Philips PCF8577CP-F2, PCF8577CP-F3, PCF8577CT-F2, PCF8577CT-F3, PCF8577CU-10-F2 Datasheet
...
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
PCF8577C
LCD direct/duplex driver with I2C-bus interface
Product specification |
1998 Jul 30 |
Supersedes data of 1997 Mar 28
File under Integrated Circuits, IC12

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
CONTENTS
1FEATURES
2GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3ORDERING INFORMATION
4BLOCK DIAGRAM
5PINNING
6FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1Hardware subaddress A0, A1, A2
6.2Oscillator A0/OSC
6.3User-accessible registers
6.4Auto-incremented loading
6.5Direct drive mode
6.6Duplex mode
6.7Power-on reset
6.8Slave address
6.9I2C-bus protocol
6.10Display memory mapping
7 |
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I2C-BUS |
7.1Bit transfer
7.2Start and stop conditions
7.3System configuration
7.4Acknowledge
8LIMITING VALUES
9HANDLING
10DC CHARACTERISTICS
11AC CHARACTERISTICS
12APPLICATION INFORMATION
13CHIP DIMENSIONS AND BONDING PAD LOCATIONS
14PACKAGE OUTLINES
15SOLDERING
15.1Plastic dual in-line packages
15.1.1By dip or wave
15.1.2Repairing soldered joints
15.2Plastic small outline packages
15.2.1By wave
15.2.2By solder paste reflow
15.2.3Repairing soldered joints (by hand-held soldering iron or pulse-heated solder tool)
16DEFINITIONS
17LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
18PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1998 Jul 30 |
2 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
1 FEATURES
∙Direct/duplex drive modes with up to
32/64 LCD-segment drive capability per device
∙Operating supply voltage: 2.5 to 6 V
∙Low power consumption
∙I2C-bus interface
∙Optimized pinning for single plane wiring
∙Single-pin built-in oscillator
∙Auto-incremented loading across device subaddress boundaries
∙Display memory switching in direct drive mode
∙May be used as I2C-bus output expander
∙System expansion up to 256 segments
∙Power-on reset blanks display
∙I2C-bus address: 0111 0100.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF8577C is a single chip, silicon gate CMOS circuit. It is designed to drive liquid crystal displays with up to
32 segments directly, or 64 segments in a duplex configuration.
The two-line I2C-bus interface substantially reduces wiring overheads in remote display applications. I2C-bus traffic is minimized in multiple IC applications by automatic address incrementing, hardware subaddressing and display memory switching (direct drive mode).To allow partial VDD shutdown the ESD protection system of the SCL and SDA pins does not use a diode connected to VDD.
TYPE NUMBER |
|
PACKAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
||
NAME |
DESCRIPTION |
VERSION |
||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
PCF8577CP |
DIP40 |
plastic dual in-line package; 40 leads (600 mil) |
SOT129-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCF8577CT |
VSO40 |
plastic very small outline package; 40 leads |
SOT158A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCF8577CT |
− |
VS040 in blister tape |
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCF8577CU/10 |
− |
chip on film-frame-carrier (FFC) |
− |
|
|
|
|
|
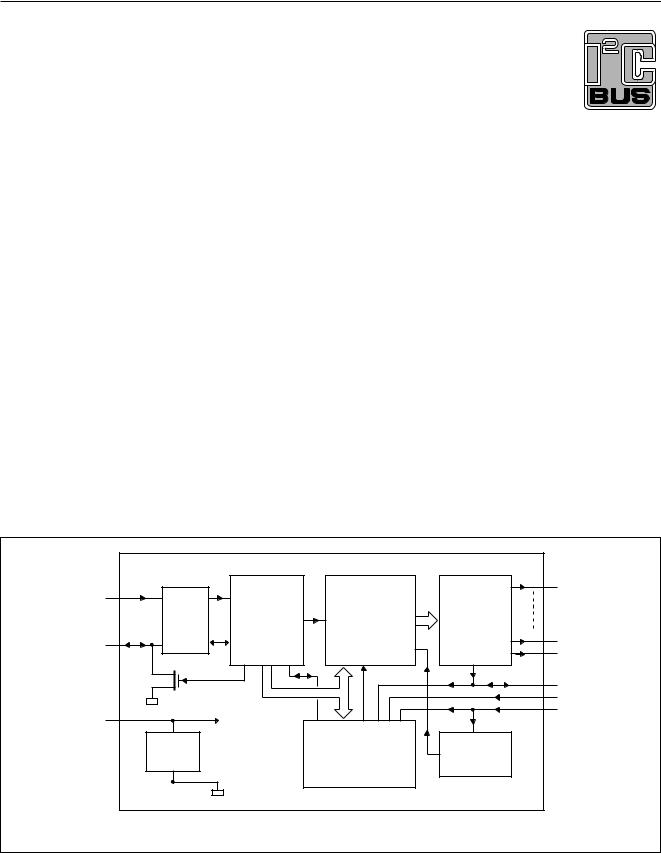
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
S32 |
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
SCL |
|
SEGMENT BYTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BACKPLANE |
|
|
||
|
|
2 |
REGISTERS |
|
|
|
I 2C - BUS |
INPUT |
AND |
|
|
||
AND |
|
|
||||
I C - BUS |
SEGMENT |
|
|
|||
|
FILTERS |
CONTROLLER |
MULTIPLEX |
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
DRIVERS |
32 |
|
|
SDA |
|
LOGIC |
S1 |
|||
|
|
|
33 |
|||
|
|
|
|
BP1 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
A2/BP2 |
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
A0/OSC |
|
VDD |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
POWER - |
|
CONTROL REGISTER |
OSCILLATOR |
|
|
|
ON |
PCF8577C |
AND |
AND |
|
|
|
RESET |
|
|
|||
|
|
COMPARATOR |
DIVIDER |
|
|
|
VSS |
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGA727 |
|
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1998 Jul 30 |
3 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
5 PINNING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SYMBOL |
|
PIN |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S32 to S1 |
|
1 to 32 |
segments outputs |
|
S32 |
1 |
|
|
|
SDA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
40 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
BP1 |
|
33 |
cascade sync input/backplane |
||||||||
|
|
S31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
output |
|
|
2 |
|
|
39 |
SCL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2/BP2 |
|
34 |
hardware address line and |
|
S30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
38 |
|||||
|
|
|
cascade sync input/backplane |
|
S29 |
|
|
|
|
|
A0/OSC |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
37 |
|||
|
|
|
output |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
S28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
36 |
A1 |
|
VDD |
|
35 |
positive supply voltage |
||||||||
|
|
S27 |
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
|||
A1 |
|
36 |
hardware address line input |
|
|
6 |
|
|
35 |
||
|
|
S26 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
A0/OSC |
|
37 |
hardware address line and |
|
|
7 |
|
|
34 |
A2/BP2 |
|
|
|
|
oscillator pin input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S25 |
|
8 |
|
|
33 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
VSS |
|
38 |
negative supply voltage |
|
S24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
32 |
S1 |
||||
SCL |
|
39 |
I2C-bus clock line input |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
S23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
31 |
S2 |
|
SDA |
|
40 |
I2C-bus data line input/output |
PCF8577C |
|||||||
|
|
S22 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
30 |
S3 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S21 |
|
12 |
|
|
29 |
S4 |
|
|
|
|
|
S20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
28 |
S5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S19 |
|
14 |
|
|
27 |
S6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S18 |
|
15 |
|
|
26 |
S7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S17 |
|
16 |
|
|
25 |
S8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S16 |
|
17 |
|
|
24 |
S9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S15 |
|
18 |
|
|
23 |
S10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S14 |
|
19 |
|
|
22 |
S11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S13 |
|
20 |
|
|
21 |
S12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGA725 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig.2 |
Pin configuration. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1998 Jul 30 |
4 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1Hardware subaddress A0, A1, A2
The hardware subaddress lines A0, A1 and A2 are used to program the device subaddress for each PCF8577C connected to the I2C-bus. Lines A0 and A2 are shared with OSC and BP2 respectively to reduce pin-out requirements.
1.Line A0 is defined as LOW (logic 0) when this pin is
used for the local oscillator or when connected to VSS. Line A0 is defined as HIGH (logic 1) when connected to VDD.
2.Line A1 must be defined as LOW (logic 0) or as HIGH (logic 1) by connection to VSS or VDD respectively.
3.In the direct drive mode the second backplane signal BP2 is not used and the A2/BP2 pin is exclusively the A2 input. Line A2 is defined as LOW (logic 0) when
connected to VSS or, if this is not possible, by leaving it unconnected (internal pull-down). Line A2 is defined as HIGH (logic 1) when connected to VDD.
4.In the duplex drive mode the second backplane signal BP2 is required and the A2 signal is undefined. In this mode device selection is made exclusively from lines A0 and A1.
6.2Oscillator A0/OSC
The PCF8577C has a single-pin built-in oscillator which provides the modulation for the LCD segment driver outputs. One external resistor and one external capacitor are connected to the A0/OSC pin to form the oscillator (see Figs 15 and 16). For correct start-up of the oscillator after power on, the resistor and capacitor must be connected to the same VSS/VDD as the chip. In an expanded system containing more than one PCF8577C the backplane signals are usually common to all devices and only one oscillator is required. The devices which are not used for the oscillator are put into the cascade mode by connecting the A0/OSC pin to either VDD or VSS depending on the required state for A0. In the cascade mode each PCF8577C is synchronized from the backplane signal(s).
6.3User-accessible registers
There are nine user-accessible 1-byte registers. The first is a control register which is used to control the loading of data into the segment byte registers and to select display options. The other eight are segment byte registers, split into two banks of storage, which store the segment data. The set of even numbered segment byte registers is called BANK A. Odd numbered segment byte registers are called BANK B.
There is one slave address for the PCF8577C (see Fig.6). All addressed devices load the second byte into the control register and each device maintains an identical copy of the control byte in the control register at all times (see I2C-bus protocol, Fig.7), i.e. all addressed devices respond to control commands sent on the I2C-bus.
The control register is shown in more detail in Fig.3. The least-significant bits select which device and which segment byte register is loaded next. This part of the register is therefore called the Segment Byte Vector (SBV).
The upper three bits of the SBV (V5 to V3) are compared with the hardware subaddress input signals A2, A1
and A0. If they are the same then the device is enabled for loading, if not the device ignores incoming data but remains active.
The three least-significant bits of the SBV (V2 to V0) address one of the segment byte registers within the enabled chip for loading segment data.
The control register also has two display control bits. These bits are named MODE and BANK. The MODE bit selects whether the display outputs are configured for direct or duplex drive displays. The BANK bit allows the user to display BANK A or BANK B.
6.4Auto-incremented loading
After each segment byte is loaded the SBV is incremented automatically. Thus auto-incremented loading occurs if more than one segment byte is received in a data transfer.
Since the SBV addresses both device and segment registers in all addressed chips, auto-incremented loading may proceed across device boundaries provided that the hardware subaddresses are arranged contiguously.
1998 Jul 30 |
5 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
|
|
|
CONTROL REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SEGMENT BYTE REGISTERS |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
DISPLAY |
SEGMENT BYTE VECTOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SBV) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
msb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lsb |
|
msb |
lsb |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V4 |
V3 |
V2 |
|
V1 |
V0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
segment byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
register |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
(1) |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
address |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BANK 'A' |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
comparison |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2 |
|
A1 |
A0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
device |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
subaddress |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BANK 'B' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
BANK 'A' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BANK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
BANK 'B' |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
DIRECT DRIVE |
|
DISPLAY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MODE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGA733 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
DUPLEX DRIVE |
|
|
|
(1) Bits ignored in duplex mode. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Fig.3 PCF8577C register organization.
OFF ON
VDD
BP1
VSS
VDD
Segment x
(Sx)
VSS
VDD VSS
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
BP1 |
|
Sx |
|
|
|
|
|
(VDD VSS )
1
f LCD MGA737
Von(rms) = VDD − VSS; Voff(rms) = 0.
Fig.4 Direct drive mode display output waveforms.
1998 Jul 30 |
6 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
6.5Direct drive mode
The PCF8577C is set to the direct drive mode by loading the MODE control bit with logic 0. In this mode only four bytes are required to store the data for the 32 segment drivers. Setting the BANK bit to logic 0 selects even bytes (BANK A), setting the BANK bit to logic 1 selects odd bytes (BANK B).
In the direct drive mode the SBV is auto-incremented by two after the loading of each segment byte register. This means that auto-incremented loading of BANK A or BANK B is possible. Either bank may be completely or partially loaded irrespective of which bank is being displayed. Direct drive output waveforms are shown in Fig.4.
6.6Duplex mode
The PCF8577C is set to the duplex mode by loading the MODE bit with logic 1. In this mode a second backplane signal (BP2) is needed and pin A2/BP2 is used for this; therefore A2 and its equivalent SBV bit V5 are undefined. The SBV auto-increments by one between loaded bytes.
All of the segment bytes are required to store data for the 32 segment drivers and the BANK bit is ignored.
Duplex mode output waveforms are shown in Fig.5.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OFF / OFF |
|
|
|
ON / OFF |
|
|
|
OFF / ON |
|
|
ON / ON |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0.5 (VDD |
|
|
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BP1 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0.5 (VDD |
|
|
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BP2 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
VDD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Segment x |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Sx) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
VDD |
|
|
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
0.5 (VDD |
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BP1 |
|
|
Sx |
0.5 (VDD |
|
|
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
(VDD |
|
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
VDD |
|
|
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
0.5 (VDD |
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BP2 |
|
Sx |
|
0.5 (VDD |
|
|
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
(VDD |
|
|
|
VSS ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f LCD |
|
|
MGA738 |
|||||||
Von(rms) = 0.791 (VDD − VSS); Voff(rms) = 0.354 (VDD − VSS).
Von ( rms)
----------------------- = 2.236 Voff ( rms)
Fig.5 Duplex mode display output waveforms.
1998 Jul 30 |
7 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
6.7Power-on reset
At power-on reset the PCF8577C resets to a defined starting condition as follows:
1.Both backplane outputs are set to VSS in master mode; to 3-state in cascade mode
2.All segment outputs are set to VSS
3.The segment byte registers and control register are cleared
4.The I2C-bus interface is initialized.
6.8Slave address
The PCF8577C slave address is shown in Fig.6.
Before any data is transmitted on the I2C-bus, the device which should respond is addressed first. The addressing is always done with the first byte transmitted after the start procedure.
6.9I2C-bus protocol
The PCF8577C I2C-bus protocol is shown in Fig.7.
The PCF8577C is a slave receiver and has a fixed slave address (see Fig.6). All PCF8577Cs with the same slave address acknowledge the slave address in parallel.
The second byte is always the control byte and is loaded into the control register of each PCF8577C connected to the I2C-bus. All addressed devices acknowledge the control byte. Subsequent data bytes are loaded into the segment registers of the selected device. Any number of data bytes may be loaded in one transfer and in an expanded system rollover of the SBV from 111 111 to 000 000 is allowed. If a stop (P) condition is given after the control byte acknowledge the segment data will remain unchanged. This allows the BANK bit to be toggled without changing the segment register contents. During loading of segment data only the selected PCF8577C gives an acknowledge. Loading is terminated by generating a stop
(P) condition.
S 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 A
 SLAVE ADDRESS
SLAVE ADDRESS 
MGA731
Fig.6 PCF8577C slave address.
|
|
acknowledge by |
||||
|
|
all PCF8577C |
||||
S |
|
|
|
|
MODE BANK |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
SLAVE ADDRESS |
0 A |
|||||
|
||||||
R/W
MGA732
acknowledge by |
|
acknowledge by |
|||||||
|
all PCF8577C |
selected PCF8577C only |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
msb |
|
|
lsb |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
SEGMENT |
A |
SEGMENT DATA |
|
A P |
|||||
BYTE VECTOR |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
control byte |
|
|
|
|
n bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
auto increment |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
segment byte vector |
|||
Fig.7 I2C-bus protocol.
1998 Jul 30 |
8 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
LCD direct/duplex driver with
PCF8577C
I2C-bus interface
6.10Display memory mapping
The mapping between the eight segment registers and the segment outputs S1 to S32 is given in Tables 1 and 2.
Since only one register bit per segment is needed in the direct drive mode, the BANK bit allows swapping of display information. If BANK is set to logic 0 even bytes (BANK A) are displayed; if BANK is set to logic 1 odd bytes (BANK B) are displayed. BP1 is always used for the backplane output in the direct drive mode. In duplex mode even bytes (BANK A) correspond to backplane 1 (BP1) and odd bytes (BANK B) correspond to backplane 2 (BP2).
Table 1 Segment byte-segment driver mapping in direct drive mode
|
|
V |
V |
V |
SEGMENT/ |
MSB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSB |
BACK- |
|
MODE |
BANK |
BIT/ |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|||||||
2 |
1 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
PLANE |
||||||||||
|
|
REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
S8 |
S7 |
S6 |
S5 |
S4 |
S3 |
S2 |
S1 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
S8 |
S7 |
S6 |
S5 |
S4 |
S3 |
S2 |
S1 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
S16 |
S15 |
S14 |
S13 |
S12 |
S11 |
S10 |
S9 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
S16 |
S15 |
S14 |
S13 |
S12 |
S11 |
S10 |
S9 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
S24 |
S23 |
S22 |
S21 |
S20 |
S19 |
S18 |
S17 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
S24 |
S23 |
S22 |
S21 |
S20 |
S19 |
S18 |
S17 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
S32 |
S31 |
S30 |
S29 |
S28 |
S27 |
S26 |
S25 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
7 |
S32 |
S31 |
S30 |
S29 |
S28 |
S27 |
S26 |
S25 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mapping example: bit 0 of register 7 controls the LCD segment S25 if BANK bit is a logic 1.
Table 2 Segment byte-segment driver mapping in duplex mode
|
|
V |
V |
V |
SEGMENT/ |
MSB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSB |
BACK- |
|
MODE |
BANK(1) |
BIT/ |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|||||||
2 |
1 |
0 |
7 |
0 |
PLANE |
||||||||||
|
|
REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
S8 |
S7 |
S6 |
S5 |
S4 |
S3 |
S2 |
S1 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
S8 |
S7 |
S6 |
S5 |
S4 |
S3 |
S2 |
S1 |
BP2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
S16 |
S15 |
S14 |
S13 |
S12 |
S11 |
S10 |
S9 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
0 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
S16 |
S15 |
S14 |
S13 |
S12 |
S11 |
S10 |
S9 |
BP2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
1 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
S24 |
S23 |
S22 |
S21 |
S20 |
S19 |
S18 |
S17 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
1 |
0 |
1 |
5 |
S24 |
S23 |
S22 |
S21 |
S20 |
S19 |
S18 |
S17 |
BP2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
1 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
S32 |
S31 |
S30 |
S29 |
S28 |
S27 |
S26 |
S25 |
BP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
X |
1 |
1 |
1 |
7 |
S32 |
S31 |
S30 |
S29 |
S28 |
S27 |
S26 |
S25 |
BP2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note
1. Where X = don’t care.
Mapping example: bit 7 of register 5 controls the LCD segment S24/BP2.
1998 Jul 30 |
9 |
 Loading...
Loading...