Philips P87C766BDR-C, P83C766BDA-005, P83C766BDA-004, P83C766BDA-003 Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
P8xCx66 family
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV with OSD and VST
Product specification |
|
1999 Mar 10 |
|||||
File under Integrated Circuits, IC20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
CONTENTS
1FEATURES
2GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3ORDERING INFORMATION
4BLOCK DIAGRAM
5PINNING INFORMATION
6MEMORY ORGANIZATION
7I/O FACILITY
8TIMERS AND EVENT COUNTERS
9REDUCED POWER MODE
10I2C-BUS SERIAL I/O
11INTERRUPT SYSTEM
12OSCILLATOR CIRCUITRY
13RESET CIRCUITRY
14PIN FUNCTION SELECTION
15ANALOG CONTROL
16ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS (ADC)
17ON-SCREEN DISPLAY (OSD)
18EPROM PROGRAMMER
19SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS ADDRESS MAP
20LIMITING VALUES
21CHARACTERISTICS
22PINNING CHARACTERIZATION
23PACKAGE OUTLINES
24SOLDERING
25DEFINITIONS
26LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
27PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1999 Mar 10 |
2 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
1 FEATURES
1.1P80C51 CPU core
∙80C51 8-bit CPU
∙64-kbyte Multiple Programming ROM (MTP ROM)
∙Two 16-bit timer/event counters
∙Crystal oscillator for system clock (up to 12 MHz)
∙12 source, 12 vector interrupt structure with two priority levels
∙Enhanced architecture with:
–Non-page orientated instructions
–Direct addressing
–Four 8-byte RAM register banks
–Stack depth up to 128 bytes
–Multiply, divide, subtract and compare instructions.
1.2P8xCx66 family
∙ROM/RAM: see Table 1
∙Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) outputs:
–One 14-bit PWM output for Voltage Synthesized Tuning (VST)
–Eight 7-bit PWM outputs for analog controls.
∙3 Analog-to-Digital (ADC) inputs with 4-bit DAC and comparator
∙LED driver port:
–All I/O port lines with 10 mA LED drive capability (VO <1.0 V)
–Up to 5 LEDs can be driven at any one time.
∙Serial I/O:
–Multi-master I2C-bus interface
–Maximum I2C-bus frequency 400 kHz.
∙Watchdog timer
∙Improved EMC measures and slope controlled I/Os
∙OSD functions:
–Programmable VSYNC and HSYNC active levels
–Display RAM: 192 × 12 bits
–Display character fonts: 128 (126 customer fonts plus 2 reserved codes)
–63 vertical starting positions controlled by software
–110 horizontal starting positions controlled by software
–Character size: 4 different character sizes on a line-by-line basis
–Character matrix: 12 × 18 with no spacing between characters
–Foreground colours: 8 on a character-by-character basis
–Background/shadowing modes: two primary modes - TV mode and Frame mode on a frame basis. Each primary mode has four sub-modes on a line basis: Sub-mode 1: Superimpose (no background) Sub-mode 2: North-West shadowing
Sub-mode 3: Box background Sub-mode 4: Border shadowing
–Background colours: 8 on a word-by-word basis, available in all four sub-modes
–Display RAM starting address is programmable; fast switching between banks of display (RAM) characters is possible through software control
–HSYNC driven PLL for OSD clock (4 to 12 MHz)
–Character blinking ratio: 1 : 1
–Character blinking frequency: programmable using fVSYNC divisors of 32 and 64, on a character basis
–Flexible display format using the Carriage Return code and the Space codes
–Display RAM address post incremented each time new data is written into RAM
–Vertical jitter cancelling circuit to avoid unstable VSYNC leading edge mismatch with HSYNC signal
–OSD meshing.
∙Power-on reset
∙Packages: SDIL42 (PLCC68 for piggy-back only)
∙Operating voltage: 4.5 to 5.5 V
∙Operating temperature: −20 to +70 °C
∙System clock frequency: 4 to 12 MHz
∙OSD clock frequency: 4 to 12 MHz.
1999 Mar 10 |
3 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The P8xCx66 family consists of the following devices:
∙P83C266
∙P83C366
∙P83C566
∙P83C766
∙P87C766.
The P8xCx66 family are 80C51-based microcontrollers designed for medium-high to high-end TV control applications. The P8xCx66 devices incorporate many unique features on-chip, giving them a competitive edge over similar devices from other manufacturers.
The Philips 80C51 CPU is object code compatible with the industry standard 80C51. All devices are manufactured in an advanced CMOS technology.
The P8xCx66 family also function as arithmetic processors having facilities for both binary and BCD arithmetic plus bit handling capabilities. The instruction set consists of over 100 instructions: 49 one-byte, 46 two-byte and
16 three-byte. Multiply and divide instructions are implemented by hardware with a cycle time of 4 μs (fCLK = 12 MHz).
The term P8xCx66 is used throughout this data sheet to refer to all family members; differences between devices are highlighted in the text.
Table 1 Memory structure for the different family members
MEMORY |
|
P83C266 |
P83C366 |
P83C566 |
P83C766 |
P87C766 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ROM |
|
24 kbytes |
32 kbytes |
48 kbytes |
64 kbytes |
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RAM |
|
512 bytes |
512 bytes |
1 kbyte |
1 kbyte |
2 kbytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EPROM |
|
− |
− |
− |
− |
64 kbytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main memory |
|
256 bytes |
256 bytes |
256 bytes |
256 bytes |
256 bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Auxiliary RAM |
|
256 bytes |
256 bytes |
768 bytes |
768 bytes |
1792 bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 ORDERING INFORMATION |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE NUMBER |
|
|
|
PACKAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NAME |
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
VERSION |
||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
P83C266BDR |
|
SDIP42 |
plastic shrink dual in-line package; 42 leads (600 mil) |
SOT270-1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P83C366BDR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P83C366CBP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P83C566BDR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P83C766BDP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P87C766BDR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P87C766CBP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
P83C366BDA |
|
PLCC68 |
plastic leaded chip carrier; 68 leads |
|
SOT188-2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P83C566BDA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P83C766BDA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P87C766CBA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
4 |

|
_ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 Mar 1999 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pagewidth full ook, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BLOCK 4 |
|
|
VDDD VSSD |
T1(3) |
T0(3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
FB |
B |
G |
R |
VSYNC |
HSYNC |
DIAGRAM |
|
|
|
TWO 16-BIT |
8-BIT |
|
|
ROM |
RAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDDA |
|
|
XTALIN |
|
|
32 KBYTES(1) |
|
(1) |
ON SCREEN DISPLAY |
||||||||||
|
|
TIMER/ |
WATCHDOG |
|
OR |
512 BYTES |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
COUNTERS |
TIMER |
|
|
OR |
|
|
|
|
(OSD) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
EPROM |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(T0 AND T1) |
(T3) |
|
|
2 KBYTES |
|
|
|
|
|
VSSA |
||||
|
XTALOUT |
|
|
64 KBYTES(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PLL |
|
|
|
|
P8xCx66 |
||
|
|
CPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8-bit internal bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
VPP |
80C51 CORE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
EXCLUDING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ROM/RAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FUNCTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 × 4-BIT |
I2C-BUS |
||
|
|
|
PARALLEL |
COMBINED |
|
8 × 7-BIT |
|
14-BIT DAC |
|
||||||||
|
|
6 |
I/O PORT |
PARALLEL |
|
|
DACS |
|
|
ADCS |
|
INTERFACE |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
I/O PORTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
internal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGL302 |
|
|
6 |
|
8 |
8 |
4 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADC1(5) |
|
|
|
|
external |
|
P0 |
P1 |
P3 |
P5 |
PWM0 to PWM7(4) |
|
|
TPWM(4) |
ADC0(5) |
ADC2(5) |
SDA(3) SCL(3) |
|||
|
|
interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1)For the P83C366.
(2)For the P87C766.
(3)Alternative functions of Port 1.
(4)Alternative functions of Port 5, except PWM7 which is an alternative function of Port 3.
(5)Alternative functions of Port 3.
Fig.1 P83C366 and P87C766 block diagram.
TV PAL/SECAM for Microcontrollers VST and OSD with
family P8xCx66
Semiconductors Philips
specification Product
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1Pinning
|
|
|
|
VDDD |
P5.0/TPWM |
1 |
|
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5.1/PWM0 |
2 |
|
41 |
P1.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
P5.2/PWM1 |
3 |
|
40 |
P1.6/SDA |
|
|
|
|
|
P5.3/PWM2 |
4 |
|
39 |
P1.5/SCL |
|
|
|
|
|
P5.4/PWM3 |
5 |
|
38 |
P1.4/T1 |
|
|
|
|
|
P5.5/PWM4 |
6 |
|
37 |
P1.3/INT0 |
|
|
|
|
|
P5.6/PWM5 |
7 |
|
36 |
P1.2/T0 |
|
|
|
|
|
P5.7/PWM6 |
8 |
|
35 |
P1.1/INT1 |
|
|
|
|
|
P3.0/ADC0 |
9 |
|
34 |
P1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
P3.1/ADC1 |
10 |
|
33 |
RESET |
|
|
P8xCx66 |
|
|
P3.2/ADC2 |
11 |
32 |
XTALOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P3.3/PWM7 |
12 |
|
31 |
XTALIN |
|
|
|
|
VPP |
P0.0 |
13 |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
VSSA |
P0.1 |
14 |
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
VDDA |
P0.2 |
15 |
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.3 |
16 |
|
27 |
VSYNC |
|
|
|
|
|
P0.4 |
17 |
|
26 |
HSYNC |
|
|
|
|
|
P0.5 |
18 |
|
25 |
FB |
|
|
|
|
|
P0.6 |
19 |
|
24 |
R |
|
|
|
|
|
P0.7 |
20 |
|
23 |
G |
VSSD |
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
22 |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGL301 |
|
|
Fig.2 Pin configuration (SDIP42).
1999 Mar 10 |
6 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
n.c. 10 P5.6/PWM5 11 P5.7/PWM6 12 P3.0/ADC0 13 PH1SEM 14 S1ESEM 15 P3.1/ADC1 16 P2.0 17
P3.2/ADC2 18 P2.1 19 P3.3/PWM7 20 P2.2 21 P2.3 22 P0.0 23 P0.1 24 P0.2 25
OSD_EPR_TST 26
n.c. |
|
P5.5/PWM4 |
|
P5.4/PWM3 |
|
P5.3/PWM2 |
|
P5.2/PWM1 |
|
P5.1/PWM0 |
|
P5.0/TPWM |
|
INTD |
|
V |
|
V |
|
V |
|
P1.7 |
|
P1.6/SDA |
|
P1.5/SCL |
|
P1.4/T1 |
|
P1.3/INT0 |
|
n.c. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SS |
|
DDD1 |
|
SSD1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
8 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
68 |
|
67 |
|
66 |
|
65 |
|
64 |
|
63 |
|
62 |
|
61 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
n.c. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 |
P1.2/T0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
58 |
P1.1/INT1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57 |
P1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56 |
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
EMUPBX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54 |
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53 |
IDLPDEM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P87C766 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52 |
P2.7 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
XTALOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
XTALIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
VPP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
P2.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
VSSA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
VDDA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
n.c. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
28 |
|
29 |
|
30 |
|
31 |
|
32 |
|
33 |
|
34 |
|
35 |
|
36 |
|
37 |
|
38 |
|
39 |
|
40 |
|
41 |
|
42 |
|
43 |
MGL329 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
n.c. |
|
P0.3 |
|
P0.4 |
|
P0.5 |
|
P0.6 |
|
P0.7 |
|
DDD |
|
SS |
|
P2.4 |
|
P2.5 |
|
B |
|
G |
|
R |
|
FB |
|
HSYNC |
|
VSYNC |
|
n.c. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Fig.3 Pin configuration (PLCC68).
1999 Mar 10 |
7 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
5.2Pin description
Table 2 Pin description for SDIP42 and PLCC68 packages
SYMBOL |
PIN |
I/O |
DESCRIPTION |
||
|
|
||||
SDIP42 |
PLCC68 |
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5.0/TPWM |
1 |
3 |
I/O |
Port 5: 8-bit open-drain, bidirectional port.(P5.0 to P5.7) with 8 alternative |
|
|
|
|
|
functions. |
|
P5.1/PWM0 |
2 |
4 |
|
||
|
TWPM: 14-bit PWM output. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
P5.2/PWM1 |
3 |
5 |
|
||
|
PWM0 to PWM6: 7-bit PWM outputs. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
P5.3/PWM2 |
4 |
6 |
|
||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5.4/PWM3 |
5 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5.5/PWM4 |
6 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5.6/PWM5 |
7 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5.7/PWM6 |
8 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P3.0/ADC0 |
9 |
13 |
I/O |
Port 3: 4-bit open-drain, bidirectional port.(P3.0 to P3.3) with 4 alternative |
|
|
|
|
|
functions. |
|
P3.1/ADC1 |
10 |
16 |
|
||
|
ADC0 to ADC2: ADC inputs. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
P3.2/ADC2 |
11 |
18 |
|
||
|
PWM7: 7-bit PWM output. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
P3.3/PWM7 |
12 |
20 |
|
||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.0 to P0.7 |
13 to 20 |
23 to 25, |
I/O |
Port 0: 8-bit open-drain, bidirectional port (P0.0 to P0.7). |
|
|
|
28 to 32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSSD |
21 |
|
− |
Ground line for digital circuits. |
|
B |
22 |
37 |
O |
OSD blue colour output. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G |
23 |
38 |
O |
OSD green colour output. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
24 |
39 |
O |
OSD red colour output. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FB |
25 |
40 |
O |
OSD fast blanking output. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HSYNC |
26 |
41 |
I |
TV horizontal sync Schmitt trigger input (for OSD synchronization). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSYNC |
27 |
42 |
I |
TV vertical sync Schmitt trigger input (for OSD synchronization). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDDA |
28 |
45 |
− |
5 V analog power supply. |
|
VSSA |
29 |
46 |
− |
Ground line for analog circuits. |
|
VPP |
30 |
48 |
I |
+12.75 V programming voltage supply (OTP) for EPROM only. 0 V in |
|
|
|
|
|
normal application. For the ROM version this pin is not connected. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XTALIN |
31 |
50 |
I |
Crystal input. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XTALOUT |
32 |
51 |
O |
Crystal output. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
8 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
SYMBOL |
PIN |
I/O |
DESCRIPTION |
||
|
|
||||
SDIP42 |
PLCC68 |
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESET |
33 |
54 |
I |
Reset input. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1.0 |
34 |
57 |
I/O |
Port 1: 8-bit open-drain, bidirectional port (P1.0 to P1.7) with 6 alternative |
|
|
|
|
|
functions. |
|
P1.1/INT1 |
35 |
58 |
|
||
|
INT1 and INT0: external interrupts 1 and 0. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
P1.2/T0 |
36 |
59 |
|
||
|
T1 and T0: 16-bit timer/counter 1 and 0 inputs |
||||
|
|
|
|
||
P1.3/INT0 |
37 |
62 |
|
||
|
SCL: I2C-bus clock line |
||||
P1.4/T1 |
38 |
63 |
|
SDA: I2C-bus data line |
|
P1.5/SCL |
39 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1.6/SDA |
40 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1.7 |
41 |
66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDDD |
42 |
33 |
− |
5 V digital power supply. |
|
VSS |
− |
1, 49, 56 |
− |
Ground lines. |
|
n.c. |
− |
9, 10, 27, |
− |
not connected |
|
|
|
43, 44, |
|
|
|
|
|
60, 61 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTD |
− |
2 |
I |
These 3 signals are used for metalink+ emulation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PH1SEM |
− |
14 |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S1ESEM |
− |
15 |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.0 |
− |
17 |
I/O |
Port 2: 8-bit open-drain, bidirectional port (P2.0 to P2.7). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.1 |
− |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.2 |
− |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.3 |
− |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.4 |
− |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.5 |
− |
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.6 |
− |
47 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2.7 |
− |
52 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OSD_EPR_ |
− |
26 |
I/O |
OSD EPROM test enable. |
|
TST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IDLPDEM |
− |
53 |
I/O |
These 2 signals are used for metalink+ emulation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EMUPBX |
− |
55 |
I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSSD1 |
− |
67 |
− |
Ground line for digital circuits. |
|
VDDD1 |
− |
68 |
− |
5 V digital power supply. |
|
1999 Mar 10 |
9 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
6 MEMORY ORGANIZATION
The P8xCx66 family provides 24, 32, 48 or 64 kbytes of program memory (ROM/EPROM) plus 512, 1024 or 2048 bytes of data memory (RAM) on-chip (see Table 1). The device has separate address spaces for program and data memory (see Fig.4). These devices have no external memory access capability as the RD (read), WR (write), EA (External Access), PSEN (read strobe) and ALE (Address Latch Enable) signals are not bonded out.
6.1Data memory
The P8xCx66 family contains 512, 1024 or 2048 bytes of internal RAM and 56 Special Function Registers (SFRs). Figure 4 shows the internal data memory space divided into the lower 128, the upper 128, AUX-RAM and the SFR space. The lower 128 bytes of internal RAM are organized as shown in Fig.5. The lowest 32 bytes are grouped into 4 banks of 8 registers. Program instructions refer to these registers as R0 to R7. Two bits in the Program Status Word (PSW) select which register bank is in use. The next 16 bytes above the register bank form a block of bit-addressable memory space. The 128 bits in this area can be directly addressed by the single-bit manipulation instructions. The remaining registers (30H to 7FH) are directly and indirectly byte addressable. The registers that reside at addresses above 7FH and up to FFH can only be accessed indirectly. These register addresses overlap the SFR addresses as described in Section 6.2.
6.2Special Function Registers
The upper 128 bytes are the address locations of the SFRs when accessed directly. SFRs include the port latches, timers, 7-bit PWMs, 14-bit VST PWM, ADCs and OSD control registers. These registers can only be accessed by direct addressing. There are
128 bit-addressable locations in the SFR address space (SFRs with addresses divisible by eight). Their addresses are a multiple of 08H, from 80H to F8H. (i.e., 80H, 88H, 90H, 98H etc.). See Chapter 19 for SFR list.
6.3AUX RAM
The 1792 byte (P87C766) or 768 byte (P83C766) AUX RAM, while physically located on-chip, logically
occupies the first 1792/768 bytes of external data memory. As such, it is indirectly addressed in the same way as external data memory using MOVX instructions in combination with any of the registers R0, R1 or DPTR.
6.4Addressing
The P80C51 CPU has five methods for addressing source operands
∙Register
∙Direct
∙Register-indirect
∙Immediate
∙Base-register-plus index-register-indirect.
The first three methods can be used for addressing destination operands. Most instructions have a ‘destination/source’ field that specifies the data type, addressing methods and operands involved.
For operations other than MOVs, the destination operand is also a source operand.
Access to memory addressing is as follows:
∙Registers in one of the four register banks through register direct or indirect
∙Internal RAM (128 bytes) through direct or register-indirect
∙Special Function Registers through direct
∙External data memory through register-indirect (for AUX RAM)
∙Program memory look-up tables through base-register-plus index-register-indirect.
1999 Mar 10 |
10 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
|
64 KBYTES(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OVERLAPPED SPACE |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
AUX RAM |
255 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1792 BYTES(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SPECIAL |
|
|
|
|
|
OR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FUNCTION |
|
|
|
|
|
768 BYTES(3) |
127 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REGISTERS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERNAL |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DATA RAM |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERNAL |
|
|
|
INTERNAL DATA MEMORY |
MGM680 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
PROGRAM MEMORY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(1)For the P83C766 and the P87C766.
(2)For the P87C766.
(3)For the P83C566 and the P83C766.
Fig.4 Memory map.
7FH
|
|
30H |
|
|
|
2FH |
|
|
|
|
bit-addressable space |
|
|
|
(bit addresses 00H to 7FH) |
|
|
20H |
|
R7 |
1FH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R0 |
18H |
|
|
R7 |
17H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R0 |
10H |
4 banks of 8 registers |
|
R7 |
0FH |
(R0 to R7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R0 |
08H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R7 |
07H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R0 |
0 |
MGM677 |
|
Fig.5 The lower 128 bytes of internal RAM.
1999 Mar 10 |
11 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
7 I/O FACILITY
7.1I/O ports
The SDIP42 package has 28 I/O lines treated as 28 individual addressable bits or as 3 parallel 8-bit
addressable ports (Ports 0, 1 and 5) and one 4-bit port (Port 3).
When these 28 I/O lines are used as input ports, the corresponding bits in SFRs P0, P1, P3 and P5 should be set to a logic 1 to facilitate the external input signal.
Ports 1, 3 and 5 also perform the following alternative functions.
Port 1. Used for a number of special functions:
∙Provides the external interrupt inputs (INT0 and INT1)
∙Provides the 16-bit timer/counter inputs (T0 and T1)
∙Provides the I2C-bus data and clock signals (SDA and SCL)
∙P1.0 and P1.7 can be used as external interrupt inputs.
Port 3. Only 4 lines available for alternative functions:
∙7-bit PWM output (PWM7)
∙ADC inputs ADC0 to ADC2.
Port 5.
∙Provides the 14-bit PWM output (TPWM)
∙7-bit PWMs outputs (PWM0 to PWM6).
To enable the alternative functions of Ports 1, 3 and 5, the port bit latch of its associated SFR must contain a logic 1.
Each port consists of a latch (SFRs P0, P1, P3 and P5), an output driver and an input buffer.
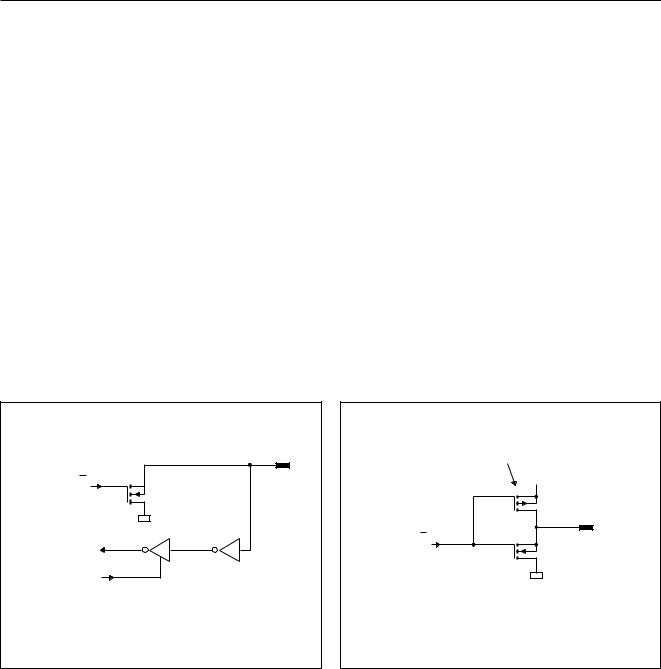
7.2Port configurations
1.Open-drain quasi-bidirectional I/O with n-channel pull-down (see Fig.6). Use as an output requires the connection of an external pull-up resistor. Use as an input requires to write a logic 1 to the port latch before reading the port line.
2.Push-pull; gives drive capability of the output in both polarities, see Fig.7.
|
I/O pin |
handbook, halfpage |
strong pull-up |
Q |
|
|
+5 V |
|
|
|
|
from port latch |
n |
|
p1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
output pin |
|
|
Q |
|
input data |
|
from port latch |
n |
|
INPUT |
|
|
read port pin |
BUFFER |
|
MGM679 |
MGK547 |
|
Fig.6 Open-drain port. |
Fig.7 Push-pull port. |
1999 Mar 10 |
12 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
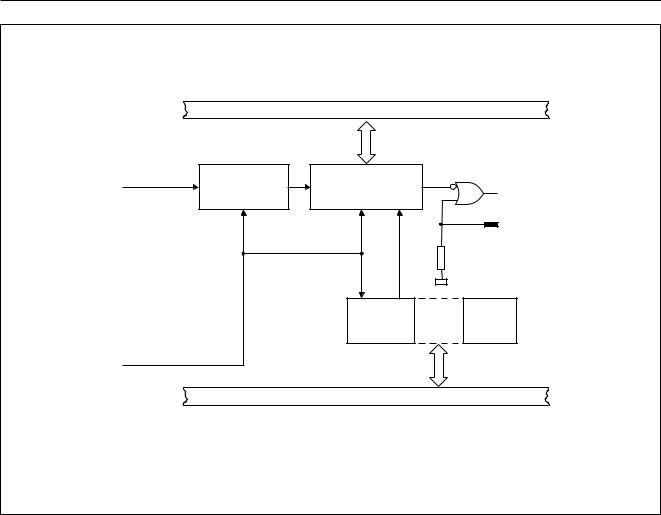
8 TIMERS AND EVENT COUNTERS
The P8xCx66 contains two 16-bit timers/counters: Timer 0 and Timer 1 and also an 8-bit Watchdog timer.
8.116-bit timer/counters (T0 and T1)
Timer 0 and Timer 1 perform the following functions:
·Measure time intervals and pulse durations
·Count events
·Generate interrupt requests.
Timer 0 and Timer 1 can be independently programmed to operate in one of four modes.
Mode 0 8-bit timer or counter with divide-by-32 prescaler.
Mode 1 16-bit time-interval or event counter.
Mode 2 8-bit time-interval or event counter with automatic reload upon overflow.
Mode 3 Timer 0 establishes TL0 and TL1 as two separate counters.
In the ‘timer’ function, the register is incremented every machine cycle. Since a machine cycle consists of
12 oscillator periods, the count rate is 1¤12fosc.
In the ‘counter’ function, the register is incremented in response to a HIGH-to-LOW transition. Since it takes 2 machine cycles (24 oscillator periods) to recognize a HIGH-to-LOW transition, the maximum count rate is
1¤24fosc. To ensure that a given level is sampled, it should be held for at least one complete machine cycle.
8.2Watchdog timer (T3)
In addition to the standard timers, a Watchdog timer is implemented on-chip. The Watchdog timer generates a hardware reset upon overflow. In this way a microcontroller system can recover from erroneous processor states caused by electrical noise, RFI or unexpected ROM code behaviour.
The Watchdog timer consists of an 8-bit timer with an 11-bit prescaler as shown in Fig.8. The prescaler input frequency is 1¤12fosc. The 8-bit timer is incremented every ‘t’ seconds where ‘t’ is calculated as shown below:
t |
= 12 ´ 2048 |
1 |
´ -------- |
||
|
|
fosc |
The 8-bit timer is an up-counter so a value 00H gives the maximum timer interval (510 ms at 12 MHz, 1536 ms at 4 MHz), and a value of FFH gives the minimum timer interval (2 ms at 12 MHz, 6 ms at 4 MHz). When the 8-bit timer produces an overflow a short internal reset pulse is generated which will reset the P8xCx66.
The timer has no disable function. Consequently, all applications must reload the timer within the previously loaded timer interval otherwise a reset will occur. The timer is not stopped in the Idle mode. The interrupt routine for the Idle mode should also service the Watchdog timer.
The Watchdog timer is controlled by the WLE bit in the Power Control Register (see Section 9.6). The WLE bit must be set by the Watchdog timer service routine before the timer interval can be loaded into T3. A load of T3 automatically clears the WLE bit.
A system reset clears the Watchdog timer and the prescaler.
8.2.1WATCHDOG TIMER REGISTER (WDT)
Table 3 Watchdog timer Register (SFR address FFH)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T37 |
T36 |
T35 |
T34 |
T33 |
T32 |
T31 |
T30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
13 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
andbook, full pagewidth |
INTERNAL BUS |
1/12 fosc |
PRESCALER |
WDT REGISTER |
|
11-BIT |
(8-BIT) |
internal reset |
|
|
CLEAR |
LOAD LOADEN |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
RESET |
|
|
|
RRESET |
|
|
CLEAR |
|
|
|
WLE |
IDL |
|
|
|
LOADEN |
|
|
PCON.4 |
PCON.0 |
write T3 |
|
|
|
|
|
INTERNAL BUS |
|
|
|
|
MGL298 |
Fig.8 Block diagram of the Watchdog timer.
1999 Mar 10 |
14 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
9 REDUCED POWER MODE
Only one reduced power mode is implemented; this is the Idle mode.
During Idle mode all blocks are inactive except Timer 0, Timer 1, INT0, INT1 and the Watchdog timer. These active functions may generate an interrupt (if their interrupts are enabled) and this will cause the device to leave the Idle mode.
The Idle mode is activated by software using the PCON register; this register is described in Section 9.6.
9.1Idle mode
The instruction that sets PCON.0 is the last instruction executed before entering the Idle mode. Once in the Idle mode, the internal clock is gated away from the CPU and from all derivative functions (PWM/TPWM/ADC/I2C-bus), except Timer 0, Timer 1 and interrupts INT0 and INT1. The Watchdog timer remains active. The CPU status is preserved along with the Stack Pointer, Program Counter, Program Status Word and the Accumulator. The RAM and all other registers maintain their data during Idle mode and the port pins retain the logic states held at Idle mode activation. The OSD clock is gated away from OSD circuit in Idle mode.
9.2Recover from Idle mode
There are 3 methods used to terminate the Idle mode.
9.2.1VIA AN INTERRUPT
Activation of INT0, INT1 or an interrupt from Timer 0 or Timer 1 will cause PCON to be cleared by hardware thus terminating the Idle mode. The interrupt is serviced and following the RETI instruction, the next instruction to be executed will be the one following the instruction that put the device in the Idle mode. All the other interrupts are disabled and will not generate an interrupt to wake-up the CPU.
9.2.2VIA RESET
The second method of terminating the Idle mode is with an external hardware reset. Since the oscillator is still running, the hardware reset is required to be active for only two machine cycles to complete the reset operation. Reset redefines all SFRs, but does not effect the on-chip RAM.
9.2.3VIA A WATCHDOG TIMER OVERFLOW
If the Watchdog timer is allowed to overflow or an erroneous processor state causes an overflow, a hardware reset will be generated, thus terminating the Idle mode.
9.3General purpose flags (GF0 and GF1)
Flags GF0 and GF1 may be used to determine whether the interrupt was received during normal execution or Idle mode. For example, the instruction that writes to PCON.0 to set the Idle mode can also set or clear one or both flags. When the Idle mode is terminated by an interrupt, the service routine can examine the status of the flag bits.
9.4Output in Idle mode
∙Ports will keep the value they had before entering the Idle mode
∙The PWM0 to PWM7 outputs will be LOW
∙The TPWM output will be LOW
∙The I2C-bus output is HIGH
∙The pins R, G, B and FB will be the ‘inverse of Bp’, (defined by bit 2 of SFR OSCON).
9.5Pending interrupts in Idle mode
If pending interrupts (I2C-bus, VSYNC, P1.0 to P1.4 or P1.7) are present at the moment the CPU is switched to Idle mode, then these interrupts will wake-up the CPU.
If this is not wanted then before entering the Idle mode all interrupts must be disabled, except those interrupts allowed to wake-up the CPU (INT0, INT1, Timer 0 and Timer1). New interrupts from I2C-bus, VSYNC,
P1.0 to P1.4 or P1.7 are disabled as soon as Idle mode is entered.
For example if a high priority interrupt is serviced just before the instruction which sets PCON.0 and a lower priority interrupt is generated during the interrupt service routine of the high priority interrupt, then the lower priority interrupt is pending. After the high priority interrupt is serviced (last instruction of routine is RETI) the main program will execute at least one more instruction to prevent a deadlock of the main program. In this case, it is the instruction which sets the PCON.0 bit (enter Idle mode). The pending lower level interrupt will, if enabled, immediately wake-up the CPU for an interrupt service, even though this interrupt is not INT0, INT1 or an interrupt from Timer 1 or Timer 0.
1999 Mar 10 |
15 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
9.6Power Control Register (PCON)
PCON is byte addressable only.
Table 4 Power Control Register (SFR address 87H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
− |
− |
WLE |
|
GF1 |
|
GF0 |
0 |
IDL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 5 Description of PCON bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7 |
− |
These 3 bits are reserved. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
4 |
WLE |
Watchdog Load Enable. If WLE = 1, the Watchdog timer can be loaded. If WLE = 0, |
|||||||
|
|
the Watchdog timer cannot be loaded. |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
3 |
GF1 |
General purpose flag 1. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2 |
GF0 |
General purpose flag 0. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 |
− |
This bit is reserved and must be set to a logic 0. |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||||
0 |
IDL |
Idle mode select. If IDL = 1, the Idle mode is selected. If IDL = 0, the Idle mode is |
|||||||
|
|
inhibited, i.e. normal operation. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
16 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
10 I2C-BUS SERIAL I/O
10.1The I2C-bus
The serial port supports the two line I2C-bus. The I2C-bus consists of a serial data line (SDA) and a serial clock line (SCL). These lines can also function as I/O port lines P1.6 and P1.5 respectively. To utilize this facility pins P1.5/SCL and P1.6/SDA must be configured as alternative functions instead of port lines; see Section 10.8.
The system is unique because data transport, clock generation, address recognition and bus control arbitration are all controlled by hardware.
Full details of the I2C-bus are given in the document
“The I2C-bus and how to use it”. This document may be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
10.2Operation modes
The I2C-bus serial I/O has complete autonomy in byte handling and operates in four modes
∙Master transmitter
∙Master receiver
∙Slave transmitter
∙Slave receiver.
These functions are controlled by the S1CON register. S1STA is the status register whose contents may also be used as a vector to various service routines. S1DAT is the data shift register and S1ADR the slave address register. Slave address recognition is performed by hardware.
SLAVE ADDRESS GC 

S1ADR
SDA 

 SHIFT REGISTER
SHIFT REGISTER
S1DAT
ARBITRATION LOGIC
SCL 
 BUS CLOCK GENERATOR
BUS CLOCK GENERATOR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S1CON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTERNAL BUS
S1STA |
MBC749 - 1 |
Fig.9 Block diagram of I2C-bus serial I/O.
1999 Mar 10 |
17 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
10.3Serial Control Register (S1CON)
Table 6 Serial Control Register (SFR address D8H)
7 |
6 |
|
5 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CR2 |
ENS1 |
|
STA |
STO |
|
SI |
|
AA |
|
CR1 |
|
CR0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Table 7 Description of S1CON bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
6 |
ENSI |
Enable Serial I/O. When ENSI = 0, the SIO is disabled and reset. The SDA and SCL |
|||||||||||
|
|
outputs are in a high-impedance state; P1.5 and P1.6 function as open-drain ports. |
|||||||||||
|
|
When ENSI = 1, the SIO is enabled. The P1.5 and P1.6 port latches must be set to |
|||||||||||
|
|
logic 1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
5 |
STA |
START flag. When the STA bit is set in Slave mode, the SIO hardware checks the |
|||||||||||
|
|
status of the I2C-bus and generates a START condition if the bus is free. If STA is set |
|||||||||||
|
|
while the SIO is in Master mode, SIO transmits a repeated START condition. |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
4 |
STO |
STOP flag. With this bit set while in Master mode a STOP condition is generated. When |
|||||||||||
|
|
a STOP condition is detected on the bus, the SIO hardware clears the STO flag. In the |
|||||||||||
|
|
Slave mode, the STO flag may also be set to recover from an error condition. In this |
|||||||||||
|
|
case, no STOP condition is transmitted to the I2C-bus interface. However, the SIO |
|||||||||||
|
|
hardware behaves as if a STOP condition has been received and releases SDA and |
|||||||||||
|
|
SCL. The SIO then switches to the ‘not addressed’ slave receiver mode. The STO flag |
|||||||||||
|
|
is automatically cleared by hardware. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
3 |
SI |
SIO interrupt flag. When the SI flag is set, an acknowledge is returned after any one of |
|||||||||||
|
|
the following conditions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
∙ |
A START condition is generated in Master mode |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
∙ |
Own slave address received during AA = 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
∙ |
General call address received while S1ADR.0 = 1 and AA = 1 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
∙ |
Data byte received or transmitted in Master mode (even if arbitration is lost) |
|
|||||||||
|
|
∙ |
Data byte received or transmitted as selected slave |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
∙ |
STOP or START condition received as selected slave receiver or transmitter. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
2 |
AA |
Assert Acknowledge. When the AA flag is set, an acknowledge (LOW level to SDA) |
|||||||||||
|
|
will be returned during the acknowledge clock pulse on the SCL line when: |
|
||||||||||
|
|
∙ |
Own slave address is received |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
∙ |
General call address is received (S1ADR.0 = 1) |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
∙ |
Data byte received while device is programmed as a Master receiver |
|
|||||||||
|
|
∙ |
Data byte received while device is a selected Slave receiver. |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
With AA = 0, no acknowledge will be returned. Consequently, no interrupt is requested |
|||||||||||
|
|
when the ‘own slave address’ or general call address is received. |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
7 |
CR2 |
Clock Rate selection. These three bits determine the serial clock frequency when SIO |
|||||||||||
|
|
is in a Master mode; see Table 8. The maximum I2C-bus frequency is 400 KHz. |
|||||||||||
1 |
CR1 |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
CR0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
18 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
Table 8 Selection of SCL frequency in Master mode
CR2 |
CR1 |
CR0 |
fosc DIVISOR |
BIT RATE (kHz) at fosc = 12 MHz |
0 |
0 |
0 |
60 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
1600 |
7.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
40 |
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
30 |
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
240 |
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
3200 |
3.75 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
160 |
75 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
120 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.4Status Register (S1STA)
S1STA is an 8-bit read-only Special Function Register. The contents of S1STA may be used as a vector to a service routine. This optimizes response time of the software and consequently that of the I2C-bus. The status codes for all possible modes of the I2C-bus interface are given in Table 12. The abbreviations used in Table 12 are defined in Table 11.
Table 9 Status Register (SFR address D9H)
7 |
|
6 |
5 |
|
4 |
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SC4 |
|
|
|
SC3 |
SC2 |
|
SC1 |
|
SC0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Table 10 Description of S1STA bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BIT |
|
|
|
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
7 to 3 |
|
|
SC4 to SC0 |
5-bit status code; see Table 12. |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2 to 0 |
|
|
− |
These 3 bits are held LOW. |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Table 11 Abbreviations used in Table 12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
SLA |
7-bit slave address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
R |
read bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
W |
write bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
ACK |
acknowledgment (Acknowledge bit = 0) |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
not acknowledge (Acknowledge bit = 1) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
ACK |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
DATA |
8-bit byte to or from the I2C-bus |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
MST |
master |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
SLV |
slave |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
TRX |
transmitter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
REC |
receiver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
19 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
Table 12 Status codes
S1STA VALUE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MST/TRX mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
08H |
a START condition has been transmitted |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
10H |
a repeated START condition has been transmitted |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
18H |
SLA and W have been transmitted, ACK received |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
20H |
SLA and W have been transmitted. |
|
|
|
|
received |
|||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
28H |
DATA of S1DAT has been transmitted, ACK received |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
30H |
DATA of S1DAT has been transmitted, |
|
|
|
received |
||||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
38H |
arbitration lost in SLA, R/W or DATA |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MST/REC mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
38H |
arbitration lost while returning |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
40H |
SLA and R have been transmitted, ACK received |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
48H |
SLA and R have been transmitted, |
|
|
|
|
received |
|||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
50H |
DATA has been received, ACK returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
58H |
DATA has been received, |
|
|
returned |
|||||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLV/REC mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
60H |
own SLA and W have been received, ACK returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
68H |
arbitration lost in SLA, R/W as MST; own SLA and W have been received, |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
ACK |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
70H |
general CALL has been received, ACK returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
78H |
arbitration lost in SLA, R/W as MST; general CALL has been received |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
80H |
previously addressed with own SLA; DATA byte received, ACK returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
88H |
previously addressed with own SLA; DATA byte received, |
|
returned |
||||||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
90H |
previously addressed with general CALL; DATA byte has been received, ACK returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
98H |
previously addressed with general CALL; DATA byte has been received, |
|
|
returned |
|||||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
A0H |
a STOP condition or repeated START condition has been received while still addressed |
||||||||||||||||||
|
as SLV/REC or SLV/TRX |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLV/TRX mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
A8H |
own SLA and R have been received. ACK returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
B0H |
arbitration lost in SLA, R/W as MST. Own SLA and R have been received, ACK |
||||||||||||||||||
|
returned |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
B8H |
DATA byte has been transmitted, ACK received |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
C0H |
DATA byte has been transmitted, |
|
|
|
|
received |
|||||||||||||
ACK |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
C8H |
last DATA byte has been transmitted (AA = logic 0) ACK received |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Miscellaneous |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
00H |
bus error during MST mode or SLV mode, due to an erroneous START or STOP |
||||||||||||||||||
|
condition |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
20 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
10.5Data Shift Register (S1DAT)
S1DAT contains the serial data to be transmitted or data that has just been received. Bit 7 is transmitted or received first.
Table 13 |
Data Shift Register (SFR address DAH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
6 |
5 |
|
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D7 |
|
D6 |
D5 |
|
D4 |
D3 |
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.6Slave Address Register (S1ADR)
This 8-bit register may be loaded with the 7-bit slave address to which the controller will respond when programmed as slave receiver/transmitter. The LSB bit (GC) is used to determine whether the general CALL address is recognized.
Table 14 Slave Address Register (SFR address DBH)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLA6 |
SLA5 |
SLA4 |
SLA3 |
|
SLA2 |
SLA1 |
SLA0 |
GC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 15 Description of S1ADR bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
7 to 1 |
SLA6 to |
Own slave address. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
SLA0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
0 |
GC |
When GC = 0, the general CALL address is not recognized. When GC = 1, the general |
||||||
|
|
CALL address is recognized. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.7Internal Status Register (S1IST)
S1IST is an 8-bit read-only Special Function Register and will exist in the design but is not mapped for the user.
Table 16 Internal Status Register (SFR address DCH)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MST |
TRX |
BB |
FB |
ARL |
SEL |
AD0 |
SHRA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.8I2C-bus Control Register (I2CCON)
Table 17 I2C-bus Control Register (SFR address 86H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
− |
− |
− |
− |
I2CE |
− |
− |
Table 18 Description of I2CCON bits |
|
|
|
|
|
||
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 to 3 |
− |
These 5 bits are not used. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
2 |
I2CE |
I2C-bus enable. This bit selects the functions of pins 39 and 40 for the SDIP42 package |
|||||
|
|
(or pins 64 and 65 for the PLCC68 package). When I2CE = 1, the alternative functions |
|||||
|
|
SCL and SDA are selected. When I2CE = 0, these pins act as port lines P1.5 and P1.6. |
|||||
1 to 0 |
− |
These bits are not used. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
21 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
11 INTERRUPT SYSTEM
External events and the real-time driven on-chip peripherals require service by the CPU asynchronous to the execution of any particular section of code. To tie the asynchronous activities of these functions to normal program execution a multiple-source, two-priority-level, nested interrupt system is provided. The P8xCx66 acknowledges interrupt requests from twelve sources as shown in Table 20.
Each interrupt vectors to a separate location in program memory for its service routine. Each source can be individually enabled or disabled by using corresponding bits in the Interrupt Enable Registers (IEN0 and IEN1). The priority level is selected via the Interrupt Priority Registers (IP0 and IP1). All enabled sources can be globally disabled or enabled. The minimum width of the external interrupt signal is ³6 XTAL clocks. The maximum width of the interrupt signal is the total length of all instructions in the interrupt service routine until the clear instruction of the IRQ bit. The external interrupts are INT0, INT1, P1.0, P1.1, P1.2, P1.3, P1.4 and P1.7.
11.1External interrupts INT2 to INT7 and INT9
Port 1 lines also serve as additional interrupts
INT2 to INT7 (P1.0, P1.1, P1.2, P1.3, P1.4 and P1.7). INT7 is used by the derivative functional blocks as follows:
X7 VSYNC interrupt 0063H
Using the IX1 register, each pin may be initialized to be either active HIGH or active LOW except INT7 which is fixed active HIGH because this interrupt is from another derivative function. IRQ1 is the Interrupt Request Flag
Table 20 Interrupt request (priority within level)
Register. Each flag will be set on interrupt request but it must be cleared by software, i.e. via the interrupt software.
11.2Interrupt priority
Each interrupt source can be set to either high or low priority. If both priorities are requested simultaneously, the controller will branch to the high priority vector.
A low priority interrupt can only be interrupted by a high priority interrupt. A high priority interrupt routine cannot be interrupted
11.3Related registers
The following registers are used in conjunction with the interrupt system.
Table 19 Interrupt registers
REGISTER |
ADDRESS |
|
|
Interrupt Polarity Register (IX1) |
E9H |
|
|
Interrupt Request Flag Register (IRQ1) |
C0H |
|
|
Interrupt Enable Register 0 (IEN0) |
A8H |
|
|
Interrupt Enable Register 1 (IEN1); |
E8H |
interrupts INT2 to INT9 |
|
|
|
Interrupt Priority Register 0 (IP0) |
B8H |
|
|
Interrupt Priority Register 1 (IP1); |
F8H |
interrupts INT2 to INT9 |
|
|
|
INTERRUPT MNEMONIC |
SOURCE |
VECTOR ADDRESS |
|
|
|
PX0 (highest) |
external interrupt 0 (INT0) |
0003H |
|
|
|
S1 |
I2C-bus |
002BH |
T0 |
Timer 0 overflow |
000BH |
|
|
|
PX2 |
P1.0 port line |
0033H |
|
|
|
PX6 |
P1.4 port line |
005BH |
|
|
|
PX1 |
external interrupt 1 (INT1) |
0013H |
|
|
|
PX3 |
P1.1 port line |
003BH |
|
|
|
PX7 |
VSYNC interrupt |
0063H |
|
|
|
T1 |
Timer 1 overflow |
001BH |
|
|
|
PX4 |
P1.2 port line |
0043H |
|
|
|
PX5 |
P1.3 port line |
004BH |
|
|
|
PX9 (lowest) |
P1.7 port line |
0073H |
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
22 |
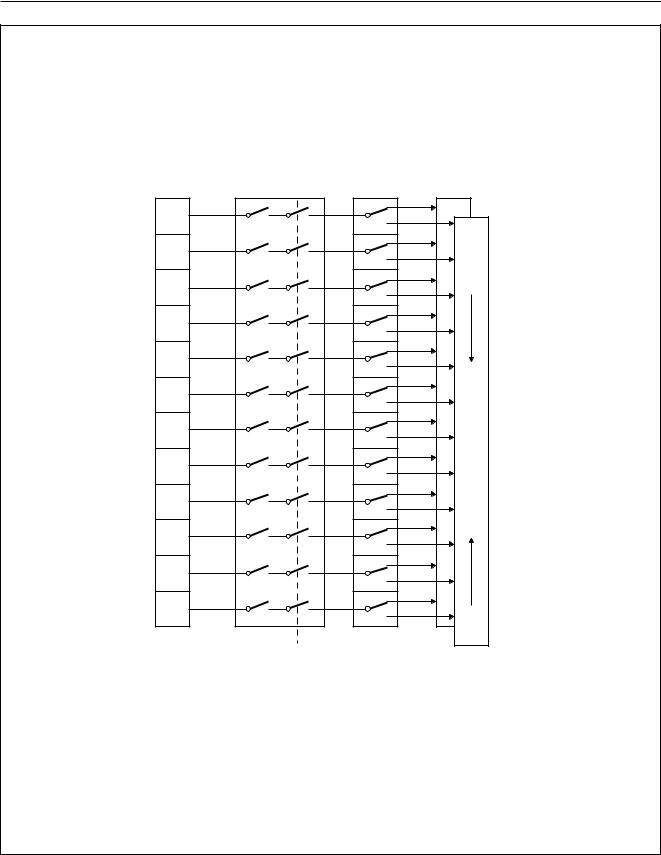
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
INTERRUPT |
IEN0/1 |
IP0/1 |
PRIORITY |
SOURCES |
REGISTERS |
REGISTERS |
|
|
|
HIGH |
PX0 |
|
LOW |
|
|
|
S1 |
|
|
T0 |
|
|
PX2 |
|
|
PX6 |
|
SEQUENCE |
PX1 |
|
|
|
|
|
PX3 |
|
POLLING |
PX7 |
|
|
|
INTERRUPT |
|
T1 |
|
|
|
|
|
PX4 |
|
|
PX5 |
|
|
PX9 |
|
|
|
GLOBAL |
MGL297 |
|
ENABLE |
|
|
|
Fig.10 Interrupt system.
1999 Mar 10 |
23 |
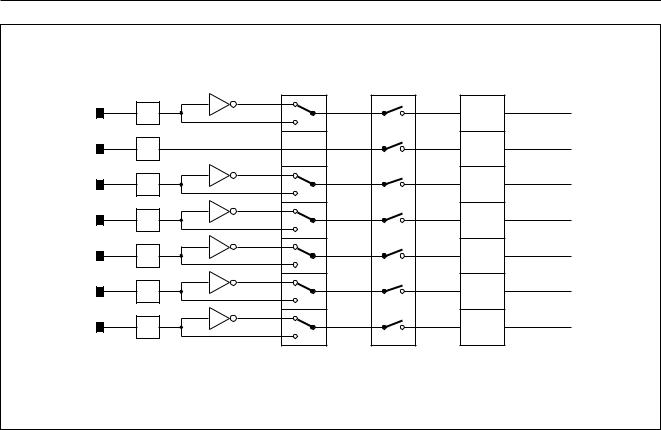
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
IX1 |
IEN1 |
IRQ1 |
P1.7 |
|
X9 |
VSYNC |
|
X7 |
P1.4 |
|
X6 |
P1.3 |
|
X5 |
P1.2 |
|
X4 |
P1.1 |
|
X3 |
P1.0 |
|
X2 |
MGL296 |
|
|
Fig.11 External and derivative interrupt configuration.
1999 Mar 10 |
24 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
11.4Interrupt Enable Register 0 (IEN0)
Table 21 |
Interrupt Enable Register (SFR address A8H) |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EA |
|
− |
ES1 |
− |
ET1 |
EX1 |
ET0 |
EX0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 22 Description of IEN0 bits
A logic 0 disables the interrupt; a logic 1 enables the interrupt.
BIT |
SYMBOL |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
7 |
EA |
General enable/disable control. When EA = 0, no interrupt is enabled. When EA = 1, |
|
|
any individually enabled interrupt will be accepted. |
|
|
|
6 |
− |
not used |
|
|
|
5 |
ES1 |
enable I2C-bus SIO interrupt |
4 |
− |
not used |
|
|
|
3 |
ET1 |
enable Timer 1 interrupt |
|
|
|
2 |
EX1 |
enable external interrupt 1 |
|
|
|
1 |
ET0 |
enable Timer 0 interrupt |
|
|
|
0 |
EX0 |
enable external interrupt 0 |
|
|
|
11.5Interrupt Enable Register 1 (IEN1)
Table 23 Interrupt Enable Register (SFR address E8H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EX9 |
− |
EX7 |
EX6 |
|
EX5 |
|
EX4 |
EX3 |
EX2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 24 Description of IEN1 bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Where EXx = 0, interrupt disabled. EXx = 1, interrupt enabled |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
7 |
EX9 |
enable external interrupt 9 (P1.7 port line) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
− |
not used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5 |
EX7 |
enable external interrupt 7 (VSYNC interrupt) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
4 |
EX6 |
enable external interrupt 6 (P1.4 port line) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
3 |
EX5 |
enable external interrupt 5 (P1.3 port line) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2 |
EX4 |
enable external interrupt 4 (P1.2 port line) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 |
EX3 |
enable external interrupt 3 (P1.1 port line) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
0 |
EX2 |
enable external interrupt 2 (P1.0 port line) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
25 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
11.6Interrupt Priority Register 0 (IP0)
Table 25 Interrupt Priority Register 0 (SFR address B8H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
− |
PS1 |
− |
PT1 |
PX1 |
PT0 |
PX0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 26 Description of IP0 bits
A logic 0 selects low priority; a logic 1 selects high priority.
BIT |
SYMBOL |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
7 |
− |
These 2 bits are not used. |
|
|
|
6 |
− |
|
|
|
|
5 |
PS1 |
I2C-bus SIO interrupt priority level |
4 |
− |
This bit is not used. |
|
|
|
3 |
PT1 |
Timer 1 interrupt priority level |
|
|
|
2 |
PX1 |
external interrupt 1 priority level |
|
|
|
1 |
PT0 |
Timer 0 interrupt priority level |
|
|
|
0 |
PX0 |
external interrupt 0 priority level |
|
|
|
11.7Interrupt Priority Register 1 (IP1)
Table 27 Interrupt Priority Register 1 (SFR address F8H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PX9 |
− |
PX7 |
PX6 |
PX5 |
PX4 |
PX3 |
PX2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 28 Description of IP1 bits
Where PXx = 0 selects low priority; PXx = 1 selects high priority.
BIT |
SYMBOL |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
7 |
PX9 |
enable external interrupt 9 priority level (P1.7 port line) |
|
|
|
6 |
− |
not used |
|
|
|
5 |
PX7 |
enable external interrupt 7 priority level (VSYNC interrupt) |
|
|
|
4 |
PX6 |
enable external interrupt 6 priority level (P1.4 port line) |
|
|
|
3 |
PX5 |
enable external interrupt 5 priority level (P1.3 port line) |
|
|
|
2 |
PX4 |
enable external interrupt 4 priority level (P1.2 port line) |
|
|
|
1 |
PX3 |
enable external interrupt 3 priority level (P1.1 port line) |
|
|
|
0 |
PX2 |
enable external interrupt 2 priority level (P1.0 port line) |
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
26 |
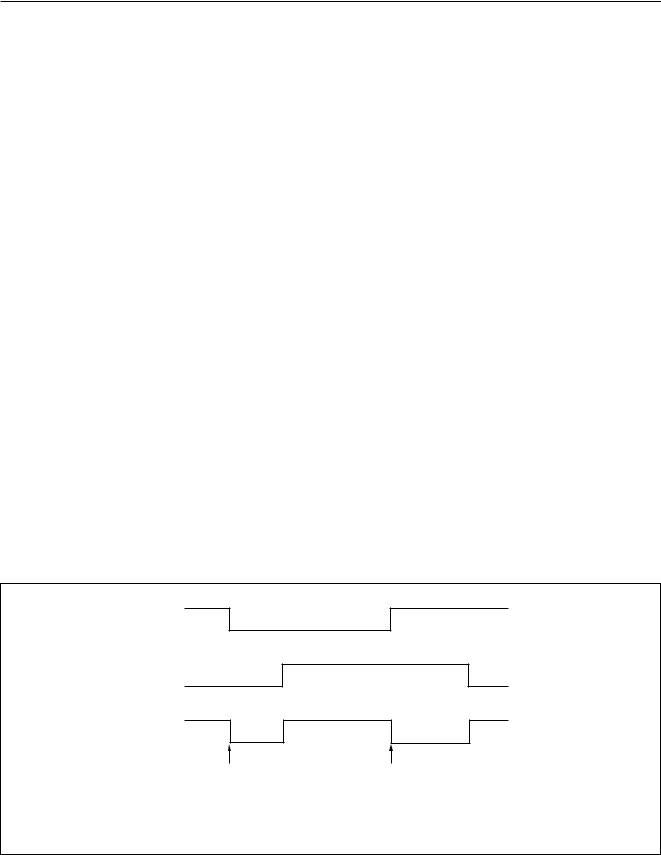
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
11.8Interrupt Polarity Register (IX1)
Writing a logic 1 to bits IL9, IL6, IL5, IL4, IL3 and IL2 will set the polarity level of the corresponding external interrupt to be active HIGH. Writing a logic 0 to these bits will set the corresponding external interrupt to be active LOW.
External interrupts INT1 and INT0 however can be programmed to be edge sensitive. Writing a logic 1 to bits IL8 and IL7 will activate the external interrupts INT1 and INT0 on a rising edge (LOW-to-HIGH). Writing a logic 0 to bits IL8 and IL7 will activate the external interrupts INT1 and INT0 on a falling edge (HIGH-to-LOW). This feature is useful for pulse width measurement; see Section 11.8.1.
Table 29 Interrupt Polarity Register (SFR address E9H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IL9 |
IL8 |
IL7 |
IL6 |
IL5 |
|
IL4 |
IL3 |
IL2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 30 Description of IX1 bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7 |
IL9 |
external interrupt 9 polarity level (P1.7 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
6 |
IL8 |
external interrupt 1 polarity level (INT1) polarity level |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5 |
IL7 |
external interrupt 0 polarity level (INT0) polarity level |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
4 |
IL6 |
external interrupt 6 polarity level (P1.4 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3 |
IL5 |
external interrupt 5 polarity level (P1.3 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2 |
IL4 |
external interrupt 4 polarity level (P1.2 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
IL3 |
external interrupt 3 polarity level (P1.1 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0 |
IL2 |
external interrupt 2 polarity level (P1.0 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.8.1PULSE WIDTH MEASUREMENT EXAMPLE
To determine the LOW time of a signal on the external interrupt pin INT0 the following sequence should be followed.
1.External interrupt 0 must be programmed to edge sensitivity (SFR TCON, address 88H).
2.IL7 must be programmed as shown in Fig.12.
3.The value held in Timer 0 or Timer 1 represents the pulse width of the signal on the INT0 pin.
INT0
IL7
INT0(CPU)
Start interrupt service routine to start counting system clock periods with Timer 0 or Timer 1
Start interrupt service routine to stop counting of Timer 0 or Timer 1
MGL295
Fig.12 Pulse width measurement timing diagram.
1999 Mar 10 |
27 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Microcontrollers for PAL/SECAM TV
P8xCx66 family
with OSD and VST
11.9Interrupt Request Flag Register (IRQ1)
Bits IQ9 and IQ6 to IQ2 will be set to a logic 1, if one of the two conditions specified below is met:
∙If its associated port line is programmed to generate an interrupt when HIGH (selected using the Interrupt Polarity Register) and the state of that port line is HIGH
∙If its associated port line is programmed to generate an interrupt when LOW (selected using the Interrupt Polarity Register) and the state of that port line is LOW.
IQ7 is set to a logic 1, if the interrupt condition is met within the corresponding derivative function. Therefore, all IRQ1 bits serve not only as pending interrupt request bits but also as interrupt status bits. This means that even if the external interrupts are disabled (using the Interrupt Enable Register 1) the IRQ1 bits can still be set to a logic 1 if the interrupt condition is met within the corresponding derivative function. For example, if the interrupt condition within VSYNC is met then:
∙If IEN0.7 = X, IEN1.5 = 0 then IRQ1.5 = 1, no pending interrupt to CPU
∙If IEN0.7 = 0, IEN1.5 = 1 then IRQ1.5 = 1, interrupt to CPU is pending
∙If IEN0.7 = 1, IEN1.5 = 1 then IRQ1.5 = 1, interrupt will be serviced when either:
–The CPU finishes current instruction, if not in the interrupt service routine
–The current interrupt service routine is interrupted if the VSYNC has a higher interrupt priority
–This VSYNC interrupt becomes pending, waiting until the current higher priority level interrupt is serviced.
Bits IQ9 and IQ7 to IQ2 can be reset by software.
Table 31 Interrupt Request Flag Register (SFR address C0H)
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IQ9 |
− |
IQ7 |
IQ6 |
IQ5 |
|
IQ4 |
IQ3 |
IQ2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 32 Description of IRQ1 bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
BIT |
SYMBOL |
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7 |
IQ9 |
external interrupt 9 request flag (P1.7 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
− |
reserved |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
5 |
IQ7 |
external interrupt 7 request flag (VSYNC interrupt) |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
4 |
IQ6 |
external interrupt 6 request flag (P1.4 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3 |
IQ5 |
external interrupt 5 request flag (P1.3 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2 |
IQ4 |
external interrupt 4 request flag (P1.2 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
IQ3 |
external interrupt 3 request flag (P1.1 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0 |
IQ2 |
external interrupt 2 request flag (P1.0 port line) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Mar 10 |
28 |
 Loading...
Loading...