Motorola MCM69P737TQ4R, MCM69P737TQ3.8R, MCM69P737TQ3.5R, MCM69P737TQ3.5, MCM69P737ZP3.5 Datasheet
...
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document by MCM69P737/D
128K x 36 Bit Pipelined
BurstRAM Synchronous
Fast Static RAM
The MCM69P737 is a 4M bit synchronous fast static RAM designed to provide a burstable, high performance, secondary cache for the PowerPC and other high performance microprocessors. It is organized as 128K words of 36 bits each. This device integrates input registers, an output register, a 2±bit address counter, and high speed SRAM onto a single monolithic circuit for reduced parts count in cache data RAM applications. Synchronous design allows precise cycle control with the use of an external clock (K).
Addresses (SA), data inputs (DQx), and all control signals except output enable (G) and linear burst order (LBO) are clock (K) controlled through positive± edge±triggered noninverting registers.
Bursts can be initiated with either ADSP or ADSC input pins. Subsequent burst addresses can be generated internally by the MCM69P737 (burst sequence operates in linear or interleaved mode dependent upon the state of LBO) and controlled by the burst address advance (ADV) input pin.
Write cycles are internally self±timed and are initiated by the rising edge of the clock (K) input. This feature eliminates complex off±chip write pulse generation and provides increased timing flexibility for incoming signals.
Synchronous byte write (SBx), synchronous global write (SGW), and synchronous write enable (SW) are provided to allow writes to either individual bytes or to all bytes. The four bytes are designated as ªaº, ªbº, ªcº, and ªdº.controlsSBa DQa, SBb controls DQb, etc. Individual bytes are written if the selected byte writes SBx are asserted with SW. All bytes are written if either SGW is asserted or if all SBx and SW are asserted.
For read cycles, pipelined SRAMs output data is temporarily stored by an edge±triggered output register and then released to the output buffers at the next rising edge of clock (K).
The MCM69P737 operates from a 3.3 V core power supply and all outputs operate on a 2.5 V or 3.3 V power supply. All inputs and outputs are JEDEC standard JESD8±5 compatible.
•MCM69P737±3.5: 3.5 ns Access/6 ns Cycle (166 MHz) MCM69P737±3.8: 3.8 ns Access/6.7 ns Cycle (150 MHz) MCM69P737±4: 4 ns Access/7.5 ns Cycle (133 MHz)
•3.3 V + 10%, ± 5% Core Power Supply, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O Supply
•ADSP, ADSC, and ADV Burst Control Pins
•Selectable Burst Sequencing Order (Linear/Interleaved)
•Single±Cycle Deselect Timing
•Internally Self±Timed Write Cycle
•Byte Write and Global Write Control
•PB1 Version 2.0 Compatible
•JEDEC Standard 119±Pin PBGA and 100±Pin TQFP Packages
MCM69P737
ZP PACKAGE
PBGA
CASE 999±02
TQ PACKAGE
TQFP
CASE 983A±01
The PowerPC name is a trademark of IBM Corp., used under license therefrom.
REV 6 1/20/98
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM |
MCM69P737 |
Motorola, Inc. 1998 |
|
|
1 |
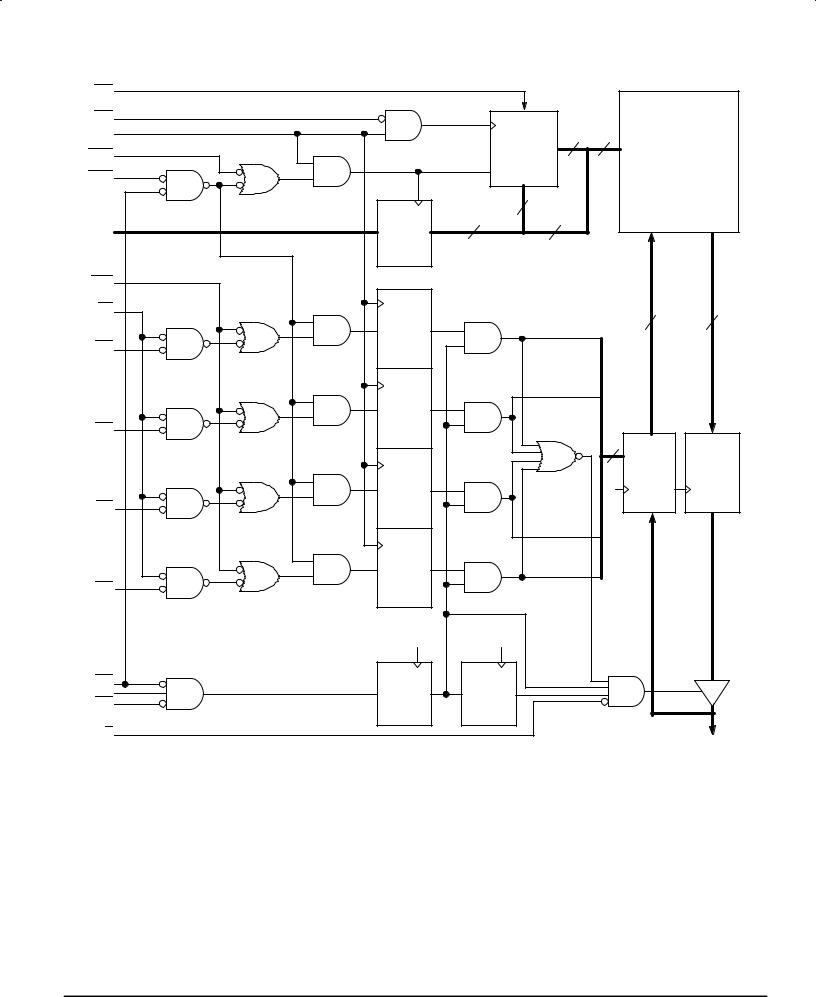
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
LBO |
|
|
|
|
ADV |
|
|
|
|
K |
|
BURST |
2 |
17 |
|
|
|||
ADSC |
K2 |
COUNTER |
|
|
|
CLR |
|
|
|
ADSP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
SA |
ADDRESS |
17 |
15 |
|
SA1 |
|
|||
REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
SA0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SGW |
|
|
|
|
SW |
WRITE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REGISTER |
|
|
|
SBa |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WRITE |
|
|
|
|
REGISTER |
|
|
|
SBb |
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
WRITE |
|
|
|
|
REGISTER |
|
|
K |
|
c |
|
|
|
SBc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WRITE |
|
|
|
|
REGISTER |
|
|
|
SBd |
d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K2 |
K |
|
|
SE1 |
ENABLE |
ENABLE |
|
|
SE2 |
|
|
||
REGISTER |
REGISTER |
|
|
|
SE3 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
128K x 36 ARRAY
36 36
DATA±IN DATA±OUT REGISTER REGISTER
G
DQa ± DQd
MCM69P737 |
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM |
2 |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
VDDQ |
VDDQ |
SA |
SA |
ADSP |
SA |
SA |
|
B |
SE2 |
SA |
ADSC |
SA |
SE3 |
NC |
NC |
||||||
C |
SA |
SA |
VDD |
SA |
SA |
NC |
NC |
||||||
D |
|
VSS |
|
VSS |
|
DQb |
DQc |
DQc |
NC |
DQb |
|||
E |
|
|
|
|
|
DQb |
DQc |
DQc |
VSS |
SE1 |
VSS |
DQb |
|
F |
|
VSS |
|
VSS |
DQb |
VDDQ |
VDDQ |
DQc |
G |
||||
G |
|
|
ADV |
SBb |
DQb |
DQb |
DQc |
DQc |
SBc |
||||
H |
|
VSS |
|
VSS |
DQb |
DQb |
DQc |
DQc |
SGW |
||||
J |
VDD |
|
VDD |
|
VDD |
VDDQ |
VDDQ |
NC |
NC |
||||
K |
|
|
|
|
|
DQa |
DQd |
DQd |
VSS |
K |
VSS |
DQa |
|
L |
|
|
NC |
|
|
DQa |
DQd |
DQd |
SBd |
SBa |
DQa |
||
M |
|
|
SW |
VSS |
|
VDDQ |
VDDQ |
DQd |
VSS |
DQa |
|||
N |
|
VSS |
|
VSS |
|
DQa |
DQd |
DQd |
SA1 |
DQa |
|||
P |
|
VSS |
|
VSS |
|
|
DQd |
DQd |
SA0 |
DQa |
DQa |
||
R |
SA |
LBO |
VDD |
NC |
SA |
NC |
NC |
||||||
T |
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
NC |
NC |
SA |
SA |
SA |
NC |
|
U |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
VDDQ |
VDDQ |
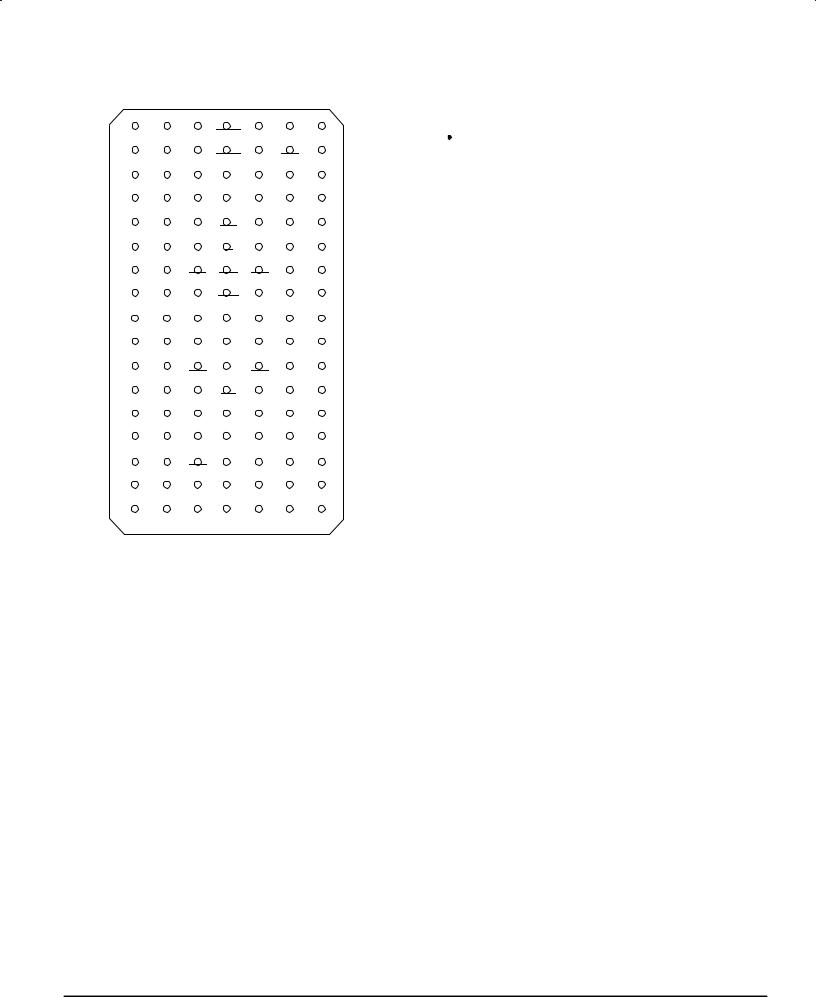
TOP VIEW 119 BUMP PBGA
PIN ASSIGNMENTS
SA SA SE1 SE2 SBd |
SBc SBb SBa SE3 |
V |
V K |
|
SGW SW |
G |
|
ADSC |
|
ADSP ADV SA SA |
|||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DD |
SS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQc |
|
100 99 9897 9695 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
DQc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
79 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
DQc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
VDDQ |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
77 |
|
VDDQ |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
VSS |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
76 |
|
VSS |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DQc |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75 |
|
DQb |
|||||||||||
DQc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
74 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
DQc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
DQc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
72 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
VSS |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
71 |
|
VSS |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
VDDQ |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
VDDQ |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DQc |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
69 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DQc |
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
68 |
|
DQb |
||||||||||||
NC |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
67 |
|
VSS |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
VDD |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66 |
|
NC |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
NC |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65 |
|
VDD |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
VSS |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64 |
|
NC |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
DQd |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
63 |
|
DQa |
||||||||||||
DQd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
62 |
|
DQa |
|||||||||||||
VDDQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
61 |
|
VDDQ |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
VSS |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
V |
||||||||||||
DQd |
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 |
|
DQa |
||||||||||||||
DQd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
58 |
|
DQa |
|||||||||||||
DQd |
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57 |
|
DQa |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
DQd |
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56 |
|
DQa |
||||||||||||
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
|
VSS |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
VDDQ |
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54 |
|
VDDQ |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
DQd |
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53 |
|
DQa |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
DQd |
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52 |
|
DQa |
||||||||||||
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
DQd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
|
DQa |
|||||||||||||
|
|
31 32 33 34 35 36 3738 39 40 41 42 43 444546 4748 49 50 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LBO SA SA SA SA SA1 SA0 |
|
|
|
|
SS |
DD |
NC NC SA SA SA SA SA SA SA |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
NC NC V |
V |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TOP VIEW 100 PIN TQFP
Not to Scale
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM |
MCM69P737 |
|
3 |

PBGA PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Locations |
Symbol |
Type |
Description |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4B |
ADSC |
Input |
Synchronous Address Status Controller: Active low, interrupts any |
||||
|
|
|
ongoing burst and latches a new external address. Used to initiate a |
||||
|
|
|
READ, WRITE, or chip deselect. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4A |
ADSP |
Input |
Synchronous Address Status Processor: Active low, interrupts any |
||||
|
|
|
ongoing burst and latches a new external address. Used to initiate a |
||||
|
|
|
new READ, WRITE, or chip deselect (exception Ð chip deselect does |
||||
|
|
|
not occur when ADSP is asserted and SE1 is high). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4G |
ADV |
Input |
Synchronous Address Advance: Increments address count in |
||||
|
|
|
accordance with counter type selected (linear/interleaved). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) 6K, 7K, 6L, 7L, 6M, 6N, 7N, 6P, 7P |
DQx |
I/O |
Synchronous Data I/O: ªxº refers to the byte being read or written |
||||
(b) 6D, 7D, 6E, 7E, 6F, 6G, 7G, 6H, 7H |
|
|
(byte a, b, c, d). |
||||
(c) 1D, 2D, 1E, 2E, 2F, 1G, 2G, 1H, 2H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) 1K, 2K, 1L, 2L, 2M, 1N, 2N, 1P, 2P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4F |
G |
Input |
Asynchronous Output Enable Input: |
||||
|
|
|
Low Ð enables output buffers (DQx pins). |
||||
|
|
|
High Ð DQx pins are high impedance. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4K |
K |
Input |
Clock: This signal registers the address, data in, and all control signals |
||||
|
|
|
except G and LBO. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3R |
LBO |
Input |
Linear Burst Order Input: This pin must remain in steady state (this |
||||
|
|
|
signal not registered or latched). It must be tied high or low. |
||||
|
|
|
Low Ð linear burst counter (68K/PowerPC). |
||||
|
|
|
High Ð interleaved burst counter (486/i960/Pentium). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2A, 3A, 5A, 6A, 3B, 5B, 2C, 3C, |
SA |
Input |
Synchronous Address Inputs: These inputs are registered and must |
||||
5C, 6C, 2R, 6R, 3T, 4T, 5T |
|
|
meet setup and hold times. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4N, 4P |
SA1, SA0 |
Input |
Synchronous Address Inputs: These pins must be wired to the two |
||||
|
|
|
LSBs of the address bus for proper burst operation. These inputs are |
||||
|
|
|
registered and must meet setup and hold times. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5L, 5G, 3G, 3L |
SBx |
Input |
Synchronous Byte Write Inputs: ªxº refers to the byte being written (byte |
||||
(a) (b) (c) (d) |
|
|
a, b, c, d). SGW overrides SBx. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4E |
SE1 |
Input |
Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low to enable chip. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Negated high Ð blocks ADSP or deselects chip when ADSC is |
||||
|
|
|
asserted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2B |
SE2 |
Input |
Synchronous Chip Enable: Active high for depth expansion. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
6B |
SE3 |
Input |
Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low for depth expansion. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4H |
SGW |
Input |
Synchronous Global Write: This signal writes all bytes regardless of the |
||||
|
|
|
status of the SBx and SW signals. If only byte write signals SBx are |
||||
|
|
|
being used, tie this pin high. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4M |
SW |
Input |
Synchronous Write: This signal writes only those bytes that have been |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
selected using the byte write SBx pins. If only byte write signals SBx |
||||
|
|
|
are being used, tie this pin low. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
4C, 2J, 4J, 6J, 4R |
VDD |
Supply |
Core Power Supply. |
||||
1A, 7A, 1F, 7F, 1J, 7J, 1M, 7M, 1U, 7U |
VDDQ |
Supply |
I/O Power Supply. |
||||
3D, 5D, 3E, 5E, 3F, 5F, 3H, 5H, |
VSS |
Supply |
Ground. |
||||
3K, 5K, 3M, 5M, 3N, 5N, 3P, 5P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1B, 7B, 1C, 7C, 4D, 3J, 5J, 4L, 1R, 5R, |
NC |
Ð |
No Connection: There is no connection to the chip. |
||||
7R, 1T, 2T, 6T, 7T, 2U, 3U, 4U, 5U, 6U |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MCM69P737 |
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM |
4 |
|

TQFP PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Locations |
Symbol |
Type |
Description |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85 |
ADSC |
Input |
Synchronous Address Status Controller: Active low, interrupts any |
||||
|
|
|
ongoing burst and latches a new external address. Used to initiate a |
||||
|
|
|
READ, WRITE, or chip deselect. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
84 |
ADSP |
Input |
Synchronous Address Status Processor: Active low, interrupts any |
||||
|
|
|
ongoing burst and latches a new external address. Used to initiate a |
||||
|
|
|
new READ, WRITE, or chip deselect (exception Ð chip deselect does |
||||
|
|
|
not occur when ADSP is asserted and SE1 is high). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
83 |
ADV |
Input |
Synchronous Address Advance: Increments address count in |
||||
|
|
|
accordance with counter type selected (linear/interleaved). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) 51, 52, 53, 56, 57, 58, 59, 62, 63 |
DQx |
I/O |
Synchronous Data I/O: ªxº refers to the byte being read or written |
||||
(b) 68, 69, 72, 73, 74, 75, 78, 79, 80 |
|
|
(byte a, b, c, d). |
||||
(c) 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) 18, 19, 22, 23, 24, 25, 28, 29, 30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86 |
G |
Input |
Asynchronous Output Enable Input: |
||||
|
|
|
Low Ð enables output buffers (DQx pins). |
||||
|
|
|
High Ð DQx pins are high impedance. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
89 |
K |
Input |
Clock: This signal registers the address, data in, and all control signals |
||||
|
|
|
except G and LBO. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
LBO |
Input |
Linear Burst Order Input: This pin must remain in steady state (this |
||||
|
|
|
signal not registered or latched). It must be tied high or low. |
||||
|
|
|
Low Ð linear burst counter (68K/PowerPC). |
||||
|
|
|
High Ð interleaved burst counter (486/i960/Pentium). |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32, 33, 34, 35, 44, 45, 46, |
SA |
Input |
Synchronous Address Inputs: These inputs are registered and must |
||||
47, 48, 49, 50, 81, 82, 99, 100 |
|
|
meet setup and hold times. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36, 37 |
SA1, SA0 |
Input |
Synchronous Address Inputs: these pins must be wired to the two LSBs |
||||
|
|
|
of the address bus for proper burst operation. These inputs are |
||||
|
|
|
registered and must meet setup and hold times. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93, 94, 95, 96 |
SBx |
Input |
Synchronous Byte Write Inputs: ªxº refers to the byte being written (byte |
||||
(a) (b) (c) (d) |
|
|
a, b, c, d). SGW overrides SBx. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
98 |
SE1 |
Input |
Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low to enable chip. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
Negated high Ð blocks ADSP or deselects chip when ADSC is |
||||
|
|
|
asserted. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
97 |
SE2 |
Input |
Synchronous Chip Enable: Active high for depth expansion. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
92 |
SE3 |
Input |
Synchronous Chip Enable: Active low for depth expansion. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
88 |
SGW |
Input |
Synchronous Global Write: This signal writes all bytes regardless of the |
||||
|
|
|
status of the SBx and SW signals. If only byte write signals SBx are |
||||
|
|
|
being used, tie this pin high. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
87 |
SW |
Input |
Synchronous Write: This signal writes only those bytes that have been |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
selected using the byte write SBx pins. If only byte write signals SBx |
||||
|
|
|
are being used, tie this pin low. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||||
15, 41, 65, 91 |
VDD |
Supply |
Core Power Supply. |
||||
4, 11, 20, 27, 54, 61, 70, 77 |
VDDQ |
Supply |
I/O Power Supply. |
||||
5, 10, 17, 21, 26, 40, |
VSS |
Supply |
Ground. |
||||
55, 60, 67, 71, 76, 90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
14, 16, 38, 39, 42, 43, 64, 66 |
NC |
Ð |
No Connection: There is no connection to the chip. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM |
MCM69P737 |
|
5 |

TRUTH TABLE (See Notes 1 Through 5)
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
Write 2, 4 |
Next Cycle |
Used |
|
SE1 |
SE2 |
|
SE3 |
|
ADSP |
|
|
ADSC |
|
ADV |
|
|
G |
DQx |
|||||
Deselect |
None |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
X |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deselect |
None |
|
0 |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deselect |
None |
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
X |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
X |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deselect |
None |
|
X |
X |
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
X |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Deselect |
None |
|
X |
0 |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
X |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Begin Read |
External |
|
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
X5 |
|
Begin Read |
External |
|
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
READ5 |
||
Continue Read |
Next |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
High±Z |
READ |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Continue Read |
Next |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
DQ |
READ |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Continue Read |
Next |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
1 |
High±Z |
READ |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Continue Read |
Next |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
DQ |
READ |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Suspend Read |
Current |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
High±Z |
READ |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Suspend Read |
Current |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
DQ |
READ |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Suspend Read |
Current |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
High±Z |
READ |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Suspend Read |
Current |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
DQ |
READ |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Begin Write |
External |
|
0 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
WRITE |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Continue Write |
Next |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
WRITE |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Continue Write |
Next |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
WRITE |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Suspend Write |
Current |
|
X |
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
WRITE |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Suspend Write |
Current |
|
1 |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
X |
High±Z |
WRITE |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.X = Don't Care. 1 = logic high. 0 = logic low.
2.Write is defined as either 1) any SBx and SW low or 2) SGW is low.
3.G is an asynchronous signal and is not sampled by the clock K. G drives the bus immediately (tGLQX) following G going low.
4.On write cycles that follow read cycles, G must be negated prior to the start of the write cycle to ensure proper write data setup times. G must also remain negated at the completion of the write cycle to ensure proper write data hold times.
5.This read assumes the RAM was previously deselected.
LINEAR BURST ADDRESS TABLE (LBO = VSS)
1st Address (External) |
2nd Address (Internal) |
3rd Address (Internal) |
4th Address (Internal) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X00 |
X . |
. . X01 |
X . . . |
X10 |
X . . . |
X11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X01 |
X . |
. . X10 |
X . . . |
X11 |
X . . . |
X00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X10 |
X . |
. . X11 |
X . . . |
X00 |
X . . . |
X01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X11 |
X . |
. . X00 |
X . . . |
X01 |
X . . . |
X10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERLEAVED BURST ADDRESS TABLE (LBO = VDD)
1st Address (External) |
2nd Address (Internal) |
3rd Address (Internal) |
4th Address (Internal) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X00 |
X . . . |
X01 |
X . . . |
X10 |
X . . . |
X11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X01 |
X . . . |
X00 |
X . . . |
X11 |
X . . . |
X10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X10 |
X . . . |
X11 |
X . . . |
X00 |
X . . . |
X01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X . . . |
X11 |
X . . . |
X10 |
X . . . |
X01 |
X . . . |
X00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WRITE TRUTH TABLE
|
Cycle Type |
SGW |
SW |
SBa |
SBb |
SBc |
SBd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read |
H |
H |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read |
H |
L |
H |
H |
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Byte a |
H |
L |
L |
H |
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Byte b |
H |
L |
H |
L |
H |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Byte c |
H |
L |
H |
H |
L |
H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Byte d |
H |
L |
H |
H |
H |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write All Bytes |
H |
L |
L |
L |
L |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write All Bytes |
L |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MCM69P737 |
MOTOROLA FAST SRAM |
6 |
|
 Loading...
Loading...