Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk Metrics User Manual

USER GUIDE
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
Supersedes Publication PLTMT-UM001L-EN-P-June 2013

Contacting Rockwell
Copyright Notice
Trademark Notices
Other Trademarks
Warranty
Customer Support Telephone — 1.440.646.3434
Online Support — http://www.rockwellautomation.com/support/overview.page
© 2014 Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
This document and any accompanying Rockwell Software products are copyrighted by Rockwell Automation,
Inc. Any reproduction and/or distribution without prior written consent from Rockwell Automation, Inc. is
strictly prohibited. Please refer to the license agreement for details.
FactoryTalk, FactoryTalk Activation, FactoryTalk Diagnostics, FactoryTalk Directory, FactoryTalk Live Data,
FactoryTalk Metrics, FactoryTalk Services Platform, FactoryTalk Transaction Manager, FactoryTalk
VantagePoint, FactoryTalk ProductionCentre, Report Expert, Rockwell, Rockwell Automation, Rockwell
Software, and RSBizWare are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Any Rockwell Automation logo, software or hardware not mentioned herein is also a trademark, registered or
otherwise, of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
For a complete list of products and their respective trademarks, go to
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/rockwellautomation/legal-notices/overview.page?%23tab4#/tab4.
ActiveX, Microsoft, Microsoft Access, SQL Server, Visual Basic, Visual C++, Visual SourceSafe, Windows,
Windows ME, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows Server, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and
Windows 8 are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries.
Adobe, Acrobat, and Reader are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in
the United States and/or other countries.
ControlNet is a registered trademark of ControlNet International.
DeviceNet is a trademark of the Open DeviceNet Vendor Association, Inc. (ODVA)
OLE for Process Control (OPC) is a registered trademark of the OPC Foundation.
Oracle, SQL*Net, and SQL*Plus are registered trademarks of Oracle Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective holders and are hereby acknowledged.
This product is warranted in accordance with the product license. The product’s performance may be affected
by system configuration, the application being performed, operator control, maintenance, and other related
factors. Rockwell Automation is not responsible for these intervening factors. The instructions in this
document do not cover all the details or variations in the equipment, procedure, or process described, nor do
they provide directions for meeting every possible contingency during installation, operation, or
maintenance. This product’s implementation may vary among users.
This document is current as of the time of release of the product; however, the accompanying software may
have changed since the release. Rockwell Automation, Inc. reserves the right to change any information
contained in this document or the software at any time without prior notice. It is your responsibility to obtain
the most current information available from Rockwell when installing or using this product.

Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics
Getting Started
Collecting Performance Data
Table of Contents
Chapter 1
What Is FactoryTalk Metrics? ................................................................... 9
Features and Benefits .................................................................................. 10
Intended Audience ...................................................................................... 10
Where Can I Go for Help? ....................................................................... 12
Get Web Support ................................................................................... 12
Get Phone Support ................................................................................ 13
Get Consulting Services ....................................................................... 13
Contact Us .............................................................................................. 13
Chapter 2
The RSBizWare Architecture .................................................................. 15
Importing Sample Data to the RSBizWare Database......................... 16
Connecting to the Information Services Manager .............................. 17
Using the Information Services Manager in Internet Explorer .. 17
Using the Information Services Manager in the Configuration
Console ..................................................................................................... 18
Getting Started with the Configuration Console .......................... 19
The Plant Model .......................................................................................... 20
Configuring the Plant Model .............................................................. 21
Loading Sample Activity Areas ........................................................... 23
Chapter 3
Collecting Part Count Data When the Metrics Server Manager Is
Stopped .......................................................................................................... 25
OEE Rating ................................................................................................... 27
Fault Metrics Ratings ................................................................................. 28
Mean Time Between Failure ............................................................... 28
Mean Time To Repair .......................................................................... 29
Configuring Activity Area Schedules ..................................................... 29
Time Patterns ......................................................................................... 29
Configuring Time Patterns ............................................................ 30
Configuring Work Day Time Patterns ....................................... 34
Configuring Work Week Time Patterns .................................... 36
Composites and Schedule Exceptions ............................................... 38
Configuring Composites and Schedule Exceptions ................. 39
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 3
Table of Contents
Configuring OEE Performance Parameters For Activity Areas ...... 41
Configuring Data Collection .............................................................. 44
Configuring Cycle Time ...................................................................... 44
Configuring a Part ID/Cycle Time Lookup List ...................... 47
Configuring Part Id ............................................................................... 50
Configuring Summarization Criteria ............................................... 52
Configuring Part Count ....................................................................... 55
Configuring Part Count Using an Unscheduled Data Point 58
Configuring Part Count Using an Unscheduled Data Point
and a FTTM Expression ................................................................. 58
Configuring Part Count Using a FTTM Expression On a
Scheduled Basis ................................................................................. 59
Configuring a Formula .................................................................... 60
Availability ............................................................................................... 63
Configuring Scheduled Availability ............................................. 65
Configuring Monitored Availability ............................................ 73
Configuring Running State ............................................................ 78
Generating Performance Parameter Events ..................................... 81
Viewing Performance Parameter Events for an Activity Area .......... 81
System-generated Events ...................................................................... 83
User-defined Events .............................................................................. 85
Manual Events ........................................................................................ 88
The Recycle Bin ...................................................................................... 89
Configuring User-defined Performance Parameter Events .............. 90
Configuring the Event Data Summary ............................................. 90
Event Data Summarization Types ................................................ 92
Configuring the Event Trigger ........................................................... 93
Event Trigger Types ......................................................................... 96
Configuring the Event Value .............................................................. 99
Event Value Types ......................................................................... 101
Using the Expression Editor ....................................................... 104
Creating Event Value Reason Code Lookup Lists ................ 109
Configuring the Machine State / Faults ........................................ 111
Configuring the Reporting ............................................................... 113
Advanced Properties ................................................................................ 115
Scheduled Part Count Collection Parameters ............................. 115
4 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
Table of Contents
Automated Configuration
System-generated Event Data Summarization ............................. 116
Availability Interpretation Options ............................................... 117
Performance Data Trending Rate ................................................... 118
Machine States .......................................................................................... 118
Machine States at the Sample Enterprise ...................................... 120
Prioritizing Machine States .............................................................. 122
Configuring Machine States ............................................................. 123
Mapping Machine States to User-defined Events ....................... 125
Determining Availability and Running State From Machine State
.................................................................................................... 126
Configuring FactoryTalk Metrics to Perform Downtime Tracking ...
126
Running Versus Downtime .............................................................. 128
User-defined Downtime Events ...................................................... 129
Machine State ...................................................................................... 130
Reviewing the Status of Performance Parameters Events ............... 131
Start Data Collection .............................................................................. 133
Stop Data Collection ............................................................................... 134
Manual Data Collection ......................................................................... 134
Chapter 4
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 5
FactoryTalk Metrics UDT ..................................................................... 139
UDT Tags and FactoryTalk Metrics Performance Parameters 140
Setting up Communication Between a ControlLogix Controller and
FactoryTalk Metrics ................................................................................ 143
Configuring RSLinx Enterprise ....................................................... 144
Importing the FactoryTalk Metrics UDT to the ControlLogix
Controller ............................................................................................. 148
Creating Tags Based on the FactoryTalk Metrics UDT ........... 150
Creating FactoryTalk Transaction Manager and FactoryTalk
Metrics Configurations ..................................................................... 154
Configuration Types ..................................................................... 154
Configuration Flow ...................................................................... 154
Guidelines for Modifying Imported Performance Parameters 168
Table of Contents
Analyzing FactoryTalk Metrics
Data
Chapter 5
Create a New RSBizWare Report ........................................................ 171
Insert Text, Pictures, and Hyperlinks .................................................. 172
Save the Report ......................................................................................... 174
Move the Report and Set Report Permissions ................................... 175
Add a Saved Report Object to the Report .......................................... 177
Adjust the Time Range For a Time-based Report Object ........ 180
Configure the Report Object To Use Global Credentials ............. 182
Create a New Chart ................................................................................. 185
Step 1: Plan the Chart ........................................................................ 186
Step 2: Select the Data On Which To Report ............................. 187
Step 3: Choose a Chart Type ........................................................... 187
Step 4: Describe the Data .................................................................. 187
Step 5: Select Summary or Detail .................................................... 188
Step 6: Select the Fields To Be Charted ........................................ 189
Step 7: Enter the Chart Title ........................................................... 190
Step 8: Filter the Data ........................................................................ 190
Step 9: Insert Your New Chart Into the Report ......................... 193
Create a New Text Report Object ....................................................... 194
Step 1: Start the Text Report Object Wizard .............................. 194
Step 2: Select the Data On Which To Report ............................. 194
Step 3: Group the Records ................................................................ 195
Step 4: Sort the Records .................................................................... 196
Step 5: Format the Table ................................................................... 197
Step 6: Name the Report Object ..................................................... 199
Step 7: Filter the Data ........................................................................ 199
Step 8: Insert Your New Table Into the Report .......................... 199
Create an OEE Box Chart...................................................................... 200
Step 1: Add a Chart to the Report .................................................. 200
Step 2: Select an Activity Area ......................................................... 201
Step 3: Specify the Layout of the Chart ......................................... 202
Step 4: Create a Filter ......................................................................... 203
Step 5: Customize the OEE Bar Colors ........................................ 205
Step 6: Preview Your OEE Box Chart ........................................... 207
Create a FactoryTalk Metrics Detail Chart ....................................... 207
Export the Report to HTML ................................................................ 210
6 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
Table of Contents
Customizing RSBizWare Charts
and Tables
Advanced Reporting Topics
Load the Report From File ..................................................................... 211
Chapter 6
Customizing Charts ................................................................................ 213
Working With the Component Parts of a Chart ....................... 214
Resizing a Component ................................................................. 215
Moving a Component .................................................................. 215
Deleting a Component ................................................................. 215
Editing the Chart Title or Text Field ....................................... 215
Changing Chart Component Properties ................................. 216
Working With Chart “Pens” ........................................................... 216
Customizing Text Report Objects ....................................................... 217
Show and Hide Columns .................................................................. 217
Resize Table Columns ....................................................................... 218
Aggregate, Group, Format, Sort, Chart, and Rename Columns .....
.................................................................................................... 218
Aggregate ......................................................................................... 220
Group ............................................................................................ 220
Format ............................................................................................ 220
Sort ............................................................................................ 221
Chart ............................................................................................ 221
Rename ............................................................................................ 221
Quick Filter .......................................................................................... 221
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 7
Chapter 7
The Excel Add-in ..................................................................................... 223
Scheduling Report Objects and Reports ............................................. 227
Schedule a Report Object .................................................................. 228
Schedule a Report ............................................................................... 231
View the History of the Scheduled Task ....................................... 235
Analyzing Non-RSBizWare Data ........................................................ 236
Create an External Data Source....................................................... 236
Report Data Sources ........................................................................... 237
Step 1: Start the Report Data Source Wizard ......................... 237
User-derived Fields .................................................................................. 241
Create Detailed Derived Fields ........................................................ 243
Create Summary Derived Fields ...................................................... 247
Table of Contents
FactoryTalk Metrics Icon
Definitions
Object Permissions
Report Data Sources
Configuring Reports ................................................................................ 250
Chapter 8
Plant Model Element State Icons ......................................................... 253
Performance Parameter Event State Icons ......................................... 254
Chapter 9
Filter permissions ..................................................................................... 258
Report permissions ................................................................................... 258
Report data source permissions ............................................................. 259
Report object permissions ...................................................................... 259
Appendix A
Workcell History ...................................................................................... 261
Event History ............................................................................................ 263
Machine State Data.................................................................................. 264
8 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014

What Is FactoryTalk Metrics?
Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics
In this chapter you will learn about the following:
• What Is FactoryTalk Metrics? (page 9)
• Features and Benefits (page 10)
Chapter 1
• Intended Audience (page 10)
• Where Can I Go for Help? (page 12)
Companies in the discrete and repetitive manufacturing industries
are being challenged by management to maximize production from
existing lines, to meet required cycle times and delivery dates for
each product, and to reduce costs. To meet this challenge,
production management is striving to operate the equipment at its
highest efficiency.
Real-time identification of production assets that fail to reach the
required standard is critical to maintaining world-class efficiency. A
thorough understanding of the details behind production
performance will allow you to identify sources of production
inefficiencies, and to maximize asset utilization.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 9
The RSBizWare software is a suite of tools and services aimed at
increasing your manufacturing floor effectiveness and profitability
with solutions that target performance analysis and improvement,
and with data acquisition and integration. FactoryTalk Metrics is
just one of the applications that are available within the RSBizWare
software. FactoryTalk Metrics builds on the report, analysis, and
management capabilities of the RSBizWare software by providing a
Chapter 1 Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics
Features and Benefits
Intended Audience
powerful, yet simple set of tools to analyze the performance of
production assets.
FactoryTalk Metrics provides ratings - Overall Equipment
Effectiveness (OEE), Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF), and
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) - that allow you to evaluate the
performance of your production assets. A production asset (or
activity area) can be anything from a single piece of equipment to a
complete manufacturing plant. These ratings provide a simple way
to determine quickly whether a production asset is performing
adequately, based on data collected from the control system.
FactoryTalk Metrics offers the following features and benefits:
• Rich reporting, graphing, analyzing, and querying
functionality providing a complete and easy-to-use solution for
performance analysis.
• High-level analysis tools to easily identify poorly performing
assets, including the ability to drill into the underlying detail to
identify the causes of production inefficiencies.
• The ability to evaluate every production asset based on OEE,
MTBF, and MTTR ratings.
• The ability to isolate each asset so that its rating is not affected
by upstream or downstream performance.
• The ability to connect most of the OEE parameters to either a
data point or a formula, providing flexibility in the
configuration of the OEE rating.
• The ability to embed a report object in any Microsoft ActiveX
container, such as Visual Basic or Internet Explorer.
10 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
The FactoryTalk Metrics User Guide is designed to help you
understand how to access and use the FactoryTalk Metrics product.
This document focuses on the end-user functions of FactoryTalk

Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics Chapter 1
Metrics and does not cover the installation and operation of
underlying system services.
This document is intended for the following types of users of the
RSBizWare software:
• RSBizWare administrators
RSBizWare administrators configure the RSBizWare system
so that it can capture performance data for use by report
designers and report users.
They should be familiar with:
• Control systems, process information (line and plant), and
databases.
• Microsoft Windows operating system.
• The location and structure of databases.
• Report designers
Report designers create the reports that will be used by report
users.
They should be familiar with:
• Process information (the physical representation of the
production line and plant).
• Microsoft Windows operating systems.
• Query logic (how to write a database query).
• Web publishing tools.
• The location and structure of databases.
• Report users
Report users make use of the reports created by the report
designer to perform their jobs.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 11

Chapter 1 Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics
technical support resources, please visit the support site.
Where Can I Go for Help?
Get Web Support
They should be familiar with:
• Microsoft Windows operating systems.
Consult the following resources for additional information about
the product:
• Release Notes
The release notes contain current information about the
product, including hardware and software requirements, new
features, known and fixed anomalies.
• RSBizWare Administration Guide
The administration guide helps the RSBizWare administrator
install and configure the software as well as understand the
architecture of the RSBizWare suite and its components.
• Online help
The online help provides general information and step-by-step
procedures for working with the product.
• Rockwell Automation Support Center
The support center provides a variety of services, such as
trainings, webinars, and online support that will improve your
experience using the RSBizWare suite.
TIP
For web-based product support, and for detailed information on
Access the Rockwell Automation Knowledge base for 24/7 technical
information and assistance. You can also download software patches
and new software versions, ask questions via email, participate in
user forums, and access other useful problem-solving tools.
The support resources available vary, depending on the product
purchased. The latest information can be obtained from the
Rockwell Automation Technical Support website.
12 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics Chapter 1
Get Phone Support
Get Consulting Services
Contact Us
A current TechConnect Support contract may be required to use
some online features.
To speak with a Technical Support representative in North
America, call 1-440-646-3434.
For information on how to contact Technical Support in other
locations worldwide, please visit the support site.
A current TechConnect Support contract may be required to obtain
phone support.
Rockwell Automation provides expert consulting and turnkey
implementation of this product. Please contact your local
representative for more information.
We strive to help all of our customers become successful in their
manufacturing improvement efforts. Toward this objective, we
invite you to contact your local representative or Rockwell
Automation at any time that we may be of service to you.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 13
Chapter 1 Welcome to FactoryTalk Metrics
14 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
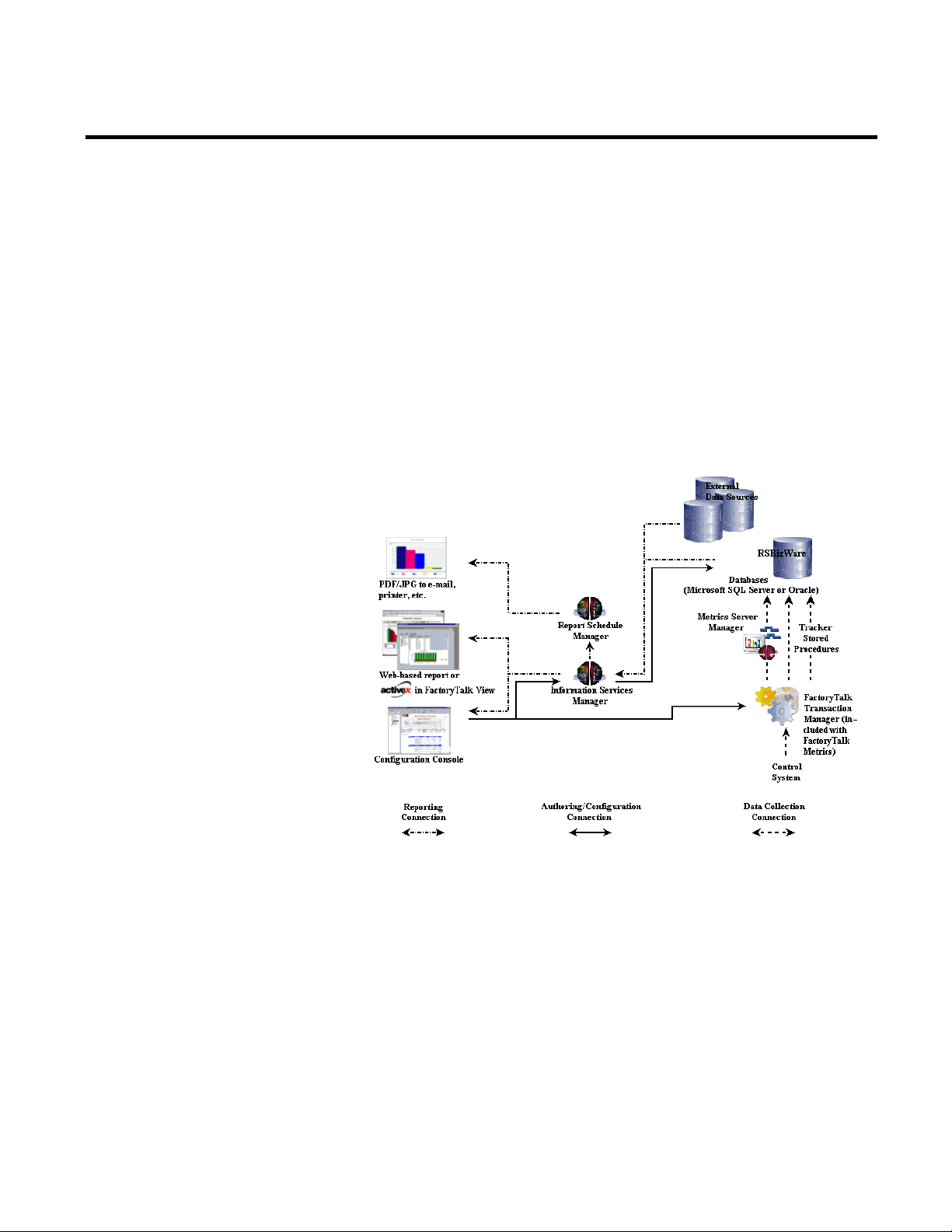
The RSBizWare Architecture
Chapter 2
Getting Started
Before you walk through the examples and tutorials that are
discussed in this book, it is assumed that the RSBizWare
administrator has installed, configured, and started the RSBizWare
server on the server computer.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 15
The RSBizWare architecture is a scalable, multi-tiered, distributed
architecture consisting of a data collection subsystem, an Oracle or
SQL Server database repository, the Information Services Manager,
and clients. Rockwell Automation’s FactoryTalk Transaction
Manager is the embedded engine that collects data from the control
system(s), and the Metrics Server Manager logs it to the predefined
RSBizWare database repository. There are several types of clients,
including the Configuration Console and the Internet Explorer
Web client.
Chapter 2 Getting Started
Importing Sample Data to the RSBizWare Database
The RSBizWare architecture can be configured to run on a single
computer, or it can be distributed across multiple computers. In the
simplest case, the Configuration Console, the Information Services
Manager, the RSBizWare administrative tools used by the
RSBizWare administrator, the database, the Metrics Server
Manager, and the FactoryTalk Transaction Manager data collection
engine run on a single computer. In a distributed setting, these
components may reside on separate computers. Clients connect to
the Information Services Manager using TCP/IP, so they can be
deployed over a LAN, WAN, intranet, or the Internet. The
scalability of the RSBizWare architecture allows many clients to
connect to a single server.
You may import the FactoryTalk Metrics sample data so that you
can use it as a reference and/or for demonstration purposes.
To import the sample data into the RSBizWare database:
1. Go to Start > All Programs > Rockwell Software >
FactoryTalk Tools > Database Wizard.
The Database Load and Update Wizard appears.
2. Click Next.
The Product and Database Connection page appears.
3. In the ODBC DSN list, select your ODBC data source.
4. In the User text box, type the user name of your RSBizWare
database owner.
5. In the Password box, type the password of your RSBizWare
database owner.
6. Click Connect.
Under Available Product Modules, a list of sample data
appears.
16 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014

Getting Started Chapter 2
Connecting to the Information Services Manager
Using the Information Services Manager in Internet Explorer
7. Select the data that you want to import.
8. Click Finish.
The Processing page with the import status appears.
After the import is complete, the Completing the Database
Load and Update Wizard page appears.
9. Click Close.
RSBizWare reports created by the report designer are saved to the
Information Services Manager, and are available online over a
TCP/IP network. If you wish to create and edit RSBizWare reports
using Microsoft Internet Explorer, you need to run the
Configuration Console.
Using Microsoft Internet Explorer to view RSBizWare reports, you
can connect to the Information Services Manager without having
the RSBizWare software installed on your computer. Instead, the
server hosts a special Web page, the Quick Web, to give you access to
the RSBizWare reports stored on the server. This option only allows
you to view RSBizWare reports.
To access the Quick Web, open Internet Explorer, type the Web
address for the Information Services Manager computer, and press
Enter on your keyboard.
The Web address is made up of the name of the server computer and
the HTTP port number used by the server computer, separated by a
colon.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 17
Chapter 2 Getting Started
Using the Information Services Manager in the Configuration Console
For example, if you were attempting to connect to a server computer
named
would use the following address:
rsi-rockwell that uses the default HTTP port 8080, you
http://rsi-rockwell:8080.
Please contact your RSBizWare administrator for the specific
Information Services Manager Web address to which you should
connect.
The first time you try to use the Quick Web, you need to download
several ActiveX controls from the server computer. The download
will begin automatically.
After you have downloaded the ActiveX controls from the
Information Services Manager, you may be prompted to log on. If
prompted, type the user name and password for the account that
your RSBizWare administrator has authorized for you, and then
click OK. A connection to the RSBizWare server is established.
If you wish to configure your plant model, manage the collection of
control system data, and/or edit RSBizWare reports, you should
connect to the Information Services Manager via the Configuration
Console. Your RSBizWare administrator needs to assign a
FactoryTalk Metrics Author license and the appropriate privileges
to you, to enable you to perform these functions.
You need to have the client software installed on your computer to
run the Configuration Console. To install the Configuration
Console from the RSBizWare DVD, select the Minimal installation
option.
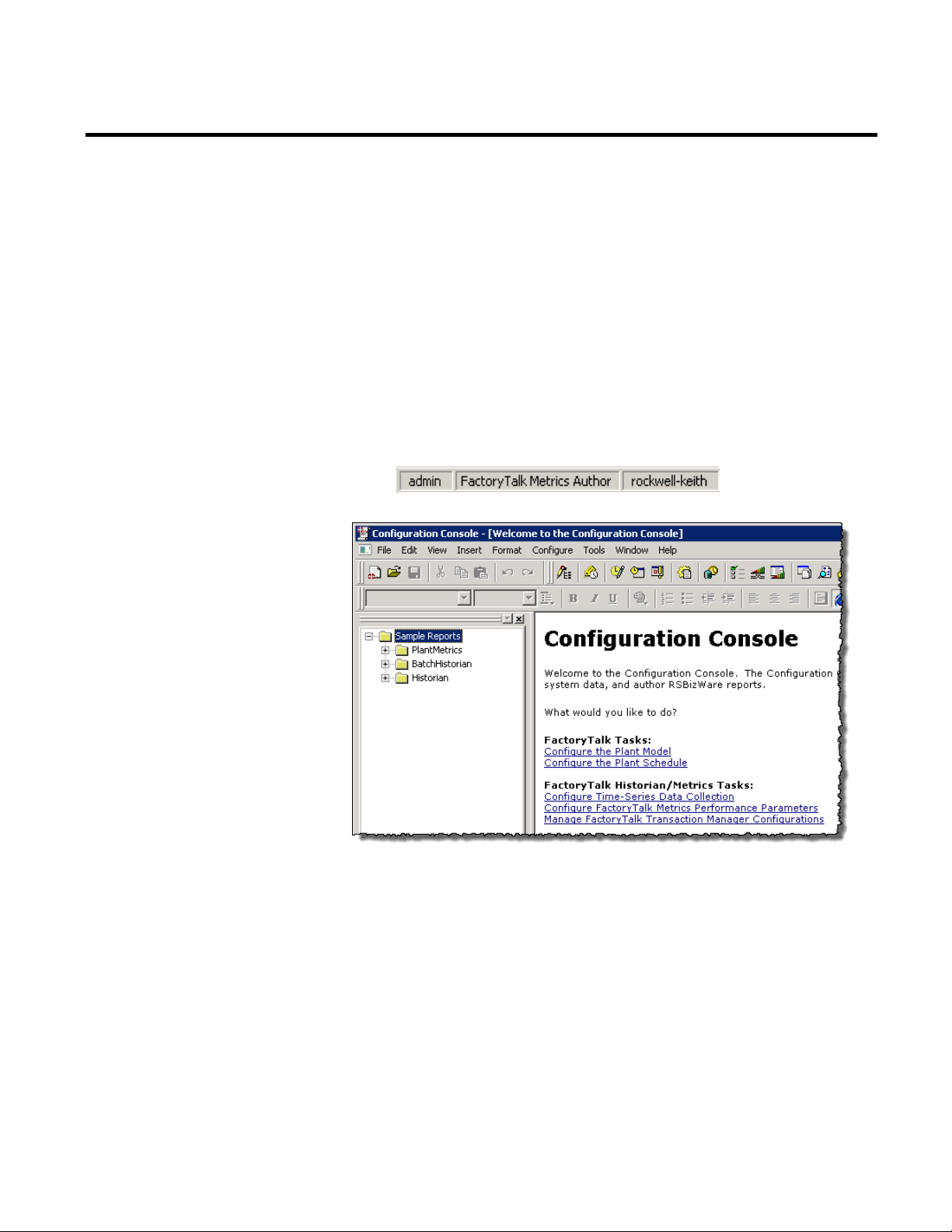
To start the Configuration Console:
1. Go to Start > All Programs > Rockwell Software >
RSBizWare > Configuration Console.
18 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
The RSBizWare Login dialog box appears.
Getting Started Chapter 2
Getting Started with the Configuration Console
2. If prompted, type the user name and password for the account
that your RSBizWare administrator has authorized for you,
type the name of the server computer where the Information
Services Manager is running in the Server box, and then click
Login.
A client session with the RSBizWare server is established.
The status bar at the bottom of the client application shows
your user name, the activations that have been assigned to you,
and the Information Services Manager to which you are
connected.
The Configuration Console user interface is made up of two main
components:
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 19
• The Report Explorer pane on the left.
The Report Explorer is a hierarchical navigation tool used for
organizing the RSBizWare reports that have been saved for
future use. The Report Explorer contains the reports saved in
the Information Services Manager to which you are connected
and for which you have been granted view permissions. Your
Chapter 2 Getting Started
selection is made.
workcell in the line).
location.
location at which products are manufactured.
Enterprise
The highest-level activity area, typically representing the business.
The Plant Model
ability to modify and delete the reports listed in the Report
Explorer depends on the licenses and features that you have
been assigned by your RSBizWare administrator, and the
permissions that you have been granted by the creator of each
individual report.
• The report design and display work area on the right.
When you click an item in the Report Explorer, the specified
RSBizWare report appears in this area. The work area is a
region where report designers can create and modify reports.
The plant model is made up of activity areas - enterprises, sites, areas,
lines, and workcells - as well as of equipment and labor resources.
The activity areas are based on the terms defined by the Instrument
Society of America (ISA) S95 standard in order to provide common
terminology for improved communication and integration between
control systems and enterprise systems.
Item Description
Workcell A location and/or group of equipment used to perform work in a
manufacturing process. The operations in a manufacturing process
are performed at workcells. A workcell is typically a physical
location and a primary resource (e.g., a machine); however, it may
also represent a logical grouping of primary resources from which a
Line A collection of one or more workcells that are combined to perform
work. The workcells in a line are either physically located close to
one another, or are related to one another in the production process
(the production result of the first workcell in a line feeds the second
Area A physical, geographical, or logical grouping of lines and/or
workcells within a site, typically representing a main production
capability (e.g., electronic assembly) within a manufacturing
Site A group of areas, lines, and workcells representing a geographical
20 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
Getting Started Chapter 2
To create and edit the plant model, you must be granted the
Activity Areas (page 23)".
Configuring the Plant Model
The plant model may be used by all RSBizWare applications in your
organization (FactoryTalk Metrics, FactoryTalk Historian Classic,
and FactoryTalk Scheduler). The enterprises, sites, areas, lines, and
workcells in your plant model are the subjects of your performance
parameter evaluation. For implementations of RSBizWare that
incorporate the FactoryTalk Scheduler application, the plant model
also includes capacity, which is the property of an activity area
describing its availability over time. The performance parameters
can also be configured for resources.
NOTE:
Organize Plant Model privilege by your RSBizWare administrator.
If you want to have access to sample data, see "Loading Sample
To configure the plant model in the Configuration Console:
1. On the Configure menu, click Plant Model.
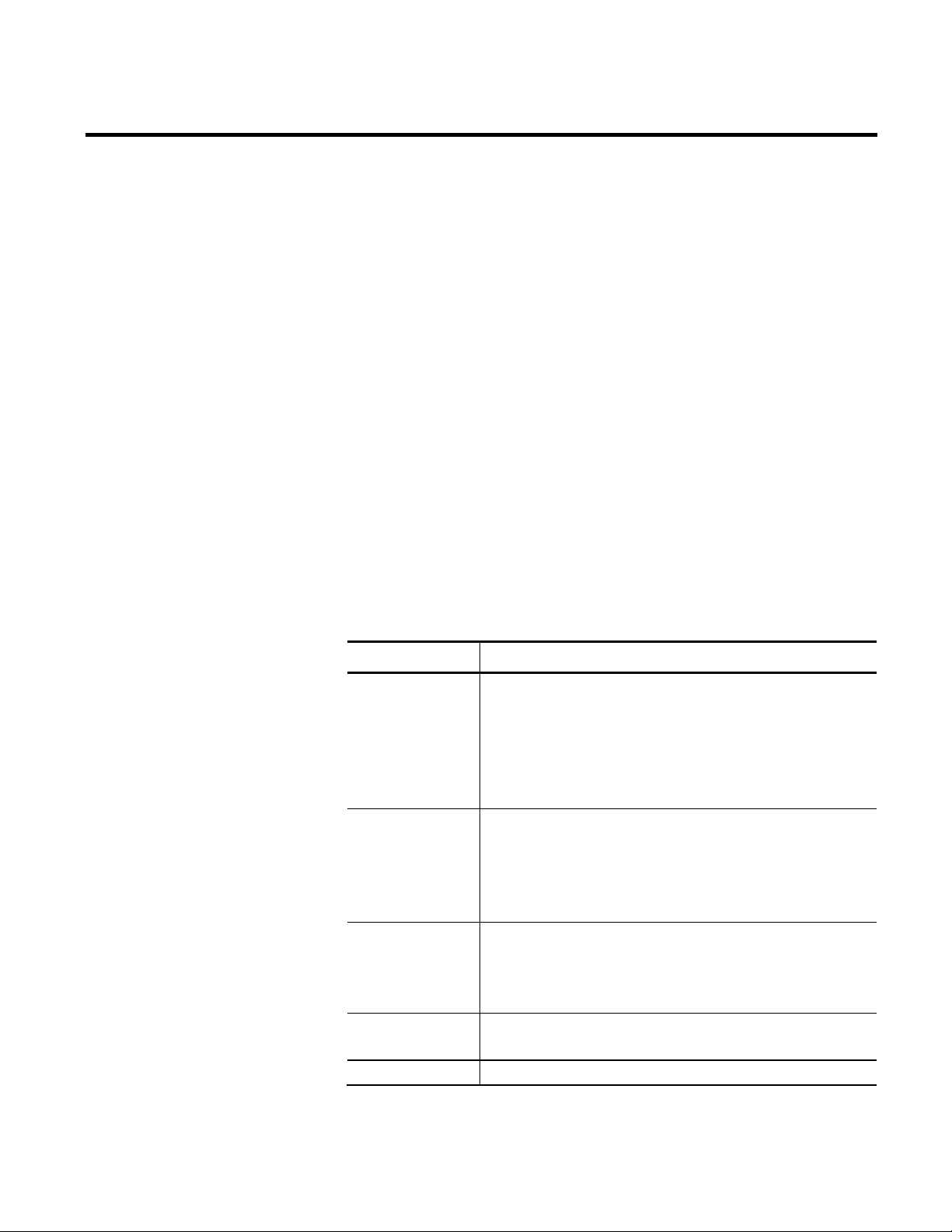
The Plant Model dialog box appears.
2. Right-click in the area under the plant model tree, and then
click New Root Enterprise.
A new enterprise is added to the tree.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 21
3. Change the default name to
Sample Enterprise, and then press
Enter.
4. Right-click Sample Enterprise, and then click New Activity
Area > Site.

Chapter 2 Getting Started
them with time patterns.
A new site is added to the tree.
5. Change the default name to
Sample Site.
6. Right-click Sample Site, and then click New Activity Area >
Area.
A new area is added to the tree.
7. Change the default name to
Sample Area.
8. Right-click Sample Area, and then click New Activity Area >
Line.
A new line is added to the tree.
9. Change the default name to
Sample Line.
10. Right-click Sample Line, and then click New Activity Area >
Work Cell.
A new workcell is added to the tree.
11. Change the default name to
Sample Work Cell 1.
22 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
12. Right-click each activity area that you have created, and then
click Add Capacity.
TIP
The capacity of an activity area describes its availability over
time.
Add capacity for your activity areas so that you can associate

section "Clean installation: supported installation scenarios".
Item
Description
configured for your RSBizWare SQL Server database.
User
Type the user name of your RSBizWare database.
Password
Type the password for the RSBizWare database user.
Loading Sample Activity Areas
13. Click OK.
Getting Started Chapter 2
NOTE
Follow these steps on the database server computer, on which Report
Expert is installed. For more information, see the Administration Guide,
To load FactoryTalk Metrics sample data:
1. Go to Start > All Programs > Rockwell Software >
FactoryTalk Tools > Database Wizard.
The Database Load and Update wizard appears.
2. On the Welcome page, click Next.
3. On the Product and Database Connection page, provide the
following information:
ODBC DSN Select the name of the ODBC data source that you have
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 23
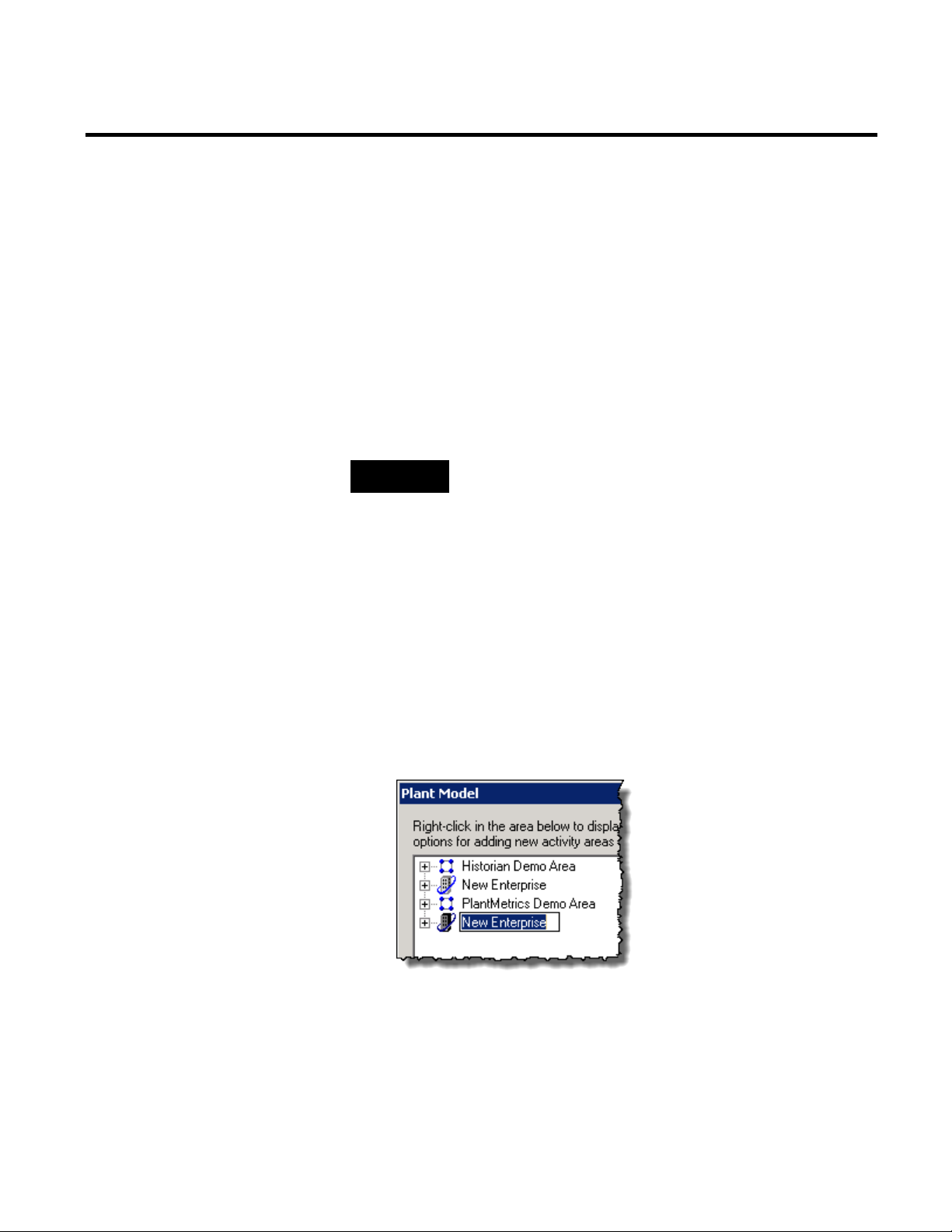
4. Click Connect. The Available Product Modules list is
populated with FactoryTalk components.
5. Under Available Product Modules, select these options:
Chapter 2 Getting Started
Metrics and Report Expert sample data.
Parameters.
TIP
Select both options so that you have access to FactoryTalk
6. Click Finish to load data.
7. Click Close to exit the wizard.
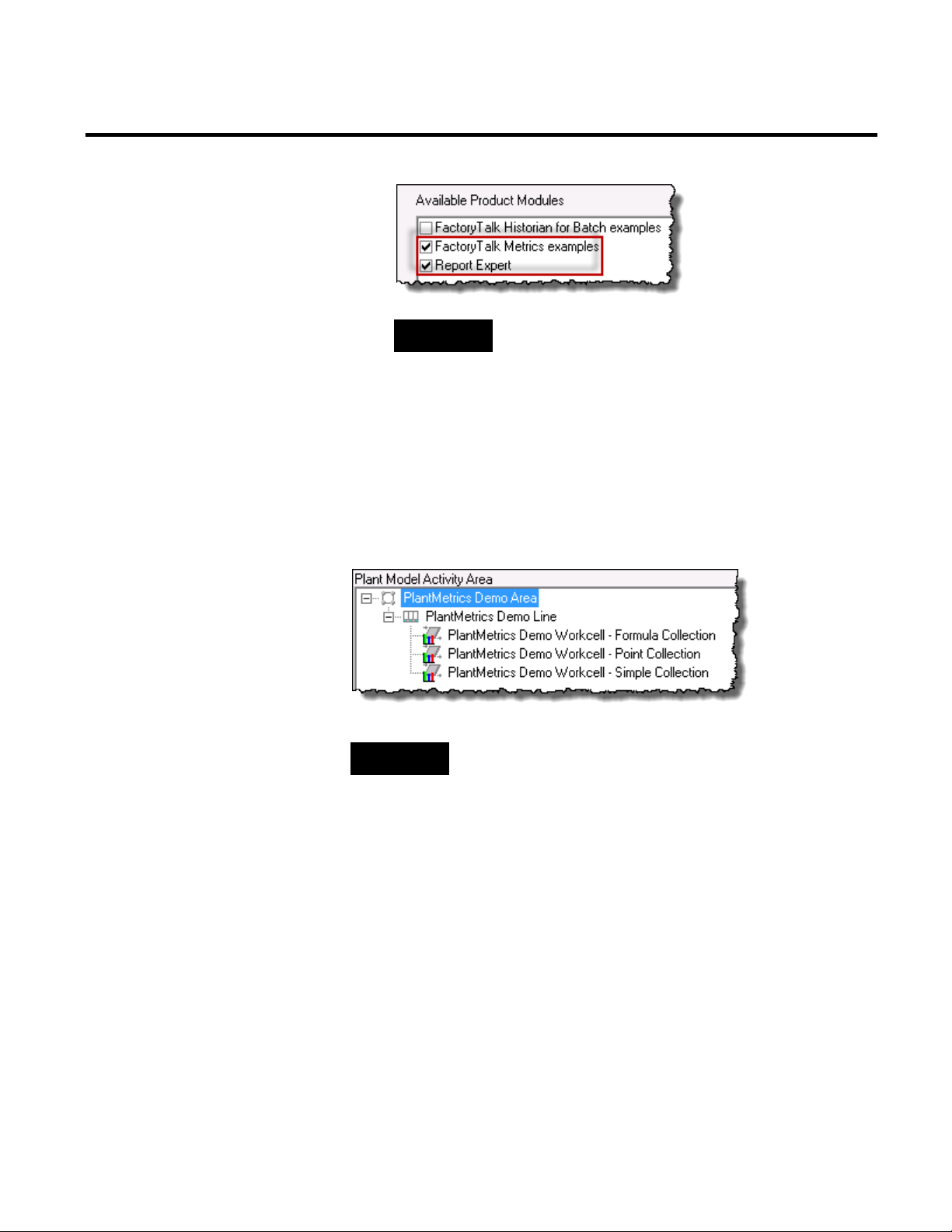
Now you can examine the OEE performance parameters that are
configured for sample activity areas. The activity areas are listed in
the Manage Performance Parameters dialog box, under
PlantMetrics Demo Area.
TIP
To open the Manage Performance Parameters dialog box, on the
Configure menu, click FactoryTalk Metrics > Performance
24 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014

Collecting Part Count Data When the Metrics Server Manager Is Stopped
Chapter 3
Collecting Performance Data
The primary functions of FactoryTalk Metrics are collecting and
analyzing production data to provide performance ratings for every
activity area. Before the report designer can create performance
rating reports for the report user, the RSBizWare administrator
must set up the application to collect data from the control system.
This chapter will help you understand the two key categories of
ratings used to evaluate the performance of a production asset, and
understand how to identify and configure the data points that will
be used to collect the production data necessary to calculate
performance ratings.
We will:
• Define the OEE and Fault Metrics ratings.
• Configure the FactoryTalk Metrics application, including
plant model configuration, time pattern configuration, time
pattern exception configuration, composite time pattern
configuration, and performance parameter configuration.
• Start and stop data collection.
• Perform manual data collection.
The examples in "Analyzing FactoryTalk Metrics Data (page 171)"
will help you understand how to analyze the data that is collected in
FactoryTalk Metrics.
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 25
In version 7.0 of FactoryTalk Metrics a change was made to the way
the data collection is initialized. Prior to this it was possible to have
partial FactoryTalk Transaction Manager .rsl files (still stored on
Chapter 3 Collecting Performance Data
disk when data collection started) processed as current data values.
This approach could lead to inaccurate count information being
recorded in the event of a part count reset in the control system. The
most serious effect of this issue was observed when the counter used
in a FactoryTalk Metrics part count formula was reset, and the
resulting formula evaluated to a negative number. The change
required that the initial data used as a baseline for calculations all
come from the same time period. In certain environments with
continuous counters that do not get reset, this change could result in
the loss of count data that was collected erroneously in previous
versions. The data collected this way can account for part counts
that were produced since the last time the Metrics server was
running.
In order to accommodate customers that found this data useful, the
Metrics Server Manager settings file
(PlantMetricsServerSettings.xml) can be configured so that it
forces the Metrics Server Manager to initialize its data in the pre-7.0
manner.
The file is located in the <ProgramFiles>\Rockwell
Software\RSBizWare folder. It contains the
InitializeFromSingleTimestamp tag. The tag is set by default to 1.
The default value causes the Metrics Server Manager to process data
in the standard way to prevent the inclusion of older data. If you
change the value to
0, the Metrics Server Manager will process data
regardless of its timestamp. This change may be appropriate for
some production environments, but in others may lead to incorrect
values being logged for count information.
For more information on the Metrics Server Manager settings file,
refer to "The Metrics Server Manager settings file" in the RSBizWare
Administration Guide.
26 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014

Collecting Performance Data Chapter 3
OEE Rating
FactoryTalk Metrics uses the OEE (Overall Equipment
Effectiveness) model to measure the performance of manufacturing
equipment. The OEE model yields a single performance rating for
every activity area (workcell, line, area, or plant) being monitored,
thereby providing a simple way to determine quickly if an activity
area is performing adequately. The OEE value can be used to assess a
single machine’s performance over time, or to compare the
performance of machines.
Three components contribute to the OEE value:
• Availability
The ratio of running time to available time.
Available time may be defined by a schedule, or modified by
planned downtime events such as preventive maintenance.
Available time may also be modified by events such as being
starved for parts or being blocked by a downstream process.
Availability = RunningTime / AvailableTime
• Throughput
The performance of a machine when it is running compared to
its ideal cycle time.
The ideal cycle time depends upon the product being
produced, and is measured in units of seconds per part.
Throughput = (TotalParts x IdealCycleTime) / RunningTime
• Quality
The percentage of good parts that are produced.
GoodParts = TotalParts – Scrap
Quality = GoodParts ⁄ TotalParts
The OEE calculation that is used by FactoryTalk Metrics is the
product of these three components:
OEE = Availability × Throughput × Quality
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 27

Chapter 3 Collecting Performance Data
Fault Metrics Ratings
Mean Time Between Failure
This reduces to:
FactoryTalk Metrics gathers and stores all of the raw data necessary
to make this calculation for specific time periods, as well as by
activity area, by part number, and by shift. All of the individual
components of the calculation are stored and available for analysis.
OEE is a valuable method of analyzing performance, because it is
widely recognized and can be applied to any type of industry, factory,
or machine. However, it is merely the default efficiency calculation
performed by FactoryTalk Metrics, and additional or alternate
calculations can be implemented. Furthermore, FactoryTalk Metrics
supports the collection of detailed event data, which can be used to
analyze the specific causes of inefficiencies.
FactoryTalk Metrics uses the Fault Metrics ratings to measure the
reliability of manufacturing equipment. These metrics provide a
simple way to determine quickly if an activity area is performing
reliably. The Fault Metrics values can be used to assess a single
machine’s reliability over time, or to compare the reliability of
machines to each other.
MTBF = Uptime ⁄ FaultCount
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) is the ratio of running time to
the total number of failures. It measures the average amount of time
when a piece of equipment was in a running state between failures.
MTBF is a derived field that contains aggregate functions and, as
28 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
Collecting Performance Data Chapter 3
Area (page 81)”.
To define time patterns, configure composites, and schedule exceptions,
RSBizWare administrator.
Mean Time To Repair
Configuring Activity Area Schedules
Time Patterns
such, can only be used in summary report objects and cannot have
aggregate functions applied.
MTTR = FaultTime ⁄ FaultCount
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) is the ratio of the time spent in a
failure state to the total number of failures. It measures the average
amount of time when a piece of equipment was in a failure state.
MTTR is a derived field that contains aggregate functions and, as
such, can only be used in summary report objects and cannot have
aggregate functions applied.
NOTE
To collect fault metrics for an activity area, you will need to create
custom events for the workcell. For information on creating custom
events, see “Viewing the Performance Parameter Events for an Activity
FactoryTalk Metrics allows you to create time patterns that will be
used to calculate the amount of available time for an activity area.
The OEE calculation is based on available time, so the calculation
will not be accurate unless the available time is defined accurately.
It is not necessary for you to use a time pattern to define available
time for an activity area; however, if you do, the OEE calculation for
the activity area will not be negatively impacted by the periods of
time when the activity area is scheduled to be unavailable (e.g.,
weekends or evenings).
NOTE
you must be granted the Manage Time Pattern privilege by your
A time pattern defines the availability of an activity area over time,
which repeats as necessary during the activity area schedule. We can
define the following durations of repeating periods:
Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014 29
Chapter 3 Collecting Performance Data
Configuring Time Patterns
• Day
A time pattern for a 24-hour day.
• Week
A time pattern for a standard 7-day week.
• Custom
A time pattern for arbitrary duration, e.g., a 14-day cycle or an
8-hour shift.
A time pattern is composed of a default value and a series of time
spans. The default value defines the value of the time pattern during
intervals where no time span is specified. Each time span specifies
the start time, end time, value (e.g., Available, Unavailable), and the
optional report name for the span. The default value for the time
pattern and the value for the time span can be a named state, a
numeric value, or another time pattern. Named states are simply a
set of values (e.g., 1, 0) to which you have applied descriptions (e.g.,
Available, Unavailable).
The sample time patterns available with FactoryTalk Metrics consist
of three 8-hour shift periods, each with a 30-minute break
(Unavailable), that make up the work day. The time pattern applies
Monday through Friday, and the facility is closed (Unavailable)
during the weekends.
The ability to reference other time patterns allows you to build time
patterns from other time patterns.
In the following tutorials you will create sample shift time patterns
in the Configuration Console: a Work Day time pattern that is
made up of shifts, and a Work Week time pattern made up of five
Work Days.
30 Rockwell Automation Publication PLTMT-UM001M-EN-P-June 2014
 Loading...
Loading...