Philips 74HCT85U, 74HCT85NB, 74HCT85N, 74HCT85DB, 74HCT85D Datasheet
...
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SHEET
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
∙The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
∙The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
∙The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
74HC/HCT85
4-bit magnitude comparator
Product specification |
|
December 1990 |
|||||
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Philips Semiconductors |
Product specification |
|
|
|
|
4-bit magnitude comparator |
74HC/HCT85 |
|
|
|
|
FEATURES
·Serial or parallel expansion without extra gating
·Magnitude comparison of any binary words
·Output capability: standard
·ICC category: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT85 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL (LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC standard no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT85 are 4-bit magnitude comparators that can be expanded to almost any length. They perform comparison of two 4-bit binary, BCD or other monotonic codes and present the three possible magnitude results at the outputs (QA>B, QA=B and QA<B). The 4-bit inputs are
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; Tamb = 25 °C; tr = tf = 6 ns
weighted (A0 to A3 and B0 to B3), where A3 and B3 are the most significant bits.
The operation of the “85” is described in the function table, showing all possible logic conditions. The upper part of the table describes the normal operation under all conditions that will occur in a single device or in a series expansion scheme. In the upper part of the table the three outputs are mutually exclusive. In the lower part of the table, the outputs reflect the feed forward conditions that exist in the parallel expansion scheme.
For proper compare operation the expander inputs (IA>B, IA=B and IA<B) to the least significant position must be connected as follows: IA<B = IA>B = = LOW and
IA=B = HIGH.
For words greater than 4-bits, units can be cascaded by
connecting outputs QA<B, QA>Β and QA=B to the corresponding inputs of the significant comparator.
SYMBOL |
PARAMETER |
CONDITIONS |
TYPICAL |
UNIT |
||
|
|
|||||
HC |
HCT |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tPHL/ tPLH |
propagation delay |
CL = 15 pF; VCC = 5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
An, Bn to QA>B, QA<B |
|
20 |
22 |
ns |
|
|
An, Bn to QA=B |
|
18 |
20 |
ns |
|
|
IA<B,, IA=B, IA>B to QA<B, QA>B |
|
15 |
15 |
ns |
|
|
IA=B to QA=B |
|
11 |
15 |
ns |
|
CI |
input capacitance |
|
3.5 |
3.5 |
pF |
|
CPD |
power dissipation capacitance per package |
notes 1 and 2 |
18 |
20 |
pF |
|
Notes
1. CPD is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PD in mW): PD = CPD ´ VCC2 ´ fi + å (CL ´ VCC2 ´ fo) where:
fi = input frequency in MHz
fo = output frequency in MHz
å (CL ´ VCC2 ´ fo) = sum of outputs
CL = output load capacitance in pF
VCC = supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI = GND to VCC
For HCT the condition is VI = GND to VCC - 1.5 V
ORDERING INFORMATION
See “74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”.
December 1990 |
2 |
Philips Semiconductors |
|
Product specification |
|
|
|
4-bit magnitude comparator |
74HC/HCT85 |
|
|
|
|
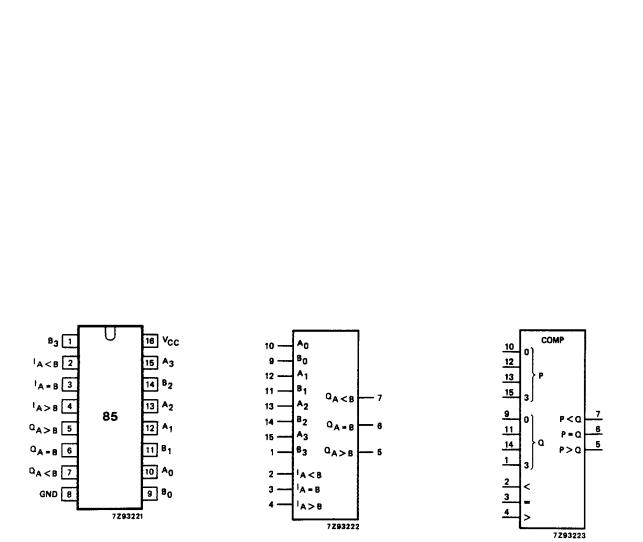
PIN DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
PIN NO. |
SYMBOL |
NAME AND FUNCTION |
|
|
|
2 |
IA<B |
A < B expansion input |
3 |
IA=B |
A = B expansion input |
4 |
IA>B |
A > B expansion input |
5 |
QA>B |
A > B output |
6 |
QA=B |
A = B output |
7 |
QA<B |
A < B output |
8 |
GND |
ground (0 V) |
9, 11, 14, 1, |
B0 to B3 |
word B inputs |
10, 12, 13, 15 |
A0 to A3 |
word A inputs |
16 |
VCC |
positive supply voltage |
Fig.1 Pin configuration. |
|
Fig.2 Logic symbol. |
|
Fig.3 IEC logic symbol. |
|
|
|
|
|
December 1990 |
3 |
 Loading...
Loading...