Philips TDA8722T-C2, TDA8722T-C3, TDA8722T-C1, TDA8722M-C2, TDA8722M-C3 Datasheet
...
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
TDA8722
I2C-bus programmable modulator for negative video modulation and FM sound
Product specification |
1998 Jun 23 |
Supersedes data of 1995 Mar 21
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
FEATURES
∙Video amplifier with clamp and white clip circuits
∙FM sound modulator
∙Asymmetrical and symmetrical RF outputs available
∙Symmetrical RF oscillator using only a few external components
∙External adjusting of modulation depth and level of the sound subcarrier
∙I2C-bus receiver for frequency setting and test-mode selection
∙One I2C programmable output port
∙On-chip Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer
∙On-chip power supply regulator
∙Bus switchable oscillator
∙On-chip Test Pattern Signal Generator (TPSG).
APPLICATIONS
∙Video recorders
∙Cable converters
∙Satellite receivers.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8722 is a programmable modulator which generates an RF TV channel from a baseband video signal and a baseband audio signal in the event of negative video and FM sound standards (PAL B/G, I, D/K and NTSC).
It is especially suited for satellite receivers, video recorders and cable converters. The video carrier frequency is set exactly to the correct channel frequency by a PLL synthesizer which is programmed in accordance with the I2C-bus format.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE |
|
PACKAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
NUMBER |
NAME |
DESCRIPTION |
VERSION |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
TDA8722T |
SO20 |
plastic small outline package; 20 leads; body width 7.5 mm |
SOT163-1 |
|
|
|
|
TDA8722M |
SSOP20 |
plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm |
SOT266-1 |
|
|
|
|
1998 Jun 23 |
2 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
VDDA = VDDD = 5 V; Tamb = 25 °C after the IC has reached thermal equilibrium; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL |
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
MIN. |
TYP. |
MAX. |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDDA |
analog supply voltage |
|
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.5 |
V |
VDDD |
digital supply voltage |
|
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.5 |
V |
IDD |
total supply current |
normal mode |
41 |
52 |
63 |
mA |
m |
typical modulation depth range |
video level (pin 19) = 0.5 V (p-p); |
65 |
− |
90 |
% |
|
|
note 1; see Fig.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P/S |
typical picture-to-sound level |
note 2; see Fig.11 |
−18 |
− |
−10 |
dB |
|
range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VRF |
RF output voltage level |
frequency between |
77 |
80 |
83 |
dBμV |
|
asymmetrical on a 75 Ω load |
471.25 and 855.25 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
δf |
FM deviation on audio |
fi = 400 Hz; V1 = 0.5 V (RMS); |
20 |
25 |
30 |
kHz |
|
subcarrier |
before pre-emphasis filter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes
1.Value depends on value of resistor R17 (see Fig.7).
2.Value depends on value of capacitor C17 (see Fig.7).
1998 Jun 23 |
3 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
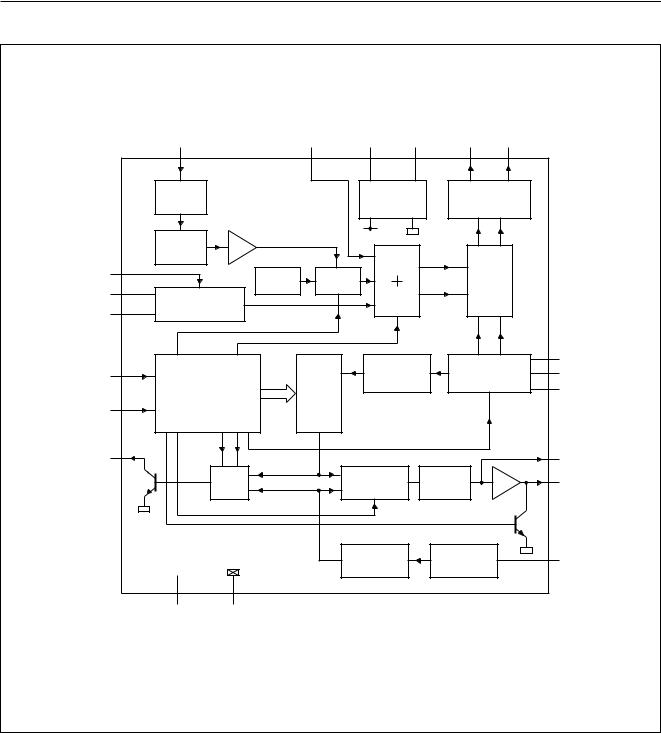
BLOCK DIAGRAM
|
VIDEO |
ADJUST |
AGND |
VDDA |
|
RFA |
RFB |
|
|
|||
|
19 |
|
17 |
18 |
20 |
|
|
16 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
CLAMP |
TDA8722 |
|
VOLTAGE |
ASYMMETRICAL |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
REGULATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
BUFFER |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
VIDEO AMP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AUDIO |
|
TPSG |
SWITCH |
|
|
|
MIXER |
|
|
|
||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOSCA |
AUDIO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FM MODULATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
SOSCB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TPSG on |
balance test |
|
|
|
PC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
UOSCA |
|
|
|
|
PRESCALER |
|
|
UHF |
|
|
5 |
||
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OGND |
||||
SDA |
|
|
|
(8) |
|
OSCILLATOR |
4 |
|||||
I 2C-BUS |
12-BIT |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UOSCB |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
12 |
RECEIVER |
DIVIDER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(N) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
SCL |
|
10 bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
enable/ |
|
|
RF oscillator on |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
||
select |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
P0 |
f DIV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
PHASE |
CHARGE |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|||
|
LOGIC |
|
AMP |
|
AMP |
|||||||
|
|
DETECTOR |
|
PUMP |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
f ref |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
enable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
DIVIDER |
|
4 MHz |
|
|
9 |
XTAL |
||
|
|
31.25 kHz |
(M = 128) |
|
OSCILLATOR |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
11 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDDD |
DGND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MBE401 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1998 Jun 23 |
4 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
PINNING
SYMBOL |
PIN |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
AUDIO |
1 |
audio input |
|
|
|
SOSCA |
2 |
sound oscillator A |
|
|
|
SOSCB |
3 |
sound oscillator B |
|
|
|
UOSCB |
4 |
UHF oscillator B |
|
|
|
OGND |
5 |
RF oscillator ground |
|
|
|
UOSCA |
6 |
UHF oscillator A |
|
|
|
AMP |
7 |
tuning amplifier output |
|
|
|
CP |
8 |
charge pump output |
|
|
|
XTAL |
9 |
crystal oscillator |
|
|
|
DGND |
10 |
digital ground |
|
|
|
VDDD |
11 |
digital supply voltage |
SCL |
12 |
serial clock input (I2C-bus) |
SDA |
13 |
serial data input (I2C-bus) |
P0 |
14 |
NPN open-collector output Port |
|
|
|
RFB |
15 |
asymmetrical RF output B |
|
|
|
RFA |
16 |
asymmetrical RF output A |
|
|
|
ADJUST |
17 |
modulation depth and picture-to-sound |
|
|
distance adjustment pin |
|
|
|
AGND |
18 |
analog ground |
|
|
|
VIDEO |
19 |
video input |
|
|
|
VDDA |
20 |
analog supply voltage |
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8722 is a programmable modulator which can be divided into two main blocks:
∙A modulator for negative video modulation and FM sound TV standards
∙A programmable PLL frequency synthesizer.
The video part of the modulator consists of a clamping circuit which sets the internal reference voltage to the bottom of the synchronizing pulse, followed by a white clip which avoids over modulation in case the video signal is too strong. Typically, the IC starts to clip the video signal when the voltage at the video input (pin 19) is
>560 mV (p-p) while the normal voltage at the video input is 500 mV (p-p). This clipping function ensures that the video modulation depth is not too high. The modulation depth is adjusted in the application between at least
65 and 90% by changing the resistor value between pin 17
handbook, halfpage |
|
|
|
VDDA |
AUDIO |
1 |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOSCA |
2 |
|
19 |
VIDEO |
SOSCB |
|
|
|
AGND |
3 |
|
18 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
UOSCB |
4 |
|
17 |
ADJUST |
|
|
|
|
|
OGND |
5 |
TDA8722 |
16 |
RFA |
|
|
|
|
|
UOSCA |
6 |
|
15 |
RFB |
|
|
|
|
|
AMP |
7 |
|
14 |
P0 |
|
|
|
|
|
CP |
8 |
|
13 |
SDA |
|
|
|
|
|
XTAL |
9 |
|
12 |
SCL |
DGND |
|
|
|
VDDD |
10 |
|
11 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MBE394 |
|
|
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
and ground (R17). The value can change between 47 kΩ and infinite (R17 removed); see Fig.10.
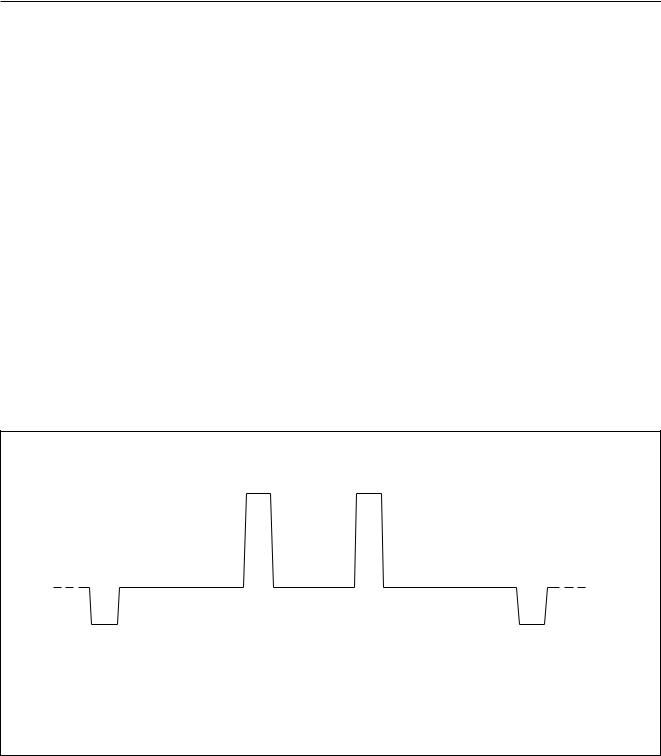
The video part also contains a test pattern signal generator to simplify the adjustment of the receiving channel of the TV set to the required channel of the modulator. The pattern consists of a synchronization pulse and two vertical white bars on screen (see Fig.3).
The audio part of the modulator contains an FM sound modulator. The frequency of the sound subcarrier is set in the application by external components (C3, L3 and R3). The difference between the video carrier level and the sound subcarrier level is adjusted in the application by changing the value of the capacitor between pin 17 and ground (C17). The value can change between
0 and 47 pF. The distance between the video carrier and the sound subcarrier can be adjusted between at least −10 and −18 dB (see Fig.11).
1998 Jun 23 |
5 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
To bias the audio input it is necessary to put a resistor in the application between pin 1 and ground. The resistor has a typical value of 12 kΩ.
The RF part of the oscillator consists of:
∙An oscillator which operates at the required video carrier frequency. The range of the oscillator is determined in the application by C5, C6, L5 and D5.
∙An RF mixer. It first combines the video signal and the sound subcarrier to build a baseband TV channel. Then the baseband signal is mixed with the oscillator signal to get the RF TV channel. The mixer has two outputs which can be used as two independent asymmetrical outputs, or as one symmetrical output. In
the event of asymmetrical use, the unused output must be loaded with a 75 Ω resistor (see Fig.7).
The oscillator frequency is set by a programmable PLL frequency synthesizer in accordance with equation:
fosc = 8 × N × fref
Where:
fosc is the local oscillator frequency.
N is a 12-bit dividing number (10 bits are programmable by the I2C-bus).
fref is the crystal frequency (4 MHz) divided by 128 (31.25 kHz).
The circuit allows a step of 250 kHz but because only 10 bits are programmable, the programming steps are 1 MHz.
When the PLL loop is locked, both inputs of the phase comparator are equal, which gives equation:
fosc |
fxtal |
|
fDIV = 8-------------× N |
= 128--------- |
= fref |
During the test mode operation, fDIV and fref can be monitored on the output Port pin (pin 14).
Software information
The synthesizer is controlled via a two-wire I2C-bus receiver. For programming, the address byte (C8 HEX) has to be sent first. Then one or two data bytes are used to set the 10 programmable bits of the dividing number N, the test bits (see Table 1) and the output Port state. Note that after power-up of the IC, the two data bytes must be sent.
MBE395
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
60 |
|
|
70 |
||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t (μs) |
64 |
|
|
||||
Fig.3 Test pattern signal.
1998 Jun 23 |
6 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
Table 1 Data format; notes 1 and 2
BYTE |
BIT 7 |
BIT 6 |
BIT 5 |
BIT 4 |
BIT 3 |
BIT 2 |
BIT 1 |
BIT 0 |
ACKNOWLEDGE BIT |
|
MSB |
LSB |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address byte C8 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data byte 1 |
0 |
b11 |
b10 |
b9 |
b8 |
b7 |
b6 |
b5 |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data byte 2 |
1 |
T0(3) |
T1(3) |
T2(3) |
P0(4) |
b4 |
b3 |
b2 |
ACK |
Notes
1.The 10 programmable bits of N are: b2 to b11.
2.Internal hardware sets: b1 = 0 and b0 = 1.
3.T0, T1 and T2 are bits used for test purposes (see Table 5).
4.P0 is a bit used for controlling the state of the output Port (see Table 6).
Table 2 Structure of the dividing number N
RESULT |
|
|
|
|
|
BITS(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
b11 |
b10 |
b9 |
b8 |
b7 |
b6 |
b5 |
b4 |
b3 |
b2 |
b1(2) |
b0(2) |
||
|
|||||||||||||
Frequency (MHz)(3) |
512 |
256 |
128 |
64 |
32 |
16 |
8 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
|
Notes
1.Bits b2 to b11 are programmable and represent the integer part of the frequency in MHz. Bits b1 and b0 are fixed internally to b1 = 0 and b0 = 1 to get the added 0.25 MHz, common for most TV channels.
2.Bits b1 and b0 are not programmable.
3.fosc = 512b11 + 256b10 + 128b9 + 64b8 + 32b7 + 16b6 + 8b5 + 4b4 + 2b3 + b2 + 0.25 (MHz).
Table 3 Dividing number N for programming channel 21 (471.25 MHz)
RESULT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BITS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b11 |
b10 |
b9 |
b8 |
b7 |
b6 |
|
b5 |
b4 |
b3 |
b2 |
b1(1) |
b0(1) |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Value |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (MHz)(2) |
0 |
256 |
128 |
64 |
0 |
16 |
|
0 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
0.25 |
Notes
1.Bits b1 and b0 are not programmable.
2.fosc = 0 + 256 + 128 + 64 + 0 + 16 + 0 + 4 + 2 + 1 + 0.25 (MHz) = 471.25 MHz.
Table 4 Content of the data bytes to program channel 21 (471.25 MHz)
BYTE |
BIT 7 |
BIT 6 |
BIT 5 |
BIT 4 |
BIT 3 |
BIT 2 |
BIT 1 |
BIT 0 |
ACKNOWLEDGE BIT |
|
MSB |
LSB |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address byte C8 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data byte 1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data byte 2 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
ACK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It is possible to change only one data byte. The circuit will recognize which one is received with the value of MSB
(0 for data byte 1 and 1 for data byte 2). It is possible to change the frequency by 1 MHz with data byte 2. It is easy to increment the channel frequency when its frequency width is 8 MHz by simply incrementing data byte 1.
1998 Jun 23 |
7 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
The bits T0 to T2 are available for test purposes and the possibilities are shown in Table 5.
Table 5 |
Test modes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T0 |
|
T1 |
T2 |
OPERATIONAL MODE |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
0 |
0 |
normal operation |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
Test Pattern Signal Generator (TPSG) on; note 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
1 |
0 |
RF oscillator off; note 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
1 |
1 |
balance test; note 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
0 |
0 |
fref out (if p0 = 0); note 4 |
1 |
|
0 |
1 |
high-impedance test; note 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
fDIV out (if p0 = 0); note 4 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
phase detector disabled; baseband signals on RF outputs; note 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
Notes
1.In ‘TPSG on’ mode the video carrier is modulated by the test signal consisting of a synchronization pulse and two vertical white bars on a black screen. This mode should be selected to adjust the TV set receiving the modulated signal to the right frequency.
2.In ‘RF oscillator off’ mode, the RF oscillator and the RF mixer are switched-off and there is no RF carrier coming out of the device. This mode can be selected to avoid RF radiation to other parts when the modulator output is not used.
3.In ‘balance test’, the video carrier is over modulated. This simplifies residual carrier measurements.
4.In ‘fref’ and ‘fDIV’ modes, the reference frequency fref in the phase comparator or the divided RF oscillator frequency fDIV is available on the output Port pin. This mode requires that bit P0 = 0.
5.The ‘high-impedance test’ mode may be used to inject an external tuning voltage to the RF tank circuit, to test the oscillator. In this mode, the phase detector is disabled and the external transistor of the tuning amplifier is switched-off. The AMP output (pin 7) is LOW (<200 mV).
6.In the ‘phase detector disabled’ mode, it is possible to measure the leakage current at the input of the tuning amplifier, on the CP pin. In this mode the RF oscillator is off, and the baseband TV channel signal is present on the RF outputs for testing the audio and video parts.
The possibilities of bit P0, which controls the output Port (pin 14) are given in Table 6.
The Port is an NPN open-collector type. For monitoring the
fref or fDIV frequency on the output Port, the P0 bit must be logic 0 to let the output Port free.
Table 6 Output Port programming
P0 |
OUTPUT PORT STATE |
|
|
0 |
off; high impedance |
|
|
1 |
on; sinking current |
|
|
1998 Jun 23 |
8 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
I2C-bus programmable modulator for
TDA8722
negative video modulation and FM sound
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL |
PARAMETER |
MIN. |
MAX. |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
VDDA |
analog supply voltage |
−0.3 |
+6 |
V |
VDDD |
digital supply voltage |
−0.3 |
+6 |
V |
VDD |
operating supply voltage |
4.5 |
5.5 |
V |
Vmax |
maximum voltage on all pins |
−0.3 |
VDD |
V |
Tstg |
IC storage temperature |
−40 |
+125 |
°C |
Tamb |
operating ambient temperature |
−20 |
+85 |
°C |
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be completely safe, it is desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling integrated circuits. Every pin withstands the ESD test in accordance with “MIL-STD-883C category B” (2000 V). Every pin withstands the ESD test in accordance with Philips Semiconductors Machine Model (MM) 0 Ω, 200 pF (200 V).
THERMAL RESISTANCE
SYMBOL |
PARAMETER |
VALUE |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
Rth j-a |
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air |
|
|
|
SO20; SOT163-1 |
85 |
K/W |
|
SSOP20; SOT266-1 |
120 |
K/W |
|
|
|
|
1998 Jun 23 |
9 |
 Loading...
Loading...