Microchip Technology Inc PIC16C923T-04-PT, PIC16C923T-04I-CL, PIC16C923T-04I-L, PIC16C923T-04I-PT, PIC16C923T-04I-SP Datasheet
...
PIC16C9XX
8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller with LCD Driver
Devices included in this data sheet:
•PIC16C923
•PIC16C924
Microcontroller Core Features:
•High performance RISC CPU
•Only 35 single word instructions to learn
•4K x 14 on-chip EPROM program memory
•176 x 8 general purpose registers (SRAM)
•All single cycle instructions (500 ns) except for program branches which are two-cycle
•Operating speed: DC - 8 MHz clock input
DC - 500 ns instruction cycle
•Interrupt capability
•Eight level deep hardware stack
•Direct, indirect and relative addressing modes
Peripheral Features:
•25 I/O pins with individual direction control
•25-27 input only pins
•Timer0: 8-bit timer/counter with 8-bit prescaler
•Timer1: 16-bit timer/counter, can be incremented during sleep via external crystal/clock
•Timer2: 8-bit timer/counter with 8-bit period register, prescaler and postscaler
•One pin that can be configured a capture input, PWM output, or compare output
-Capture is 16-bit, max. resolution 31.25 ns
-Compare is 16-bit, max. resolution 500 ns
-PWM max resolution is 10-bits.
Maximum PWM frequency @ 8-bit resolution = 32 kHz, @ 10-bit resolution = 8 kHz
•Programmable LCD timing module
-Multiple LCD timing sources available
-Can drive LCD panel while in Sleep mode
-Static, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4 multiplex
-Static drive and 1/3 bias capability
-16 bytes of dedicated LCD RAM
-Up to 32 segments, up to 4 commons
Common |
Segment |
Pixels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
32 |
32 |
|
|
|
2 |
31 |
62 |
|
|
|
3 |
30 |
90 |
|
|
|
4 |
29 |
116 |
|
|
|
Available in Die Form
•Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) with SPI and I2C
•8-bit multi-channel Analog to Digital converter (PIC16C924 only)
Special Microcontroller Features:
•Power-on Reset (POR)
•Power-up Timer (PWRT) and Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST)
•Watchdog Timer (WDT) with its own on-chip RC oscillator for reliable operation
•Programmable code-protection
•Power saving SLEEP mode
•Selectable oscillator options
•In-Circuit Serial Programming™ (via two pins)
CMOS Technology
•Low-power, high-speed CMOS EPROM technology
•Fully static design
•Wide operating voltage range: 2.5V to 6.0V
•Commercial and Industrial temperature ranges
•Low-power consumption:
-< 2 mA @ 5.5V, 4 MHz
-22.5 A typical @ 4V, 32 kHz
-< 1 A typical standby current @ 3.0V
ICSP is a trademark of Microchip Technology Inc. I2C is a trademark of Philips Corporation. SPI is a trademark of Motorola Corporation.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 1 |

PIC16C9XX
Pin Diagrams
Shrink PDIP (750 mil)
MCLR/VPP |
1 |
|
RB3 |
2 |
|
RB2 |
3 |
|
RA0 |
4 |
|
RA1 |
5 |
|
VSS |
6 |
|
RA2 |
7 |
|
RA3 |
8 |
|
RA4/T0CKI |
9 |
|
RA5/SS |
10 |
|
RB1 |
11 |
PIC16C923 |
VLCD3 |
19 |
|
RB0/INT |
12 |
|
RC3/SCK/SCL |
13 |
|
RC4/SDI/SDA |
14 |
|
RC5/SDO |
15 |
|
C1 |
16 |
|
C2 |
17 |
|
VLCD2 |
18 |
|
VDD |
20 |
|
VSS |
21 |
|
OSC1/CLKIN |
22 |
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
23 |
|
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI |
24 |
|
RC1/T1OSI |
25 |
|
RC2/CCP1 |
26 |
|
VLCD1 |
27 |
|
VLCDADJ |
28 |
|
RD0/SEG00 |
29 |
|
RD1/SEG01 |
30 |
|
RD2/SEG02 |
31 |
|
RD3/SEG03 |
32 |
|
LEGEND:
Input Pin
Output Pin
Input/Output Pin
Digital Input/LCD Output Pin
LCD Output Pin
PLCC
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/SS
RB1
RB0/INT
RC3/SCK/SCL
RC4/SDI/SDA
RC5/SDO
C1
C2
VLCD2
VLCD3
VDD
VDD
VSS
OSC1/CLKIN
OSC2/CLKOUT
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI
64 

 RB4
RB4
63 

 RB5
RB5
62 

 RB7
RB7
61 

 RB6
RB6
60 
 VDD
VDD
59 
 COM0
COM0
58 
 RD7/SEG31/COM1
RD7/SEG31/COM1
57 

 RD6/SEG30/COM2
RD6/SEG30/COM2
56 

 RD5/SEG29/COM3
RD5/SEG29/COM3
55 
 RG6/SEG26
RG6/SEG26
54 

 RG5/SEG25
RG5/SEG25
53 

 RG4/SEG24
RG4/SEG24
52 
 RG3/SEG23
RG3/SEG23
51 

 RG2/SEG22
RG2/SEG22
50 

 RG1/SEG21
RG1/SEG21
49 

 RG0/SEG20
RG0/SEG20
48 

 RF7/SEG19
RF7/SEG19
47 

 RF6/SEG18
RF6/SEG18
46 

 RF5/SEG17
RF5/SEG17
45 
 RF4/SEG16
RF4/SEG16
44 


 RF3/SEG15
RF3/SEG15
43 


 RF2/SEG14
RF2/SEG14
42 


 RF1/SEG13
RF1/SEG13
41 

 RF0/SEG12
RF0/SEG12
40 


 RE6/SEG11
RE6/SEG11
39 


 RE5/SEG10
RE5/SEG10
38 


 RE4/SEG09
RE4/SEG09
37 


 RE3/SEG08
RE3/SEG08
36 

 RE2/SEG07
RE2/SEG07
35 


 RE1/SEG06
RE1/SEG06
34 

 RE0/SEG05
RE0/SEG05
33 


 RD4/SEG04
RD4/SEG04
RA4/T0CKI 

RA5/SS 

RB1 

RB0/INT 

RC3/SCK/SCL 

RC4/SDI/SDA 

RC5/SDO 

C1 
C2 
VLCD2
VLCD3
VDD
VSS
OSC1/CLKIN 
OSC2/CLKOUT 
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI 

RA3 |
RA2 |
VSS RA1 |
RA0 |
RB2 |
RB3 |
MCLR/VPP |
N/C |
RB4 |
RB5 RB7 RB6 VDD |
COM0 |
RD7/SEG31/COM1 |
RD6/SEG30/COM2 |
|||
9 |
8 7 6 5 |
4 3 2 1 |
68 |
67 66 65 64 63 |
62 61 |
||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
58 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
16 |
|
PIC16C923 |
|
|
54 |
||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
53 |
|||||||||||
18 |
|
|
|
52 |
|||||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
27 28 |
29 30 |
31 32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 |
||
RC1/T1OSI |
RC2/CCP1 |
VLCD1 VLCDADJ |
RD0/SEG00 |
RD1/SEG01 |
RD2/SEG02 |
RD3/SEG03 |
RD4/SEG04 |
RE7/SEG27 |
RE0/SEG05 |
RE1/SEG06 |
RE2/SEG07 |
RE3/SEG08 |
RE4/SEG09 |
RE5/SEG10 |
RE6/SEG11 |
RA3 |
RA2 |
VSS |
RA1 |
RA0 |
RB2 |
RB3 |
MCLR/VPP |
RB4 |
RB5 RB7 RB6 VDD |
COM0 |
RD7/SEG31/COM1 |
RD6/SEG30/COM2 |
|||
64 |
63 |
62 |
61 |
60 |
59 |
58 |
57 |
56 |
55 |
54 |
53 |
52 |
51 |
50 |
49 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
7 |
|
|
PIC16C923 |
|
|
42 |
|||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
|
41 |
||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
|
40 |
||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
RC1/T1OSI |
RC2/CCP1 |
VLCD1 |
VLCDADJ |
RD0/SEG00 |
RD1/SEG01 |
RD2/SEG02 |
RD3/SEG03 |
RD4/SEG04 |
RE0/SEG05 |
RE1/SEG06 |
RE2/SEG07 |
RE3/SEG08 |
RE4/SEG09 |
RE5/SEG10 |
RE6/SEG11 |

 RD5/SEG29/COM3
RD5/SEG29/COM3


 RG6/SEG26
RG6/SEG26


 RG5/SEG25
RG5/SEG25


 RG4/SEG24
RG4/SEG24

 RG3/SEG23
RG3/SEG23

 RG2/SEG22
RG2/SEG22


 RG1/SEG21
RG1/SEG21


 RG0/SEG20
RG0/SEG20


 RG7/SEG28
RG7/SEG28

 RF7/SEG19
RF7/SEG19

 RF6/SEG18
RF6/SEG18

 RF5/SEG17
RF5/SEG17


 RF4/SEG16
RF4/SEG16

 RF3/SEG15
RF3/SEG15


 RF2/SEG14
RF2/SEG14


 RF1/SEG13
RF1/SEG13 

 RF0/SEG12
RF0/SEG12
TQFP
RD5/SEG29/COM3
RG6/SEG26
RG5/SEG25
RG4/SEG24
RG3/SEG23
RG2/SEG22
RG1/SEG21
RG0/SEG20
RF7/SEG19
RF6/SEG18
RF5/SEG17
RF4/SEG16
RF3/SEG15
RF2/SEG14
RF1/SEG13
RF0/SEG12
DS30444E - page 2 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
Pin Diagrams (Cont.’d)
Shrink PDIP (750 mil)
MCLR/VPP |
1 |
|
RB3 |
2 |
|
RB2 |
3 |
|
RA0/AN0 |
4 |
|
RA1/AN1 |
5 |
|
VSS |
6 |
|
RA2/AN2 |
7 |
|
RA3/AN3/VREF |
8 |
|
RA4/T0CKI |
9 |
|
RA5/AN4/SS |
10 |
|
RB1 |
11 |
PIC16C924 |
VLCD3 |
19 |
|
RB0/INT |
12 |
|
RC3/SCK/SCL |
13 |
|
RC4/SDI/SDA |
14 |
|
RC5/SDO |
15 |
|
C1 |
16 |
|
C2 |
17 |
|
VLCD2 |
18 |
|
VDD |
20 |
|
VSS |
21 |
|
OSC1/CLKIN |
22 |
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
23 |
|
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI |
24 |
|
RC1/T1OSI |
25 |
|
RC2/CCP1 |
26 |
|
VLCD1 |
27 |
|
VLCDADJ |
28 |
|
RD0/SEG00 |
29 |
|
RD1/SEG01 |
30 |
|
RD2/SEG02 |
31 |
|
RD3/SEG03 |
32 |
|
LEGEND:
Input Pin
Output Pin
Input/Output Pin
Digital Input/LCD Output Pin
LCD Output Pin
PLCC |
RA3/AN3/VREF RA2/AN2 |
VSS RA1/AN1 |
RA0/AN0 RB2 |
RB3 |
MCLR/VPP |
N/C |
RB4 |
RB5 |
RB7 |
RB6 |
VDD |
COM0 |
RD7/SEG31/COM1 |
RD6/SEG30/COM2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 8 7 6 5 4 |
3 2 1 |
68 67 66 65 64 63 |
62 61 |
|
||||||||||
RA4/T0CKI |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
RD5/SEG29/COM3 |
RA5/AN4/SS |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 |
RG6/SEG26 |
RB1 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
58 |
RG5/SEG25 |
RB0/INT |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57 |
RG4/SEG24 |
RC3/SCK/SCL |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56 |
RG3/SEG23 |
RC4/SDI/SDA |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55 |
RG2/SEG22 |
RC5/SDO |
16 |
PIC16C924 |
|
|
54 |
RG1/SEG21 |
|||||||||
C2 |
18 |
|
|
52 |
RG7/SEG28 |
||||||||||
C1 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53 |
RG0/SEG20 |
VLCD2 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
RF7/SEG19 |
VLCD3 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
RF6/SEG18 |
AVDD |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
RF5/SEG17 |
VDD |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
RF4/SEG16 |
VSS |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
RF3/SEG15 |
OSC1/CLKIN |
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
RF2/SEG14 |
OSC2/CLKOUT |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
RF1/SEG13 |
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
RF0/SEG12 |
|
27 28 |
29 30 |
31 32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 |
|
64 

 RB4
RB4
63 

 RB5
RB5
62 

 RB7
RB7
61 

 RB6
RB6
60 
 VDD
VDD
59 
 COM0
COM0
58 
 RD7/SEG31/COM1
RD7/SEG31/COM1
57 

 RD6/SEG30/COM2
RD6/SEG30/COM2
56 

 RD5/SEG29/COM3
RD5/SEG29/COM3
55 
 RG6/SEG26
RG6/SEG26
54 

 RG5/SEG25
RG5/SEG25
53 

 RG4/SEG24
RG4/SEG24
52 

 RG3/SEG23
RG3/SEG23
51 
 RG2/SEG22
RG2/SEG22
50 

 RG1/SEG21
RG1/SEG21
49 

 RG0/SEG20
RG0/SEG20
48 
 RF7/SEG19
RF7/SEG19
47 
 RF6/SEG18
RF6/SEG18
46 
 RF5/SEG17
RF5/SEG17
45 
 RF4/SEG16
RF4/SEG16
44 

 RF3/SEG15
RF3/SEG15
43 


 RF2/SEG14
RF2/SEG14
42 


 RF1/SEG13
RF1/SEG13
41 

 RF0/SEG12
RF0/SEG12
40 


 RE6/SEG11
RE6/SEG11
39 

 RE5/SEG10
RE5/SEG10
38 

 RE4/SEG09
RE4/SEG09
37 


 RE3/SEG08
RE3/SEG08
36 


 RE2/SEG07
RE2/SEG07
35 


 RE1/SEG06
RE1/SEG06
34 


 RE0/SEG05
RE0/SEG05
33 


 RD4/SEG04
RD4/SEG04
TQFP
RA4/T0CKI 

RA5/AN4/SS 

RB1 

RB0/INT 

RC3/SCK/SCL 

RC4/SDI/SDA 

RC5/SDO 

C1 
C2 
VLCD2
VLCD3
VDD
VSS
OSC1/CLKIN 
OSC2/CLKOUT 
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI 

RC1/T1OSI |
RC2/CCP1 |
VLCD1 |
VLCDADJ |
RD0/SEG00 |
RD1/SEG01 |
RD2/SEG02 |
RD3/SEG03 |
RD4/SEG04 |
RE7/SEG27 |
RE0/SEG05 |
RE1/SEG06 |
RE2/SEG07 |
RE3/SEG08 |
RE4/SEG09 |
RE5/SEG10 |
RE6/SEG11 |
RA3/AN3/VREF |
RA2/AN2 |
VSS |
RA1/AN1 |
RA0/AN0 |
RB2 |
RB3 |
MCLR/VPP |
RB4 |
RB5 |
RB7 |
RB6 |
VDD |
COM0 |
RD7/SEG31/COM1 |
RD6/SEG30/COM2 |
64 |
63 |
62 |
61 |
60 |
59 |
58 |
57 |
56 |
55 |
54 |
53 |
52 |
51 |
50 |
49 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
7 |
|
PIC16C924 |
|
|
42 |
||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
41 |
|||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
40 |
|||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
RC1/T1OSI |
RC2/CCP1 |
VLCD1 |
VLCDADJ |
RD0/SEG00 |
RD1/SEG01 |
RD2/SEG02 |
RD3/SEG03 |
RD4/SEG04 |
RE0/SEG05 |
RE1/SEG06 |
RE2/SEG07 |
RE3/SEG08 |
RE4/SEG09 |
RE5/SEG10 |
RE6/SEG11 |
RD5/SEG29/COM3
RG6/SEG26
RG5/SEG25
RG4/SEG24
RG3/SEG23
RG2/SEG22
RG1/SEG21
RG0/SEG20
RF7/SEG19
RF6/SEG18
RF5/SEG17
RF4/SEG16
RF3/SEG15
RF2/SEG14
RF1/SEG13
RF0/SEG12
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 3 |

PIC16C9XX |
|
||
Table of Contents |
|
||
1.0 |
General Description ..................................................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
2.0 |
PIC16C9XX Device Varieties ...................................................................................................................................................... |
7 |
|
3.0 |
Architectural Overview ................................................................................................................................................................ |
9 |
|
4.0 |
Memory Organization ................................................................................................................................................................ |
17 |
|
5.0 |
Ports .......................................................................................................................................................................................... |
|
31 |
6.0 |
Overview of Timer Modules ....................................................................................................................................................... |
43 |
|
7.0 |
Timer0 Module .......................................................................................................................................................................... |
45 |
|
8.0 |
Timer1 Module .......................................................................................................................................................................... |
51 |
|
9.0 |
Timer2 Module .......................................................................................................................................................................... |
55 |
|
10.0 |
Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) Module .................................................................................................................................... |
57 |
|
11.0 |
Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) Module .................................................................................................................................... |
63 |
|
12.0 |
Analog - to - Digital Converter (A/D) Module ................................................................................................................................. |
79 |
|
13.0 |
LCD Module .............................................................................................................................................................................. |
89 |
|
14.0 |
Special Features of the CPU ................................................................................................................................................... |
103 |
|
15.0 |
Instruction Set Summary ......................................................................................................................................................... |
119 |
|
16.0 |
Development Support .............................................................................................................................................................. |
137 |
|
17.0 |
Electrical Characteristics ......................................................................................................................................................... |
141 |
|
18.0 |
DC and AC Characteristics Graphs and Tables ...................................................................................................................... |
161 |
|
19.0 |
Packaging Information ............................................................................................................................................................. |
171 |
|
Appendix A: |
................................................................................................................................................................................... |
175 |
|
Appendix B: |
Compatibility ............................................................................................................................................................. |
175 |
|
Appendix C: |
What’s New................................................................................................................................................................ |
176 |
|
Appendix D: |
What’s Changed ........................................................................................................................................................ |
176 |
|
Index |
.................................................................................................................................................................................................. |
|
177 |
List of ........................................................................................................................................................Equations And Examples |
181 |
||
List of .....................................................................................................................................................................................Figures |
|
181 |
|
List of ......................................................................................................................................................................................Tables |
|
182 |
|
Reader ..............................................................................................................................................................................Response |
186 |
||
PIC16C9XX ........................................................................................................................................Product Identification System |
187 |
||
To Our Valued Customers
We constantly strive to improve the quality of all our products and documentation. We have spent an exceptional amount of time to ensure that these documents are correct. However, we realize that we may have missed a few things. If you find any information that is missing or appears in error, please use the reader response form in the back of this data sheet to inform us. We appreciate your assistance in making this a better document.
DS30444E - page 4 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
1.0GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PIC16C9XX is a family of low-cost, high-perfor- mance, CMOS, fully-static, 8-bit microcontrollers with an integrated LCD Driver module, in the PIC16CXXX mid-range family.
All PICmicro™ microcontrollers emplo y an advanced RISC architecture. The PIC16CXXX microcontroller family has enhanced core features, eight-level deep stack, and multiple internal and external interrupt sources.The separate instruction and data buses of the Harvard architecture allow a 14-bit wide instruction word with the separate 8-bit wide data. The two stage instruction pipeline allows all instructions to execute in a single cycle, except for program branches (which require two cycles). A total of 35 instructions (reduced instruction set) are available. Additionally, a large register set gives some of the architectural innovations used to achieve a very high performance.
PIC16CXXX microcontrollers typically achieve a 2:1 code compression and a 4:1 speed improvement over other 8-bit microcontrollers in their class.
The PIC16C923 devices have 176 bytes of RAM and 25 I/O pins. In addition several peripheral features are available including: three timer/counters, one Capture/Compare/PWM module, one serial port and one LCD module. The Synchronous Serial Port can be configured as either a 3-wire Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) or the two-wire Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) bus. The LCD module features programmable multiplex mode (static, 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4) and drive bias (static and 1/3). It is capable of driving up to 32 segments and up to 4 commons. It can also drive the LCD panel while in SLEEP mode.
The PIC16C924 devices have 176 bytes of RAM and 25 I/O pins. In addition several peripheral features are available including: three timer/counters, one Capture/Compare/PWM module, one serial port and one LCD module. The Synchronous Serial Port can be configured as either a 3-wire Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) or the two-wire Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) bus. The LCD module features programmable multiplex mode (static, 1/2, 1/3 and 1/4) and drive bias (static and 1/3). It is capable of driving up to 32 segments and up to 4 commons. It can also drive the LCD panel while in SLEEP mode. The PIC16C924 also has an 5-channel high-speed 8-bit A/D. The 8-bit resolution is ideally suited for applications requiring low-cost analog interface, e.g. thermostat control, pressure sensing, and meters.
The PIC16C9XX family has special features to reduce external components, thus reducing cost, enhancing system reliability and reducing power consumption. There are four oscillator options, of which the single pin RC oscillator provides a low-cost solution, the LP oscillator minimizes power consumption, XT is a standard crystal, and the HS is for High Speed crystals. The SLEEP (power-down) feature provides a power saving
mode. The user can wake up the chip from SLEEP through several external and internal interrupts and reset(s).
A highly reliable Watchdog Timer with its own on-chip RC oscillator provides recovery in the event of a software lock-up.
A UV erasable CERQUAD (compatible with PLCC) packaged version is ideal for code development while the cost-effective One-Time-Programmable (OTP) version is suitable for production in any volume.
The PIC16C9XX family fits perfectly in applications ranging from handheld meters, thermostats, to home security products. The EPROM technology makes customization of application programs (LCD panels, calibration constants, sensor interfaces, etc.) extremely fast and convenient.The small footprint packages make this microcontroller series perfect for all applications with space limitations. Low cost, low power, high performance, ease of use and I/O flexibility make the PIC16C9XX very versatile even in areas where no microcontroller use has been considered before (e.g. timer functions, capture and compare, PWM functions and coprocessor applications).
1.1Family and Upward Compatibility
Users familiar with the PIC16C5X microcontroller family will realize that this is an enhanced version of the PIC16C5X architecture. Please refer to Appendix A for a detailed list of enhancements. Code written for the PIC16C5X can be easily ported to the PIC16CXXX family of devices (Appendix B).
1.2Development Support
PIC16C9XX devices are supported by the complete line of Microchip Development tools.
Please refer to Section 16.0 for more details about Microchip’s development tools.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444Epage 5 |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 1-1: PIC16C9XX FAMILY OF DEVICES
|
|
|
PIC16C923 |
|
PIC16C924 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clock |
Maximum Frequency of Operation (MHz) |
8 |
|
8 |
|
Memory |
EPROM Program Memory |
4K |
|
4K |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Memory (bytes) |
176 |
|
176 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Timer Module(s) |
TMR0, |
|
TMR0, |
|
|
|
TMR1, |
|
TMR1, |
|
|
|
TMR2 |
|
TMR2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capture/Compare/PWM Module(s) |
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Peripherals |
Serial Port(s) |
SPI/I2C |
|
SPI/I2C |
|
(SPI/I2C, USART) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parallel Slave Port |
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A/D Converter (8-bit) Channels |
— |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LCD Module |
4 Com, |
|
4 Com, |
|
|
|
32 Seg |
|
32 Seg |
|
|
Interrupt Sources |
8 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O Pins |
25 |
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Input Pins |
27 |
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Voltage Range (Volts) |
2.5-6.0 |
|
2.5-6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Features |
In-Circuit Serial Programming |
Yes |
|
Yes |
|
|
Brown-out Reset |
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Packages |
64-pin SDIP, |
|
64-pin SDIP, |
|
|
|
TQFP; |
|
TQFP; |
|
|
|
68-pin PLCC, |
|
68-pin PLCC, |
|
|
|
Die |
|
Die |
|
|
|
|
|
|
All PICmicro Family devices have Power-on Reset, selectable Watchdog Timer, selectable code protect and high I/O current capability. All PIC16C9XX Family devices use serial programming with clock pin RB6 and data pin RB7.
DS30444E - page 6 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
2.0PIC16C9XX DEVICE VARIETIES
A variety of frequency ranges and packaging options are available. Depending on application and production requirements, the proper device option can be selected using the information in the PIC16C9XX Product Identification System section at the end of this data sheet. When placing orders, please use that page of the data sheet to specify the correct part number.
For the PIC16C9XX family, there are two device “types” as indicated in the device number:
1.C, as in PIC16C924. These devices have EPROM type memory and operate over the standard voltage range.
2.LC, as in PIC16LC924. These devices have EPROM type memory and operate over an extended voltage range.
2.1UV Erasable Devices
The UV erasable version, offered in CERQUAD package, is optimal for prototype development and pilot programs.
The UV erasable version can be erased and reprogrammed to any of the configuration modes. Microchip'sPICSTART Plus and PRO MATE II programmers both support the PIC16C9XX. Third party programmers also are available; refer to the Microchip Third Party Guide for a list of sources.
2.2One-Time-Programmable (OTP) Devices
The availability of OTP devices is especially useful for customers who need the flexibility for frequent code updates and small volume applications.
The OTP devices, packaged in plastic packages, permit the user to program them once. In addition to the program memory, the configuration bits must also be programmed.
2.3Quick-Turnaround-Production (QTP) Devices
Microchip offers a QTP Programming Service for factory production orders. This service is made available for users who choose not to program a medium to high quantity of units and whose code patterns have stabilized. The devices are identical to the OTP devices but with all EPROM locations and configuration options already programmed by the factory. Certain code and prototype verification procedures apply before production shipments are available. Please contact your local Microchip Technology sales office for more details.
2.4Serialized Quick-Turnaround Production (SQTPSM) Devices
Microchip offers a unique programming service where a few user-defined locations in each device are programmed with different serial numbers. The serial numbers may be random, pseudo-random or sequential.
Serial programming allows each device to have a unique number which can serve as an entry-code, password or ID number.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 7 |

PIC16C9XX
NOTES:
DS30444E - page 8 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
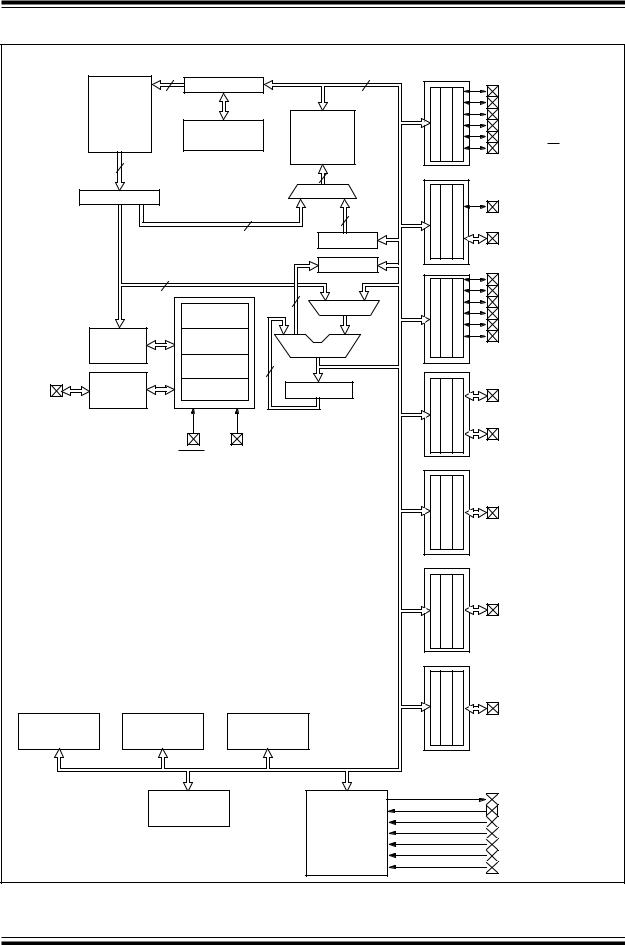
3.0ARCHITECTURAL OVERVIEW
The high performance of the PIC16CXXX family can be attributed to a number of architectural features commonly found in RISC microprocessors. To begin with, the PIC16CXXX uses a Harvard architecture, in which, program and data are accessed from separate memories using separate buses. This improves bandwidth over traditional von Neumann architecture where program and data are fetched from the same memory using the same bus. Separating program and data buses further allows instructions to be sized differently than the 8-bit wide data word. Instruction opcodes are 14-bits wide making it possible to have all single word instructions. A 14-bit wide program memory access bus fetches a 14-bit instruction in a single cycle. A two-stage pipeline overlaps fetch and execution of instructions (Example 3-1). Consequently, all instructions execute in a single cycle (500 ns @ 8 MHz) except for program branches.
The PIC16C923 and PIC16C924 both address 4K x 14 of program memory and 176 x 8 of data memory.
The PIC16CXXX can directly or indirectly address its register files or data memory. All special function registers, including the program counter, are mapped in the data memory. The PIC16CXXX has an orthogonal (symmetrical) instruction set that makes it possible to carry out any operation on any register using any addressing mode. This symmetrical nature and lack of ‘special optimal situations’ make programming with the PIC16CXXX simple yet efficient, thus significantly reducing the learning curve.
PIC16CXXX devices contain an 8-bit ALU and working register. The ALU is a general purpose arithmetic unit. It performs arithmetic and Boolean functions between the data in the working register and any register file.
The ALU is 8-bits wide and capable of addition, subtraction, shift and logical operations. Unless otherwise mentioned, arithmetic operations are two's complement in nature. In two-operand instructions, typically one operand is the working register (W register). The other operand is a file register or an immediate constant. In single operand instructions, the operand is either the W register or a file register.
The W register is an 8-bit working register used for ALU operations. It is not an addressable register.
Depending on the instruction executed, the ALU may affect the values of the Carry (C), Digit Carry (DC), and Zero (Z) bits in the STATUS register. The C and DC bits operate as a borrow bit and a digit borrow out bit, respectively, in subtraction. See the SUBLW and SUBWF instructions for examples.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 9 |

PIC16C9XX
FIGURE 3-1: PIC16C923 BLOCK DIAGRAM
|
13 |
Data Bus |
8 |
PORTA |
|
|
EPROM |
Program Counter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program |
|
|
|
|
|
Memory |
|
RAM |
|
|
|
|
8 Level Stack |
|
|
|
|
4K x 14 |
File |
|
|
|
|
(13-bit) |
|
|
||
|
Registers |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program |
|
|
176 x 8 |
|
|
14 |
RAM Addr |
9 |
|
PORTB |
|
Bus |
|
||||
|
|
||||
Addr MUX
Instruction reg
|
|
|
Direct Addr 7 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
Indirect |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSR reg |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
8 |
|
|
|
STATUS reg |
PORTC |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power-up |
|
3 |
MUX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Timer |
|
|
|
|
|
Instruction |
Oscillator |
|
|
|
|
|
Decode & |
Start-up Timer |
|
|
ALU |
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power-on |
|
|
|
|
||
|
8 |
|
|
PORTD |
||
|
Reset |
|
|
|||
Timing |
Watchdog |
|
W reg |
|
||
Generation |
Timer |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
OSC1/CLKIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MCLR |
VDD, VSS |
|
|
|
PORTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTF
PORTG
Timer0 |
|
|
|
Timer1, Timer2, |
|
|||
|
|
|
CCP1 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synchronous
Serial Port
LCD
RA0
RA1
RA2
RA3
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/SS
RB0/INT
RB1-RB7
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI RC1/T1OSI RC2/CCP1 RC3/SCK/SCL RC4/SDI/SDA RC5/SDO
RD0-RD4/SEGnn
RD5-RD7/SEGnn/COMn
RE0-RE7/SEGnn
RF0-RF7/SEGnn
RG0-RG7/SEGnn
COM0
VLCD1
VLCD2
VLCD3
C1
C2
VLCDADJ
DS30444E - page 10 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C9XX |
FIGURE 3-2: |
PIC16C924 BLOCK DIAGRAM |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
13 |
|
Data Bus |
8 |
PORTA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
EPROM |
Program Counter |
|
|
|
RA0/AN0 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA1/AN1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA2/AN2 |
|
|
Memory |
|
|
|
|
RAM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RA3/AN3/VREF |
||
|
|
8 Level Stack |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
File |
|
||||
|
4K x 14 |
|
|
RA4/T0CKI |
||||
|
(13-bit) |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Registers |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
RA5/AN4/SS |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
176 x 8 |
|
|
Program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
RAM Addr |
|
9 |
|
PORTB |
|
Bus |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Instruction reg |
|
|
Addr MUX |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RB0/INT |
|
|
|
Direct Addr |
7 |
|
|
Indirect |
||
|
|
|
8 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSR reg |
|
RB1-RB7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
STATUS reg |
PORTC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC1/T1OSI |
|
|
Power-up |
3 |
MUX |
|
RC2/CCP1 |
||
|
|
|
RC3/SCK/SCL |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Timer |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RC4/SDI/SDA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Instruction |
Oscillator |
|
|
|
|
RC5/SDO |
|
|
Decode & |
Start-up Timer |
|
|
ALU |
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power-on |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
PORTD |
||
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|||
|
Timing |
Watchdog |
|
W reg |
|
|
||
|
Generation |
Timer |
|
|
RD0-RD4/SEGnn |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
OSC1/CLKIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RD5-RD7/SEGnn/COMn |
|
|
MCLR |
VDD, VSS |
|
|
|
PORTE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RE0-RE7/SEGnn |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RF0-RF7/SEGnn |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RG0-RG7/SEGnn |
Timer0 |
|
A/D |
Timer1, Timer2, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CCP1 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Synchronous |
|
|
|
|
|
COM0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCD1 |
|
|
|
Serial Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCD2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LCD |
|
VLCD3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCDADJ |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 11 |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 3-1: PIC16C9XX PINOUT DESCRIPTION
|
Pin Name |
DIP |
PLCC |
TQFP |
|
Pin |
|
Buffer |
Description |
|||
|
Pin# |
Pin# |
Pin# |
|
Type |
|
Type |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
OSC1/CLKIN |
22 |
24 |
14 |
|
I |
|
ST/CMOS |
Oscillator crystal input or external clock source input. This |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
buffer is a Schmitt Trigger input when configured in RC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
oscillator mode and a CMOS input otherwise. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
23 |
25 |
15 |
|
O |
|
— |
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or resonator |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
in crystal oscillator mode. In RC mode, OSC2 pin outputs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLKOUT which has 1/4 the frequency of OSC1, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
denotes the instruction cycle rate. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
57 |
|
I/P |
|
ST |
Master clear (reset) input or programming voltage input. |
|
MCLR/VPP |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This pin is an active low reset to the device. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTA is a bi-directional I/O port. The AN and VREF multi- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
plexed functions are used by the PIC16C924 only. |
|
RA0/AN0 |
4 |
5 |
60 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
RA0 can also be Analog input0. |
|||
|
RA1/AN1 |
5 |
6 |
61 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
RA1 can also be Analog input1. |
|||
|
RA2/AN2 |
7 |
8 |
63 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
RA2 can also be Analog input2. |
|||
|
RA3/AN3/VREF |
8 |
9 |
64 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
RA3 can also be Analog input3 or A/D Voltage Refer- |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ence. |
|
RA4/T0CKI |
9 |
10 |
1 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RA4 can also be the clock input to the Timer0 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
timer/counter. Output is open drain type. |
|
RA5/AN4/SS |
|
|
10 |
11 |
2 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
RA5 can be the slave select for the synchronous serial |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
port or Analog input4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTB is a bi-directional I/O port. PORTB can be software |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
programmed for internal weak pull-ups on all inputs. |
|
RB0/INT |
12 |
13 |
4 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL/ST |
RB0 can also be the external interrupt pin. This buffer |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
is a Schmitt Trigger input when configured as an exter- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nal interrupt. |
|
RB1 |
11 |
12 |
3 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
|
|||
|
RB2 |
3 |
4 |
59 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
|
|||
|
RB3 |
2 |
3 |
58 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
|
|||
|
RB4 |
64 |
68 |
56 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
Interrupt on change pin. |
|||
|
RB5 |
63 |
67 |
55 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL |
Interrupt on change pin. |
|||
|
RB6 |
61 |
65 |
53 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL/ST |
Interrupt on change pin. Serial programming clock. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This buffer is a Schmitt Trigger input when used in |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
serial programming mode. |
|
RB7 |
62 |
66 |
54 |
|
I/O |
|
TTL/ST |
Interrupt on change pin. Serial programming data. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This buffer is a Schmitt Trigger input when used in |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
serial programming mode. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTC is a bi-directional I/O port. |
|
RC0/T1OSO/T1CKI |
24 |
26 |
16 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RC0 can also be the Timer1 oscillator output or |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timer1 clock input. |
|
RC1/T1OSI |
25 |
27 |
17 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RC1 can also be the Timer1 oscillator input. |
|||
|
RC2/CCP1 |
26 |
28 |
18 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RC2 can also be the Capture1 input/Compare1 out- |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
put/PWM1 output. |
|
RC3/SCK/SCL |
13 |
14 |
5 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RC3 can also be the synchronous serial clock |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
input/output for both SPI and I2C modes. |
|
RC4/SDI/SDA |
14 |
15 |
6 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RC4 can also be the SPI Data In (SPI mode) or data |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O (I2C mode). |
|
RC5/SDO |
15 |
16 |
7 |
|
I/O |
|
ST |
RC5 can also be the SPI Data Out (SPI mode). |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
C1 |
16 |
17 |
8 |
|
P |
|
|
LCD Voltage Generation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
C2 |
17 |
18 |
9 |
|
P |
|
|
LCD Voltage Generation. |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Legend: I = input |
O = output |
|
P = power |
|
L = LCD Driver |
|||||||
|
|
|
— = Not used |
|
|
TTL = TTL input |
ST = Schmitt Trigger input |
|||||
DS30444E - page 12 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 3-1: PIC16C9XX PINOUT DESCRIPTION (Cont.’d)
Pin Name |
DIP |
PLCC |
TQFP |
|
Pin |
|
Buffer |
Description |
Pin# |
Pin# |
Pin# |
|
Type |
|
Type |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COM0 |
59 |
63 |
51 |
|
L |
|
|
Common Driver0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTD is a digital input/output port. These pins are also |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
used as LCD Segment and/or Common Drivers. |
RD0/SEG00 |
29 |
31 |
21 |
|
I/O/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver00/Digital Input/Output. |
RD1/SEG01 |
30 |
32 |
22 |
|
I/O/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver01/Digital Input/Output. |
RD2/SEG02 |
31 |
33 |
23 |
|
I/O/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver02/Digital Input/Output. |
RD3/SEG03 |
32 |
34 |
24 |
|
I/O/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver03/Digital Input/Output. |
RD4/SEG04 |
33 |
35 |
25 |
|
I/O/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver04/Digital Input/Output. |
RD5/SEG29/COM3 |
56 |
60 |
48 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver29/Common Driver3/Digital Input. |
RD6/SEG30/COM2 |
57 |
61 |
49 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver30/Common Driver2/Digital Input. |
RD7/SEG31/COM1 |
58 |
62 |
50 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver31/Common Driver1/Digital Input. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTE is a digital input or LCD Segment Driver port. |
RE0/SEG05 |
34 |
37 |
26 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver05. |
RE1/SEG06 |
35 |
38 |
27 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver06. |
RE2/SEG07 |
36 |
39 |
28 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver07. |
RE3/SEG08 |
37 |
40 |
29 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver08. |
RE4/SEG09 |
38 |
41 |
30 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver09. |
RE5/SEG10 |
39 |
42 |
31 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver10. |
RE6/SEG11 |
40 |
43 |
32 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver11. |
RE7/SEG27 |
- |
36 |
- |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver27 (Not available on 64-pin devices). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTF is a digital input or LCD Segment Driver port. |
RF0/SEG12 |
41 |
44 |
33 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver12. |
RF1/SEG13 |
42 |
45 |
34 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver13. |
RF2/SEG14 |
43 |
46 |
35 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver14. |
RF3/SEG15 |
44 |
47 |
36 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver15. |
RF4/SEG16 |
45 |
48 |
37 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver16. |
RF5/SEG17 |
46 |
49 |
38 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver17. |
RF6/SEG18 |
47 |
50 |
39 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver18. |
RF7/SEG19 |
48 |
51 |
40 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver19. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PORTG is a digital input or LCD Segment Driver port. |
RG0/SEG20 |
49 |
53 |
41 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver20. |
RG1/SEG21 |
50 |
54 |
42 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver21. |
RG2/SEG22 |
51 |
55 |
43 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver22. |
RG3/SEG23 |
52 |
56 |
44 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver23. |
RG4/SEG24 |
53 |
57 |
45 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver24. |
RG5/SEG25 |
54 |
58 |
46 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver25. |
RG6/SEG26 |
55 |
59 |
47 |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver26. |
RG7/SEG28 |
— |
52 |
— |
|
I/L |
|
ST |
Segment Driver28 (Not available on 64-pin devices). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCDADJ |
28 |
30 |
20 |
|
P |
|
|
LCD Voltage Generation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AVDD |
— |
21 |
— |
|
P |
|
|
Analog Power (PIC16C924 only). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
— |
21 |
— |
|
P |
|
|
Power (PIC16C923 only). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCD1 |
27 |
29 |
19 |
|
P |
|
|
LCD Voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCD2 |
18 |
19 |
10 |
|
P |
|
— |
LCD Voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: I = input |
O = output |
|
P = power |
|
L = LCD Driver |
|||
— = Not used |
|
|
TTL = TTL input |
ST = Schmitt Trigger input |
||||
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 13 |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 3-1: PIC16C9XX PINOUT DESCRIPTION (Cont.’d)
Pin Name |
DIP |
PLCC |
TQFP |
|
Pin |
|
Buffer |
Description |
Pin# |
Pin# |
Pin# |
|
Type |
|
Type |
||
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VLCD3 |
19 |
20 |
11 |
|
P |
|
— |
LCD Voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDD |
20, 60 |
22, 64 |
12, 52 |
|
P |
|
— |
Digital power. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSS |
6, 21 |
7, 23 |
13, 62 |
|
P |
|
— |
Ground reference. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NC |
— |
1 |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
These pins are not internally connected. These pins should |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
be left unconnected. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: I = input |
O = output |
|
P = power |
|
L = LCD Driver |
|||
— = Not used |
|
|
TTL = TTL input |
ST = Schmitt Trigger input |
||||
DS30444E - page 14 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
3.1Clocking Scheme/Instruction Cycle
The clock input (from OSC1) is internally divided by four to generate four non-overlapping quadrature clocks namely Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4. Internally, the program counter (PC) is incremented every Q1, the instruction is fetched from the program memory and latched into the instruction register in Q4. The instruction is decoded and executed during the following Q1 through Q4. The clocks and instruction execution flow is shown in Figure 3-3.
3.2Instruction Flow/Pipelining
An “Instruction Cycle” consists of four Q cycles (Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4). The instruction fetch and execute are pipelined such that fetch takes one instruction cycle while decode and execute takes another instruction cycle. However, due to the pipelining, each instruction effectively executes in one cycle. If an instruction causes the program counter to change (e.g. GOTO) then two cycles are required to complete the instruction (Example 3-1).
A fetch cycle begins with the program counter (PC) incrementing in Q1.
In the execution cycle, the fetched instruction is latched into the “Instruction Register" in cycle Q1. This instruction is then decoded and executed during the Q2, Q3, and Q4 cycles. Data memory is read during Q2 (operand read) and written during Q4 (destination write).
FIGURE 3-3: CLOCK/INSTRUCTION CYCLE
Q1 |
Q2 |
Q3 |
Q4 |
Q1 |
Q2 |
Q3 |
Q4 |
Q1 |
Q2 |
Q3 |
Q4 |
OSC1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
Q3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
phase |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
clock |
|
Q4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PC |
|
PC |
|
|
PC+1 |
|
|
|
|
PC+2 |
|
OSC2/CLKOUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(RC mode) |
Fetch INST (PC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Execute INST (PC-1) |
|
|
Fetch INST (PC+1) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Execute INST (PC) |
|
|
Fetch INST (PC+2) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Execute INST (PC+1) |
|
|
EXAMPLE 3-1: |
INSTRUCTION PIPELINE FLOW |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Tcy0 |
Tcy1 |
Tcy2 |
Tcy3 |
Tcy4 |
Tcy5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
MOVLW |
55h |
|
Fetch 1 |
Execute 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
MOVWF |
PORTB |
|
|
Fetch 2 |
Execute 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
CALL |
SUB_1 |
|
|
|
Fetch 3 |
Execute 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
BSF |
PORTA, BIT3 (Forced NOP) |
|
|
Fetch 4 |
Flush |
|
|
||
5. |
Instruction @ address SUB_1 |
|
|
|
Fetch SUB_1 |
Execute SUB_1 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All instructions are single cycle, except for any program branches. These take two cycles since the fetch instruction is “flushed” from the pipeline while the new instruction is being fetched and then executed.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 15 |

PIC16C9XX
NOTES:
DS30444E - page 16 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
PIC16C9XX
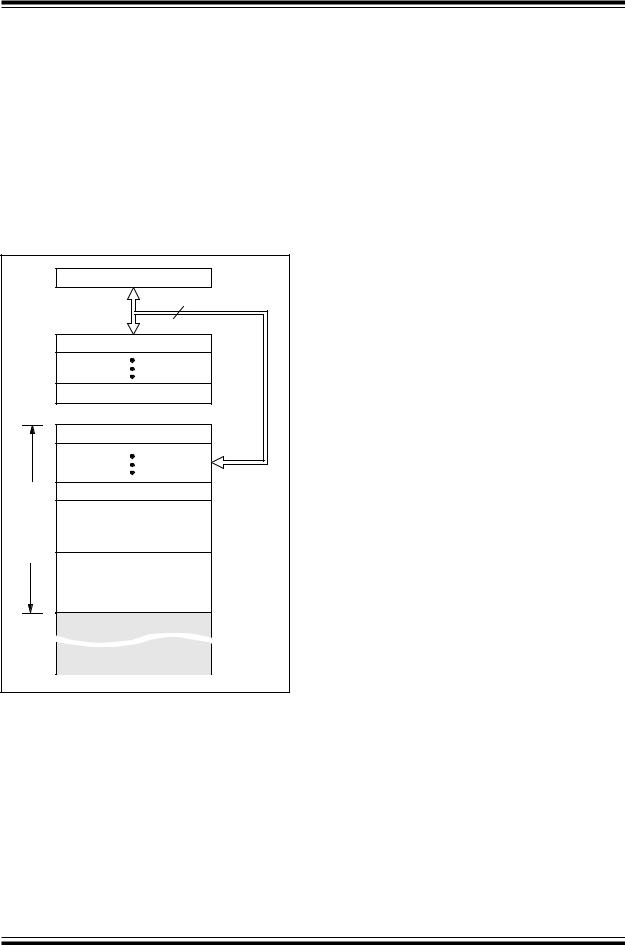
4.0MEMORY ORGANIZATION
4.1Program Memory Organization
The PIC16C9XX family has a 13-bit program counter capable of addressing an 8K x 14 program memory space.
Only the first 4K x 14 (0000h-0FFFh) is physically implemented. Accessing a location above the physically implemented addresses will cause a wraparound. The reset vector is at 0000h and the interrupt vector is at 0004h.
FIGURE 4-1: PROGRAM MEMORY MAP
AND STACK
|
|
PC<12:0> |
|
|
|
|
CALL, RETURN |
13 |
|
||
|
RETFIE, RETLW |
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Stack Level 1 |
|
||
|
|
Stack Level 8 |
|
||
|
|
Reset Vector |
0000h |
||
User Memory |
|
Interrupt Vector |
0004h |
||
Space |
On-chip Program |
0005h |
|||
|
|||||
Memory (Page 0) |
07FFh |
||||
|
|
||||
On-chip Program |
0800h |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
Memory (Page 1) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
0FFFh |
|
|
|
|
|
1000h |
|
|
|
|
|
1FFFh |
|
4.2Data Memory Organization
The data memory is partitioned into four Banks which contain the General Purpose Registers and the Special Function Registers. Bits RP1 and RP0 are the bank select bits.
RP1:RP0 (STATUS<6:5>)
11 = Bank 3 (180h-1FFh)
10 = Bank 2 (100h-17Fh)
01 = Bank 1 (80h-FFh)
00 = Bank 0 (00h-7Fh)
The lower locations of each Bank are reserved for the Special Function Registers. Above the Special Function Registers are General Purpose Registers implemented as static RAM. All four banks contain special function registers. Some “high use”special function registers are mirrored in other banks for code reduction and quicker access.
4.2.1GENERAL PURPOSE REGISTER FILE
The register file can be accessed either directly, or indirectly through the File Select Register FSR (Section 4.5).
The following General Purpose Registers are not physically implemented:
•F0h-FFh of Bank 1
•170h-17Fh of Bank 2
•1F0h-1FFh of Bank 3
These locations are used for common access across banks.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 17 |

PIC16C9XX
FIGURE 4-2: REGISTER FILE MAP
|
File |
|
Address |
|
|
Indirect addr.(1) |
00h |
TMR0 |
01h |
|
02h |
PCL |
|
STATUS |
03h |
FSR |
04h |
PORTA |
05h |
PORTB |
06h |
PORTC |
07h |
PORTD |
08h |
PORTE |
09h |
PCLATH |
0Ah |
INTCON |
0Bh |
PIR1 |
0Ch |
|
0Dh |
TMR1L |
0Eh |
|
0Fh |
TMR1H |
|
|
10h |
T1CON |
|
|
11h |
TMR2 |
|
|
12h |
T2CON |
|
|
13h |
SSPBUF |
|
|
14h |
SSPCON |
|
|
15h |
CCPR1L |
|
|
16h |
CCPR1H |
|
|
17h |
CCP1CON |
|
|
18h |
|
|
|
19h |
|
1Ah |
|
1Bh |
|
1Ch |
|
1Dh |
ADRES(2) |
1Eh |
ADCON0(2) |
1Fh |
|
20h |
|
General
Purpose
Register
7Fh
Bank 0
|
|
File |
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect addr.(1) |
|
80h |
|
OPTION |
|
81h |
|
PCL |
|
82h |
|
STATUS |
|
83h |
|
FSR |
|
84h |
|
TRISA |
|
85h |
|
TRISB |
|
86h |
|
TRISC |
|
87h |
|
TRISD |
|
88h |
|
TRISE |
|
89h |
|
PCLATH |
|
8Ah |
|
INTCON |
|
8Bh |
|
PIE1 |
|
8Ch |
|
|
|
8Dh |
|
PCON |
|
8Eh |
|
|
|
8Fh |
|
|
|
90h |
|
|
|
91h |
|
PR2 |
|
92h |
|
SSPADD |
|
93h |
|
SSPSTAT |
|
94h |
|
|
|
95h |
|
|
|
96h |
|
|
|
97h |
|
|
|
98h |
|
|
|
99h |
|
|
|
9Ah |
|
|
|
9Bh |
|
|
|
9Ch |
|
|
|
9Dh |
|
|
|
9Eh |
|
ADCON1(2) |
|
9Fh |
|
|
|
A0h |
|
General |
|
|
|
Purpose |
|
|
|
Register |
|
|
|
|
|
EFh |
|
Mapped in |
|
F0h |
|
Bank 0 |
|
|
|
70h-7Fh |
|
FFh |
|
|
|
||
Bank 1 |
|||
|
|
|
File |
|
Address |
|
|
Indirect addr.(1) |
100h |
TMR0 |
101h |
PCL |
102h |
|
103h |
STATUS |
|
FSR |
104h |
|
105h |
PORTB |
106h |
PORTF |
107h |
PORTG |
108h |
|
109h |
PCLATH |
10Ah |
INTCON |
10Bh |
|
10Ch |
LCDSE |
10Dh |
LCDPS |
10Eh |
LCDCON |
10Fh |
LCDD00 |
110h |
LCDD01 |
111h |
LCDD02 |
112h |
LCDD03 |
113h |
LCDD04 |
114h |
LCDD05 |
115h |
LCDD06 |
116h |
LCDD07 |
117h |
LCDD08 |
118h |
LCDD09 |
119h |
LCDD10 |
11Ah |
LCDD11 |
11Bh |
LCDD12 |
11Ch |
LCDD13 |
11Dh |
LCDD14 |
11Eh |
LCDD15 |
11Fh |
|
120h |
16F
Mapped in 170 Bank 0
70h-7Fh
17F
Bank 2
|
File |
Address |
|
|
|
Indirect addr.(1) |
180h |
OPTION |
181h |
PCL |
182h |
STATUS |
183h |
FSR |
184h |
|
185h |
TRISB |
186h |
TRISF |
187h |
TRISG |
188h |
|
189h |
PCLATH |
18Ah |
INTCON |
18Bh |
|
18Ch |
|
18Dh |
|
18Eh |
|
18Fh |
|
190h |
|
191h |
|
192h |
|
193h |
|
194h |
|
195h |
|
196h |
|
197h |
|
198h |
|
199h |
|
19Ah |
|
19Bh |
|
19Ch |
|
19Dh |
|
19Eh |
|
19Fh |
|
1A0h |
|
|
1EFh
Mapped in 1F0h
Bank 0
70h-7Fh
1FFh
Bank 3

 Unimplemented data memory locations, read as '0'. Note 1: Not a physical register.
Unimplemented data memory locations, read as '0'. Note 1: Not a physical register.
2: These registers are not implemented on the PIC16C923.
DS30444E - page 18 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
4.2.2SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS
The Special Function Registers are registers used by the CPU and Peripheral Modules for controlling the desired operation of the device. These registers are implemented as static RAM.
The special function registers can be classified into two sets (core and peripheral). Those registers associated with the “core”functions are described in this section, and those related to the operation of the peripheral features are described in the section of that peripheral feature.
TABLE 4-1: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on |
Value on all |
||
Address |
Name |
Bit 7 |
Bit 6 |
Bit 5 |
|
Bit 4 |
Bit 3 |
|
Bit 2 |
Bit 1 |
Bit 0 |
Power-on |
||||||||||
|
|
other resets |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
00h |
INDF |
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
01h |
TMR0 |
Timer0 module’s register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
02h |
PCL |
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
03h |
STATUS |
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
C |
0001 |
1xxx |
000q |
quuu |
||
|
TO |
PD |
||||||||||||||||||||
04h |
FSR |
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
05h |
PORTA |
— |
— |
PORTA Data Latch when written: PORTA pins when read |
|
(4) |
(4) |
|||||||||||||||
06h |
PORTB |
PORTB Data Latch when written: PORTB pins when read |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
07h |
PORTC |
— |
— |
PORTC Data Latch when written: PORTC pins when read |
|
--xx xxxx |
--uu uuuu |
|||||||||||||||
08h |
PORTD |
PORTD Data Latch when written: PORTD pins when read |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
09h |
PORTE |
PORTE pins when read |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
0Ah |
PCLATH |
— |
— |
— |
|
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the Program Counter |
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
||||||||||||||
0Bh |
INTCON |
GIE |
PEIE |
T0IE |
|
INTE |
RBIE |
|
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
0000 |
000x |
0000 |
000u |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
0Ch |
PIR1 |
LCDIF |
ADIF(2) |
— |
|
|
— |
SSPIF |
|
CCP1IF |
TMR2IF |
TMR1IF |
00-- 0000 |
00-- 0000 |
||||||||
0Dh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
0Eh |
TMR1L |
Holding register for the Least Significant Byte of the 16-bit TMR1 register |
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
0Fh |
TMR1H |
Holding register for the Most Significant Byte of the 16-bit TMR1 register |
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
10h |
T1CON |
— |
— |
T1CKPS1 |
|
T1CKPS0 |
T1OSCEN |
|
|
|
|
|
TMR1CS |
TMR1ON |
--00 0000 |
--uu uuuu |
||||||
|
T1SYNC |
|||||||||||||||||||||
11h |
TMR2 |
Timer2 module’s register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
12h |
T2CON |
— |
TOUTPS3 |
TOUTPS2 |
TOUTPS1 |
TOUTPS0 |
TMR2ON |
T2CKPS1 |
T2CKPS0 |
-000 0000 |
-000 0000 |
|||||||||||
13h |
SSPBUF |
Synchronous Serial Port Receive Buffer/Transmit Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
14h |
SSPCON |
WCOL |
SSPOV |
SSPEN |
|
CKP |
SSPM3 |
|
SSPM2 |
SSPM1 |
SSPM0 |
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
15h |
CCPR1L |
Capture/Compare/PWM Register (LSB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
16h |
CCPR1H |
Capture/Compare/PWM Register (MSB) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
17h |
CCP1CON |
— |
— |
CCP1X |
|
CCP1Y |
CCP1M3 |
CCP1M2 |
CCP1M1 |
CCP1M0 |
--00 0000 |
--00 0000 |
||||||||||
18h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
19h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
1Ah |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
1Bh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
1Ch |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
1Dh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|
||
1Eh(1) |
ADRES |
A/D Result Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||
1Fh(1) |
ADCON0 |
ADCS1 |
ADCS0 |
CHS2 |
|
CHS1 |
CHS0 |
|
|
|
(5) |
ADON |
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||||||
GO/DONE |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend: |
x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as '0', |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Note 1: Registers ADRES, ADCON0, and ADCON1 are not implemented in the PIC16C923, read as '0'. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
2:These bits are reserved on the PIC16C923, always maintain these bits clear.
3:These pixels do not display, but can be used as general purpose RAM.
4:PIC16C923 reset values for PORTA: --xx xxxx for a POR, and --uu uuuu for all other resets, PIC16C924 reset values for PORTA: --0x 0000 when read.
5:Bit1 of ADCON0 is reserved on the PIC16C924, always maintain this bit clear.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 19 |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 4-1: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY (Cont.’d)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on |
Value on all |
|
Address |
Name |
|
Bit 7 |
Bit 6 |
Bit 5 |
|
Bit 4 |
Bit 3 |
Bit 2 |
|
Bit 1 |
Bit 0 |
Power-on |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
other resets |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
80h |
INDF |
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
81h |
OPTION |
|
|
|
INTEDG |
T0CS |
|
T0SE |
PSA |
PS2 |
|
PS1 |
PS0 |
1111 1111 |
1111 |
1111 |
|||||||||
|
RBPU |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
82h |
PCL |
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
83h |
STATUS |
|
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
|
DC |
C |
0001 1xxx |
000q |
quuu |
||||||
|
|
TO |
PD |
||||||||||||||||||||||
84h |
FSR |
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
85h |
TRISA |
|
— |
— |
PORTA Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
--11 1111 |
--11 1111 |
|||||||||||
86h |
TRISB |
PORTB Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 |
1111 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
87h |
TRISC |
|
— |
— |
PORTC Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
--11 1111 |
--11 1111 |
|||||||||||
88h |
TRISD |
PORTD Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 |
1111 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
89h |
TRISE |
PORTE Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 |
1111 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
8Ah |
PCLATH |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the PC |
|
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
|||||||||||||||
8Bh |
INTCON |
|
GIE |
PEIE |
T0IE |
|
INTE |
RBIE |
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
0000 000x |
0000 |
000u |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
8Ch |
PIE1 |
LCDIE |
ADIE(2) |
— |
|
|
— |
SSPIE |
CCP1IE |
TMR2IE |
TMR1IE |
00-- 0000 |
00-- 0000 |
||||||||||||
8Dh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
8Eh |
PCON |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
— |
|
|
|
— |
---- --0- |
---- --u- |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
POR |
|||||||||||||||||||||
8Fh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
90h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
91h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
92h |
PR2 |
Timer2 Period Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 |
1111 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
93h |
SSPADD |
Synchronous Serial Port (I2C mode) Address Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||||||||||||
94h |
SSPSTAT |
|
SMP |
CKE |
D/A |
|
|
|
P |
|
S |
R/W |
|
UA |
BF |
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||||||
95h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
96h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
97h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
98h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
99h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
9Ah |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
9Bh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
9Ch |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
9Dh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
9Eh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
||||
9Fh(1) |
ADCON1 |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
PCFG2 |
PCFG1 |
PCFG0 |
---- -000 |
---- -000 |
||||||||||
Legend: |
x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as '0', |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Note 1: Registers ADRES, ADCON0, and ADCON1 are not implemented in the PIC16C923, read as '0'. |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
2:These bits are reserved on the PIC16C923, always maintain these bits clear.
3:These pixels do not display, but can be used as general purpose RAM.
4:PIC16C923 reset values for PORTA: --xx xxxx for a POR, and --uu uuuu for all other resets, PIC16C924 reset values for PORTA: --0x 0000 when read.
5:Bit1 of ADCON0 is reserved on the PIC16C924, always maintain this bit clear.
DS30444E - page 20 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 4-1: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY (Cont.’d)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on |
Value on all |
||
Address |
Name |
Bit 7 |
Bit 6 |
|
Bit 5 |
|
Bit 4 |
Bit 3 |
Bit 2 |
Bit 1 |
Bit 0 |
Power-on |
|||||||
|
|
other resets |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
100h |
INDF |
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
101h |
TMR0 |
Timer0 module’s register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
102h |
PCL |
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
103h |
STATUS |
IRP |
RP1 |
|
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
C |
0001 |
1xxx |
000q |
quuu |
|
TO |
PD |
|||||||||||||||||
104h |
FSR |
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
105h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
||
106h |
PORTB |
PORTB Data Latch when written: PORTB pins when read |
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
107h |
PORTF |
PORTF pins when read |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
108h |
PORTG |
PORTG pins when read |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 |
0000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
109h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
||
10Ah |
PCLATH |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the PC |
|
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
|||||||||
10Bh |
INTCON |
GIE |
PEIE |
|
T0IE |
|
INTE |
RBIE |
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
0000 |
000x |
0000 |
000u |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10Ch |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
||
10Dh |
LCDSE |
SE29 |
SE27 |
|
SE20 |
|
SE16 |
SE12 |
SE9 |
SE5 |
SE0 |
1111 1111 |
1111 |
1111 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
10Eh |
LCDPS |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
LP3 |
LP2 |
LP1 |
LP0 |
---- 0000 |
---- 0000 |
|||||
10Fh |
LCDCON |
LCDEN |
SLPEN |
|
— |
|
VGEN |
CS1 |
CS0 |
LMUX1 |
LMUX0 |
00-0 0000 |
00-0 0000 |
||||||
110h |
LCDD00 |
SEG07 |
SEG06 |
|
SEG05 |
|
SEG04 |
SEG03 |
SEG02 |
SEG01 |
SEG00 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM0 |
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
111h |
LCDD01 |
SEG15 |
SEG14 |
|
SEG13 |
|
SEG12 |
SEG11 |
SEG10 |
SEG09 |
SEG08 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM0 |
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
112h |
LCDD02 |
SEG23 |
SEG22 |
|
SEG21 |
|
SEG20 |
SEG19 |
SEG18 |
SEG17 |
SEG16 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM0 |
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
113h |
LCDD03 |
SEG31 |
SEG30 |
|
SEG29 |
|
SEG28 |
SEG27 |
SEG26 |
SEG25 |
SEG24 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM0 |
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
|
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
COM0 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
114h |
LCDD04 |
SEG07 |
SEG06 |
|
SEG05 |
|
SEG04 |
SEG03 |
SEG02 |
SEG01 |
SEG00 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM1 |
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
115h |
LCDD05 |
SEG15 |
SEG14 |
|
SEG13 |
|
SEG12 |
SEG11 |
SEG10 |
SEG09 |
SEG08 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM1 |
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
116h |
LCDD06 |
SEG23 |
SEG22 |
|
SEG21 |
|
SEG20 |
SEG19 |
SEG18 |
SEG17 |
SEG16 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM1 |
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
117h |
LCDD07 |
SEG31 |
SEG30 |
|
SEG29 |
|
SEG28 |
SEG27 |
SEG26 |
SEG25 |
SEG24 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM1(3) |
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
|
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
COM1 |
||||||||||
118h |
LCDD08 |
SEG07 |
SEG06 |
|
SEG05 |
|
SEG04 |
SEG03 |
SEG02 |
SEG01 |
SEG00 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM2 |
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
119h |
LCDD09 |
SEG15 |
SEG14 |
|
SEG13 |
|
SEG12 |
SEG11 |
SEG10 |
SEG09 |
SEG08 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM2 |
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
11Ah |
LCDD10 |
SEG23 |
SEG22 |
|
SEG21 |
|
SEG20 |
SEG19 |
SEG18 |
SEG17 |
SEG16 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM2 |
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
11Bh |
LCDD11 |
SEG31 |
SEG30 |
|
SEG29 |
|
SEG28 |
SEG27 |
SEG26 |
SEG25 |
SEG24 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM2(3) |
COM2(3) |
|
COM2 |
|
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
COM2 |
||||||||||
11Ch |
LCDD12 |
SEG07 |
SEG06 |
|
SEG05 |
|
SEG04 |
SEG03 |
SEG02 |
SEG01 |
SEG00 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM3 |
COM3 |
|
COM3 |
|
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
11Dh |
LCDD13 |
SEG15 |
SEG14 |
|
SEG13 |
|
SEG12 |
SEG11 |
SEG10 |
SEG09 |
SEG08 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM3 |
COM3 |
|
COM3 |
|
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
11Eh |
LCDD14 |
SEG23 |
SEG22 |
|
SEG21 |
|
SEG20 |
SEG19 |
SEG18 |
SEG17 |
SEG16 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM3 |
COM3 |
|
COM3 |
|
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
11Fh |
LCDD15 |
SEG31 |
SEG30 |
|
SEG29 |
|
SEG28 |
SEG27 |
SEG26 |
SEG25 |
SEG24 |
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
||||||
COM3(3) |
COM3(3) |
|
COM3(3) |
|
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
COM3 |
||||||||||
Legend: |
x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as '0', |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note 1: Registers ADRES, ADCON0, and ADCON1 are not implemented in the PIC16C923, read as '0'. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
2:These bits are reserved on the PIC16C923, always maintain these bits clear.
3:These pixels do not display, but can be used as general purpose RAM.
4:PIC16C923 reset values for PORTA: --xx xxxx for a POR, and --uu uuuu for all other resets, PIC16C924 reset values for PORTA: --0x 0000 when read.
5:Bit1 of ADCON0 is reserved on the PIC16C924, always maintain this bit clear.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 21 |

PIC16C9XX
TABLE 4-1: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER SUMMARY (Cont.’d)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Value on |
Value on all |
Address |
Name |
|
Bit 7 |
|
Bit 6 |
Bit 5 |
|
Bit 4 |
Bit 3 |
Bit 2 |
Bit 1 |
Bit 0 |
Power-on |
|||||
|
|
|
other resets |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bank 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
180h |
INDF |
Addressing this location uses contents of FSR to address data memory (not a physical register) |
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
181h |
OPTION |
|
|
|
INTEDG |
T0CS |
|
T0SE |
PSA |
PS2 |
PS1 |
PS0 |
1111 1111 |
1111 1111 |
||||
|
RBPU |
|||||||||||||||||
182h |
PCL |
Program Counter's (PC) Least Significant Byte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000 0000 |
0000 0000 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
183h |
STATUS |
|
IRP |
|
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
C |
0001 1xxx |
000q quuu |
|
|
TO |
PD |
|||||||||||||||
184h |
FSR |
Indirect data memory address pointer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
xxxx xxxx |
uuuu uuuu |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
185h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
186h |
TRISB |
PORTB Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 1111 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
187h |
TRISF |
PORTF Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 1111 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
188h |
TRISG |
PORTG Data Direction Register |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1111 1111 |
1111 1111 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
189h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
18Ah |
PCLATH |
|
— |
|
— |
— |
|
Write Buffer for the upper 5 bits of the PC |
|
---0 0000 |
---0 0000 |
|||||||
18Bh |
INTCON |
|
GIE |
|
PEIE |
T0IE |
|
INTE |
RBIE |
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
0000 000x |
0000 000u |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18Ch |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
18Dh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
18Eh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
18Fh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
190h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
191h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
192h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
193h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
194h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
195h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
196h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
197h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
198h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
199h |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19Ah |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19Bh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19Ch |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19Dh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19Eh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
19Fh |
— |
Unimplemented |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
— |
|||
Legend: |
x = unknown, u = unchanged, q = value depends on condition, - = unimplemented read as '0', |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
shaded locations are unimplemented, read as ‘0’. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Note 1: Registers ADRES, ADCON0, and ADCON1 are not implemented in the PIC16C923, read as '0'. |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
2:These bits are reserved on the PIC16C923, always maintain these bits clear.
3:These pixels do not display, but can be used as general purpose RAM.
4:PIC16C923 reset values for PORTA: --xx xxxx for a POR, and --uu uuuu for all other resets, PIC16C924 reset values for PORTA: --0x 0000 when read.
5:Bit1 of ADCON0 is reserved on the PIC16C924, always maintain this bit clear.
DS30444E - page 22 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
4.2.2.1STATUS REGISTER
The STATUS register, shown in Figure 4-3, contains the arithmetic status of the ALU, the RESET status and the bank select bits for data memory.
The STATUS register can be the destination for any instruction, as with any other register. If the STATUS register is the destination for an instruction that affects the Z, DC or C bits, then the write to these three bits is disabled. These bits are set or cleared according to the device logic. Furthermore, the TO and PD bits are not writable. Therefore, the result of an instruction with the STATUS register as destination may be different than intended.
For example, CLRF STATUS will clear the upper-three bits and set the Z bit. This leaves the STATUS register as 000u u1uu (where u = unchanged).
It is recommended, therefore, that only BCF, BSF, SWAPF and MOVWF instructions are used to alter the STATUS register because these instructions do not affect the Z, C or DC bits from the STATUS register. For other instructions, not affecting any status bits, see the “Instruction Set Summary.”
Note 1: The C and DC bits operate as a borrow and digit borrow bit, respectively, in subtraction. See the SUBLW and SUBWF instructions for examples.
FIGURE 4-3: STATUS REGISTER (ADDRESS 03h, 83h, 103h, 183h)
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R-1 |
R-1 |
R/W-x |
R/W-x |
R/W-x |
|
|
||||
IRP |
RP1 |
RP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Z |
DC |
C |
|
R = Readable bit |
|
TO |
PD |
|||||||||||
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W = Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U = Unimplemented bit, |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
bit 7: IRP: Register Bank Select bit (used for indirect addressing) 1 = Bank 2, 3 (100h - 1FFh)
0 = Bank 0, 1 (00h - FFh)
bit |
6-5: RP1:RP0: Register Bank Select bits (used for direct addressing) |
||||||||||||
|
|
11 = Bank 3 (180h - 1FFh) |
|||||||||||
|
|
10 = Bank 2 (100h - 17Fh) |
|||||||||||
|
|
01 = Bank 1 (80h - FFh) |
|||||||||||
|
|
00 = Bank 0 (00h - 7Fh) |
|||||||||||
bit |
4: |
|
: Time-out bit |
||||||||||
TO |
|||||||||||||
|
|
1 |
= After power-up, CLRWDT instruction, or SLEEP instruction |
||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= A WDT time-out occurred |
||||||||||
bit |
3: |
|
: Power-down bit |
||||||||||
PD |
|||||||||||||
|
|
1 |
= After power-up or by the CLRWDT instruction |
||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= By execution of the SLEEP instruction |
||||||||||
bit |
2: |
Z: Zero bit |
|||||||||||
|
|
1 |
= The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is zero |
||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is not zero |
||||||||||
bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1: DC: Digit carry/borrow |
bit (ADDWF, ADDLW,SUBLW,SUBWF instructions) (for borrow the polarity is reversed) |
||||||||||||
|
|
1 |
= A carry-out from the 4th low order bit of the result occurred |
||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= No carry-out from the 4th low order bit of the result |
||||||||||
bit |
0: |
|
|
bit (ADDWF, ADDLW,SUBLW,SUBWF instructions) (for |
|
the polarity is reversed) |
|||||||
C: Carry/borrow |
borrow |
||||||||||||
|
|
1 |
= A carry-out from the most significant bit of the result occurred |
||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= No carry-out from the most significant bit of the result occurred |
||||||||||
Note: A subtraction is executed by adding the two’s complement of the second operand. For rotate (RRF, RLF) instructions, this bit is loaded with either the high or low order bit of the source register.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 23 |

PIC16C9XX
4.2.2.2 |
OPTION REGISTER |
Note: |
To achieve a 1:1 prescaler assignment for |
|
|
||
The OPTION register is a readable and writable regis- |
|
the TMR0 register, assign the prescaler to |
|
ter which contains various control bits to configure the |
|
the Watchdog Timer. |
|
TMR0/WDT prescaler, the external RB0/INT pin inter- |
|
|
|
rupt, TMR0, and the weak pull-ups on PORTB. |
|
||
FIGURE 4-4: OPTION REGISTER (ADDRESS 81h, 181h)
|
R/W-1 |
|
|
R/W-1 |
|
R/W-1 |
|
|
R/W-1 |
|
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
R/W-1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTEDG |
|
T0CS |
|
|
T0SE |
|
PSA |
PS2 |
PS1 |
|
PS0 |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
||||
|
|
RBPU |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7: |
|
|
|
: PORTB Pull-up Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
RBPU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= PORTB pull-ups are disabled |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
= PORTB pull-ups are enabled by individual port latch values |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
bit |
6: |
|
INTEDG: Interrupt Edge Select bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= Interrupt on rising edge of RB0/INT pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
= Interrupt on falling edge of RB0/INT pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
bit |
5: |
|
T0CS: TMR0 Clock Source Select bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= Transition on RA4/T0CKI pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
= Internal instruction cycle clock (CLKOUT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
bit |
4: |
|
T0SE: TMR0 Source Edge Select bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= Increment on high-to-low transition on RA4/T0CKI pin |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
= Increment on low-to-high transition on RA4/T0CKI pin |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
bit |
3: |
|
PSA: Prescaler Assignment bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
= Prescaler is assigned to the WDT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
= Prescaler is assigned to the Timer0 module |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
bit |
2-0: |
PS2:PS0: Prescaler Rate Select bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bit Value |
|
TMR0 Rate WDT Rate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
000 |
|
1 : |
2 |
|
|
1 |
: 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
001 |
|
1 : |
4 |
|
|
1 |
: 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
010 |
|
1 : |
8 |
|
|
1 |
: 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
011 |
|
1 : |
16 |
|
1 |
: 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
1 : |
32 |
|
1 |
: 16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101 |
|
1 : |
64 |
|
1 |
: 32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
110 |
|
1 : |
128 |
|
1 |
: 64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
111 |
|
1 : |
256 |
|
1 |
: 128 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DS30444E - page 24 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

|
|
|
PIC16C9XX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.2.2.3 |
INTCON REGISTER |
|
|
|
Note: |
Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt |
|||
|
|
|||
The INTCON Register is a readable and writable regis- |
|
condition occurs regardless of the state of |
||
ter which contains various enable and flag bits for the |
|
its corresponding enable bit or the global |
||
TMR0 register overflow, RB Port change and external |
|
enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). |
||
RB0/INT pin interrupts. |
|
|
||
FIGURE 4-5: INTCON REGISTER (ADDRESS 0Bh, 8Bh, 10Bh, 18Bh)
R/W-0 |
|
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-x |
|
|
|
|||
|
GIE |
|
PEIE |
T0IE |
INTE |
|
RBIE |
|
T0IF |
INTF |
RBIF |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
bit 7: |
GIE: Global Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables all un-masked interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables all interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
bit |
6: |
PEIE: Peripheral Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables all un-masked peripheral interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables all peripheral interrupts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
bit |
5: |
T0IE: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the TMR0 interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the TMR0 interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
bit |
4: |
INTE: RB0/INT External Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the RB0/INT external interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the RB0/INT external interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
bit |
3: |
RBIE: RB Port Change Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
1 |
= Enables the RB port change interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
0 |
= Disables the RB port change interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
bit |
2: |
T0IF: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 |
= TMR0 register has overflowed (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
0 |
= TMR0 register did not overflow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
bit |
1: |
INTF: RB0/INT External Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 |
= The RB0/INT external interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= The RB0/INT external interrupt did not occur |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
bit |
0: |
RBIF: RB Port Change Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 |
= At least one of the RB7:RB4 pins changed state (see Section 5.2 to clear interrupt) |
|||||||||||
|
|
0 |
= None of the RB7:RB4 pins have changed state |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt condition occurs regardless of the state of its corresponding enable bit or the global enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). User software should ensure the appropriate interrupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an interrupt.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 25 |

PIC16C9XX
4.2.2.4PIE1 REGISTER
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: Bit PEIE |
(INTCON<6>) must be set to |
||||
This register contains the individual enable bits for the |
|
enable any peripheral interrupt. |
|||||||||||||||||
peripheral interrupts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
FIGURE 4-6: PIE1 REGISTER (ADDRESS 8Ch) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
LCDIE |
|
ADIE(1) |
— |
— |
|
SSPIE |
|
CCP1IE |
|
TMR2IE |
TMR1IE |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
|||
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7: |
|
LCDIE: LCD Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= Enables the LCD interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Disables the LCD interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit |
6: |
|
ADIE: A/D Converter Interrupt Enable bit(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= Enables the A/D interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Disables the A/D interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit |
5-4: Unimplemented: Read as '0' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
bit |
3: |
|
SSPIE: Synchronous Serial Port Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= Enables the SSP interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Disables the SSP interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit |
2: |
|
CCP1IE: CCP1 Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= Enables the CCP1 interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Disables the CCP1 interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
bit |
1: |
|
TMR2IE: TMR2 to PR2 Match Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= Enables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Disables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
bit |
0: |
|
TMR1IE: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= Enables the TMR1 overflow interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Disables the TMR1 overflow interrupt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Note |
1: Bit ADIE is reserved on the PIC16C923, always maintain this bit clear. |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DS30444E - page 26 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIC16C9XX |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.2.2.5 |
PIR1 REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: |
Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
This register contains the individual flag bits for the |
|
condition occurs regardless of the state of |
||||||||||||||||||
peripheral interrupts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
its corresponding enable bit or the global |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). User soft- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ware should ensure the appropriate inter- |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
interrupt. |
|
|
|
|
FIGURE 4-7: PIR1 REGISTER (ADDRESS 0Ch) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
R/W-0 |
|
|
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
R/W-0 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
LCDIF |
|
|
ADIF(1) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
SSPIF |
|
CCP1IF |
|
TMR2IF |
TMR1IF |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
|
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7: |
|
LCDIF: LCD Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= LCD interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= LCD interrupt did not occur |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
bit |
6: |
|
ADIF: A/D Converter Interrupt Flag bit(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= An A/D conversion completed (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= The A/D conversion is not complete |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
bit |
5-4: Unimplemented: Read as '0' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
bit |
3: |
|
SSPIF: Synchronous Serial Port Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= The transmission/reception is complete (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= Waiting to transmit/receive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
bit |
2: |
|
CCP1IF: CCP1 Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
Capture Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
1 |
= A TMR1 register capture occurred (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= No TMR1 register capture occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
Compare Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
1 |
= A TMR1 register compare match occurred (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= No TMR1 register compare match occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
PWM Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Unused in this mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
bit |
1: |
|
TMR2IF: TMR2 to PR2 Match Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= TMR2 to PR2 match occurred (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= No TMR2 to PR2 match occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
bit |
0: |
|
TMR1IF: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
= TMR1 register overflowed (must be cleared in software) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
0 |
= TMR1 register did not overflow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Note 1: Bit ADIF is reserved on the PIC16C923, always maintain this bit clear.
Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt condition occurs regardless of the state of its corresponding enable bit or the global enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>). User software should ensure the appropriate interrupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an interrupt.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 27 |

PIC16C9XX
4.2.2.6 |
PCON REGISTER |
|
|
|
|
|
For various |
reset |
conditions see Table 14-4 and |
||||||||||
The Power Control (PCON) register contains a flag bit |
|
Table 14-5. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
to allow differentiation between a Power-on Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
(POR) to an external |
|
Reset or WDT Reset. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
MCLR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
FIGURE 4-8: PCON REGISTER (ADDRESS 8Eh) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
U-0 |
R/W-0 |
U-0 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
R |
= Readable bit |
|
||
|
|
|
POR |
||||||||||||||||
|
bit7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bit0 |
|
W |
= Writable bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= Unimplemented bit, |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
read as ‘0’ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- n = Value at POR reset |
|
|
|
bit 7-2: |
Unimplemented: Read as '0' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
bit 1: |
|
: Power-on Reset Status bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
POR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
1 = No Power-on Reset occurred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
0 = A Power-on Reset occurred (must be set in software after a Power-on Reset occurs) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
bit 0: |
Unimplemented: Read as '0' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DS30444E - page 28 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |

PIC16C9XX
4.3PCL and PCLATH
The program counter (PC) is 13-bits wide. The low byte comes from the PCL register, which is a readable and writable register. The upper bits (PC<12:8>) are not readable, but are indirectly writable through the PCLATH register. On any reset, the upper bits of the PC will be cleared. Figure 4-9 shows the two situations for the loading of the PC. The upper example in the figure shows how the PC is loaded on a write to PCL (PCLATH<4:0> → PCH). The lower example in the figure shows how the PC is loaded during a CALL or GOTO instruction (PCLATH<4:3> → PCH).
FIGURE 4-9: LOADING OF PC IN DIFFERENT SITUATIONS
|
|
|
|
PCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCL |
|
|
|
||||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
0 |
Instruction with |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCL as |
|
|
5 |
|
|
PCLATH<4:0> |
|
8 |
Destination |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
ALU result |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCLATH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
PCH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCL |
|
|
|
|||||
12 |
11 |
10 |
8 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GOTO, CALL |
2 |
|
PCLATH<4:3> |
|
|
|
11 |
Opcode <10:0> |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCLATH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
4.3.1COMPUTED GOTO
A computed GOTO is accomplished by adding an offset to the program counter (ADDWF PCL). When doing a table read using a computed GOTO method, care should be exercised if the table location crosses a PCL memory boundary (each 256 byte block). Refer to the application note “Implementing aTable Read” (AN556).
4.3.2STACK
The PIC16CXXX family has an 8 level deep x 13-bit wide hardware stack. The stack space is not part of either program or data space and the stack pointer is not readable or writable. The PC is PUSHed onto the stack when a CALL instruction is executed or an interrupt causes a branch. The stack is POPed in the event of a RETURN, RETLW or a RETFIE instruction execution. PCLATH is not affected by a PUSH or POP operation.
The stack operates as a circular buffer. This means that after the stack has been PUSHed eight times, the ninth push overwrites the value that was stored from the first push. The tenth push overwrites the second push (and so on).
Note 1: There are no status bits to indicate stack overflow or stack underflow conditions.
Note 2: There are no instructions/mnemonics called PUSH or POP. These are actions that occur from the execution of the
CALL, RETURN, RETLW, and RETFIE instructions, or the vectoring to an interrupt address.
4.4Program Memory Paging
PIC16C9XX devices are capable of addressing a continuous 8K word block of program memory. The CALL and GOTO instructions provide only 11 bits of address to allow branching within any 2K program memory page. When doing a CALL or GOTO instruction the upper 2 bits of the address are provided by PCLATH<4:3>. When doing a CALL or GOTO instruction, the user must ensure that the page select bits are programmed so that the desired program memory page is addressed. If a return from a CALL instruction (or interrupt) is executed, the entire 13-bit PC is pushed onto the stack. Therefore, manipulation of the PCLATH<4:3> bits are not required for the return instructions (which POPs the address from the stack).
Note: The PIC16C9XX ignores paging bit PCLATH<4>, which is used to access program memory pages 2 and 3. The use of PCLATH<4> as a general purpose read/write bit is not recommended since this may affect upward compatibility with future products.
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
DS30444E - page 29 |

PIC16C9XX
Example 4-1 shows the calling of a subroutine in page 1 of the program memory. This example assumes that PCLATH is saved and restored by the interrupt service routine (if interrupts are used).
EXAMPLE 4-1: CALL OF A SUBROUTINE IN
|
|
PAGE 1 FROM PAGE 0 |
ORG 0x500 |
|
|
BSF |
PCLATH,3 |
;Select page 1 (800h-FFFh) |
CALL |
SUB1_P1 |
;Call subroutine in |
|
: |
;page 1 (800h-FFFh) |
|
: |
|
|
: |
|
ORG 0x900 |
|
|
SUB1_P1: |
;called subroutine |
|
|
: |
;page 1 (800h-FFFh) |
|
: |
|
RETURN |
|
;return to Call subroutine |
|
|
;in page 0 (000h-7FFh) |
4.5Indirect Addressing, INDF and FSR Registers
The INDF register is not a physical register. Addressing the INDF register will cause indirect addressing.
Indirect addressing is possible by using the INDF register. Any instruction using the INDF register actually accesses the register pointed to by the File Select Register (FSR). Reading the INDF register itself indirectly (FSR = '0') will produce 00hWriting. to the INDF register indirectly results in a no-operation (although status bits may be affected). An effective 9-bit address is obtained by concatenating the 8-bit FSR register and the IRP bit (STATUS<7>), as shown in Figure 4-10.
A simple program to clear RAM locations 20h-2Fh using indirect addressing is shown in Example 4-2.
EXAMPLE 4-2: INDIRECT ADDRESSING
|
movlw |
0x20 |
;initialize pointer |
|
movwf |
FSR |
;to RAM |
NEXT |
clrf |
INDF |
;clear INDF register |
|
incf |
FSR,F |
;inc pointer |
|
btfss |
FSR,4 |
;all done? |
|
goto |
NEXT |
;no clear next |
CONTINUE |
|
|
|
|
: |
|
;yes continue |
FIGURE 4-10: DIRECT/INDIRECT ADDRESSING
|
|
|
|
Direct Addressing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect Addressing |
|
|||||||||||||||
RP1:RP0 |
6 |
from opcode |
0 |
|
|
|
IRP |
7 |
|
FSR register |
0 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bank select |
location select |
|
|
00 |
01 |
10 |
11 |
bank select |
|
|
|
|
location select |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
00h |
|
|
|
00h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data
Memory
7Fh |
|
|
7Fh |
|
Bank 0 Bank 1 Bank 2 |
Bank 3 |
|
For memory map detail see Figure 4-2. |
|
|
|
DS30444E - page 30 |
1997 Microchip Technology Inc. |
 Loading...
Loading...