NSC DS485TN, DS485TMX, DS485TM, DS485N, DS485MX Datasheet
...
July 1998
DS485
Low Power RS-485/RS-422 Multipoint Transceiver
General Description
The DS485 is a low-power transceiver for RS-485 and RS-422 communication. The device contains one driver and one receiver. The drivers slew rate allows for operation up to 2.5 Mbps (see Applications Information section).
The transceiver draws 200 µA of supply current when unloaded or fully loaded with the driver disabled and operates from a single +5V supply.
The driver is short-circuit current limited and is protected against excessive power dissipation by thermal shutdown circuitry that places the driver outputs into TRI-STATE® (High Impedance state) under fault conditions. The driver guarantees a minimum of 1.5V differential output voltage with maximum loading across the common mode range (VOD3).
The receiver has a failsafe feature that guarantees a logic-high output if the input is open circuit.
The DS485 is available in surface mount and DIP packages and is characterized for Industrial and Commercial temperature range operation.
Features
nMeets TIA/EIA RS-485 multipoint standard
nGuaranteed full load output voltage (V OD3)
nLow quiescent current: 200 µA typ
n−7V to +12V common-mode input voltage range
nTRI-STATE outputs on driver and receiver
nAC performance:
ÐDriver transition time: 25 ns typ
ÐDriver propagation delay: 40 ns typ
ÐDriver skew: 1 ns typ
ÐReceiver propagation delay: 200 ns typ
ÐReceiver skew: 20 ns typ
nHalf-duplex flow through pinout
nOperates from a single 5V supply
nAllows up to 32 transceivers on the bus
nCurrent-limiting and thermal shutdown for driver overload protection
nIndustrial temperature range operation
nPin and functional compatible with MAX485 and LTC485
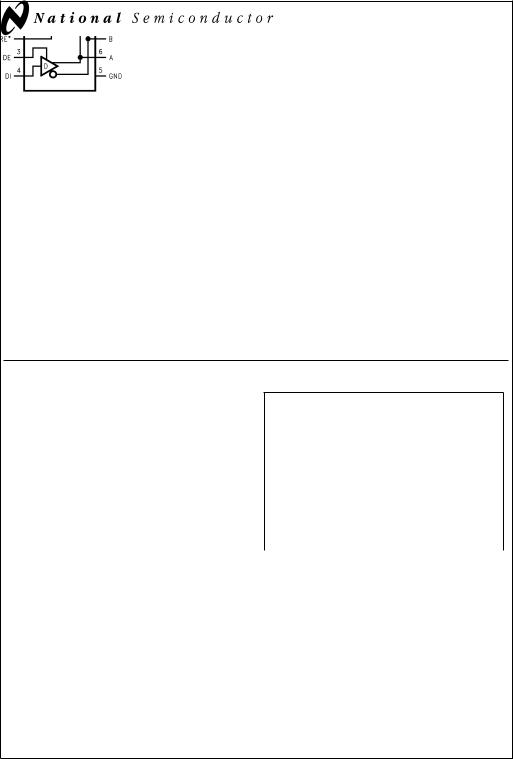
Connection and Logic Diagram
DIP and SOIC
|
|
DS012880-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Order Number |
Temp. Range |
|
Package/### |
|
|
|
|
DS485N |
0ÊC to +70ÊC |
|
DIP/N08E |
|
|
|
|
DS485M |
0ÊC to +70ÊC |
|
SOP/M08A |
|
|
|
|
DS485TN |
−40ÊC to +85ÊC |
|
DIP/N08E |
|
|
|
|
DS485TM |
−40ÊC to +85ÊC |
|
SOP/M08A |
|
|
|
|
Truth Table
DRIVER SECTION
RE* |
DE |
DI |
|
A |
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
H |
H |
|
H |
L |
X |
H |
L |
|
L |
H |
X |
L |
X |
|
Z |
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RECEIVER SECTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RE* |
DE |
|
A-B |
RO |
|
L |
L |
|
³+0.2V |
H |
|
L |
L |
|
£−0.2V |
L |
|
H |
X |
|
X |
Z |
|
L |
L |
|
OPEN* |
H |
|
*Note: Non Terminated, Open Input only X = indeterminate
Z = TRI-STATE
TRI-STATE® is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
Transceiver Multipoint 422-485/RS-RS Power Low DS485
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation |
DS012880 |
www.national.com |

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (VCC) |
+12V |
Enable Input Voltage (RE*, DE) |
−0.5V to (V CC + 0.5V) |
Driver Input Voltage (DI) |
−0.5V to (V CC + 0.5V) |
Driver Output Voltage (A, B) |
−14V to +14V |
Receiver Input Voltage (A, B) |
−14V to +14V |
Receiver Output Voltage (RO) |
−0.5V to (V CC + 0.5V) |
Maximum Package Power Dissipation @ +25ÊC |
|
M Package |
1.19W |
N Package |
0.74W |
Derate M Package 9.5 mW/ÊC above +25ÊC |
|
Derate N Package 6.0 mW/ÊC above +25ÊC |
|
Maximum Package Power Dissipation @ +70ÊC |
|
M Package |
0.76W |
N Package |
0.47W |
Storage Temperature Range |
−65ÊC to +150ÊC |
Lead Temperature Range |
|
(Soldering, 4 sec.) |
+260ÊC |
ESD (HBM) |
³2 kV |
Recommended Operating
Conditions
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
Supply Voltage (VCC) |
+4.75 |
+5.0 |
+5.25 |
V |
Operating Free Air |
|
|
|
|
Temperature (TA) |
|
|
|
|
DS485 |
0 |
+25 |
+70 |
ÊC |
DS485T |
−40 |
+25 |
+85 |
ÊC |
Bus Common Mode Voltage |
−7 |
|
+12 |
V |
Electrical Characteristics
Over Supply Voltage and Operating Temperature Ranges, unless otherwise specified (Notes 2, 3)
Symbol |
Parameter |
|
Conditions |
Pin |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOD1 |
Differential Driver Output Voltage |
(No Load) |
A, B |
|
|
5 |
V |
|
VOD2 |
Differential Driver Output Voltage |
RL = 50W, (RS422), Figure 1 |
|
2 |
2.8 |
|
V |
|
|
with Load |
RL = 27W, (RS485), Figure 1 |
|
1.5 |
2.3 |
5 |
V |
|
DVOD |
Change in Magnitude of Output |
RL = 27W or 50W (Note 4) |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|V| |
|
|
Differential Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOD3 |
Differential Driver Output Voltage Ð |
R1 = 54W, R2 = 375W |
|
1.5 |
2.0 |
5 |
V |
|
|
Full Load with Max VCM |
VTEST = −7V to +12V, Figure 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOC |
Driver Common-Mode Output Voltage |
RL = 27W or 50W, Figure 1 |
|
|
|
3 |
V |
|
DVOC |
Change in Magnitude of Common-Mode |
RL = 27W or 50W, Figure 1 (Note 4) |
|
|
|
0.2 |
|V| |
|
|
Output Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIH |
Input High Voltage |
|
|
DI, |
2.0 |
|
|
V |
VIL |
Input Low Voltage |
|
|
DE, |
|
|
0.8 |
V |
|
|
|
|
RE* |
|
|
|
|
IIN1 |
Input Current |
VIN = 0V or VCC |
|
|
±2 |
µA |
||
|
|
|
||||||
IIN2 |
Input Current (Note 5) |
VIN = +12V |
A, B |
|
|
1.0 |
mA |
|
|
DE = 0V, VCC = 0V or 5.25V |
VIN = −7V |
|
|
|
−0.8 |
mA |
|
VTH |
Receiver Differential Threshold Voltage |
−7V |
£ VCM £ +12V |
|
−0.2 |
|
0.2 |
V |
DVTH |
Receiver Input Hysteresis |
VCM = 0V |
|
|
70 |
|
mV |
|
VOH |
Receiver Output High Voltage |
IO = −4 mA, V ID = 0.2V |
RO |
3.5 |
|
|
V |
|
VOL |
Receiver Output Low Voltage |
IO = 4 mA, VID = −0.2V |
|
|
|
0.4 |
V |
|
IOZR |
TRI-STATE Output Current at Receiver |
0.4V £ VO £ 2.4V |
|
|
|
±1 |
µA |
|
RIN |
Receiver Input Resistance |
−7V |
£ VIN £ +12V |
A, B |
12 |
|
|
kW |
ICC |
No-Load Supply Current (Note 6) |
DE = VCC, RE* = 0V or VCC |
VCC |
|
200 |
900 |
µA |
|
|
|
DE = 0V, RE* = 0V or VCC |
|
|
200 |
500 |
µA |
|
IOSD1 |
Driver Short Circuit Current, VO = HIGH |
−7V |
£ VO £ +12V |
A, B |
35 |
|
250 |
mA |
IOSD2 |
Driver Short Circuit Current, VO = LOW |
−7V |
£ VO £ +12V |
|
35 |
|
250 |
mA |
IOSR |
Receiver Short Circuit Current |
0V £ VO £ VCC |
RO |
7 |
|
85 |
mA |
|
www.national.com |
2 |

Switching Characteristics
Over Supply Voltage and Operating Temperature Ranges, unless otherwise specified (Notes 3, 7, 8)
Symbol |
Parameter |
Conditions |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tPLHD |
Driver Differential Propagation Delay Ð Low to High |
R L = 54Ω, CL = 100 pF |
10 |
40 |
65 |
ns |
tPHLD |
Driver Differential Propagation Delay Ð High to Low |
|
10 |
39 |
65 |
ns |
tSKEW |
Differential Skew |tPHLD − t PLHD| |
|
|
1 |
10 |
ns |
tr |
Driver Rise Time |
|
3 |
25 |
40 |
ns |
tf |
Driver Fall Time |
|
3 |
25 |
40 |
ns |
tZH |
Driver Enable to Output High |
CL = 100 pF |
|
|
170 |
ns |
tZL |
Driver Enable to Output Low |
CL = 100 pF |
|
|
170 |
ns |
tLZ |
Driver Disable from Output Low |
CL = 15 pF |
|
|
170 |
ns |
tHZ |
Driver Disable from Output High |
CL = 15 pF |
|
|
170 |
ns |
tPLHD |
Receiver Differential Propagation Delay Ð Low to High |
C L = 15 pF (RO) |
70 |
190 |
320 |
ns |
tPHLD |
Receiver Differential Propagation Delay Ð High to Low |
|
70 |
210 |
320 |
ns |
tSKEW |
Differential Skew |tPHLD − t PLHD| |
|
|
20 |
50 |
ns |
tZH |
Receiver Enable to Output High |
CL = 15 pF |
|
|
110 |
ns |
tZL |
Receiver Enable to Output Low |
|
|
|
110 |
ns |
tLZ |
Receiver Disable from Output Low |
|
|
|
110 |
ns |
tHZ |
Receiver Disable from Output High |
|
|
|
110 |
ns |
fmax |
Maximum Data Rate |
(Note 9) |
2.5 |
|
|
Mbps |
Note 1: ªAbsolute Maximum Ratingsº are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the devices should be operated at these limits. The table of ªElectrical Characteristicsº specifies conditions of device operation.
Note 2: Current into device pins is defined as positive. Current out of device pins is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VOD1/2/3 and VID.
Note 3: All typicals are given for: VCC = +5.0V, TA = +25ÊC.
Note 4: |VOD| and |VOC| are changes in magnitude of V OD and VOCrespectively, that occur when the input changes state.
Note 5: IIN2 includes the receiver input current and driver TRI-STATE leakage current.
Note 6: Supply current specification is valid for loaded transmitters when DE = 0V or enabled (DE = H) with no load. Note 7: f = 1 MHz, tr and tf ≤ 6 ns, ZO = 50Ω.
Note 8: CL includes jig and probe capacitance.
Note 9: fmax is the guaranteed data rate for 50 ft of twisted pair cable. f max may be conservatively determined from the ratio of driver transition time (tr) to the data rate unit interval (1/fmax). Using a 10% ratio yields fmax = (0.1)/40 ns = 2.5 Mb/s. Higher data rates may be supported by allowing larger ratios.
3 |
www.national.com |
 Loading...
Loading...