Philips UBA1707TS-C2, UBA1707TS-C1, UBA1707T-C2, UBA1707T-C1 Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
UBA1707
Cordless telephone, answering machine line interface
Product specification |
1999 Feb 17 |
Supersedes data of 1998 Jun 11
File under Integrated Circuits, IC03

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
FEATURES
Line interface
∙Low DC line voltage; operates down to 1.2 V (excluding polarity guard)
∙Voltage regulator with adjustable DC voltage
∙DC mask for voltage or current regulation (CTR 21)
∙Line current limitation for protection
∙Electronic hook switch control input
∙Transmit amplifier with:
–Symmetrical inputs
–Fixed gain
–Large signals handling capability.
∙Receive amplifier with fixed gain
∙Transmit and receive amplifiers AGC for line loss compensation.
Auxiliary amplifier
∙ Fixed gain.
Loudspeaker channel
∙Dual inputs
∙Rail-to-rail output stage for single-ended load drive
∙High output current capability
∙Dynamic limiter to prevent distortion
∙Digital volume control
∙Fixed maximum gain.
General purpose switches
∙ Three switches with open-collector.
3-wires serial bus interface
Allows to control:
∙DC mask (voltage or current regulation)
∙Receive amplifier mute function
∙AGC:
–On/off
–Slope
–Istart line current.
∙Auxiliary amplifier mute function
∙Loudspeaker channel:
–Input selection
–Volume setting
–Dynamic limiter inhibition
–Power-down mode.
∙General purpose switches state
∙Global power-down mode.
Supply
Operates with external supply voltage from 3.0 to 5.5 V.
APPLICATIONS
∙Cordless base stations
∙Answering machines
∙Mains or battery-powered telephone sets.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The UBA1707 is a BiCMOS integrated circuit intended for use in mains-powered telecom terminals. It performs all speech and line interface functions, DC mask for voltage or current regulation and electronic hook switch control. The device includes an auxiliary amplifier, a loudspeaker channel and general purpose switches.
Most of the characteristics are programmable via a 3-wire serial bus interface.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE |
|
PACKAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
NUMBER |
NAME |
DESCRIPTION |
VERSION |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
UBA1707T |
SO28 |
plastic small outline package; 28 leads; body width 7.5 mm |
SOT136-1 |
|
|
|
|
UBA1707TS |
SSOP28 |
plastic shrink small outline package; 28 leads; body width 5.3 mm |
SOT341-1 |
|
|
|
|
1999 Feb 17 |
2 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
Iline = 15 mA; VCC = 3.3 V; RSLPE = 10 Ω; AGC pin connected to GND; Zline = 600 Ω; ZSET = 619 Ω; EHI = HIGH; f = 1 kHz; Tamb = 25 °C; bit AGC at logic 1, all other configuration bits at logic 0; measured in test circuit of Fig.17; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL |
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
MIN. |
TYP. |
MAX. |
UNIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC |
operating voltage range |
|
3.0 |
− |
5.5 |
V |
ICC |
current consumption from pin VCC |
normal operation; bit PD = 0 |
− |
2.2 |
3.2 |
mA |
|
|
power-down mode; bit PD = 1 |
− |
110 |
150 |
μA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iline |
line current operating range |
normal operation |
11 |
− |
140 |
mA |
|
|
with reduced performance |
3 |
− |
11 |
mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLN |
DC line voltage |
|
2.7 |
3.0 |
3.3 |
V |
RREGC |
DC mask slope in current regulation |
Iline > 35 mA (typical); |
− |
1.4 |
− |
kΩ |
|
mode |
RLVI = 1 MΩ; RRGL = 7.15 kΩ; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit CRC = 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gv(trx) |
voltage gain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
transmit amplifier from TXI to LN |
VTXI = 50 mV (RMS) |
10.6 |
11.6 |
12.6 |
dB |
|
receive amplifier from RXI to RXO |
VRXI = 2 mV (RMS) |
36.9 |
37.9 |
38.9 |
dB |
Gv(trx) |
gain control range for transmit and |
Iline = 90 mA |
− |
6.5 |
− |
dB |
|
receive amplifiers with respect to |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iline = 15 mA |
|
|
|
|
|
Gv(AX) |
voltage gain from AXI to AXO |
VAXI = 2 mV (RMS) |
30.8 |
31.8 |
32.8 |
dB |
Gv(LSA) |
voltage gain from LSAI1 or LSAI2 to |
VLSAI = 8 mV (RMS); |
26.5 |
28 |
29.5 |
dB |
|
LSAO for maximum volume |
bits LSA1 = 1 and LSA2 = 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gv(LSA) |
voltage gain adjustment range for |
bits (VOL0, VOL1, VOL2) |
− |
21 |
− |
dB |
|
loudspeaker channel |
from (0, 0, 0) to (1, 1, 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gv(LSA)s |
voltage gain adjustment step for |
VOL0 from 0 to 1 |
− |
3 |
− |
dB |
|
loudspeaker channel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Feb 17 |
3 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
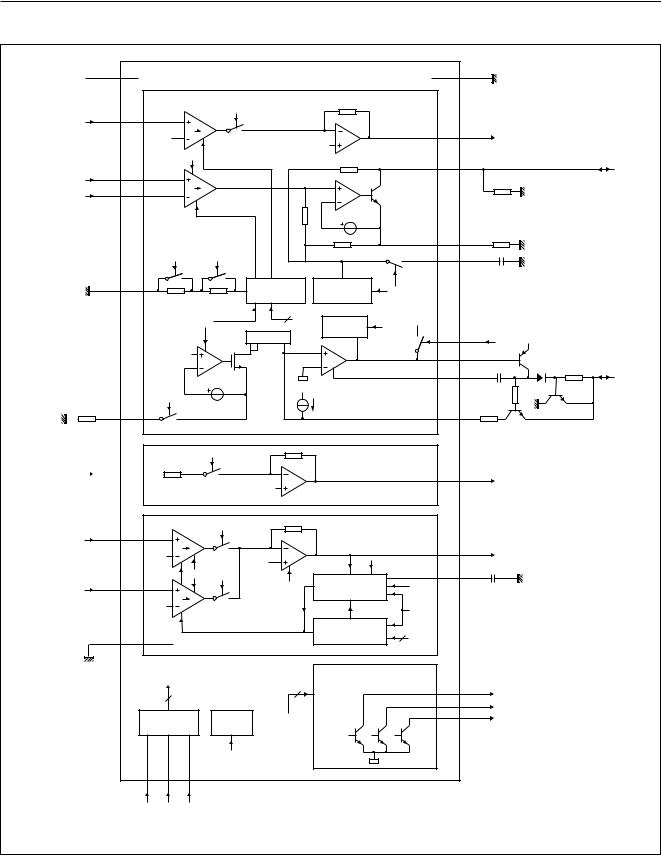
BLOCK DIAGRAM
|
VCC |
25 |
|
|
|
|
UBA1707 |
|
|
22 |
GND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXM |
|
|
LINE INTERFACE |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXI |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2Vd |
V |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
RXO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2Vd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
LN |
|
LN + |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
TXI+ |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZSET |
|
|
TXI− |
17 |
V |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
SLPE |
RSLPE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
RAGC2 |
|
RAGC1 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
REG |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CREG |
|
|
AGC |
9 |
|
|
|
|
AGC |
|
LOW VOLTAGE |
EHI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EHI |
|
2 |
SAGC, |
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AGC |
CURRENT |
SLPE |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIMITATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
EHI |
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
REG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
LCC |
|
TPDARL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CCST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
CST |
LN − |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
600 mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CRC |
|
|
|
|
|
200 nA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RRGL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RLVI |
TNSW |
|
RGL |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
LVI |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TNON-HOOK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AXM |
|
|
AUXILIARY AMPLIFIER |
|
|
|
|||
|
AXI |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
AXO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2Vd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSA1 |
|
|
LOUDSPEAKER CHANNEL |
|
|
|
||
|
LSAI1 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2Vd |
V |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
LSAO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSPD |
LSA2 |
0.5VCC |
|
VCC |
28 |
DLC |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSAI2 |
27 |
|
|
|
|
LSPD |
DYNAMIC LIMITER |
|
DLCI |
|
CDLC |
|
|
|
|
2Vd |
V |
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSPD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSPGND |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLUME CONTROL |
|
VOL0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
TO |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOL2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GENERAL SWITCHES |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
21 |
SWI1 |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
SWI2 |
|
|
|
|
SERIAL |
|
|
|
SWC1, SWC2, |
|
|
19 |
SWI3 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
SUPPLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
INTERFACE |
|
|
SWC3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
PD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
14 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EN |
CLK |
DATA |
|
|
|
|
|
MGK705 |
|
|
|
|
Bit names are given in italics.
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1999 Feb 17 |
4 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
PINNING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SYMBOL |
PIN |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLPE |
1 |
connection for slope resistor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LN |
2 |
positive line terminal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REG |
3 |
line voltage regulator decoupling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LVI |
4 |
negative line voltage sense input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RGL |
5 |
reference for current regulation mode |
|
handbook, halfpage |
|
|
|
|
|
LCC |
6 |
line current control output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CST |
7 |
input for stability capacitor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXO |
8 |
receive amplifier output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AGC |
9 |
automatic gain control/line loss |
|
|
|
|
compensation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXI |
10 |
receiver amplifier input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EHI |
11 |
electronic hook switch control input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DATA |
12 |
serial bus data input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EN |
13 |
programming serial bus enable input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLK |
14 |
serial bus clock input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AXI |
15 |
auxiliary amplifier input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AXO |
16 |
auxiliary amplifier output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TXI− |
17 |
inverted transmit amplifier input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TXI+ |
18 |
non-inverted transmit amplifier input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWI3 |
19 |
NPN open-collector output 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWI2 |
20 |
NPN open-collector output 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWI1 |
21 |
NPN open-collector output 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GND |
22 |
ground reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSPGND |
23 |
ground reference for the loudspeaker |
|
|
|
|
amplifier |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSAO |
24 |
loudspeaker amplifier output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCC |
25 |
supply voltage |
|
|
LSAI1 |
26 |
loudspeaker amplifier input 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LSAI2 |
27 |
loudspeaker amplifier input 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DLC |
28 |
dynamic limiter timing adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLPE |
1 |
|
|
DLC |
|
28 |
|||
LN |
|
|
|
LSAI2 |
2 |
|
27 |
||
REG |
3 |
|
|
LSAI1 |
|
26 |
|||
LVI |
4 |
|
|
VCC |
|
25 |
|||
RGL |
|
|
|
LSAO |
5 |
|
24 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
LCC |
6 |
|
23 |
LSPGND |
CST |
|
|
|
GND |
7 |
UBA1707 |
22 |
||
|
8 |
|
|
|
RXO |
|
21 |
SWI1 |
|
AGC |
9 |
|
|
SWI2 |
|
20 |
|||
RXI |
10 |
|
|
SWI3 |
|
19 |
|||
EHI |
11 |
|
|
TXI+ |
|
18 |
|||
DATA |
12 |
|
|
TXI− |
|
17 |
|||
EN 13 |
|
|
AXO |
|
|
16 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
CLK |
14 |
|
15 |
AXI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGK704 |
|
|
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1999 Feb 17 |
5 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
All data given in this chapter are typical values, except when otherwise specified.
Supply (pins VCC and GND; bits PD and LSPD)
The UBA1707 must be supplied with an external stabilized voltage source between pins VCC and GND.
Pins GND and LSPGND must be connected together.
Without any signal, with the loudspeaker channel enabled at minimum volume and without any general purpose switch selected, the internal current consumption is
2.2 mA at VCC = 3.3 V. Each selected switch (pins SWI1, SWI2, or SWI3) increases the current consumption by 600 μA.
The supply current can be reduced when the loudspeaker channel is not used by switching it off (bit LSPD at logic 1). The current consumption is then decreased by approximately 800 μA at minimum volume.
To drastically reduce current consumption, the UBA1707 is provided with a power-down mode controlled by bit PD. When bit PD is at logic 1, the current consumption from VCC becomes 110 μA. In this mode, the serial interface is the only function which remains active.
Line interface
DC CHARACTERISTICS (PINS LN, SLPE, REG, CST, LVI, LCC, RGL AND GND; BIT CRC)
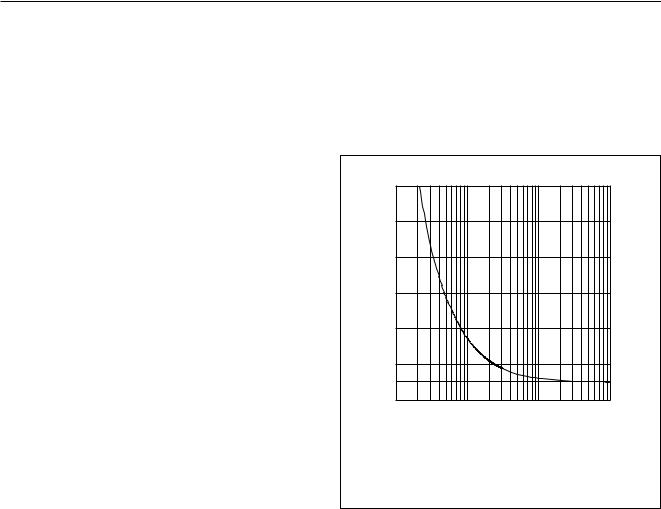
The IC generates a stabilized reference voltage (Vref) between pins LN and SLPE. This reference voltage is equal to 2.9 V, is temperature compensated and can be adjusted by means of an external resistor (RVA). It can be increased by connecting the RVA resistor between
pins REG and SLPE (see Fig.3).
The voltage at pin REG is used by the internal regulator to generate the stabilized reference voltage and is decoupled by a capacitor (CREG) which is connected to GND. This capacitor, converted into an equivalent inductance
(see Section “Set impedance”) realizes the set impedance
conversion from its DC value (RSLPE) to its AC value (ZSET in the audio-frequency range). Figure 4 illustrates
the reference voltage supply configuration. As can be seen from Fig.4, part of the line current flows into the ZSET impedance network and is not sensed by the UBA1707. Therefore using the RVA resistor to change value of the reference voltage will also modify all parameters related to the line current such as:
∙The automatic gain control
∙The DC mask management
∙The low voltage area characteristics.
In the same way, changing the value of ZSET also affects the characteristics. The IC has been optimized for
Vref = 2.9 V and ZSET = 619 Ω.
8.5 |
|
|
MGK706 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
handbook, halfpage |
|
|
|
|
Vref |
|
|
|
|
(V) |
|
|
|
|
7.5 |
|
|
|
|
6.5 |
|
|
|
|
5.5 |
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
(1) |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
103 |
104 |
105 |
RVA (Ω) |
106 |
(1)Influence of RVA on Vref.
(2)Vref without influence of RVA.
Fig.3 Reference voltage adjustment with RVA.
The IC regulates the line voltage at pin LN which can be calculated as follows:
VLN = Vref + RSLPE × ISLPE
ISLPE = Iline –IZSET –I* Iline –IZSET
Where:
Iline = line current
IZSET = current flowing through ZSET
I* = current consumed between LN and GND (approximately 100 μA).
The preferred value for RSLPE is 10 Ω. Changing RSLPE will affect more than the DC characteristics; it also influences
the transmit gain, the gain control characteristics, the sidetone level and the maximum output swing on the line. However, for compliance with CTR 21 8.66 Ω is the best value for RSLPE.
1999 Feb 17 |
6 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
handbook, full pagewidth |
LN+ |
|
|
|
ILN |
|
Iline |
|
Rp |
|
LN |
UBA1707 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I* |
ZSET |
|
|
|
|
IZSET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
619 Ω |
|
|
Vd |
|
|
|
|
Rd |
|
|
|
|
|
4 kΩ |
|
|
|
|
REG |
|
|
SLPE |
GND |
|
CREG |
I |
SLPE |
RSLPE |
|
|
4.7 μF |
|
10 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
MGK707 |
|
Fig.4 Reference voltage supply configuration.
handbook, full pagewidth |
|
|
|
LN+ |
Zline |
|
|
|
ILN |
|
|||
|
|
|
Iline |
|
||
|
Rp |
LN |
|
|
|
|
|
35 kΩ |
|
UBA1707 |
|
||
|
|
|
IZSET |
Rexch |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Vref |
|
ZSET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Vd |
|
|
619 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Rd |
|
HOOK SWITCH |
Vline |
||
|
|
|
||||
|
4 kΩ |
|
MANAGEMENT |
|
||
|
|
|
|
Vexch |
||
REG |
GND |
SLPE |
LCC |
EHI |
||
|
||||||
CREG |
ISLPE |
RSLPE |
VEHI |
|
||
4.7 μF |
|
10 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TNSW |
VCE (TNSW) |
|
||
|
|
LN− |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
MGK708 |
|
Fig.5 Line current settling simplified configuration.
1999 Feb 17 |
7 |

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
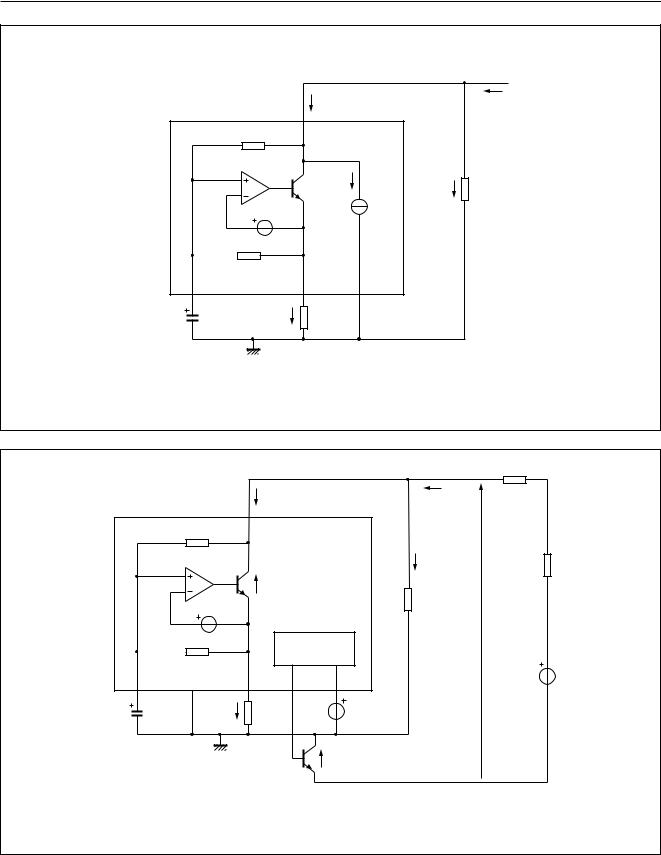
The DC line current flowing into the set is determined by the exchange supply voltage (Vexch), the feeding bridge
resistance (Rexch), the DC resistors of the telephone line (Rline) and the set (RSET), the reference voltage (Vref) and the voltage introduced by the transistor (TNSW) used as
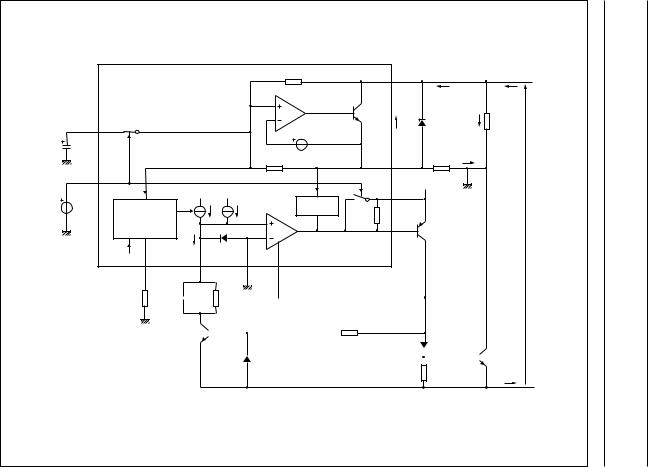
line interrupter (see Fig.5). With a line current below Ilow (8 mA with ZSET = 619 Ω), the internal reference voltage (Vref) is automatically adjusted to a lower value. This means that more sets can operate in parallel with DC line voltages (excluding the polarity guard) down to 1.2 V.
At line current below Ilow, the circuit has limited transmit and receive levels. This is called the low voltage area.
Figure 6 shows in more details how the UBA1707, in association with some external components, manages the line interrupter (TNSW external transistor).
In on-hook conditions (voltage at pin EHI is LOW), the voltage at pin LCC is pulled-up to the supply voltage level
(VCC) to turn off the TPDARL transistor. As a result, because of the RPLD resistor, the TNSW and TNON-HOOK transistors are switched off. The TNON-HOOK transistor disconnects the RLVI resistor from the LN− line terminal in order to
guarantee a high on-hook impedance.
In off-hook conditions (voltage at pin EHI is HIGH), an operational amplifier drives (at pin LCC) the base of TPDARL which forms a current amplifier structure in association with TNSW. The line current flows through
TNSW transistor. The TNON-HOOK transistor is forced into deep saturation. A virtual ground is created at pin LVI
because of the operational amplifier. A DC current (ILVI) is sourced from pin LVI into the RLVI resistor in order to generate a voltage source. Thus the voltage between pin GND and the negative line terminal (LN−) becomes:
VCE (TNSW) = RLVI × ILVI + VCE (TNON-HOOK) RLVI × ILVI
The voltage Vline between the line terminals LN+ and LN− can be calculated as follows:
Vline Vref + RSLPE × (Iline − IZSET) + VCE (TNSW)
Where:
Iline = line current
IZSET = current flowing through ZSET.
1999 Feb 17 |
8 |
_ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 Feb 1999 |
|
|
|
pagewidth full ndbook, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rp |
LN |
|
|
LN+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
35 kΩ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ILN |
|
Iline |
|
|
UBA1707 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vref |
8.2 V |
IZSET |
ZSET |
|
REG |
|
|
Vd |
|
619 Ω |
||
CREG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSLPE |
|
|
|
4.7 μF |
|
|
Rd |
|
|
ISLPE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLPE |
10 Ω |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EHI |
|
4 kΩ |
|
|
VCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VEHI |
CURRENT |
|
ILVIV |
CURRENT |
R |
|
|
|
|
LIMITATION |
|
|
|
||||
|
REGULATION |
|
200 nA |
|
PLU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
150 kΩ |
|
|
|
||
|
MODE |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
LCC |
TPDARL |
|
|
|
9 |
MANAGEMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
ILVI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vline |
|
CRC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RGL |
LVI |
GND |
CST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLVI |
|
|
|
|
CCST |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
RRGL |
|
RLVI |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
7.15 kΩ |
|
470 pF |
1 MΩ |
|
22 pF |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
TNON-HOOK |
|
|
|
|
RON-HOOK |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
100 kΩ |
DSW |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
DPROT |
RPLD |
|
|
TNSW |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iline |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 kΩ |
|
|
||
LN−
MGK709
Bit names are given in italics.
Fig.6 Line interrupter management and DC mask regulation configuration.
interface line |
telephone, Cordless |
|
machine answering |
UBA1707
Semiconductors Philips
specification Product
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
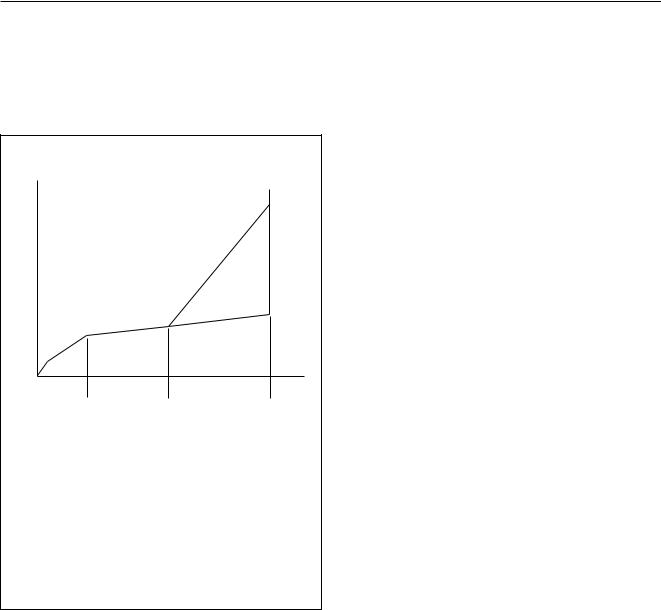
The UBA1707 offers the possibility to choose two kinds of regulations for the DC characteristic between the line terminals LN+ and LN- (see Fig.7):
·Voltage regulation mode
·Current regulation mode.
handbook, halfpage |
|
|
|
Vline |
|
|
|
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
Iline |
Ilow |
Iknee |
Iprot (4) |
|
|
MGK710 |
(1)Low voltage area.
(2)Small slope (determined by RSLPE).
(3)Small slope (dashed line; determined by RSLPE) in voltage regulation mode.
High slope (full line; determined by RSLPE, RLVI and RRGL) in current regulation mode.
(4)Current limitation.
Fig.7 General form of the DC mask as a function of regulation mode.
The regulation mode is selected by the bit CRC via the serial interface.
The DC mask regulation is realised by adjusting the DC voltage VCE (TNSW) between pin GND and line terminal LNas a function of the line current.
Voltage regulation mode
In voltage regulation mode (bit CRC at logic 0),
VCE (TNSW) voltage is fixed by means of a 200 nA DC constant current ILVIV flowing through RLVI.
Therefore VCE (TNSW) @ RLVI ´ ILVIV = 200 mV in typical application (see Fig.18).
The slope DVline/DIline of the Vline, Iline characteristic is
RREGV @ RSLPE.
Current regulation mode
In current regulation mode (bit CRC at logic 1), when the line current is lower than Iknee = 35 mA (with
ZSET = 619 W), VCE (TNSW) is fixed by means of a 200 nA DC constant current ILVIV flowing through RLVI. When the line current is higher than 35 mA, an additional current (proportional to the line current) flows through RLVI. As a result, TNSW works as a DC voltage source increasing with the line current. VCE (TNSW) can be calculated as follows:
V |
|
(TN |
|
) @ R |
|
æ RSLPE |
´ (I |
|
–I |
|
) + I |
ö |
|
|
|
´ ç --------------- |
|
|
÷ |
||||||
|
CE |
|
SW |
|
LVI |
è RRGL |
|
line |
|
knee |
|
LVIVø |
Where:
Iline = line current
RRGL = resistor connected at pin RGL.
The slope DVline/DIline of the Vline, Iline characteristic is determined by the ratio of resistors connected at pins SLPE, LVI and RGL, and can be calculated as
@ ´ RSLPE W
follows: RREGC RSLPE + RLVI --------------- = 1400 in
RRGL
typical application (see Fig.18).
Current limitation
Whatever the selected mode is, the line current is limited to approximately 145 mA. This current is sensed on SLPE, for this purpose the external zener diode must be connected between pins LN and SLPE. The speech function no longer operates in this condition.
ELECTRONIC HOOK SWITCH CONTROL (PIN EHI)
The electronic hook switch input (EHI) controls the state of
TPDARL transistor. When the voltage applied at pin EHI is LOW, TPDARL transistor is turned off. Voltage at pin LCC is pulled up to supply voltage (VCC). TNSW and TNON-HOOK transistors are also turned off by means of a pull-down
resistor (RPLD). When the voltage applied at pin EHI is HIGH, TPDARL transistor is driven by the operational
amplifier at pin LCC and the regulation mode selected is operating. An internal 165 kW pull-up resistor is connected between pins LCC and VCC.
1999 Feb 17 |
10 |
Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
Cordless telephone, answering machine
UBA1707
line interface
The EHI input can also be used for pulse dialling or register recall (timed loop break). During line breaks (voltage at pin EHI is LOW or open-circuit), the voltage regulator is switched off and the capacitor at pin REG is internally disconnected to prevent its discharge. As a result, the voltage stabilizer will have negligible switch-on delay after line interruptions. This minimizes the contribution of the IC to the current waveform during pulse dialling or register recall.
When the UBA1707 is in power-down mode (bit PD at
logic 1), the TPDARL transistor is forced to be turned off whatever the voltage applied at pin EHI.
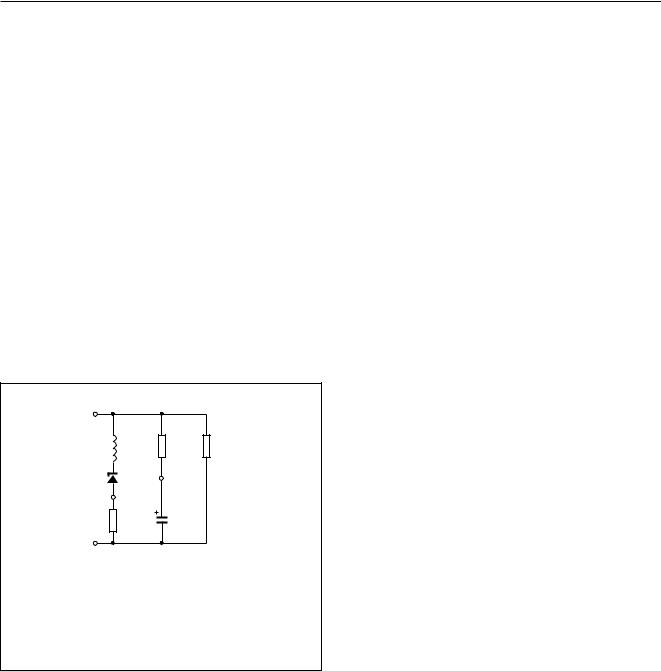
SET IMPEDANCE
In the audio frequency range, the dynamic impedance between pins LN and GND (illustrated in Fig.8) is mainly determined by the ZSET impedance.
The impedance introduced by the external TNSW transistor connected between pin GND and the negative line terminal (LN−) is negligible.
handbook, halfpage LN
LEQ |
RP |
ZSET |
619 Ω |
||
Vref |
REG |
|
SLPE |
|
|
RSLPE |
CREG |
|
10 Ω |
4.7 μF |
|
GND |
MGL215 |
|
|
|
Leq = CREG × RSLPE × RP
RP = internal resistance = 35 kΩ.
Fig.8 Equivalent impedance between
LN and GND.
TRANSMIT AMPLIFIER (PINS TXI+ AND TXI−)
The UBA1707 has symmetrical transmit inputs TXI+ and TXI−. The input impedance between pins TXI+ or TXI− and GND is 21 kΩ. The voltage gain from pins TXI+ or TXI− to
pin LN is set at 11.6 dB with 600 Ω line load (Zline) and 619 Ω set impedance. The inputs are biased at
2 × Vd 1.4 V, with Vd representing the diode voltage. Automatic gain control is provided on this amplifier for line loss compensation.
RECEIVE AMPLIFIER (PINS RXI AND RXO; BIT RXM)
The receive amplifier (see Fig.9) has one input (RXI) and one output (RXO). The input impedance between pins RXI and GND is 21 kΩ. The rail-to-rail output stage is designed to drive a 500 μA peak current. The output impedance at pin RXO is approximately 100 Ω.
The voltage gain from pin RXI to pin RXO is set at 37.9 dB. This gain value compensates typically the attenuation of the anti-sidetone network (see Fig.10). The output as well as the input are biased at 2 × Vd 1.4 V. Automatic gain control is provided on this amplifier for line loss compensation. This amplifier can be muted by activating the receive mute function (bit RXM at logic 1).
1999 Feb 17 |
11 |
 Loading...
Loading...