Philips P89C536NBBB, P89C538NBBB, P89C536NBAA, P89C538NBAA Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
89C536/89C538
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
16K/64K/512 FLASH
Preliminary specification |
1998 Apr 24 |
Supersedes data of 1997 Dec 02
IC20 Data Handbook
m n r

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
DESCRIPTION
The 89C536/89C538 are Single-Chip 8-Bit Microcontrollers manufactured in advanced CMOS process and are derivatives of the 80C51 microcontroller family. All the devices have the same instruction set as the 80C51.
The devices also have four 8-bit I/O ports, three 16-bit timer/event counters, a multi-source, two-priority-level, nested interrupt structure, UART and on-chip oscillator and timing circuits. For systems that require extra data memory capability up to 64k bytes, each can be expanded using standard TTL-compatible memories and logic.
The 89C536/89C538 contain a non-volatile FLASH program memory (16k bytes in the 89C536, and 64k bytes in the 89C538). The devices have 512 bytes of RAM data memory.
FEATURES
•80C51 Central Processing Unit
•16k × 8 (89C536) or 64k × 8 (89C538), FLASH EPROM Program
Memory
•512 × 8 RAM, externally expandable to 64k × 8 Data Memory
•Three 16-bit counter/timers
•Up to 3 external interrupt request inputs
•6 interrupt sources with 2 priority levels
•Four 8-bit I/O ports
•Full-duplex UART
•Power control modes
±Idle mode
±Power down mode, with wakeup from power down using external interrupt
•44-pin PLCC and QFP packages
ORDERING INFORMATION
PART NUMBER |
MEMORY SIZE |
TEMPERATURE RANGE (°C) AND PACKAGE |
FREQ. |
DRAWING |
|
(MHz) |
NUMBER |
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P89C536NBA A |
16k bytes |
0 to +70, 44-pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier |
33 |
SOT187-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P89C536NBB B |
16k bytes |
0 to +70, 44-pin Plastic Quad Flat Package |
33 |
SOT307-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P89C538NBA A |
64k bytes |
0 to +70, 44-pin Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier |
33 |
SOT187-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P89C538NBB B |
64k bytes |
0 to +70, 44-pin Plastic Quad Flat Package |
33 |
SOT307-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1998 Apr 24 |
2 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
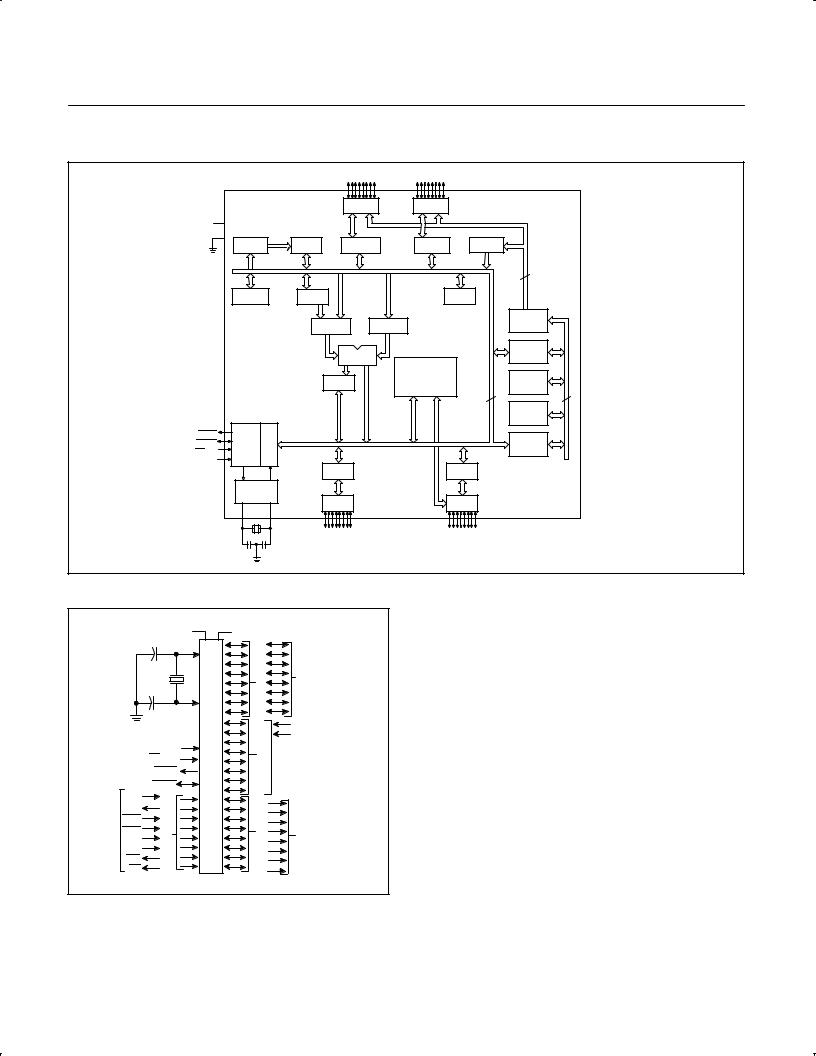
BLOCK DIAGRAM
|
|
P0.0±P0.7 |
P2.0±P2.7 |
|
|
|
PORT 0 |
PORT 2 |
|
|
|
DRIVERS |
DRIVERS |
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
RAM ADDR |
RAM |
PORT 0 |
PORT 2 |
ROF/ |
REGISTER |
LATCH |
LATCH |
EPROM |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
B |
|
ACC |
STACK |
|
|
REGISTER |
POINTER |
|
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
PROGRAM |
|
|
|
TMP2 |
TMP1 |
ADDRESS |
|
|
|
REGISTER |
||
|
|
|
|
ALU |
BUFFER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SFRs |
PC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSW |
TIMERS |
INCRE- |
|
|
|
|
|
MENTER |
|
|
|
|
8 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
PROGRAM |
|
|
INSTRUCTION REGISTER |
|
|
COUNTER |
RST |
|
|
|
|
|
PSEN |
TIMING |
|
|
|
DPTR'S |
ALE/PROG |
AND |
|
|
|
MULTIPLE |
EAVPP |
|
|
|
||
CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PD |
|
PORT 1 |
PORT 3 |
|
|
|
LATCH |
LATCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
OSCILLATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORT 1 |
PORT 3 |
|
|
XTAL1 |
XTAL2 |
DRIVERS |
DRIVERS |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
P1.0±P1.7 |
P3.0±P3.7 |
|
SU00854
LOGIC SYMBOL
VCC
XTAL1
|
|
XTAL2 |
|
|
RST |
|
|
EA/VPP |
|
|
PSEN |
FUNCTIONSSECONDARY |
ALE/PROG |
|
RxD |
3PORT |
|
|
TxD |
|
|
INT0 |
|
|
INT1 |
|
|
T0 |
|
|
T1 |
|
|
WR |
|
|
RD |
|
VSS |
|
0 |
ADDRESS AND |
PORT |
DATA BUS |
|
|
|
T2 |
PORT 1 |
T2EX |
|
|
2 |
|
PORT |
ADDRESS BUS |
|
|
|
SU00830 |
PROGRAMMING INFORMATION:
Programmers are provided by:
Company |
Phone Number |
Internet Address |
Advin |
1±800±627±2456 |
|
BP Microsystem |
1±800±225±2102 |
http://www.bpmicro.com |
Data I/O |
1±206±881±6444 |
http://www.data±io.com |
HiLo |
|
|
1998 Apr 24 |
3 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
PLASTIC LEADED CHIP CARRIER PIN FUNCTIONS |
PLASTIC QUAD FLAT PACK PIN FUNCTIONS |
6 |
1 |
40 |
44 |
34 |
|
|
|
||
7 |
|
39 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
33 |
|
LCC |
|
|
PQFP |
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
29 |
11 |
23 |
18 |
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
22 |
Pin |
Function |
Pin |
Function |
Pin |
Function |
Pin |
Function |
Pin |
Function |
Pin |
Function |
||||||||||||||||
1 |
NIC* |
16 |
P3.4/T0 |
31 |
P2.7/A15 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
1 |
P1.5/CEX2 |
16 |
VSS |
31 |
P0.6/AD6 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
P1.0/T2 |
17 |
P3.5/T1 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
PSEN |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
P1.6/CEX3 |
17 |
NIC* |
32 |
P0.5/AD5 |
||||||||
3 |
P1.1/T2EX |
18 |
P3.6/WR |
33 |
ALE/PROG |
||||||||||||||||||||||
3 |
P1.7/CEX4 |
18 |
P2.0/A8 |
33 |
P0.4/AD4 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
NIC* |
|||||||||||||||||
4 |
P1.2/ECI |
19 |
P3.7/RD |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
RST |
19 |
P2.1/A9 |
34 |
P0.3/AD3 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
5 |
P1.3/CEX0 |
20 |
XTAL2 |
35 |
EA/VPP |
||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
P3.0/RxD |
20 |
P2.2/A10 |
35 |
P0.2/AD2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
P1.4/CEX1 |
21 |
XTAL1 |
36 |
P0.7/AD7 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
NIC* |
21 |
P2.3/A11 |
36 |
P0.1/AD1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
P1.5/CEX2 |
22 |
VSS |
37 |
P0.6/AD6 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
P3.1/TxD |
22 |
P2.4/A12 |
37 |
P0.0/AD0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
P1.6/CEX3 |
23 |
NIC* |
38 |
P0.5/AD5 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
VCC |
|||||||||||||||
8 |
P3.2/INT0 |
23 |
P2.5/A13 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
P1.7/CEX4 |
24 |
P2.0/A8 |
39 |
P0.4/AD4 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
P2.6/A14 |
39 |
NIC* |
||||||||||||||||||
10 |
RST |
25 |
P2.1/A9 |
40 |
P0.3/AD3 |
9 |
P3.3/INT1 |
||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
P3.4/T0 |
25 |
P2.7/A15 |
40 |
P1.0/T2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
11 |
P3.0/RxD |
26 |
P2.2/A10 |
41 |
P0.2/AD2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
P1.1/T2EX |
|||||||||||||||
12 |
NIC* |
27 |
P2.3/A11 |
42 |
P0.1/AD1 |
11 |
P3.5/T1 |
26 |
PSEN |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42 |
P1.2/ECI |
|||||||||||||||
13 |
P3.1/TxD |
28 |
P2.4/A12 |
43 |
P0.0/AD0 |
12 |
P3.6/WR |
27 |
ALE/PROG |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
P1.3/CEX0 |
|||||||||||||||
13 |
P3.7/RD |
28 |
NIC* |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
VCC |
|||||||||||||||||
14 |
P3.2/INT0 |
29 |
P2.5/A13 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
P1.4/CEX1 |
|||||||||||||||
14 |
XTAL2 |
29 |
EA/VPP |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
15 |
P3.3/INT1 |
30 |
P2.6/A14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
XTAL1 |
30 |
P0.7/AD7 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
* NO INTERNAL CONNECTION |
|
|
|
|
|
SU00023 |
* NO INTERNAL CONNECTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SU00024 |
|||||||||||||
1998 Apr 24 |
4 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIN NUMBER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MNEMONIC |
LCC |
QFP |
TYPE |
NAME AND FUNCTION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSS |
1, 22 |
16, 39 |
I |
Ground: 0V reference. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
VCC |
23, 44 |
17, 38 |
I |
Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power-down operation. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P0.0±0.7 |
43±36 |
37±30 |
I/O |
Port 0: Port 0 is an open-drain, bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to them float |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and can be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed low-order address and |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In this application, it uses strong |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. Port 0 also outputs the code bytes during program verification and |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
received code bytes during EEPROM programming. External pull-ups are required during program |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
verification. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
P1.0±P1.7 |
2±9 |
40±44, |
I/O |
Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 1 pins that have 1s written |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1±3 |
|
to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 1 pins that |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
are externally pulled low will source current because of the internal pull-ups. (See DC Electrical |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics: IIL). Port 1 also receives the low-order address byte during program memory |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
verification. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alternate functions for Port 1 include: |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
40 |
I/O |
|
|
T2 (P1.0): Timer/Counter 2 external count input |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
41 |
I |
|
|
T2EX (P1.1): Timer/Counter 2 Reload/Capture |
|||||||||||||||||
|
P2.0±P2.7 |
24±31 |
18±25 |
I/O |
Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s written |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 2 pins that |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
are externally being pulled low will source current because of the internal pull-ups. (See DC |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Electrical Characteristics: IIL). Port 2 emits the high-order address byte during fetches from external |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
program memory and during accesses to external data memory that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
@DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. Some Port 2 pins |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
receive the high order address bits during EEPROM programming and verification. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
P3.0±P3.7 |
11, |
5, |
I/O |
Port 3: Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s written |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
13±19 |
7±13 |
|
to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 3 pins that |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
are externally being pulled low will source current because of the pull-ups. (See DC Electrical |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics: IIL). Port 3 also serves the special features of the 80C51 family, as listed below: |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
5 |
I |
|
|
RxD (P3.0): Serial input port |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
7 |
O |
|
|
TxD (P3.1): Serial output port |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
8 |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(P3.2): External interrupt |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INT0 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
9 |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(P3.3): External interrupt |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INT1 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
10 |
I |
|
|
T0 (P3.4): Timer 0 external input |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
11 |
I |
|
|
T1 (P3.5): Timer 1 external input |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
12 |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
(P3.6): External data memory write strobe |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WR |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
13 |
O |
|
|
|
(P3.7): External data memory read strobe |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RD |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
RST |
10 |
4 |
I |
Reset: A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running, resets the device. An |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
internal diffused resistor to VSS permits a power-on reset using only an external capacitor to VCC. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
27 |
O |
Address Latch Enable/Program Pulse: Output pulse for latching the low byte of the address |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
ALE/PROG |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during an access to external memory. In normal operation, ALE is emitted at a constant rate of 1/6 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the oscillator frequency, and can be used for external timing or clocking. Note that one ALE pulse is |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
skipped during each access to external data memory. This pin is also the program pulse input |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
during EEPROM programming. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(PROG) |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
32 |
26 |
O |
Program Store Enable: The read strobe to external program memory. When the processor is |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
PSEN |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
executing code from the external program memory, |
|
|
is activated twice each machine cycle, |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSEN |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
except that two |
|
activations are skipped during each access to external data memory. |
|
is |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PSEN |
PSEN |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
not activated during fetches from internal program memory. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
35 |
29 |
I |
External Access Enable/Programming Supply Voltage: |
|
|
must be externally held low to enable |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
EA/VPP |
EA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the device to fetch code from external program memory. If |
EA |
is held high, the device executes from |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
internal program memory. This pin also receives the 12V programming supply voltage (VPP) during |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EPROM programming. |
EA |
is internally latched on Reset. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
XTAL1 |
21 |
15 |
I |
Crystal 1: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock generator circuits. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
XTAL2 |
20 |
14 |
O |
Crystal 2: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE: |
+ 0.5V or V |
|
± 0.5V, respectively. |
To avoid ªlatch-upº effect at power-on, the voltage on any pin at any time must not be higher than V |
SS |
||
CC |
|
||
1998 Apr 24 |
5 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
Table 1. Special Function Registers
SYMBOL |
DESCRIPTION |
DIRECT |
|
BIT ADDRESS, SYMBOL, OR ALTERNATIVE PORT FUNCTION |
RESET |
||||||||||||||||||||||
ADDRESS |
MSB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSB |
VALUE |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACC* |
Accumulator |
E0H |
|
E7 |
|
E6 |
E5 |
E4 |
|
E3 |
|
E2 |
E1 |
E0 |
00H |
||||||||||||
B* |
B register |
F0H |
|
F7 |
|
F6 |
F5 |
F4 |
|
F3 |
|
F2 |
F1 |
F0 |
00H |
||||||||||||
DPTR: |
Data Pointer (2 bytes) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DPH |
Data Pointer High |
83H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
DPL |
Data Pointer Low |
82H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
|
|
|
|
AF |
|
AE |
AD |
AC |
|
AB |
|
AA |
A9 |
A8 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IE* |
Interrupt Enable |
A8H |
|
EA |
± |
|
|
ET2 |
ES |
|
ET1 |
|
EX1 |
ET0 |
EX0 |
00H |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BF |
|
BE |
BD |
BC |
|
BB |
|
BA |
B9 |
B8 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IP* |
Interrupt Priority |
B8H |
± |
|
± |
|
|
PT2 |
PS |
|
PT1 |
|
PX1 |
PT0 |
PX0 |
x0000000B |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
87 |
|
86 |
|
|
85 |
84 |
83 |
|
82 |
|
|
81 |
|
80 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0* |
Port 0 |
80H |
AD7 |
AD6 |
AD5 |
AD4 |
|
AD3 |
|
AD2 |
AD1 |
AD0 |
FFH |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97 |
|
96 |
|
|
95 |
94 |
93 |
|
92 |
|
|
91 |
|
90 |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1* |
Port 1 |
90H |
± |
|
± |
|
|
± |
± |
± |
|
± |
|
|
T2EX |
T2 |
FFH |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A7 |
|
A6 |
A5 |
A4 |
|
A3 |
|
A2 |
A1 |
A0 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2* |
Port 2 |
A0H |
AD15 |
AD14 |
AD13 |
AD12 |
AD11 |
AD10 |
AD9 |
AD8 |
FFH |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B7 |
|
B6 |
B5 |
B4 |
|
B3 |
|
B2 |
B1 |
B0 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P3* |
Port 3 |
B0H |
|
RD |
|
|
WR |
|
T1 |
T0 |
|
INT1 |
|
|
INT0 |
|
TxD |
RxD |
FFH |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
PCON# |
Power Control |
87H |
SMOD |
EXTRAM |
± |
± |
|
GF1 |
|
GF0 |
PD |
IDL |
00xx0000B |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
D7 |
|
D6 |
D5 |
D4 |
|
D3 |
|
D2 |
D1 |
D0 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
PSW* |
Program Status Word |
D0H |
|
CY |
|
AC |
F0 |
RS1 |
|
RS0 |
|
OV |
± |
|
P |
00H |
|||||||||||
RACAP2H# |
Timer 2 Capture High |
CBH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
RACAP2L# |
Timer 2 Capture Low |
CAH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
SBUF |
Serial Data Buffer |
99H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxxxxxxB |
|
|
|
|
9F |
|
9E |
9D |
9C |
|
9B |
|
9A |
99 |
|
98 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
SCON* |
Serial Control |
98H |
SM0 |
SM1 |
SM2 |
REN |
|
TB8 |
|
RB8 |
TI |
RI |
00H |
||||||||||||||
SP |
Stack Pointer |
81H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
07H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
8F |
|
8E |
8D |
8C |
|
8B |
|
8A |
89 |
|
88 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TCON* |
Timer Control |
88H |
TF1 |
TR1 |
TF0 |
TR0 |
|
IE1 |
|
IT1 |
IE0 |
IT0 |
00H |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
CF |
|
CE |
CD |
CC |
|
CB |
|
CA |
C9 |
C8 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
T2CON* |
Timer 2 Control |
C8H |
TF2 |
EXF2 |
RCLK |
TCLK |
EXEN2 |
|
TR2 |
C/T2 |
|
CP/RL2 |
00H |
||||||||||||||
TH0 |
Timer High 0 |
8CH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
TH1 |
Timer High 1 |
8DH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
TH2# |
Timer High 2 |
CDH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
TL0 |
Timer Low 0 |
8AH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
TL1 |
Timer Low 1 |
8BH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
TL2# |
Timer Low 2 |
CCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00H |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
TMOD |
Timer Mode |
89H |
GATE |
|
C/T |
|
M1 |
M0 |
GATE |
|
C/T |
M1 |
M0 |
00H |
|||||||||||||
*SFRs are bit addressable.
# SFRs are modified from or added to the 80C51 SFRs.
± Reserved bits.
1998 Apr 24 |
6 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
OSCILLATOR CHARACTERISTICS
XTAL1 and XTAL2 are the input and output, respectively, of an inverting amplifier. The pins can be configured for use as an on-chip oscillator.
To drive the device from an external clock source, XTAL1 should be driven while XTAL2 is left unconnected. There are no requirements on the duty cycle of the external clock signal, because the input to the internal clock circuitry is through a divide-by-two flip-flop. However, minimum and maximum high and low times specified in the data sheet must be observed.
RESET
A reset is accomplished by holding the RST pin high for at least two machine cycles (24 oscillator periods), while the oscillator is running. To insure a good power-on reset, the RST pin must be high long enough to allow the oscillator time to start up (normally a few milliseconds) plus two machine cycles. At power-on, the voltage on
VCC and RST must come up at the same time for a proper start-up. Ports 1, 2, and 3 will asynchronously be driven to their reset condition when a voltage above VIH1 (min.) is applied to RESET.
LOW POWER MODES
Idle Mode
In the idle mode (see Table 2), the CPU puts itself to sleep while all of the on-chip peripherals stay active. The instruction to invoke the idle mode is the last instruction executed in the normal operating mode before the idle mode is activated. The CPU contents, the on-chip RAM, and all of the special function registers remain intact during this mode. The idle mode can be terminated either by any enabled interrupt (at which time the process is picked up at the
interrupt service routine and continued), or by a hardware reset which starts the processor in the same manner as a power-on reset.
Power-Down Mode
To save even more power, a Power Down mode (see Table 2) can be invoked by software. In this mode, the oscillator is stopped and the instruction that invoked Power Down is the last instruction executed. The on-chip RAM and Special Function Registers retain their values down to 2.0V and care must be taken to return VCC to the minimum specified operating voltages before the Power Down Mode is terminated.
Either a hardware reset or external interrupt can be used to exit from Power Down. Reset redefines all the SFRs but does not change the on-chip RAM. An external interrupt allows both the SFRs and the on-chip RAM to retain their values.
To properly terminate Power Down the reset or external interrupt should not be executed before VCC is restored to its normal operating level and must be held active long enough for the oscillator to restart and stabilize (normally less than 10ms).
With an external interrupt, INT0 and INT1 must be enabled and configured as level-sensitive. Holding the pin low restarts the oscillator but bringing the pin back high completes the exit. Once the interrupt is serviced, the next instruction to be executed after RETI will be the one following the instruction that put the device into
Power Down.
Design Consideration
•To eliminate the possibility of an unexpected write when Idle is terminated by reset, the instruction following the one that invokes
Idle should not be one that writes to a port pin or to memory.
Table 2. External Pin Status During Idle and Power-Down Mode
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MODE |
PROGRAM MEMORY |
ALE |
|
PSEN |
PORT 0 |
PORT 1 |
PORT 2 |
PORT 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle |
Internal |
1 |
|
1 |
|
Data |
Data |
Data |
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle |
External |
1 |
|
1 |
|
Float |
Data |
Address |
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power-down |
Internal |
0 |
|
0 |
|
Data |
Data |
Data |
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power-down |
External |
0 |
|
0 |
|
Float |
Data |
Data |
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1998 Apr 24 |
7 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
TIMER 2 OPERATION
Timer 2
Timer 2 is a 16-bit Timer/Counter which can operate as either an event timer or an event counter, as selected by C/T2* in the special function register T2CON (see Figure 1). Timer 2 has three operating modes:Capture, Auto-reload, and Baud Rate Generator, which are selected by bits in the T2CON as shown in Table 3.
Capture Mode
In the capture mode there are two options which are selected by bit EXEN2 in T2CON. If EXEN2=0, then timer 2 is a 16-bit timer or counter (as selected by C/T2* in T2CON) which, upon overflowing sets bit TF2, the timer 2 overflow bit. This bit can be used to generate an interrupt (by enabling the Timer 2 interrupt bit in the
IE register/SFR table). If EXEN2= 1, Timer 2 operates as described above, but with the added feature that a 1- to -0 transition at external input T2EX causes the current value in the Timer 2 registers, TL2 and TH2, to be captured into registers RCAP2L and RCAP2H, respectively. In addition, the transition at T2EX causes bit EXF2 in T2CON to be set, and EXF2 like TF2 can generate an interrupt
(which vectors to the same location as Timer 2 overflow interrupt. The Timer 2 interrupt service routine can interrogate TF2 and EXF2 to determine which event caused the interrupt). The capture mode is
illustrated in Figure 2 (There is no reload value for TL2 and TH2 in this mode. Even when a capture event occurs from T2EX, the counter keeps on counting T2EX pin transitions or osc/12 pulses.).
Auto-Reload Mode
In the 16-bit auto-reload mode, Timer 2 can be configured as either a timer or counter (C/T2* in T2CON).
Figure 3 shows the auto±reload mode of Timer 2. In this mode there are two options selected by bit EXEN2 in T2CON register. If EXEN2=0, then Timer 2 counts up to 0FFFFH and sets the TF2
(Overflow Flag) bit upon overflow. This causes the Timer 2 registers to be reloaded with the 16-bit value in RCAP2L and RCAP2H.
The values in RCAP2L and RCAP2H are preset by software. If EXEN2=1, then a 16-bit reload can be triggered either by an overflow or by a 1-to-0 transition at input T2EX. This transition also sets the EXF2 bit. The Timer 2 interrupt, if enabled, can be generated when either TF2 or EXF2 are 1.
The external flag EXF2 toggles when Timer 2 underflows or overflows. This EXF2 bit can be used as a 17th bit of resolution if needed. The EXF2 flag does not generate an interrupt in this mode of operation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(MSB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(LSB) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TF2 |
|
EXF2 |
RCLK |
TCLK |
EXEN2 |
TR2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
C/T2 |
|
CP/RL2 |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Symbol |
Position |
Name and Significance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
TF2 |
T2CON.7 |
Timer 2 overflow flag set by a Timer 2 overflow and must be cleared by software. TF2 will not be set |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
when either RCLK or TCLK = 1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
EXF2 |
T2CON.6 |
Timer 2 external flag set when either a capture or reload is caused by a negative transition on T2EX and |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXEN2 = 1. When Timer 2 interrupt is enabled, EXF2 = 1 will cause the CPU to vector to the Timer 2 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
interrupt routine. EXF2 must be cleared by software. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
RCLK |
T2CON.5 |
Receive clock flag. When set, causes the serial port to use Timer 2 overflow pulses for its receive clock |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in modes 1 and 3. RCLK = 0 causes Timer 1 overflow to be used for the receive clock. |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
TCLK |
T2CON.4 |
Transmit clock flag. When set, causes the serial port to use Timer 2 overflow pulses for its transmit clock |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in modes 1 and 3. TCLK = 0 causes Timer 1 overflows to be used for the transmit clock. |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
EXEN2 |
T2CON.3 |
Timer 2 external enable flag. When set, allows a capture or reload to occur as a result of a negative |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
transition on T2EX if Timer 2 is not being used to clock the serial port. EXEN2 = 0 causes Timer 2 to |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ignore events at T2EX. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
TR2 |
T2CON.2 |
Start/stop control for Timer 2. A logic 1 starts the timer. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
T2CON.1 |
Timer or counter select. (Timer 2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
C/T2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 = Internal timer (OSC/12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 = External event counter (falling edge triggered). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
T2CON.0 |
Capture/Reload flag. When set, captures will occur on negative transitions at T2EX if EXEN2 = 1. When |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CP/RL2 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cleared, auto-reloads will occur either with Timer 2 overflows or negative transitions at T2EX when |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXEN2 = 1. When either RCLK = 1 or TCLK = 1, this bit is ignored and the timer is forced to auto-reload |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
on Timer 2 overflow. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SU00866 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 1. Timer/Counter 2 (T2CON) Control Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Table 3. Timer 2 Operating Modes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
RCLK + TCLK |
|
CP/RL2 |
|
|
|
TR2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MODE |
|
||||||||||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
16-bit Auto-reload |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
16-bit Capture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
1 |
|
|
Baud rate generator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
0 |
|
|
(off) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1998 Apr 24 |
8 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
OSC |
12 |
|
|
|
|
C/T2 = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
TL2 |
TH2 |
TF2 |
|
|
(8-bits) |
(8-bits) |
|
|
|
|
||
|
C/T2 = 1 |
|
|
|
T2 Pin |
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TR2 |
Capture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transition |
|
|
Timer 2 |
|
Detector |
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
RCAP2L |
RCAP2H |
|
T2EX Pin |
|
|
|
EXF2 |
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
EXEN2 |
|
|
SU00066 |
|
|
|
|
Figure 2. Timer 2 in Capture Mode
OSC |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
C/T2 = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
TL2 |
TH2 |
|
|
|
(8-BITS) |
(8-BITS) |
|
|
C/T2 = 1 |
|
|
T2 PIN |
|
|
CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TR2 |
RELOAD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRANSITION |
|
|
|
|
DETECTOR |
|
RCAP2L |
RCAP2H |
|
|
|
|
TF2 |
|
|
|
|
TIMER 2 |
|
|
|
|
INTERRUPT |
T2EX PIN |
|
|
|
EXF2 |
|
|
CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
EXEN2 |
|
SU00067 |
Figure 3. Timer 2 in Auto-Reload Mode
1998 Apr 24 |
9 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Preliminary specification |
|
|
|
|
80C51 8-bit microcontroller family
89C536/89C538
16K/64K/512 FLASH
|
|
|
|
|
Timer 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overflow |
|
|
|
NOTE: OSC. Freq. is divided by 2, not 12. |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OSC |
2 |
|
|
|
ª0º |
ª1º |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
C/T2 = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
SMOD |
|
|
|
|
ª1º |
ª0º |
|
|
|
|
TL2 |
TH2 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
(8-bits) |
(8-bits) |
|
|
|
RCLK |
|
C/T2 = 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
T2 Pin |
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
RX Clock |
|
TR2 |
|
Reload |
ª1º |
ª0º |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TCLK |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Detector |
RCAP2L |
RCAP2H |
|
|
16 |
TX Clock |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
T2EX Pin |
EXF2 |
Timer 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXEN2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note availability of additional external interrupt. |
|
|
|
|
SU00068 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 4. Timer 2 in Baud Rate Generator Mode
Table 4. Timer 2 Generated Commonly Used
Baud Rates
Baud Rate |
Osc Freq |
Timer 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
RCAP2H |
|
RCAP2L |
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
375K |
12MHz |
FF |
|
FF |
9.6K |
12MHz |
FF |
|
D9 |
2.8K |
12MHz |
FF |
|
B2 |
2.4K |
12MHz |
FF |
|
64 |
1.2K |
12MHz |
FE |
|
C8 |
300 |
12MHz |
FB |
|
1E |
110 |
12MHz |
F2 |
|
AF |
300 |
6MHz |
FD |
|
8F |
110 |
6MHz |
F9 |
|
57 |
|
|
|
|
|
Baud Rate Generator Mode
Bits TCLK and/or RCLK in T2CON (Table 3) allow the serial port transmit and receive baud rates to be derived from either Timer 1 or Timer 2. When TCLK= 0, Timer 1 is used as the serial port transmit baud rate generator. When TCLK= 1, Timer 2 is used as the serial port transmit baud rate generator. RCLK has the same effect for the serial port receive baud rate. With these two bits, the serial port can have different receive and transmit baud rates ± one generated by
Timer 1, the other by Timer 2.
Figure 4 shows the Timer 2 in baud rate generation mode. The baud rate generation mode is like the auto-reload mode,in that a rollover in TH2 causes the Timer 2 registers to be reloaded with the 16-bit value in registers RCAP2H and RCAP2L, which are preset by software.
The baud rates in modes 1 and 3 are determined by Timer 2's overflow rate given below:
Modes 1 and 3 Baud Rates Timer 2 Overflow Rate 16
The timer can be configured for either ªtimerº or ªcounterº operation. In many applications, it is configured for ªtimerº operation (C/T2*=0). Timer operation is different for Timer 2 when it is being used as a baud rate generator.
Usually, as a timer it would increment every machine cycle (i.e., 1/12 the oscillator frequency). As a baud rate generator, it increments every state time (i.e., 1/2 the oscillator frequency). Thus the baud rate formula is as follows:
Modes 1 and 3 Baud Rates =
Oscillator Frequency
[32 [65536 (RCAP2H, RCAP2L)]]
Where: (RCAP2H, RCAP2L)= The content of RCAP2H and RCAP2L taken as a 16-bit unsigned integer.
The Timer 2 as a baud rate generator mode shown in Figure 4, is valid only if RCLK and/or TCLK = 1 in T2CON register. Note that a rollover in TH2 does not set TF2, and will not generate an interrupt.
Thus, the Timer 2 interrupt does not have to be disabled when
Timer 2 is in the baud rate generator mode. Also if the EXEN2 (T2 external enable flag) is set, a 1-to-0 transition in T2EX (Timer/counter 2 trigger input) will set EXF2 (T2 external flag) but will not cause a reload from (RCAP2H, RCAP2L) to (TH2,TL2).
Therefore when Timer 2 is in use as a baud rate generator, T2EX can be used as an additional external interrupt, if needed.
1998 Apr 24 |
10 |
 Loading...
Loading...