Motorola MPX2200GS, MPX2200GSX, MPX2200GVP, MPX2200GVS, MPX2200D Datasheet
...
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document by MPX2200/D
200 kPa
On-Chip Temperature Compensated & Calibrated Pressure Sensors
The MPX2200 and MPX2201 series device is a silicon piezoresistive pressure sensor providing a highly accurate and linear voltage output Ð directly proportional to the applied pressure. The sensor is a single monolithic silicon diaphragm with the strain gauge and a thin±film resistor network integrated on±chip. The chip is laser trimmed for precise span and offset calibration and temperature compensation. They are designed for use in applications such as pump/motor controllers, robotics, level indicators, medical diagnostics, pressure switching, barometers, altimeters, etc.
Features
•Temperature Compensated Over 0°C to +85°C
•Patented Silicon Shear Stress Strain Gauge
•±0.25% Linearity (MPX2200D)
•Easy to Use Chip Carrier Package
•Available in Absolute, Differential and Gauge Configurations
Application Examples
•Pump/Motor Controllers
•Robotics
•Level Indicators
•Medical Diagnostics
•Pressure Switching
•Barometers
•Altimeters
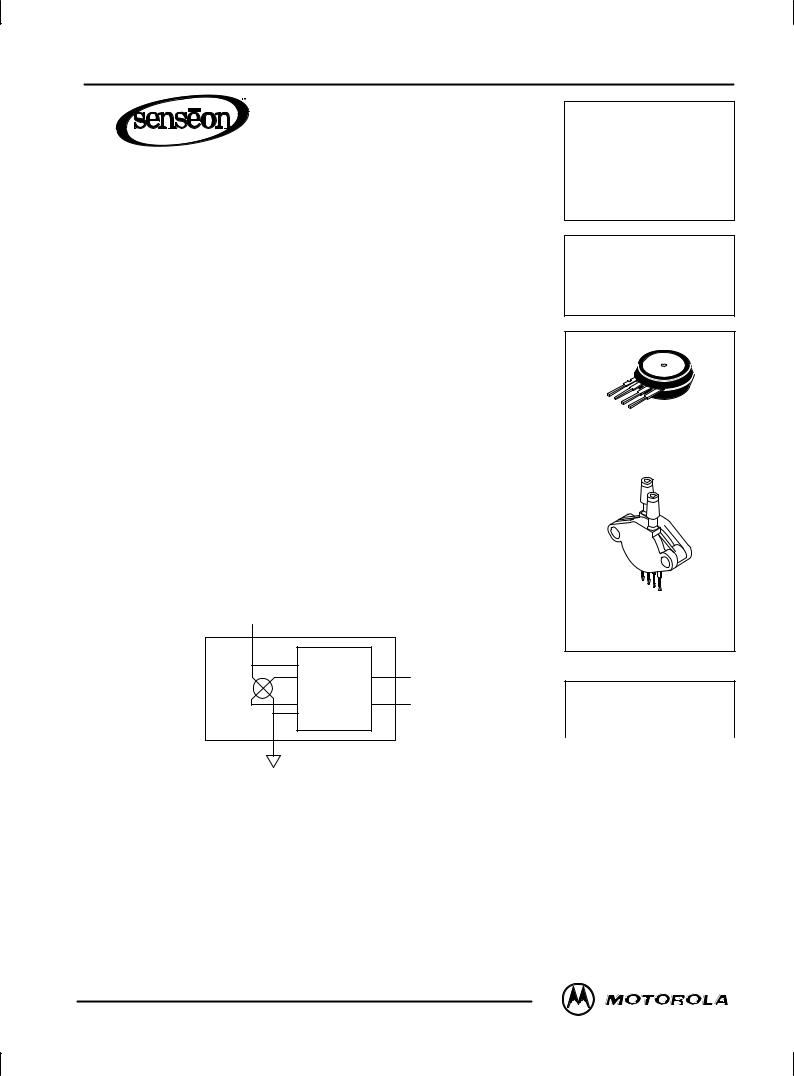
Figure 1 illustrates a block diagram of the internal circuitry on the stand±alone pressure sensor chip.
|
VS |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
THIN FILM |
2 |
|
|
X±ducer |
TEMPERATURE |
Vout+ |
||
COMPENSATION |
|
|||
SENSING |
|
|
||
AND |
|
|
||
ELEMENT |
4 |
Vout± |
||
CALIBRATION |
||||
|
|
|||
|
CIRCUITRY |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
GND |
|
|
MPX2200
MPX2201
SERIES
Motorola Preferred Device
0 to 200 kPa (0 to 29 psi)
40 mV FULL SCALE SPAN (TYPICAL)
BASIC CHIP
CARRIER ELEMENT
CASE 344±15, STYLE 1
DIFFERENTIAL
PORT OPTION
CASE 344C±01, STYLE 1
NOTE: Pin 1 is the notched pin.
PIN NUMBER
1 |
Gnd |
3 |
VS |
2 |
+Vout |
4 |
±Vout |
Figure 1. Temperature Compensated Pressure Sensor Schematic
VOLTAGE OUTPUT versus APPLIED DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE
The differential voltage output of the X±ducer is directly proportional to the differential pressure applied.
The absolute sensor has a built±in reference vacuum. The output voltage will decrease as vacuum, relative to ambient, is drawn on the pressure (P1) side.
The output voltage of the differential or gauge sensor increases with increasing pressure applied to the pressure (P1) side relative to the vacuum (P2) side. Similarly, output voltage increases as increasing vacuum is applied to the vacuum (P2) side relative to the pressure (P1) side.
Preferred devices are Motorola recommended choices for future use and best overall value.
Senseon and X±ducer are trademarks of Motorola, Inc.
REV 7
Motorola Sensor Device Data |
1 |
Motorola, Inc. 1997 |
|

MPX2200 MPX2201 SERIES
MAXIMUM RATINGS
Rating |
|
Symbol |
|
|
|
Value |
|
Unit |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overpressure(8) (P1 > P2) |
|
|
Pmax |
|
|
400 |
|
|
kPa |
||
Burst Pressure(8) (P1 > P2) |
|
|
Pburst |
|
|
2000 |
|
|
kPa |
||
Storage Temperature |
|
|
Tstg |
|
|
± 40 to +125 |
|
°C |
|||
Operating Temperature |
|
|
TA |
|
|
± 40 to +125 |
|
°C |
|||
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS (VS = 10 Vdc, TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted, P1 > P2) |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Characteristics |
Symbol |
Min |
|
Typ |
|
Max |
|
Unit |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pressure Range(1) |
|
|
P |
0 |
|
Ð |
|
200 |
|
kPa |
|
|
|
|
OP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply Voltage |
|
|
VS |
Ð |
|
10 |
|
16 |
|
Vdc |
|
Supply Current |
|
|
Io |
Ð |
|
6.0 |
|
Ð |
|
mAdc |
|
Full Scale Span(3) |
MPX2200A, MPX2200D, MPX2201D |
V |
38.5 |
|
40 |
|
41.5 |
|
mV |
||
|
MPX2201A |
FSS |
37.5 |
|
40 |
|
42.5 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Offset(4) |
MPX2200A, MPX2200D |
Voff |
±1.0 |
|
Ð |
|
1.0 |
|
mV |
||
|
MPX2200A |
|
± 2.0 |
|
Ð |
|
2.0 |
|
|
||
|
MPX2201A |
|
± 3.0 |
|
Ð |
|
3.0 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensitivity |
|
|
V/ P |
Ð |
|
0.2 |
|
Ð |
|
mV/kPa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Linearity(5) |
MPX2200D |
Ð |
± 0.25 |
|
Ð |
|
0.25 |
|
%VFSS |
||
|
MPX2200A |
|
± 1.0 |
|
Ð |
|
1.0 |
|
|
||
|
MPX2201D |
|
± 0.5 |
|
Ð |
|
0.5 |
|
|
||
|
MPX2201A |
|
± 2.0 |
|
Ð |
|
2.0 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Pressure Hysteresis(5) (0 to 200 kPa) |
Ð |
Ð |
|
± 0.1 |
|
Ð |
|
%V |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSS |
Temperature Hysteresis(5) (± 40°C to +125°C) |
Ð |
Ð |
|
± 0.5 |
|
Ð |
|
%V |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSS |
Temperature Effect on Full Scale Span(5) |
TCV |
±1.0 |
|
Ð |
|
1.0 |
|
%V |
|||
|
|
|
FSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSS |
Temperature Effect on Offset(5) |
|
|
TCVoff |
±1.0 |
|
Ð |
|
1.0 |
|
mV |
|
Input Impedance |
|
|
Zin |
1300 |
|
Ð |
|
2500 |
|
Ω |
|
Output Impedance |
|
|
Zout |
1400 |
|
Ð |
|
3000 |
|
Ω |
|
Response Time(6) (10% to 90%) |
|
|
tR |
Ð |
|
1.0 |
|
Ð |
|
ms |
|
Warm±Up |
|
|
Ð |
Ð |
|
20 |
|
Ð |
|
ms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Offset Stability(9) |
|
|
Ð |
Ð |
|
± 0.5 |
|
Ð |
|
%V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FSS |
MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Characteristics |
Symbol |
Min |
|
Typ |
|
Max |
|
Unit |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Weight, (Basic Element Case 344±15) |
Ð |
Ð |
|
2.0 |
|
Ð |
|
Grams |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Mode Line Pressure(7) |
|
|
Ð |
Ð |
|
Ð |
|
690 |
|
kPa |
|
NOTES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.1.0 kPa (kiloPascal) equals 0.145 psi.
2.Device is ratiometric within this specified excitation range. Operating the device above the specified excitation range may induce additional error due to device self±heating.
3.Full Scale Span (VFSS) is defined as the algebraic difference between the output voltage at full rated pressure and the output voltage at the minimum rated pressure.
4.Offset (Voff) is defined as the output voltage at the minimum rated pressure.
5.Accuracy (error budget) consists of the following:
• |
Linearity: |
Output deviation from a straight line relationship with pressure, using end point method, over the specified |
|
|
pressure range. |
• |
Temperature Hysteresis: |
Output deviation at any temperature within the operating temperature range, after the temperature is |
|
|
cycled to and from the minimum or maximum operating temperature points, with zero differential pressure |
|
|
applied. |
• |
Pressure Hysteresis: |
Output deviation at any pressure within the specified range, when this pressure is cycled to and from the |
|
|
minimum or maximum rated pressure, at 25°C. |
• |
TcSpan: |
Output deviation at full rated pressure over the temperature range of 0 to 85°C, relative to 25°C. |
• |
TcOffset: |
Output deviation with minimum rated pressure applied, over the temperature range of 0 to 85°C, relative |
|
|
to 25°C. |
6.Response Time is defined as the time for the incremental change in the output to go from 10% to 90% of its final value when subjected to a specified step change in pressure.
7.Common mode pressures beyond specified may result in leakage at the case±to±lead interface.
8.Exposure beyond these limits may cause permanent damage or degradation to the device.
9.Offset stability is the product's output deviation when subjected to 1000 hours of Pulsed Pressure, Temperature Cycling with Bias Test.
2 |
Motorola Sensor Device Data |
LINEARITY
Linearity refers to how well a transducer's output follows the equation: Vout = Voff + sensitivity x P over the operating pressure range. There are two basic methods for calculating nonlinearity: (1) end point straight line fit (see Figure 2) or (2) a least squares best line fit. While a least squares fit gives the ªbest caseº linearity error (lower numerical value), the calculations required are burdensome.
Conversely, an end point fit will give the ªworst caseº error (often more desirable in error budget calculations) and the calculations are more straightforward for the user. Motorola's specified pressure sensor linearities are based on the end point straight line method measured at the midrange pressure.
|
MPX2200 |
MPX2201 |
SERIES |
||
|
LEAST SQUARES FIT |
|
|
|
|
OUTPUT |
EXAGGERATED |
|
|
|
|
PERFORMANCE |
|
|
|
||
CURVE |
LEAST |
STRAIGHT LINE |
|||
|
|||||
|
DEVIATION |
||||
VOLTAGE |
|
||||
SQUARE |
|||||
|
|
||||
DEVIATION |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
RELATIVE |
END POINT |
|
|
|
|
STRAIGHT LINE FIT |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
OFFSET |
|
|
|
|
0 |
50 |
|
100 |
|
|
PRESSURE (% FULLSCALE)
Figure 2. Linearity Specification Comparison
ON±CHIP TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION and CALIBRATION
Figure 3 shows the output characteristics of the MPX2200 series at 25°C. The output is directly proportional to the differential pressure and is essentially a straight line.
The effects of temperature on Full Scale Span and Offset are very small and are shown under Operating Characteristics.
40
35
(mVdc) |
30 |
|
|
||
OUTPUT |
25 |
|
20 |
||
|
||
|
15 |
10
5
0
± 5 kPa 0
PSI
VS = 10 Vdc
TA = 25°C
P1 > P2
TYP
SPAN MAX  RANGE (TYP)
RANGE (TYP)
|
|
|
|
MIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
150 |
175 |
200 |
|
|
OFFSET |
||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
7.25 |
|
14.5 |
|
21.75 |
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
PRESSURE
Figure 3. Output versus Pressure Differential
SILICONE GEL |
DIFFERENTIAL/GAUGE |
STAINLESS STEEL |
SILICONE GEL |
ABSOLUTE |
STAINLESS STEEL |
DIE COAT |
DIE |
METAL COVER |
DIE COAT |
DIE |
METAL COVER |
|
P1 |
|
|||
|
EPOXY |
|
P1 |
EPOXY |
|
WIRE BOND |
|
WIRE BOND |
|
||
|
CASE |
|
CASE |
||
LEAD FRAME |
|
DIE |
LEAD FRAME |
|
DIE |
DIFFERENTIAL/GAUGE ELEMENT |
BOND |
|
|
||
|
ABSOLUTE ELEMENT |
BOND |
|||
|
|
||||
|
P2 |
|
|
P2 |
|
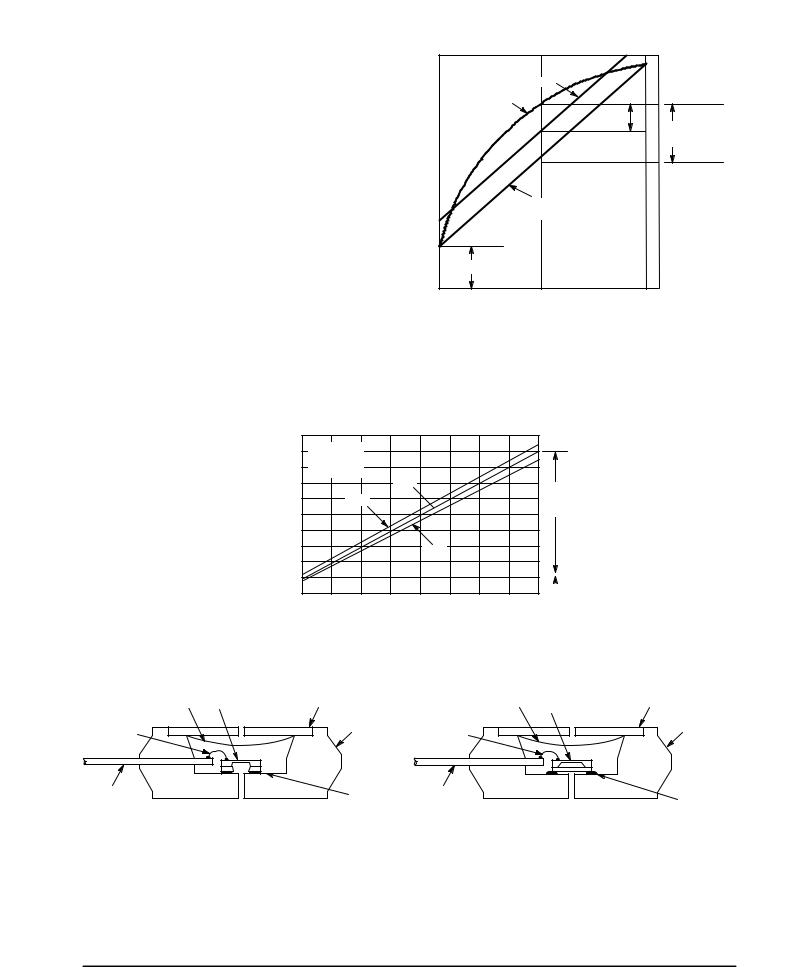
Figure 4. Cross±Sectional Diagrams (Not to Scale)
Figure 4 illustrates an absolute sensing die (right) and the differential or gauge die in the basic chip carrier (Case 344±15). A silicone gel isolates the die surface and wire bonds from the environment, while allowing the pressure signal to be transmitted to the silicon diaphragm.
The MPX2200 series pressure sensor operating charac-
teristics and internal reliability and qualification tests are based on use of dry air as the pressure media. Media other than dry air may have adverse effects on sensor performance and long term reliability. Contact the factory for information regarding media compatibility in your application.
Motorola Sensor Device Data |
3 |
 Loading...
Loading...