Dell PowerConnect M6220, PowerConnect M6348, PowerConnect M8024, PowerConnect 7024, PowerConnect 7024F Troubleshooting
...
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.Multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM
A Dell technical white paper
Version 1.1
Victor Teeter
Network Solutions Engineer
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.Multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM
This document is for informational purposes only and may contain typographical errors and technical inaccuracies. The content is provided as is, without express or implied warranties of any kind.
© 2013 Dell Inc. All rights reserved. Dell and its affiliates cannot be responsible for errors or omissions in typography or photography. Dell, the Dell logo, and PowerEdge are trademarks of Dell Inc. Intel and Xeon are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows Server are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. Dell disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of others.
April 2013| Rev 1.1
2
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.Multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM |
|
Contents |
|
Introduction ........................................................................................ |
4 |
Multicast Overview ................................................................................ |
4 |
Scenarios in this Document....................................................................... |
5 |
Scenario 1: Layer 2 Video Distribution on a Single VLAN (Using IGMP Querier) ..... |
5 |
Multicast Using IGMP Querier Setup ................................................... |
6 |
Testing the Multicast Setup ........................................................... |
10 |
Troubleshooting Tips ................................................................... |
11 |
Scenario 2: Layer 3 Video Distribution with Multiple VLANs (Using PIM-DM) ...... |
12 |
Multicast Using PIM-DM Setup......................................................... |
12 |
Testing the Multicast Setup ........................................................... |
17 |
Troubleshooting Tips ................................................................... |
18 |
Multicast Frames Explained .................................................................... |
19 |
Bandwidth Considerations ...................................................................... |
19 |
Useful Links ....................................................................................... |
19 |
About Dell......................................................................................... |
20 |
3
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.Multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM
Introduction
Dell PowerConnectTM firmware revision 5.1 has added vast improvements in the areas of IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) snooping and IP Multicast Failover. Starting with PowerConnect 5.1 firmware, Dell PowerConnect users have a new set of commands to configure IGMP snooping, MLD snooping, MVR (Multicast VLAN Registration), and bridge multicast filtering. This white paper uses several of the new commands to show how an administrator would set up common video distribution networks.
PowerConnect 5.1 firmware is supported on the following Dell PowerConnect devices:
M6220 |
7024 |
7048P |
8132 |
M6348 |
7024F |
7048R |
8132F |
M8024 |
7024P |
8024 |
8164 |
M8024k |
7048 |
8024F |
8164F |
Multicast Overview
Multicast services are used to distribute streaming media, such as audio and video traffic, over the network. These applications typically generate large amounts of traffic taking up network bandwidth. Both multicast and broadcast allow a network device to send single packets to multiple destinations. The difference is broadcast is designed to forward packets to all nodes on the VLAN, whereas multicast is designed to only forward to nodes in a multicast group. Multicast is therefore a better solution when trying to conserve network bandwidth. Also, since all nodes must process every frame they receive, multicast saves processing cycles on nodes that do not need to receive the multicast frames.
The multicast model consists of groups, transmitters, and receivers. A typical multicast group contains one transmitter (or sender) and one or more receivers. The receiver sends a “group join” message to network switches and routers via the Internet Group Multicast Protocol (IGMP). The switches and routers then forward multicast traffic only to the receivers that have joined the multicast group.
Dell PowerConnect switches by default will forward multicast frames to all interfaces in a VLAN. No additional configuration is required to pass this traffic; however, the default behavior provides no benefit over using broadcast. To limit unnecessary traffic on the network, an IGMP Querier (layer 2) or PIM router (layer 3) must be seen on the network for multicast to stop broadcasting to all ports. Starting with firmware 5.1.0.0, IGMP snooping is enabled on all switches; however, this does not keep the multicast traffic from broadcasting until the switches can see a Querier or PIM router.
Note: By creating an IGMP Querier or PIM router on the network, switches are able to stop multicast frames from being broadcasted and can forward those frames to transmitters and receivers in a specified multicast group.
Switches can use IGMP snooping to automatically collect information about which interfaces are participating in multicast groups. The switches then use this information to direct multicast traffic away from devices that are not interested in the IP multicast traffic.
Switches that are not “multicast aware” can use static multicast groups to manually select the interfaces that will pass multicast traffic.
4
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.Multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM
IGMP snooping and static multicast groups accomplish the same task. One is dynamic; requiring less setup and maintenance, while the other is static; requiring more setup and maintenance time. This paper only discusses how to set up the dynamic IGMP snooping feature with and without a PIM router. If it is desired to set up Static multicast groups, please see the documentation that came with your particular switch for instructions.
Scenarios in this Document
This document provides instructions for setting up two scenarios. In the first scenario, the desire is to keep the multicast network Layer 2 switched only, and therefore the IGMP snooping querier is used to perform the query functions of a Layer 3 multicast router.
The second scenario explores PIM and IGMP enabled in a Layer 3 network with IP multicast routing between multiple VLANs. In this case, the IP multicast router acts as the IGMP querier.
Firmware Versions
The firmware used on the PowerConnect 8100 switches in these scenarios was version 5.1.0.0. Only attempt these setups after updating firmware to 5.1.x.x or later on each participating switch. As always, it is best practice to update all BIOS code on computers and use the latest NIC drivers.
Scenario 1: Layer 2 Video Distribution on a Single VLAN (Using IGMP Querier)
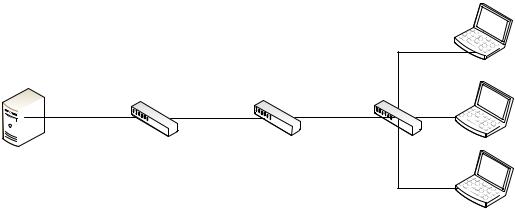
The first scenario for this paper consists of three PowerConnect switches, a video server, and multiple clients to receive the streaming video. The particular setup for generating this document contains a Dell PowerEdge R815 (Video Server), three Dell PowerConnect 8132 switches, and three Dell laptops for use as multicast receivers (Figure 2). VLC Media Player is used on a Windows server and Windows clients to generate and receive the multicast stream. The server is Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise, and clients include both Windows 7 and Windows XP.
This white paper includes instructions on how to set up and configure the hardware, how to download and install the VLC Media Player, and then how to test the entire setup using VLC.
Figure 1. Single VLAN Video Distribution Using IGMP Querier
|
|
|
Client |
|
|
|
|
IP addr: 10.0.0.51 /24 |
|
Video |
VLAN 10 with |
VLAN 10 with |
VLAN 10 with |
|
Server |
||||
IP addr: 10.0.0.1 /24 |
IP addr: 10.0.0.2 /24 |
IP addr: 10.0.0.3 /24 |
||
|
||||
|
|
|
Client |
|
|
|
|
IP addr: 10.0.0.52 /24 |
|
IP addr: 10.0.0.50 /24 |
Enable IGMP |
Enable IGMP |
Enable IGMP |
|
snooping and IGMP |
snooping |
snooping |
||
|
||||
|
querier |
|
Client |
|
|
|
IP addr: 10.0.0.53 /24 |
||
|
|
|
5
Efficient Video Distribution Networks with.Multicast: IGMP Querier and PIM-DM
Without IGMP snooping, multicast packets are broadcast throughout the network, causing unnecessary traffic. This impedes the efficiency of both the network and every system on the network that has to process and drop multicast packets they were not expecting. For example, all three laptops in Figure 2 would receive the traffic although only one or two of them may desire to.
Follow the steps below to set up and test the Multicast topology shown in Figure 2.
Multicast Using IGMP Querier Setup (CLI commands are given below)
Note: Best practice, particularly in a production environment, is to configure new switches before connecting them into the existing network. In an isolated test network such as this, it is okay to connect the switches together in the first step, provided they have no significant configuration other than for management. This will allow the administrator to telnet to each switch for configuring. Otherwise, use a console cable to each switch for configuring, and make cabling the switches together the last step.
1.Bring up all three switches and connect them together in a daisy chain with a LAG or single cable between switches as shown in Figure 2.
2.On all three switches, create VLAN 10. Assign VLAN 10 an IP address on each switch so that each switch’s VLAN 10 is on the same subnet.
Note: Non-querier switches such as the second and third switch here, do not require a VLAN IP address, but it is nice to have for management and troubleshooting purposes.
3.For each trunk port (going from one switch to another switch), configure the port in trunk mode and assign it to VLAN 10.
4.Plug in the server at one end of the network and the clients at the opposite end as shown in Figure 2.
5.On the two end switches, for each access port (going to a video server or client), configure the port in access mode and assign them VLAN 10.
6.Provide the server and each client an IP address within the same subnet as VLAN 10. For this example we gave the video server an IP address of 10.0.0.50, and we gave the clients IP addresses 10.0.0.51 through 10.0.0.53.
7.From a client, ping the server and all three VLAN IP addresses on the three switches to ensure the network is configured correctly.
8.Enable IGMP snooping on VLAN 10 on all three switches.
Note: With PowerConnect 5.1 and later firmware, IGMP snooping is enabled globally and on all VLANs by default. The vlan parameter is used to enable IGMP snooping on a specific VLAN, and the no parameter is used to remove IGMP snooping from a particular VLAN.
9.Remove IGMP snooping on VLAN 1.
10.Enable IGMP querier on the switch closest to the video server.
On a layer 2 network with a single VLAN, IGMP snooping must be enabled on all switches in the multicast route. With PowerConnect 5.1, IGMP snooping is enabled by default. A PIM router is not required for Multicast Routing to occur on a layer 2 network with one VLAN.
6
 Loading...
Loading...