Dell Precision M4500 User Manual

Intel® Active Management Technology v6.0
Administrator's Guide
Overview
Product Overview
Out of Box Experience
Operational Modes
Setup and Configuration Overview
Menus and Defaults
MEBx Settings Overview
ME General Settings
AMT Configuration
Intel Fast Call for Help
ME General Settings
AMT Configuration
Management
Intel AMT Web GUI
AMT Redirection (SOL/IDE-R)
AMT Redirection Overview
Intel Management and
Security Status Application
Intel Management and Security Status
Application
Setup and Configuration |
Troubleshooting |
|
|
Methods Overview |
Troubleshooting |
Configuration Service--Using a USB Device |
|
Configuration Service--USB Device Procedure |
|
System Deployment |
|
Operating System Drivers |
|
If you purchased a DELL™ n Series computer, any references in this document to Microsoft® Windows® operating systems are not applicable.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. © 2010 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, Latitude, and the DELL logo are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries; Microsoft and Windows are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
April 2010 |
Rev. A00 |

Back to Contents Page
Overview
Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel AMT) allows companies to easily manage their networked computers.
 Discover computing assets on a network regardless of whether the computer is turned on or off – Intel AMT uses information stored in nonvolatile system memory to access the computer. The computer can even be accessed while it is powered off (also called out-of-band or OOB access).
Discover computing assets on a network regardless of whether the computer is turned on or off – Intel AMT uses information stored in nonvolatile system memory to access the computer. The computer can even be accessed while it is powered off (also called out-of-band or OOB access).
 Remotely repair computers even after operating system failures – In the event of a software or operating system failure, Intel AMT can be used to access the computer remotely for repair purposes. IT administrators can also detect computer system problems easily with the assistance of Intel AMT's out-of-band event logging and alerting.
Remotely repair computers even after operating system failures – In the event of a software or operating system failure, Intel AMT can be used to access the computer remotely for repair purposes. IT administrators can also detect computer system problems easily with the assistance of Intel AMT's out-of-band event logging and alerting.
 Protect networks from incoming threats while easily keeping software and virus protection up to date across the network.
Protect networks from incoming threats while easily keeping software and virus protection up to date across the network.
Software Support
Several independent software vendors (ISVs) are building software packages to work with Intel AMT features. This provides IT administrators many options when it comes to remotely managing the networked computer assets within their company.
Features and Benefits
Features
 Out-of-band (OOB) access
Out-of-band (OOB) access
Remote troubleshooting and recovery
 Proactive alerting
Proactive alerting
Intel AMT
Benefits
Allows remote management of platforms regardless of system power or operating system state
 Significantly reduces desk-side visits, increasing the efficiency of IT technical staff Decreases downtime and minimizes repair times
Significantly reduces desk-side visits, increasing the efficiency of IT technical staff Decreases downtime and minimizes repair times
Computer Requirements
The computer referred to in this document consists of the Intel® 5 Series Chipset Family/Intel® PCH platform, and is managed by Intel Management Engine. The following firmware and software requirements are required for the installation and set up before the Intel Management Engine can be configured and run in the client computer:
 An SPI flash device programmed with Intel AMT 6.0 flash image integrating BIOS, Intel Management Engine, and GbE component images.
An SPI flash device programmed with Intel AMT 6.0 flash image integrating BIOS, Intel Management Engine, and GbE component images.
 BIOS set up with Intel AMT enabled can access MEBx setup from F12 menu.
BIOS set up with Intel AMT enabled can access MEBx setup from F12 menu.
 To enable all of the Intel Management Engine features within Microsoft Operating System, device drivers (Intel® MEI/SOL/LMS) must be installed and configured on the client system for features to work/run correctly run in the client system.
To enable all of the Intel Management Engine features within Microsoft Operating System, device drivers (Intel® MEI/SOL/LMS) must be installed and configured on the client system for features to work/run correctly run in the client system.
* Information on this page provided by Intel.
Back to Contents Page
NOTE: The Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) is an optional ROM module provided to Dell™ from Intel that is included in the Dell BIOS. The MEBx has been customized for Dell computers.
Back to Contents Page
Out of Box Experience
The following materials are available with an Intel™ Active Management Technology (Intel AMT) computer:
 Factory installation
Factory installation
 Intel AMT 6.0 is shipped in the factory-default state from Dell factories.
Intel AMT 6.0 is shipped in the factory-default state from Dell factories.
 Setup and Quick Reference Guide
Setup and Quick Reference Guide
 Intel AMT overview with link to the Dell Technology Guide.
Intel AMT overview with link to the Dell Technology Guide.
 Dell Technology Guide
Dell Technology Guide
 High-level Intel AMT overview, setup, provisioning, and support.
High-level Intel AMT overview, setup, provisioning, and support.
 Backup media
Backup media
 Firmware and critical drivers are available on the Resource CD.
Firmware and critical drivers are available on the Resource CD.
See the Administrator Guide for detailed information about Intel AMT. The guide is posted on the Web and is available with the computer manuals on support.dell.com.
Back to Contents Page
Back to Contents Page
Operational Modes
Earlier versions of Intel® AMT supported two operational modes – Small and Medium Business (SMB) and Enterprise. In the current version, their functionality has been integrated to exhibit the functionality of the earlier Enterprise mode.
The new configuration options for SMB customers are: Manual Setup and Configuration and Automatic Setup and Configuration.
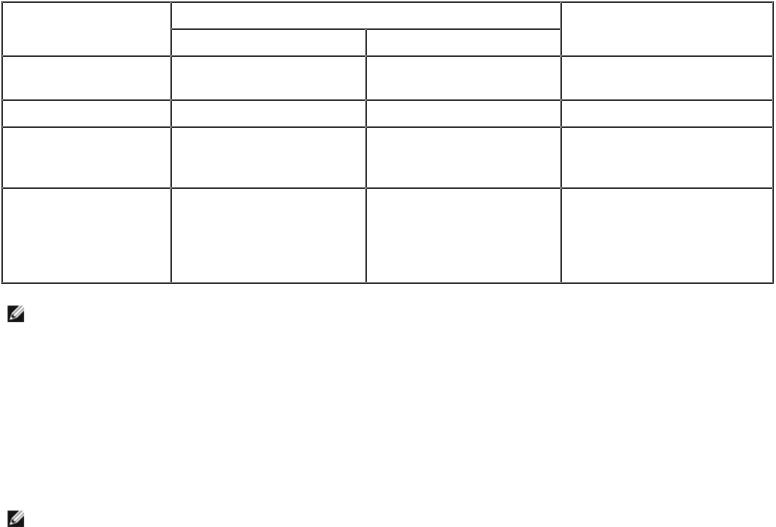
Setting |
Intel AMT 5.0 Default |
||
Enterprise Mode |
SMB Mode |
||
|
|||
TLS mode |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
Web UI |
Disabled |
Enabled |
|
IDER/SOL/KVM |
|
Enabled if feature |
|
Redirection network |
Disabled |
||
enabled in Intel® MEBx |
|||
interface enabled |
|
||
|
|
||
Legacy Redirection |
|
|
|
Mode (Controls FW |
Disabled |
Enabled if feature |
|
listening for incoming |
|||
enabled in Intel MEBx |
|||
redirection |
|
||
|
|
||
connections)
Intel AMT 6.0 Default
Disabled, can be enabled at a later time
Enabled
Enabled, can be disabled at a later time
Disabled (set to Enabled to work with Legacy SMB consoles)
NOTE: KVM is supported only with integrated graphics CPU. The system should be in the integrated graphics mode.
Perform manual configuration using the following steps:
1.Flash image with system BIOS and FW.
2.Navigate to the Intel MEBx by pressing the F12 menu and typing the default password admin. After you are logged in, change the password.
3.Navigate to Intel ME General Settings menu.
4.Select Activate Network Access.
5.Choose “Y” in the confirmation message.
6.Exit the Intel MEBx.
NOTE: You can also accomplish the activation through external means or through the operating system using the Intel Activator tool.
Back to Contents Page
Back to Contents Page
Setup and Configuration Overview
The following is a list of important terms related to the Intel® AMT setup and configuration.
 Setup and configuration — The process that populates the Intel AMT-managed computer with usernames, passwords, and network parameters that enable the computer to be administered remotely.
Setup and configuration — The process that populates the Intel AMT-managed computer with usernames, passwords, and network parameters that enable the computer to be administered remotely.
 Configuration service — A third-party application that completes the Intel AMT provisioning.
Configuration service — A third-party application that completes the Intel AMT provisioning.
 Intel AMT WebGUI — A Web browser-based interface for limited remote computer management.
Intel AMT WebGUI — A Web browser-based interface for limited remote computer management.
You must set up and configure Intel AMT on a computer before using it. Intel AMT setup readies the computer for Intel AMT mode and enables network connectivity. This setup is generally performed only once in the lifetime of a computer. When Intel AMT is enabled, it can be discovered by management software over a network.
Once Intel AMT is set up in Enterprise mode, it is ready to initiate configuration of its own capabilities. When all required network elements are available, simply connect the computer to a power source and the network and Intel AMT automatically initiates its own configuration. The configuration service (a third-party application) completes the process for you. Intel AMT is then ready for remote management. This configuration typically takes only a few seconds. When Intel AMT is set up and configured, you can reconfigure the technology as needed for your business environment.
Once Intel AMT is set up in the SMB mode, the computer does not have to initiate any configuration across the network. It is set up manually and is ready to use with the Intel AMT Web GUI.
Intel AMT Setup and Configuration States
The act of setting up and configuring Intel AMT is also known as provisioning. An Intel AMT-capable computer can be in one of three setup and configuration states (SCS):
 Factory-default state
Factory-default state
 Setup state
Setup state
 Provisioned state
Provisioned state
The factory-default state is a fully un-configured state in which security credentials are not yet established and Intel AMT capabilities are not yet available to management applications. In the factory-default state, Intel AMT has the factory-defined settings.
The setup state is a partially configured state in which Intel AMT has been set up with initial networking and transport layer security (TLS) information: an initial administrator password, the provisioning passphrase (PPS), and the provisioning identifier (PID). When Intel AMT has been set up, Intel AMT is ready to receive enterprise configuration settings from a configuration service.
The provisioned state is a fully configured state in which the Intel Management Engine (ME) has been configured with power options, and Intel AMT has been configured with its security settings, certificates, and the settings that activate the Intel AMT capabilities. When Intel AMT has been configured, the capabilities are ready to interact with management applications.
Provisioning Methods
TLS-PKI
TLS-PKI is also known as "Remote Configuration". The SCS uses TLS-PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) certificates to securely connect to an Intel AMT-enabled computer. The certificates can be generated in the following ways:
 The SCS can connect using one of the default certificates pre-programmed on the computer, as detailed in the MEBx interface section of this document.
The SCS can connect using one of the default certificates pre-programmed on the computer, as detailed in the MEBx interface section of this document.
 The SCS can create a custom certificate, which can be deployed on the AMT computer by means of a desk-side visit with a specially formatted USB thumb drive as detailed in the Configuration Service section of this document.
The SCS can create a custom certificate, which can be deployed on the AMT computer by means of a desk-side visit with a specially formatted USB thumb drive as detailed in the Configuration Service section of this document.
 The SCS could use a custom certificate which was pre-programmed at the Dell factory through the Custom Factory Integration (CFI) process.
The SCS could use a custom certificate which was pre-programmed at the Dell factory through the Custom Factory Integration (CFI) process.
TLS-PSK
TLS-PSK is also known as "One-Touch Configuration". The SCS uses PSK's (Pre-Shared Key's) to establish a secure

connection with the AMT computer. These 52-character keys can be created by the SCS, and then deployed on the AMT computer with a desk-side visit in one of two ways:
The key can be manually typed into the MEBx.
The SCS can create a list of custom keys, and put them onto a specially formatted USB thumb drive. Then each AMT computer retrieves a custom key from the specially formatted USB thumb drive during BIOS boot as detailed in the Configuration Service section of this document.
Back to Contents Page

Back to Contents Page
MEBx Settings Overview
The Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) provides platform-level configuration options for you to configure the behavior of the Management Engine (ME) platform. Options include enabling and disabling individual features and setting power configurations.
This section provides details about MEBx configuration options and constraints, if any.
NOTE: All the ME Platform Configuration setting changes are not cached in MEBx. They are committed to ME nonvolatile memory (NVM) until you exit MEBx. Hence, if MEBx crashes, the changes made until that point are NOT going to be committed to ME NVM.
Accessing the MEBx Configuration User Interface
The MEBx configuration user interface can be accessed on a computer through the following steps:
1.Turn on (or restart) your computer.
2.When the blue DELL™ logo appears, press <F12> immediately and select MEBx.
If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Microsoft® Windows® desktop. Then shut down your computer and try again.
3.Type the ME password. Press <Enter>.The default password is 'admin'. and it can be altered by the user.
NOTE: Another method to access the MEBx is to press <F12> for the one-time boot menu. When the menu appears, use the upand down-arrow keys to select Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx). Press <Enter>.
The MEBx screen appears as shown below.
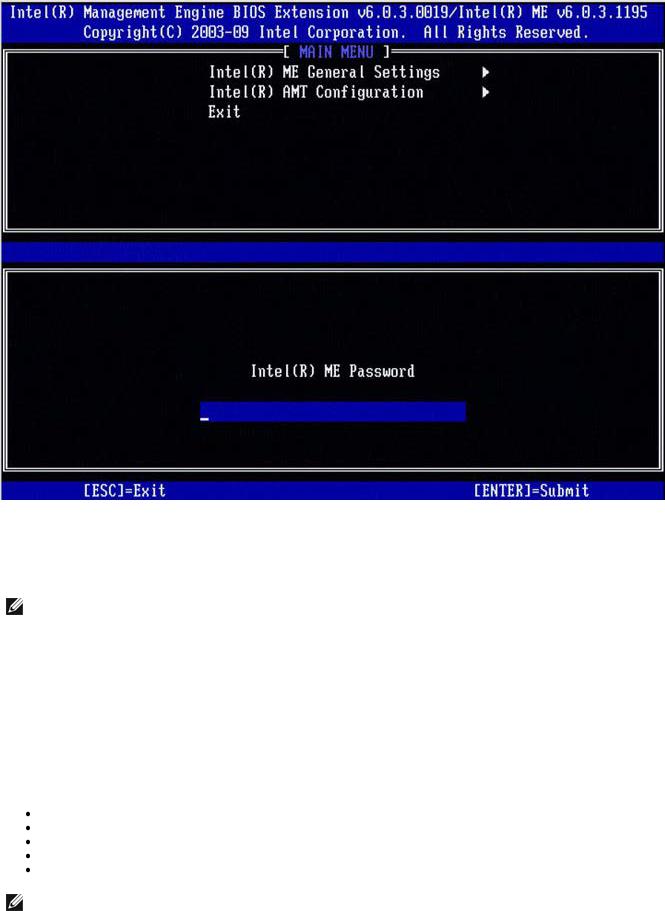
The main menu presents three function selections:
 Intel ME General Settings
Intel ME General Settings
 Intel AMT Configuration
Intel AMT Configuration
 Exit
Exit
NOTE: Intel MEBx will display only detected options. If one or more of these options do not appear, verify that the system supports the relevant missing feature.
Changing the Intel ME Password
The default password is admin and is the same on all newly deployed platforms. You must change the default password before changing any feature configuration options.
When an IT administrator first enters the Intel MEBx configuration menu with the default password, he or she must change the default password before any feature can be used.
The new password must include the following elements:
Eight characters, no more than 32
One uppercase letter
One lowercase letter
A number
A special (non-alphanumeric) character, such as !, $, or ; excluding the :, ", and , characters.)
NOTE: The underscore ( _ ) and spacebar are valid password characters but do NOT add to the password complexity.
* Information on this page provided by Intel.
Back to Contents Page

ME General Settings
To navigate to the Intel® Management Engine (ME) Platform Configuration page, follow these steps:
1.Under the Management Engine BIOS Extension (MEBx) main menu, select Intel ME General Settings. Press <Enter>.
2.The following message appears:
Acquiring General Settings configuration
The ME General Configuration page appears. This page allows the IT administrator to configure the specific functionality of the Intel ME, such as password, power options, and so on. Below are quick links to the various sections.
Intel ME State Control
 Change Intel ME Password
Change Intel ME Password
 Password Policy
Password Policy
 Network Setup
Network Setup
 Network Name Settings
Network Name Settings
Host Name
Domain Name
FQDN
Dynamic DNS
Periodic Update Interval
TTL
Previous Menu
 TCP/IP Settings
TCP/IP Settings
Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration
DHCP Mode
IPv4 Address
Default Gateway Address
Preferred DNS Address
Alternate DNS Address
Previous Menu
Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration
IPv6 Feature Selection
IPv6 Interface ID Type
IPv6 Address
IPv6 Default Router
Preferred DNS IPv6 Address
Alternate DNS IPv6 Address
Previous Menu
Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration
IPv6 Feature Selection
IPv6 Interface ID Type
Previous Menu
 Unconfigure Network Access
Unconfigure Network Access
 Remote Setup And Configuration
Remote Setup And Configuration
 Current Provisioning Mode
Current Provisioning Mode
 Provisioning Record
Provisioning Record
Start Configuration
Previous Menu
 Provisioning Server IPv4/IPv6
Provisioning Server IPv4/IPv6
 Provisioning Server FQDN
Provisioning Server FQDN
 TLS PSK
TLS PSK
Set PID and PPS
Deleting PID and PPS
Previous Menu
 TLS PKI
TLS PKI
Remote Configuration
PKI DNS Suffix
Manage Hashes
Adding Customized Hash
Deleting a Hash
Changing the Active State
Viewing a Certificate Hash
Previous Menu
 Previous Menu
Previous Menu
 FW Update Settings
FW Update Settings
 Local FW Update
Local FW Update
 Secure FW Update
Secure FW Update
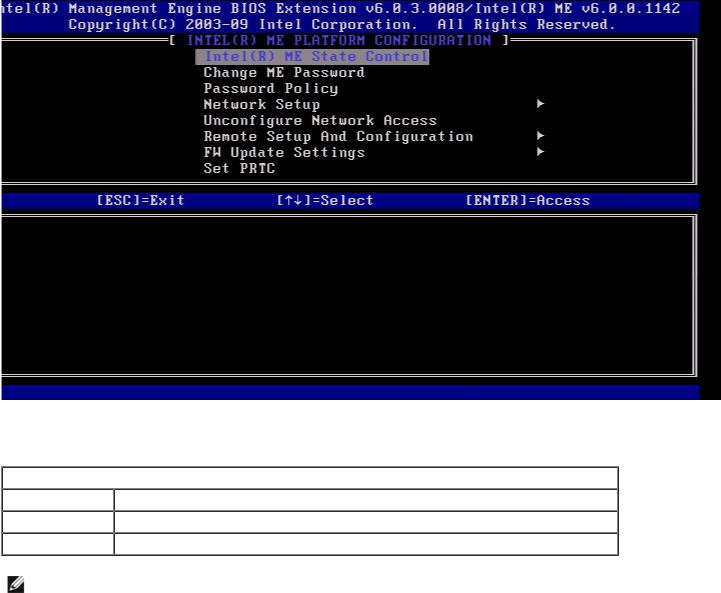
 Previous Menu
Previous Menu
 Set PRTC
Set PRTC
 Power Control
Power Control
 Intel ME ON in Host Sleep
Intel ME ON in Host Sleep
 Idle Time Out
Idle Time Out
 Previous Menu
Previous Menu
Intel ME State Control
When the ME State Control option is selected on the ME Platform Configuration menu, the ME State Control menu appears. You can disable ME to isolate the ME computer from the main platform until the end of the debugging process.
The Intel ME State Control option (enable/disable) provides the ability to disable the Intel ME for debugging purposes. Disabling the Intel ME through the MEBx prevents the Intel ME code from executing. This allows an IT technician to eliminate the Intel ME as the potential problem.
|
ME Platform State Control |
Option |
Description |
Enabled |
Enable the Management Engine on the platform |
Disabled |
Disable the Management Engine on the platform |
NOTE: “Disabling” the Intel ME does not really disable it. It causes the Intel ME code to be halted at an early stage of the Intel ME’s booting so that the system has no traffic originating from the Intel ME on any of the buses. This is not intended to be normal operation mode nor is it supported configuration and is for debug only. This allows an IT technician to debug a system problem without any interference from the Intel ME.
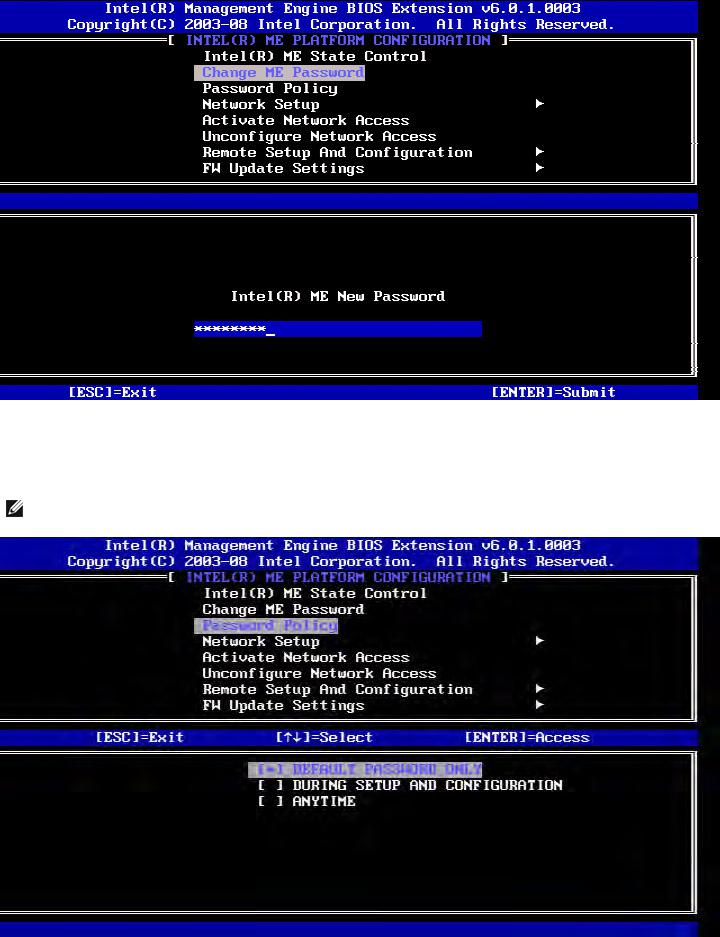
Change Intel ME Password
1.At the Intel ME New Password prompt, type your new password. (Please be aware of the password policies and restrictions mentioned in changing the Intel ME Password requirement)
2.At the Verify Password prompt, re-type your new password.
Password Policy
This option determines when the user is allowed to change the Intel MEBx password through the network.
NOTE: The Intel MEBx password can always be changed via the Intel MEBx user interface.
Description of these options.
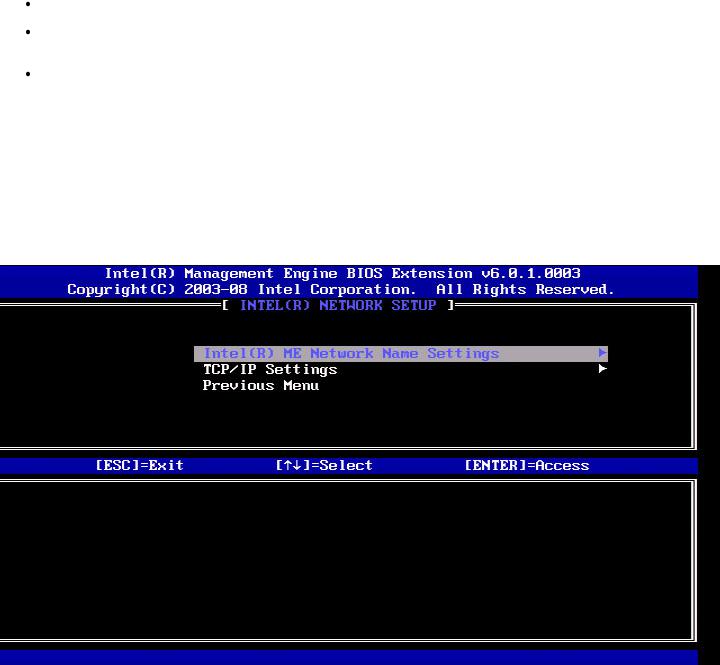
Default Password Only — The Intel MEBx password can be changed through the network interface if the default password has not been changed yet.
During Setup and Configuration — The Intel MEBx password can be changed through the network interface during the setup and configuration process but at no other time. Once the setup and configuration process is complete, the Intel MEBx password cannot be changed via the network interface.
Anytime — The Intel MEBx password can be changed through the network interface at any time.
Network Setup
Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu, select Network Setup and press Enter.
The Intel ME Platform Configuration menu changes to the Intel ME Network Setup page.
Network Name Settings
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Intel ME Network Name Settings and press Enter.
1. Host Name
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Host Name and press Enter.
A host name can be assigned to the Intel AMT machine. This will be the host name of the Intel AMT-enabled system.
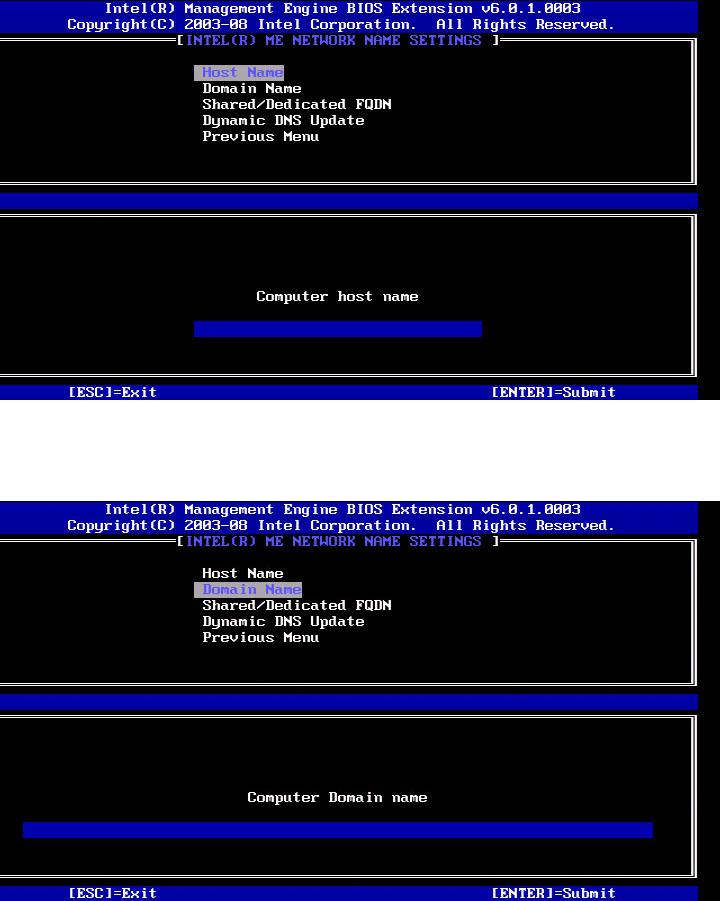
2. Domain Name
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Domain Name and press Enter. A domain name can be assigned to the Intel AMT machine.
3. Shared/Dedicated FQDN
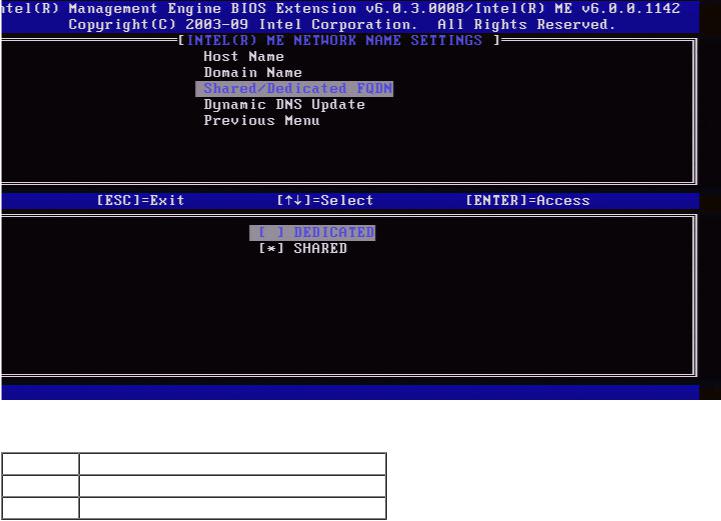
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Shared/Dedicated FQDN and press Enter.
This setting determines whether the Intel ME Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) (that is, the "HostName.DomainName") is shared with the host and identical to the operating system machine name or dedicated to the Intel ME.
Option |
Description |
Dedicated |
The FQDN domain name is dedicated to ME |
Shared |
The FQDN domain name is shared with the Host |
4. Dynamic DNS Update
Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Dynamic DNS Update and press Enter.
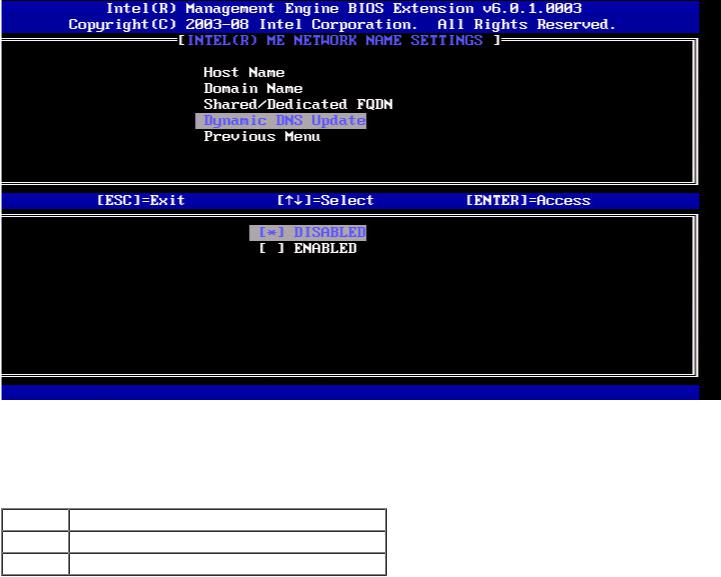
If Dynamic DNS Update is enabled, then the firmware will actively try to register its IP addresses and FQDN in DNS using the Dynamic DNS Update protocol. If DDNS Update is disabled, then the firmware will not make an attempt to update DNS using DHCP option 81 or Dynamic DNS update. If the DDNS Update state (Enabled or Disabled) is not configured by the user at all, then the firmware will assume its old implementation where the firmware used DHCP option 81 for DNS registration but did not directly update DNS using the DDNS update protocol. For selecting “Enabled” for Dynamic DNS Update, it is required that the Host Name and Domain Name are set.
Option |
Description |
Enabled |
The Dynamic DNS Update Client in FW is enabled. |
Disabled |
The Dynamic DNS Update Client in FW is disabled. |
5.Periodic Update Interval
1.Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Periodic Update Interval and press Enter.
2.Type the desired interval and press Enter.
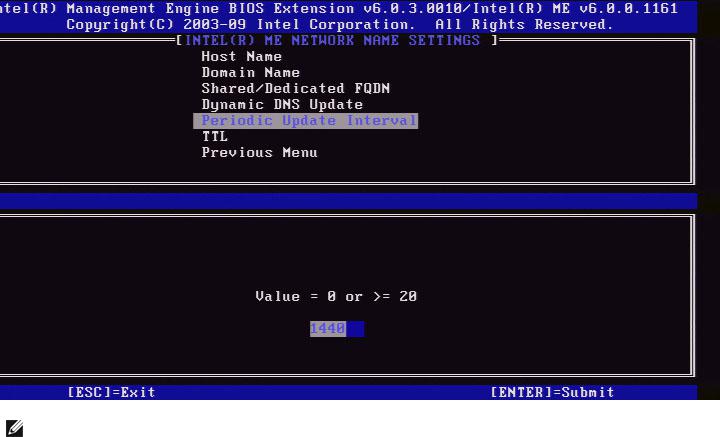
NOTE: This option is only available when Dynamic DNS Update is enabled.
Defines the interval at which the firmware DDNS Update client will send periodic updates. It should be set according to corporate DNS scavenging policy. Units are minutes. A value of 0 disables periodic update. The value set should be equal or greater than 20 minutes. The default value for this property is 24 hours - 1440 minutes.
6.TTL
1.Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select TTL and press Enter.
2.Type the desired time (in seconds) and press Enter.
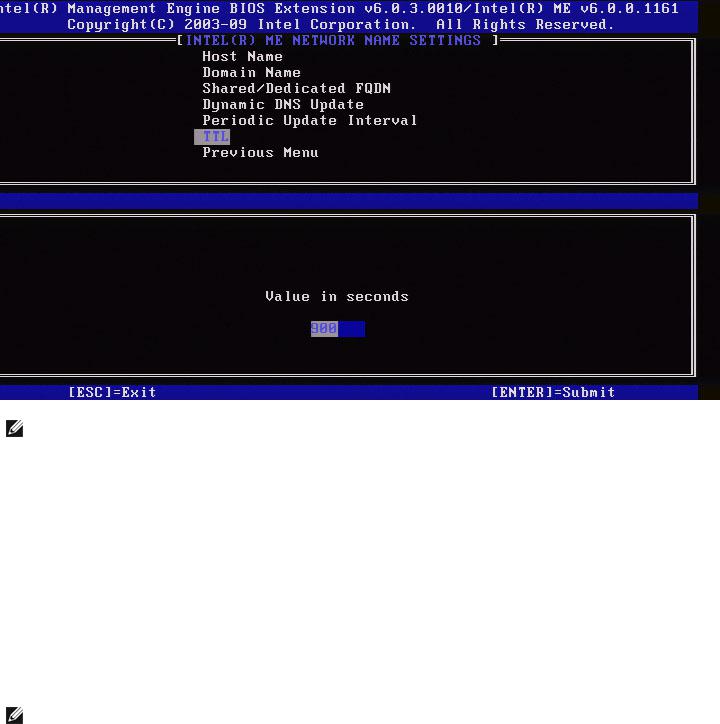
NOTE: This option is only available when Dynamic DNS Update is enabled.
This setting allows configuring the TTL time in seconds. This number should be greater than zero. If set to zero, the firmware uses its internal default value, which is 15 min or 1/3 of lease time for DHCP.
7.Previous Menu
1.Under the Intel ME Network Name Settings, select Previous Menu and press Enter.
2.The Intel ME Network Name Settings menu changes to the Intel Network Setup page.
TCP/IP Settings
1.Under the Network Setup menu, select TCP/IP Settings and press Enter.
2.The Intel ME Network Name Settings menu changes to the Intel Network Setup page.
The Intel Network Setup menu changes to the TCP/IP Settings page.
NOTE: The Intel MEBx has menus for Wireless IPv6, but no menu for wireless IPv4. When the Intel MEBx starts, it will check for the wireless interface to make the decision to display the wireless IPv6 menu or not.
Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration
Under the TCP/IP Settings, select Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration and press Enter. The TCP/IP Settings menu changes to the Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration page.

1. DHCP Mode
Under Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration, select DHCP Mode and press Enter.
The TCP/IP Settings menu changes to the Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration page.
ENABLED: If DHCP Mode is enabled, TCP/IP settings will be configured by a DHCP server. More options will be displayed on the screen. Select ENABLED and press Enter, no additional steps are required.
DHCP mode enabled.

Select DISABLED and press Enter. If you disable DHCP, more options will be displayed.
DHCP mode disabled.
2. IPv4 Address
Select IPv4 Address and press Enter.
Type the IPv4 Address in the address column and press Enter.
3. Subnet Mask Address
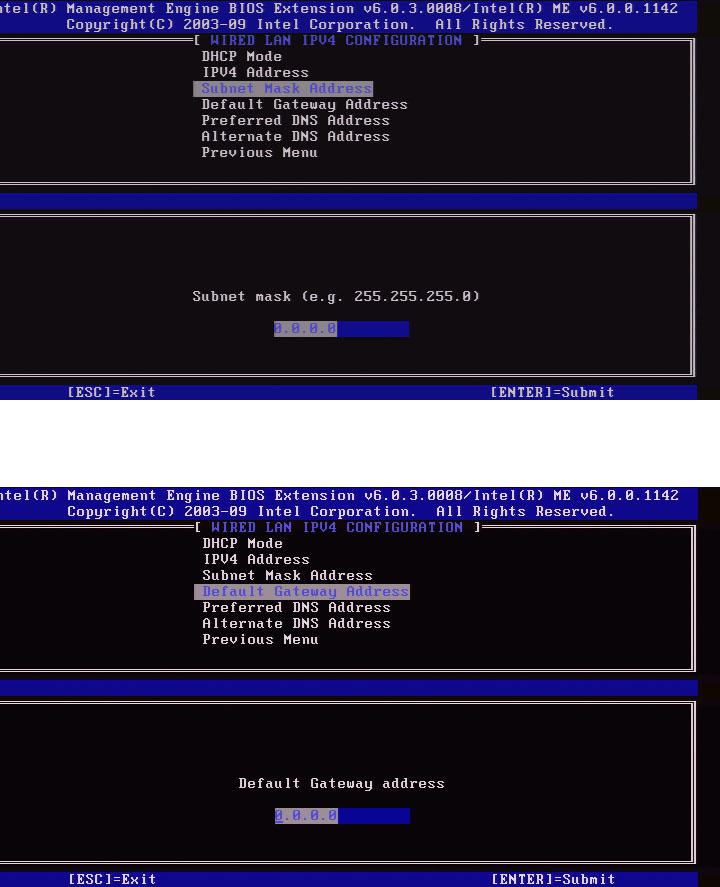
Select Subnet Mask Address and press Enter.
Type the Subnet Mask Address in the address column and press Enter.
4. Default Gateway Address
Select Default Gateway Address and press Enter.
Type the Default Gateway Address in the address column and press Enter.
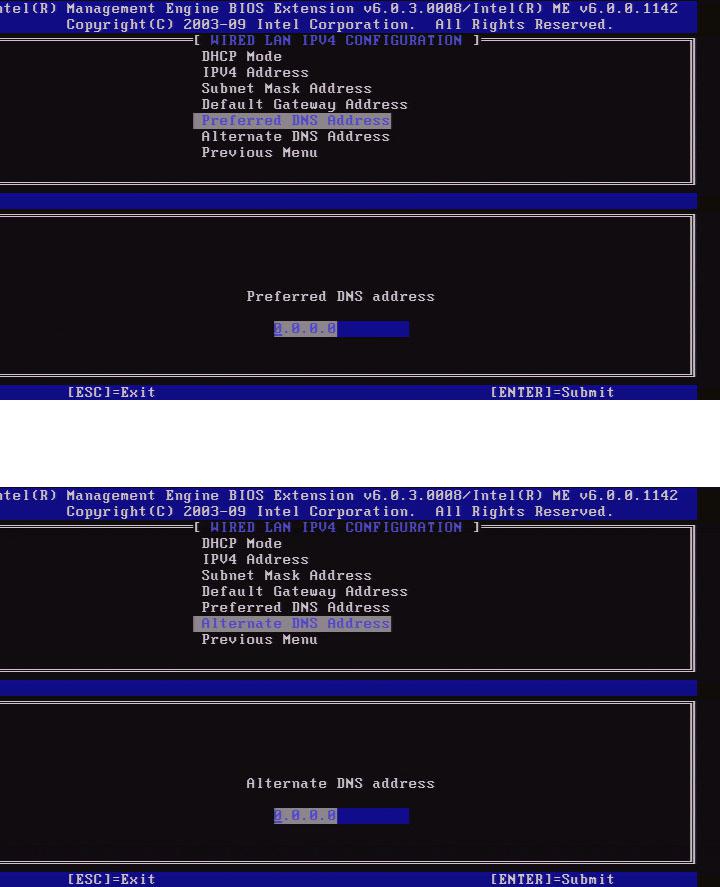
5. Preferred DNS Address
Select Preferred DNS Address and press Enter.
Type the Preferred DNS Address in the address column and press Enter.
6. Alternate DNS Address
Select Alternate DNS Address and press Enter.
Type the Alternate DNS Address in the address column and press Enter.
7. Previous Menu
Under the Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration, select Previous Menu and press Enter.
The Wired LAN IPv4 Configuration menu changes to the TCP/IP Settings menu.
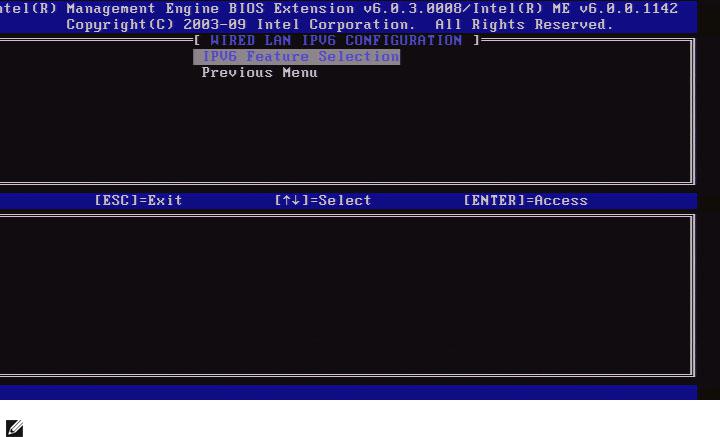
Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration
Under the TCP/IP Settings, select Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration and press Enter.
The TCP/IP Settings menu changes to the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration page.
The Intel ME IPv6 addresses are dedicated and not shared with the host operating system. To enable Dynamic DNS registration for IPv6 addresses, a dedicated FQDN must be configured.
NOTE: The Intel ME network stack supports a multi-homed IPv6 interface. Each network interface can be configured with the following IPv6 addresses:
1.One link local auto-configured address
2.Three auto-configured global addresses
3.One DHCPv6 configured address
4.One statically configured IPv6 address
1.IPv6 Feature Selection
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select IPv6 Feature Selection and press Enter.
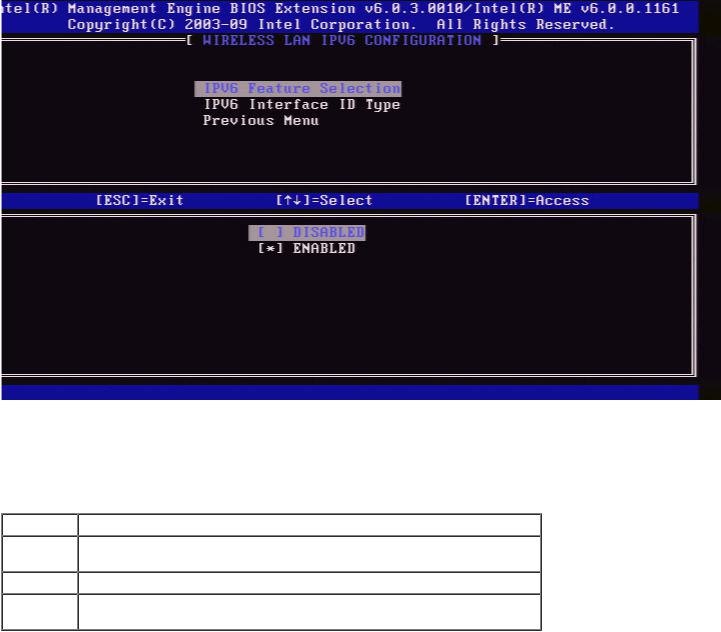
DISABLED: select 'Disabled' and press Enter. IPv6 Feature Selection is disabled.
ENABLED: select 'Enabled' and press Enter.
IPv6 Feature Selection is enabled as more configuration is allowed.
2. IPv6 Interface ID Type
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select IPv6 Interface ID Type and press Enter.
The auto-configured IPv6 address consists of two parts; the IPv6 Prefix set by the IPv6 router is the first part and the interface ID is the second part (64 bits each).
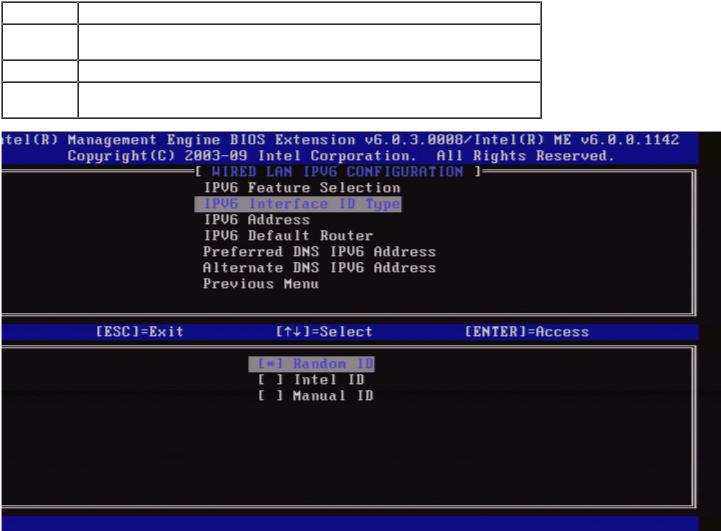
Option |
Description |
Random |
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using a random number |
ID |
as described in RFC 3041. This is the default. |
Intel ID |
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using the MAC address. |
Manual |
The IPv6 Interface ID is configured manually. Selecting this type requires |
ID |
that the Manual Interface ID is set with a valid value. |
3. IPv6 Address
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select IPv6 Address and press Enter. Type the IPv6 Address and press Enter.
4. IPv6 Default Router
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select IPv6 Default Router and press Enter. Type the IPv6 Default Router and press Enter.
5. Preferred DNS IPv6 Address
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select Preferred DNS IPv6 Address and press Enter. Type the Preferred DNS IPv6 Address and press Enter.
6. Alternate DNS IPv6 Address
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select Alternate DNS IPv6 Address and press Enter. Type the Alternate DNS IPv6 Address and press Enter.
7. Previous Menu
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select Previous Menu and press Enter. The Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration menu changes to the TCP/IP Settings menu.
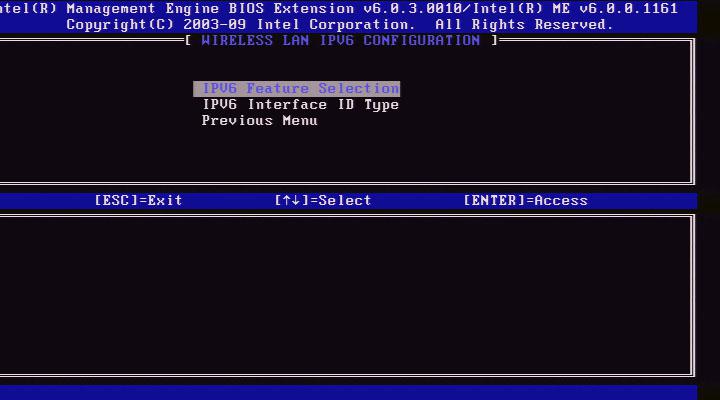
Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration
Under the TCP/IP Settings, select Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration and press Enter. The TCP/IP Settings menu changes to the Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration page.
1. IPv6 Feature Selection
Under the Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration, select IPv6 Feature Selection and press Enter.
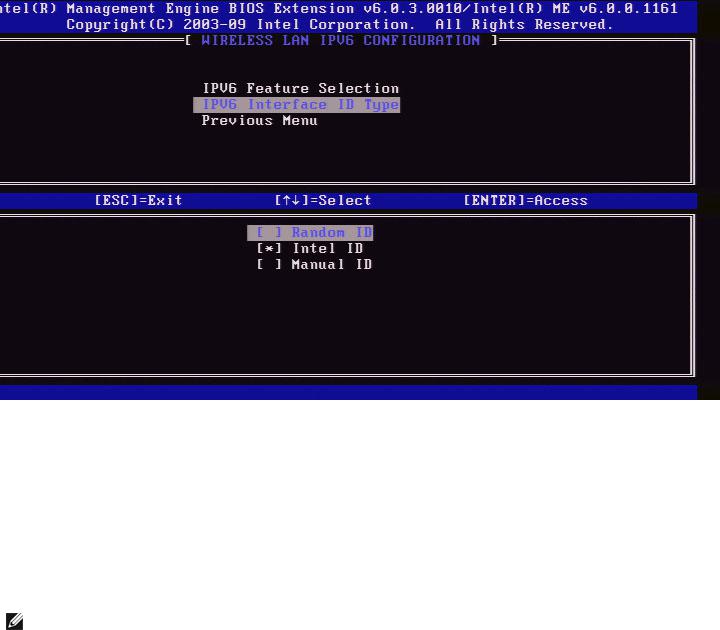
2. IPv6 Interface ID Type
Under the Wired LAN IPv6 Configuration, select IPv6 Interface ID Type and press Enter.
The auto-configured IPv6 address consists of two parts; the IPv6 Prefix set by the IPv6 router is the first part and the interface ID is the second part (64 bits each).
Option |
Description |
Random |
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using a random number |
ID |
as described in RFC 3041. This is the default. |
Intel ID |
The IPv6 Interface ID is automatically generated using the MAC address. |
Manual |
The IPv6 Interface ID is configured manually. Selecting this type requires |
ID |
that the Manual Interface ID is set with a valid value. |
3. Previous Menu
Under the Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration, select Previous Menu and press Enter. The Wireless LAN IPv6 Configuration menu changes to the TCP/IP Settings menu.
Unconfigure Network Access
1. Under the Intel ME Platform Configuration menu, select Unconfigure Network Access and press Enter.
NOTE: This will cause Intel ME to transition to the PRE-provisioning state.
 Loading...
Loading...