Motorola MCR218-10, MCR218-8, MCR218-6, MCR218-3, MCR218-4 Datasheet
...
1
Motorola Thyristor Device Data
Thyristors
Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers
. . . designed primarily for half-wave ac control applications, such as motor controls,
heating controls and power supplies; or wherever half-wave silicon gate-controlled,
solid-state devices are needed.
• Glass-Passivated Junctions
• Blocking Voltage to 800 Volts
• TO-220 Construction — Low Thermal Resistance, High Heat Dissipation and
Durability
MAXIMUM RATINGS
(T
J
= 25°C unless otherwise noted.)
Rating
Symbol Value Unit
Peak Repetitive Forward and Reverse Voltage
(1)
(T
J
= 25 to 125°C, Gate Open) MCR218-2
MCR218-3
MCR218-4
MCR218-6
MCR218-8
MCR218-10
V
DRM
V
RRM
50
100
200
400
600
800
Volts
Forward Current RMS
(All Conduction Angles)
I
T(RMS)
8 Amps
Peak Forward Surge Current
(1/2 Cycle, Sine Wave, 60 Hz)
I
TSM
80 Amps
Circuit Fusing Considerations
(t = 8.3 ms)
I
2
t 26 A
2
s
Forward Peak Gate Power P
GM
5 Watts
Forward Average Gate Power P
G(AV)
0.5 Watt
Forward Peak Gate Current I
GM
2 Amps
Operating Junction Temperature Range T
J
–40 to +125 °C
Storage Temperature Range T
stg
–40 to +150 °C
1. V
DRM
and V
RRM
for all types can be applied on a continuous basis. Ratings apply for zero or negative gate voltage; however, positive gate
voltage shall not be applied concurrent with negative potential on the anode. Blocking voltages shall not be tested with a constant current
source such that the voltage ratings of the devices are exceeded.
Order this document
by MCR218/D
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Motorola, Inc. 1995
MCR218
Series
CASE 221A-04
(TO-220AB)
STYLE 3
SCRs
8 AMPERES RMS
50 thru 800 VOLTS
K
G
A
2 Motorola Thyristor Device Data
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Characteristic Symbol Max Unit
Thermal Resistance, Junction to Case R
θJC
2 °C/W
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (T
J
= 25°C unless otherwise noted.)
Characteristic
Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Peak Forward or Reverse Blocking Current
(V
AK
= Rated V
DRM
or V
RRM
, Gate Open) T
J
= 25°C
T
J
= 125°C
I
DRM
, I
RRM
—
—
—
—
10
2
µA
mA
Peak On-State Voltage
(1)
(I
TM
= 16 A Peak)
V
TM
— 1.5 1.8 Volts
Gate Trigger Current (Continuous dc)
(V
D
= 12 V, R
L
= 100 Ohms)
I
GT
— 10 25 mA
Gate Trigger Voltage (Continuous dc)
(V
D
= 12 V, R
L
= 100 Ohms)
(Rated V
DRM
, R
L
= 1000 Ohms, T
J
= 125°C)
V
GT
—
0.2
—
—
1.5
—
Volts
Holding Current
(Anode Voltage = 24 Vdc, Peak Initiating On-State Current = 0.5 A,
0.1 to 10 ms Pulse, Gate Trigger Source = 7 V, 20 Ohms)
I
H
— 16 30 mA
Critical Rate-of-Rise of Off-State Voltage
(V
D
= Rated V
DRM
, Exponential Waveform, Gate Open, T
J
= 125°C)
dv/dt — 100 — V/µs
1. Pulse Test: Pulse Width = 1 ms, Duty Cycle
p
2%.
60
°
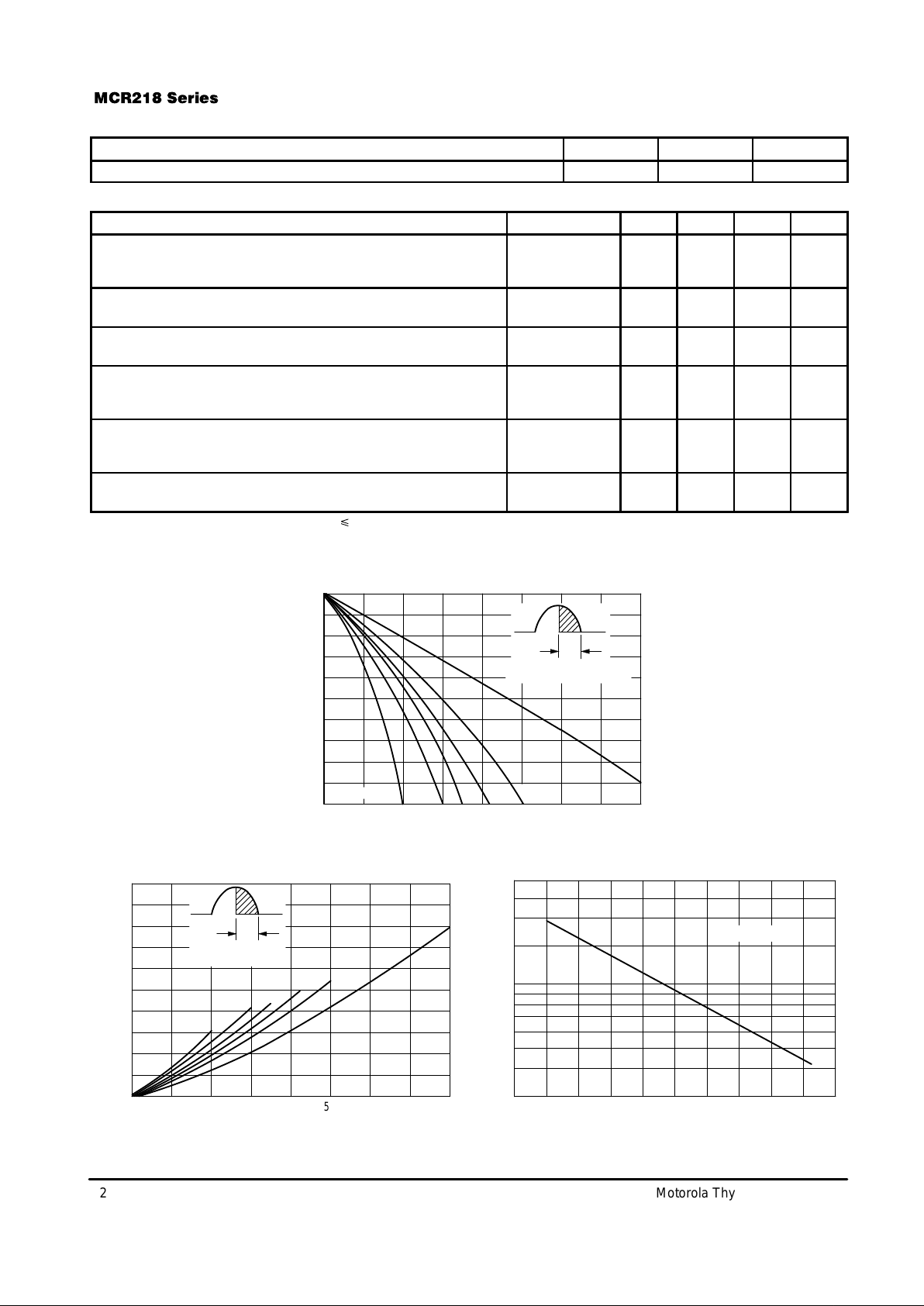
7.06.05.04.03.02.01.0 8.0
3.0
6.0
9.0
α
= Conduction Angle
12
15
0.4
0.5
0.7
0.9
1.0
1.5
2.0
40
3.0
1401201008060–40 0 20–20
I
T(AV)
, AVERAGE ON-STATE FORWARD CURRENT (AMPS)
α
= CONDUCTION ANGLE
87654321
85
95
75
105
115
0
α
α
= 30
°
60
°
I
T(AV)
, AVG. ON-STATE CURRENT (AMPS)
FIGURE 2 — ON-STATE POWER DISSIPATION
0
90
°
120
°
180
°
dc
T
J
, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (
°
C)
FIGURE 3 — NORMALIZED GATE TRIGGER CURRENT
0.3
–60
V
D
= 12 Vdc
FIGURE 1 — CURRENT DERATING
0
dc
α
= 30
°
α
120
°
90
°
125
T , MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE CASE TEMPERATURE ( C)
C
°
P , AVERAGE ON-STATE POWER DISSIPATION
(AV)
(WATTS)
I , NORMALIZED GATE TRIGGER CURRENT (mA)
GT
180
°
 Loading...
Loading...