Texas Instruments MSP430P325ACY, MSP-EVK430X320, MSP430P325AIPM, MSP430P325AIFN, MSP-STK430X320 Datasheet
...
|
|
MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A |
||
|
|
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER |
||
|
|
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
D Low Supply Voltage Range, 2.5 V ± 5.5 V |
D |
Integrated 12+2 Bit A/D Converter |
||
D Low Operation Current, 400 mA at 1 MHz, |
D |
Family Members Include: |
||
3 V |
|
± MSP430C323, 8KB ROM, 256 Byte RAM |
||
D Ultra-Low Power Consumption (Standby |
|
± MSP430C325, 16KB ROM, 512 Byte RAM |
||
Mode Down to 0.1 mA) |
|
± MSP430P325A, 16KB OTP, 512 Byte RAM |
||
D Five Power-Saving Modes |
D EPROM Version Available for Prototyping: |
|||
|
PMS430E325A |
|||
D Wakeup From Standby Mode in 6 ms |
|
|||
D |
Serial Onboard Programming |
|||
D 16-Bit RISC Architecture, 300 ns Instruction |
||||
D |
Programmable Code Protection by Security |
|||
Cycle Time |
||||
D Single Common 32 kHz Crystal, Internal |
|
Fuse |
||
D |
Avaliable in 64 Pin Quad Flatpack (QFP), |
|||
System Clock up to 3.3 MHz |
||||
D Integrated LCD Driver for up to 84 |
|
68 Pin Plastic J-Leaded Chip Carrier |
||
|
|
|
||
Segments
(PLCC), 68 Pin J-Leaded Ceramic Chip
Carrier (JLCC) Package (EPROM Version)
description
The Texas Instruments MSP430 is an ultra-low power mixed-signal microcontroller family consisting of several devices which feature different sets of modules targeted to various applications. The microcontroller is designed to be battery operated for an extended application lifetime. With 16-bit RISC architecture, 16-bit integrated registers on the CPU, and a constant generator, the MSP430 achieves maximum code efficiency. The digitallycontrolled oscillator, together with the frequency-locked-loop (FLL), provides a wakeup from a low-power mode to active mode in less than 6 ms.
PG Package
(TOP VIEW)
|
|
|
DV |
AV |
A1 |
A0 |
XBUF |
|
RST/NMI |
TCK |
|
TMS |
|
TDI/VPP |
|
TDO/TDI |
|
COM3 |
|
COM2 |
|
COM1 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
SS |
SS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64 636261 60 595857 56 55 545352 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
AVCC |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51 |
|
COM0 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
DVCC |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
|
S20/O20/CMPI |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
SVCC |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
|
S19/O19 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Rext |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
S18/O18 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
A2 |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
S17/O17 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
A3 |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
|
S16/O16 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
A4 |
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45 |
|
S15/O15 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
A5 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44 |
|
S14/O14 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Xin |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43 |
|
S13/O13 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Xout/TCLK |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42 |
|
S12/O12 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
CIN |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41 |
|
S11/O11 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TP0.0 |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
S10/O10 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TP0.1 |
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39 |
|
S9/O9 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TP0.2 |
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
S8/O8 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TP0.3 |
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
S7/O7 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TP0.4 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
S6/O6 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TP0.5 |
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
S5/O5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
P0.0 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
S4/O4 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
P0.1/RXD |
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
S3/O3 |
||
|
20 2122 23 2425 26 27282930 31 32 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.2/TXD |
P0.3 |
P0.4 |
P0.5 |
P0.6 |
|
P0.7 |
R33 |
|
R23 |
|
R13 |
|
R03 |
|
S0 |
|
S1 |
|
S2/O2 |
|
|
|||||||
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
1 |
MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
description (continued)
Typical applications include sensor systems that capture analog signals, convert them to digital values, and then process the data and display them or transmit them to a host system. The MSP430x32x offers an integrated 12+2 bit A/D converter with six multiplexed inputs.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AVAILABLE OPTIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PACKAGED DEVICES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TA |
|
|
|
|
|
PLASTIC |
|
PLASTIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PLASTIC |
|
|
|
|
CERAMIC |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64-PIN QFP |
|
64-PIN QFP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
68-PIN PLCC |
|
|
|
68-PIN JLCC |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(PG) |
|
(PM) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(FN) |
|
|
|
|
|
(FZ) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C to 85°C |
|
MSP430C323IPG |
|
MSP430C323IPM |
|
|
MSP430C323IFN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
MSP430C325IPG |
|
MSP430C325IPM |
|
|
MSP430C325IFN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ð |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSP430P325AIPG |
|
MSP430P325AIPM |
|
MSP430P325AIFN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
Ð |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ð |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ð |
|
|
|
|
PMS430E325AFZ |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
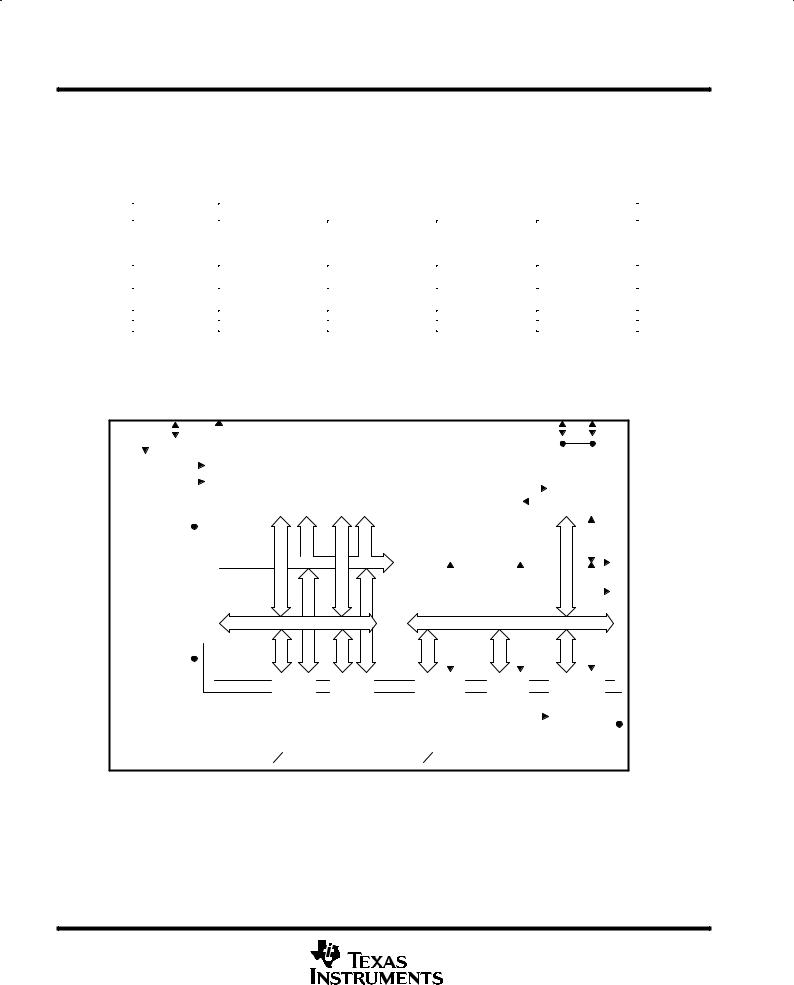
functional block diagram |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
XIN Xout/TCLK XBUF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RST/NMI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.0 |
P0.7 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oscillator |
|
|
ACLK |
|
8/16 kB ROM |
|
|
256/512 B |
|
|
|
Power-on- |
|
8 b Timer/ |
|
|
|
|
|
I/O Port |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
FLL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 kB OTP |
|
|
RAM |
|
|
|
|
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|
Counter |
TXD |
|
8 I/O's, All With |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
System Clock |
|
|
MCLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
'C': ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Serial Protocol |
|
|
|
|
|
Interr. Cap. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Support |
|
|
|
|
|
3 Int. Vectors |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
'P': OTP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
TDI/VPP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RXD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
TDO/TDI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAB, 16 Bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAB, 4 Bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
CPU |
|
|
|
Test |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MCB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Incl. 16 Reg. |
|
JTAG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
MDB, 16 Bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MDB, 8 Bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TMS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conv |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
TCK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADC |
|
|
Watchdog |
|
|
Timer/Port |
|
Basic |
|
|
|
|
LCD |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 + 2 Bit |
|
|
timer |
|
|
Applications: |
|
Timer1 |
|
|
|
84 Segments |
|
|
|
Com0±3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 Channels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A/D Conv. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15/16 Bit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
f LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S0±19/O2±19 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current S. |
|
|
|
|
|
Timer, O/P |
|
|
|
1, 2, 3, 4 MUX |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S20/O20CMPI |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CMPI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A0±5 |
|
SVCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.0±5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R33 |
|
R13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rext |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R23 |
|
R03 |
|
||||||||||||||
2 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

|
|
|
|
|
MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Terminal Functions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TERMINAL |
|
I/O |
DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
NAME |
NO. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AVCC |
1 |
|
Positive analog supply voltage |
|
|
|
AVSS |
63 |
|
Analog ground reference |
|
|
|
A0 |
61 |
I |
Analog-to-digital converter input port 0 or digital input port 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A1 |
62 |
I |
Analog-to-digital converter input port 1 or digital input port 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A2±A5 |
5±8 |
I |
Analog-to-digital converter inputs ports 2±5 or digital inputs ports 2±5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CIN |
11 |
I |
Input used as enable of counter TPCNT1 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COM0±3 |
51±54 |
O |
Common outputs, used for LCD backplanes ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DVCC |
2 |
|
Positive digital supply voltage |
|
|
|
DVSS |
64 |
|
Digital ground reference |
|
|
|
P0.0 |
18 |
I/O |
General-purpose digital I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.1/RXD |
19 |
I/O |
General-purpose digital I/O, receive digital input port, 8-bit Timer/Counter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.2/TXD |
20 |
I/O |
General-purpose digital I/O, transmit data output port, 8-bit Timer/Counter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0.3±P0.7 |
21±25 |
I/O |
Five general-purpose digital I/Os, bit 3 to bit 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rext |
4 |
I |
Programming resistor input of internal current source |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
59 |
I |
Reset input or non-maskable interrupt input |
|
|
RST/NMI |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R03 |
29 |
I |
Input of fourth positive analog LCD level (V4) ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R13 |
28 |
I |
Input of third positive analog LCD level (V3) ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R23 |
27 |
I |
Input of second positive analog LCD level (V2) ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R33 |
26 |
O |
Output of first positive analog LCD level (V1) ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SVCC |
3 |
|
Switched AVCC to analog-to-digital converter |
|
|
|
S0 |
30 |
O |
Segment line S0 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S1 |
31 |
O |
Segment line S1 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S2±S5/O2±O5 |
32±35 |
O |
Segment lines S2 to S5 or digital output ports O2±O5, group 1 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S20/O20/CMPI |
50 |
I/O |
Segment line S20 can be used as comparator input port CMPI ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S6±S9/O6±O9 |
36±39 |
O |
Segment lines S6 to S9 or digital output ports O6±O9, group 2 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S10±S13/O10±O13 |
40±43 |
O |
Segment lines S10 to S13 or digital output ports O10±O13, group 3 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S14±S17/O14±O17 |
44±47 |
O |
Segment lines S14 to S17 or digital output ports O14 to O17, group 4 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S18-S19/O18-O19 |
48, 49 |
O |
Segment lines S18 and S19 or digital output port O18 and O19, group 5 ± LCD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TCK |
58 |
I |
Test clock, clock input terminal for device programming and test |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TDO/TDI |
55 |
I/O |
Test data output, data output terminal or data input during programming |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TDI/VPP |
56 |
I |
Test data input, data input terminal or input of programming voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TMS |
57 |
I |
Test mode select, input terminal for device programming and test |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.0 |
12 |
O |
General-purpose 3-state digital output port, bit 0 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.1 |
13 |
O |
General-purpose 3-state digital output port, bit 1 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.2 |
14 |
O |
General-purpose 3-state digital output port, bit 2 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.3 |
15 |
O |
General-purpose 3-state digital output port, bit 3 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.4 |
16 |
O |
General-purpose 3-state digital output port, bit 4 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TP0.5 |
17 |
I/O |
General-purpose digital input/output port, bit 5 ± Timer/Port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XBUF |
60 |
O |
Clock signal output of system clock MCLK or crystal clock ACLK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xin |
9 |
I |
Input terminal of crystal oscillator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Xout/TCLK |
10 |
I/O |
Output terminal of crystal oscillator or test clock input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
3 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
short-form description
processing unit
The processing unit is based on a consistent and orthogonally-designed CPU and instruction set. This design structure results in a RISC-like architecture, highly transparent to the application development and is distinguished due to ease of programming. All operations other than program-flow instructions are consequently performed as register operations in conjunction with seven addressing modes for source and four modes for destination operand.
Program Counter |
PC/R0 |
CPU
Sixteen registers are located inside the CPU, providing reduced instruction execution time. This reduces a register-register operation execution time to one cycle of the processor frequency.
Four of the registers are reserved for special use as a program counter, a stack pointer, a status register and a constant generator. The remaining registers are available as general-purpose registers.
Peripherals are connected to the CPU using a data address and control bus and can be handled easily with all instructions for memory manipulation.
instruction set
Stack Pointer |
SP/R1 |
|
SR/CG1/R2 |
|
|
Status Register |
|
|
CG2/R3 |
|
|
Constant Generator |
|
|
R4 |
|
|
General-Purpose Register |
|
|
R5 |
|
|
General-Purpose Register |
|
|
|
|
|
General-Purpose Register |
R14 |
|
R15 |
|
|
General-Purpose Register |
|
|
|
The instruction set for this register-register architecture provides a powerful and easy-to-use assembler language. The instruction set consists of 51 instructions with three formats and seven addressing modes. Table 1 provides a summation and example of the three types of instruction formats; the addressing modes are listed in Table 2.
Table 1. Instruction Word Formats
Dual operands, source-destination |
e.g. ADD R4, R5 |
R4 + R5 → R5 |
Single operands, destination only |
e.g. CALL R8 |
PC → (TOS), R8 → PC |
Relative jump, un-/conditional |
e.g. JNE |
Jump-on equal bit = 0 |
Each instruction that operates on word and byte data is identified by the suffix B.
Examples: |
Instructions for word operation |
Instructions for byte operation |
||
|
MOV |
EDE, TONI |
MOV.B |
EDE, TONI |
|
ADD |
#235h, &MEM |
ADD.B |
#35h, &MEM |
|
PUSH |
R5 |
PUSH.B |
R5 |
|
SWPB |
R5 |
Ð |
|
4 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2. Address Mode Descriptions |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADDRESS MODE |
|
s |
|
d |
|
SYNTAX |
EXAMPLE |
OPERATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Register |
|
√ |
|
√ |
|
MOV Rs, Rd |
MOV R10, R11 |
R10 → R11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indexed |
|
√ |
|
√ |
|
MOV X(Rn), Y(Rm) |
MOV 2(R5), 5(R6) |
M(2 + R5) → M(6 + R6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Symbolic (PC relative) |
|
√ |
|
√ |
|
MOV EDE, TONI |
|
M(EDE) → M(TONI) |
|
Absolute |
|
√ |
|
√ |
|
MOV &MEM, &TCDAT |
|
M(MEM) → M(TCDAT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect |
|
√ |
|
|
|
MOV @Rn, Y(Rm) |
MOV @R10, Tab(R6) |
M(R10) → M(Tab + R6) |
|
Indirect autoincrement |
|
√ |
|
|
|
MOV @Rn+, RM |
MOV @R10+, R11 |
M(R10) → R11, R10 + 2 → R10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Immediate |
|
√ |
|
|
|
MOV #X, TONI |
MOV #45, TONI |
#45 → M(TONI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: s = source |
d = destination |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Computed branches (BR) and subroutine calls (CALL) instructions use the same addressing modes as the other instructions. These addressing modes provide indirect addressing, ideally suited for computed branches and calls. The full use of this programming capability permits a program structure different from conventional 8- and 16-bit controllers. For example, numerous routines can easily be designed to deal with pointers and stacks instead of using flag type programs for flow control.
operation modes and interrupts
The MSP430 operating modes support various advanced requirements for ultra low power and ultra low energy consumption. This is achieved by the intelligent management of the operations during the different module operation modes and CPU states. The requirements are fully supported during interrupt event handling. An interrupt event awakens the system from each of the various operating modes and returns with the RETI instruction to the mode that was selected before the interrupt event. The clocks used are ACLK and MCLK. ACLK is the crystal frequency and MCLK is a multiple of ACLK and is used as the system clock.
The software can configure five operating modes:
DActive mode (AM). The CPU is enabled with different combinations of active peripheral modules.
DLow power mode 0 (LPM0). The CPU is disabled, peripheral operation continues, ACLK and MCLK signals are active, and loop control for MCLK is active.
DLow power mode 1 (LPM1). The CPU is disabled, peripheral operation continues, ACLK and MCLK signals are active, and loop control for MCLK is inactive.
DLow power mode 2 (LPM2). The CPU is disabled, peripheral operation continues, ACLK signal is active, and MCLK and loop control for MCLK are inactive.
DLow power mode 3 (LPM3). The CPU is disabled, peripheral operation continues, ACLK signal is active, MCLK and loop control for MCLK are inactive, and the dc generator for the digital controlled oscillator (DCO) (³MCLK generator) is switched off.
DLow power mode 4 (LPM4). The CPU is disabled, peripheral operation continues, ACLK signal is inactive (crystal oscillator stopped), MCLK and loop control for MCLK are inactive, and the dc generator for the DCO is switched off.
The special function registers (SFR) include module-enable bits that stop or enable the operation of the specific peripheral module. All registers of the peripherals may be accessed if the operational function is stopped or enabled. However, some peripheral current-saving functions are accessed through the state of local register bits. An example is the enable/disable of the analog voltage generator in the LCD peripheral, which is turned on or off using one register bit.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
5 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
operation modes and interrupts (continued)
The most general bits that influence current consumption and support fast turnon from low-power operating modes are located in the status register (SR). Four of these bits control the CPU and the system clock generator: SCG1, SCG0, OscOff, and CPUOff.
15 |
9 |
8 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
Reserved For Future |
|
V |
SCG1 |
SCG0 |
OscOff |
CPUOff |
GIE |
N |
Z |
C |
|||
|
Enhancements |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw-0
interrupt vector addresses
The interrupt vectors and the power-up starting address are located in the ROM with an address range of 0FFFFh-0FFE0h. The vector contains the 16-bit address of the appropriate interrupt handler instruction sequence.
INTERRUPT SOURCE |
INTERRUPT FLAG |
SYSTEM INTERRUPT |
WORD ADDRESS |
PRIORITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power-up, external reset, watchdog |
WDTIFG (see Note1) |
Reset |
0FFFEh |
15, highest |
|
NMI, oscillator fault |
NMIIFG (see Notes 1 and 3) |
Non-maskable, |
0FFFCh |
14 |
|
OFIFG (see Notes 1 and 4) |
(Non)-maskable |
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dedicated I/O P0.0 |
P0.0IFG |
maskable |
0FFFAh |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dedicated I/O P0.1 or 8-bit Timer/Counter |
P0.1IFG |
maskable |
0FFF8h |
12 |
|
RXD |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFF6h |
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Watchdog Timer |
WDTIFG |
maskable |
0FFF4h |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFF2h |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFF0h |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFEEh |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFECh |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADC |
ADCIFG |
maskable |
0FFEAh |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timer/Port |
RC1FG, RC2FG, EN1FG |
maskable |
0FFE8h |
4 |
|
(see Note 2) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFE6h |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0FFE4h |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Timer1 |
BTIFG |
maskable |
0FFE2h |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O port 0, P0.2±7 |
P0.27IFG (see Note 1) |
maskable |
0FFE0h |
0, lowest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE 1: Multiple source flags
NOTE 2: Timer/Port interrupt flags are located in the T/P registers
NOTE 3: Non-maskable: neither the individual nor the general interrupt enable bit will disable an interrupt event.
NOTE 4: (Non)-maskable: the individual interrupt enable bit can disable on interrupt event, but the general interrupt enable bit cannot.
6 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
operation modes and interrupts (continued)
special function registers
Most interrupt and module enable bits are collected into the lowest address space. Special function register bits that are not allocated to a functional purpose are not physically present in the device. Simple SW access is provided with this arrangement.
interrupt enable 1 and 2
Address |
7 |
6 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|||
0h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P0IE.1 |
|
P0IE.0 |
OFIE |
WDTIE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw-0 |
rw-0 |
rw-0 |
rw-0 |
||
WDTIE: |
|
Watchdog Timer enable signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
OFIE: |
|
Oscillator fault enable signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
P0IE.0: |
|
Dedicated I/O P0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
P0IE.1: |
|
P0.1 or 8-bit Timer/Counter, RXD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Address |
7 |
6 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|||
01h |
|
BTIE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TPIE |
|
ADIE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw-0 |
rw-0 |
|
|
||
ADIE: |
|
A/D converter enable signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
TPIE: |
|
Timer/Port enable signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
BTIE: |
|
Basic Timer1 enable signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
interrupt flag register 1 and 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Address |
7 |
6 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|||
02h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NMIIFG |
P0IFG.1 |
|
P0IFG.0 |
OFIFG |
WDTIFG |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw-0 |
|
rw-0 |
rw-0 |
rw-1 |
rw-0 |
||
WDTIFG: |
|
Set on overflow or security key violation |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reset on VCC power on or reset condition at |
RST/NMI-pin |
|
|
||||||||
OFIFG: |
|
Flag set on oscillator fault |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
P0.0IFG: |
|
Dedicated I/O P0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
P0.1IFG: |
|
P0.1 or 8-bit Timer/Counter, RXD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
NMIIFG: |
|
Signal at |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
RST/NMI-pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Address |
7 |
6 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
3 |
|
2 |
1 |
0 |
|||
03h |
|
BTIFG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADIFG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
rw-0 |
|
|
|
BTIFG |
|
Basic Timer1 flag |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
ADFIG |
|
Analog-to-digital converter flag |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
7 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
operation modes and interrupts (continued)
module enable register 1 and 2
Address |
7 |
6 |
5 |
|
4 |
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
04h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
7 |
6 |
5 |
|
4 |
|
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
05h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend |
rw: |
Bit can be read and written. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
rw-0: |
Bit can be read and written. It is reset by PUC. |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
SFR bit not present in device. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
memory organization
|
|
|
MSP430P325A |
|
|
||
|
MSP430C323 |
|
PMS430E325A |
|
MSP430C325 |
||
FFFFh |
|
FFFFh |
|
|
FFFFh |
|
|
Int. Vector |
Int. Vector |
Int. Vector |
|||||
FFE0h |
FFE0h |
FFE0h |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|||||
FFDFh |
FFDFh |
FFDFh |
|||||
|
8 kB ROM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
E000h |
|
|
16 kB OTP |
|
16 kB ROM |
||
|
|
or |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
EPROM |
|
|
||
|
|
C000h |
|
|
C000h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
02FFh |
|
03FFh |
512B RAM |
03FFh |
512B RAM |
|
|
||||||
256B RAM |
0200h |
0200h |
||||
0200h |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
01FFh |
16b Per. |
01FFh |
16b Per. |
01FFh |
16b Per. |
|
0100h |
0100h |
0100h |
||||
|
|
|
||||
00FFh |
8b Per. |
00FFh |
8b Per. |
00FFh |
8b Per. |
|
0010h |
0010h |
0010h |
||||
|
|
|
||||
000Fh |
SFR |
000Fh |
SFR |
000Fh |
SFR |
|
0000h |
|
0000h |
|
0000h |
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
peripherals
Peripherals connect to the CPU through data, address, and control busses and can be handled easily with all instructions for memory manipulation.
peripheral file map
PERIPHERALS WITH WORD ACCESS
Watchdog |
|
Watchdog Timer control |
|
WDTCTL |
0120h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADC |
|
Data register |
|
ADAT |
0118h |
|
|
Reserved |
|
|
0116h |
|
|
Control register |
|
ACTL |
0114h |
|
|
Input enable register |
|
AEN |
o112h |
|
|
Input register |
|
AIN |
0110h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
PERIPHERALS WITH BYTE ACCESS |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
EPROM |
|
EPROM control |
|
EPCTL |
054h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crystal buffer |
|
Crystal buffer control |
|
CBCTL |
053h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
System clock |
|
SCG frequency control |
|
SCFQCTL |
052h |
|
|
SCG frequency integrator |
|
SCFI1 |
051h |
|
|
SCG frequency integrator |
|
SCFI0 |
050h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timer/Port |
|
Timer/Port enable |
|
TPE |
04Fh |
|
|
Timer/Port data |
|
TPD |
04Eh |
|
|
Timer/Port counter2 |
|
TPCNT2 |
04Dh |
|
|
Timer/Port counter1 |
|
TPCNT1 |
04Ch |
|
|
Timer/Port control |
|
TPCTL |
04Bh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8-Bit Timer/Counter |
|
8-Bit Timer/Counter data |
|
TCDAT |
044h |
|
|
8-Bit Timer/Counter preload |
|
TCPLD |
043h |
|
|
8-Bit Timer/Counter control |
|
TCCTL |
042h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Timer1 |
|
Basic Timer counter2 |
|
BTCNT2 |
047h |
|
|
Basic Timer counter1 |
|
BTCNT1 |
046h |
|
|
Basic Timer control |
|
BTCTL |
040h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LCD |
|
LCD memory 15 |
|
LCDM15 |
03Fh |
|
|
: |
|
: |
: |
|
|
LCD memory 1 |
|
LCDM1 |
031h |
|
|
LCD control & mode |
|
LCDCTL |
030h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port P0 |
|
Port P0 interrupt enable |
|
P0IE |
015h |
|
|
Port P0 interrupt edge select |
|
P0IES |
014h |
|
|
Port P0 interrupt flag |
|
P0IFG |
013h |
|
|
Port P0 direction |
|
P0DIR |
012h |
|
|
Port P0 output |
|
P0OUT |
011h |
|
|
Port P0 input |
|
P0IN |
010h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Special function |
|
SFR interrupt flag2 |
|
IFG2 |
003h |
|
|
SFR interrupt flag1 |
|
IFG1 |
002h |
|
|
SFR interrupt enable2 |
|
IE2 |
001h |
|
|
SFR interrupt enable1 |
|
IE1 |
000h |
oscillator and system clock
Two clocks are used in the system, the system (master) clock (MCLK) and the auxiliary clock (ACLK). The MCLK is a multiple of the ACLK. The ACLK runs with the crystal oscillator frequency. The special design of the oscillator supports the feature of low current consumption and the use of a 32 768 Hz crystal. The crystal is connected across two terminals without any other external components being required.
The oscillator starts after applying VCC, due to a reset of the control bit (OscOff) in the status register (SR). It can be stopped by setting the OscOff bit to a 1. The enabled clock signals ACLK, ACLK/2, ACLK/4, or MCLK are accessible for use by external devices at output terminal XBUF.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
9 |

MSP430C32x, MSP430P325A
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS219B ± MARCH 1999 ± REVISED MARCH 2000
oscillator and system clock (continued)
The controller system clock has to operate with different requirements according to the application and system conditions. Requirements include:
DHigh frequency in order to react quickly to system hardware requests or events
DLow frequency in order to minimize current consumption, EMI, etc.
DStable frequency for timer applications e.g. real time clock (RTC)
DEnable start-stop operation with a minimum of delay
These requirements cannot all be met with fast frequency high-Q crystals or with RC-type low-Q oscillators. The compromise selected for the MSP430 uses a low-crystal frequency which is multiplied to achieve the desired nominal operating range:
f(system) = (N+1) × f(crystal)
The crystal frequency multiplication is acheived with a frequency locked loop (FLL) technique. The factor N is set to 31 after a power-up clear condition. The FLL technique, in combination with a digital controlled oscillator (DCO) provides immediate start-up capability together with long term crystal stability. The frequency variation of the DCO with the FLL inactive is typically 330 ppm which means that with a cycle time of 1 µs the maximum possible variation is 0.33 ns. For more precise timing, the FLL can be used which forces longer cycle times if the previous cycle time was shorter than the selected one. This switching of cycle times makes it possible to meet the chosen system frequency over a long period of time.
The start-up operation of the system clock depends on the previous machine state. During a power up clear (PUC), the DCO is reset to its lowest possible frequency. The control logic starts operation immediately after recognition of PUC. Connect operation of the FLL control logic requires the presence of a stable crystal oscillator.
digital I/O
One 8-bit I/O port (Port0) is implemented. Six control registers give maximum flexibility of digital input/output to the application:
DAll individual I/O bits are programmable independently.
DAny combination of input, output, and interrupt conditions is possible.
DInterrupt processing of external events is fully implemented for all eight bits of port P0.
DProvides read/write access to all registers with all instructions.
The six registers are:
D |
Input register |
Contains information at the pins |
D |
Output register |
Contains output information |
D |
Direction register |
Controls direction |
D |
Interrupt flags |
Indicates if interrupt(s) are pending |
D |
Interrupt edge select |
Contains input signal change necessary for interrupt |
D |
Interrupt enable |
Contains interrupt enable pins |
All six registers contain eight bits except for the interrupt flag register and the interrupt enable register. The two LSBs of the interrupt flag and interrupt enable registers are located in the special functions register (SFR). Three interrupt vectors are implemented, one for Port0.0, one for Port0.1, and one commonly used for any interrupt event on Port0.2 to Port0.7. The Port0.1 and Port0.2 pin function is shared with the 8-bit Timer/Counter.
10 |
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 •DALLAS, TEXAS 75265 |
 Loading...
Loading...