Motorola MMQA18VT1, MMQA13VT1, MMQA13VT3, MMQA15VT1, MMQA12VT1 Datasheet
...
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document by MMQA/D
SC 59 Quad Monolithic Common Anode
Transient Voltage Suppressor for ESD Protection
This quad monolithic silicon voltage suppressor is designed for applications requiring transient overvoltage protection capability. It is intended for use in voltage and ESD sensitive equipment such as computers, printers, business machines, communication systems, medical equipment, and other applications. Its quad junction common anode design protects four separate lines using only one package. These devices are ideal for situations where board space is at a premium.
Specification Features:
•SC-59 Package Allows Four Separate Unidirectional Configurations
•Peak Power Ð Min. 24 W @ 1.0 ms (Unidirectional), per Figure 5 Waveform
•Peak Power Ð Min. 150 W @ 20 ms (Unidirectional), per Figure 6 Waveform
•Maximum Clamping Voltage @ Peak Pulse Current
•Low Leakage < 2.0 μA
•ESD Rating of Class N (exceeding 16 kV) per the Human Body Model
Mechanical Characteristics:
•Void Free, Transfer-Molded, Thermosetting Plastic Case
•Corrosion Resistant Finish, Easily Solderable
•Package Designed for Optimal Automated Board Assembly
•Small Package Size for High Density Applications
•Available in 8 mm Tape and Reel
Use the Device Number to order the 7 inch/3,000 unit reel. Replace with ªT3º in the Device Number to order the 13 inch/10,000 unit reel.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
MMQA Series
Motorola Preferred Devices
SC-59 QUAD
TRANSIENT VOLTAGE
SUPPRESSOR
24 WATTS PEAK POWER
5.6 ± 33 VOLTS
6 5 

 4
4
1 2 

 3
3
CASE 318F-01
STYLE 1
SC-59 PLASTIC
1  6
6
2  5
5
3  4
4
PIN 1. CATHODE
2.ANODE
3.CATHODE
4.CATHODE
5.ANODE
6.CATHODE
Characteristic |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
Peak Power Dissipation @ 1.0 ms (1) @ TA ≤ 25°C |
Ppk |
24 |
Watts |
Peak Power Dissipation @ 20 ms (2) @ TA ≤ 25°C |
Ppk |
150 |
Watts |
Total Power Dissipation on FR-5 Board (3) @ TA = 25°C |
PD |
225 |
mW |
|
|
1.8 |
mW/°C |
|
|
|
|
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Ambient |
RθJA |
556 |
°C/W |
Total Power Dissipation on Alumina Substrate (4) @ TA = 25°C |
PD |
300 |
mW |
Derate above 25°C |
|
2.4 |
mW/°C |
|
|
|
|
Thermal Resistance from Junction to Ambient |
RθJA |
417 |
°C/W |
Junction and Storage Temperature Range |
TJ, Tstg |
± 55 to +150 |
°C |
Lead Solder Temperature Ð Maximum (10 Second Duration) |
TL |
260 |
°C |
1.Non-repetitive current pulse per Figure 5 and derate above TA = 25°C per Figure 4.
2.Non-repetitive current pulse per Figure 6 and derate above TA = 25°C per Figure 4.
3.FR-5 = 1.0 x 0.75 x 0.62 in.
4.Alumina = 0.4 x 0.3 x 0.024 in., 99.5% alumina
Preferred devices are Motorola recommended choices for future use and best overall value.
Thermal Clad is a trademark of the Bergquist Company
Motorola, Inc. 1996
MMQA Series
1
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
UNIDIRECTIONAL (Circuit tied to pins 1, 2, and 5; Pins 2, 3, and 5; Pins 2, 4, and 5; or Pins 2, 5, and 6) (VF = 0.9 V Max @ IF = 10 mA)
|
|
Breakdown Voltage |
|
Max Reverse |
Max Zener |
Max Reverse |
Max Reverse |
Maximum |
|||
|
|
|
Leakage Current |
Voltage @ |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Impedance (7) |
Surge |
IRSM(6) |
|
|
|
|
VZT (5) |
|
|
|
|
Coefficient of |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
(Clamping |
||
|
|
|
|
|
IR |
VR |
|
VZ |
|||
|
|
|
(V) |
|
@ IZT |
|
|
Voltage) |
|||
Device |
Min |
|
Nom |
Max |
(mA) |
(nA) |
(V) |
ZZT @ IZT |
IRSM(4) |
VRSM |
(mV/°C) |
|
(Ω) (mA) |
(A) |
(V) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA5V6T1,T3 |
5.32 |
|
5.6 |
5.88 |
1.0 |
2000 |
3.0 |
400 |
3.0 |
8.0 |
1.26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA6V2T1,T3 |
5.89 |
|
6.2 |
6.51 |
1.0 |
700 |
4.0 |
300 |
2.66 |
9.0 |
10.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA6V8T1,T3 |
6.46 |
|
6.8 |
7.14 |
1.0 |
500 |
4.3 |
300 |
2.45 |
9.8 |
10.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA12VT1,T3 |
11.4 |
|
12 |
12.6 |
1.0 |
75 |
9.1 |
80 |
1.39 |
17.3 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA13VT1,T3 |
12.4 |
|
13 |
13.7 |
1.0 |
75 |
9.8 |
80 |
1.29 |
18.6 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA15VT1,T3 |
14.3 |
|
15 |
15.8 |
1.0 |
75 |
11 |
80 |
1.1 |
21.7 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA18VT1,T3 |
17.1 |
|
18 |
18.9 |
1.0 |
75 |
14 |
80 |
0.923 |
26 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA20VT1,T3 |
19 |
|
20 |
21 |
1.0 |
75 |
15 |
80 |
0.84 |
28.6 |
20.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA21VT1,T3 |
20 |
|
21 |
22.1 |
1.0 |
75 |
16 |
80 |
0.792 |
30.3 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA22VT1,T3 |
20.9 |
|
22 |
23.1 |
1.0 |
75 |
17 |
80 |
0.758 |
31.7 |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA24VT1,T3 |
22.8 |
|
24 |
25.2 |
1.0 |
75 |
18 |
100 |
0.694 |
34.6 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA27VT1,T3 |
25.7 |
|
27 |
28.4 |
1.0 |
75 |
21 |
125 |
0.615 |
39 |
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA30VT1,T3 |
28.5 |
|
30 |
31.5 |
1.0 |
75 |
23 |
150 |
0.554 |
43.3 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMQA33VT1,T3 |
31.4 |
|
33 |
34.7 |
1.0 |
75 |
25 |
200 |
0.504 |
48.6 |
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(5)VZ measured at pulse test current IT at an ambient temperature of 25°C.
(6)Surge current waveform per Figure 5 and derate per Figure 4.
(7)ZZT is measured by dividing the AC voltage drop across the device by the AC current supplied. The specified limits are IZ(AC) = 0.1 IZ(DC), with AC frequency = 1 kHz.
NOTE: SPECS LISTED ABOVE ARE PRELIMINARY
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
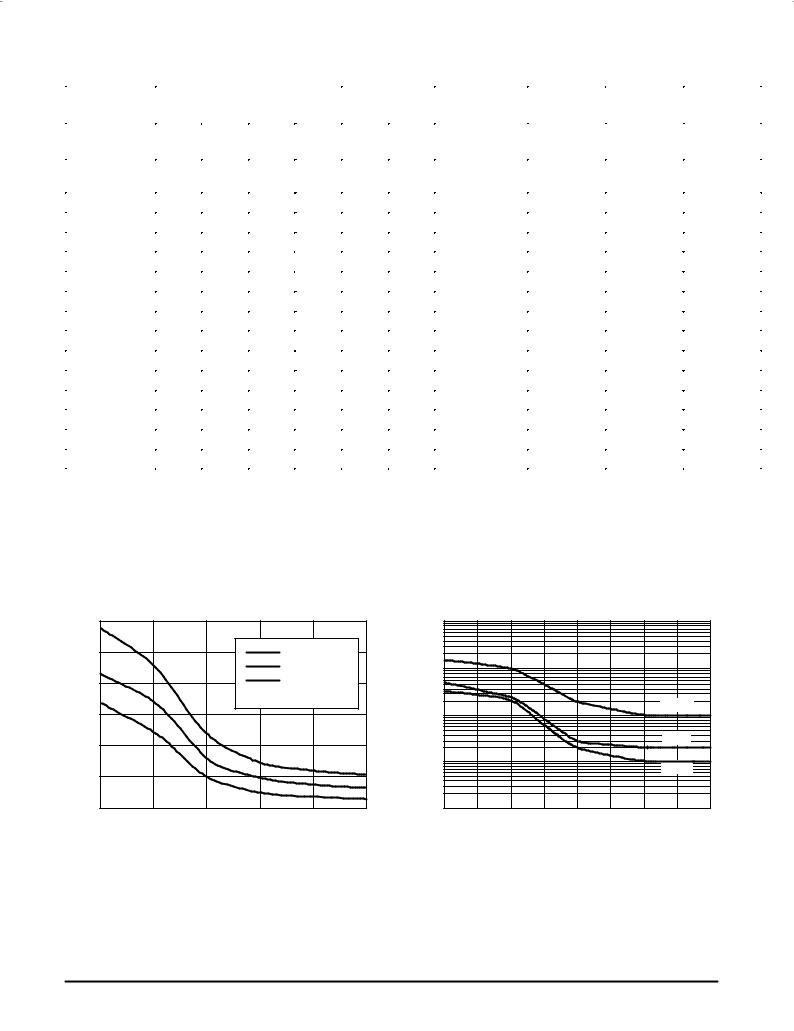
C, CAPACITANCE (pF)
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
BIASED AT 0 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BIASED AT 1 V |
|
|
1,000 |
|
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
BIASED AT 50% |
|
(nA) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OF VZ NOM |
|
|
|
|
|
+25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LEAKAGE, |
|
|
|
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
+150°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C |
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
5.6 |
6.8 |
12 |
20 |
27 |
33 |
|
5.6 |
6.8 |
20 |
27 |
33 |
VZ, NOMINAL ZENER VOLTAGE (V) |
VZ, NOMINAL ZENER VOLTAGE (V) |
Figure 1. Typical Capacitance |
Figure 2. Typical Leakage Current |
MOTOROLA |
MMQA Series |
2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DERATING IN % OF PEAK POWER |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
POWER DISSIPATION (mW) |
250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALUMINA SUBSTRATE |
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
° |
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT @ T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
FR-5 BOARD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PULSE |
OR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PEAK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
150 |
175 |
|
0 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
150 |
175 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
T , AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C) |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
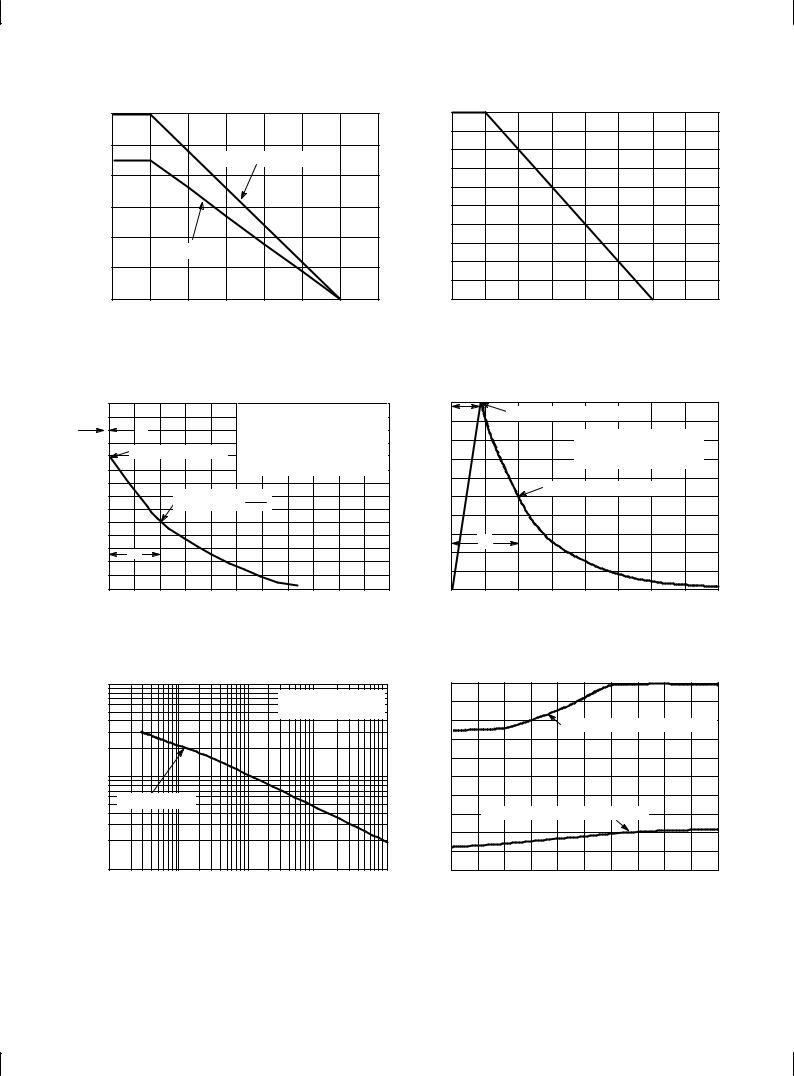
Figure 3. Steady State Power Derating Curve |
Figure 4. Pulse Derating Curve |
|
|
|
|
PULSE WIDTH (tP) IS DEFINED |
|
100 |
PEAK VALUE I |
|
@ 8 ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
RSM |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
AS THAT POINT WHERE THE |
|
r |
|
|
|
|
||
|
tr |
|
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
PEAK CURRENT DECAYS TO 50% |
CURRENTPULSEPEAK |
80 |
|
PULSE WIDTH (tP) IS DEFINED |
|
||||
(%)VALUE |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
PEAK VALUE Ð I RSM |
|
OF IRSM. |
|
|
|
AS THAT POINT WHERE THE |
|
|||||
100 |
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
tr ≤ 10 ms |
|
|
|
PEAK CURRENT DECAY = 8 ms |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
HALF VALUE IRSM/2 @ 20 ms |
|
|||
|
|
HALF VALUE Ð |
IRSM |
|
|
50 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tP |
|
|
|
|
OF% |
30 |
tP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
3 |
4 |
|
0 |
20 |
40 |
60 |
80 |
|
0 |
|
|
0 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
t, TIME (ms) |
|
|
|
|
t, TIME (ms) |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Figure 5. 10 × 1000 ms Pulse Waveform |
|
|
||
100 |
|
|
RECTANGULAR |
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
180 |
|
|
|
|
WAVEFORM, TA = 25°C |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
, PEAK SURGE POWER (W) |
160 |
|
|
|
|
140 |
|
|
|
|
|
120 |
|
10 |
|
|
|
100 |
|
PEAKPOWERSURGE(W) |
UNIDIRECTIONAL |
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
60 |
||
|
|
|
|
||
Ppk |
|
|
|
PK |
40 |
|
|
|
P |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
10 |
100 |
1000 |
0 |
0.1 |
|
||||
PW, PULSE WIDTH (ms)
|
Figure 6. 8 × 20 ms Pulse Waveform |
|
|||
|
|
|
8 ×20 WAVEFORM AS PER FIGURE 6 |
||
|
10 ×100 WAVEFORM AS PER FIGURE 5 |
|
|
||
5.6 |
6.8 |
12 |
20 |
27 |
33 |
|
|
|
NOMINAL VZ |
|
|
Figure 7. Maximum Non±Repetitive Surge |
Figure 8. Typical Maximum Non±Repetitive |
Power, Ppk versus PW |
Surge Power, Ppk versus VBR |
Power is defined as VRSM x IZ(pk) where VRSM |
|
is the clamping voltage at IZ(pk). |
|
|
|
MMQA Series |
MOTOROLA |
|
3
 Loading...
Loading...