fanuc IO – A Maintenance Manual

GE Fanuc Automation Europe
Computer Numerical Controls
I/O Unit - Model A
Connection
Maintenance Manual
B-63813EN/03
TECHNOLOGY AND
MORE

B-61813E/03 |
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE |
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and preventing damage to the machine. Precautions are classified into Warning and Caution according to their bearing on safety. Also, supplementary information is described as a Note. Read the Warning, Caution, and Note thoroughly before attempting to use the machine.
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being injured or when there is a damage of both the user being injured and the equipment being damaged if the approved procedure is not observed.
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment being damaged, if the approved procedure is not observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary information other than Warning and Caution.
•Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s 1

B-61813E/03 |
PREFACE |
PREFACE
This manual describe the following products:
Applicable models
Name of products |
Abbreviation |
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL A |
I/O Unit-A |
FANUC I/O Unit-MODEL B |
I/O Unit-B |
Applicable CNCs
Name of products |
Abbreviation |
FANUC Power Mate-MODEL A |
Power Mate-A |
FANUC Power Mate-MODEL B |
Power Mate-B |
FANUC Power Mate-MODEL C |
Power Mate-C |
FANUC Series 0(MODEL C) |
Series 0-C |
FANUC Series 15 |
Series 15 |
FANUC Series 16 |
Series 16 |
FANUC Series 18 |
Series 18 |
FANUC SYSTEM F-MODEL D Mate |
F-D Mate |
p 1
B-61813E/03 |
|
Contents |
|
PREFACE |
|
|
|
I CONNECTIONS |
|
||
1. FANUC I/O LINK............................................................................................................. |
3 |
||
1.1 |
CONFIGURATION......................................................................................................................... |
4 |
|
1.2 |
ALLOCATION OF I/O POINTS...................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
2. I/O UNIT CONFIGURATION........................................................................................... |
8 |
||
3. INSTALLATION .............................................................................................................. |
9 |
||
3.1 |
ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS ................................................................................................ |
9 |
|
3.2 |
DESIGNING CONDITION FOR A CABINET............................................................................... |
10 |
|
3.3 |
OUTER DIMENSION OF I/O Unit................................................................................................ |
11 |
|
3.4 |
MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING MODULES ........................................................................... |
13 |
|
4. CONNECTION.............................................................................................................. |
14 |
||
4.1 |
GENERAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM......................................................................................... |
14 |
|
4.2 |
CONNECTING INPUT POWER SOURCE.................................................................................. |
15 |
|
4.3 |
GROUNDING............................................................................................................................... |
16 |
|
4.4 |
REQUIRED CURRENT ............................................................................................................... |
17 |
|
4.5 |
INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01A, AIF01B)................................................................................... |
18 |
|
4.6 |
INTERFACE MODULE (AIF02C) CONNECTION ....................................................................... |
21 |
|
4.6.1 |
Overview .............................................................................................................................................. |
21 |
|
4.6.2 |
Connection........................................................................................................................................... |
22 |
|
4.6.3 |
Setting with the DIP switch .................................................................................................................. |
24 |
|
4.7 |
CONNECTING WITH I/O MODULES.......................................................................................... |
25 |
|
5. DIGITAL INPUT / OUTPUT MODULES........................................................................ |
27 |
||
5.1 |
LIST OF MODULES..................................................................................................................... |
27 |
|
5.2 |
CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN I/O SIGNALS AND ADDRESSES IN A MODULE................ |
29 |
|
5.3 |
SPECIFICATION FOR EACH MODULE ..................................................................................... |
30 |
|
6. ANALOG INPUT MODULE (AAD04A).......................................................................... |
61 |
||
6.1 |
SPECIFICATIONS FOR ANALOG INPUT MODULE .................................................................. |
61 |
|
6.2 |
CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN INPUT SIGNALS AND ADDRESSES IN A MODULE.......... |
62 |
|
6.3 |
CONNECTING WITH ANALOG INPUT MODULE ...................................................................... |
64 |
|
7. ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE....................................................................................... |
65 |
||
7.1 |
12-BIT ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE (ADA02A)......................................................................... |
65 |
|
7.1.1 |
Specification ........................................................................................................................................ |
65 |
|
7.1.2 Correspondence between Output Signals and Addresses in a Module............................................... |
66 |
||
7.1.3 |
Connection to Analog Output Module .................................................................................................. |
67 |
|
7.2 |
FOURTEEN-BIT ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE (ADA02B)......................................................... |
68 |
|
7.2.1 |
Specification ........................................................................................................................................ |
68 |
|
7.2.2 |
Correspondence between Output Signals and Addresses in the Module............................................ |
68 |
|
7.2.3 Connection between the Analog Output Module and Load.................................................................. |
69 |
||
c 1
Contents |
B-61813E/03 |
8. HIGH SPEED COUNTER MODULE............................................................................. |
70 |
||
8.1 |
OUTLINE OF HIGH SPEED COUNTER MODULE..................................................................... |
70 |
|
8.2 |
SPECIFICATIONS OF HIGH SPEED COUNTER MODULE....................................................... |
72 |
|
8.2.1 |
Pulse counter....................................................................................................................................... |
72 |
|
8.2.2 |
Comparison function............................................................................................................................ |
72 |
|
8.2.3 |
Pulse Interface..................................................................................................................................... |
74 |
|
8.2.4 |
External contact input .......................................................................................................................... |
76 |
|
8.2.5 |
External contact output ........................................................................................................................ |
76 |
|
8.2.6 |
Marker processing ............................................................................................................................... |
76 |
|
8.2.7 |
LED Indicators ..................................................................................................................................... |
77 |
|
8.3 |
PMC INTERFACE........................................................................................................................ |
79 |
|
8.3.1 Mode A................................................................................................................................................. |
79 |
||
8.3.2 Mode B................................................................................................................................................. |
81 |
||
8.3.3 |
Details of PMC interface signals .......................................................................................................... |
83 |
|
8.4 |
TOTAL CONNECTION OF HIGH SPEED COUNTER MODULE................................................ |
86 |
|
8.4.1 |
Connection diagram............................................................................................................................. |
86 |
|
8.4.2 |
Connector signal list ............................................................................................................................ |
87 |
|
8.5 |
CONNECTION WITH PULSE GENERATOR.............................................................................. |
88 |
|
8.5.1 Use of phase A and B pulses............................................................................................................... |
88 |
||
8.5.2 |
Use of positive/negative pulses ........................................................................................................... |
89 |
|
8.6 |
CONNECTION WITH POWER MAGNETICS CABINET ............................................................ |
90 |
|
8.7 |
I/O SIGNALS CONVENTIONS .................................................................................................... |
91 |
|
8.7.1 |
Solid state relay output signals (OUT0 to OUT7)................................................................................. |
91 |
|
8.7.2 DC input signals (ME and CSP)........................................................................................................... |
92 |
||
8.8 |
SUPPLEMENT............................................................................................................................. |
93 |
|
8.8.1 |
Configuration of mode A ...................................................................................................................... |
93 |
|
8.8.2 |
Counter presetting and counting.......................................................................................................... |
94 |
|
8.8.3 |
Setting data.......................................................................................................................................... |
95 |
|
8.8.4 |
Reading data........................................................................................................................................ |
97 |
|
8.8.5 |
Miscellaneous information ................................................................................................................... |
98 |
|
9. TEMPERATURE INPUT MODULE............................................................................... |
99 |
||
9.1 |
OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................................. |
99 |
|
9.2 |
TEMPERATURE INPUT MODULE SPECIFICATION............................................................... |
100 |
|
9.3 |
PMC INTERFACE...................................................................................................................... |
101 |
|
9.3.1 PMC I/O area ..................................................................................................................................... |
101 |
||
9.3.2 Measurement mode ........................................................................................................................... |
102 |
||
9.3.3 |
Details of output signals (PMC → temperature module).................................................................... |
102 |
|
9.3.4 |
Details of input signals (temperature module → PMC)...................................................................... |
104 |
|
9.4 |
COMPLETE CONNECTION OF TEMPERATURE INPUT MODULE ....................................... |
107 |
|
9.4.1 |
Temperature input module connection diagram ................................................................................ |
107 |
|
9.4.2 |
Connector signal lists......................................................................................................................... |
108 |
|
9.4.3 |
Terminal board unit connection diagram............................................................................................ |
109 |
|
9.5 |
TIMING CHARTS....................................................................................................................... |
110 |
|
9.6 |
MEASUREMENT EXAMPLES................................................................................................... |
111 |
|
9.7 |
TERMINAL BOARD UNIT DIMENSIONS.................................................................................. |
118 |
|
10. OPTICAL I/O LINK ADAPTER.................................................................................. |
119 |
||
10.1 |
EXTERNAL DIMENSION OF OPTICAL I/O LINK ................................................................... |
120 |
|
10.2 |
WEIGHT OF OPTICAL I/O LINK ............................................................................................. |
120 |
|
10.3 |
CONNECTION OF OPTICAL I/O LINK.................................................................................... |
121 |
|
10.4 |
POWER SOURCE OF OPTICAL I/O LINK ADAPTER............................................................ |
121 |
|
10.5 |
INSTALLATION CONDITIONS OF OPTICAL I/O LINK ADAPTER ........................................ |
122 |
|
10.6 |
OPTICAL FIBER CABLE ......................................................................................................... |
122 |
|
10.6.1 |
External view of optical fiber cable................................................................................................... |
122 |
|
10.6.2 |
Notice of optical fiber cable handling ............................................................................................... |
123 |
|
10.6.3 |
Optical fiber cable clamping method................................................................................................ |
124 |
|
10.6.4 |
Relay using an optical fiber adapter................................................................................................. |
125 |
|
c 2
B-61813E/03 |
|
|
Contents |
10.6.5 |
Maximum transmission distance by optical fiber cable .................................................................... |
125 |
|
11. I/O LINK DUMMY UNIT ............................................................................................ |
126 |
||
11.1 |
OVERVIEW.............................................................................................................................. |
126 |
|
11.2 |
EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS ...................................................................................................... |
126 |
|
11.3 |
LED INDICATORS................................................................................................................... |
127 |
|
11.4 |
WEIGHT................................................................................................................................... |
127 |
|
11.5 |
POWER REQUIREMENTS ..................................................................................................... |
127 |
|
11.6 |
INSTALLATION CONDITIONS................................................................................................ |
127 |
|
11.7 |
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS..................................................................................................... |
128 |
|
11.7.1 When not connecting FANUC I/O Link dummy units in series ........................................................ |
128 |
||
11.7.2 Connecting FANUC I/O Link dummy units in series ........................................................................ |
129 |
||
11.7.3 |
Grounding ........................................................................................................................................ |
129 |
|
11.7.4 K3X cable......................................................................................................................................... |
130 |
||
12. SAFETY FOR USING AC ......................................................................................... |
131 |
||
12.1 |
INSTALLATION ENVIRONMENT............................................................................................ |
132 |
|
12.1.1 |
Installation Category (Overvoltage Category).................................................................................. |
132 |
|
12.1.2 |
Pollution Degree .............................................................................................................................. |
132 |
|
II MAINTENANCE
1. OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................ |
135 |
|
1.1 |
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................................... |
135 |
1.2 |
I/O UNIT-A CONFIGURATION.................................................................................................. |
136 |
1.3 |
BLOCK DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................................... |
137 |
1.4 |
LIST OF UNITS.......................................................................................................................... |
138 |
2. INDICATION ............................................................................................................... |
140 |
||
2.1 |
INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01A) LEDS .................................................................................... |
140 |
|
2.2 |
INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01B) LEDS .................................................................................... |
144 |
|
2.3 |
INTERFACE MODULE (AIF02C) LED INDICATORS ............................................................... |
146 |
|
2.3.1 |
PWR indicator.................................................................................................................................... |
146 |
|
2.3.2 |
LNK indicators.................................................................................................................................... |
146 |
|
2.3.3 |
ER indicators...................................................................................................................................... |
146 |
|
2.3.4 |
LED indicators.................................................................................................................................... |
146 |
|
2.3.5 |
M/S indicator ...................................................................................................................................... |
147 |
|
2.3.6 |
No. Indicators..................................................................................................................................... |
148 |
|
2.4 |
LED INDICATORS ON THE INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES |
|
|
|
(HAVING 16 OR FEWER INPUT/OUTPUT POINTS) ............................................................... |
148 |
|
3. FUSES........................................................................................................................ |
|
149 |
|
4. REMOVING PC BOARDS .......................................................................................... |
150 |
||
4.1 |
HOW TO REMOVE TERMINAL BOARD-TYPE I/O MODULE PC BOARDS ........................... |
150 |
|
4.2 |
HOW TO REMOVE INTERFACE AND CONNECTOR-TYPE I/O MODULE PC BOARDS...... |
152 |
|
c 3
I. CONNECTIONS

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
1. FANUC I/O LINK |
1 FANUC I/O Link
I/O Link is a serial interface with a purpose to transfer I/O signals (bit data) betweenCNC, cell controller, the I/O Unit-A, the Power Mate-A, etc. at high speed.
3

1. FANUC I/O LINK |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
1.1 CONFIGURATION
1)The FANUC I/O Link is made up of one master and a number of slaves.
Master : Series 0-C, Series 15/16/18/20/21, Series 15i/16i/18i/20i/21i, Power Mate-D/H, Power Mate i- D/H, F-D Mate
Slave : I/O Unit-A, Power Mate operator's panel connection unit, Series 0-C
2)Up to 16 groups of slaves can be connected with a single I/O Link. Number of slaves per one group is as follows.
I/O Unit-A : Up to 4 units (i.e.4 bases) but when Master is CNC and Pwer Mate up to 2 units.
Power Mate : |
1 |
Operator's panel connection unit : 1
Series 0-C, : |
1 |
3)Any slave can be connected with any group. However, different types of slaves can not be connected with a single group.
4

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
1. FANUC I/O LINK |
1.2 ALLOCATION OF I/O POINTS
I/O Link has 1024 input points and 1024 output points as viewed from the master.
I/O data is periodically transferred between the master and slaves by allotting these I/O points to each slave.
Each slave occupies specified number of I/O points. Sum of I/O points occupied by all slaves in an I/O Link is restricted as follows:
Number of input points 1024 Number of output points 1024
Number of actual I/O points may differ from that of the occupied ones. How to determine the number of I/O points to be allotted to each slave and restrictions for allocation are shown in the followings.
(For the allocation method for I/O points, refer to the PMC PROGRAMMING MANUAL.)
Number of actual and occupied I/O points are shown in Table 1.2.
Table 1.2
Kind of slave |
|
Actual I/O points |
Occupied I/O point |
Remarks |
|||
|
|
|
Input |
Output |
Input |
Output |
|
|
|
|
points |
points |
points |
points |
|
I/O Unit-A |
|
Each |
Each |
Refer 3 of next page |
|
||
|
|
|
input |
output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
moudle |
module |
|
|
|
|
|
|
points |
points |
|
|
|
Operator's |
|
A |
96 |
64 |
128 |
64 |
|
panel conne- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
64 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
ction unit |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Mate |
|
32 |
32 |
32 |
32 |
Either I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
point |
|
|
|
64 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
can be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
allocated. |
Series 0-C |
|
32 |
32 |
32 |
32 |
Either I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
point |
|
|
|
64 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
can be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
allocated. |
5

1. FANUC I/O LINK |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
1)Sum the numbers of the occupied I/O points in Table 1 for all slaves connected with a single I/O Link. The sum must satisfy the following restriction :
Number of input points 1024 (per one I/O Link)
Number of output points 1024 (per one I/O Link)
2)Number of the occupied I/O points per one group must satisfy the following restriction :
Number of input points 256 (per one group)
Number of output points 256 (per one group)
3)Determine the number of I/O points for the I/O Unit-A using the
following. |
|
|
[Output points] |
|
|
Sum of the actual output |
Occupied output |
|
points in a group |
|
points |
0 to 32 |
Þ |
32 points |
40 to 64 |
Þ |
64 points |
72 to 128 |
Þ |
128 points |
136 to 256 |
Þ |
256 points |
NOTE
Count AOA05E as 8 points AOA12F as 16 points.
[Input points] |
|
|
Sum of the actual output |
Occupied output |
|
points in a group |
|
points |
0 to 32 |
Þ |
32 points |
40 to 64 |
Þ |
64 points |
72 to 128 |
Þ |
128 points |
136 to 256 |
Þ |
256 points |
However, as result of the calculation above, when the number of input points is not larger than that of the output points in a single group, the number of input points is assumed to be equal to that of the output points.
Example 1 : |
When the following modules are used in the group |
|||
|
No. 0. |
|
|
|
|
AOD32C |
3 |
AID32A |
5 |
|
AOA12F |
2 |
AIA16G |
3 |
|
[Output points] |
|
|
|
|
32 × 3 + 16 × 2 = 128 Þ 128 points |
|||
|
[Input points] |
|
|
|
|
32 × 5 + 16 × 3 = 208 Þ 256 points |
|||
Example 2: |
When the following modules are used in the group |
|||
|
No.2 |
|
|
|
|
AOD16C |
7 |
AID16C |
4 |
|
AOA05E |
9 |
AIA16G |
3 |
[Output points]
16 ×7 + 8 ×9 = 184 Þ 256 points [Input points]
16 ×4 + 16×3 = 112 Þ 128 points
6
B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
1. FANUC I/O LINK |
In this case, as the number of input points is not larger than that of the output points, the number of input points is assumed to be equal to that of the output points, in other words, 256 points.
7

2. I/O UNIT CONFIGURATION |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
2 I/O UNIT CONFIGURATION
5-slot horizontal base unit (ABU05A)
10-slot horizontal base unit (ABU10A)
5-slot vertical base unit (ABU05B)
10-slot vertical base unit (ABU10B)
NOTE
I/F :Interface module (AIF01A, AIF01B, or AIF02C) 1 to 10: I/O modules
8

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
3. INSTALLATION |
3 INSTALLATION
3.1 ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
Install the cabinet containing the I/O Unit-A where the following conditions are satisfied.
1)Surrounding temperature During operation: 0 to 45
During preservation and transportation: -20 to 60
2)Temperature changing rate: Max. 1.1 /min
3)Humidity
Normal condition: 75% or less (relative humidity) Short period (one month or shorter): Max.95%
4)Vibration
During operation: 0.5G or less
5)Atmosphere
When the unit is used in areas with high density of dust, cutting fluid ororganic solvent,the user should consult FANUC.
9

3. INSTALLATION |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
3.2 DESIGNING CONDITION FOR A CABINET
When designing a cabinet to contain the I/O Unit-A, take the same care as taken for the cabinet containing the CNC control unit and other units. For details, refer to the CNC CONNECTING MANUAL.
In addition, when mounting the I/O unit,conform to the followings in view of maintenance, environmental durability, noise resistance and the like.
1)In order to ventilate inside the module well, mount the I/O unit in the direction shown in the figure below.
Upside
Downside
2)Mount the I/O unit vertically apart from other units by 100 mm or more taking ventilation and wiring into consideration.
3)Do not put equipments which generate a large amount of heat under the I/O unit.
4)Low-level signals are transferred through the signal cables K1X and K2X.(For these cables,see the general connection diagram.) Lay out these cables apart from the wires for AC power source and the I/O wires of the I/O module by 100 mm or more.
5)Make sure that there is no protruding portion such as a screw on the mounting surface of the I/O unit.
6)Heat values of I/O unit are listed in Table 3.3
10

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
3. INSTALLATION |
3.3 OUTER DIMENSION OF I/O Unit
Horizontal base units (ABU05A and ABU10A)
Hole for an M4 screw (4 places) |
Hole for an M4 screw (4 places) |
Vertical base units (ABU05B and ABU10B)
Hole for an M2 screw (4 places) |
Hole for an M4 screw (4 places) |
11

3. INSTALLATION |
CONNECTIONS |
|
B-61813E/03 |
||
|
|
Table 3.3 Heat value of each module |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Module name |
Basic heat |
Heat value per |
|
|
|
|
value (W) |
1 I/O point (W) |
|
|
|
AIF01A |
1.2 |
- |
|
*1 |
|
AIF01B |
1.2 |
- |
|
|
AID32A1 |
1.2 |
0.23 |
|
|
*2 |
|
AID32B1 |
1.2 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
AID32H1 |
1.2 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
AID16C |
0.1 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
AID16K |
0.1 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
AID16D |
0.1 |
0.21 |
|
*3 |
|
AID16L |
0.1 |
0.21 |
|
|
AID32E1 |
0.1 |
0.23 |
|
|
*4 |
|
AID32E2 |
0.1 |
0.23 |
|
|
AID32F1 |
0.1 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
|
AID32F2 |
0.1 |
0.23 |
|
*5 |
|
AIA16G |
0.1 |
0.21 |
|
|
AOD32A1 |
0.3 |
- |
|
|
|
|
AOD08C |
0.1 |
0.04+0.4×IL2 |
|
|
|
AOD08D |
0.1 |
0.04+0.6×IL2 |
|
|
|
AOD16C |
0.1 |
0.04+1.4×IL2 |
|
*6 |
|
AOD16D |
0.1 |
0.04+1.4×IL2 |
|
|
AOD32C1 |
0.1 |
0.01+0.8×IL2 |
|
|
*7 |
|
AOD32C2 |
0.1 |
0.01+0.8×IL2 |
|
|
AOD32D1 |
0.1 |
0.01+0.8×IL2 |
|
|
|
|
AOD32D2 |
0.1 |
0.01+0.8×IL2 |
|
|
|
AOA05E |
0.1 |
0.13+1.5×IL |
|
|
|
AOA08E |
0.1 |
0.13+1.5×IL |
|
|
|
AOA12F |
0.1 |
0.11+1.5×IL |
|
|
|
AOR08G |
0.1 |
0.3+0.1×IL2 |
|
|
|
AOR16G |
0.1 |
0.3+0.1×IL2 |
|
|
|
AOR16H2 |
0.1 |
0.3+0.1×IL2 |
|
|
|
AAD04A |
3.1 |
- |
|
|
|
ADA02A |
3.1 |
- |
|
|
|
ADA02B |
3.1 |
- |
|
|
|
ACT01A |
4.1 |
- |
|
|
|
ATI04A |
4.0 |
- |
|
|
|
ATI04B |
4.0 |
- |
|
•Total `Heat value per 1 I/O point' for simultaneous ON points plus `Basic heat value' is the heat value of the module.
•IL : Load current of output
•A D32
D32  1 of “*1 to *7" is the same module as former A
1 of “*1 to *7" is the same module as former A
 D32
D32  .
.
(Example : AID32E1 is equal to former AID32E.)
12

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
3. INSTALLATION |
3.4 MOUNTING AND DISMOUNTING MODULES
Interface modules and various types of I/O modules can be mounted to and dismounted from the base unit easily as shown below.
Mounting
Hang the hook at the top of the module on the groove in the upper side of the base unit, and make the connector of the module engage with that of the base unit. Push the module in the lower groove of the base unit till the stopper in the lower side of the module stops.
Dismounting
Release the stopper by pushing the lever at the bottom of the module, and then push the module upwards.
13
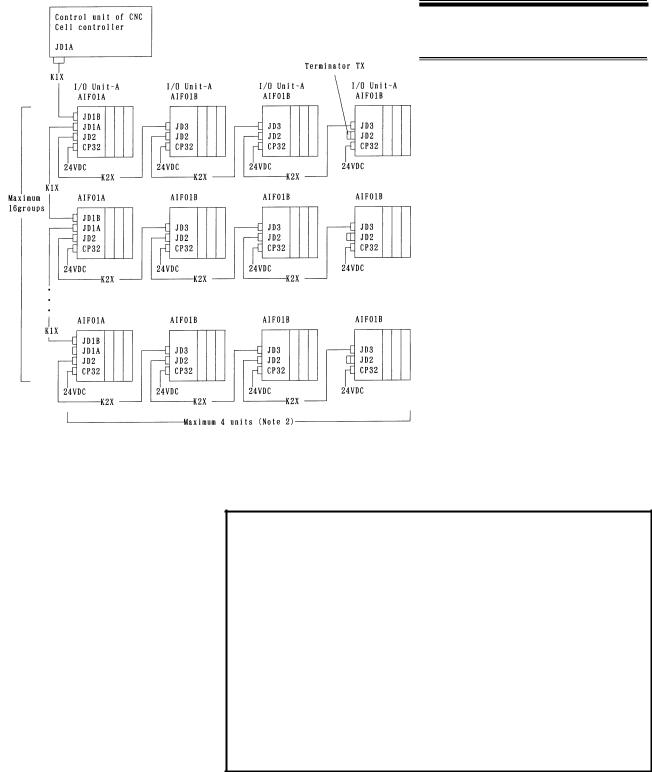
4. CONNECTION |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
4 CONNECTION
4.1 GENERAL CONNECTION DIAGRAM
NOTE
1Number of I/O Units and connecting method are restricted depending on the allocation of the I/O points. Refer to the section 1.2,"Allocation of I/O points."
2The number of I/O units per group is limited to 2 when the master equipment is the CNC.
3Cable K1X can be an optical fiber cable by using the optical I/O link adapter.
See chapter 10.
4 Terminator TX is required for connector JD2 of the AIF01B that is the last unit to be connected in the group. The terminator is not required when the
AIF01B is not used.
14

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
4. CONNECTION |
4.2 CONNECTING INPUT POWER SOURCE
Connect the following power source with the connector CP32 of the interface module (AIF01A, AIF01B, or AIF02C).
•Voltage: 24VDC ±10%
•Current: Determine from Table 4.4
1 |
+24V |
2 |
GND |
3 |
|
BURNDY JAPAN Tripolur connector (Brown) Hoursing : SMS3PNS-5 A63L-0001-0202#3HN Contact : RC16M-SCT3 A63L-0001-0226
24VDC
NOTE
Turn ON the power for the I/O unit just when or before the power for the CNC or the cell controller is turned
ON. When the CNC or cell controller power is turned OFF,make sure to turn the power to the I/O unit OFF as well. If the power is not turned on and off according to the above procedure, an error occurs in the CNC or the controller, or the I/O unit is not normally connected to the power.
Power for the master device
Power for the I/O unit
t > 500 ms (Turn ON of the power for I/O unit can be late 500 ms or less.)
15

4. CONNECTION |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
4.3 GROUNDING
Connect the grounding terminal of the base unit (ABU05A, ABU05B,
ABU10A, or ABU10B) to ground.
(1)Horizontal type base unit
Use a wire of 2 mm2 or more for grounding.
(2)Vertical type base unit
(a) For metal case
Grounding terminal (M3 screw terminal)
M4 hole for gronding
NOTE
Connect the grounding terminal to the grounding hole portion.
(b) For plastic case
Grounding terminal (M3 screw terminal)
(2)When the cable K1X ( See overall connection figure in section
4.1) runs between different cabinets, make sure to connect the cabinets with a wire more than 5.5 mm2.
16

B-61813E/03 CONNECTIONS 4. CONNECTION
4.4 |
REQUIRED CURRENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 4.4 |
Required current of each module |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Module name |
Required current (mA) of+24V |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
B |
|
|
|
AIF01A |
50 |
|
|
|
|
AIF01B |
50 |
|
|
|
|
AIF0K |
50 |
|
|
|
|
AID32A1 |
20+0.5×n |
3.0+7.5×n |
|
|
|
AID32B1 |
20+0.5×n |
3.0+7.5×n |
|
|
|
AID32H1 |
20+0.5×n |
3.0+7.5×n |
|
|
|
AID16C |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID16K |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID16D |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID16L |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID32E1 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID32E2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID32F1 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AID32F2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
AIA16G |
5+1.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD32A1 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
AOD08C |
5+2×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD08D |
5+2×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD16C |
5+2×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD16D |
5+2×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD32C1 |
5+0.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD32C2 |
5+0.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD32D1 |
5+0.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOD32D2 |
5+0.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOA05E |
5+5.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOA08E |
5+5.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOA12F |
5+4.5×n |
|
|
|
|
AOR08G |
5 |
10×n |
|
|
|
AOR16G |
5 |
10×n |
|
|
|
AOR16H2 |
5 |
10×n |
|
|
|
AAD04A |
5 |
130 |
|
|
|
ADA02A |
6 |
120 |
|
|
|
ADA04B |
5 |
130 |
|
|
|
ACT01A |
170+0.3×α |
|
|
|
|
ATI04A |
62.5 |
100 |
|
|
|
ATI04B |
62.5 |
100 |
|
n:Number of the input and output points (for each module) which turn ON simultaneously
α: +5-V current (mA) output to the outside
•Add the sums of the columns A and B for the modules to be used. The sum is the required current.(Unit:mA)
•For each base unit, keep the sum of column A and the sum of column B to within 500 mA and 1,500 mA, respectively.
17

4. CONNECTION |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
4.5 INTERFACE MODULE (AIF01A, AIF01B)
Details of the cables K1X,K2X and the terminator shown in the general connection diagram are as follows.
1)Cable K1X
a)Make sure to use twisted pair wires for signal SIN and *SIN, and signals SOUT and *SOUT.
i)Reconnecnded cable material: A66L-0001-0284#10P (twisted pair/shielded)
ii)Shielding wires should be connected with the grounding plate of the cabinet at the JD1A side using a cable clamp. (Refer to the CONNECTING MANUAL for the CNC and the cell controller.)
iii)Maximum cable length: 10 m
iv)Make sure not to connect to the connector spare pins.
v)In the following cases, make sure to use an optical I/O link adapter and an optical fiber cable.(See chapter 10)
•When the cable is more than 10 meters long.
•When the cable runs between different cabinets and there is no appropriate ground wire between the cabinets.
•When there is concern that the cable is influenced by strong noise.
vi)When an optical I/O link adapter is used: Cable to be used between the interface module (AIF01A) and the optical I/O link adapter is dissimilar to this cable. (See chapter 10.)
18

B-61813E/03 |
CONNECTIONS |
4. CONNECTION |
2)Cable K2X
AIF01A or AIF01B |
|
AIF01B |
|
|
|
•Connect the signals with a same name.
•Make sure to use twisted pair wires for the following signals: S1 and * S1, S2 and *S2, S3 and *S3
S4 and * S4, S5 and *S5, S6 and *S6
•Do not connect the pins No.10, No.19 and No.20 as they are used internally.
•Recommended cable material: A66L - 0001 - 0284#10P (twisted pair/shielded)
•Maximum cable length: 2m
19

4. CONNECTION |
CONNECTIONS |
B-61813E/03 |
3)Terminator TX
Short-circuit
•Terminate the connector JD2 of the last AIF01B in a single group with the terminator. The connector need not be terminated when the AIF01B is not used.
•Short-circuit the TRM1s, the TRM2s and the TRM 3s one another respectively in a manner that a TRM1 is with another TRM1 and so on.
20
 Loading...
Loading...