Analog Devices OP285GP, OP285GSR, OP285GS Datasheet

a |
Dual 9 MHz Precision |
|||||
Operational Amplifier |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
OP285* |
|
FEATURES |
PIN CONNECTIONS |
||||
|
Low Offset Voltage: 250 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Low Noise: 6 nV/√ Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Low Distortion: 0.0006% |
8-Lead Narrow-Body SO (S-Suffix) |
||||
|
High Slew Rate: 22 V/ s |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wide Bandwidth: 9 MHz |
|
|
|
|
V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Low Supply Current: 5 mA |
OUT A |
1 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT B |
|
|
Low Offset Current: 2 nA |
–IN A |
2 |
OP285 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Unity-Gain Stable |
+IN A |
3 |
TOP VIEW |
6 |
–IN B |
|
(Not to Scale) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
+IN B |
||
|
SO-8 Package |
V– |
4 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APPLICATIONS
High Performance Audio
Active Filters
Fast Amplifiers
Integrators
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The OP285 is a precision high-speed amplifier featuring the Butler Amplifier front-end. This new front-end design combines the accuracy and low noise performance of bipolar transistors with the speed of JFETs. This yields an amplifier with high slew rates, low offset and good noise performance at low supply currents. Bias currents are also low compared to bipolar designs.
The OP285 offers the slew rate and low power of a JFET amplifier combined with the precision, low noise and low drift of a bipolar amplifier. Input offset voltage is laser-trimmed and guaranteed less than 250 V. This makes the OP285 useful in dc-coupled or summing applications without the need for special selections or the added noise of additional offset adjustment circuitry. Slew rates of 22 V/ s and a bandwidth of 9 MHz make the OP285 one of the most accurate medium speed amplifiers available.
8-Lead Epoxy DIP (P-Suffix)
OUT A |
1 |
|
|
|
8 |
V+ |
–IN A |
2 |
– + |
|
|
7 |
OUT B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+IN A |
3 |
|
+ |
– |
6 |
–IN B |
V– |
4 |
OP285 |
|
|
5 |
+IN B |
The combination of low noise, speed and accuracy can be used to build high speed instrumentation systems. Circuits such as instrumentation amplifiers, ramp generators, bi-quad filters and dc-coupled audio systems are all practical with the OP285. For applications that require long term stability, the OP285 has a guaranteed maximum long term drift specification.
The OP285 is specified over the XIND—extended industrial— (–40°C to +85°C) temperature range. OP285s are available in 8-pin plastic DIP and SOIC-8 surface mount packages.
*Patents pending
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 |
www.analog.com |
Fax: 781/326-8703 |
© Analog Devices, Inc., 2001 |
OP285–SPECIFICATIONS (@ Vs = 15.0 V, TA = 25 C, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter |
Symbol |
Conditions |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
µV |
Offset Voltage |
VOS |
|
|
35 |
250 |
|
|
VOS |
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
|
|
600 |
µV |
Input Bias Current |
IB |
VCM = 0 V |
|
100 |
350 |
nA |
|
IB |
VCM = 0 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
|
|
400 |
nA |
Input Offset Current |
IOS |
VCM = 0 V |
|
2 |
±50 |
nA |
|
IOS |
VCM = 0 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
|
2 |
±100 |
nA |
Input Voltage Range |
VCM |
VCM = ±10.5 V, |
–10.5 |
|
10.5 |
V |
Common-Mode Rejection |
CMRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
80 |
106 |
|
dB |
Large-Signal Voltage Gain |
AVO |
RL = 2 kΩ |
250 |
|
|
V/mV |
|
AVO |
RL = 2 kΩ, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
175 |
|
|
V/mV |
|
AVO |
RL = 600 Ω |
|
200 |
|
V/mV |
Common-Mode Input Capacitance |
|
|
|
7.5 |
|
pF |
Differential Input Capacitance |
|
|
|
3.7 |
|
pF |
Long-Term Offset Voltage |
∆VOS |
Note 1 |
|
|
300 |
µV |
Offset Voltage Drift |
∆VOS/∆T |
|
|
1 |
|
µV/°C |
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS |
|
RL = 2 kΩ |
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage Swing |
VO |
–13.5 |
+13.9 |
+13.5 |
V |
|
|
VO |
RL = 2 kΩ, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
–13 |
+13.9 |
+13 |
V |
|
|
RL = 600 Ω, VS = ±18 V |
|
–16/+14 |
|
V |
POWER SUPPLY |
|
VS = ±4.5 V to ±18 V |
|
|
|
|
Power Supply Rejection Ratio |
PSRR |
85 |
111 |
|
dB |
|
|
PSRR |
VS = ±4.5 V to ±18 V, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
80 |
|
|
dB |
Supply Current |
ISY |
VS = ±4.5 V to ±18 V, VO = 0 V, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = x, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
|
4 |
5 |
mA |
|
ISY |
VS = ±22 V, VO, = 0 V, RL = x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C |
± 4.5 |
|
5.5 |
mA |
Supply Voltage Range |
VS |
|
|
±22 |
V |
|
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE |
|
RL = 2 kΩ |
|
|
|
V/µs |
Slew Rate |
SR |
15 |
22 |
|
||
Gain Bandwidth Product |
GBP |
|
|
9 |
|
MHz |
Phase Margin |
o |
|
|
62 |
|
Degrees |
Settling Time |
ts |
To 0.1%, 10 V Step |
|
625 |
|
ns |
|
ts |
To 0.01%, 10 V Step |
|
750 |
|
ns |
Distortion |
|
AV = 1, VOUT = 8.5 V p-p, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 1 kHz, RL = 2 kΩ |
|
–104 |
|
dB |
Voltage Noise Density |
en |
f = 30 Hz |
|
7 |
|
nV/√Hz |
|
en |
f = 1 kHz |
|
6 |
|
nV/√Hz |
Current Noise Density |
in |
f = 1 kHz |
|
0.9 |
|
pA/√Hz |
Headroom |
|
THD + Noise ≤ 0.01%, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 2 kΩ, VS = ±18 V |
|
>12.9 |
|
dBu |
NOTE
1Long-term offset voltage is guaranteed by a 1,000 hour life test performed on three independent wafer lots at 125 °C, with an LTPD of 1.3.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2– |
REV. A |

OP285
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS1 |
± 22 |
|
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
V |
|
Input Voltage2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . ± 18 |
V |
Differential Input Voltage2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . ± 7.5 |
V |
Output Short-Circuit Duration to Gnd3 . . . . |
. . . . . Indefinite |
|
Storage Temperature Range |
–65°C to +150°C |
|
P, S Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
||
Operating Temperature Range |
–40°C to +85°C |
|
OP285G . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
||
Junction Temperature Range |
–65°C to +150°C |
|
P, S Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
||
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 Sec) |
. . . . . . . . 300°C |
|
Package Type |
JA4 |
JC |
Unit |
8-Pin Plastic DIP (P) |
103 |
43 |
°C/W |
8-Pin SOIC (S) |
158 |
43 |
°C/W |
NOTES
1Absolute Maximum Ratings apply to packaged parts, unless otherwise noted. 2For supply voltages less than ± 7.5 V, the absolute maximum input voltage is equal to the supply voltage.
3Shorts to either supply may destroy the device. See data sheet for full details. 4 JA is specified for the worst case conditions, i.e., JA is specified for device in socket for cerdip, P-DIP, and LCC packages; JA is specified for device soldered in circuit board for SOIC package.
ORDERING GUIDE
|
Temperature |
Package |
Package |
Model |
Range |
Description |
Option |
|
|
|
|
OP285GP* |
–40°C to +85°C |
8-Pin Plastic DIP |
N-8 |
OP285GS |
–40°C to +85°C |
8-Pin SOIC |
S0-8 |
OP285GSR |
–40°C to +85°C |
S0-8 Reel, 2500 pcs. |
|
*Not for new designs. Obsolete April 2002.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the OP285 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. A |
–3– |
OP285 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
25 |
TA = 25 C |
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
– V |
RL = 2k |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
+VOM |
|
|
SWING |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLTAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
–10 |
|
|
|
|
|
–15 |
|
|
|
–VOM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–25 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
|
0 |
|||||
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – V
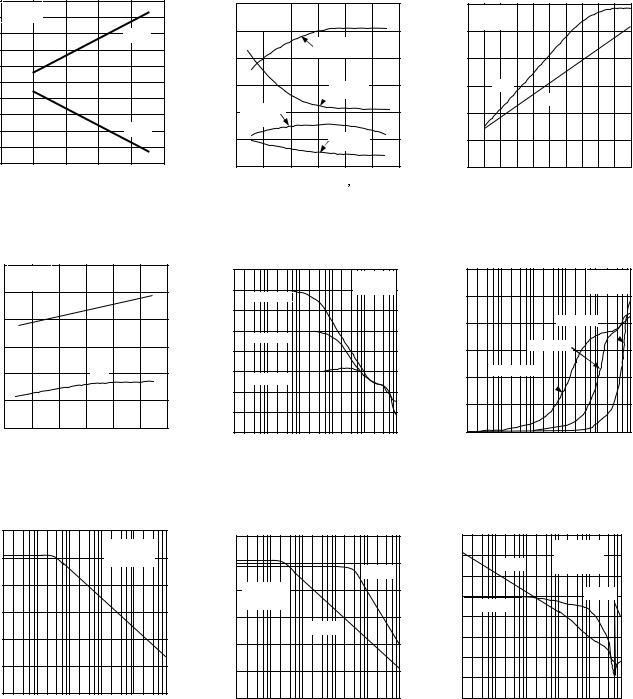
TPC 1. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
|
1500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VO = 10V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
V/MV |
1250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+GAIN |
|
|
||
1000 |
|
|
RL = 2k |
|
|
||
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GAIN |
750 |
|
|
|
–GAIN |
|
|
-LOOP |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
RL = 2k |
|
||
500 |
+GAIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPEN |
|
|
|
|
|
||
RL = 600 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
250 |
|
|
|
–GAIN |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 600 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–50 |
–25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
|
|
TEMPERATURE – |
C |
|
|||
TPC 2. Open-Loop Gain
vs. Temperature
|
50 |
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 15V |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
RL = 2k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
TA = +25 C |
||
|
|
|
|
–SR |
|
|
|
AVCL = +100 |
|
|||||
s |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
–dB |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
–RATESLEWV/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GAINLOOP-CLOSED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
AVCL = +10 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
+SR |
|
|
|
0 |
AVCL = +1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
–50 |
–25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
10k |
100k |
1M |
10M |
100M |
|||||||
|
|
|
TEMPERATURE – C |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
TPC 4. Slew Rate vs. Temperature |
TPC 5. Closed-Loop Gain |
|
|
|
vs. Frequency |
|
30 |
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
RL = 2k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
– V/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RATE |
15 |
+SR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–SR |
|
|
|
SLEW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0.2 |
0.4 |
0.6 |
0.8 |
1.0 |
DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE – V
TPC 3. Slew Rate vs. Differential Input Voltage
|
60 |
|
|
|
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
50 |
|
|
|
TA = 25 C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
AVCL = +1 |
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IMPEDANCE |
30 |
|
AVCL = +10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
20 |
AVCL = +100 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1k |
10k |
100k |
1M |
10M |
|
100 |
|||||
|
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz |
|
|
|
TPC 6. Closed-Loop Output Imped ance vs. Frequency
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
dB |
|
|
|
|
VS = 15V |
|
100 |
|
|
|
TA = 25 C |
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
REJECTION |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MODE |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
COMMON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1k |
10k |
100k |
1M |
10M |
|
100 |
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 7. Common-Mode Rejection vs. Frequency
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
dB |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
+PSRR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
REJECTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25 C |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–PSRR |
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
POWER |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
100 |
1k |
10k |
100k |
1M |
|
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz |
|
|
|
TPC 8. Power Supply Rejection vs. Frequency
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
GAIN |
RL = 2k |
|
0 |
|
||
|
60 |
|
TA = 25 C |
|
45 |
|
||
– dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
0N = 58 |
|
PHASE – Degrees |
||
MIN |
40 |
PHASE |
|
90 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
OPEN-LOOP G |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
135 |
||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
180 |
||
–20 |
|
|
|
|
|
225 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
–40 |
|
|
|
|
|
270 |
|
|
–60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
10k |
100k |
1M |
10M |
100M |
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 9. Open-Loop Gain, Phase vs. Frequency
–4– |
REV. A |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
65 |
|
MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MARGINPHASE– Degrees |
BANDWIDTHGAINPRODUCT – |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
10 |
|
|
|
øM |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
|
|
|
GBW |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
7 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
40 |
|
–50 |
–25 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
|
TEMPERATURE – C
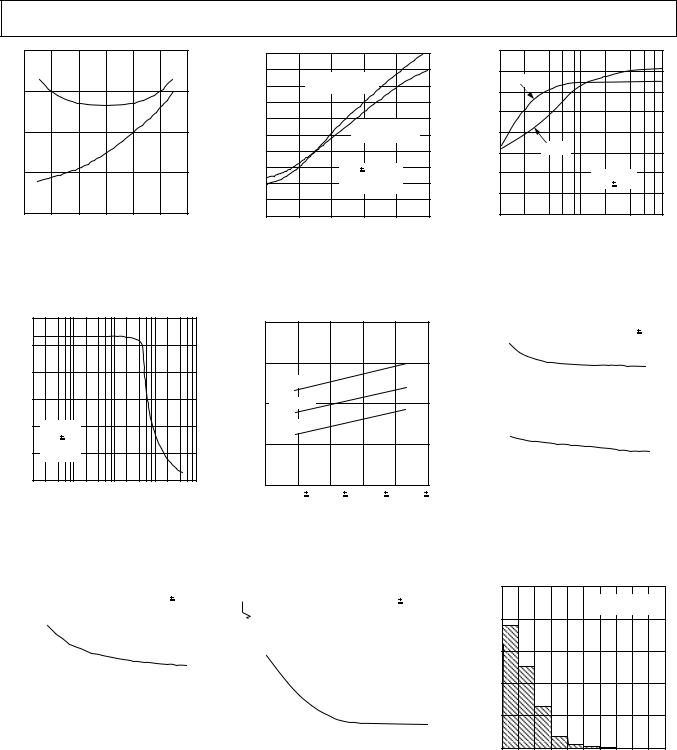
TPC 10. Gain Bandwidth Product, Phase Margin vs. Temperature
Typical Performance Characteristics–OP285
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
AVCL = +1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
NEGATIVE EDGE |
|
|
|
– % |
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OVERSHOOT |
|
AVCL= +1 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
50 |
|
POSITIVE EDGE |
|
||
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
VS = |
15V |
|
|
|
20 |
|
RL = 2k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIN = 100mV p-p |
|
||
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
100 |
200 |
300 |
400 |
500 |
LOAD CAPACITANCE – pF
TPC 11. Small-Signal Overshoot vs.| Load Capacitance
|
16 |
|
|
Volts |
14 |
|
|
–VOM |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWING |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
8 |
|
|
6 |
+VOM |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
MAXIMUM |
4 |
TA = 25 C |
|
2 |
VS = |
15V |
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
|
|
|
100 |
1k |
10k |
LOAD RESISTANCE –
TPC 12. Maximum Output Voltage vs. Load Resistance
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
mA–CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
SWINGOUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = +85 C |
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.0 |
TA = +25 C |
|
|
|
MAXIMUM |
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLY |
|
|
|
||
5 |
TA = 25 C |
|
|
|
|
TA = –40 C |
|
|
|
||
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AVCL = +1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RL = 2k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
1k |
10k |
100k |
1M |
10M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
25 |
|||||
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLY VOLTAGE – V |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
TPC 13. Maximum Output Swing |
TPC 14. Supply Current vs. |
|
vs. Frequency |
||
Supply Voltage |
||
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = 15V |
|
|
|
– nA |
250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BIAS |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
INPUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–50 |
–25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
|||||||
TEMPERATURE – C
TPC 16. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS |
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15V |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA = 25 C |
|
|
||||||
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
– pA/ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DENSITY |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOISE |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
100 |
|
|
|
1k |
|
|
100k |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
FREQUENCY – Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
TPC 17. Current Noise Density vs. Frequency
|
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– mA |
110 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VS = |
|
15V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SINK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
OUTPUT |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ABSOLUTE |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
SOURCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
–50 |
–25 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
||||||||||
TEMPERATURE – C
TPC 15. Short Circuit Current vs. Temperature
250
–40 C  TA
TA  +85 C
+85 C
402 OP AMPS
200
150 UNITS
100
50
0
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
TC VOS – V/ |
C |
|
|
|
||
TPC 18. tC VOS Distribution
REV. A |
–5– |
 Loading...
Loading...