |
± 3.05 |
0.442 |
3.58 |
19.04 |
34.51 |
41.13 |
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||
tr |
|
Output rise time, XO |
|
14.39 |
64.87 |
115.35 |
136.98 |
|
|
tf |
|
Output fall time, XO |
|
5.06 |
26.53 |
48.01 |
57.21 |
|
|
receiver switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature (see Note 10)
|
PARAMETER |
ALT. SYMBOL |
FIGURE |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN MAX |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
td12 |
Delay time, RCLK to sample clock |
tSCD |
7 |
|
10 |
ns |
|
|
Delay time, stop to set receiver error inter- |
|
7, 8, 9, |
|
|
RCLK |
|
td13 |
rupt or read RBR to LSI interrupt or stop to |
tSINT |
|
2 |
|||
10, 11 |
|
cycle |
|||||
|
RXRDY↓ |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
td14 |
Delay time, read RBR/LSR low to reset |
tRINT |
7, 8, 9, |
CL = 75 pF |
120 |
ns |
|
interrupt low |
10, 11 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE 10: In the FIFO mode, the read cycle (RC) = 425 ns (minimum) between reads of the receive FIFO and the status registers (interrupt identification register or line status register).
transmitter switching characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air temperature
|
PARAMETER² |
ALT. SYMBOL |
FIGURE |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
||||
td15 |
Delay time, INTRPT to transmit start |
tIRS |
12 |
|
8 |
24 |
baudout |
||||
|
cycles |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
td16 |
Delay time, start to interrupt |
tSTI |
12 |
|
8 |
10 |
baudout |
||||
|
cycles |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
td17 |
Delay time, WR THR to reset interrupt |
tHR |
12 |
CL = 75 pF |
|
50 |
ns |
||||
td18 |
Delay time, initial write to interrupt (THRE) |
tSI |
12 |
|
16 |
34 |
baudout |
||||
|
cycles |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
td19 |
Delay time, read IIR to reset interrupt (THRE) |
tIR |
12 |
CL = 75 pF |
|
70 |
ns |
||||
td20 |
Delay time, write to |
|
|
inactive |
tWXI |
13, 14 |
CL = 75 pF |
|
75 |
ns |
|
TXRDY |
|
||||||||||
td21 |
|
|
|
|
|
tSXA |
13, 14 |
CL = 75 pF |
|
9 |
baudout |
Delay time, start to TXRDY active |
|
||||||||||
|
cycles |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
² THRE = transmitter holding register empty, IIR = interrupt identification register.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
11 |
 Loading...
Loading...