Microchip Technology Inc PIC16C717-I-SO, PIC16C717-I-SS, PIC16C717-JW, PIC16C717-P, PIC16C717-SO Datasheet
...
PIC16C717/770/771
18/20-Pin, 8-Bit CMOS Microcontrollers with 10/12-Bit A/D
Microcontroller Core Features:
•High-performance RISC CPU
•Only 35 single word instructions to learn
•All single cycle instructions except for program branches which are two cycle
•Operating speed: DC - 20 MHz clock input
DC - 200 ns instruction cycle
|
Memory |
|
A/D |
A/D |
||
Device |
|
|
Pins |
|||
Program |
Data |
|||||
Resolution |
Channels |
|||||
|
x14 |
x8 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C717 |
2K |
256 |
18, 20 |
10 bits |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C770 |
2K |
256 |
20 |
12 bits |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C771 |
4K |
256 |
20 |
12 bits |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Interrupt capability (up to 10 internal/external interrupt sources)
•Eight level deep hardware stack
•Direct, indirect and relative addressing modes
•Power-on Reset (POR)
•Power-up Timer (PWRT) and Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST)
•Watchdog Timer (WDT) with its own on-chip RC oscillator for reliable operation
•Selectable oscillator options:
-INTRC - Internal RC, dual speed (4MHz and 37KHz) dynamically switchable for power savings
-ER - External resistor, dual speed (user selectable frequency and 37KHz) dynamically switchable for power savings
-EC - External clock
-HS - High speed crystal/resonator
-XT - Crystal/resonator
-LP - Low power crystal
•Low-power, high-speed CMOS EPROM technology
• In-Circuit Serial Programming™ (ISCP)
•Wide operating voltage range: 2.5V to 5.5V
•15 I/O pins with individual control for:
-Direction (15 pins)
-Digital/Analog input (6 pins)
-PORTB interrupt on change (8 pins)
-PORTB weak pull-up (8 pins)
-High voltage open drain (1 pin)
•Commercial and Industrial temperature ranges
•Low-power consumption:
-< 2 mA @ 5V, 4 MHz
-22.5 A typical @ 3V, 32 kHz
-< 1 A typical standby current
Pin Diagram
20-Pin PDIP, SOIC, SSOP
|
RA0/AN0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB3/CCP1/P1A |
||
RA1/AN1/LVDIN |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB2/SCK/SCL |
|||
RA4/T0CKI |
|
|
|
|
3 |
PIC16C770/771 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C |
|
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
RA5/MCLR/VPP |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT |
|||
|
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
|
|
AVSS |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
AVDD |
||
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB7/T1OSI/P1D |
|||
RB0/AN4/INT |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB5/SDO/P1B |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
RB1/AN5/SS |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB4/SDI/SDA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Peripheral Features:
• Timer0: 8-bit timer/counter with 8-bit prescaler
• Timer1: 16-bit timer/counter with prescaler,
|
can be incremented during sleep via external |
||
|
crystal/clock |
||
• Timer2: 8-bit timer/counter with 8-bit period |
|||
|
register, prescaler and postscaler |
||
• |
Enhanced Capture, Compare, PWM (ECCP) |
||
|
module |
||
|
- Capture is 16 bit, max. resolution is 12.5 ns |
||
|
- Compare is 16 bit, max. resolution is 200 ns |
||
|
- PWM max. resolution is 10 bit |
||
|
- |
Enhanced PWM: |
|
|
|
- |
Single, Half-Bridge and Full-Bridge output |
|
|
|
modes |
|
|
- |
Digitally programmable deadband delay |
• Analog-to-Digital converter: |
|||
|
- |
PIC16C770/771 12-bit resolution |
|
|
- |
PIC16C717 10-bit resolution |
|
• On-chip absolute bandgap voltage reference |
|||
|
generator |
||
• |
Programmable Brown-out Reset (PBOR) |
||
|
circuitry |
||
• |
Programmable Low-Voltage Detection (PLVD) |
||
|
circuitry |
||
• |
Master Synchronous Serial Port (MSSP) with two |
||
|
modes of operation: |
||
|
- 3-wire SPI™ (supports all 4 SPI modes) |
||
|
- I2C™ compatible including master mode |
||
|
|
support |
|
• Program Memory Read (PMR) capability for lookup table, character string storage and checksum calculation purposes
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 1
PIC16C717/770/771
Pin Diagrams
18-Pin PDIP, SOIC
|
RA0/AN0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
||
RA1/AN1/LVDIN |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|||
|
RA4/T0CKI |
|
|
|
|
3 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA5/MCLR/V |
PP |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
VSS |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|||
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|||
RB0/AN4/INT |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|||
RB1/AN5/SS |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C717
18 

 RB3/CCP1/P1A
RB3/CCP1/P1A
17 


 RB2/SCK/SCL
RB2/SCK/SCL
16 


 RA7/OSC1/CLKIN
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN
15 


 RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT
14 

 VDD
VDD
13 

 RB7/T1OSI/P1D
RB7/T1OSI/P1D
12 


 RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C
11 


 RB5/SDO/P1B
RB5/SDO/P1B
10 

 RB4/SDI/SDA
RB4/SDI/SDA
20-Pin SSOP
|
RA0/AN0 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB3/CCP1/P1A |
||
RA1/AN1/LVDIN |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB2/SCK/SCL |
|||
RA4/T0CKI |
|
|
|
|
3 |
PIC16C717 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA5/MCLR/VPP |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT |
|||
|
VSS(1) |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
VDD(2) |
||
|
VSS(1) |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
VDD(2) |
||
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB7/T1OSI/P1D |
|||
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C |
|||
RB0/AN4/INT |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB5/SDO/P1B |
|||
RB1/AN5/SS |
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
RB4/SDI/SDA |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note 1: VSS pins 5 and 6 must be tied together.
2: VDD pins 15 and 16 must be tied together.
Key Features |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PICmicroTM Mid-Range Reference Manual |
PIC16C717 |
PIC16C770 |
PIC16C771 |
||||||
(DS33023) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
Operating Frequency |
DC - 20 MHz |
DC - 20 MHz |
DC - 20 MHz |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Resets (and Delays) |
POR, BOR, |
|
|
POR, BOR, |
|
|
POR, BOR, |
|
|
MCLR, |
MCLR, |
MCLR, |
|||||||
|
WDT (PWRT, OST) |
WDT (PWRT, OST) |
WDT (PWRT, OST) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
Program Memory (14-bit words) |
2K |
2K |
4K |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Memory (bytes) |
256 |
|
|
256 |
|
|
256 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupts |
10 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
I/O Ports |
Ports A,B |
Ports A,B |
Ports A,B |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timers |
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM (ECCP) |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
modules |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Serial Communications |
MSSP |
MSSP |
MSSP |
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
12-bit Analog-to-Digital Module |
|
6 input channels |
6 input channels |
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
10-bit Analog-to-Digital Module |
6 input channels |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
Instruction Set |
35 Instructions |
35 Instructions |
35 Instructions |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DS41120A-page 2 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

|
|
PIC16C717/770/771 |
Table of Contents |
|
|
1.0 |
Device Overview ................................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
2.0 |
Memory Organization.......................................................................................................................................... |
11 |
3.0 |
I/O Ports.............................................................................................................................................................. |
27 |
4.0 |
Program Memory Read (PMR) ........................................................................................................................... |
43 |
5.0 |
Timer0 Module .................................................................................................................................................... |
47 |
6.0 |
Timer1 Module .................................................................................................................................................... |
49 |
7.0 |
Timer2 Module .................................................................................................................................................... |
53 |
8.0 |
Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM(ECCP) Modules ......................................................................................... |
55 |
9.0 |
Master Synchronous Serial Port (MSSP) Module............................................................................................... |
67 |
10.0 |
Voltage Reference Module and Low-voltage Detect......................................................................................... |
109 |
11.0 |
Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) Module ........................................................................................................ |
113 |
12.0 |
Special Features of the CPU ............................................................................................................................ |
125 |
13.0 |
Instruction Set Summary................................................................................................................................... |
141 |
14.0 |
Development Support ....................................................................................................................................... |
149 |
15.0 |
Electrical Characteristics................................................................................................................................... |
155 |
16.0 |
DC and AC Characteristics Graphs and Tables ............................................................................................... |
177 |
17.0 |
Packaging Information ...................................................................................................................................... |
179 |
Revision History ........................................................................................................................................................ |
189 |
|
Device Differences ..................................................................................................................................................... |
189 |
|
Index |
.......................................................................................................................................................................... |
191 |
On-Line Support.......................................................................................................................................................... |
197 |
|
Reader Response ....................................................................................................................................................... |
198 |
|
PIC16C717/770/771 Product Identification System .................................................................................................... |
199 |
|
To Our Valued Customers
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page. The last character of the literature number is the version number. e.g., DS30000A is version A of document DS30000.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
Errata
An errata sheet may exist for current devices, describing minor operational differences (from the data sheet) and recommended workarounds. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the revision of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
•Microchip’s Worldwide Web site; http://www.microchip.com
•Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
•The Microchip Corporate Literature Center; U.S. FAX: (480) 786-7277
When contacting a sales office or the literature center, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are using.
Corrections to this Data Sheet
We constantly strive to improve the quality of all our products and documentation. We have spent a great deal of time to ensure that this document is correct. However, we realize that we may have missed a few things. If you find any information that is missing or appears in error, please:
•Fill out and mail in the reader response form in the back of this data sheet.
•E-mail us at webmaster@microchip.com.
We appreciate your assistance in making this a better document.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 3

PIC16C717/770/771
NOTES:
DS41120A-page 4 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
PIC16C717/770/771
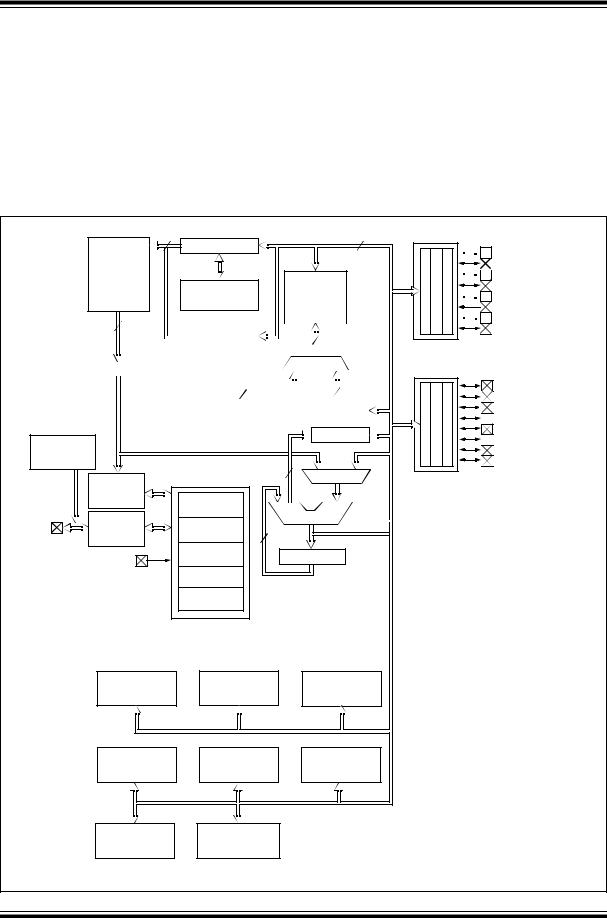
1.0DEVICE OVERVIEW
This document contains device-specific information. Additional information may be found in the PICmicroTM Mid-Range Reference Manual, (DS33023), which may be obtained from your local Microchip Sales Representative or downloaded from the Microchip website. The Reference Manual should be considered a complementary document to this data sheet, and is highly recommended reading for a better understanding of the device architecture and operation of the peripheral modules.
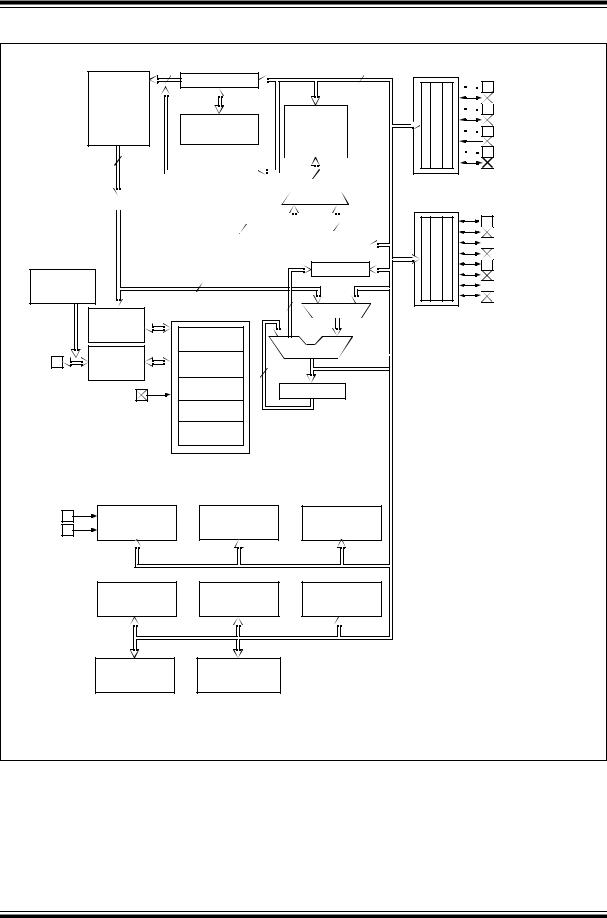
FIGURE 1-1: PIC16C717 BLOCK DIAGRAM
There are three devices (PIC16C717, PIC16C770 and PIC16C771) covered by this datasheet. The PIC16C717 device comes in 18/20-pin packages and the PIC16C770/771 devices come in 20-pin packages.
The following two figures are device block diagrams of the PIC16C717 and the PIC16C770/771.
|
13 |
Data Bus |
8 |
|
Program Counter |
|
|
EPROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program |
|
|
|
Memory |
|
RAM |
|
|
8 Level Stack |
|
|
2K x 14 |
File |
|
|
(13-bit) |
|
||
Registers |
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
256 x 8 |
|
Program |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
Program Memory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RAM |
|||||||
Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read (PMR) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
Addr(1) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr MUX |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Instruction reg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct Addr |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
Indirect |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSR reg |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
8 |
|
STATUS reg |
|
|
||
4MHz, 37KHz |
|
|
|
and ER mode |
|
|
|
Instruction |
|
3 |
MUX |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Decode & |
Power-up |
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
Timer |
|
ALU |
Timing |
Oscillator |
|
|
|
|
||
Generation |
Start-up Timer |
8 |
|
OSC1/CLKIN |
Power-on |
|
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
W reg |
|
VDD, VSS |
Reset |
|
|
|
Watchdog |
|
|
|
Timer |
|
|
|
Brown-out |
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
10-bit |
Bandgap |
|
Low-voltage |
ADC |
Reference |
|
Detect |
Timer0 |
Timer1 |
|
Timer2 |
Enhanced CCP |
Master |
|
|
Synchronous |
|
|
|
(ECCP1) |
|
|
|
Serial Port (MSSP) |
|
||
|
|
||
PORTA


 RA0/AN0
RA0/AN0
RA1/AN1/LVDIN

 RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH

 RA4/T0CKI
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/MCLR/VPP

 RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN
PORTB |
RB0/AN4/INT |
RB1/AN5/SS |
RB2/SCK/SCL |
RB3/CCP1/P1A |
RB4/SDI/SDA |
RB5/SDO/P1B |
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C |
RB7/T1OSI/P1O |
Note 1: Higher order bits are from the STATUS register.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc.
Advanced Information
DS41120A-page 5
PIC16C717/770/771
FIGURE 1-2: PIC16C770/771 BLOCK DIAGRAM
|
13 |
Data Bus |
8 |
|
Program Counter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
EPROM |
|
|
|
Program |
|
RAM |
|
Memory(2) |
8 Level Stack |
|
|
File |
|
||
|
(13-bit) |
Registers |
|
|
|
256 x 8 |
|
Program |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
Program Memory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RAM |
|||||||
Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Read (PMR) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
Addr(1) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr MUX |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Instruction reg |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct Addr |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
Indirect |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSR reg |
|
|||
Internal |
|
8 |
|
STATUS reg |
|
|
|
||
4MHz, 37KHz |
|
|
|
|
and ER mode |
|
|
|
|
|
Instruction |
|
3 |
MUX |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decode & |
Power-up |
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
Timer |
|
ALU |
|
Timing |
Oscillator |
|
|
|
|
|
||
OSC1/CLKIN |
Generation |
Start-up Timer |
8 |
|
|
Power-on |
|
|
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
|
W reg |
|
|
VDD, VSS |
Reset |
|
|
|
|
Watchdog |
|
|
|
|
Timer |
|
|
|
|
Brown-out |
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
AVDD |
12-bit |
Bandgap |
|
Low-voltage |
AVSS |
ADC |
Reference |
|
Detect |
|
Timer0 |
Timer1 |
|
Timer2 |
|
Enhanced CCP |
Master |
|
|
|
Synchronous |
|
|
|
|
(ECCP1) |
|
|
|
|
Serial Port (MSSP) |
|
||
|
|
|
||
PORTA

 RA0/AN0
RA0/AN0
RA1/AN1/LVDIN

 RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH
 RA4/T0CKI
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/MCLR/VPP
 RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN
PORTB |
RB0/AN4/INT |
RB1/AN5/SS |
RB2/SCK/SCL |
RB3/CCP1/P1A |
RB4/SDI/SDA |
RB5/SDO/P1B |
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C |
RB7/T1OSI/P1O |
Note 1: Higher order bits are from the STATUS register.
2: Program memory for PIC16C770 is 2K x 14. Program memory for PIC16C771 is 4K x 14.
DS41120A-page 6 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C717/770/771 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TABLE 1-1: |
PIC16C770/771 PINOUT DESCRIPTION |
||||||||||
Name |
|
Function |
Input |
Output |
Description |
||||||
|
Type |
Type |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
RA0/AN0 |
|
|
RA0 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||||
|
|
AN0 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
RA1 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA1/AN1/LVDIN |
|
AN1 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
LVDIN |
AN |
|
LVD input reference |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RA2 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL |
|
AN2 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||||
|
VREF- |
AN |
|
Negative analog reference input |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
VRL |
|
AN |
Internal voltage reference low output |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RA3 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH |
|
AN3 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||||
VREF+ |
AN |
|
Positive analog reference input |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
VRH |
|
AN |
Internal voltage reference high output |
|||
RA4/T0CKI |
|
|
RA4 |
ST |
OD |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||||
|
|
T0CKI |
ST |
|
TMR0 clock input |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
RA5 |
ST |
|
Input port |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ST |
|
Master clear |
RA5/MCLR/V |
PP |
|
MCLR |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
VPP |
Power |
|
Programming voltage |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RA6 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
OSC2 |
|
XTAL |
Crystal/resonator |
||||||
|
|
|
|
CLKOUT |
|
CMOS |
FOSC/4 output |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
RA7 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN |
|
OSC1 |
XTAL |
|
Crystal/resonator |
||||||
|
|
|
|
CLKIN |
ST |
|
External clock input/ER resistor connection |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
RB0 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
|||
RB0/AN4/INT |
|
AN4 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
INT |
ST |
|
Interrupt input |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RB1 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
|||
RB1/AN5/SS |
|
|
|
AN5 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ST |
|
SSP slave select input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SS |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
RB2 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional input(1) |
|||
RB2/SCK/SCL |
|
SCK |
ST |
CMOS |
Serial clock I/O for SPI |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
SCL |
ST |
OD |
Serial clock I/O for I2C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RB3 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional input(1) |
|||
RB3/CCP1/P1A |
|
CCP1 |
ST |
CMOS |
Capture 1 input/Compare 1 output |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
P1A |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1A output |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RB4 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional input(1) |
|||
RB4/SDI/SDA |
|
SDI |
ST |
|
Serial data in for SPI |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
SDA |
ST |
OD |
Serial data I/O for I2C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RB5 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
|||
RB5/SDO/P1B |
|
SDO |
|
CMOS |
Serial data out for SPI |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
P1B |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1B output |
|||
Note 1: Bit programmable pull-ups.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 7

PIC16C717/770/771
TABLE 1-1: |
PIC16C770/771 PINOUT DESCRIPTION (CONTINUED) |
||||
Name |
|
Function |
Input |
Output |
Description |
|
Type |
Type |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB6 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C |
T1OSO |
|
XTAL |
Crystal/Resonator |
|
T1CKI |
ST |
|
TMR1 clock input |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
P1C |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1C output |
|
|
RB7 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
RB7/T1OSI/P1D |
T1OSI |
XTAL |
|
TMR1 crystal/resonator |
|
|
|
P1D |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1D output |
VSS |
|
VSS |
Power |
|
Ground reference for logic and I/O pins |
VDD |
|
VDD |
Power |
|
Positive supply for logic and I/O pins |
AVSS |
|
AVSS |
Power |
|
Ground reference for analog |
AVDD |
|
AVDD |
Power |
|
Positive supply for analog |
Note 1: Bit programmable pull-ups.
DS41120A-page 8 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C717/770/771 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TABLE 1-2: |
PIC16C717 PINOUT DESCRIPTION |
|
||||||||||
Name |
|
|
Function |
Input |
Output |
Description |
||||||
|
|
Type |
Type |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
RA0/AN0 |
|
|
|
RA0 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||||
|
|
|
AN0 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA1 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA1/AN1/LVDIN |
|
AN1 |
AN |
|
A/D input reference |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
LVDIN |
AN |
|
LVD input reference |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA2 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL |
|
AN2 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
|||||||
|
VREF- |
AN |
|
Negative analog reference input |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
VRL |
|
AN |
Internal voltage reference low output |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA3 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH |
|
AN3 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
|||||||
VREF+ |
AN |
|
Positive analog reference high output |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
VRH |
|
AN |
Internal voltage reference high output |
|||
RA4/T0CKI |
|
RA4 |
ST |
OD |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||||||
T0CKI |
ST |
|
TMR0 clock input |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA5 |
ST |
|
Input port |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ST |
|
Master Clear |
RA5/MCLR/V |
PP |
MCLR |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
VPP |
Power |
|
Programming Voltage |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA6 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA6/OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
OSC2 |
|
XTAL |
Crystal/Resonator |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
CLKOUT |
|
CMOS |
FOSC/4 output |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA7 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O |
|||
RA7/OSC1/CLKIN |
|
OSC1 |
XTAL |
|
Crystal/Resonator |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
CLKIN |
ST |
|
External clock input/ER resistor connection |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB0 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
|||
RB0/AN4/INT |
|
AN4 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
INT |
ST |
|
Interrupt input |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB1 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
|||
RB1/AN5/SS |
|
|
|
|
AN5 |
AN |
|
A/D input |
||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ST |
|
SSP slave select input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SS |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB2 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional input(1) |
|||
RB2/SCK/SCL |
|
SCK |
ST |
CMOS |
Serial clock I/O for SPI |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCL |
ST |
OD |
Serial clock I/O for I2C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB3 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional input(1) |
|||
RB3/CCP1/P1A |
|
CCP1 |
ST |
CMOS |
Capture 1 input/Compare 1 output |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1A |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1A output |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB4 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional input(1) |
|||
RB4/SDI/SDA |
|
SDI |
ST |
|
Serial data in for SPI |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDA |
ST |
OD |
Serial data I/O for I2C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB5 |
ST |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
|||
RB5/SDO/P1B |
|
SDO |
|
CMOS |
Serial data out for SPI |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P1B |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1B output |
|||
Note 1: Bit programmable pull-ups.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 9

PIC16C717/770/771
TABLE 1-2: |
PIC16C717 PINOUT DESCRIPTION (CONTINUED) |
||||
Name |
|
Function |
Input |
Output |
Description |
|
Type |
Type |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB6 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
RB6/T1OSO/T1CKI/P1C |
T1OSO |
|
XTAL |
TMR1 Crystal/Resonator |
|
T1CKI |
ST |
|
TMR1 Clock input |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
P1C |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1C output |
|
|
RB7 |
TTL |
CMOS |
Bi-directional I/O(1) |
RB7/T1OSI/P1D |
T1OSI |
XTAL |
|
TMR1 Crystal/Resonator |
|
|
|
P1D |
|
CMOS |
PWM P1D output |
VSS |
|
VSS |
Power |
|
Ground |
VDD |
|
VDD |
Power |
|
Positive Supply |
Note 1: Bit programmable pull-ups.
DS41120A-page 10 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
2.0MEMORY ORGANIZATION
There are two memory blocks in each of these PICmicro® microcontrollers. Each block (Program Memory and Data Memory) has its own bus, so that concurrent access can occur.
Additional information on device memory may be found in the PICmicro Mid-Range Reference Manual, (DS33023).
2.1Program Memory Organization
The PIC16C717/770/771 devices have a 13-bit program counter capable of addressing an 8K x 14 program memory space. The PIC16C717 and the PIC16C770 have 2K x 14 words of program memory. The PIC16C771 has 4K x 14 words of program memory. Accessing a location above the physically implemented address will cause a wraparound.
The reset vector is at 0000h and the interrupt vector is at 0004h.
FIGURE 2-1: PROGRAM MEMORY MAP AND STACK OF THE PIC16C717 AND PIC16C770
|
|
|
|
|
PC<12:0> |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CALL, RETURN |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
RETFIE, RETLW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Stack Level 1 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Stack Level 2 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Stack Level 8 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Reset Vector |
0000h |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interrupt Vector |
0004h |
|
|||||
On-chip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0005h |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Program |
|
|
Page 0 |
|
|
|
|||||
Memory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
07FFh |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
3FFFh
FIGURE 2-2: PROGRAM MEMORY MAP AND STACK OF THE PIC16C771
|
PC<12:0> |
|
|
CALL, RETURN |
13 |
|
|
RETFIE, RETLW |
|
|
|
|
Stack Level 1 |
|
|
|
Stack Level 2 |
|
|
|
Stack Level 8 |
|
|
|
Reset Vector |
0000h |
|
|
Interrupt Vector |
0004h |
|
|
|
|
0005h |
On-chip |
Page 0 |
|
|
|
|
07FFh |
|
Program |
|
|
|
|
|
0800h |
|
Memory |
Page 1 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFFh |
|
|
|
1000h |
|
|
|
3FFFh |
2.2Data Memory Organization
The data memory is partitioned into multiple banks, which contain the General Purpose Registers and the Special Function Registers. Bits RP1 and RP0 are the bank select bits.
RP1 RP0 (STATUS<6:5>)
=00 → Bank0
=01 → Bank1
=10 → Bank2
=11 → Bank3
Each bank extends up to 7Fh (128 bytes). The lower locations of each bank are reserved for the Special Function Registers. Above the Special Function Registers are General Purpose Registers, implemented as static RAM. All implemented banks contain special function registers. Some frequently used special function registers from one bank are mirrored in another bank for code reduction and quicker access.
2.2.1GENERAL PURPOSE REGISTER FILE
The register file can be accessed either directly, or indirectly, through the File Select Register FSR.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc.
Advanced Information
DS41120A-page 11
PIC16C717/770/771
FIGURE 2-3: REGISTER FILE MAP
|
File |
|
Address |
||
|
|
|
Indirect addr.(*) |
00h |
|
TMR0 |
01h |
|
|
02h |
|
PCL |
||
|
03h |
|
STATUS |
||
FSR |
04h |
|
PORTA |
05h |
|
|
06h |
|
PORTB |
||
|
07h |
|
|
08h |
|
|
09h |
|
PCLATH |
0Ah |
|
INTCON |
0Bh |
|
PIR1 |
0Ch |
|
PIR2 |
0Dh |
|
TMR1L |
0Eh |
|
|
0Fh |
|
TMR1H |
||
|
10h |
|
T1CON |
||
|
11h |
|
TMR2 |
||
|
12h |
|
T2CON |
||
SSPBUF |
13h |
|
|
14h |
|
SSPCON |
||
|
15h |
|
CCPR1L |
||
|
16h |
|
CCPR1H |
||
CCP1CON |
17h |
|
|
18h |
|
|
||
|
19h |
|
|
1Ah |
|
|
1Bh |
|
|
1Ch |
|
|
1Dh |
|
ADRESH |
1Eh |
|
ADCON0 |
1Fh |
|
General |
20h |
|
|
||
Purpose |
|
|
Register |
|
|
96 Bytes |
|
|
|
7Fh |
|
Bank 0 |
||
|
||
|
|
File |
|
Address |
|||
|
|
|
|
Indirect addr.(*) |
|
80h |
|
OPTION_REG |
|
81h |
|
PCL |
|
82h |
|
STATUS |
|
83h |
|
FSR |
|
84h |
|
TRISA |
|
85h |
|
TRISB |
|
86h |
|
|
|
87h |
|
|
|
88h |
|
|
|
89h |
|
PCLATH |
|
8Ah |
|
INTCON |
|
8Bh |
|
PIE1 |
|
8Ch |
|
PIE2 |
|
8Dh |
|
PCON |
|
8Eh |
|
|
|
8Fh |
|
|
|
90h |
|
SSPCON2 |
|
91h |
|
PR2 |
|
92h |
|
SSPADD |
|
93h |
|
SSPSTAT |
|
94h |
|
WPUB |
|
95h |
|
IOCB |
|
96h |
|
P1DEL |
|
97h |
|
|
|
98h |
|
|
|
99h |
|
|
|
9Ah |
|
REFCON |
|
9Bh |
|
LVDCON |
|
9Ch |
|
ANSEL |
|
9Dh |
|
ADRESL |
|
9Eh |
|
ADCON1 |
|
9Fh |
|
|
|
A0h |
|
|
|
||
General |
|
|
|
Purpose |
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
80 Bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
EFh |
|
accesses |
|
F0h |
|
|
|
||
70h-7Fh |
|
FFh |
|
|
|
||
Bank 1 |
|||
|
|
||
Unimplemented data memory locations, read as ’0’.
*Not a physical register.
|
File |
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
Indirect addr.(*) |
100h |
|
TMR0 |
101h |
|
PCL |
102h |
|
STATUS |
103h |
|
FSR |
104h |
|
|
105h |
|
PORTB |
106h |
|
|
107h |
|
|
108h |
|
|
109h |
|
PCLATH |
10Ah |
|
INTCON |
10Bh |
|
PMDATL |
10Ch |
|
|
10Dh |
|
PMADRL |
||
|
10Eh |
|
PMDATH |
||
PMADRH |
10Fh |
|
|
110h |
|
|
111h |
|
|
112h |
|
|
||
|
113h |
|
|
||
|
114h |
|
|
||
|
115h |
|
|
||
|
116h |
|
|
||
|
117h |
|
|
||
|
118h |
|
|
||
|
119h |
|
|
||
|
11Ah |
|
|
||
|
11Bh |
|
|
||
|
11Ch |
|
|
||
|
11Dh |
|
|
||
|
11Eh |
|
|
||
|
11Fh |
|
|
||
|
120h |
|
General |
||
|
||
Purpose |
|
|
Register |
|
|
80 Bytes |
|
|
|
6Fh |
|
accesses |
70h |
|
70h - 7Fh |
17Fh |
|
|
||
Bank 2 |
|
|
|
File |
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect addr.(*) |
180h |
|
OPTION_REG |
181h |
|
PCL |
182h |
|
STATUS |
183h |
|
FSR |
184h |
|
|
185h |
|
TRISB |
186h |
|
|
187h |
|
|
188h |
|
|
189h |
|
PCLATH |
18Ah |
|
INTCON |
18Bh |
|
PMCON1 |
18Ch |
|
|
18Dh |
|
|
18Eh |
|
|
18Fh |
|
|
190h |
|
|
191h |
|
|
192h |
|
|
193h |
|
|
194h |
|
|
195h |
|
|
196h |
|
|
197h |
|
|
198h |
|
|
199h |
|
|
19Ah |
|
|
19Bh |
|
|
19Ch |
|
|
19Dh |
|
|
19Eh |
|
|
|
|
|
19Fh |
|
|
|
|
|
1A0h |
|
|
|
1EFh accesses 1F0h 70h - 7Fh
1FFh
Bank 3
DS41120A-page 12 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS
The Special Function Registers are registers used by the CPU and Peripheral Modules for controlling the desired operation of the device. These registers are implemented as static RAM. A list of these registers is given in Table 2-1.
The special function registers can be classified into two sets; core (CPU) and peripheral. Those registers associated with the core functions are described in detail in this section. Those related to the operation of the peripheral features are described in detail in that peripheral feature section.
TABLE 2-1: |
PIC16C717/770/771 SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on: |
Value on all |
||
Address |
Name |
|
Bit 7 |
Bit 6 |
Bit 5 |
Bit 4 |
Bit 3 |
|
Bit 2 |
Bit 1 |
Bit 0 |
POR, |
other resets |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOR |
(2) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
00h(3) |
INDF |
|
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||||||||||||||
01h |
TMR0 |
|
Timer0 module’s register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
02h(3) |
PCL |
|
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||||
03h(3) |
STATUS |
|
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
TO |
|
|
PD |
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
C |
0001 |
1xxx |
000q |
quuu |
||
04h(3) |
FSR |
|
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||
05h |
PORTA |
|
RA7 |
RA6 |
RA5 |
RA4 |
RA3 |
|
RA2 |
RA1 |
RA0 |
xxxx 0000 |
uuuu 0000 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
06h |
PORTB |
|
RB7 |
RB6 |
RB5 |
RB4 |
RB3 |
|
RB2 |
RB1 |
RB0 |
xxxx xx00 |
uuuu uu00 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
07h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
08h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
09h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
0Ah(1,3) |
PCLATH |
|
— |
— |
— |
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the Program Counter |
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
||||||||||||||
0Bh(3) |
INTCON |
|
GIE |
PEIE |
T0IE |
INTE |
RBIE |
|
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
0000 |
000x |
0000 |
000u |
|||||||
0Ch |
PIR1 |
|
— |
ADIF |
— |
|
— |
SSPIF |
CCP1IF |
TMR2IF |
TMR1IF |
-0-- 0000 |
-0-- 0000 |
|||||||||
0Dh |
PIR2 |
|
LVDIF |
— |
— |
|
— |
BCLIF |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
0--- 0--- |
0--- 0--- |
|||||||
0Eh |
TMR1L |
|
Holding register for the Least Significant Byte of the 16-bit TMR1 register |
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
0Fh |
TMR1H |
|
Holding register for the Most Significant Byte of the 16-bit TMR1 register |
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
10h |
T1CON |
|
— |
— |
T1CKPS1 |
T1CKPS0 |
T1OSCEN |
|
|
|
|
|
TMR1CS |
TMR1ON |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
T1SYNC |
--00 0000 |
--uu uuuu |
|||||||||||||||||||
11h |
TMR2 |
|
Timer2 module’s register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
12h |
T2CON |
|
— |
TOUTPS3 |
TOUTPS2 |
TOUTPS1 |
TOUTPS0 |
TMR2ON |
T2CKPS1 |
T2CKPS0 |
-000 0000 |
-000 0000 |
||||||||||
13h |
SSPBUF |
|
Synchronous Serial Port Receive Buffer/Transmit Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
14h |
SSPCON |
|
WCOL |
SSPOV |
SSPEN |
CKP |
SSPM3 |
|
SSPM2 |
SSPM1 |
SSPM0 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
15h |
CCPR1L |
|
Capture/Compare/PWM Register1 (LSB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
16h |
CCPR1H |
|
Capture/Compare/PWM Register1 (MSB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
17h |
CCP1CON |
PWM1M1 |
PWM1M0 |
DC1B1 |
DC1B0 |
CCP1M3 |
CCP1M2 |
CCP1M1 |
CCP1M0 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
1Ah |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
1Bh |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
1Ch |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
1Dh |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
1Eh |
ADRESH |
|
A/D High Byte Result Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
1Fh |
ADCON0 |
|
ADCS1 |
ADCS0 |
CHS2 |
CHS1 |
CHS0 |
GO/DONE |
|
CHS3 |
ADON |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as ’0’. Shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’.
Note 1: The upper byte of the program counter is not directly accessible. PCLATH is a holding register for the PC<12:8> whose contents are transferred to the upper byte of the program counter.
2:Other (non power-up) resets include external reset through MCLR and Watchdog Timer Reset.
3:These registers can be addressed from any bank.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 13

PIC16C717/770/771
TABLE 2-1: |
PIC16C717/770/771 SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY (CONTINUED) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on: |
Value on all |
|
Address |
Name |
|
|
Bit 7 |
Bit 6 |
Bit 5 |
Bit 4 |
|
Bit 3 |
Bit 2 |
Bit 1 |
|
Bit 0 |
POR, |
other resets |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOR |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
80h(3) |
INDF |
|
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
81h |
OPTION_REG |
|
|
|
INTEDG |
T0CS |
T0SE |
|
PSA |
PS2 |
|
PS1 |
|
PS0 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
RBPU |
1111 |
1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
82h(3) |
PCL |
|
Program Counter’s (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||
83h(3) |
STATUS |
|
|
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
TO |
|
|
|
PD |
|
Z |
|
DC |
|
C |
0001 |
1xxx |
000q quuu |
|||||||
84h(3) |
FSR |
|
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||||||
85h |
TRISA |
|
PORTA Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 |
1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
86h |
TRISB |
|
PORTB Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 |
1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
87h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
88h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
89h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
8Ah(1,3) |
PCLATH |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the Program Counter |
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
|||||||||||||||||||
8Bh(3) |
INTCON |
|
|
GIE |
PEIE |
T0IE |
INTE |
|
RBIE |
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
0000 |
000x |
0000 000u |
|||||||||||||
8Ch |
PIE1 |
|
|
— |
ADIE |
— |
|
— |
|
SSPIE |
CCP1IE |
TMR2IE |
TMR1IE |
-0-- 0000 |
-0-- 0000 |
|||||||||||||
8Dh |
PIE2 |
|
LVDIE |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
BCLIE |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
0--- 0--- |
0--- 0--- |
||||||||||||
8Eh |
PCON |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
OSCF |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
POR |
BOR |
---- 1-qq |
---- 1-uu |
|||||||||||||||||||||
8Fh |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
90h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
91h |
SSPCON2 |
|
GCEN |
ACKSTAT |
ACKDT |
ACKEN |
|
RCEN |
PEN |
RSEN |
|
SEN |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
92h |
PR2 |
|
Timer2 Period Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 |
1111 |
1111 1111 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
93h |
SSPADD |
|
Synchronous Serial Port (I2C mode) Address Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||
94h |
SSPSTAT |
|
|
SMP |
CKE |
D/A |
|
|
P |
|
|
S |
R/W |
|
UA |
|
BF |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
95h |
WPUB |
|
PORTB Weak Pull-up Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 |
1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
96h |
IOCB |
|
PORTB Interrupt on Change Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 |
0000 |
1111 0000 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
97h |
P1DEL |
|
PWM 1 Delay value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 |
0000 |
0000 0000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
98h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
99h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
9Ah |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|||
9Bh |
REFCON |
|
VRHEN |
VRLEN |
VRHOEN |
VRLOEN |
|
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
0000 ---- |
0000 ---- |
||||||||||||
9Ch |
LVDCON |
|
|
— |
— |
BGST |
LVDEN |
|
LVV3 |
LVV2 |
LVV1 |
LVV0 |
--00 0101 |
--00 0101 |
||||||||||||||
9Dh |
ANSEL |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Channel Select |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 |
1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||||
9Eh |
ADRESL |
|
A/D Low Byte Result Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
9Fh |
ADCON1 |
|
ADFM |
VCFG2 |
VCFG1 |
VCFG0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as ’0’. Shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’.
Note 1: The upper byte of the program counter is not directly accessible. PCLATH is a holding register for the PC<12:8> whose contents are transferred to the upper byte of the program counter.
2:Other (non power-up) resets include external reset through MCLR and Watchdog Timer Reset.
3:These registers can be addressed from any bank.
DS41120A-page 14 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
TABLE 2-1: |
PIC16C717/770/771 SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY (CONTINUED) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on: |
Value on all |
Address |
Name |
|
|
Bit 7 |
Bit 6 |
Bit 5 |
Bit 4 |
Bit 3 |
Bit 2 |
Bit 1 |
|
Bit 0 |
POR, |
other resets |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BOR |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
100h(3) |
INDF |
|
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||||||
101h |
TMR0 |
|
Timer0 module’s register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
102h(3) |
PCL |
|
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
|||||||
103h(3) |
STATUS |
|
|
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
|
C |
0001 1xxx |
000q quuu |
|
|
TO |
PD |
|||||||||||||||||
104h(3) |
FSR |
|
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||
105h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
106h |
PORTB |
|
PORTB Data Latch when written: PORTB pins when read |
|
|
|
|
xxxx xx00 |
uuuu uu00 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
107h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
108h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
109h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
10Ah(1,3) |
PCLATH |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the Program Counter |
|
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
|||||||||
10Bh(3) |
INTCON |
|
|
GIE |
PEIE |
T0IE |
INTE |
RBIE |
T0IF |
INTF |
|
RBIF |
0000 000x |
0000 000u |
|||||
10Ch |
PMDATL |
|
Program memory read data low |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10Dh |
PMADRL |
|
Program memory read address low |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10Eh |
PMDATH |
|
|
— |
— |
Program memory read data high |
|
|
|
|
--xx xxxx |
--uu uuuu |
|||||||
10Fh |
PMADRH |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
Program memory read address high |
|
---- xxxx |
---- uuuu |
|||||||
110h- |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
11Fh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
180h(3) |
INDF |
|
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||||||
181h |
OPTION_REG |
|
|
|
INTEDG |
T0CS |
T0SE |
PSA |
PS2 |
PS1 |
|
PS0 |
1111 1111 |
1111 1111 |
|||||
RBPU |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
182h(3) |
PCL |
|
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
|||||||
183h(3) |
STATUS |
|
|
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
|
C |
0001 1xxx |
000q quuu |
|
|
|
|
TO |
PD |
|||||||||||||||
184h(3) |
FSR |
|
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||
185h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
186h |
TRISB |
|
PORTB Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
187h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
188h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
189h |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
18Ah(1,3) |
PCLATH |
|
|
— |
— |
— |
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the Program Counter |
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
||||||||||
18Bh(3) |
INTCON |
|
|
GIE |
PEIE |
T0IE |
INTE |
RBIE |
T0IF |
INTF |
|
RBIF |
0000 000x |
0000 000u |
|||||
18Ch |
PMCON1 |
|
Reserved |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
RD |
1--- ---0 |
1--- ---0 |
||||
18Dh- |
— |
|
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
18Fh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as ’0’. Shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’.
Note 1: The upper byte of the program counter is not directly accessible. PCLATH is a holding register for the PC<12:8> whose contents are transferred to the upper byte of the program counter.
2:Other (non power-up) resets include external reset through MCLR and Watchdog Timer Reset.
3:These registers can be addressed from any bank.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 15

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.1STATUS REGISTER
The STATUS register, shown in Register 2-1, contains the arithmetic status of the ALU, the RESET status and the bank select bits for data memory.
The STATUS register can be the destination for any instruction, as with any other register. If the STATUS register is the destination for an instruction that affects the Z, DC or C bits, then the write to these three bits is disabled. These bits are set or cleared according to the device logic. Furthermore, the TO and PD bits are not writable. Therefore, the result of an instruction with the STATUS register as destination may be different than intended.
For example, CLRF STATUS will clear the upper-three bits and set the Z bit. This leaves the STATUS register as 000u u1uu (where u = unchanged).
It is recommended, therefore, that only BCF, BSF, SWAPF and MOVWF instructions are used to alter the STATUS register, because these instructions do not affect the Z, C or DC bits from the STATUS register. For other instructions not affecting any status bits, see the "Instruction Set Summary."
Note 2: The C and DC bits operate as a borrow and digit borrow bit, respectively, in subtraction. See the SUBLW and SUBWF instructions for examples.
REGISTER 2-1: STATUS REGISTER (STATUS: 03h, 83h, 103h, 183h)
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R-1 |
R-1 |
R/W-x |
R/W-x |
R/W-x |
|
|
|
||||
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
TO |
|
|
PD |
|
Z |
DC |
C |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n |
= Value at POR reset |
bit 7: IRP: Register Bank Select bit (used for indirect addressing) 1 = Bank 2, 3 (100h - 1FFh)
0 = Bank 0, 1 (00h - FFh)
bit 6-5: RP<1:0>: Register Bank Select bits (used for direct addressing) 11 = Bank 3 (180h - 1FFh)
10 = Bank 2 (100h - 17Fh)
01 = Bank 1 (80h - FFh)
00 = Bank 0 (00h - 7Fh) Each bank is 128 bytes
bit 4: TO: Time-out bit
1 = After power-up, CLRWDT instruction, or SLEEP instruction 0 = A WDT time-out occurred
bit 3: PD: Power-down bit
1 = After power-up or by the CLRWDT instruction 0 = By execution of the SLEEP instruction
bit 2: Z: Zero bit
1 = The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is zero
0 = The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is not zero
bit 1: DC: Digit carry/borrow bit (ADDWF, ADDLW,SUBLW,SUBWF instructions) (for borrow the polarity is reversed) 1 = A carry-out from the 4th low order bit of the result occurred
0 = No carry-out from the 4th low order bit of the result
bit 0: C: Carry/borrow bit (ADDWF, ADDLW,SUBLW,SUBWF instructions) 1 = A carry-out from the most significant bit of the result occurred 0 = No carry-out from the most significant bit of the result occurred
Note: For borrow, the polarity is reversed. A subtraction is executed by adding the two’s complement of the second operand. For rotate (RRF, RLF) instructions, this bit is loaded with either the high or low order bit of the source register.
DS41120A-page 16 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.2OPTION_REG REGISTER
The OPTION_REG register is a readable and writable |
Note: |
To achieve a 1:1 prescaler assignment for |
||||||||||||||
|
the TMR0 register, assign the prescaler to |
|||||||||||||||
register, which contains various control bits to configure |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
the Watchdog Timer. |
|||||||||||||||
the TMR0 prescaler/WDT postscaler (single assign- |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
able register known also as the prescaler), the External |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
INT Interrupt, TMR0 and the weak pull-ups on PORTB. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
REGISTER 2-2: OPTION REGISTER (OPTION_REG: 81h, 181h) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
R/W-1 |
|
R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
RBPU |
|
INTEDG |
T0CS |
T0SE |
PSA |
PS2 |
|
PS1 |
PS0 |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
|
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7: |
|
|
PORTB Pull-up Enable bit(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
RBPU: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
1 = PORTB weak pull-ups are disabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
0 = PORTB weak pull-ups are enabled by the WPUB register |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
bit 6: INTEDG: Interrupt Edge Select bit
1 = Interrupt on rising edge of RB0/INT pin
0 = Interrupt on falling edge of RB0/INT pin
bit 5: T0CS: TMR0 Clock Source Select bit 1 = Transition on RA4/T0CKI pin
0 = Internal instruction cycle clock (CLKOUT)
bit 4: T0SE: TMR0 Source Edge Select bit
1 = Increment on high-to-low transition on RA4/T0CKI pin 0 = Increment on low-to-high transition on RA4/T0CKI pin
bit 3: PSA: Prescaler Assignment bit
1 = Prescaler is assigned to the WDT
0 = Prescaler is assigned to the Timer0 module
bit 2-0: PS<2:0>: Prescaler Rate Select bits
Bit Value |
TMR0 Rate |
WDT Rate |
||
|
|
|
|
|
000 |
1 |
: 2 |
1 |
: 1 |
001 |
1 |
: 4 |
1 |
: 2 |
010 |
1 |
: 8 |
1 |
: 4 |
011 |
1 |
: 16 |
1 |
: 8 |
100 |
1 |
: 32 |
1 |
: 16 |
101 |
1 |
: 64 |
1 |
: 32 |
110 |
1 |
: 128 |
1 |
: 64 |
111 |
1 |
: 256 |
1 |
: 128 |
Note 1: Individual weak pull-up on RB pins can be enabled/disabled from the weak pull-up PORTB Register (WPUB).
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 17

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.3INTCON REGISTER
The INTCON Register is a readable and writable regis- |
Note: |
Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt |
||||||||||||
|
condition occurs, regardless of the state of |
|||||||||||||
ter, which contains various enable and flag bits for the |
|
|||||||||||||
|
its corresponding enable bit or the global |
|||||||||||||
TMR0 register overflow, RB Port change and External |
|
|||||||||||||
|
enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). User soft- |
|||||||||||||
RB0/INT pin interrupts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
ware should ensure the appropriate inter- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
interrupt. |
|
|
|
|
REGISTER 2-3: INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER (INTCON: 0Bh, 8Bh, 10Bh, 18Bh) |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-x |
|
|
|
|||
|
GIE |
PEIE |
|
T0IE |
INTE |
RBIE |
T0IF |
|
INTF |
RBIF |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
bit 7: GIE: Global Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables all un-masked interrupts
0 = Disables all interrupts
bit 6: PEIE: Peripheral Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables all un-masked peripheral interrupts
0 = Disables all peripheral interrupts
bit 5: T0IE: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Enables the TMR0 interrupt
0 = Disables the TMR0 interrupt
bit 4: INTE: RB0/INT External Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Enables the RB0/INT external interrupt 0 = Disables the RB0/INT external interrupt
bit 3: RBIE: RB Port Change Interrupt Enable bit(1) 1 = Enables the RB port change interrupt
0 = Disables the RB port change interrupt
bit 2: T0IF: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR0 register has overflowed (must be cleared in software) 0 = TMR0 register did not overflow
bit 1: INTF: RB0/INT External Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The RB0/INT external interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software) 0 = The RB0/INT external interrupt did not occur
bit 0: RBIF: RB Port Change Interrupt Flag bit(1)
1 = At least one of the RB<7:0> pins changed state (must be cleared in software) 0 = None of the RB<7:0> pins have changed state
Note 1: Individual RB pin interrupt on change can be enabled/disabled from the Interrupt on Change PORTB register (IOCB).
DS41120A-page 18 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.4 |
PIE1 REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: Bit PEIE |
|
(INTCON<6>) must be set to |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
This register contains the individual enable bits for the |
|
|
enable any peripheral interrupt. |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
peripheral interrupts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
REGISTER 2-4: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER 1 (PIE1: 8Ch) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U-0 |
|
|
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
|
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
— |
|
|
ADIE |
— |
— |
|
SSPIE |
|
CCP1IE |
TMR2IE |
TMR1IE |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
||
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7: |
|
Unimplemented: Read as ’0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit 6: |
|
ADIE: A/D Converter Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the A/D interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the A/D interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit 5-4: Unimplemented: Read as ’0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
bit 3: |
|
SSPIE: Synchronous Serial Port Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the SSP interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the SSP interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit 2: |
|
CCP1IE: CCP1 Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the CCP1 interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the CCP1 interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
bit 1: |
|
TMR2IE: TMR2 to PR2 Match Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
bit 0: |
|
TMR1IE: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the TMR1 overflow interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the TMR1 overflow interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 19

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.5 |
PIR1 REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Note: |
Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
This register contains the individual flag bits for the |
|
condition occurs, regardless of the state of |
|||||||||||
peripheral interrupts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
its corresponding enable bit or the global |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). User soft- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ware should ensure the appropriate inter- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
interrupt. |
|
|
|
|
REGISTER 2-5: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REGISTER 1 (PIR1: 0Ch) |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
|
|
|
||
|
— |
ADIF |
— |
— |
SSPIF |
CCP1IF |
|
TMR2IF |
TMR1IF |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7: |
Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
bit 6: |
ADIF: A/D Converter Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1 = An A/D conversion completed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
0 = The A/D conversion is not complete |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
bit 5-4: Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit 3: |
SSPIF: Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) Interrupt Flag |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 = The SSP interrupt condition has occurred, and must be cleared in software before returning from the |
|||||||||||
|
|
interrupt service routine. The conditions that will set this bit are: |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
SPI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A transmission/reception has taken place. I2C Slave / Master
A transmission/reception has taken place. I2C Master
The initiated start condition was completed by the SSP module. The initiated stop condition was completed by the SSP module. The initiated restart condition was completed by the SSP module.
The initiated acknowledge condition was completed by the SSP module.
A start condition occurred while the SSP module was idle (Multimaster system). A stop condition occurred while the SSP module was idle (Multimaster system).
0 = No SSP interrupt condition has occurred.
bit 2: CCP1IF: CCP1 Interrupt Flag bit Capture Mode
1 = A TMR1 register capture occurred (must be cleared in software) 0 = No TMR1 register capture occurred
Compare Mode
1 = A TMR1 register compare match occurred (must be cleared in software) 0 = No TMR1 register compare match occurred
PWM Mode Unused in this mode
bit 1: TMR2IF: TMR2 to PR2 Match Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR2 to PR2 match occurred (must be cleared in software) 0 = No TMR2 to PR2 match occurred
bit 0: TMR1IF: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR1 register overflowed (must be cleared in software) 0 = TMR1 register did not overflow
DS41120A-page 20 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.6PIE2 REGISTER
This register contains the individual enable bits for the
SSP bus collision and low voltage detect interrupts.
REGISTER 2-6: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REGISTER 2 (PIE2: 8Dh)
R/W-0 |
|
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
|
|
|
|
LVDIE |
|
— |
— |
— |
BCLIE |
|
— |
— |
— |
R |
= Readable bit |
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
bit 7: |
LVDIE: Low-voltage Detect Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
1 |
= LVD Interrupt is enabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0 |
= LVD Interrupt is disabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
bit 6-4: Unimplemented: Read as ’0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
bit 3: |
BCLIE: Bus Collision Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1 |
= Bus Collision interrupt is enabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
0 |
= Bus Collision interrupt is disabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
bit 2-0: Unimplemented: Read as ’0’
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 21

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.7 |
PIR2 REGISTER |
. |
|
This register contains the SSP Bus Collision and low- |
Note: Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt |
||
condition occurs, regardless of the state of |
|||
voltage detect interrupt flag bits. |
|||
its corresponding enable bit or the global |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). User soft- |
|
|
|
ware should ensure the appropriate inter- |
|
|
|
rupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an |
|
|
|
interrupt. |
|
REGISTER 2-7: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REGISTER 2 (PIR2: 0Dh)
R/W-0 |
|
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
|
|
|
|
LVDIF |
|
— |
— |
— |
BCLIF |
— |
— |
|
— |
R |
= Readable bit |
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
bit 7: |
LVDIF: Low-voltage Detect Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1 |
= The supply voltage has fallen below the specified LVD voltage (must be cleared in software) |
||||||||||
|
0 |
= The supply voltage is greater than the specified LVD voltage |
|
|
|
|
||||||
bit 6-4: Unimplemented: Read as ’0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
bit 3: |
BCLIF: Bus Collision Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
1 |
= A bus collision has occurred while the SSP module configured in I2C Master was transmitting |
||||||||||
|
(must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
0 |
= No bus collision occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
bit 2-0: Unimplemented: Read as ’0’
DS41120A-page 22 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
2.2.2.8 |
PCON REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: BOR is unknown on Power-on Reset. It |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
The Power Control (PCON) register contains a flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
must then be set by the user and checked |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
on subsequent resets to see if BOR is |
|||||||||||||||||||||
to allow differentiation |
between |
a Power-on Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
clear, indicating a brown-out has occurred. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
(POR) to an external MCLR Reset or WDT Reset. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
The BOR status bit is a don’t care and is |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Those devices with brown-out detection circuitry con- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
not necessarily predictable if the brown-out |
|||||||||||||||||||||
tain an additional bit to differentiate a Brown-out Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
circuit is disabled (by clearing the BODEN |
|||||||||||||||||||||
condition from a Power-on Reset condition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit in the Configuration word). |
|||||||||||||||||||
The PCON register also contains the frequency select |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
bit of the INTRC or ER oscillator. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
REGISTER 2-8: POWER CONTROL REGISTER (PCON: 8Eh) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-1 |
U-0 |
R/W-q |
R/W-q |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
— |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
OSCF |
|
— |
|
|
POR |
|
|
|
BOR |
|
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
|||||
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
W |
= Writable bit |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|||
|
bit 7-4,2:Unimplemented: Read as ’0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
bit 3: |
OSCF: Oscillator speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
INTRC Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 = 4 MHz nominal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
0 = 37 KHz nominal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
ER Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1 = Oscillator frequency depends on the external resistor value on the OSC1 pin. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
0 = 37 KHz nominal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
All other modes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
x = Ignored |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
bit 1: |
|
|
Power-on Reset Status bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
POR: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
1 = No Power-on Reset occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
0 = A Power-on Reset occurred (must be set in software after a Power-on Reset occurs) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
bit 0: |
|
Brown-out Reset Status bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
BOR: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
1 = No Brown-out Reset occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
0 = A Brown-out Reset occurred (must be set in software after a Brown-out Reset occurs) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 23

PIC16C717/770/771
2.3PCL and PCLATH
The program counter (PC) specifies the address of the instruction to fetch for execution. The PC is 13 bits wide. The low byte is called the PCL register. This register is readable and writable. The high byte is called the PCH register. This register contains the PC<12:8> bits and is not directly readable or writable. All updates to the PCH register occur through the PCLATH register.
2.3.1PROGRAM MEMORY PAGING
PIC16C717/770/771 devices are capable of addressing a continuous 8K word block of program memory. The CALL and GOTO instructions provide only 11 bits of address to allow branching within any 2K program memory page. When doing a CALL or GOTO instruction, the upper 2 bits of the address are provided by PCLATH<4:3>. When doing a CALL or GOTO instruction, the user must ensure that the page select bits are programmed so that the desired program memory page is addressed. A return instruction pops a PC address off the stack onto the PC register. Therefore, manipulation of the PCLATH<4:3> bits are not required for the return instructions (which POPs the address from the stack).
2.4Stack
The stack allows a combination of up to 8 program calls and interrupts to occur. The stack contains the return address from this branch in program execution.
Mid-range devices have an 8-level deep x 13-bit wide hardware stack. The stack space is not part of either program or data space and the stack pointer is not readable or writable. The PC is PUSHed onto the stack when a CALL instruction is executed or an interrupt causes a branch. The stack is POPed in the event of a RETURN, RETLW or a RETFIE instruction execution. PCLATH is not modified when the stack is PUSHed or POPed.
After the stack has been PUSHed eight times, the ninth push overwrites the value that was stored from the first push. The tenth push overwrites the second push (and so on).
DS41120A-page 24 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
The INDF register is not a physical register. Addressing INDF actually addresses the register whose address is contained in the FSR register (FSR is a pointer). This is indirect addressing.
Reading INDF itself indirectly (FSR = 0) will produce 00h. Writing to the INDF register indirectly results in a no-operation (although STATUS bits may be affected).
A simple program to clear RAM locations 20h-2Fh using indirect addressing is shown in Example 2-1.
EXAMPLE 2-1: HOW TO CLEAR RAM USING INDIRECT ADDRESSING
|
movlw |
0x20 |
;initialize pointer |
|
movwf |
FSR |
; to RAM |
NEXT |
clrf |
INDF |
;clear INDF register |
|
incf |
FSR |
;inc pointer |
|
btfss |
FSR,4 |
;all done? |
|
goto |
NEXT |
;NO, clear next |
CONTINUE |
|
|
|
|
: |
|
;YES, continue |
An effective 9-bit address is obtained by concatenating the 8-bit FSR register and the IRP bit (STATUS<7>), as shown in Figure 2-4.
FIGURE 2-4: DIRECT/INDIRECT ADDRESSING
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct Addressing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect Addressing |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
RP1:RP0 |
6 |
|
from opcode |
0 |
|
|
|
IRP |
7 |
|
|
FSR register |
0 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
bank select |
location select |
|
|
|
|
00 |
|
01 |
10 |
11 |
bank select |
|
|
|
|
location select |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00h |
80h |
100h |
180h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Memory(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7Fh |
FFh |
17Fh |
1FFh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 0 |
Bank 1 |
Bank 2 |
Bank 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Note 1: |
For register file map detail see Figure 2-3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 25

PIC16C717/770/771
NOTES:
DS41120A-page 26 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C717/770/771
3.0I/O PORTS
Some pins for these I/O ports are multiplexed with an alternate function for the peripheral features on the device. In general, when a peripheral is enabled, that pin may not be used as a general purpose I/O pin.
Additional information on I/O ports may be found in the PICmicro™ Mid-Range Reference Manual, (DS33023).
3.1I/O Port Analog/Digital Mode
The PIC16C717/770/771 have two I/O ports: PORTA and PORTB. Some of these port pins are mixed-signal (can be digital or analog). When an analog signal is
present on a pin, the pin must be configured as an analog input to prevent unnecessary current draw from the power supply. The Analog Select Register (ANSEL) allows the user to individually select the digital/analog mode on these pins. When the analog mode is active, the port pin will always read 0.
Note 1: On a Power-on Reset, the ANSEL register configures these mixed-signal pins as analog mode.
2:If a pin is configured as analog mode, the pin will always read '0', even if the digital output is active.
REGISTER 3-1: |
ANALOG SELECT REGISTER (ANSEL: 9Dh) |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ANS5 |
ANS4 |
ANS3 |
ANS2 |
|
ANS1 |
ANS0 |
|
R = Readable bit |
|
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W = Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U = Unimplemented bit, read as |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
bit 7-6: Reserved: Do not use |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
bit 5-0: ANS<5:0>: Analog Select between analog or digital function on pins AN<5:0>, respectively. |
|||||||||||
|
|
0 = Digital I/O. Pin is assigned to port or special function. |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 = Analog Input. Pin is assigned as analog input. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Note: |
Setting a pin to an analog input disables digital inputs and any pull-up that may be present. The corre- |
||||||||||
|
|
sponding TRIS bit should be set to input mode when using pins as analog inputs. |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.2PORTA and the TRISA Register
PORTA is a 8-bit wide bi-directional port. The corresponding data direction register is TRISA. Setting a TRISA bit (=1) will make the corresponding PORTA pin an input, i.e., put the corresponding output driver in a hi-impedance mode. Clearing a TRISA bit (=0) will make the corresponding PORTA pin an output, i.e., put the contents of the output latch on the selected pin.
Reading the PORTA register reads the status of the pins, whereas writing to it will write to the port latch. All write operations are read-modify-write operations. Therefore, a write to a port implies that the port pins are read, this value is modified, and then written to the port data latch.
Pins RA<3:0> are multiplexed with analog functions, such as analog inputs to the A/D converter, analog VREF inputs, and the on-board bandgap reference outputs. When the analog peripherals are using any of
these pins as analog input/output, the ANSEL register must have the proper value to individually select the analog mode of the corresponding pins.
Note: Upon reset, the ANSEL register configures the RA<3:0> pins as analog inputs. All RA<3:0> pins will read as ’0’.
Pin RA4 is multiplexed with the Timer0 module clock input to become the RA4/T0CKI pin. The RA4/T0CKI pin is a Schmitt Trigger input and an open drain output.
Pin RA5 is multiplexed with the device reset (MCLR) and programming input (VPP) functions. The RA5/ MCLR/VPP input only pin has a Schmitt Trigger input buffer. All other RA port pins have Schmitt Trigger input buffers and full CMOS output buffers.
Pins RA6 and RA7 are multiplexed with the oscillator input and output functions.
The TRISA register controls the direction of the RA pins, even when they are being used as analog inputs. The user must ensure the bits in the TRISA register are maintained set when using them as analog inputs.
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 27

PIC16C717/770/771
EXAMPLE 3-1: INITIALIZING PORTA
BCF |
STATUS, RP0 |
; |
Select Bank 0 |
CLRF |
PORTA |
; |
Initialize PORTA by |
;clearing output
;data latches
BSF |
STATUS, RP0 |
; |
Select Bank 1 |
MOVLW |
0Fh |
; |
Value used to |
;initialize data
;direction
MOVWF |
TRISA |
; Set |
RA<3:0> as |
inputs |
|
|
|
; RA<7:4> as outputs. RA<7:6>availability depends on oscillator selection. |
|||
MOVLW |
03 |
; |
Set |
RA<1:0> as |
analog inputs, RA<7:2> are digital I/O |
MOVWF |
ANSEL |
|
|
|
|
BCF |
STATUS, RP0 |
; |
Return to Bank |
0 |
|
FIGURE 3-1: BLOCK DIAGRAM OF RA0/AN0, RA1/AN1/LVDIN |
|
|||
Data |
Data Latch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bus |
D |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
||
WR |
|
|
VDD |
VDD |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
PORT |
CK |
Q |
|
|
|
P |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRIS Mode |
|
|
|
|
D |
Q |
N |
|
|
|
|
||
WR |
|
|
|
|
TRIS |
CK |
Q |
VSS |
VSS |
|
|
|
||
RD |
|
|
|
|
TRIS |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Select |
|
|
|
|
D |
Q |
|
Schmitt |
|
|
Trigger |
||
|
|
|
|
|
WR |
|
|
|
|
ANSEL |
CK |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Q |
D |
|
|
|
|
EN |
|
RD |
|
|
|
|
PORT |
|
|
|
|
To A/D Converter input or LVD Module input |
|
|
||
DS41120A-page 28 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |

|
|
|
PIC16C717/770/771 |
|
FIGURE 3-2: BLOCK DIAGRAM OF RA2/AN2/VREF-/VRL AND RA3/AN3/VREF+/VRH |
||||
Data |
Data Latch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bus |
D |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
||
WR |
|
|
VDD |
VDD |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
PORT |
CK |
Q |
|
|
|
P |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRIS Mode |
|
|
|
|
D |
Q |
N |
|
|
|
|
||
WR |
|
|
|
|
TRIS |
CK |
Q |
VSS |
VSS |
|
||||
RD |
|
|
|
|
TRIS |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Select |
|
|
|
|
D |
Q |
|
Schmitt |
WR |
|
|
|
Trigger |
|
|
|
|
|
ANSEL |
CK |
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Q |
D |
|
|
|
|
EN |
|
RD |
|
|
|
|
PORT |
|
|
|
|
To A/D Converter input |
|
|
|
|
and Vref+, Vrefinputs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VRH, VRL outputs |
|
|
|
(From Vref-LVD-BOR Module) |
|
|
|
|
VRH, VRL output enable |
|
|
|
|
Sense input for |
|
|
|
|
VRH, VRL amplifier |
|
|
|
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
Advanced Information |
DS41120A-page 29

PIC16C717/770/771
FIGURE 3-3: BLOCK DIAGRAM OF RA4/T0CKI
Data |
Data Latch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bus |
D |
Q |
|
|
|
||
WR |
|
|
|
Port |
CK |
Q |
|
|
|
||
|
TRIS Latch |
|
|
|
D |
Q |
N |
WR |
|
|
|
TRIS |
CK |
Q |
VSS |
|
|||
RD |
|
|
|
TRIS |
|
|
|
|
|
Q |
D |
|
|
|
EN |
RD |
|
|
|
PORT |
|
|
|
VSS
Schmitt Trigger
Input Buffer
TMR0 clock input
DS41120A-page 30 |
Advanced Information |
1999 Microchip Technology Inc. |
 Loading...
Loading...