HP System Fault Management User Manual

System Fault Management C.07.05.08.01 administrator guide
HP-UX 11i v3
HP Part Number: 5900-2058
Published: March 2012
© Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P
Legal Notices
©Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group. Intel and Itanium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.

Contents |
|
1 Introduction............................................................................................... |
7 |
Overview................................................................................................................................ |
7 |
Features and benefits................................................................................................................ |
7 |
Components of SFM................................................................................................................. |
9 |
EVWEB.............................................................................................................................. |
9 |
EMT................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
CIMUtil.............................................................................................................................. |
9 |
IPMI event viewer................................................................................................................. |
9 |
Providers............................................................................................................................. |
9 |
instance providers........................................................................................................... |
9 |
Indication providers....................................................................................................... |
12 |
Cron job........................................................................................................................... |
15 |
User interfaces....................................................................................................................... |
15 |
HP Systems Insight Manager............................................................................................... |
15 |
HP System Management Homepage..................................................................................... |
15 |
Architecture........................................................................................................................... |
15 |
2 Installing the SFM software........................................................................ |
18 |
Prerequisites........................................................................................................................... |
18 |
Installing the SFM software from the media................................................................................ |
19 |
Installing using the TUI........................................................................................................ |
19 |
Installing using the CLI........................................................................................................ |
21 |
Installing the SFM software from the web................................................................................... |
22 |
Verifying the installation.......................................................................................................... |
22 |
Verifying the installation using the TUI................................................................................... |
23 |
Verifying the installation using the CLI................................................................................... |
24 |
Removing the SFM software..................................................................................................... |
24 |
Removing the software using the TUI..................................................................................... |
24 |
Removing the software using the CLI..................................................................................... |
27 |
Verifying removal of the SFM software....................................................................................... |
27 |
Verifying removal using the TUI............................................................................................ |
27 |
Verifying removal using the CLI............................................................................................ |
28 |
3 Configuring indication providers................................................................. |
29 |
Configuring indication filters.................................................................................................... |
29 |
Configuring error logging in SFM............................................................................................. |
30 |
Configuring the monitoring mode............................................................................................. |
30 |
4 Administering indications and instances using HP SIM.................................. |
32 |
Creating subscriptions and viewing indications using HP SIM ...................................................... |
32 |
Creating subscriptions........................................................................................................ |
32 |
Viewing Indications............................................................................................................ |
37 |
Viewing instances................................................................................................................... |
43 |
5 Administering indications and instances using HP SMH................................. |
44 |
Viewing instances................................................................................................................... |
44 |
Viewing information about processors................................................................................... |
44 |
Viewing information about memory...................................................................................... |
45 |
Viewing information about System Summary.......................................................................... |
46 |
Viewing information about Cooling Devices........................................................................... |
46 |
Viewing Power Supply instances.......................................................................................... |
46 |
Viewing Temperature status and events................................................................................. |
46 |
Viewing Voltage status and events........................................................................................ |
46 |
Contents 3
Viewing FRU information..................................................................................................... |
46 |
Viewing information about Management Processor................................................................. |
47 |
Viewing information about Firmware information.................................................................... |
47 |
Viewing information about Onboard Administrator................................................................. |
47 |
Viewing information about Complex-wide info....................................................................... |
47 |
Viewing information about Cell Board.................................................................................. |
47 |
Viewing Partition information............................................................................................... |
47 |
Viewing information about Blade......................................................................................... |
47 |
Viewing information about Cell Blade................................................................................... |
48 |
Viewing Health Test report of Memory.................................................................................. |
48 |
Viewing Health Test report of Processors............................................................................... |
48 |
Administering indications using Evweb...................................................................................... |
49 |
Evweb overview................................................................................................................. |
49 |
Launching Evweb for administration...................................................................................... |
50 |
Creating Evweb event subscriptions...................................................................................... |
50 |
Creating an event subscription using the GUI.................................................................... |
51 |
Creating an event subscription using the CLI..................................................................... |
51 |
Copying and creating a new event subscription using the GUI............................................ |
51 |
Modifying Evweb event subscriptions.................................................................................... |
52 |
Modifying an event subscription using the GUI.................................................................. |
52 |
Modifying an event subscription using the CLI................................................................... |
53 |
Copying and modifying an event subscription using the GUI............................................... |
54 |
Deleting Evweb event subscriptions....................................................................................... |
55 |
Deleting an event subscription using the GUI.................................................................... |
55 |
Deleting an event subscription using the CLI...................................................................... |
55 |
Configuring E-mail Consumer.............................................................................................. |
56 |
Viewing event subscriptions using Evweb................................................................................... |
56 |
Viewing Evweb event subscriptions....................................................................................... |
56 |
Viewing a summary of an Evweb event subscription using the GUI....................................... |
56 |
Viewing a Summary of an Evweb event Subscription using the CLI....................................... |
57 |
Viewing details of an event subscription using the GUI....................................................... |
57 |
Viewing details of an event subscription using the CLI........................................................ |
58 |
Viewing external event subscriptions..................................................................................... |
58 |
Viewing an external event subscription using the GUI......................................................... |
58 |
Viewing external event subscriptions using the CLI............................................................. |
59 |
Viewing indications using Evweb.............................................................................................. |
59 |
Launching Evweb for viewing WBEM indications................................................................... |
60 |
Searching for the subscribed WBEM events........................................................................... |
60 |
Filtering WBEM events using the GUI............................................................................... |
60 |
Searching for the subscribed WBEM events using the GUI.................................................. |
61 |
Searching for the subscribed WBEM events using the CLI................................................... |
61 |
Viewing summary information about WBEM events................................................................ |
61 |
Viewing summary information using GUI.......................................................................... |
62 |
Viewing summary information using CLI........................................................................... |
62 |
Viewing detailed information about WBEM events................................................................. |
62 |
Viewing detailed information using GUI........................................................................... |
62 |
Viewing Detailed Information using CLI............................................................................ |
62 |
Deleting WBEM Events from the Event Archive....................................................................... |
62 |
Deleting an Event using GUI........................................................................................... |
62 |
Deleting an Event using CLI............................................................................................ |
63 |
Viewing Low Level Logs using Evweb......................................................................................... |
63 |
Overview.......................................................................................................................... |
63 |
Searching Low Level Logs using Simple Search....................................................................... |
64 |
Searching Low Level Logs using Advanced Search.................................................................. |
65 |
Searching Low Level Logs using CLI.................................................................................. |
65 |
4Contents
Viewing List of Low Level Logs.............................................................................................. |
65 |
Viewing List Of Low Level Logs using GUI......................................................................... |
66 |
Viewing List Of Low Level Logs using CLI........................................................................... |
66 |
Viewing Details of Low Level Logs......................................................................................... |
66 |
Viewing Details Of Low Level Logs using GUI.................................................................... |
67 |
Viewing Details Of Low Level Logs using CLI..................................................................... |
67 |
Tracing Evweb........................................................................................................................ |
67 |
Enabling Tracing using the Evweb GUI................................................................................. |
69 |
Enabling Tracing using the Evweb CLI................................................................................... |
69 |
Modifying Tracing using the Evweb GUI............................................................................... |
70 |
Modifying Tracing using the Evweb CLI................................................................................. |
70 |
Disabling Tracing using the Evweb GUI................................................................................ |
70 |
Disabling Tracing using the Evweb CLI.................................................................................. |
71 |
Querying the Common Error Repository..................................................................................... |
71 |
EMT Overview................................................................................................................... |
71 |
Launching EMT.................................................................................................................. |
72 |
Querying the CER using Simple Search................................................................................ |
72 |
Querying CER for Events using the GUI............................................................................ |
72 |
Querying CER for Events using the CLI............................................................................. |
72 |
Querying CER using Advanced Search................................................................................. |
73 |
Viewing an Event from CER................................................................................................. |
73 |
Viewing Summary Information using the GUI.................................................................... |
73 |
Viewing Summary Information using the CLI...................................................................... |
73 |
Viewing Detailed Information using the GUI...................................................................... |
74 |
Viewing Detailed Information using the CLI....................................................................... |
74 |
Administering Events in CER..................................................................................................... |
74 |
Adding a Custom Solution.................................................................................................. |
74 |
Adding a Custom Solution using the GUI.......................................................................... |
74 |
Adding a Custom Solution using the CLI........................................................................... |
75 |
Modifying a Custom Solution............................................................................................... |
75 |
Modifying a Custom Solution using the GUI...................................................................... |
75 |
Modifying a Custom Solution using the CLI....................................................................... |
76 |
Deleting a Custom Solution ................................................................................................ |
76 |
Deleting a Custom Solution using the GUI........................................................................ |
76 |
Deleting a Custom Solution using the CLI.......................................................................... |
76 |
Tracing EMT.......................................................................................................................... |
77 |
Enabling Tracing using the EMT GUI.................................................................................... |
77 |
Enabling Tracing using the EMT CLI...................................................................................... |
78 |
Modifying Tracing using the EMT GUI.................................................................................. |
78 |
Modifying Tracing using the EMT CLI.................................................................................... |
78 |
Disabling Tracing using the EMT GUI................................................................................... |
78 |
Disabling Tracing using the EMT CLI..................................................................................... |
78 |
6 Troubleshooting SFM................................................................................ |
79 |
Troubleshooting instance providers............................................................................................ |
79 |
Troubleshooting indication providers......................................................................................... |
84 |
Troubleshooting EVWEB.......................................................................................................... |
89 |
A EMT Message Definition........................................................................... |
93 |
B Interpretation of HP SMH instances............................................................. |
96 |
Processor instances................................................................................................................. |
97 |
Memory instances.................................................................................................................. |
98 |
System Summary instances..................................................................................................... |
101 |
Cooling Device instances....................................................................................................... |
103 |
Power supply instances.......................................................................................................... |
104 |
Contents 5
Temperature instances........................................................................................................... |
105 |
Voltage instances.................................................................................................................. |
106 |
FRU Information instances...................................................................................................... |
107 |
Management Processor instances........................................................................................... |
108 |
Firmware Information instances............................................................................................... |
109 |
Enclosure Information instances.............................................................................................. |
110 |
Complex-wide Info instances.................................................................................................. |
111 |
Cell Board instances............................................................................................................. |
113 |
Partition Information instances................................................................................................ |
115 |
Blade instances.................................................................................................................... |
117 |
Cell Blade instances.............................................................................................................. |
118 |
Launch the Onboard Administrator......................................................................................... |
119 |
C Syslog property order............................................................................. |
120 |
Glossary.................................................................................................. |
121 |
Index....................................................................................................... |
124 |
7 Support and other resources.................................................................... |
126 |
About this document ............................................................................................................ |
126 |
Intended audience................................................................................................................ |
126 |
Publishing history.................................................................................................................. |
126 |
Document organization......................................................................................................... |
126 |
Typographic conventions................................................................................................... |
127 |
HP-UX release name and release identifier.......................................................................... |
127 |
New and changed information in this edition........................................................................... |
128 |
Related information............................................................................................................... |
128 |
HP welcomes your comments................................................................................................. |
128 |
6Contents

1 Introduction
The System Fault Management (SFM) supports HP Integrity Superdome 2 (HP Superdome 2), HP Integrity BL860c i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 Server Blades and rx2800 i2 in addition to other HP Integrity Servers. All the features supported on systems running the HP-UX 11i v3 operating system are available for HP Integrity Servers.
This chapter introduces you to the System Fault Management (SFM) software and the tools that SFM includes.
The chapter discusses the following topics:
•“Overview” (page 7)
•“Features and benefits” (page 7)
•“Components of SFM” (page 9)
•“User interfaces” (page 15)
•“Architecture” (page 15)
Overview
The SFM software is a collection of tools used to monitor the health of HP servers running HP-UX and deconfiguring the CPU, memory etc. based on the events. SFM retrieves information about a system’s hardware devices such as CPU, memory, power supply, and cooling devices. SFM operates within the Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) environment.
WBEM is an industry-wide standards-based initiative to aid the management of large scale systems. WBEM has the following components:
•A WBEM infrastructure, such as HP WBEM services. SFM uses the Common Information Model Object Manager (CIMOM) WBEM service to route query requests and responses between WBEM providers and clients. Clients must be compliant with the Common Information Model (CIM) (2.7.2 or later) schema of the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF).
•A WBEM-based network management application, such as the HP Systems Insight Manager (HP SIM) and HP System Management Homepage (HP SMH), a user interface for controlling and monitoring resources within a large-scale system. SFM can use HP SIM to display query information for local and remote systems.
•WBEM providers that obtain information. SFM includes instance and indication providers, which are one set of WBEM providers among many. SFM providers query and provide system hardware property and event information.
You must be familiar with WBEM technology before reading this guide. For more information on WBEM technology, see the HP WBEM Services for HP-UX and Linux System Administrator's Guide and HP WBEM Services Release Notes at:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-networking-docs
Features and benefits
SFM dynamically queries property information about a hardware device on a local or remote system. It offers the following features and benefits:
•Displays information on standards-compliant graphical and command-line system management applications, such as HP SIM and HP SMH.
•Operates within the WBEM environment.
•Supports the Central Management Server (CMS) running on HP-UX, Linux®, or Windows®.
Overview 7

•Enables you to view and administer WBEM indications.
•Provides the same features and benefits as those found in the EMS hardware monitors.
NOTE: SFM is the replacement of EMS hardware monitors.
8Introduction

Components of SFM
This section discusses the following topics:
•EVWEB
•Error Management Technology (EMT)
•CIMUtil
•IPMI Event Viewer
•providers
EVWEB
EVWEB is a component of SFM that enables you to administer and view WBEM indications generated on the local system on which SFM is installed. For more information on EVWEB, see “Evweb overview” (page 49).
EMT
EMT is a component of SFM that enables you to view and administer information about errors which can occur on the server. For more information on EMT, see “EMT Overview” (page 71).
CIMUtil
SFM introduces the CIMUtil command. Using CIMUtil, you can enumerate instances related to various devices and create filters, handlers, and subscriptions supported by SFM. For more information on CIMUtil, see man CIMUtil
IPMI event viewer
Starting March 2009 release, the IPMI Event Viewer, slview will be delivered as part of SysFaultMgmt. In the earlier releases it was delivered as part of Online Diagnostics bundle. IPMI Event Viewer is used to display low-level system log information.
Starting September 2009 release, the IPMI Event Viewer support will be available for the new IPMI event format.
Providers
SFM providers are components of SFM that retrieve information about the inventory on a system and the events that occur on the hardware resources. SFM providers can be classified as instance providers or as indication providers.
instance providers
On request, an SFM instance provider dynamically queries the local or remote system for the property information described in Table 1 and reports the information to the CIMOM.
Table 1 Instance providers
Instance provider |
Description |
|
Blade |
The Blade instance provider retrieves the following information: |
|
|
• |
Blade ID |
|
• |
Blade Physical location |
|
• |
Blade Hardware path |
|
• |
Blade Serial number |
|
• |
Blade Part number |
|
• |
Blade Status |
Components of SFM |
9 |
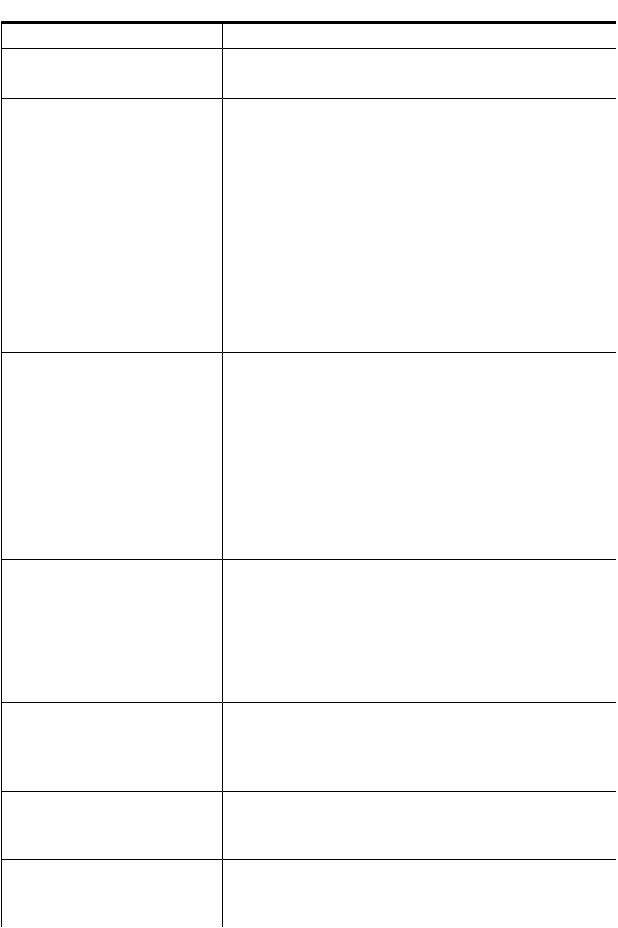
 Table 1 Instance providers (continued)
Table 1 Instance providers (continued)
Instance provider |
Description |
||
|
NOTE: The Blade instance provider is available on HP Integrity BL860c |
||
|
i2/BL870c i2/BL890c i2 Server Blades, HP Integrity Superdome 2. |
||
CPU |
The CPU instance provider gathers the following types of information: |
||
|
• Logical processor information, such as: |
||
|
|
◦ |
Current clock speed |
|
|
◦ |
Processor family |
|
|
◦ Processor status information, including configuration and |
|
|
|
|
deconfiguration, failure status, and active and inactive status |
|
|
◦ |
Load percentage |
|
• Physical processor chip information, such as chip revisions and |
||
|
|
architecture revisions |
|
|
• Location details, such as: |
||
|
|
◦ Location attributes such as cabinet number, cell number, slot number, |
|
|
|
|
and so on. Only information for filled slots is available. |
|
|
◦ |
Processor IDs |
Memory |
The Memory instance provider gathers the following types of information: |
||
|
• |
Memory slot information |
|
|
• Memory module information, such as: |
||
|
|
◦ |
Serial number |
|
|
◦ |
Part number |
|
|
◦ |
Memory capacity |
|
|
◦ |
Module form factor |
|
|
◦ Module status (for example, configuration status, failure status) |
|
|
The Memory instance provider depends on the EMS Wrapper provider to |
||
|
update the memory inventory on HP 9000 and HP Integrity servers. |
||
Environmental |
The Environmental instance provider gathers information about the following |
||
|
hardware components: |
||
|
• |
Fans |
|
|
• |
Power supply |
|
|
• |
Bulk power supply |
|
|
• |
AC input lines |
|
|
Enumeration of Power supply and Fan on a blade system is not supported. |
||
Filter Metadata (FMD) |
The FMD instance provider does the following: |
||
|
• Provides the ability to predefine a filter in a repository |
||
|
• Ensures that chosen indications are logged to the Event Archive |
||
|
• Creates HP-advised subscriptions when SFM is installed |
||
Firmware Revision |
The Firmware Revision provider retrieves the following types of information: |
||
|
• |
System firmware revision |
|
|
• Management Processor (MP) firmware revision |
||
DAS provider |
Starting with HP-UX 11i v3 March 2009 release, SFM does not monitor |
||
|
information of storage disks or disk enclosures. However, the DAS provider |
||
|
collects inventory details of the direct attached storage disks and monitors |
||
|
the systems for errors. |
||
10 Introduction
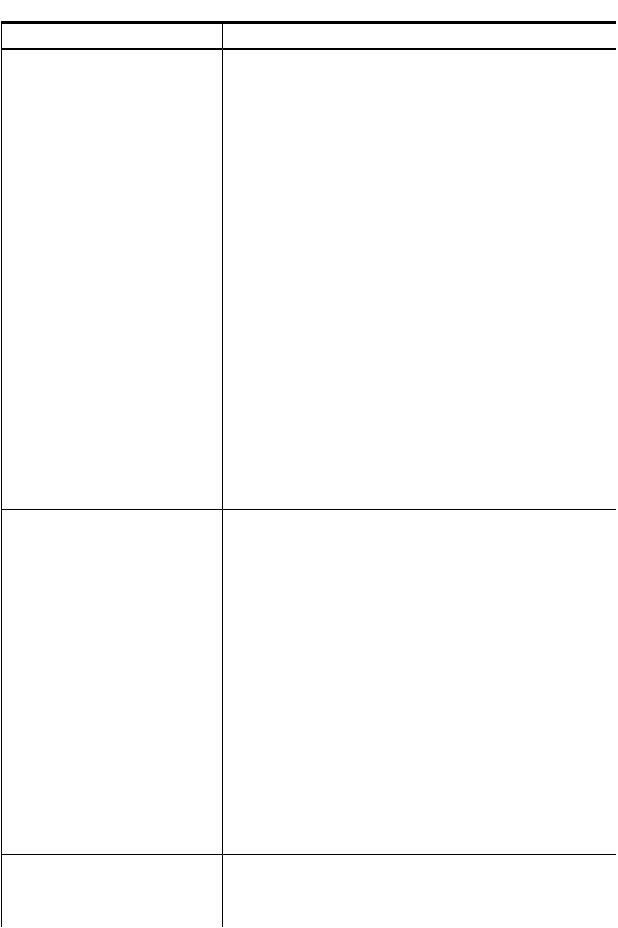
 Table 1 Instance providers (continued)
Table 1 Instance providers (continued)
Instance provider |
Description |
|
|
For more information on the DAS provider, see the HP-UX WBEM Direct |
|
|
Attached Storage (DAS) provider Data Sheet and Release Notes at: http:// |
|
|
www.hp.com/go/hpux-wbem-docs |
|
Management Processor |
Retrieves information about the management processor on the system. |
|
Enclosure |
The Enclosure instance provider retrieves the following types of information: |
|
|
• Onboard Administrator (OA) description |
|
|
• |
OA IP address |
|
• |
OA MAC address |
|
• URL to launch the OA |
|
|
NOTE: The Enclosure instance provider is available on all integrity Blade |
|
|
systems except for BL60p and HP Integrity Superdome 2. |
|
Temperature Sensor |
The Temperature Sensor provider retrieves the following types of information: |
|
|
Describes properties such as sensor number, current temperature reading, |
|
|
and temperature sensor status. |
|
|
• |
Sensor number |
|
• |
Current temperature reading |
|
• |
Temperature sensor status |
|
• |
Processor temperature |
|
• |
Memory board temperature |
|
On HP 9000 and HP Integrity ® systems running a supported version of |
|
|
HP-UX, the Temperature Sensor provider retrieves information related to the |
|
|
ambient temperature in the system. On HP 9000 and HP Integrity ® system |
|
|
not supporting the system and numeric sensor, the Temperature Sensor |
|
|
instance provider doesn’t retrieve any information. |
|
Record Log |
Enables event analysis tools such as Web-Based Enterprise Services (WEBES) |
|
|
to access details of indications generated by the SFMIndicationProvider |
|
|
that are available in the SFM database, for event analysis. The provider |
|
|
also supports MCA logs. Event analysis tools can access MCA log details |
|
|
for event analysis. |
|
|
For more information, see Recordlog and MCA indication provider at: |
|
|
http://bizsupport1.austin.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/ |
|
|
c02578184/c02578184.pdf |
|
ComputerSystem Chassis provider |
Retrieves properties such as the serial number, product ID, and virtual |
|
|
Universally Unique ID (UUID). It provides the following details related to the |
|
|
physical system: |
|
|
• |
SerialNumber |
|
• |
ProductId |
|
• |
Model |
|
The ComputerSystem Chassis provider provides the following details related |
|
|
to the logical server: |
|
|
• |
VirtualSerialNumber |
|
• |
VirtualUUID |
|
These values are retained when an OS instance is moved to another server. |
|
Consolidated Status provider |
The Consolidated Status provider provides the overall health status of various |
|
|
subsystems of the managed node. The overall health status is consolidated |
|
|
from the health status of individual status providers registered with WBEM. |
|
The SFM providers that contribute to the overall health status are:
Components of SFM 11
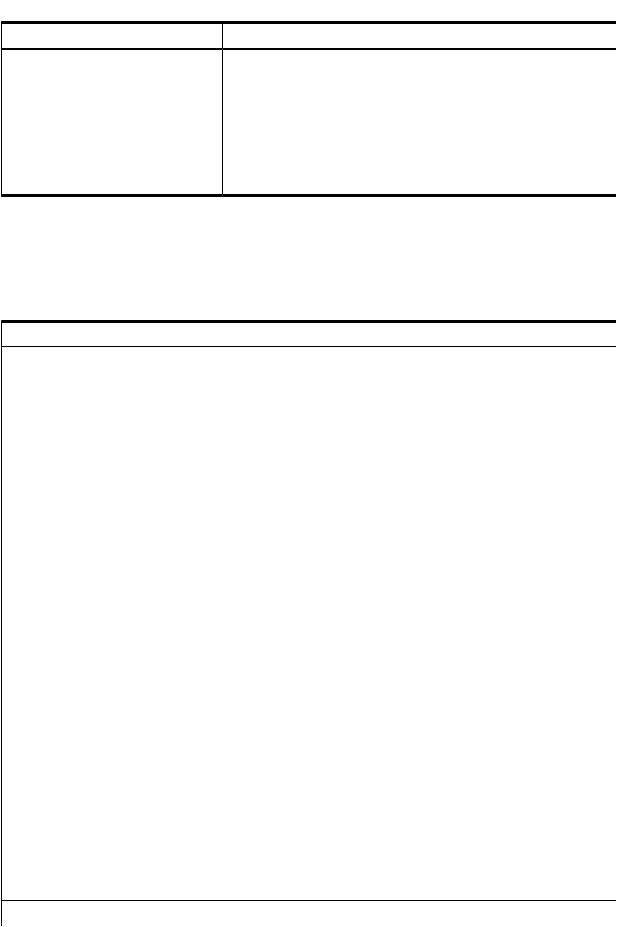
 Table 1 Instance providers (continued)
Table 1 Instance providers (continued)
Instance provider |
Description |
|
Blade |
|
CPU |
|
Memory |
|
Environmental |
|
Firmware Revision |
|
Management Processor |
|
Enclosure |
|
Temperature Sensor |
Indication providers
SFM includes four indication providers, the EMS Wrapper provider, the Event Manager Common Information Model (EVM CIM) provider, SFMIndicationProvider and MCA indication provider. Table 2 describes the SFM indication providers.
Table 2 Indication providers
Indication provider |
Description |
|
EMS Wrapper provider |
The EMS Wrapper provider does the following: |
|
|
1. |
Converts hardware events generated by the EMS Hardware |
|
|
Monitors into WBEM indications. |
|
2. |
Reports the WBEM indications to the CIMOM. Using a |
|
|
WBEM-based management application, such as HP SIM, you |
|
|
can subscribe to and receive Event Monitoring Service (EMS) |
|
|
events generated on a remote system. On the system on which |
|
|
SFM is installed, you can use an SFM tool, called EVWEB, to |
|
|
view and administer events through the HP SMH interface. |
|
The following EMS Hardware Monitors are supported on HP 9000 |
|
|
servers running the HP-UX 11i v3 operating system: |
|
|
• |
LPMC (now CPU) (lpmc_em) |
|
• |
Memory (dm_memory) |
|
• |
Core HW (dm_core_hw) |
|
• |
Chassis Code (dm_chassis) |
|
• |
Integrity Core Hardware Monitor(ia64_corehw) |
|
• |
IPMI Forward Progress Log Monitor (fpl_em) |
|
The following EMS Hardware Monitors are supported on HP |
|
|
Integrity® servers running the HP-UX 11i v3 operating system: |
|
|
• |
Corrected Platform Error Monitor (cpe_em) |
|
• |
IPMI Forward Progress Log Monitor (fpl_em) |
|
• |
CMC Monitor (cmc_em) |
|
• |
Itanium Core Hardware Monitor(ia64_corehw) |
|
• |
Itanium Memory Monitor (memory_ia64) |
|
NOTE: This provider and WBEM to EMS Consumer is not |
|
|
supported on HP Integrity BL860c i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 |
|
|
Server Blades, HP Integrity rx2800 i2 server, and HP Integrity |
|
|
Superdome 2. |
|
|
For a list of EMS Event Descriptions, see: |
|
|
http://www.hp.com/go/ |
|
|
hpux-diagnostics-online-events |
|
EVM CIM provider |
The EVM CIM provider does the following: |
|
12 Introduction

 Table 2 Indication providers (continued)
Table 2 Indication providers (continued)
Indication provider
SFMIndicationProvider
MCA indication provider
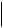 Description
Description
1.Converts hardware, software, and kernel events generated by the EVM into WBEM indications.
2.Reports the WBEM indications to the CIMOM. Using a WBEM-based management application, such as HP SIM, you can subscribe to and receive EVM events generated on a remote system. On the system on which SFM is installed, you can use an SFM tool, called EVWEB, to view and administer events through the HP SMH interface.
3.Logs messages logged by EVMCimProvider in
/var/opt/sfm/EvmCimProvider.log log file.
The SFMIndicationProvider generates indications that are compliant with the WBEM standards. On HP Integrity systems, it replaces the following EMS monitors:
•cmc_em
•cpe_em
•memory_ia64
•fpl_em
•ia64_corehw
On HP 9000 systems, it replaces the following EMS monitors:
•fpl_em
•ia64_corehw
On HP Superdome 2, the core analysis engine monitors core hardware and generates events. DPR and PCI Error Recovery events are generated on HP-UX . The following indication providers generate the event respectively:
•CMC_IndicationProviderIA
•PCIeIndicationProvider
You can choose to use either the SFMIndicationProvider or the EMS monitors that it replaces, to monitor your hardware. The remaining EMS monitors continue to function as usual irrespective of whether you choose the SFMIndicationProvider or the EMS monitors that it replaces. If you choose the SFMIndicationProvider, it does the following:
1.Generates WBEM indications equivalent to the events that the monitors it replaces generate.
2.Reports these WBEM indications to the CIMOM.
In the WBEM indication details, the provider name displayed corresponds with the device to which the indication is related. For example, if the name of the provider displayed in the event details is MemoryIndicationProviderIA, the event is related to memory. For a complete list of the names of providers displayed in the WBEM indication details, in the SFM mode, see
Table 6 (page 40). The provider names indicate the device to which the event is related.
For a list of WBEM indications and their details, see the SFM Event Descriptions at:
http://www.hp.com/go/hpux-diagnostics-sfm-events
The MCA indication provider generates an indication when Machine Check Abort (MCA) logs are present due to an MCA.
The MCA indication provider is available on all HP 9000 and Integrity systems except for HP Integrity Superdome 2.
Components of SFM 13
NOTE: The following apply to indication providers:
•The terms events and indications are used interchangeably.
•Although both EMS Wrapper provider and EVM CIM provider generate events related to system hardware, the nature of events are different.
In addition, the support for CPUIndicationProvider and MemoryIndicationProvider has been added with additional support for hardware events on HP Integrity BL860c i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 Server Blades. The support for MemoryIndicationProvider has been added for Legacy memory events and that for MemoryIndicationProviderIA for HP Integrity BL860c i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 Server Blades, HP Integrity Superdome 2 and rx2800 i2 servers. For the listing of new events reported by SFM on these indication providers, see the SFM Event Descriptions.
CIMOM identifies the SFM providers using SFMProviderModule. If a provider is not working properly, SFMProviderModule stops all the SFM providers.
Table 3 Instance / Indication providers support
Instance / Indication providers |
PA-RISC provider |
IA legacy provider1 |
IA NGIS providers2 |
CPUProvider and |
√ |
√ |
√ |
CPUStatusProvider |
|
|
|
BladeProvider and |
Х |
√ |
√ |
BladeStatusProvider |
|
Supported only on BL860c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 |
|
EMDProvider |
√ |
Х |
Х |
Environmental |
√ |
√ |
√ |
Memory provider and |
√ |
√ |
√ |
MemoryStatus provider |
|
Supported only on BL860c |
Not supported on HP |
|
|
||
|
|
i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 |
Superdome 2 |
EnclosureProvider and |
Х |
√ |
√ |
EnclosureStatusProvider |
|
Supported only on BL860c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 |
|
MPProvider and MPStatusProvider |
√ |
√ |
√ |
CSChassisProvider |
√ |
√ |
√ |
RecordLog provider |
√ |
√ |
√ |
Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) |
√ |
√ |
√ |
instance provider |
|
|
Not supported on HP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Superdome 2 |
EMS Wrapper provider |
√ |
√ |
Х |
EVM CIM provider |
Х |
√ |
√ |
SFMIndicationProvider |
√ |
√ |
√ |
MCAIndicationProvider |
X |
√ |
√ |
|
|
|
Not supported on HP |
|
|
|
Superdome 2 |
Temperature Sensor |
√ |
√ |
√ |
Firmware Revision provider |
√ |
√ |
√ |
StatusChangeIndication provider |
√ |
√ |
X |
14 Introduction |
|
|
|
1 Legacy : HP Integrity platforms supporting processors prior Intel 9300.
2 NGIS : HP Integrity platfroms supporting Intel 9300 processors
Table 4 (page 15) lists the detection status of SFMIndication providers
Table 4 Representation of Monitors
Provider |
Detection status |
CPUIndicationProvider |
asynchronous |
MCAIndicationProvider |
polling |
CMC_IndicationProviderIA |
asynchronous |
CPE_IndicationProviderIA |
asynchronous |
CoreHardwareIndicationProvider |
asynchronous |
ChassisIndicationProvider |
asynchronous |
DiskIndicationProvider |
polling and asynchronous |
FPL_IndicationProvider |
polling |
SEL02_IndicationProvider |
polling |
LPMC_IndicationProvider |
asynchronous |
MemoryIndicationProvider |
asynchronous |
PCIeIndicationProvider |
asynchronous |
Cron job
SFM includes the following features from the HP-UX 11i v3 February 2007 release:
•Cron job: When restart is attempted, /opt/sfm/bin/restart_sfm.sh script handles restart if module is in degraded state.
•Vacuum cron job: Configured to be invoked once a day, the vacuum cron job is used to free up unused memory space of SFM PostgresSQL database.
User interfaces
You can use two types of interfaces to view SFM provider queries: HP SIM and HP SMH. This section describes these interfaces.
HP Systems Insight Manager
HP SIM is a WBEM-based user interface for controlling and monitoring resources within a large-scale system. You can use HP SIM to create subscriptions and to view indications and instances on a remote system. You must install HP SIM on the CMS. You can use HP SIM to launch HP SMH.
HP System Management Homepage
HP SMH is a secure, Web-based management application. You must install HP SMH on a local system to view hardware configuration, status data, performance metrics, system thresholds, and software version control information. You can also launch HP SMH from HP SIM remotely.
Architecture
Figure 1 illustrates the architecture of SFM installed on a client system. The client system is managed by the CMS.
User interfaces 15

Figure 1 Block Diagram of SFM
The following list describes the sequence of events when a request is made for information:
1.The CIMOM receives requests from the CMS for information about devices.
2.The CIMOM directs the requests to the appropriate SFM provider, for example, the CPU instance provider.
3.The SFM provider queries the associated hardware device for property information.
4.The SFM provider returns the query information to the CIMOM.
5.The CIMOM conveys the responses from the provider to the CMS.
You can view the information using HP SIM on the remote system and HP SMH on the local system.
The following list describes the sequence of events when an event is generated from an EMS monitor:
1.EVWEB and CMS subscriptions are created.
2.The EMS Wrapper provider receives events generated by the EMS monitors through the EMS framework.
3.The provider converts these events into WBEM indications and reports these indications to the CIMOM.
4.CIMOM directs these indications to the CMS that has created subscriptions for indications. EVWEB retrieves the errors that occurred on the local system and stores the indications either in the Event Archive or in your E-mail box, or both, depending on your configuration.
You can view indications using HP SIM on the remote system and HP SMH on the local system.
The sequence of events if you choose to use the SFMIndicationProvider instead of the EMS monitors it substitutes, is as follows:
1.EVWEB and CMS subscriptions are created.
2.The SFMIndicationProvider generates WBEM indications that are triggered by errors on devices that it monitors.
3.The provider reports these WBEM indications to the CIMOM.
16 Introduction

4.The CIMOM directs these indications to EVWEB and to the CMS that has created subscriptions for indications. EVWEB then stores the indications either in the Event Archive, in syslog, or in your E-mail box, or all, depending on your configuration.
Indications can be viewed using HP SIM on the remote system and HP SMH on the local system.
5.The indications generated by the SFMIndicationProvider, and reported to the CIMOM, can also be directed to the EMS framework through the WBEM Wrapper Monitor. The WBEM Wrapper Monitor converts the WBEM indications into EMS events and directs them to the EMS framework.
EMS clients can receive these events, along with the other events generated by the EMS monitors, through the EMS framework.
NOTE:
a.Only those indications that are generated by the SFMIndicationProvider in the SFM monitoring mode, can be directed to the EMS framework through the WBEM Wrapper Monitor. Indications generated by the EMS Wrapper provider in the EMS monitoring mode, cannot be directed to the EMS framework.
b.You can continue to receive all events from EMS Hardware Monitors through the EMS framework along with the indications on EVWEB and CMS.
The following list describes the sequence of events when an event is generated by EVM:
1.EVWEB and CMS subscriptions are created.
2.The EVM CIM provider receives events posted by the posting clients through the EVM Daemon.
3.The provider converts these events into WBEM indications and reports these indications to the CIMOM.
4.CIMOM directs these indications to EMT and the CMS that has created subscriptions for indications. EVWEB retrieves the errors that occurred on the local system and stores the indications either in the Event Archive, in syslog, or in your E-mail box, or all, depending on your configuration.
You can view indications using HP SIM on the remote system and HP SMH on the local system.
Architecture 17

2 Installing the SFM software
The System Fault Management (SFM) software is installed by default with the HP-UX 11i v3 Operating Environment (OE) media. However, at some point you may need to install the SFM software separately. This chapter describes how to install the SFM software as a standalone component on the HP-UX 11i v3 operating system.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
•“Prerequisites” (page 18)
•“Installing the SFM software from the media” (page 19)
•“Installing the SFM software from the web” (page 22)
•“Verifying the installation” (page 22)
•“Removing the SFM software” (page 24)
•“Verifying removal of the SFM software” (page 27)
Prerequisites
Starting with HP-UX 11i v3 September 2011 release, SysFaultMgmt and its dependencies are availablethrough HP-UX WBEM Management Bundle (WBEMMgmtBundle). ThisMegabundle is available only on HP Software Depot. It is recommended to install the products together from the WBEMMgmtBundle due to the product dependency. For installation steps, see “Installing the SFM software from the web” (page 22)
Following are the prerequisites for installing the March 2012 version of SFM software:
•HP-UX 11i v3 February 2007 release or later
•OpenSSL Version A.00.09.08g.001 or later
•EVM-EventMgr B.11.31 September 2007 or later
•SysMgmtBase Version B.00.02.03 (Interface) or later
•WBEMSvcs Version A.02.09.02.00 or later
•PHCO_40289 (for Itanium only)
•SysMgmtWeb (HP-UX Web-Based System Management User Interface) Version A.3.0.0.2, September 2009 release or later
•HP Systems Insight Manager (HP SIM) Version C.06.01 or later
•ProviderSvcsBase Version C.07.00.07.01, March 2012 release or later
•SysMgmtPlus Version A.04.00, September 2010 release or later
•OnlineDiag Version B.11.31.06.xx on HP 9000 systems only, September 2009 release or later
EMS Version |
A.04.20.31 |
STM Version |
D.06.00 |
18 Installing the SFM software
NOTE:
•The listed versions of the software are the minimum supported requirements. Subsequent versions are compatible with this version of SFM unless otherwise noted.
•WBEM Services, Online Diagnostics, SysMgmtWeb, and HP SIM are available on the Operating Environment (OE) media and can be selected for install during the SFM installation.
•HP System Management Homepage (SMH) – bundled in SysMgmtWeb. You cannot access the EvWEB GUI (Event Viewer, Subscription Administration and Log Viewer interface), EMT(Error Management Technology) GUI and IPMI Event Viewer GUI without HP SMH. The command line interface for EVWEB, EMT and IPMI Event Viewer (Slview) will still be accessible.
•HP Systems Insight Manager (HP SIM) is an optional install. However, HP recommends using the latest available version to remotely administer indications and instances. The minimum requirements are the June 2010 release:
HP SIM 6.1 with Update 1 - HP-UX (C.06.01.00.00.04).
Installing the SFM software from the media
This section describes the two ways in which you can install the SFM software from the HP-UX 11i v3 OE media:
•Using the terminal user interface (TUI)
•Using the command-line interface (CLI)
Installing using the TUI
To install the SFM software using the TUI, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Mount the CD to a location of your choice as in the following example:
#mount /dev/dsk/c1t2d0 /tmp/cdrom
3.Enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#swinstall
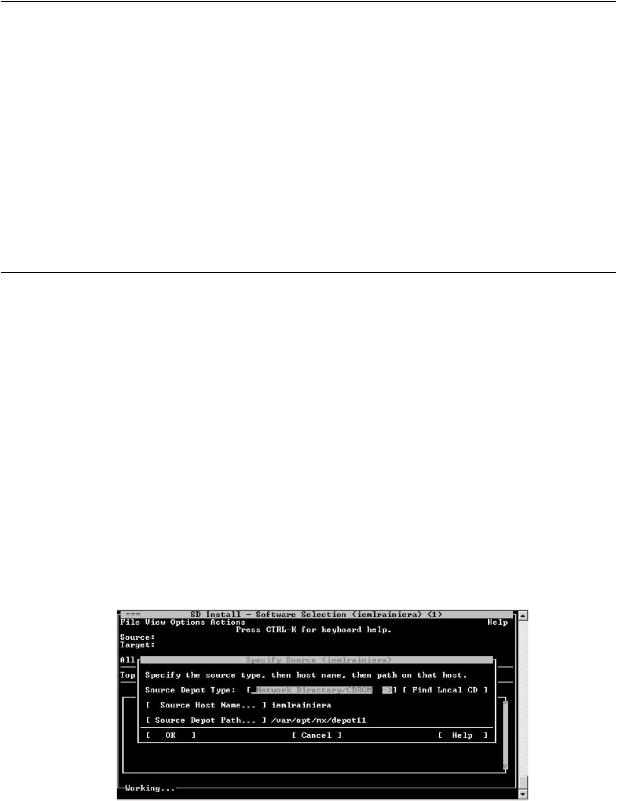
The SD Install - Software Selection window appears as shown in the following figure:
4.In the Specify Source window, select the appropriate location and click OK. The SD Install - Software Selection window is displayed.
5.In the SD Install - Software Selection window, select Options-> Autoselect dependencies when marking software.
6.Select Enforce dependency analysis errors in agent, and click OK, as shown in the following figure. The Note window is displayed.
Installing the SFM software from the media 19
Selecting these options automatically installs all the dependencies.
NOTE: The system selects some options by default. However, you must select the two options mentioned in step 5 to automatically install the prerequisites.
7.Click OK in the Note window to confirm the selection of dependencies.
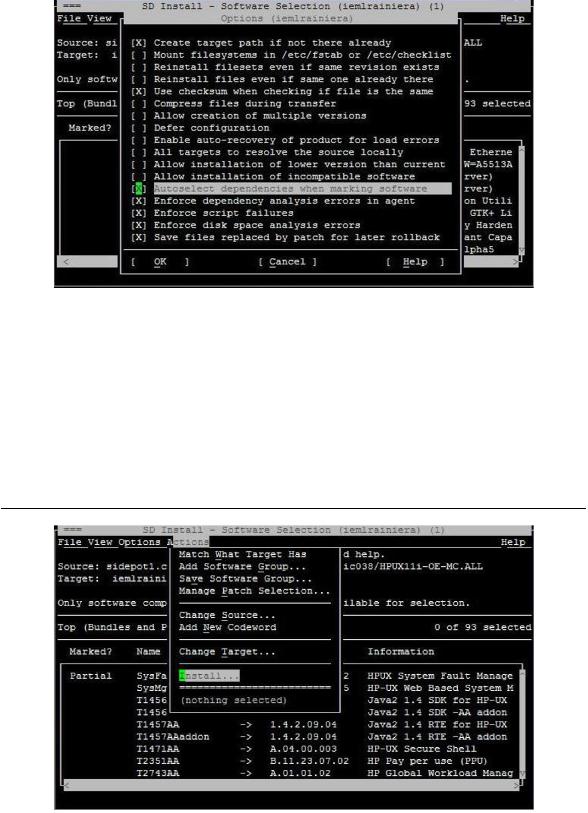
8.In the SD Install - Software Selection window, select Actions->Install, as shown in the following figure. You will need to install SysFaultMgmt, OnlineDiag and ProviderSvcsBase product together from the DiagProdCollection bundle due to the product dependency. Verify the depot by using swverify command.
NOTE: SFM is automatically configured after it is installed.
The following figure displays the beginning of the configuration phase:
20 Installing the SFM software
When the SFM software installs, the Install window appears indicating that the SFM software is installed successfully, as shown in the following figure:
9.Unmount the CD. To unmount, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#unmount /tmp/cdrom
10.To verify whether the SFM software is installed properly, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#swlist | grep SysFaultMgmt
If the SFM software is installed properly, SysFaultMgmt and the version number of the SFM software are displayed in the output. If the SFM software is not installed properly, you must repeat the installation procedure. For more information, see “Verifying the installation” (page 22).
Installing using the CLI
To install the SFM software using CLI, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Mount the CD to a location of your choice, as in the following example:
# mount /dev/dsk/c1t2d0 /tmp/cdrom
Installing the SFM software from the media 21
3.To install the SFM software and all the dependencies, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#swinstall -x autoselect_dependencies=true -x enforce_dependencies=true -s /tmp/cdrom SysFaultMgmt
4.Unmount the CD. To unmount, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#unmount /tmp/cdrom
5.To verify whether the SFM software is installed properly, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#swlist | grep SysFaultMgmt
If the SFM software is installed properly, SysFaultMgmt and the version number of the SFM software appear in the output. If the SFM software is not installed properly, you must repeat the installation procedure. For more information, see “Verifying the installation” (page 22).
Installing the SFM software from the web
Starting with HP-UX 11i v3 March 2009 release, OnlineDiag and SysFaultMgmt products are available through HP-UX Diagnostics Products Collection (DiagProdCollection) Mega bundle. This Mega bundle is available only on web. You will require to install SysFaultMgmt, OnlineDiag and ProviderSvcsBase product together from the DiagProdCollection bundle due to the product dependency.
To install the SFM software from the Software Depot, complete the following steps:
1.Go to HP Software depot at: http://www.hp.com/go/softwaredepot
2.Search for WBEMMgmtBundle and select WBEM Management bundle for HP-UX 11i v3. The Overview page is displayed. This page provides the details of solution for installation/upgrade of WBEM Management products bundle.
3.Go to the Installation page and review Prerequisites to ensure that your system meets the requirements.
4.Select the Receive for Free >> option at the bottom right of the page.
5.Select the appropriate release of the HP-UX operating system.
6.Enter your registration information. Read and accept the terms and conditions.
7.Click Next >> at the bottom right of the page.
8.Click the appropriate link under Download Software to download the software. Save the software in a local directory on your system, for example, /tmp/SysFaultMgmt.depot.
9.To install the product, login as superuser and enter the following command:
# swinstall -s <full path of depot> SysFaultMgmt
For example,
#swinstall -s /tmp/SysFaultMgmt.depot SysFaultMgmt
10.To verify whether the SFM software is installed properly, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#swlist | grep SysFaultMgmt
If the SFM software is installed properly, SysFaultMgmt and the version number appear in the output. If the SFM software is not installed properly, you must repeat the installation procedure. For more information, see “Verifying the installation” (page 22).
Verifying the installation
This section describes how to verify the SFM software installation using the TUI and the CLI.
22 Installing the SFM software

Verifying the installation using the TUI
To verify the SFM software installation, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
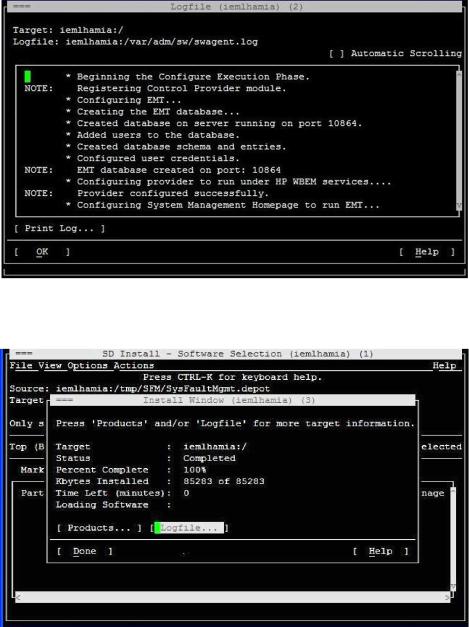
2.Click Logfile in the Install window, as shown in the following figure:
The Logfile, which includes details about the installation, is displayed. If there are no errors in the Logfile, the SFM software is installed properly. If the SFM software is not installed properly, you must repeat the installation procedure.
3.For information about errors related to installation, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob -a log <jobid> @ <system name>:/
The jobid is available in the Logfile, as underlined in the Logfile window, in the following figure:
For example, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob -a log iemlhamia-0013 @ iemlhamia.india.hp.com:/
Verifying the installation |
23 |
Verifying the installation using the CLI
To verify your installation using the CLI, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
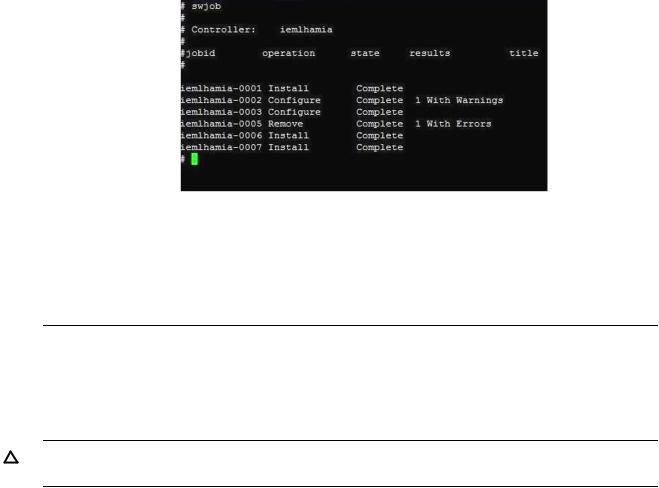
# swjob
If the output contains no errors, the SFM software is installed properly. Otherwise, you must install the SFM software again.
A sample output is shown in the following figure:
3.For information about installation-related errors, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob -a log <jobid> @ <system name>:/
For example, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob -a log iemlhamia-0005 @ iemlhamia.india.hp.com:/
NOTE: The logs to /var/opt/sfm/log/install.log are written when SFM is getting installed.
Removing the SFM software
This section describes how to remove of the SFM software using the TUI and the CLI.
CAUTION: Removing the SFM software makes your system vulnerable to failure. Also, all the software products that depend on the SFM software may not work properly.
Removing the software using the TUI
To remove the SFM software from your system, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swremove
3.Select SysFaultMgmt in the SD Remove window, as shown in the following figure:
24 Installing the SFM software
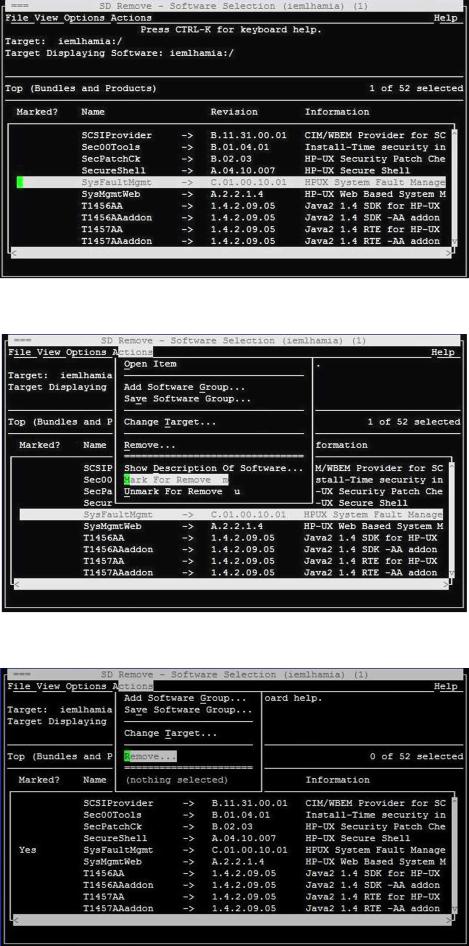
4.Select Actions->Mark for Remove in the SD Remove window, as shown in the following figure:
5.Select Actions->Remove, as shown in the following figure:
Removing the SFM software 25
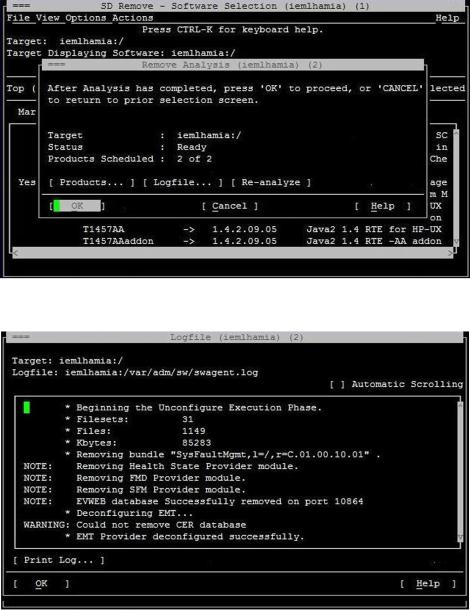
6.Click OK in the Remove Analysis window to confirm the removal of the SFM software, as shown in the following figure:
The following figure is a sample of the removal process in progress:
7.When the SFM software is removed, the Remove Window is displayed, as shown in the following figure:
26 Installing the SFM software
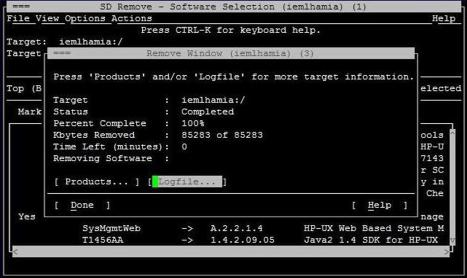
8.To verify whether the SFM software is removed properly, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swlist | grep SysFaultMgmt
If the SFM software is removed properly, SysFaultMgmt and the version number of the SFM software does not appear in the output. If the SFM software is not removed properly, you must repeat the removal procedure. For more information, see “Verifying removal of the SFM software” (page 27).
Removing the software using the CLI
To remove the SFM software from your system, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Enter the following command at the HP-UX command prompt:
#swremove SysFaultMgmt
3.To verify whether the SFM software is removed properly, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#swlist | grep SysFaultMgmt
If the SFM software is removed properly, SysFaultMgmt and the version number of the SFM software do not appear in the output. If the SFM software is not removed properly, you must repeat the removal procedure. For more information, see “Verifying removal of the SFM software” (page 27).
Verifying removal of the SFM software
This section describes how to use the TUI and the CLI to verify whether the SFM software is removed successfully.
Verifying removal using the TUI
To verify whether the SFM software is removed successfully, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Click Logfile in the Remove Window.
If there are no errors in the Logfile, the SFM software is removed successfully. If the SFM software is not removed properly, you must repeat the removal procedure. See “Removing the SFM software” (page 24) for instructions on how to remove the SFM software.
Verifying removal of the SFM software 27
3.For information about errors related to the removal of SFM, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob -a log <jobid> @ <system name>:/
The jobid is available in the Logfile.
Verifying removal using the CLI
To verify if the SFM software is removed successfully, complete the following steps:
1.Log in to the system as a superuser.
2.Enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob
If the output contains no errors, the SFM software is removed successfully. If the SFM software is not removed properly, you must repeat the removal procedure. See “Removing the SFM software” (page 24) for instructions on how to remove the SFM software.
3.For information about errors related to the removal of the SFM software, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# swjob -a log <jobid> @ <system name>:/
The jobid is available in the output of the swjob command.
28 Installing the SFM software

3 Configuring indication providers
This chapter describes how to configure indication filters, error logging, and the
SFMIndicationProvider.
Configuring indication filters
You must configure the indication filters to view desired indications. You use the Filter Metadata provider (FMD) to configure indication filters that deliver important or desired indications, for example, indications with a certain severity. The provider also ensures that all the indications that HP recommends for system management are logged in the Event Archive, available at /var/opt/psb/db/pgsql. Logging indications in the archive helps track all the events that are generated.
Filters are classified as follows:
•HP-Defined Filters
HP-Defined filters are defined by HP, and are present in the FMD repository at the time of installation. You can list, enable or disable the HP-Defined filters. Indications fulfilling the conditions in the HP-Defined filters are logged in the Event Archive. To confirm the HP-Defined Filters, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# sfmconfig -m list -t HP
The following output is displayed:
Filter Name |
: General Filter |
Filter Type |
: HP Defined Filter |
Filter Unique Identifier |
: 1 |
Filter Query |
: Select * from HP_DeviceIndication |
Filter Query Language |
: WQL |
Filter Source Namespace |
: root/cimv2 |
Filter Description |
: General Device Indications. |
Filter State |
: Enabled Filter State |
Filter Last Operation |
: No Operation |
To disable the HP-Defined filters, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# sfmconfig -m disable -t HP -n 'General Filter' -u 1
To revert the settings, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#sfmconfig -m enable -t HP -n 'General Filter' -u 1
•Admin-Defined Filters
Admin-Defined filters are defined by the administrator. HP does not provide any Admin-Defined filter. To list, create, delete, modify, enable, and disable Admin-Defined filters, use the sfmconfig command. By default, the FMD provider does not log indications fulfilling the conditions in the Admin-Defined filters, in the Event Archive. You must modify the Admin-Defined filters to log indications in the Event Archive.
To add an Admin-Defined Filter, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
#sfmconfig -m add -n <filter name> -s {ENABLE|DISABLE} -l {WQL|CQL} -q <query> -ns <name space> -d <description>
For example,
# sfmconfig -m add -n AdminFilter_2 -s ENABLE -l WQL -q "Select * from HP_AlertIndication where (PerceivedSeverity >= 4)" -ns root/cimv2 -d "Admin Filter"
The following output is displayed:
Filter |
Name |
: |
AdminFilter_2 |
|
Filter |
Type |
: |
Admin Defined |
Filter |
Configuring indication filters |
29 |

Filter Unique Identifier |
: 10002 |
Filter Query |
: Select * from HP_AlertIndication where (PerceivedSeverity >= 4) |
Filter Query Language |
: WQL |
Filter Source Namespace |
: root/cimv2 |
Filter Description |
: Admin Filter |
Filter State |
: Enabled Filter State |
Filter Last Operation |
: Add Filter |
HP_AlertIndication is derived from CIM_AlertIndication and HP_DeviceIndication is derived from HP_HardwareIndication. HP_HardwareIndication is derived from HP_AlertIndication.
WBEM severities must be used while specifying the filter query. For more information on the WBEM severity, see Table 5 (page 39).
For more information on the sfmconfig command, and its options, see the sfmconfig (1M) manpage.
Configuring error logging in SFM
Logging information about the internal operational errors of SFM such as system call errors is called, error logging. You can configure error logging parameters, such as severity, logging target, and the number of backup files by using the sfmconfig command. To configure these parameters, complete the following steps:
1.Modify the /var/opt/sfm/conf/FMLoggerConfig.xml configuration file using a text editor.
2.For the changes made in the /var/opt/sfm/conf/FMLoggerConfig.xml configuration file to take effect, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# /opt/sfm/bin/sfmconfig -c /var/opt/sfm/conf/FMLoggerConfig.xml
For more information about the sfmconfig command, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# man sfmconfig
NOTE: You can configure the parameters by using the command-line interface (CLI) only.
Configuring the monitoring mode
This section describes how to configure the monitor mode. It also describes how to switch the monitor mode between SFM and EMS.
To confirm the current monitoring mode, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# /opt/sfm/bin/sfmconfig -w -q
To switch the monitoring mode from EMS to SFM, enter the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# /opt/sfm/bin/sfmconfig -w -s
The /var/opt/sfm/log/.sfmconfig.log log file gets created in the switch script while switching modes.
./ext/stm/switch.sh: /opt/sfm/bin/CIMUtil -w /var/opt/sfm/log/.sfmconfig.log
NOTE: Starting with the HP-UX 11i v3 March 2008 release, SFM is the default monitoring mode. However, you can switch to the OnlineDiag monitoring mode. Switching the monitoring mode from SFM to EMS on HP Integrity BL860c i2, BL870c i2 & BL890c i2 Server Blades, rx2800 i2 and HP Superdome 2 servers is not available.
To check whether the SFMIndicationProvider is working properly, send a memory test event by entering the following command at the HP-UX prompt:
# /opt/sfm/bin/sfmconfig -t -m
The following output indicates that the SFMIndicationProvider is working properly:
30 Configuring indication providers
 Loading...
Loading...