Philips PCA1467U-10, PCA1467U-10-F2, PCA1461U-10, PCA1462U, PCA1462U-10-F2 Datasheet
...
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
PCA146x series
32 kHz watch circuits with adaptive motor pulse
Product specification |
1998 Apr 21 |
Supersedes data of 1998 Mar 18
File under Integrated Circuits, IC16

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
32 kHz watch circuits with adaptive motor
PCA146x series
pulse
FEATURES
∙32 kHz oscillator, amplitude regulated with excellent frequency stability
∙High immunity of the oscillator to leakage currents
∙Time calibration electrically programmable and reprogrammable (via EEPROM)
∙A quartz crystal is the only external component required
∙Very low current consumption; typically 170 nA
∙Output for bipolar stepping motors of different types
∙Up to 50% reduction in motor current compared with conventional circuits, by self adaption of the motor pulse width to match the required torque of the motor
∙No loss of motor steps possible because of on-chip detection of the induced motor voltage
∙Detector for lithium or silver-oxide battery voltage levels
∙Indication for battery end-of-life
∙Stop function for accurate timing
∙Power-on reset for fast testing
∙Various test modes for testing the mechanical parts of the watch and the IC.
ORDERING INFORMATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCA146x series devices are CMOS integrated circuits specially suited for battery-operated, quartz-crystal-controlled wrist-watches, with a bipolar stepping motor.
TYPE |
|
PACKAGE(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
NUMBER |
NAME |
DESCRIPTION |
VERSION |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
PCA1461U |
− |
chip in tray |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1461U/10 |
− |
chip on foil |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1462U |
− |
chip in tray |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1462U/7 |
− |
chip with bumps on tape |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1462U/10 |
− |
chip on foil |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1463U |
− |
chip in tray |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1463U/10 |
− |
chip on foil |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1465U/10 |
− |
chip on foil |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1465U/7 |
− |
chip with bumps on tape |
− |
|
|
|
|
PCA1467U/10 |
− |
chip on foil |
− |
|
|
|
|
Note
1.Figure 1 and Chapter “Package outline” show details of standard package, available for large orders only. Chapter “Chip dimensions and bonding pad locations” shows exact pad locations for other delivery formats.
1998 Apr 21 |
2 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
32 kHz watch circuits with adaptive motor
PCA146x series
pulse
PINNING
SYMBOL |
PIN |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
VSS |
1 |
ground (0 V) |
TEST |
2 |
test output |
|
|
|
OSC IN |
3 |
oscillator input |
|
|
|
OSC OUT |
4 |
oscillator output |
|
|
|
VDD |
5 |
supply voltage |
M1 |
6 |
motor 1 output |
|
|
|
M2 |
7 |
motor 2 output |
|
|
|
RESET |
8 |
reset input |
|
|
|
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION AND TESTING
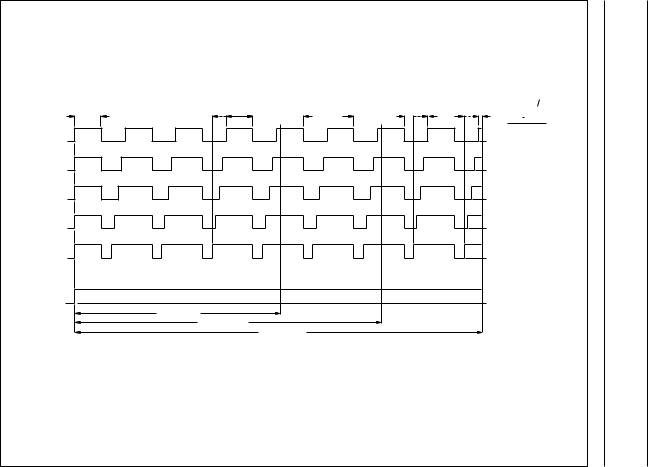
The motor output delivers pulses of six different stages depending on the torque required to turn the motor (Figs. 3 and 4). Every motor pulse is followed by a detection phase which monitors the waveform of the induced motor voltage. When a step is missed a correction sequence will be started (Fig.2).
Motor pulses
The circuit produces motor pulses of six different stages (stage 1 to 5, stage 8). Each stage has two independent modes: silver-oxide and lithium. The voltage level of VDD determines which mode is selected (see Section “Voltage level detector”).
Stages 1 to 5 (both modes) are used in normal operation, stage 8 occurs under the following conditions:
∙Correction pulse after a missing step (both modes)
∙End-of-life mode
∙If stage 5 is not enough to turn the motor (both modes).
In the silver-oxide mode, the ON state of the motor pulse varies between 56.25% and 100% of the duty factor
tDF = 977 μs depending on the stage (Fig.3). It increases in steps of 6.25% per stage.
VSS |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
8 |
RESET |
|
TEST |
|
|
|
M2 |
2 |
PCA146xT |
7 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
OSC IN |
3 |
|
6 |
M1 |
OSC OUT |
|
|
|
VDD |
4 |
|
5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSA937 |
|
|
Fig.1 Pin configuration, PCA146xT, (PMFP8).
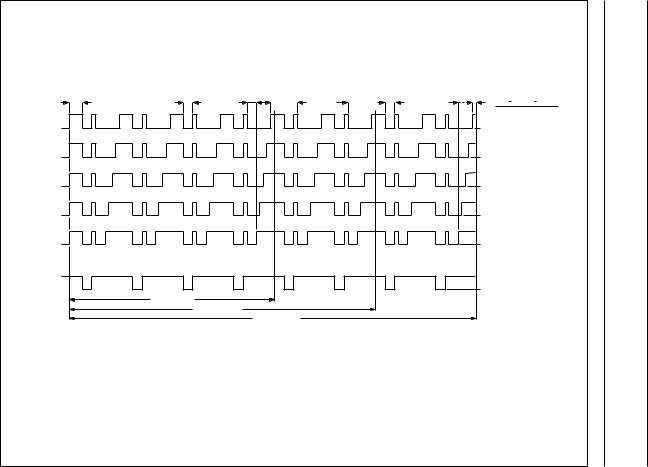
In the lithium mode, the ON state of the motor pulse is reduced by 18.75% of the duty factor tDF (Fig.4) to compensate for the increase in the voltage level.
After a RESET the circuit always starts and continues with stage 1, when all motor pulses have been executed.
A failure to execute all motor pulses results in the circuit going into stage 2, this sequence will be repeated through to stage 8.
When the motor pulses at stage 5 are not large enough to turn the motor, stage 8 is implemented for a maximum of 8 minutes with no attempt to keep current consumption low. After stage 8 has been executed the procedure is repeated from RESET.
The circuit operates for 8 minutes at a fixed stage, if every motor pulse is executed. The next 480 motor pulses are then produced at the next lower stage unless a missing step is detected. If a step is missed a correction sequence is produced and for a maximum of 8 minutes the motor pulses are increased by one stage.
1998 Apr 21 |
3 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
32 kHz watch circuits with adaptive motor
PCA146x series
pulse
MOTOR |
DETECTION |
|
POSSIBLE CORRECTION |
|
|||
PULSE |
|
|
SEQUENCE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VM1 - M2
MSA942
 t P
t P 
 t D
t D 





 t C
t C 
t T
Fig.2 Possible motor output waveform in normal operation with motor connected.
1998 Apr 21 |
4 |
_
21 Apr 1998
t SONF = 488 μs |
t SON |
t DF = 977 μs |
t SOFF |
t ON = t SON t DF |
|
t ONL |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
t DF |
t SOFF |
|
|
|
|
= |
|
STAGE 1 |
|
|
|
t DF |
|
|
|
|
|
56.25 % |
|
STAGE 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
62.50 % |
|
STAGE 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
68.75 % |
|
STAGE 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
75.00 % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STAGE 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
81.25 % |
|
STAGE 8 |
|
|
|
100.00 % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t P3 = 3.9 ms |
|
|
|
|
|
t P2 = 5.86 ms |
= 7.81 ms |
|
|
|
|
t P1 |
|
MSA947 |
|
|
tOFF for stage 1 to 5 = 488 μs − stage × 61 μs tON for stage 1 to 5 = 488 μs + stage × 61 μs
Fig.3 Motor pulses in the silver-oxide mode (VDD = 1.55 V).
motor adaptive with circuits watch kHz 32 pulse
series PCA146x
Semiconductors Philips
specification Product
21 Apr 1998
6
_
t LONF = 244 μs |
t AOFF = 183 μs |
t LOFF |
t DF = 977 μs |
t AOFF |
t ONL |
t DF |
t ON = |
t LOFF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
t LOFF |
||
STAGE 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
t DF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37.50 % |
|
|
STAGE 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.75 % |
|
|
STAGE 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50.00 % |
|
|
STAGE 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56.25 % |
|
|
STAGE 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
62.50 % |
|
|
STAGE 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
81.25 % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t P3 = 3.9 ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t P2 = 5.86 ms |
t P1 = 7.81 ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSA946 |
|
|
tOFF for stage 1 to 5 = 672 μs − stage × 61 μs tON for stage 1 to 5 = 305 μs + stage × 61 μs
Fig.4 Motor pulses in the lithium mode (VDD = 2.1 V).
motor adaptive with circuits watch kHz 32 pulse
series PCA146x
Semiconductors Philips
specification Product

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
32 kHz watch circuits with adaptive motor
PCA146x series
pulse
Voltage level detector
The supply voltage is compared with the internal voltage reference VLIT and VEOL every minute. The first voltage level detection is carried out 30 ms after RESET.
When a lithium voltage level is detected (VDD ³ VLIT), the circuit starts operating in the lithium mode (Fig.4).
When the detected VDD voltage level is between VLIT and VEOL, the circuit operates in the silver-oxide mode (Fig.3).
If the battery end-of-life is detected (VDD < VEOL), the detection and stage control is switched OFF and the
waveform produced is an unchopped version of the stage 8 waveform. To indicate this condition the waveform is produced in bursts of 4 pulses every 4 s.
Detection of motor movement
After a motor pulse, the motor is short-circuited to VDD for 1 ms. Afterwards the energy in the motor inductor will be dissipated to measure only the current generated by the induced motor voltage. During the time tDI (dissipation of energy time) all switches shown in Fig.5 are open to reduce the current as fast as possible. The current will now flow through the diodes D3 and D2, or D4 and D1. Then the first of 52 possible measurement cycles (tMC) starts to measure the induced current.
VDD
P1 |
D1 |
|
|
D2 |
P2 |
L1 |
|
M1 |
MOTOR |
M2 |
L2 |
N1 |
D3 |
|
|
D4 |
N2 |
VSS
MSA941
Fig.5 Motor driving and detecting circuit.
1998 Apr 21 |
7 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
32 kHz watch circuits with adaptive motor
PCA146x series
pulse
Detection criteria
The PCA146x uses current detection in two defined parts of the detection phase to determine if the motor has moved (refer to Figs 6 and 7). The detection criteria are:
part 1
∙Minimum value of P = 1; where P = number of measured positive current polarities after tDI.
part 2
∙Minimum value of N = 2; where N = number of measured positive current polarities since the first negative current polarity after part 1 was detected (see Fig.6).
If the opposite polarity is measured in one part, the internal counter is reset, so the results of all measurements in this part are ignored.
The waveform of the induced current must enable all these measurements within the time tD after the end of a positive motor pulse in order to be accepted as a waveform of an executed motor pulse.
If the detection criterion is satisfied earlier, a measurement cycle will not be started and the switches P1 and P2 stay closed, the motor is switched to VDD.
Every measurement cycle (tMC) has 4 phases. These are detailed in Table 1.
Note that detection and pulse width control will be switched OFF when the battery voltage is below the end-of-life
voltage (VEOL), or if stage 5 is not sufficient to turn the motor.
Table 1 Measurement cycle
SYMBOL |
PHASE |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
tM1 |
1 |
During tM1 the switches P1 and P2 are closed in order to switch the motor to VDD, so the |
|
|
|
induced current flows unaffected through the motor inductance. |
|
|
|
|
|
tM2 |
2 |
Measures the induced current; during a maximum time tM2 all switches are open until a change |
|
|
|
is sensed by one of the level detectors (L1, L2). The motor is short-circuited to VDD. |
|
|
|
Depending on the direction of the interrupted current: |
|
|
|
∙ |
The current flows through diodes D3 and D2, causing the voltage at M1 to decrease in relation |
|
|
|
to M2; |
|
|
∙ |
The current flows through diodes D4 and D1, causing the voltage at M2 to decrease in relation |
|
|
|
to M1. |
|
|
A successfully detected current polarity is normally characterized by a short pulse of |
|
|
|
0.5 to 10 μs with a voltage up to ±2.1 V, failed polarity detection by the maximum pulse width of |
|
|
|
61 μs and a voltage of ±0.5 V (see Fig.7). |
|
|
|
|
|
tM3 |
3 |
The switches P1 and P2 remain closed for the time tM3. |
|
tM4 |
4 |
If the circuit detects fewer pulses than P and N respectively, a pulse of the time tM4 occurs to |
|
|
|
reduce the induced current. Therefore P2 and P1 are opened and N1 and N2 are closed. |
|
|
|
Otherwise P1 and P2 remain closed. |
|
|
|
|
|
1998 Apr 21 |
8 |
 Loading...
Loading...