Philips 74HCT165U, 74HCT165PW, 74HCT165N, 74HCT165DB, 74HC165DB Datasheet
...
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
∙The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
∙The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
∙The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
74HC/HCT165
8-bit parallel-in/serial-out shift register
Product specification |
|
December 1990 |
|||||
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Philips Semiconductors |
|
Product specification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8-bit parallel-in/serial-out shift register |
|
74HC/HCT165 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FEATURES
·Asynchronous 8-bit parallel load
·Synchronous serial input
·Output capability: standard
·ICC category: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT165 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL (LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC standard no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT165 are 8-bit parallel-load or serial-in shift registers with complementary serial outputs (Q7 and
Q7) available from the last stage. When the parallel load
(PL) input is LOW, parallel data from the D0 to
D7 inputs are loaded into the register asynchronously.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; Tamb = 25 °C; tr = tf = 6 ns
When PL is HIGH, data enters the register serially at the Ds input and shifts one place to the right
(Q0 ® Q1 ® Q2, etc.) with each positive-going clock transition. This feature allows parallel-to-serial converter expansion by tying the Q7 output to the DS input of the succeeding stage.
The clock input is a gated-OR structure which allows one input to be used as an active LOW clock enable (CE) input. The pin assignment for the CP and CE inputs is arbitrary and can be reversed for layout convenience. The
LOW-to-HIGH transition of input CE should only take place while CP HIGH for predictable operation. Either the
CP or the CE should be HIGH before the
LOW-to-HIGH transition of PL to prevent shifting the data when PL is activated.
APPLICATIONS
· Parallel-to-serial data conversion
SYMBOL |
|
|
|
|
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
|
TYPICAL |
|
UNIT |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
HC |
|
|
HCT |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
tPHL/ tPLH |
propagation delay |
CL = 15 pF; VCC = 5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
CP to Q7, |
Q |
7 |
|
16 |
|
14 |
|
ns |
||||||
|
|
PL |
to Q7, |
Q |
7 |
|
15 |
|
17 |
|
ns |
||||
|
D7 to Q7, |
Q |
7 |
|
11 |
|
11 |
|
ns |
||||||
fmax |
maximum clock frequency |
|
56 |
|
48 |
|
MHz |
||||||||
CI |
input capacitance |
|
3.5 |
|
3.5 |
|
pF |
||||||||
CPD |
power dissipation capacitance per |
notes 1 and 2 |
35 |
|
35 |
|
pF |
||||||||
|
package |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Notes
1. CPD is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PD in mW): PD = CPD ´ VCC2 ´ fi + å (CL ´ VCC2 ´ fo) where:
fi = input frequency in MHz
fo = output frequency in MHz
å (CL ´ VCC2 ´ fo) = sum of outputs
CL = output load capacitance in pF
VCC = supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI = GND to VCC
For HCT the condition is VI = GND to VCC - 1.5 V
ORDERING INFORMATION
See “74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”.
December 1990 |
2 |
Philips Semiconductors |
|
|
|
|
|
Product specification |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8-bit parallel-in/serial-out shift register |
74HC/HCT165 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
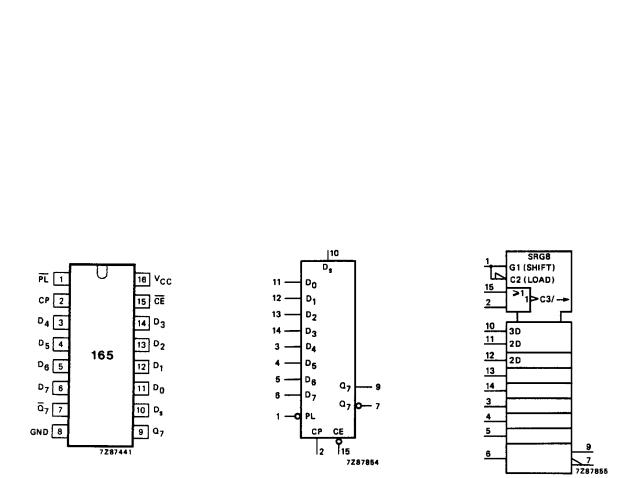
PIN DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
PIN NO. |
|
SYMBOL |
NAME AND FUNCTION |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
asynchronous parallel load input (active LOW) |
|
|
PL |
|
|
|
|||
7 |
|
|
|
complementary output from the last stage |
|
||
|
Q |
7 |
|
|
|||
9 |
|
Q7 |
serial output from the last stage |
|
|||
2 |
|
CP |
clock input (LOW-to-HIGH edge-triggered) |
|
|||
8 |
|
GND |
ground (0 V) |
|
|||
10 |
|
Ds |
serial data input |
|
|||
11, 12, 13, 14, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
|
D0 to D7 |
parallel data inputs |
|
|||
15 |
|
|
clock enable input (active LOW) |
|
|||
|
CE |
|
|
||||
16 |
|
VCC |
positive supply voltage |
|
|||
Fig.1 Pin configuration. |
|
Fig.2 Logic symbol. |
|
Fig.3 IEC logic symbol. |
|
|
|
|
|
December 1990 |
3 |
 Loading...
Loading...