NSC DS90CF386MTDX, DS90CF386MTD Datasheet
November 1999
DS90CF386/DS90CF366
+3.3V LVDS Receiver 24-Bit Flat Panel Display (FPD) LinkÐ 85 MHz, +3.3V LVDS Receiver 18-Bit Flat Panel Display (FPD) LinkÐ 85 MHz
General Description
The DS90CF386 receiver converts the four LVDS data streams (Up to 2.38 Gbps throughput or 297.5 Megabytes/ sec bandwidth) back into parallel 28 bits of CMOS/TTL data (24 bits of RGB and 4 bits of Hsync, Vsync, DE and CNTL). Also available is the DS90CF366 that converts the three LVDS data streams (Up to 1.78 Gbps throughput or 223 Megabytes/sec bandwidth) back into parallel 21 bits of CMOS/TTL data (18 bits of RGB and 3 bits of Hsync, Vsync and DE). Both Receivers' outputs are Falling edge strobe. A Rising edge or Falling edge strobe transmitter (DS90C385/ DS90C365) will interoperate with a Falling edge strobe Receiver without any translation logic.
This chipset is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size problems associated with wide, high speed TTL interfaces.
Features
n20 to 85 MHz shift clock support
nRx power consumption <142 mW (typ) @85MHz Grayscale
nRx Power-down mode <1.44 mW (max)
nESD rating >7 kV (HBM), >700V (EIAJ)
nSupports VGA, SVGA, XGA and Single Pixel SXGA.
nPLL requires no external components
nCompatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS standard
nLow profile 56-lead or 48-lead TSSOP package
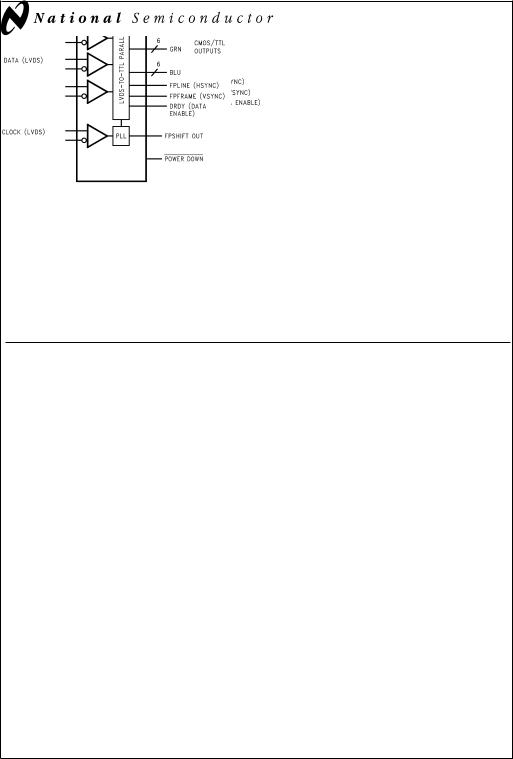
Block Diagrams
DS90CF386 |
DS90CF366 |
DS101085-27
Order Number DS90CF386MTD |
DS101085-28 |
|
Order Number DS90CF366MTD |
||
See NS Package Number MTD56 |
||
See NS Package Number MTD48 |
||
|
TRI-STATE® is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
Display Panel Flat Color-Bit-18 Receiver LVDS 3V.+3 MHz, 85 Ð Link |
Panel Flat Color-Bit-24 Receiver LVDS 3V.+3 DS90CF386/DS90CF366 |
85 Ð Link (FPD) |
(FPD) Display |
MHz |
|
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation |
DS101085 |
www.national.com |

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (VCC) |
−0.3V to +4V |
CMOS/TTL Output Voltage |
−0.3V to (V CC + 0.3V) |
LVDS Receiver Input Voltage |
−0.3V to (V CC + 0.3V) |
Junction Temperature |
+150ÊC |
Storage Temperature |
−65ÊC to +150ÊC |
Lead Temperature |
|
(Soldering, 4 sec) |
+260ÊC |
Maximum Package Power |
|
Dissipation Capacity @ 25ÊC |
|
MTD56 (TSSOP) Package: |
|
DS90CF386 |
1.61 W |
MTD48 (TSSOP) Package: |
|
DS90CF366 |
1.89 W |
Package Derating: |
|
DS90CF386 |
12.4 mW/ÊC above +25ÊC |
DS90CF366 |
15 mW/ÊC above +25ÊC |
ESD Rating |
|
(HBM, 1.5 kΩ, 100 pF) |
> 7 kV |
(EIAJ, 0Ω, 200 pF) |
> 700V |
Recommended Operating
Conditions
|
Min |
Nom |
Max |
Units |
Supply Voltage (VCC) |
3.0 |
3.3 |
3.6 |
V |
Operating Free Air |
|
|
|
|
Temperature (TA) |
−10 |
+25 |
+70 |
ÊC |
Receiver Input Range |
0 |
|
2.4 |
V |
Supply Noise Voltage (VCC) |
|
|
100 |
mVPP |
Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol |
Parameter |
|
|
Conditions |
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CMOS/TTL DC SPECIFICATIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VIH |
High Level Input Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
VCC |
V |
VIL |
Low Level Input Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
GND |
|
0.8 |
V |
VOH |
High Level Output Voltage |
|
IOH = - 0.4 mA |
|
2.7 |
3.3 |
|
V |
||
VOL |
Low Level Output Voltage |
|
IOL = 2 mA |
|
|
0.06 |
0.3 |
V |
||
VCL |
Input Clamp Voltage |
|
ICL = −18 mA |
|
|
-0.79 |
-1.5 |
V |
||
IIN |
Input Current |
|
VIN = 0.4V, 2.5V or |
|
|
+1.8 |
+15 |
uA |
||
|
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
VIN = GND |
|
-10 |
0 |
|
uA |
|||
IOS |
Output Short Circuit Current |
|
VOUT = 0V |
|
|
-60 |
-120 |
mA |
||
LVDS RECEIVER DC SPECIFICATIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VTH |
Differential Input High Threshold |
|
V CM = +1.2V |
|
|
|
+100 |
mV |
||
VTL |
Differential Input Low Threshold |
|
|
|
|
|
−100 |
|
|
mV |
I IN |
Input Current |
|
V IN = +2.4V, VCC = 3.6V |
|
|
|
±10 |
µA |
||
|
|
V IN = 0V, VCC = 3.6V |
|
|
|
±10 |
µA |
|||
RECEIVER SUPPLY CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICCRW |
Receiver Supply Current |
CL = 8 pF, |
|
f = 32.5 MHz |
|
49 |
70 |
mA |
||
|
Worst Case |
|
Worst Case Pattern, |
|
f = 37.5 MHz |
|
53 |
75 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
DS90CF386 (Figures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 65 MHz |
|
81 |
114 |
mA |
||
|
|
1, 4 ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 85 MHz |
|
96 |
135 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICCRW |
Receiver Supply Current |
CL = 8 pF, |
|
f = 32.5 MHz |
|
49 |
60 |
mA |
||
|
Worst Case |
|
Worst Case Pattern, |
|
f = 37.5 MHz |
|
53 |
65 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
DS90CF366 (Figures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 65 MHz |
|
78 |
100 |
mA |
||
|
|
1, 4 ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 85 MHz |
|
90 |
115 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICCRG |
Receiver Supply Current, |
CL = 8 pF, |
|
f = 32.5 MHz |
|
28 |
45 |
mA |
||
|
16 Grayscale |
|
16 Grayscale Pattern, |
|
f = 37.5 MHz |
|
30 |
47 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Figures 2, 3, 4 ) |
|
f = 65 MHz |
|
43 |
60 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f = 85 MHz |
|
43 |
70 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICCRZ |
Receiver Supply Current |
|
|
|
140 |
400 |
µA |
|||
|
Power Down |
= Low |
|
|
||||||
|
Power Down |
Receiver Outputs Stay Low during |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Power Down Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
www.national.com |
2 |
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Note 1: ªAbsolute Maximum Ratingsº are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the device should be operated at these limits. The tables of ªElectrical Characteristicsº specify conditions for device operation.
Note 2: Typical values are given for VCC = 3.3V and TA = +25C.
Note 3: Current into device pins is defined as positive. Current out of device pins is defined as negative. Voltages are referenced to ground unless otherwise specified (except VOD and V OD).
Receiver Switching Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified
Symbol |
Parameter |
|
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLHT |
CMOS/TTL Low-to-High Transition Time (Figure 4 ) |
|
|
2.0 |
3.5 |
ns |
CHLT |
CMOS/TTL High-to-Low Transition Time (Figure 4 ) |
|
|
1.8 |
3.5 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSPos0 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 0 (Figure 11, |
f = 85 MHz |
0.49 |
0.84 |
1.19 |
ns |
|
Figure 12 ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSPos1 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 1 |
|
2.17 |
2.52 |
2.87 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSPos2 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 2 |
|
3.85 |
4.20 |
4.55 |
ns |
RSPos3 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 3 |
|
5.53 |
5.88 |
6.23 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSPos4 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 4 |
|
7.21 |
7.56 |
7.91 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSPos5 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 5 |
|
8.89 |
9.24 |
9.59 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSPos6 |
Receiver Input Strobe Position for Bit 6 |
|
10.57 |
10.92 |
11.27 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSKM |
RxIN Skew Margin (Note 4) (Figure 13 ) |
f = 85 MHz |
290 |
|
|
ps |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RCOP |
RxCLK OUT Period (Figure 5) |
|
11.76 |
T |
50 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RCOH |
RxCLK OUT High Time (Figure 5 ) |
f = 85 MHz |
4.5 |
5 |
7 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RCOL |
RxCLK OUT Low Time (Figure 5) |
|
4.0 |
5 |
6.5 |
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSRC |
RxOUT Setup to RxCLK OUT (Figure 5 ) |
|
3.5 |
|
|
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RHRC |
RxOUT Hold to RxCLK OUT (Figure 5 ) |
|
3.5 |
|
|
ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RCCD |
RxCLK IN to RxCLK OUT Delay 25ÊC, VCC = 3.3V (Figure 6 ) |
5.5 |
7.0 |
9.5 |
ns |
|
RPLLS |
Receiver Phase Lock Loop Set (Figure 7 ) |
|
|
|
10 |
ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RPDD |
Receiver Power Down Delay (Figure 10 ) |
|
|
|
1 |
µs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note 4: Receiver Skew Margin is defined as the valid data sampling region at the receiver inputs. This margin takes into account the transmitter pulse positions (min and max) and the receiver input setup and hold time (internal data sampling window - RSPos). This margin allows for LVDS interconnect skew, inter-symbol interference (both dependent on type/length of cable), and clock jitter (less than 150 ps).
AC Timing Diagrams
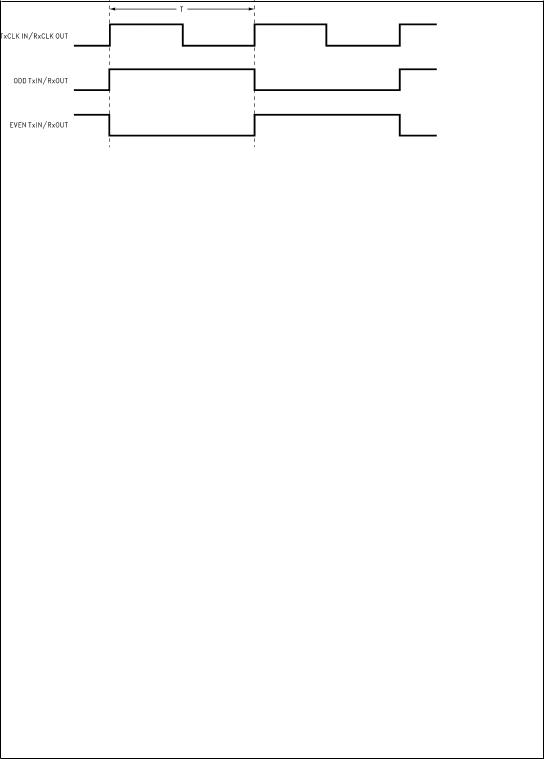
DS101085-2
FIGURE 1. ªWorst Caseº Test Pattern
3 |
www.national.com |
AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
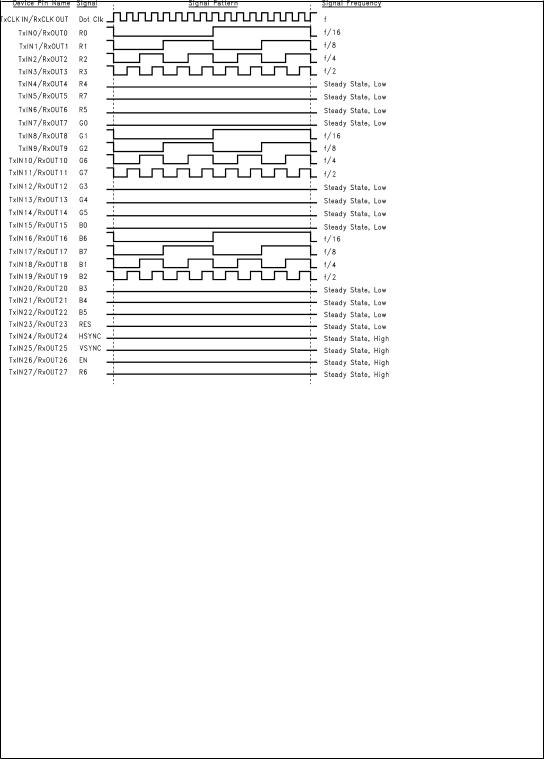
DS101085-12
FIGURE 2. ª16 Grayscaleº Test Pattern (DS90CF386)(Notes 5, 6, 7, 8)
www.national.com |
4 |
AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
DS101085-3
FIGURE 3. ª16 Grayscaleº Test Pattern (DS90CF366)(Notes 5, 6, 7, 8)
Note 5: The worst case test pattern produces a maximum toggling of digital circuits, LVDS I/O and CMOS/TTL I/O.
Note 6: The 16 grayscale test pattern tests device power consumption for a ªtypicalº LCD display pattern. The test pattern approximates signal switching needed to produce groups of 16 vertical stripes across the display.
Note 7: Figures 1, 3 show a falling edge data strobe (TxCLK IN/RxCLK OUT).
Note 8: Recommended pin to signal mapping. Customer may choose to define differently.
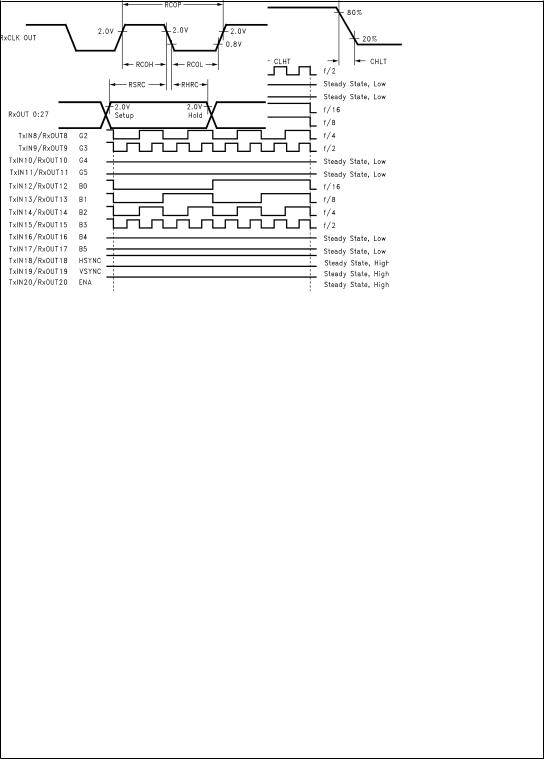
DS101085-4
FIGURE 4. DS90CF386/DS90CF366 (Receiver) CMOS/TTL Output Load and Transition Times
DS101085-5
FIGURE 5. DS90CF386/DS90CF366 (Receiver) Setup/Hold and High/Low Times
5 |
www.national.com |
 Loading...
Loading...