SGS Thomson Microelectronics M27W202-100F6, M27W202-100B6, M27W202-150N6TR, M27W202-150K6TR, M27W202-150F6 Datasheet
...
M27W202
2 Mbit (128Kb x16) Low Voltage UV EPROM and OTP EPROM
■2.7V to 3.6V SUPPLY VOLTAGE in READ OPERATION
■ACCESS TIME:
–80ns at VCC = 3.0V to 3.6V
–100ns at VCC = 2.7V to 3.6V
■LOW POWER CONSUMPTION:
–Active Current 20mA at 5MHz
–Standby Current 15µA
■PIN COMPATIBLE with M27C202
■PROGRAMMING TIME: 100µs/word
■HIGH RELIABILITY CMOS TECHNOLOGY
–2,000V ESD Protection
–200mA Latchup Protection Immunity
■ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
–Manufacturer Code: 0020h
–Device Code: 001Ch
DESCRIPTION
The M27W202 is a low voltage 2 Mbit EPROM offered in the two range UV (ultra violet erase) and OTP (one time programmable). It is ideally suited for microprocessor systems requiring large data or program storage and is organised as 131,072 by 16 bits.
The M27W202 operates in the read mode with a supply voltage as low as 2.7V at –40 to 85°C temperature range. The decrease in operating power allows either a reduction of the size of the battery or an increase in the time between battery recharges.
The FDIP40W (window ceramic frit-seal package) has a transparent lid which allows the user to expose the chip to ultraviolet light to erase the bit pattern. A new pattern can then be written to the device by following the programming procedure.
For application where the content is programmed only one time and erasure is not required, the M27W201 is offered in PDIP40, PLCC44 and TSOP40 (10 x 14 mm) packages.
40 |
40 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
FDIP40W (F) |
PDIP40 (B) |
PLCC44 (K) |
TSOP40 (N) |
|
10 x 14 mm |
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
VCC |
VPP |
17 |
16 |
A0-A16 |
Q0-Q15 |
P M27W202
E
G
VSS
AI02730
April 2000 |
1/15 |
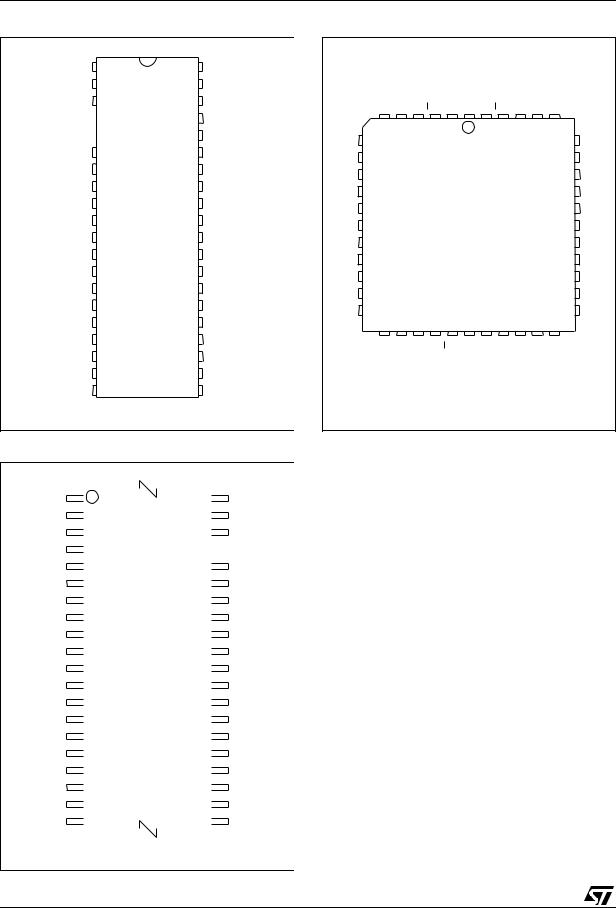
M27W202
Figure 2A. DIP Connections
VPP |
1 |
|
40 |
VCC |
||||
|
E |
2 |
|
39 |
P |
|
||
Q15 |
3 |
|
38 |
A16 |
||||
Q14 |
|
4 |
|
37 |
A15 |
|||
|
|
|||||||
Q13 |
|
5 |
|
36 |
A14 |
|||
|
|
|||||||
Q12 |
6 |
|
35 |
A13 |
||||
Q11 |
7 |
|
34 |
A12 |
||||
Q10 |
8 |
|
33 |
A11 |
||||
Q9 |
9 |
|
32 |
A10 |
||||
Q8 |
10 |
M27W202 |
31 |
A9 |
||||
VSS |
11 |
30 |
VSS |
|||||
Q7 |
12 |
|
29 |
A8 |
||||
Q6 |
13 |
|
28 |
A7 |
||||
Q5 |
14 |
|
27 |
A6 |
||||
Q4 |
15 |
|
26 |
A5 |
||||
Q3 |
16 |
|
25 |
A4 |
||||
Q2 |
17 |
|
24 |
A3 |
||||
Q1 |
18 |
|
23 |
A2 |
||||
Q0 |
19 |
|
22 |
A1 |
||||
|
|
20 |
|
21 |
A0 |
|||
|
G |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
AI02731 |
|
|
|
Figure 2C. TSOP Connections
A9 |
1 |
|
|
|
40 |
|
VSS |
||||
A10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A8 |
||||
A11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A7 |
||||
A12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A6 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
A13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A5 |
||||
A14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A4 |
||||
A15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A3 |
||||
A16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 |
|||
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
VCC |
10 |
M27W202 |
31 |
|
A0 |
||||||
VPP |
11 |
(Normal) |
30 |
|
|
G |
|
||||
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ0 |
|||
DQ15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ1 |
||||
DQ14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ2 |
||||
DQ13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ3 |
||||
DQ12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ4 |
||||
DQ11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ5 |
||||
DQ10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ6 |
||||
DQ9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DQ7 |
||||
DQ8 |
20 |
|
|
|
21 |
|
VSS |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AI02733 |
|
|
|
|
Figure 2B. LCC Connections
|
Q13 |
Q14 |
Q15 |
E |
PP |
NC |
CC |
P |
A16 |
A15 |
A14 |
|
|
V |
V |
|
|||||||||
Q12 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
44 |
|
|
|
|
A13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Q11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A12 |
Q10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A11 |
Q9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A10 |
Q8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A9 |
VSS |
12 |
|
|
|
M27W202 |
|
|
|
34 |
VSS |
||
NC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
Q7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A8 |
Q6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A7 |
Q5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A6 |
Q4 |
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
A5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q3 |
Q2 |
Q1 |
Q0 |
G |
NC |
A0 |
A1 |
A2 A3 |
A4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AI02732 |
Table 1. Signal Names
|
A0-A16 |
Address Inputs |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Q0-Q15 |
Data Outputs |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chip Enable |
|
E |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Enable |
|
G |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program |
|
|
P |
|||
|
|
|
||
|
VPP |
Program Supply |
||
|
|
|
||
|
VCC |
Supply Voltage |
||
|
|
|
||
|
VSS |
Ground |
||
|
NC |
Not Connected Internally |
||
|
|
|
|
|
2/15

|
|
|
M27W202 |
|
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings (1) |
|
|
|
|
Symbol |
Parameter |
Value |
|
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
TA |
Ambient Operating Temperature (3) |
–40 to 125 |
|
°C |
TBIAS |
Temperature Under Bias |
–50 to 125 |
|
°C |
TSTG |
Storage Temperature |
–65 to 150 |
|
°C |
|
|
|
|
|
VIO (2) |
Input or Output Voltage (except A9) |
–2 to 7 |
|
V |
VCC |
Supply Voltage |
–2 to 7 |
|
V |
VA9 (2) |
A9 Voltage |
–2 to 13.5 |
|
V |
VPP |
Program Supply Voltage |
–2 to 14 |
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
Note: 1. Except for the rating "Operating Temperature Range", stresses above those listed in the Table "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the Operating sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics SURE Program and other relevant quality documents.
2.Minimum DC voltage on Input or Output is –0.5V with possible undershoot to –2.0V for a period less than 20ns. Maximum DC voltage on Output is VCC +0.5V with possible overshoot to VCC +2V for a period less than 20ns.
3.Depends on range.
Table 3. Operating Modes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VPP |
|
Mode |
|
E |
|
G |
P |
A9 |
Q15-Q0 |
|||||
Read |
VIL |
VIL |
VIH |
X |
VCC or VSS |
Data Output |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Output Disable |
VIL |
VIH |
X |
X |
VCC or VSS |
Hi-Z |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Program |
VIL |
|
X |
VIL Pulse |
X |
VPP |
Data Input |
|||||
Verify |
VIL |
VIL |
VIH |
X |
VPP |
Data Output |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Program Inhibit |
VIH |
|
X |
X |
X |
VPP |
Hi-Z |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Standby |
VIH |
|
X |
X |
X |
VCC or VSS |
Hi-Z |
|||||
Electronic Signature |
VIL |
VIL |
VIH |
VID |
VCC |
Codes |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: X = VIH or VIL, VID = 12V ± 0.5V.
Table 4. Electronic Signature
Identifier |
A0 |
Q7 |
Q6 |
Q5 |
Q4 |
Q3 |
Q2 |
Q1 |
Q0 |
Hex Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manufacturer’s Code |
VIL |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
20h |
Device Code |
VIH |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1Ch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: Outputs Q15-Q8 are set to '0'.
3/15

M27W202
Table 5. AC Measurement Conditions
|
High Speed |
Standard |
|
|
|
Input Rise and Fall Times |
≤ 10ns |
≤ 20ns |
|
|
|
Input Pulse Voltages |
0 to 3V |
0.4V to 2.4V |
|
|
|
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages |
1.5V |
0.8V and 2V |
|
|
|
Figure 3. AC Testing Input Output Waveform |
|
Figure 4. AC Testing Load Circuit |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.3V |
|
|||||
High Speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
3V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1N914 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1.5V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.3kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
DEVICE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard |
|
|
UNDER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
||
|
|
|
|
|
TEST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.4V |
|
2.0V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4V |
|
0.8V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AI01822 |
|
|
CL = 30pF for High Speed |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
CL = 100pF for Standard |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
CL includes JIG capacitance |
AI01823B |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 6. Capacitance (1) (TA = 25 °C, f = 1 MHz)
Symbol |
Parameter |
Test Condition |
Min |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CIN |
Input Capacitance |
VIN = 0V |
|
6 |
pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
COUT |
Output Capacitance |
VOUT = 0V |
|
12 |
pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
DEVICE OPERATION
The operating modes of the M27W202 are listed in the Operating Modes table. A single power supply is required in the read mode. All inputs are TTL levels except for VPP and 12V on A9 for Electronic Signature.
Read Mode
The M27W202 has two control functions, both of which must be logically active in order to obtain data at the outputs. Chip Enable (E) is the power control and should be used for device selection. Output Enable (G) is the output control and should be used to gate data to the output pins, independent of device selection. Assuming that the addresses are stable, the address access time
(tAVQV) is equal to the delay from E to output (tELQV). Data is available at the output after a delay of tOE from the falling edge of G, assuming that E
has been low and the addresses have been stable for at least tAVQV-tGLQV.
Standby Mode
The M27W202 has a standby mode which reduces the supply current from 15mA to 15µA with low voltage operation VCC â 3.6V, see Read Mode DC Characteristics table for details.
The M27W202 is placed in the standby mode by applying a TTL high signal to the E input. When in the standby mode, the outputs are in a high impedance state, independent of the G input.
4/15

M27W202
Table 7. Read Mode DC Characteristics (1)
(TA = –40 to 85 °C; V CC = 2.7V to 3.6V; VPP = VCC)
Symbol |
Parameter |
|
Test Condition |
Min |
Max |
Unit |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
ILI |
Input Leakage Current |
|
|
0V ≤ VIN ≤ VCC |
|
±10 |
µA |
||||||
|
ILO |
Output Leakage Current |
0V ≤ VOUT ≤ VCC |
|
±10 |
µA |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= VIL, |
|
= VIL, |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
E |
G |
|
|
|
||||||
ICC |
Supply Current |
IOUT = 0mA, f = 5MHz |
|
20 |
mA |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC ≤ 3.6V |
|
|
|
||||
ICC1 |
Supply Current (Standby) TTL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
= VIH |
|
1 |
mA |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
E |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
> VCC – 0.2V |
|
|
|
||||
ICC2 |
Supply Current (Standby) CMOS |
|
E |
|
15 |
µA |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
VCC ≤ 3.6V |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
IPP |
Program Current |
|
|
|
|
VPP = VCC |
|
10 |
µA |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIL |
Input Low Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–0.6 |
0.2 VCC |
V |
V |
(2) |
Input High Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.7 VCC |
VCC + 0.5 |
V |
|
IH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOL |
Output Low Voltage |
|
|
|
|
IOL = 2.1mA |
|
0.4 |
V |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
VOH |
Output High Voltage TTL |
|
|
IOH = –400µA |
2.4 |
|
V |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: 1. VCC must be applied simultaneously with or before VPP and removed simultaneously or after VPP. 2. Maximum DC voltage on Output is VCC +0.5V.
Two Line Output Control
Because OTP EPROMs are usually used in larger memory arrays, this product features a 2 line control function which accommodates the use of multiple memory connection. The two line control function allows:
a.the lowest possible memory power dissipation,
b.complete assurance that output bus contention will not occur.
For the most efficient use of these two control lines, E should be decoded and used as the primary device selecting function, while G should be made a common connection to all devices in the array and connected to the READ line from the system control bus. This ensures that all deselected memory devices are in their low power standby mode and that the output pins are only active when data is required from a particular memory device.
System Considerations
The power switching characteristics of Advanced CMOS EPROMs require careful decoupling of the devices. The supply current, ICC, has three segments that are of interest to the system designer: the standby current level, the active current level, and transient current peaks that are produced by the falling and rising edges of E. The magnitude of transient current peaks is dependent on the capacitive and inductive loading of the device at the output. The associated transient voltage peaks can be suppressed by complying with the two line output control and by properly selected decoupling capacitors. It is recommended that a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor be used on every device between VCC and VSS. This should be a high frequency capacitor of low inherent inductance and should be placed as close to the device as possible. In addition, a 4.7µF bulk electrolytic capacitor should be used between VCC and VSS for every eight devices. The bulk capacitor should be located near the power supply connection point.The purpose of the bulk capacitor is to overcome the voltage drop caused by the inductive effects of PCB traces.
5/15
 Loading...
Loading...