D-Link DSL-G604T User Manual 2


DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router |
|
|
Table of Contents |
BEFORE YOU START.................................................................................... |
4 |
Installation Overview......................................................................................................................... |
4 |
Setup Wizard...................................................................................................................................... |
4 |
Packing List........................................................................................................................................ |
4 |
Installation Notes .............................................................................................................................. |
5 |
INTRODUCTION.......................................................................................... |
8 |
Router Description and Operation...................................................................................................... |
8 |
Router Features ................................................................................................................................. |
9 |
802.11g Wireless ............................................................................................................................. |
10 |
Installation Considerations ............................................................................................................... |
11 |
Front Panel Display .......................................................................................................................... |
12 |
Rear Panel Connections ................................................................................................................... |
13 |
Reset ............................................................................................................................................ |
14 |
HARDWARE INSTALLATION...................................................................... |
15 |
Power on Router .............................................................................................................................. |
15 |
Factory Reset Button........................................................................................................................ |
15 |
Network Connections ....................................................................................................................... |
16 |
BASIC ROUTER CONFIGURATION ............................................................. |
17 |
Computer IP Settings ...................................................................................................................... |
17 |
Access the Configuration Manager ................................................................................................... |
18 |
Login to Home Page ........................................................................................................................ |
18 |
Configure the Router........................................................................................................................ |
19 |
Wizard ............................................................................................................................................. |
20 |
Wireless ........................................................................................................................................... |
30 |
WEP.............................................................................................................................................. |
31 |
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) ........................................................................................................... |
32 |
802.1x .......................................................................................................................................... |
33 |
WAN................................................................................................................................................. |
34 |
PPPoE/PPPoA.................................................................................................................................. |
34 |
Dynamic IP Address ........................................................................................................................ |
37 |
Static IP Address ............................................................................................................................ |
40 |
Bridge Mode................................................................................................................................... |
43 |
LAN .................................................................................................................................................. |
47 |
DHCP................................................................................................................................................ |
48 |
DNS.................................................................................................................................................. |
51 |
Dynamic DNS ................................................................................................................................... |
52 |
Save Settings and Reboot ................................................................................................................ |
53 |
Multiple Virtual Connections ............................................................................................................ |
54 |
ADVANCED ROUTER MANAGEMENT .......................................................... |
56 |
UPnP ................................................................................................................................................ |
57 |
Virtual Server................................................................................................................................... |
58 |
Custom Forwarding Rules................................................................................................................. |
60 |
LAN Clients....................................................................................................................................... |
61 |
SNMP ............................................................................................................................................... |
62 |
Filters............................................................................................................................................... |
63 |
Bridge Filters ................................................................................................................................... |
65 |
Static Routing .................................................................................................................................. |
66 |
Page 2 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
DMZ.................................................................................................................................................. |
67 |
Parental Control............................................................................................................................... |
68 |
URL Blocking.................................................................................................................................. |
69 |
Domain Blocking............................................................................................................................. |
69 |
Firewall............................................................................................................................................ |
70 |
RIP................................................................................................................................................... |
71 |
ADSL ................................................................................................................................................ |
72 |
ATM VCC........................................................................................................................................... |
73 |
QoS .................................................................................................................................................. |
74 |
Wireless Management...................................................................................................................... |
80 |
Access List..................................................................................................................................... |
80 |
Associated Stations......................................................................................................................... |
81 |
Multiple SSID ................................................................................................................................. |
82 |
Wireless Performance ...................................................................................................................... |
83 |
TOOLS ...................................................................................................... |
85 |
Admin .............................................................................................................................................. |
86 |
Change System Password ................................................................................................................ |
86 |
Remote Web Management and Remote Telnet Access .......................................................................... |
87 |
Time................................................................................................................................................. |
88 |
Remote Log...................................................................................................................................... |
89 |
System............................................................................................................................................. |
90 |
Save or Load Configuration File......................................................................................................... |
90 |
Save Settings and Reboot System..................................................................................................... |
90 |
Restore Factory Default Settings ....................................................................................................... |
90 |
Force the Wireless LAN to Restart ..................................................................................................... |
90 |
Firmware.......................................................................................................................................... |
91 |
Miscellaneous................................................................................................................................... |
92 |
Ping Test ....................................................................................................................................... |
92 |
Test.................................................................................................................................................. |
93 |
STATUS..................................................................................................... |
94 |
Device Info ...................................................................................................................................... |
94 |
DHCP Clients .................................................................................................................................... |
95 |
Log................................................................................................................................................... |
96 |
Statistics .......................................................................................................................................... |
97 |
ADSL Status ..................................................................................................................................... |
98 |
Help ................................................................................................................................................. |
99 |
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS................................................................. |
100 |
CONFIGURING IP SETTINGS ON YOUR COMPUTER ................................. |
103 |
LOW PASS FILTERS FOR DSL .................................................................. |
108 |
Page 3 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
About This User Guide
This user’s guide provides instructions on how to install the DSL-G604T ADSL 2+ Router and use it to provide Internet access for an Ethernet/Wireless network or single computer.
If you are using a computer with a functioning Ethernet port, the quickest and easiest way to set up the DSLG604T is to follow the instructions provided in the Quick Installation Guide (QIG).
Before You Start
Please read and make sure you understand all the prerequisites for proper installation of your new Router. Have all the necessary information and equipment on hand before beginning the installation.
Installation Overview
The procedure to install the Router can be described in general terms in the following steps:
1.Gather information and equipment needed to install the device. Before you begin the actual installation make sure you have all the necessary information and equipment.
2.Install the hardware, connect the cables to the device, and connect the power adapter.
3.Check the IP settings on your computer and change them if necessary so the computer can access the webbased software built into the Router.
4.Use the web-based management software to configure the device to suit the requirements of your ADSL service and requirements of your local network.
Setup Wizard
Many users will be able to configure all the settings necessary to use the DSL-G604T with the Setup Wizard. For ADSL connections that use PPPoE or PPPoA connections, the simplest way to set up the DSL-G604T is to use the Setup Wizard to configure the Internet connection. Once you access the web interface used to configure the device, just launch the Setup Wizard to configure your Internet connection.
Packing List
Open the shipping carton and carefully remove all items. Make sure that you have the items listed here.
One DSL-G604T GENERATION II ADSL2+ Ethernet Router
One CD-ROM containing the User’s Guide, Quick Installation Guide and D-Link Click’n Connect Utility One twisted-pair telephone cable used for ADSL connection
One straight-through Ethernet cable
One DC power adapter suitable for your electrical service One Quick Installation Guide
Page 4 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Installation Notes
In order to establish a connection to the Internet it will be necessary to provide information to the Router that will be stored in its memory. For some users, only their account information (Username and Password) is required. For others, various parameters that control and define the Internet connection will be required. You can print out the two pages below and use the tables to list this information. This way you have a hard copy of all the information needed to setup the Router. If it is necessary to reconfigure the device, all the necessary information can be easily accessed. Be sure to keep this information safe and private.
Low Pass Filters
Since ADSL and telephone services share the same copper wiring to carry their respective signals, a filtering mechanism may be necessary to avoid mutual interference. A low pass filter device can be installed for each telephone that shares the line with the ADSL line. These filters are easy to install passive devices that connect to the ADSL device and/or telephone using standard telephone cable. Ask your service provider for more information about the use of low pass filters with your installation.
Operating Systems
The DSL-G604T uses an HTML-based web interface for setup and management. The web configuration manager may be accessed using any operating system capable of running web browser software, including Windows 98 SE, Windows ME, Windows 2000, and Windows XP. The D-Link Click’n Connect Utility will only work with a Windows operating system.
Web Browser
Any common web browser can be used to configure the Router using the web configuration management software. The program is designed to work best with more recently released browsers such as Microsoft Internet Explorer® version 6.0, Netscape Navigator® version 6.2.3, or later versions. The web browser must have JavaScript enabled. JavaScript is enabled by default on many browsers. Make sure JavaScript has not been disabled by other software (such as virus protection or web user security packages) that may be running on your computer.
Ethernet Port (NIC Adapter)
Any computer that uses the Router must be able to connect to it through the Ethernet port on the Router. The easiest method of installation is via the Ethernet connection and therefore requires that your computer be equipped with an Ethernet port as well. Most notebook computers are now sold with an Ethernet port already installed. Likewise, most fully assembled desktop computers come with an Ethernet NIC adapter as standard equipment. If your computer does not have an Ethernet port, you must install an Ethernet NIC adapter before you can use the Router. If you must install an adapter, follow the installation instructions that come with the Ethernet NIC adapter.
Additional Software
For a bridged connection, the information needed to make and maintain the Internet connection is stored on another computer or gateway device using PPP client or similar third party client software, not in the Router itself.
If your ADSL service is delivered through a PPPoE, PPPoA or Static IP connection, the information needed to establish and maintain the Internet connection can be stored in the Router. In this case, it is not necessary to install software on your computer. It may however be necessary to change some settings in the device, including account information used to identify and verify the connection.
Page 5 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
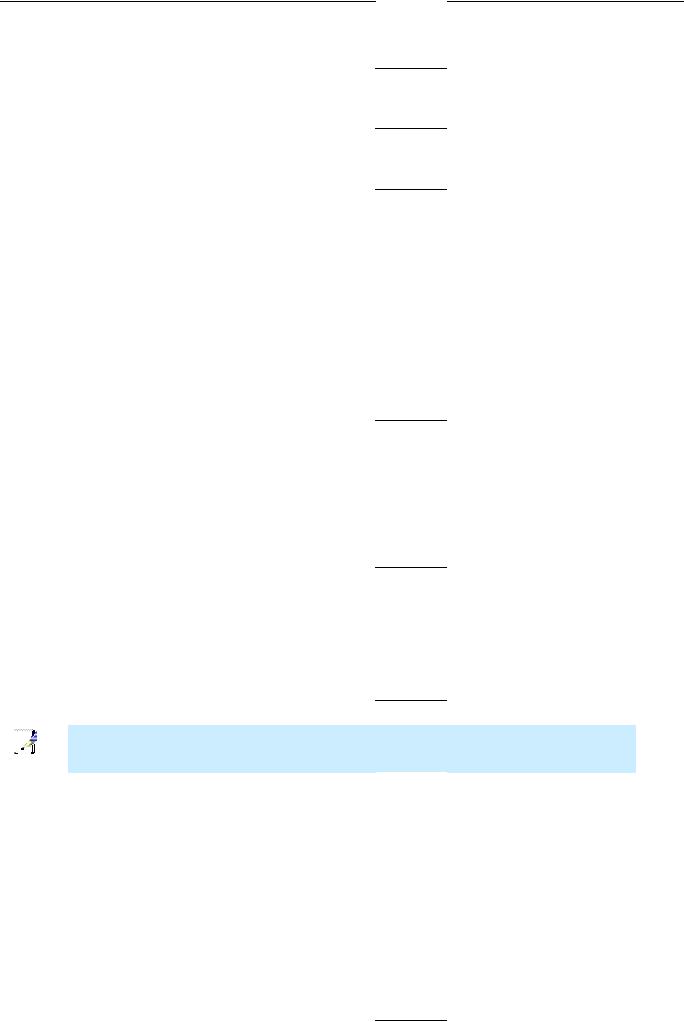
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Mo dem Router
In formatio n you will need fr om your ADSL service provider:
|
|
|
|
|
Us ername |
Thi s is the Usern ame used to log on to your ADSL service provider’s |
Record info here |
||
|
net work. It is co mmonly in the form − user@ isp.com.au Your ADSL |
|
||
|
ser vice provider uses this to identify your account. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Pa ssword |
Thi s is the Password used, in conjunction with the Username above, |
|
||
|
to l og on to your ADSL service provider’s network. This is used to |
|
||
|
verify the identity of your account. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
WA N Setting / |
These settings de scribe the me thod your AD SL service pr ovider uses |
|
||
Co nnection Ty pe |
to transport data between the Internet and your computer. Most |
|
||
users will use the default settin gs. You may need to specify one of |
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
the following WAN Setting and Connection T ype configura tions |
|
||
|
(Connection Type settings listed in parenthesis): |
|
||
|
PPPoE/PPoA (PPP oE LLC, PPPoA LLC or PPP oA VC-Mux) |
|
||
|
Brid ge Mode (14 83 Bridged IP LLC or 1483 Bridged IP VC -Mux) |
|
||
|
Sta tic IP Address (Bridged IP LLC, 1483 Bridged IP VC-Mu x, 1483 |
|
||
|
Rou ted IP LLC, 1483 Routed IP VC-Mux or IPoA) |
|
||
|
Dyn amic IP Addr ess (1483 Brid ged IP LLC or 1483 Bridged IP VC- |
|
||
|
Mu x) |
|
||
|
Default = PPPoE/ PPPoA (PPPo E LLC) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
VPI |
Mos t users will n ot be required to change this setting. Th e Virtual |
|
||
|
Pat h Identifier (VPI) is used in conjunction w ith the Virtua l Channel |
|
||
|
Identifier (VCI) t o identify the data path between your AD SL service |
|
||
|
provider’s networ k and your co mputer. If you are setting up the |
|
||
|
Rou ter for multiple virtual conn ections, you will need to c onfigure |
|
||
|
the VPI and VCI as instructed by your ADSL service provid er for the |
|
||
|
additional connec tions. This setting can be changed in the WAN |
|
||
|
Set tings window of the web management interface. Defau lt value = |
|
||
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCI |
Mos t users will n ot be required to change this setting. Th e Virtual |
|
||
|
Cha nnel Identifier (VCI) used in conjunction with the VPI to identify |
|
||
|
the data path bet ween your A DSL service provider’s network and |
|
||
|
your computer. If you are setting up the Ro uter for multip le virtual |
|
||
|
connections, you will need to configure the VPI and VCI as |
|
||
|
instructed by your ADSL service provider for the additional |
|
||
|
connections. This setting can b e changed in the WAN Sett ings |
|
||
|
window of the w eb management interface. Default value = 35 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Th e Setup Wiza rd can be us ed to configur e the Internet connection for most users.
N ote
Page 6 of 110 |
|
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Information you will need about your DSL-G604T ADSL 2+ Router:
Username |
This is the Username needed access the Router’s management |
Record info here |
|
||
|
interface. When you attempt to connect to the device through |
|
|
a web browser you will be prompted to enter this Username. |
|
|
The default Username for the Router is “admin.” The user |
|
|
cannot change this. |
|
|
|
|
Password |
This is the Password you will be prompted to enter when you |
|
|
access the Router’s management interface. The default |
|
|
Password is “admin.” The user may change this. |
|
|
|
|
LAN IP addresses for |
This is the IP address you will enter into the Address field of |
|
the DSL-G604T |
your web browser to access the Router’s configuration |
|
|
graphical user interface (GUI) using a web browser. The |
|
|
default IP address is 10.1.1.1. This may be changed to suit |
|
|
any IP address scheme the user desires. This address will be |
|
|
the base IP address used for DHCP service on the LAN when |
|
|
DHCP is enabled. |
|
|
|
|
LAN Subnet Mask for |
This is the subnet mask used by the DSL-G604T, and will be |
|
the DSL-G604T |
used throughout your LAN. The default subnet mask is |
|
|
255.255.255.0. This can be changed later. |
|
|
|
|
Information you will need about your LAN or computer:
Ethernet NIC |
If your computer has an Ethernet NIC, you can connect the |
Record info here |
|
||
|
DSL-G604T to this Ethernet port using an Ethernet cable. You |
|
|
can also use the Ethernet ports on the DSL-G604T to connect |
|
|
to other computer or Ethernet devices. |
|
|
|
|
DHCP Client status |
Your DSL-G604T ADSL 2+ Router is configured, by default, to |
|
|
be a DHCP server. This means that it can assign an IP address, |
|
|
subnet mask, and a default gateway address to computers on |
|
|
your LAN. The default range of IP addresses the DSL-G604T |
|
|
will assign are from 10.1.1.2 to 10.1.1.254. Your computer |
|
|
(or computers) needs to be configured to Obtain an IP |
|
|
address automatically (that is, they need to be configured |
|
|
as DHCP clients.) |
|
|
|
|
It is recommended that your collect and record this information here, or in some other secure place, in case you have to re-configure your ADSL connection in the future.
Once you have the above information, you are ready to setup and configure your DSL-G604T ADSL 2+ Router.
Page 7 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
1
Introduction
This section provides a brief description of the Router, its associated technologies, and a list of Router features.
Router Description and Operation
The DSL-G604T Wireless ADSL2+ Router is designed to provide connectivity for your private Ethernet LAN, and 802.11g/802.11b wireless LAN to the Internet via an ADSL connection.
The Router is easy to install and use. Standard Ethernet ports are used to connect to computer or other Ethernet devices. The 802.11g wireless interface provides connectivity to 802.11g or 802.11b wireless devices.
802.11g Wireless
The embedded 802.11g wireless access point provides Internet access and connectivity to the Ethernet for 802.11g and 802.11b wireless workstations. IEEE 802.11g is fully compatible with IEEE 802.11b wireless devices. The 802.11g standard supports data transfer rates of up to 54 Mbps. The wireless Router supports 64bit and 128-bit WEP encryption, WiFi Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2.
ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) is a broadband network technology that utilises standard twistedpair copper wire telephone lines to enable broadband high-speed digital data transmission and bandwidth hungry applications for business and residential customers.
ADSL routers and modems provide faster downloads and more reliable connectivity to the user without loss of quality or disruption of voice/fax telephone capabilities.
ADSL2/2+ provides a dedicated service over a single telephone line operating at speeds of up to 24Mbps downstream and up to 1Mbps upstream, depending on local telephone line conditions. A secure point-to-point connection is established between the user and the central office of the service provider.
D-Link ADSL devices incorporate the recommendations of the ADSL Forum regarding framing, data format, and upper layer protocols.
Page 8 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Router Features
The DSL-G604T ADSL 2+ Router utilises the latest ADSL enhancements to provide a reliable Internet portal suitable for most small to medium sized offices. DSL-G604T advantages include:
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) Security – The DSL-G604T ADSL 2+ Router supports PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) for PPP connections.
DHCP Support – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol automatically and dynamically assigns all LAN IP settings to each host on your network. This eliminates the need to reconfigure every host whenever changes in network topology occur.
Network Address Translation (NAT) – For small office environments, the DSL-G604T allows multiple users on the LAN to access the Internet concurrently through a single Internet account. This provides Internet access to everyone in the office for the price of a single user.
NAT improves network security in effect by hiding the private network behind one global and visible IP address. NAT address mapping can also be used to link two IP domains via a LAN-to-LAN connection.
TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) – The DSL-G604T supports TCP/IP protocol, the language used for the Internet. It is compatible with access servers manufactured by major vendors.
RIP-1/RIP-2 – The DSL-G604T supports both RIP-1 and RIP-2 exchanges with other routers. Using both versions lets the Router to communicate with all RIP enabled devices.
Static Routing – This allows you to select a data path to a particular network destination that will remain in the routing table and never “age out”. If you wish to define a specific route that will always be used for data traffic from your LAN to a specific destination within your LAN (for example to another router or a server) or outside your network (to an ISP defined default gateway for instance).
Default Routing – This allows you to choose a default path for incoming data packets for which the destination address is unknown. This is particularly useful when/if the Router functions as the sole connection to the Internet.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) – The DSL-G604T supports Bridged Ethernet over ATM (RFC1483), IP over ATM (RFC1577) and PPP over ATM (RFC 2364).
Precise ATM Traffic Shaping – Traffic shaping is a method of controlling the flow rate of ATM data cells. This function helps to establish the Quality of Service for ATM data transfer.
G.hs (Auto-handshake) – This allows the Router to automatically choose either the G.lite or G.dmt ADSL connection standards.
High Performance – Very high rates of data transfer are possible with the Router. Up to 8 Mbps downstream bit rate using the G.dmt standard.
Full Network Management – The DSL-G604T incorporates SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) support for web-based management and text-based network management via an RS-232 or Telnet connection.
Telnet Connection – The Telnet enables a network manager to access the Router’s management software remotely.
Easy Installation – The DSL-G604T uses a web-based graphical user interface program for convenient management access and easy set up. Any common web browser software can be used to manage the Router.
Page 9 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
802.11g Wireless
In order to get the best performance from the wireless component of the Router, you should have some basic understanding of how wireless networks operate. There are more factors to consider when setting up or designing a wireless network than designing a wired network. If you are setting up a wireless network, especially if you are using multiple access points and/or covering a large area, good planning from the outset can ensure the best possible reliability, performance, coverage and effective security.
Radio Transmission
Wireless local network (also called WI-FI) devices such as notebook computers and wireless access points use electromagnetic waves within a broad, unlicensed range of the radio spectrum (between 2.4GHz and 2.5GHz) to transmit and receive radio signals. A wireless access point (AP) becomes a base station for the wireless nodes (a notebook computer for example) in its broadcast range. Often a wireless access point such as the AP embedded in the DSL-G604T will also provide a connection to a wired network - usually Ethernet - and ultimately an Internet connection. The IEEE 802.11 standard precisely defines the encoding techniques used for data transmission. The DSL-G604T can be used by IEEE 802.11g and 802.11b devices. These two standards are compatible but use different encoding methods for data transmission.
802.11g uses a method called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for transmitting data at higher data rates. OFDM is a more efficient encoding method than Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) transmission, the method used by 802.11b devices. However, in order to support different data transmission rates while maintaining compatibility with 802.11b - 802.11g uses a combination of OFDM and DSSS when 802.11b devices are present.
Range
An access point will send and receive signals within a limited range. The actual effective range of the AP can vary depending on operating conditions. Radio signals are emitted in all directions giving the access point a spherical range. The physical environment in which the AP is operating can impact on its effectiveness and range. If you experience low signal strength or slow throughput, consider positioning the Router in a different location. See Installation Considerations below concerning the wireless environment and location of the AP (DSL-G604T).
SSID
Wireless networks use an SSID (Service Set Identifier) as means of identifying a group of wireless devices, similar to a domain or subnet. This allows wireless devices to roam from one AP to another and remain connected. Wireless devices that wish to communicate with each other must use the same SSID. Several access points can be set up using the same SSID so that wireless stations can move from one location to another without losing connection to the wireless network.
The embedded wireless access point of the Router operates in Infrastructure mode. It controls network access on the wireless interface in its broadcast area. It will allow access to the wireless network to devices using the correct SSID after a negotiation process takes place. By default, the DSL-G604T broadcasts its SSID so that any wireless station in range can learn the SSID and ask permission to associate with it. Many wireless adapters are able to survey or scan the wireless environment for access points. An access point in Infrastructure mode allows wireless devices to survey that network and select an access point with which to associate. You may disable SSID broadcasting in the web manager’s wireless menu.
Channel
The AP can operate on different channels (frequency bands). This is useful when multiple APs are used in order to avoid unwanted overlap or interference between control zones of separate APs. Wireless nodes must use the same SSID and the same channel as the AP with which it will associate. However, using the same channel on two different APs can contribute wireless congestion under certain circumstances. If you are using multiple APs on your network and are experiencing low throughput or significant transmission delay, carefully consider how channels are assigned to the different APs.
Wireless Security
Various security options are available on the Router including open or WEP, WPA and WPA2.
Page 10 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Installation Considerations
Many physical environmental factors can impact wireless networks. Radio waves are used to carry the encoded data between devices. These radio transmissions can become degraded due to signal attenuation, multi-path distortion and interference or noise. Attenuation simply means that the strength of the signal weakens with the distance it travels, even if the transmission path is unobstructed. Multi-path distortion occurs when radio signals bounce off objects like walls, ceilings, metal appliances, etc. This may cause a signal to be duplicated, with each separate yet identical signal arriving at a receiver at different times. Interference and noise from electrical devices such as microwave ovens, fluorescent lights, automobile engines and other radio emitting devices can cause signal degradation. With all of this in mind, choose a location for all your access points including the DSL-G604T.
The access point can be placed on a shelf or desktop, ideally you should be able to see the LED indicators on the front if you need to view them for troubleshooting.
Wireless networking lets you access your network from nearly anywhere you want. However, the number of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must pass through can limit signal range. Typical ranges vary depending on the types of materials and background RF noise in your home or business. To range and signal strength, use these basic guidelines:
Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the DSL-G604T and other network devices to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your D-Link wireless product’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 metres.) Position your devices so that the number of walls or ceilings is minimised.
Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (0.5 metres), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 metre) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet (14 metres) thick! Please position devices so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling (instead of at an angle) for better reception.
Materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or aluminum studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless devices and computers with wireless adapters so that the signal passes through drywall or open doorways and not dense, especially metallic, materials. Also, note that metal filing cabinets and appliances can reflect radio signals. When these metal objects are moved around, your wireless network may be affected.
Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 metres) from electrical devices or appliances that generate extreme RF noise such as microwave ovens, CRT monitors, motors, etc.
Page 11 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Front Panel Display
Place the Router in a location that permits an easy view of the LED indicators on the front panel.
The LED indicators on the front panel include Power, Status, ADSL, WLAN and Ethernet. The ADSL, WLAN and Ethernet indicators monitor link status and activity (Link/Act).
Power
Status
ADSL (Link/Act)
WLAN (Link/Act)
LAN 1-4 (Link/Act)
Steady green light indicates the unit is powered on. When the device is powered off this remains dark.
Lights steady green during power on self-test (POST). Once the connection status has been settled, the light will blink green. If the indicator lights steady green after the POST, the system has failed and the device should be rebooted.
Steady green light indicates a valid ADSL connection. This will light after the ADSL negotiation process has been settled. A blinking green light indicates activity on the WAN (ADSL) interface.
Steady green light indicates a wireless connection. A blinking green light indicates activity on the WLAN interface.
A solid green light indicates a valid link on startup. This light will blink when there is activity currently on any Ethernet port.
Page 12 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Rear Panel Connections
All cable connections to the Router are made at the rear panel. Connect the power adapter here to power on the Router. Use the Reset button to restore the settings to the factory default values in the next chapter for instructions on using the reset button).
Connect network cables:
1.Insert the ADSL (telephone) cable included with the Router into the ADSL port and then connect the cable to your telephone line.
2.Insert one end of the Ethernet cable into the Ethernet (LAN) port on the back panel of the Router and the other end of the cable to an Ethernet Adapter or available Ethernet port on your computer.
ADSL Port |
Ethernet Port |
Power Insert |
|
Use the adapter |
|||
Use the ADSL cable to connect to |
Use the Ethernet port to |
||
shipped with the |
|||
the your telephone line (RJ-11 |
connect the Router to |
Router to connect to |
|
port) |
your Ethernet LAN or |
power source |
|
|
computer |
|
Page 13 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Reset
To Reset the Router to factory default settings including the default IP address 10.1.1.1, depress the reset button on the right side panel with a ballpoint pen, paper clip or similar object for a few seconds. The device will restart with default settings.
Reset
To manually reset, depress button with the power on for at least seven seconds
Page 14 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
2
Hardware Installation
The DSL-G604T maintains two separate physical interfaces, an ADSL and an Ethernet interface. Place the Router in a location where it can be connected to the various devices as well as to a power source. The Router should not be located where it will be exposed to moisture or excessive heat. Make sure the cables and power cord are placed safely out of the way so they do not create a tripping hazard. As with any electrical appliance, observe common sense safety procedures.
The Router can be placed on a shelf or desktop, ideally you should be able to see the LED indicators on the front if you need to view them for troubleshooting.
Power on Router
CAUTION: The Router must be used with the power adapter included with the device.
To power on the Router:
1.Insert the DC Power Adapter cord into the power receptacle located on the rear panel of the Router and plug the adapter into a suitable nearby power source.
2.You should see the Power LED indicator light up and remain lit. The Status LED should light solid green and begin to blink after a few seconds.
3.If the Ethernet port is connected to a working device, check the Ethernet Link/Act LED indicators to make sure the connection is valid. The Router will attempt to establish the ADSL connection, if the ADSL line is connected and the Router is properly configured this should light up after several seconds. If this is the first time installing the device, some settings may need to be changed before the Router can establish a connection.
Factory Reset Button
The Router may be reset to the original factory default settings by depressing the reset button on the right side panel (see illustration on page 14) for a few seconds while the device is powered on. Use a ballpoint or paperclip to gently push down the reset button. Remember that this will wipe out any settings stored in flash memory including user account information and LAN IP settings. The device settings will be restored to the factory default IP address 10.1.1.1 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the default management Username is “admin” and the default Password is “admin.”
Page 15 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |

DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Network Connections
Network connections are provided through the ADSL port and Ethernet port on the back of the Router. See the Rear Panel diagram above and the illustrations below for examples.
Connect ADSL Line
Use the ADSL cable included with the Router to connect it to a telephone wall socket or receptacle. Plug one end of the cable into the ADSL port (RJ-11 receptacle) on the rear panel of the Router and insert the other end into the RJ-11 wall socket. If you are using a low pass filter device, follow the instructions included with the device or given to you by your service provider. The ADSL connection represents the WAN interface, the connection to the Internet. It is the physical link to the service provider’s network backbone and ultimately to the Internet.
Connect Router to Ethernet
The Router may be connected to a single computer or Ethernet device through the 10/100 BASE-TX Ethernet port on the rear panel. Any connection to an Ethernet concentrating device such as a switch or hub must operate at a speed of 10/100 Mbps only. When connecting the Router to any Ethernet device that is capable of operating at speeds between 0~100Mbps, be sure that the device has auto-negotiation (NWay) enabled for the connecting port.
Use Category 5 or better twisted-pair Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors. The RJ-45 port on the Router is auto MDI-X/MDI-II meaning that is will link correctly with either MDI-II through or MDI-X crossed ports.
The rules governing Ethernet cable lengths apply to the LAN to Router connection. Be sure that the cable connecting the LAN to the Router does not exceed 100 metres.
Page 16 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Mo dem Router
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
Basic |
Router Configura tion |
|
|
The first time you setup t he Router it is recomm ended that you configu re the WAN |
connection using a single |
||
computer con nected directly to the Ro uter. Once the WAN connection is functioning |
properly, you may continue |
||
to make changes to Router configuration including IP settings and DH CP setup. |
For information on how to |
||
configure adv |
nced features such as port redirection, filtering and firew all, please skip ahead t o the Advanced |
||
Router Manag ement sectio n.
C onfiguration Su mmary
1.Connect to the Router To configure variou s settings us ed by the R outer for Internet and access it is first
necessary to access the Router’s management HTML-ba sed interface. This is d one using an ordinary web browser. Y our computer must be able to “se e” the Rout er before it can manage it using a browser. If the Router is in the sam e “neighbo rhood” or subnet as the Router , you should be able to access the managem ent software . Therefore you must first make s ure your co mputer has IP settings that place it in the same subnet as th e Router. The easiest w ay to make sure your computer ha s the correct IP settings is to configure it to use the DHCP server in t he Router. The DHCP server will automatically enable your computer to use a browser to manage the Router. Th e next section describes how to change the IP configuration for a co mputer runn ing a Wind ows operatin g system t o be a DHC P client. If you are running another op erating system, make sure your co mputer is configured a s a DHCP client so it can automatically obtain IP settings fro m the Router. Some operating systems will au tomatically select the best IP settings. Consult the user manu al for the o perating system (OS) if you are unsure.
2.Configure the Internet (WAN) Connectio n Most users will be able to complete this process using the Setup Wizard. The Setup Wizard can be launched once you have su ccessfully connected with the Router’s managem ent software . There are different methods use d to establish the WAN connection to the service
provider’s network an d ultimately to the Internet. You r Router m ay already have most of the settings configured by default. However y ou will prob ably at least have to ty pe in a user name and password given to you by your ISP. You may also need to know the enc apsulation and connecti on type req uired to use for your ADSL service. Yo ur service provider sho uld provide all the information nee ded to configure the W AN connection .
C omputer IP Settings
In order to co nfigure your system to receive IP settings from the Router your com puter must first have the
TCP/IP protocol installed. If you hav e an Ethernet port on |
your com puter, it pro bably already has TCP/IP |
pr otocol installed. If you are using Windows XP the TCP/IP |
is enabled by default for standard installations. |
In structions for configuring your comp uter to rece ive IP settin gs from the Router are provided in Appendix B on page 103.
For computers running non-Windows operating systems, foll ow the instructions for your OS that configure the system to rece ive an IP ad dress from the Router, that is, configure the system to be a DHCP clie nt.
|
|
|
|
If |
you are not s ure how to co nfigure your W indows comp |
uter to be a D |
HCP client, see Configuring IP |
|
|
|
|
S |
ettings on You r Computer beginning on page 107. |
|
|
N ote |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 17 of 11 0 |
|
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Mo dem Router
Access the Configuration Ma nager
In order to m ake sure your compute r’s IP settin gs allow it to communic ate with the Router, it is advisable to configure your system be a DHCP clie nt – that is, it will get IP settings from the Router. Appendix B describes how to configu re different Windows op erating sys tems to “Obtain IP setti ngs automatically”.
Be sure that the web brow ser on your computer is not c onfigured to use a proxy server in the Internet settings. In Win dows Internet E xplorer, you can check if a prox y server is enabled using the following proced ure:
|
|
1. |
In Windows, click on the Start button and choose Control Panel. |
|
|
2. |
In the Control Pan el window, click on the Netwo rk and Internet Options icon. |
|
|
3. |
In the Network and Internet Connections wind ow, click the Internet Options icon. |
|
|
4. |
In the Internet Pro perties windo w, click on the C onnections tab and click on the LAN Settin gs button |
Note |
|||
|
|
5. |
Ver ify that the “Use a proxy serve r for your LAN (These setting s will not apply to dial-up or V PN connections).” option is |
NOT checked. If it is checked, clic k in the checked box to desele ct the option an d click OK.
Alternative ly, you can access this Intern et Options men u using the Tools pull-down m enu in Internet Explorer.
Lo gin to H ome Pag e
To use the web-based management s oftware, lau nch a suitable web browser and direct it to the IP addres s of th e Router. Ty pe in http:// followed by the default IP address, 10.1.1.1 in the a ddress bar of the brow ser. The URL in the address bar should rea d: http:// 10.1.1.1.
A dialog box prompts for t he User Na me and Pas sword. Type in the defa ult User Na me “admin” and the def ault Password “ad min” then click the OK button to access the web-based manager.
Enter Username and Password
You should ch ange the w eb-based m anager access user na me and password onc e you have verified tha t a connection can be established. The user name and password allows a ny PC withi n the same subnet as the Router to access the web-based manger.
|
Th e user name and passwor d used to acc ess the web-based manage r is NOT the same as the A DSL |
Note |
ac count user na me and password needed for PPPoE/P PPoA connections to access the Internet. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 18 of 11 0 |
|
www.dlink.com.au |
||
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Configure the Router
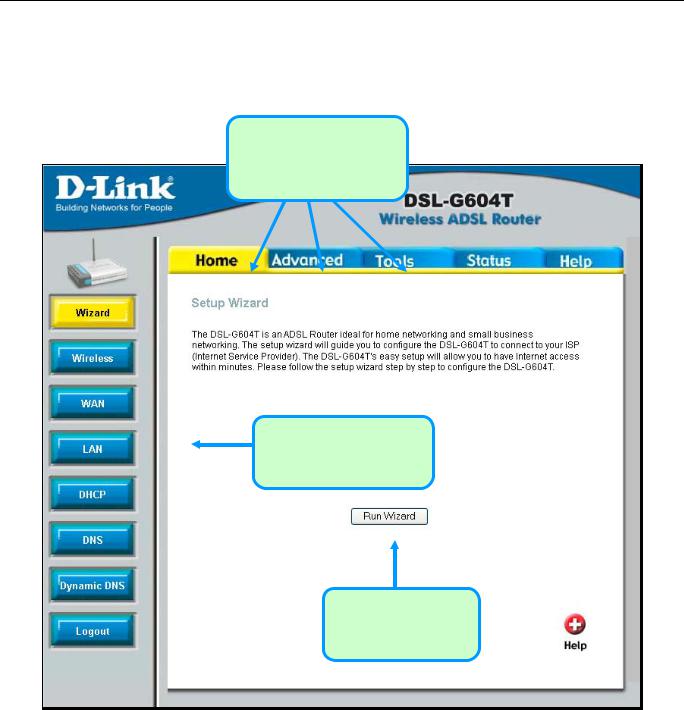
When you successfully connect to the web manager, the Home directory tab will display the Setup Wizard window. You can launch the Setup Wizard from this page or use the buttons located in the left panel of the web page to view other windows used for basic configuration.
Click on a directory tab to view the options available in that directory
Click on a button to use or view the window
Click the Run Wizard
button to launch the
Setup Wizard
Web Manager – First Time Log On
All configuration and management of the Router is done using the web-based management interface pictured in the above example. The configuration windows are accessed by clicking on the directory tabs: Home, Advanced, Tools, Status, and Help. Each tab has associated window buttons in the left hand panel of the web interface. Basic setup of the Router can be completed in the windows accessed from the Home directory including: (Setup) Wizard, Wireless (to configure the Wireless LAN), WAN (Internet), LAN (to configure the IP address of the Router) DHCP, DNS and Dynamic DNS.
Page 19 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Wizard
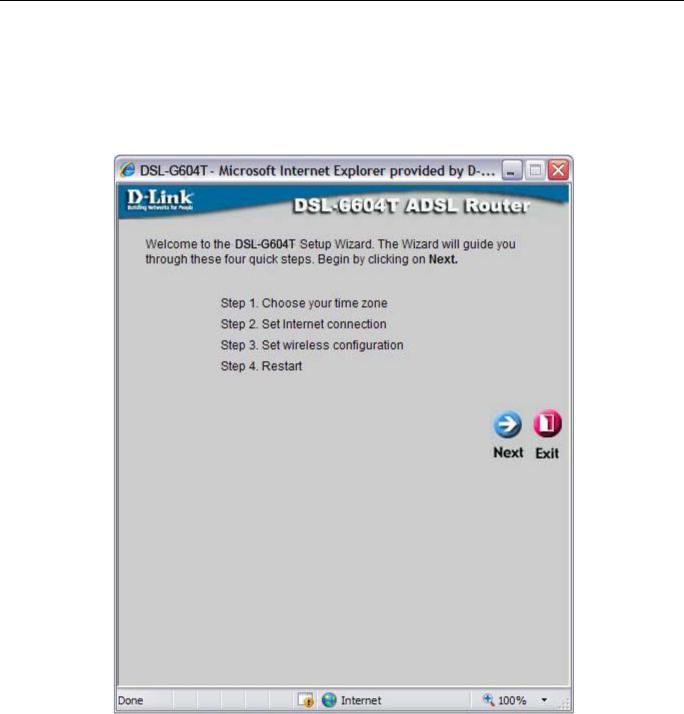
To use the Setup Wizard, click the Run Wizard button in the first browser window and follow the instructions in the pop-up window that appears.
The initial window summarizes the setup process. Click the Next button to proceed. You may stop using the Setup Wizard at any time by clicking the Exit button. If you exit the wizard you will return to the Setup Wizard window without saving any of the settings changed during the process.
The first pop-up window of the Setup Wizard lists the basic steps in the process. These steps are as follows:
1.Set the system time.
2.Configure the connection to the Internet.
3.Save the new configuration settings and reboot the system.
Page 20 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
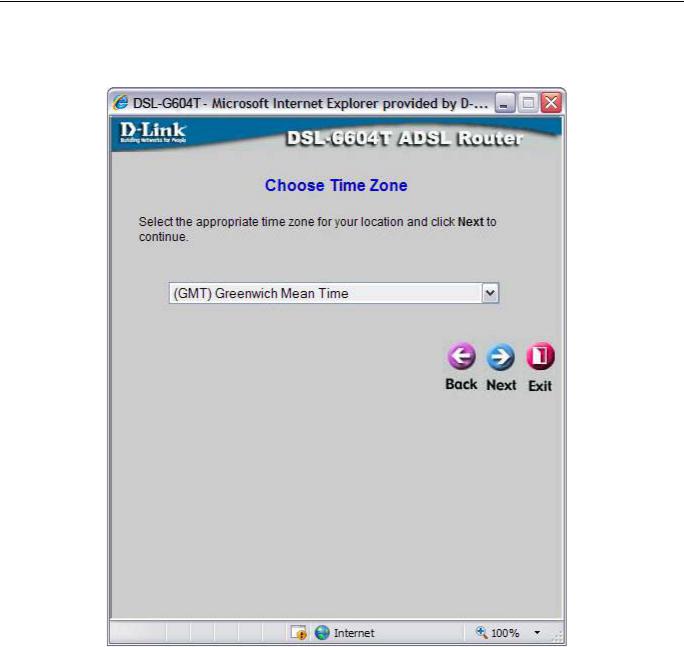
Using the Setup Wizard - Choose Time Zone
Choose the time zone you are in from the pull-down menu and click Next. This sets the system time used for the Router. If you wish to return to the previous window during the setup process, click the Back button.
Page 21 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
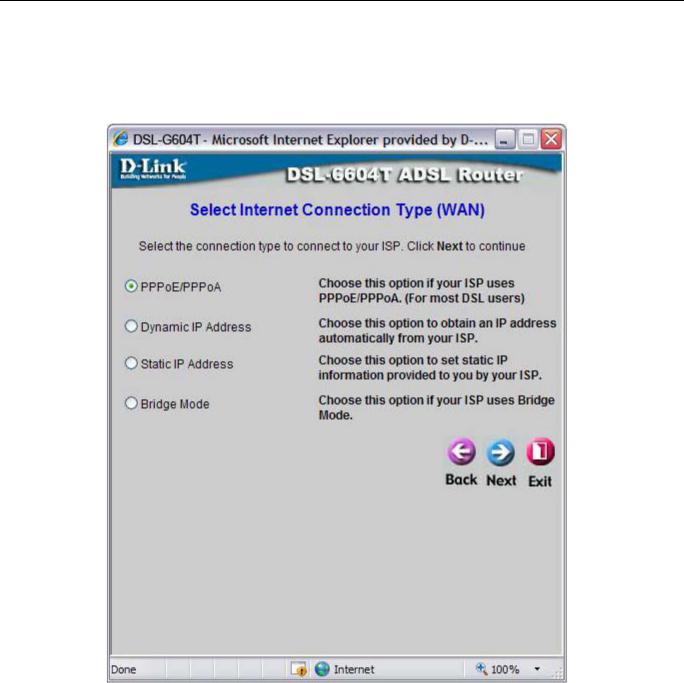
Using the Setup Wizard - Choose Connection Type
Now select the Connection Type used for the Internet connection. Your ISP has given this information to you. The connection types available for “Multi-User” Mode are PPPoE/PPPoA, Dynamic IP Address, Static IP Address, and Bridge Mode. Each connection type has different settings that are configured in the next Setup Wizard pop-up window.
Select the Connection Type specific to your service and click Next to go to the next Setup Wizard pop-up window. Follow the instructions below for the type of connection you have selected.
Page 22 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
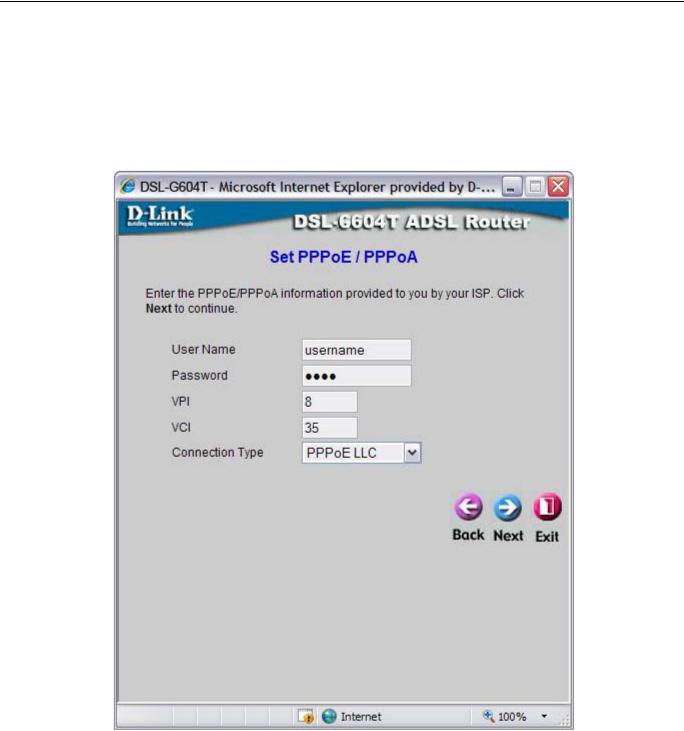
Using the Setup Wizard - For PPPoE/PPPoA connections:
1.Type in the Username and Password used to identify and verify your account to the ISP.
2.Select the specific Connection Type from the drop-down menu. The available PPP connection and encapsulation types are PPPoE LLC, PPPoA LLC and PPPoA VC-Mux.
3.If you are instructed to change the VPI or VCI number, type in the correct setting in the available entry fields. Most users will not need to change these settings. The Internet connection cannot function if these values are incorrect.
4.Click Next to go to the next window and complete the Setup Wizard.
Page 23 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
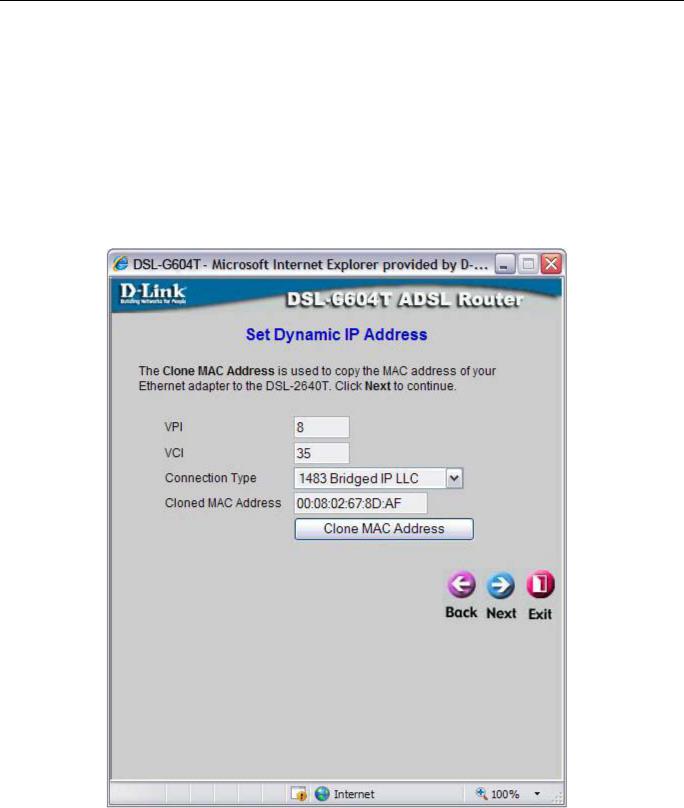
Using the Setup Wizard - For Dynamic IP Address connections:
1.Select the specific Connection Type from the drop-down menu. The available Dynamic IP Address connection and encapsulation types are 1483 Bridged IP LLC and 1483 Bridged IP VC-Mux.
2.If you are instructed to change the VPI or VCI number, type in the correct setting in the available entry fields. Most users will not need to change these settings. The Internet connection cannot function if these values are incorrect.
3.You may want to copy the MAC address of your Ethernet adapter to the Router. Some ISPs record the unique MAC address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter when you first access their network. This can prevent the Router (which has a different MAC address) from being allowed access to the ISPs network (and the Internet). To clone the MAC address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter, type in the MAC address in the Cloned MAC Address field and click the Clone MAC Address button. This will copy the information to a file used by the Router to present to the ISP’s server used for DHCP.
4.Click Next to go to the next pop-up window and complete the Setup Wizard.
Page 24 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
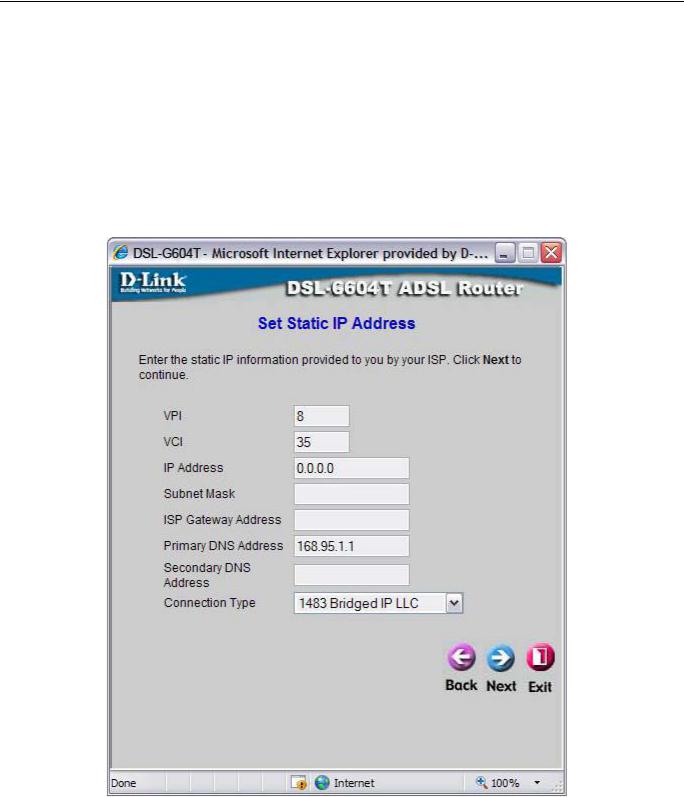
Using the Setup Wizard - For Static IP Address connections:
1.Select the specific Connection Type from the drop-down menu. The available Static IP Address connection and encapsulation types are 1483 Bridged IP LLC, 1483 Bridged IP VC-Mux, 1483 Routed IP LLC, 1483 Routed IP VC-Mux and IPoA.
2.Change the IP Address, Subnet Mask, ISP Gateway Address, Primary DNS Address, and Secondary DNS Server IP Address as instructed by your ISP. For IPoA connections it may also be necessary to change the ARP Server Address. IPoA connection users who have not been given this information should leave the field blank.
3.If you are instructed to change the VPI or VCI number, type in the correct setting in the available entry fields. Most users will not need to change these settings. The Internet connection cannot function if these values are incorrect.
4.Click Next to go to the next window and complete the Setup Wizard.
Page 25 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
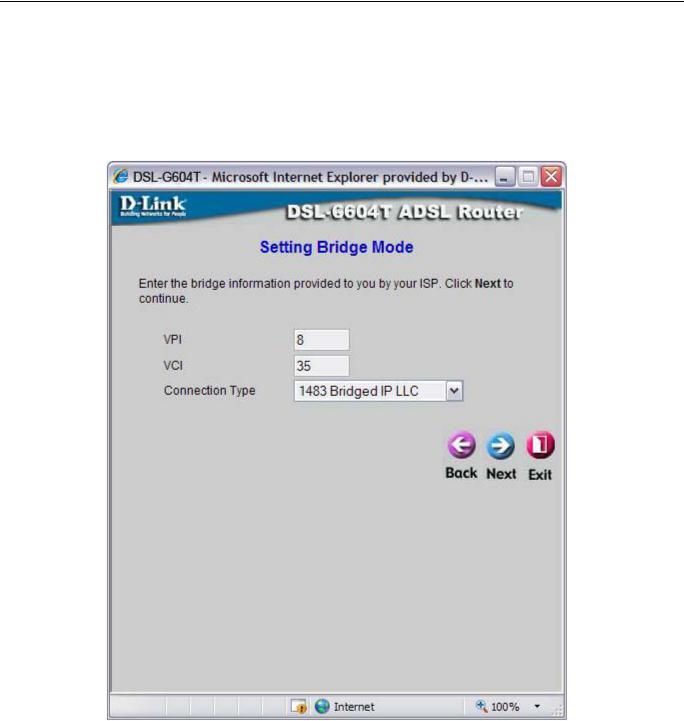
Using the Setup Wizard - For Bridge Mode connections:
1.Select the specific Connection Type from the drop-down menu. The available Bridge Mode connection and encapsulation types are 1483 Bridged IP LLC and 1483 Bridged IP VC-Mux.
2.If you are instructed to change the VPI or VCI number, type in the correct setting in the available entry fields. Most users will not need to change these settings. The Internet connection cannot function if these values are incorrect.
3.Click Next to go to the next window and complete the Setup Wizard.
Page 26 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
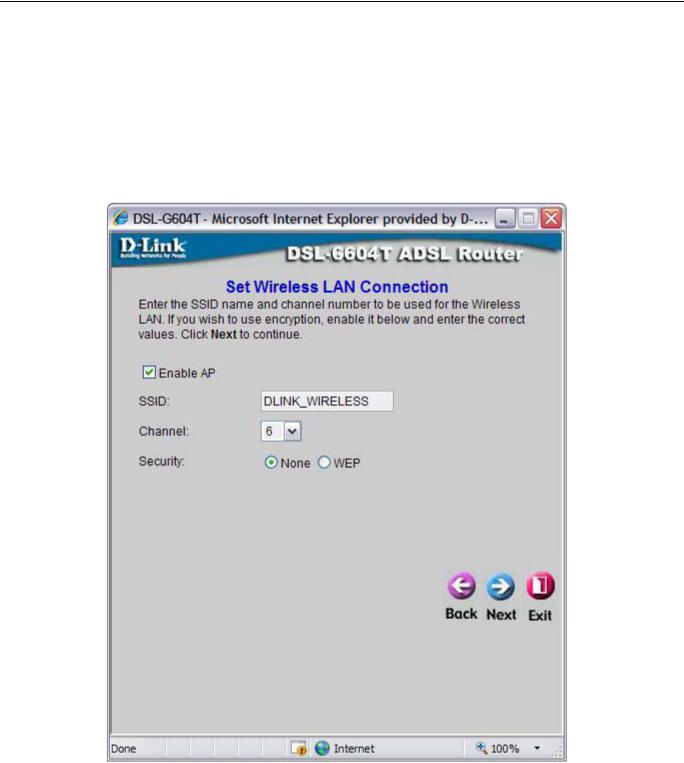
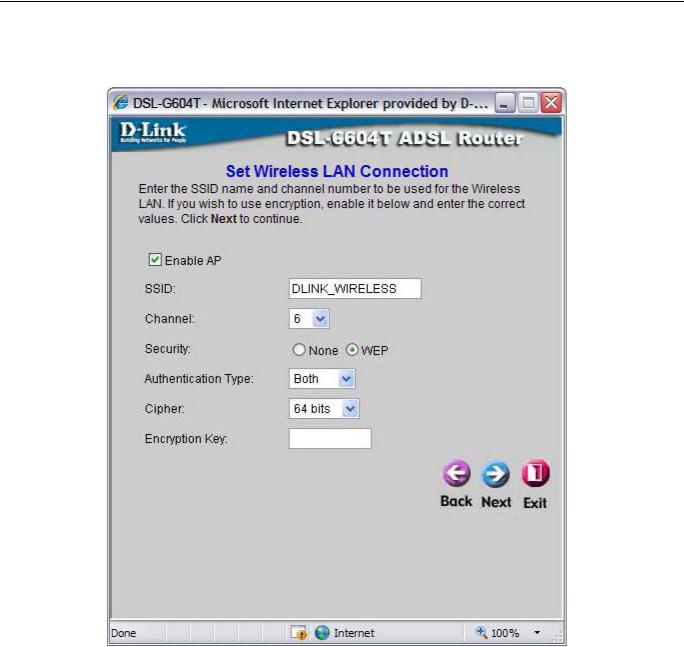
Using the Setup Wizard - Wireless LAN Configuration
Configure the SSID and Channel for the Wireless LAN. You may also configure WEP security settings at this time or configure them later using the web manager. Select None to configure WEP later. To disable the wireless access point, click the Enable AP option box to remove the green check mark. To configure Wirless LAN settings:
1.Enter the SSID for the Wireless LAN
2.Choose the wireless Channel to be used for your WLAN from the pull down menu.
3.Choose the wireless security setup. If WEP is used an additional step is required for configuration
4.Click Next
Page 27 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
Using the Setup Wizard - WEP Configuration
If you are configuring WEP security, select the Authentication Type, Cipher rate and Encryption Key. Click Next to continue to the final menu.
Page 28 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Modem Router
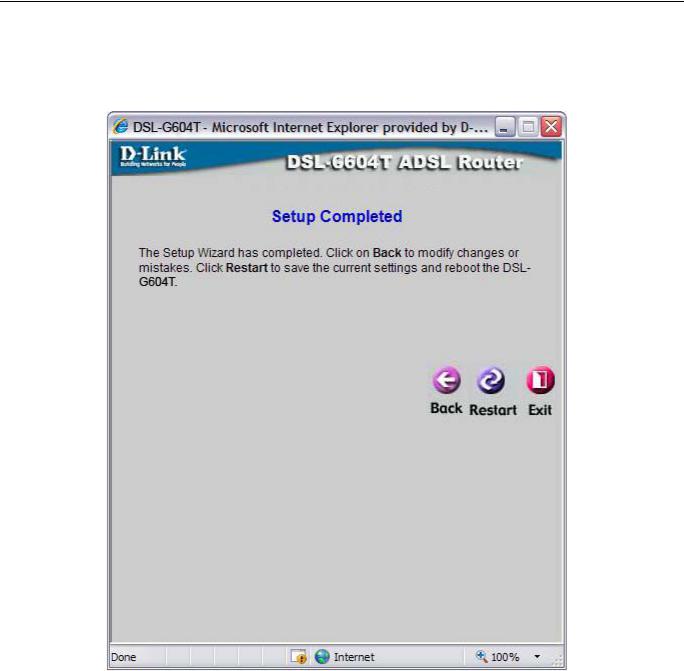
Using the Setup Wizard - Finish and Restart
Finally you can confirm that the setup process is completed. If you are satisfied that you have entered all the necessary information correctly, click the Restart button to save the new configuration settings and restart the Router. If you need to change settings from a previous window, click the Back button.
Do not turn the Router off while it is restarting. After the Router is finished restarting, you are now ready to continue to configure the Router as desired. You may want to test the WAN connection by accessing the Internet with your browser.
Page 29 of 110 |
www.dlink.com.au |
DSL-G604T Generation II ADSL2+ Wireless Mo dem Router
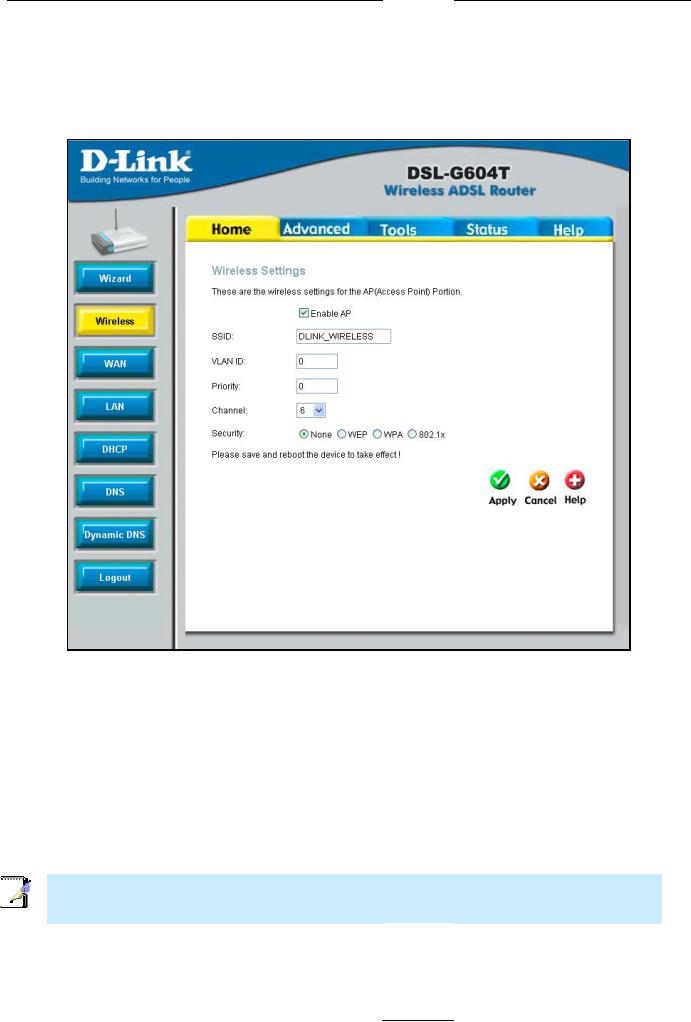
W ireless
To configure the Router’s basic configuration set tings witho ut running t he Setup W izard, you can access the wi ndows used to configure Wireless, WAN, LAN, DHCP, DN S, and Dy namic DNS settings directly from the Ho me directo ry. To access the Wirel ess Settings window, c lick on the Wireless lin k button on the left sid e of th e first window that appears when yo u successfully access th e web man ager.
|
Wireless Se ttings menu – No Security |
For Basic Wireless LAN op eration with no Securtiy settings, follow the ste ps: |
|
1. |
Click the Enable AP box to allow the router t o operate in the wireless environment. |
2. |
The SSID identifies members of t he Service S et. Accept the default name or cha nge it to som ething else. If |
|
the defaul t SSID is ch anged, all ot her devices on the wireless networ k must use the same SSID. |
3.What chan nels are av ailable for us e by the ac cess point depends on t he local reg ulatory envir onment. Remembe r that all de vices comm unicating wit h the devic e must use the same channel (and u se the sam e SSID). Us e the drop-down menu to select the Channel u sed for your 802.11g wireless LAN. The wireless channel nu mber is ava ilable from your Interne t Service Provider (ISP ).
4.The VLAN ID and Priority settings are optional settings. If your network supports VLANs or Q oS Priority (IEEE 802. 11p), type in the appropriate values here.
5.If network Security is not used, click to select None, then click Apply.
VLAN ID and Priority settings do not need to be configured in order to use the Wireless A ccess Point. 
Note
Page 30 of 11 0 |
|
www.dlink.com.au |
 Loading...
Loading...