Motorola MC74F161AD, MC74F161AN, MC74F163AN, MC54F163AJ, MC54F161AJ Datasheet
...
SYNCHRONOUS PRESETTABLE BINARY COUNTER
The MC74F161A and MC74F163A are high-speed synchronous modu- lo-16 binary counters. They are synchronously presettable for application in programmable dividers and have two types of Count Enable inputs plus a Terminal Count output for versatility in forming synchronous multistage counters. The MC74F161A has an asynchronous Master Reset input that overrides all other inputs and forces the outputs LOW. The MC74F163A has a Synchronous Reset input that overrides counting and parallel loading and allows the outputs to be simultaneously reset on the rising edge of the clock.
•Synchronous Counting and Loading
•High-Speed Synchronous Expansion
•Typical Count Frequency of 120 MHz
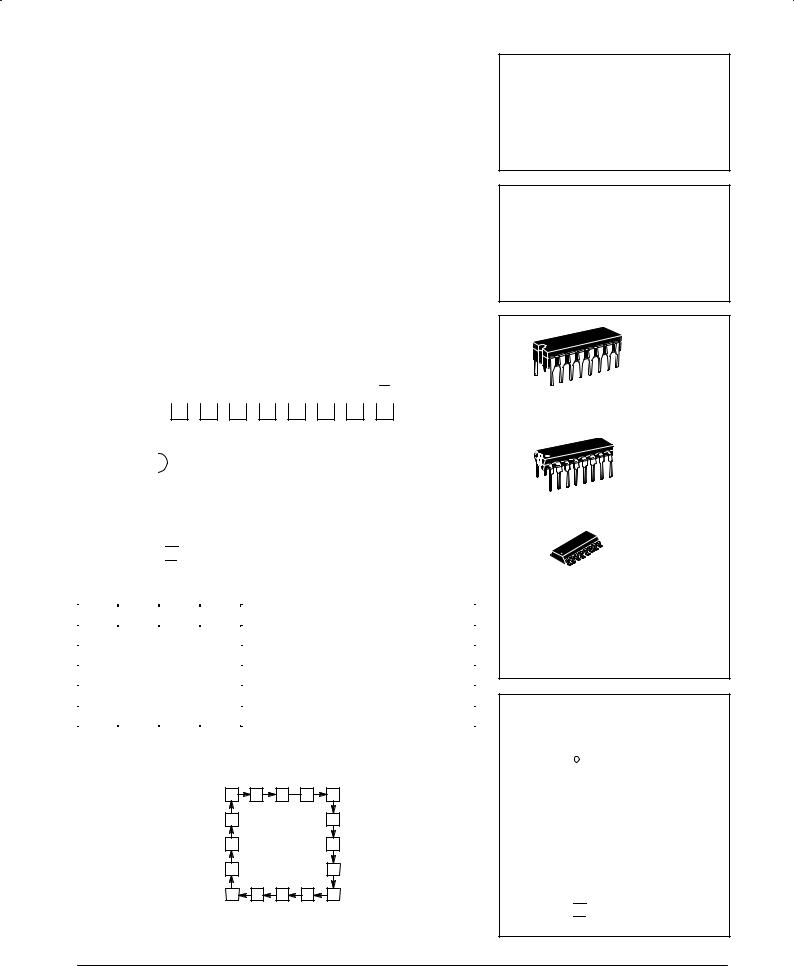
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
VCC |
TC |
|
Q0 |
|
Q1 |
|
Q2 |
|
Q3 |
|
CET |
|
PE |
|
16 |
|
15 |
|
14 |
|
13 |
|
12 |
|
11 |
|
10 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
*R |
CP |
|
P0 |
|
P1 |
|
P2 |
|
P3 |
CEP |
GND |
||||||
*MR for MC74F161A *SR for MC74F163A
FUNCTION TABLE
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SR |
PE |
CET |
CEP |
ACTION ON THE RISING CLOCK EDGE ( |
|
|
) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
L |
|
X |
X |
X |
Reset (Clear) |
||||
|
H |
|
L |
X |
X |
Load (Pn ≡ Qn) |
||||
|
H |
|
H |
H |
H |
Count (Increment) |
||||
|
H |
|
H |
L |
X |
No Change (Hold) |
||||
|
H |
|
H |
X |
L |
No Change (Hold) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H = HIGH Voltage Level; L = LOW Voltage Level; X = Don't Care
STATE DIAGRAM
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
15 |
|
|
|
5 |
14 |
|
|
|
6 |
13 |
|
|
|
7 |
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
MC74F161A
MC74F163A
SYNCHRONOUS PRESETTABLE
BINARY COUNTER
FAST SHOTTKY TTL
|
|
|
J SUFFIX |
|
|
|
CERAMIC |
|
|
|
CASE 620-09 |
16 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N SUFFIX |
|
|
|
PLASTIC |
16 |
|
|
CASE 648-08 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
D SUFFIX |
|
16 |
|
SOIC |
|
|
CASE 751B-03 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
ORDERING INFORMATION
MC74FXXXAJ Ceramic
MC74FXXXAN Plastic
MC74FXXXAD SOIC
LOGIC SYMBOL
|
|
9 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
PE |
P0 |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
|
|
|||||
|
CEP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
||
10 |
|
CET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TC |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
2 |
|
CP*R Q0 Q1 Q2 |
Q3 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
14 |
13 |
12 |
11 |
|
|
|||||
VCC = PIN 16
GND = PIN 8
*MR for MC74F161A *SR for MC74F163A
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
4-75
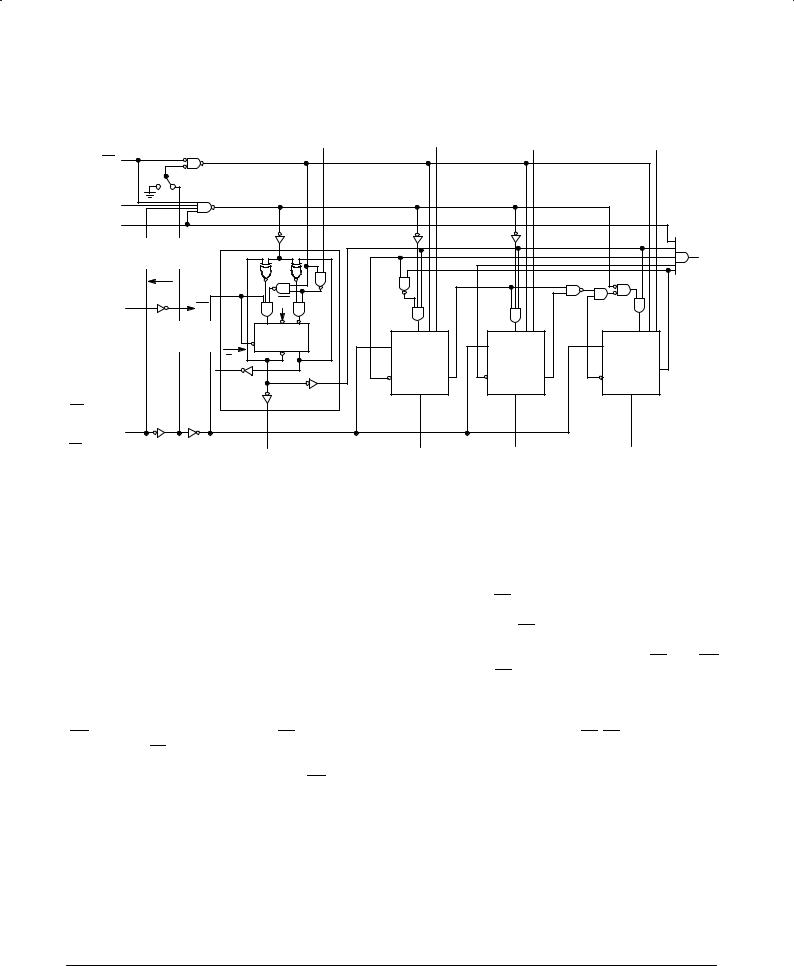
MC74F161A •MC74F163A
LOGIC DIAGRAM
|
|
|
|
P0 |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
PE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MC74F161A |
MC74F163A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CEP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MC74F163A |
|
|
|
|
|
TC |
|
ONLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CP |
CP |
|
CP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
MC74F161A |
D |
CP |
D |
|
|
|
|
ONLY |
CD |
Q |
Q |
|
|
|
|
Q0 |
|
|
Q0 |
DETAIL A |
DETAIL A |
DETAIL A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MR (MC74F161A) |
|
|
DETAIL A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SR (MC74F163A)
Q0 |
Q1 |
Q2 |
Q3 |
NOTE:
This diagram is provided only for the understanding of logic operations and should not be used to estimate propagation delays.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The MC74F161A and MC74F163A count in modulo-16 binary sequence. From state 15 (HHHH) they increment to state 0 (LLLL). The clock inputs of all flip-flops are driven in parallel through a clock buffer. Thus all changes of the Q outputs (except due to Master Reset of the MC74F161A) occur as a result of, and synchronous with, the LOW-to-HIGH transition of the CP input signal. The circuits have four fundamental modes of operation, in order of precedence: asynchronous reset (MC74F161A), synchronous reset (MC74F163A), parallel load, count-up and hold. Five control inputs Master Reset
(MR, MC74F161A), Synchronous Reset (SR, MC74F163A), Parallel Enable (PE), Count Enable Parallel (CEP) and Count Enable Trickle (CET) Ð determine the mode of operation, as shown in the Function Table. A LOW signal on MR overrides
all other inputs and asynchronously forces all outputs LOW. A
LOW signal on SR overrides counting and parallel loading and allows all outputs to go LOW on the next rising edge of CP. A LOW signal on PE overrides counting and allows information on the Parallel Data (Pn) inputs to be loaded into the flip-flops on the next rising edge of CP. With PE and MR
(MC74F161A) or SR (MC74F163A) HIGH, CEP and CET permit counting when both are HIGH. Conversely, a LOW signal on either CEP or CET inhibits counting.
The MC74F161A and MC74F163A use D-type edge-trig- gered flip-flops and changing the SR, PE, CEP, and CET inputs when the CP is in either state does not cause errors, provided that the recommended setup and hold times, with respect to the rising edge of CP, are observed.
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
4-76
 Loading...
Loading...