Motorola MVME5100 User Manual 2
MVME5100
Single Board Computer
Installation and Use
V5100A/IH4
July 2003 Edition
© Copyright 2003 Motorola, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Motorola and the Motorola logo are registered trademarks and AltiVec is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
PowerPC and the PowerPC logo are registered trademarks; and PowerPC 750 is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation and are used by Motorola, Inc. under license from International Business Machines Corporation.
All other products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.

Safety Summary
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service, and repair of this equipment. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual could result in personal injury or damage to the equipment.
The safety precautions listed below represent warnings of certain dangers of which Motorola is aware. You, as the user of the product, should follow these warnings and all other safety precautions necessary for the safe operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
Ground the Instrument.
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and enclosure must be connected to an electrical ground. If the equipment is supplied with a three-conductor AC power cable, the power cable must be plugged into an approved three-contact electrical outlet, with the grounding wire (green/yellow) reliably connected to an electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. The power jack and mating plug of the power cable meet International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) safety standards and local electrical regulatory codes.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
Do not operate the equipment in any explosive atmosphere such as in the presence of flammable gases or fumes. Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment could result in an explosion and cause injury or damage.
Keep Away From Live Circuits Inside the Equipment.
Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers. Only Factory Authorized Service Personnel or other qualified service personnel may remove equipment covers for internal subassembly or component replacement or any internal adjustment. Service personnel should not replace components with power cable connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, such personnel should always disconnect power and discharge circuits before touching components.
Use Caution When Exposing or Handling a CRT.
Breakage of a Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) causes a high-velocity scattering of glass fragments (implosion). To prevent CRT implosion, do not handle the CRT and avoid rough handling or jarring of the equipment. Handling of a CRT should be done only by qualified service personnel using approved safety mask and gloves.
Do Not Substitute Parts or Modify Equipment.
Do not install substitute parts or perform any unauthorized modification of the equipment. Contact your local Motorola representative for service and repair to ensure that all safety features are maintained.
Observe Warnings in Manual.
Warnings, such as the example below, precede potentially dangerous procedures throughout this manual. Instructions contained in the warnings must be followed. You should also employ all other safety precautions which you deem necessary for the operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
To prevent serious injury or death from dangerous voltages, use extreme caution when handling, testing, and adjusting this equipment and its
Warning components.
Flammability
All Motorola PWBs (printed wiring boards) are manufactured with a flammability rating of 94V-0 by UL-recognized manufacturers.
EMI Caution
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate electromagnetic energy. It
!may cause or be susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) if not
Caution installed and used with adequate EMI protection.
Lithium Battery Caution
This product contains a lithium battery to power the clock and calendar circuitry.
Danger of explosion if battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace battery only
!with the same or equivalent type recommended by the equipment
Caution manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Il y a danger d’explosion s’il y a remplacement incorrect de la batterie.
!Remplacer uniquement avec une batterie du même type ou d’un type
Attention équivalent recommandé par le constructeur. Mettre au rebut les batteries usagées conformément aux instructions du fabricant.
Explosionsgefahr bei unsachgemäßem Austausch der Batterie. Ersatz nur
!durch denselben oder einen vom Hersteller empfohlenen Typ. Entsorgung
Vorsicht gebrauchter Batterien nach Angaben des Herstellers.
CE Notice (European Community)
Motorola Computer Group products with the CE marking comply with the EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). Compliance with this directive implies conformity to the following European Norms:
EN55022 “Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of Information Technology Equipment”; this product tested to Equipment Class B
EN55024 “Information technology equipment—Immunity characteristics—Limits and methods of measurement”
Board products are tested in a representative system to show compliance with the above mentioned requirements. A proper installation in a CE-marked system will maintain the required EMC performance.
In accordance with European Community directives, a “Declaration of Conformity” has been made and is available on request. Please contact your sales representative.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, Motorola, Inc. assumes no liability resulting from any omissions in this document, or from the use of the information obtained therein. Motorola reserves the right to revise this document and to make changes from time to time in the content hereof without obligation of Motorola to notify any person of such revision or changes.
Electronic versions of this material may be read online, downloaded for personal use, or referenced in another document as a URL to the Motorola Computer Group website. The text itself may not be published commercially in print or electronic form, edited, translated, or otherwise altered without the permission of Motorola, Inc.
It is possible that this publication may contain reference to or information about Motorola products (machines and programs), programming, or services that are not available in your country. Such references or information must not be construed to mean that Motorola intends to announce such Motorola products, programming, or services in your country.
Limited and Restricted Rights Legend
If the documentation contained herein is supplied, directly or indirectly, to the U.S. Government, the following notice shall apply unless otherwise agreed to in writing by Motorola, Inc.
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (b)(3) of the Rights in Technical Data clause at DFARS 252.227-7013 (Nov. 1995) and of the Rights in Noncommercial Computer Software and Documentation clause at DFARS 252.227-7014 (Jun. 1995).
Motorola, Inc.
Computer Group
2900 South Diablo Way
Tempe, Arizona 85282

Contents
About This Manual |
|
|
Summary of Changes ................................................................................................ |
xvii |
|
Overview of Contents ............................................................................................... |
xvii |
|
Comments and Suggestions ....................................................................................... |
xix |
|
Conventions Used in This Manual............................................................................. |
xix |
|
Terminology ......................................................................................................... |
xx |
|
CHAPTER 1 |
Hardware Preparation and Installation |
|
Introduction ................................................................................................................ |
1-1 |
|
Getting Started ........................................................................................................... |
1-1 |
|
Overview and Equipment Requirements ............................................................ |
1-1 |
|
Unpacking Instructions ....................................................................................... |
1-2 |
|
Preparation ................................................................................................................. |
1-3 |
|
Hardware Configuration ..................................................................................... |
1-3 |
|
Jumper Settings................................................................................................... |
1-5 |
|
|
PMC/SBC (761/IPMC) Mode Selection ..................................................... |
1-6 |
Installation Considerations ................................................................................. |
1-6 |
|
Installation.................................................................................................................. |
1-8 |
|
PMC Modules ................................................................................................... |
1-10 |
|
Primary PMCspan............................................................................................. |
1-12 |
|
Secondary PMCspan......................................................................................... |
1-14 |
|
MVME5100 ...................................................................................................... |
1-16 |
|
CHAPTER 2 |
Operation |
|
Introduction ................................................................................................................ |
2-1 |
|
Switches and Indicators ............................................................................................. |
2-1 |
|
ABT/RST Switch ................................................................................................ |
2-1 |
|
|
Abort Function............................................................................................. |
2-1 |
|
Reset Function ............................................................................................. |
2-1 |
Status Indicators.................................................................................................. |
2-2 |
|
|
RST Indicator (DS1).................................................................................... |
2-2 |
|
CPU Indicator (DS2) ................................................................................... |
2-2 |
Connectors .......................................................................................................... |
2-2 |
|
|
10/100 BASE T Ports .................................................................................. |
2-3 |
vii

|
DEBUG Port ............................................................................................... |
2-3 |
System Powerup ........................................................................................................ |
2-3 |
|
Initialization Process .......................................................................................... |
2-4 |
|
CHAPTER 3 |
PPCBug Firmware |
|
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
|
PPCBug Overview..................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
|
Implementation and Memory Requirements ...................................................... |
3-3 |
|
Using PPCBug ........................................................................................................... |
3-3 |
|
Hardware and Firmware Initialization ............................................................... |
3-4 |
|
Default Settings ......................................................................................................... |
3-6 |
|
CNFG - Configure Board Information Block .................................................... |
3-7 |
|
ENV - Set Environment ..................................................................................... |
3-7 |
|
|
Configuring the PPCBug Parameters.......................................................... |
3-8 |
LED/Serial Startup Diagnostic Codes .............................................................. |
3-16 |
|
Configuring the VMEbus Interface .................................................................. |
3-17 |
|
Firmware Command Buffer ............................................................................. |
3-21 |
|
Standard Commands ................................................................................................ |
3-22 |
|
Diagnostics ....................................................................................................... |
3-26 |
|
CHAPTER 4 |
Functional Description |
|
Introduction ............................................................................................................... |
4-1 |
|
Features Summary ..................................................................................................... |
4-1 |
|
Features Descriptions ................................................................................................ |
4-3 |
|
General ............................................................................................................... |
4-3 |
|
Processor ............................................................................................................ |
4-5 |
|
System Memory Controller and PCI Host Bridge.............................................. |
4-5 |
|
Memory .............................................................................................................. |
4-5 |
|
|
Flash Memory ............................................................................................. |
4-5 |
|
ECC SDRAM Memory ............................................................................... |
4-6 |
P2 Input/Output (I/O) Modes ............................................................................. |
4-7 |
|
Input/Output Interfaces....................................................................................... |
4-7 |
|
|
Ethernet Interface ........................................................................................ |
4-7 |
|
VMEbus Interface ....................................................................................... |
4-8 |
|
Asynchronous Communications ................................................................. |
4-8 |
|
Real-Time Clock & NVRAM & Watchdog Timer..................................... |
4-8 |
|
Timers ......................................................................................................... |
4-8 |
|
Interrupt Routing ......................................................................................... |
4-8 |
|
IDSEL Routing............................................................................................ |
4-9 |
viii

CHAPTER 5 |
Pin Assignments |
|
Introduction ................................................................................................................ |
5-1 |
|
Summary ............................................................................................................. |
5-1 |
|
Jumper Settings .......................................................................................................... |
5-2 |
|
Connectors ................................................................................................................. |
5-3 |
|
IPMC761 Connector (J3) Pin Assignments........................................................ |
5-3 |
|
Memory Expansion Connector (J8) Pin Assignments ........................................ |
5-4 |
|
PCI Expansion Connector (J25) Pin Assignments ............................................. |
5-7 |
|
PCI Mezzanine Card (PMC) Connectors.......................................................... |
5-10 |
|
VMEbus Connectors P1 & P2 Pin Assignments (PMC mode) ........................ |
5-23 |
|
VMEbus P1 & P2 Connector Pin Assignments (SBC Mode) .......................... |
5-25 |
|
10 BaseT/100 BaseTx Connector Pin Assignments ......................................... |
5-29 |
|
COM1 and COM2 Connector Pin Assignments............................................... |
5-30 |
|
CHAPTER 6 Programming the MVME51xx |
|
|
Introduction ................................................................................................................ |
6-1 |
|
Memory Maps ............................................................................................................ |
6-1 |
|
Processor Bus Memory Map............................................................................... |
6-2 |
|
|
Default Processor Memory Map.................................................................. |
6-2 |
|
Processor Memory Map............................................................................... |
6-3 |
|
PCI Memory Map ........................................................................................ |
6-5 |
|
VME Memory Map ..................................................................................... |
6-5 |
PCI Local Bus Memory Map.............................................................................. |
6-5 |
|
VMEbus Memory Map ....................................................................................... |
6-6 |
|
Programming Considerations..................................................................................... |
6-6 |
|
PCI Arbitration ................................................................................................... |
6-6 |
|
Interrupt Handling............................................................................................... |
6-9 |
|
DMA Channels ................................................................................................. |
6-11 |
|
Sources of Reset................................................................................................ |
6-11 |
|
Endian Issues .................................................................................................... |
6-13 |
|
|
Processor/Memory Domain ....................................................................... |
6-13 |
|
PCI Domain ............................................................................................... |
6-13 |
|
VMEbus Domain ....................................................................................... |
6-14 |
APPENDIX A |
Specifications |
|
General Specifications .............................................................................................. |
A-1 |
|
Power Requirements ................................................................................................. |
A-2 |
|
Cooling Requirements .............................................................................................. |
A-3 |
|
ix

EMC Compliance ..................................................................................................... |
A-3 |
|
APPENDIX B |
Troubleshooting |
|
Solving Startup Problems ......................................................................................... |
B-1 |
|
APPENDIX C |
Related Documentation |
|
Motorola Computer Group Documents .................................................................... |
C-1 |
|
Manufacturers’ Documents ...................................................................................... |
C-2 |
|
Related Specifications .............................................................................................. |
C-4 |
|
APPENDIX D RAM500 Memory Expansion Module |
|
|
Overview .................................................................................................................. |
|
D-1 |
Features..................................................................................................................... |
|
D-1 |
Functional Description ............................................................................................. |
D-2 |
|
RAM500 Description ........................................................................................ |
D-2 |
|
SROM |
................................................................................................................ |
D-5 |
Host Clock Logic............................................................................................... |
D-5 |
|
RAM500 Module Installation................................................................................... |
D-5 |
|
RAM500 Connectors ................................................................................................ |
D-7 |
|
Bottom Side Memory Expansion Connector (P1)............................................. |
D-7 |
|
Top Side Memory Expansion Connector (J1) ................................................. |
D-10 |
|
RAM500 Programming Issues ............................................................................... |
D-13 |
|
Serial Presence Detect (SPD) Data ................................................................. |
D-13 |
|
APPENDIX E |
Thermal Analysis |
|
Thermally Significant Components........................................................................... |
E-1 |
|
Component Temperature Measurement..................................................................... |
E-6 |
|
Preparation.......................................................................................................... |
E-6 |
|
Measuring Junction Temperature ....................................................................... |
E-6 |
|
Measuring Case Temperature ............................................................................. |
E-6 |
|
Measuring Local Air Temperature ..................................................................... |
E-9 |
|
x

List of Figures
Figure 1-1. MVME5100 Layout ................................................................................ |
1-9 |
|
Figure 1-2. MVME5100 Installation and Removal From a VMEbus Chassis ........ |
1-11 |
|
Figure 1-3. Typical PMC Module Placement on an MVME5100 ........................... |
1-11 |
|
Figure 1-4. PMCspan-002 Installation on an MVME510 ....................................... |
1-13 |
|
Figure 1-5. PMCspan-010 Installation on a PMCspan-002/MVME5100 ............... |
1-15 |
|
Figure 2-1. |
Boot-Up Sequence .................................................................................. |
2-5 |
Figure 4-1. |
MVME5100 Block Diagram ................................................................... |
4-4 |
Figure 6-1. |
VMEbus Master Mapping ....................................................................... |
6-8 |
Figure 6-2. |
MVME510x Interrupt Architecture ...................................................... |
6-10 |
Figure D-1. RAM500 Block Diagram ..................................................................... |
D-4 |
|
Figure D-2. RAM500 Module Placement on MVME5100 ..................................... |
D-6 |
|
Figure E-1. Thermally Significant Components on the MVME5100 Single |
|
|
Board Computer - Primary Side ............................................................................. |
E-4 |
|
Figure E-2. Thermally Significant Components on the IPMC761 Module - |
|
|
Primary Side ............................................................................................................. |
E-5 |
|
Figure E-3. Mounting a Thermocouple Under a Heatsink ....................................... |
E-8 |
|
Figure E-4. Measuring Local Air Temperature ....................................................... |
E-9 |
|
xi

xii

List of Tables
Table 1-1. Manually Configured Headers/Jumpers ................................................... |
1-4 |
Table 3-1. Debugger Commands ............................................................................. |
3-22 |
Table 3-2. Diagnostic Test Groups........................................................................... |
3-27 |
Table 4-1. MVME5100 General Features.................................................................. |
4-1 |
Table 5-1. Jumper Switches and Settings................................................................... |
5-2 |
Table 5-2. IPMC761 Connector Pin Assignments ..................................................... |
5-3 |
Table 5-3. Memory Expansion Connector Pin Assignments ..................................... |
5-4 |
Table 5-4. PCI Expansion Connector |
|
Pin Assignments......................................................................................................... |
5-7 |
Table 5-5. PMC Slot 1 Connector (J11) Pin Assignments....................................... |
5-10 |
Table 5-6. PMC Slot 1 Connector (J12) Pin Assignments....................................... |
5-12 |
Table 5-7. PMC Slot 1 Connector (J13) Pin Assignments....................................... |
5-13 |
Table 5-8. PMC Slot 1 Connector (J14) |
|
Pin Assignments....................................................................................................... |
5-15 |
Table 5-9. PMC Slot 2 Connector (J21) Pin Assignments....................................... |
5-17 |
Table 5-10. PMC Slot 2 Connector (J22) Pin Assignments..................................... |
5-18 |
Table 5-11. PMC Slot 2 Connector (J23) Pin Assignments..................................... |
5-20 |
Table 5-12. PMC Slot 2 Connector (J24) Pin Assignments..................................... |
5-21 |
Table 5-13. VMEbus Connector P2 Pin Assignments |
|
(PMC Mode) ............................................................................................................ |
5-23 |
Table 5-14. VMEbus P2 Connector Pinouts with IPMC761- |
|
SBC Mode................................................................................................................ |
5-25 |
Table 5-15. VMEbus Connector P2 Pinout with IPMC712..................................... |
5-27 |
Table 5-16. 10 BaseT/100 BaseTx Connector Pin Assignment............................... |
5-29 |
Table 5-17. COM1 (J19) Connector Pin Assignments ............................................ |
5-30 |
Table 5-18. COM2 (J5) Connector Pin Assignments .............................................. |
5-30 |
Table 6-1. Default Processor Memory Map............................................................... |
6-2 |
Table 6-2. Suggested CHRP Memory Map ............................................................... |
6-3 |
Table 6-3. Hawk PPC Register Values for Suggested Memory Map......................... |
6-4 |
Table 6-4. PCI Arbitration Assignments.................................................................... |
6-9 |
Table A-1. MVME5100 Specifications ................................................................... |
A-1 |
Table A-2. Power Consumption .............................................................................. |
A-2 |
Table B-1. Troubleshooting Problems ..................................................................... |
B-1 |
Table C-1. Motorola Computer Group Documents ................................................. |
C-1 |
Table C-2. Manufacturers’ Documents .................................................................... |
C-2 |
xiii

Table C-3. Related Specifications ........................................................................... |
C-4 |
Table D-1. RAM500 Feature Summary .................................................................. |
D-1 |
Table D-2. RAM500 SDRAM Memory Size Options ............................................ |
D-3 |
Table D-3. RAM500 Bottom Side Connector (P1) |
|
Pin Assignments ...................................................................................................... |
D-8 |
Table D-4. RAM500 Top Side Connector (J1) |
|
Pin Assignments .................................................................................................... |
D-10 |
Table E-1. Thermally Significant Components on the MVME5100 Single |
|
Board Computer ....................................................................................................... |
E-2 |
Table E-2. Thermally Significant Components on the IPMC761 Module .............. |
E-3 |
xiv
About This Manual
The MVME51xx Single Board Computer Installation and Use provides the information you will need to install and configure your MVME51xx Single Board Computer. It provides specific preparation and installation information and data applicable to the board.
The MVME51xx is a high-performance VME single board computer featuring the Motorola Computer Group (MCG) PowerPlus II architecture with a choice of processors—either Motorola’s MPC7410 with AltiVec™ technology for algorithmic intensive computations or the low-power MPC755 or MPC750.
As of the printing date of this manual, the MVME51xx is available in the configurations shown below. Note: all models of the MVME51xx are available with either VME Scanbe front panel (-xxx) or IEEE 1101 compatible front panel (-xxx3) handles.
Part Number |
Description |
|
|
450 MHz MPC750 Commercial Models
MVME5100-016x 450 MHz MPC750, 512MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 1MB L2 cache
400 MHz MPC755 Extended Temperature Models
MVME5106-114x 400 MHz MPC755, 128MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 1MB L2 cache
MVME5106-115x 400 MHz MPC755, 256MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 1MB L2 cache
MVME5106-116x 400 MHz MPC755, 512MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 1MB L2 cache
400 and 500 MHz MPC7410 Commercial Models
MVME5110-216x 400 MHz MPC7410, 512MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 2MB L2 cache
MVME5110-226x 500 MHz MPC7410, 512MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 2MB L2 cache
500 MHz MPC7410 Extended Temperature Models
MVME5107-214x 500 MHz MPC7410, 128MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 2MB L2 cache
MVME5107-215x 500 MHz MPC7410, 256MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 2MB L2 cache
MVME5107-216x 500 MHz MPC7410, 512MB ECC SDRAM, 17MB Flash and 2MB L2 cache
MVME712M Compatible I/O
IPMC712-001 Multifunction rear I/O PMC module; 8-bit SCSI, Ultra Wide SCSI, one parallel port, three async and one sync/async serial port
xv
Part Number |
Description |
MVME712M Transition module connectors: One DB-25 sync/async serial port, three DB25 async serial ports, one AUI connector, one D-36 parallel port, and one 50pin 8-bit SCSI; includes 3-row DIN P2 adapter module and cable.
MVME761 Compatible I/O
IPMC761-001 Multifunction rear I/O PMC module; 8-bit SCSI, one parallel port, two async and two sync/async serial ports
MVME761-001 Transition module: Two DB-9 async serial port connectors, two HD-26 sync/async serial port connectors, one HD-36 parallel port connector, and one RJ-45 10/100 Ethernet connector; includes 3-row DIN P2 adapter module and cable (for 8-bit SCSI).
MVME761-011 Transition module: Two DB-9 async serial port connectors, two HD-26 sync/async serial port connectors, one HD-36 parallel port connector, and one RJ-45 10/100 Ethernet connector; includes 5-row DIN P2 adapter module and cable (for 16-bit SCSI); requires backplane with 5-row DIN connectors.
SIM232DCE or EIA-232 DCE or DTE Serial Interface Module
DTE
SIM530DCE or EIA-530 DCE or DTE Serial Interface Module
DTE
SIMV35DCE or V.35 DCE or DTE Module
DTE
SIMX21DCE or X.21 DCE or DTE Serial Interface Module
DTE
Related Products
PMCSPAN1-002 PMCSPAN-002 with original VME Scanbe ejector handles
PMCSPAN1-010 PMCSAN-010 with original VME Scanbe ejector handles
RAM500-004 Stackable (top) 64MB ECC SDRAM mezzanine
RAM500-006 Stackable (top) 256MB ECC SDRAM mezzanine
RAM500-016 Stackable (bottom) 256MB ECC SDRAM mezzanine
xvi

Summary of Changes
The following changes were made for the 4th revision of this manual.
Date |
Doc. Rev |
Changes |
|
|
|
08/2001 |
V5100A/IH2 |
A correction was made on page 1-5 to change the |
|
|
explanation of the jumper settings for Flash Bank A |
|
|
and B. Flash Bank B (0) is the factory setting. |
|
|
Memory Map information was also added to |
|
|
Chapter 6, Programming Information. Appendix |
|
|
B, Specifications was updated, and Appendix D, |
|
|
RAM500 Memory Expansion Module was added. |
|
|
Other corrections were made throughout the |
|
|
manual. This section titled "About this Manual" |
|
|
was also added. |
|
|
|
02/2003 |
V5100A/IH3 |
Changes were made to pages 1-4 and 5-2 |
|
|
respectively to clarify the explanation for J16 to |
|
|
state that the setting of jumpers 2 and 3 only write |
|
|
protect the upper 64KB of Flash memory. |
|
|
Additional corrections were made to Table 5-15 to |
|
|
duplicate information in Rows Z and D from Table |
|
|
5-14 and to add note below Table 5-15. |
|
|
|
07/2003 |
V5100A/IH4 |
Changes were made to this section to update model |
|
|
numbers and descriptions to coincide with the |
|
|
MVME5100 Datasheet. Changes were also made to |
|
|
correct the address of the DS1621 from $A6 to $96. |
|
|
Changes were also made to specifications for |
|
|
additional power ratings and additions were made |
|
|
to a new thermal rating chart. |
|
|
|
Overview of Contents
The following paragraphs briefly describe the contents of each chapter.
Chapter 1, Hardware Preparation and Installation, provides a description of the MVME5100 and its main integrated PMC and IPMC boards. The remainder of the chapter includes an explanation of the installation procedure, including preparation and jumper setting information.
xvii

Chapter 2, Operation, provides a description of the operational functions of the MVME5100 including tips on applying power, a description of the switch settings, the status indicators, I/O connectors, and system power up information.
Chapter 3, PPCBug Firmware, provides an explanation of the debugger firmware, PPCBug, on the MVME5100. The chapter includes an overview of the firmware, a section on how to use PPCBug, a listing of the initialization steps, a brief explanation of the two main configuration commands CNFG and ENV, and a description of the standard configuration parameters. A listing of the basic commands are also provided.
Chapter 4, Functional Description, provides a summary of the MVME5100 features, a block diagram, and a description of the major functional areas.
Chapter 5, Pin Assignments, provides a listing of all connector and header pin assignments for the MVME5100.
Chapter 6, Programming the MVME51xx, provides a description of the memory maps on the MVME5100 including tables of default processor memory maps, suggested CHRP memory maps, and Hawk PPC register values for suggested memory maps. The remainder of the chapter provides some programming considerations.
Appendix A, Specifications, provides the standard specifications for the MVME5100, as well as some general information on cooling.
Appendix B, Troubleshooting, provides a brief explanation of the possible resolutions for basic error conditions.
Appendix C, Related Documentation, provides a listing of related documentation for the MVME5100, including vendor documentation and industry related specifications.
Appendix D, RAM500 Memory Expansion Module, provides a description of the RAM500 Memory Expansion Module, a list of features, a block diagram of the module, a table of memory size allocations, an installation procedure, and pinouts of the module’s top and bottom side connectors.
xviii

Comments and Suggestions
Motorola welcomes and appreciates your comments on its documentation. We want to know what you think about our manuals and how we can make them better. Mail comments to:
Motorola Computer Group
Reader Comments DW164
2900 S. Diablo Way
Tempe, Arizona 85282
You can also submit comments to the following e-mail address: reader-comments@mcg.mot.com
In all your correspondence, please list your name, position, and company. Be sure to include the title and part number of the manual and tell how you used it. Then tell us your feelings about its strengths and weaknesses and any recommendations for improvements.
Conventions Used in This Manual
The following typographical conventions are used in this document:
bold
is used for user input that you type just as it appears; it is also used for commands, options and arguments to commands, and names of programs, directories and files.
italic
is used for names of variables to which you assign values. Italic is also used for comments in screen displays and examples, and to introduce new terms.
courier
is used for system output (for example, screen displays, reports), examples, and system prompts.
<Enter>, <Return> or <CR>
xix

<CR> represents the carriage return or Enter key.
CTRL
represents the Control key. Execute control characters by pressing the Ctrl key and the letter simultaneously, for example, Ctrl-d.
Terminology
A character precedes a data or address parameter to specify the numeric format, as follows (if not specified, the format is hexadecimal):
0x Specifies a hexadecimal number % Specifies a binary number
& Specifies a decimal number
|
An asterisk (*) following a signal name for signals that are level significant |
||
|
denotes that the signal is true or valid when the signal is low. |
||
|
An asterisk (*) following a signal name for signals that are edge significant |
||
|
denotes that the actions initiated by that signal occur on high to low |
||
|
transition. |
||
|
In this manual, assertion and negation are used to specify forcing a signal |
||
|
to a particular state. In particular, assertion and assert refer to a signal that |
||
|
is active or true; negation and negate indicate a signal that is inactive or |
||
|
false. These terms are used independently of the voltage level (high or low) |
||
|
that they represent. Data and address sizes are defined as follows: |
||
|
|
|
|
Byte |
|
8 bits, numbered 0 through 7, with bit 0 being the least significant. |
|
|
|
|
|
Half word |
|
16 bits, numbered 0 through 15, with bit 0 being the least significant. |
|
|
|
|
|
Word |
|
32 bits, numbered 0 through 31, with bit 0 being the least significant. |
|
|
|
|
|
Double word |
|
64 bits, numbered 0 through 63, with bit 0 being the least significant. |
|
|
|
|
|
xx

Hardware Preparation |
1 |
and Installation |
Introduction
This chapter provides information on hardware preparation and installation for the MVME5100 Series of Single Board Computers.
Note Unless otherwise specified, the designation “MVME5100” refers to all models of the MVME5100-series Single Board Computers.
Getting Started
The following subsections include information helpful in preparing your equipment. It includes and overview of the MVME5100, any equipment needed to complete the installation, and unpacking instructions.
Overview and Equipment Requirements
The MVME5100 interfaces to a VMEbus system via its P1 and P2 connectors and contains two IEEE 1386.1 PCI Mezzanine Card (PMC) Slots. The PMC Slots are 64-bit and support both front and rear I/O.
Additionally, the MVME5100 is user configurable by setting on-board jumpers. Two I/O modes are possible: PMC mode or SBC mode (also called 761 or IPMC mode). The SBC mode uses the IPMC712 I/O PMC and the MVME712M Transiton Module, or the IPMC761 I/O PMC and the MVME761 Transition Module. The SBC mode is backwards compatible with the MVME761 transition card and the P2 adapter card (excluding PMC I/O routing) used on the MVME2600/2700 product. This mode is accomplished by configuring the on-board jumpers and by attaching an IPMC761 PMC in PMC slot 1. Secondary Ethernet is configured to the rear.
PMC mode is backwards compatible with the MVME2300/MVME2400 and is accomplished by simply configuring the on-board jumpers.
1-1
1 |
Hardware Preparation and Installation
The following equipment list is appropriate for use in an MVME5100 system:
PMCspan PCI expansion mezzanine module (mates with MVME5100)
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Mezzanine Cards (PMCs) (installed on an MVME5100 board)
RAM500 memory mezzanine modules (installed on an MVME5100 board)
VME system enclosure
System console terminal
Disk drives (and/or other I/O) and controllers
Operating system (and/or application software)
Unpacking Instructions
Avoid touching areas of integrated circuitry; static discharge can damage these circuits.
Caution
Note If the shipping carton(s) is/are damaged upon receipt, request that the carrier's agent be present during the unpacking and inspection of the equipment.
Use ESD
Wrist Strap
Motorola strongly recommends that you use an antistatic wrist strap and a conductive foam pad when installing or upgrading a system.
Electronic components, such as disk drives, computer boards, and memory modules, can be extremely sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). After removing the component from its protective wrapper or from the system, place the component on a grounded, static-free, and adequately
1-2 |
Computer Group Literature Center Web Site |

Preparation
1
protected working surface. Do not slide the component over any surface. In the case of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB), place the board with the component side facing up.
If an ESD station is not available, you can avoid damage resulting from ESD by wearing an antistatic wrist strap (available locally) that is attached to an active electrical ground.
Note A system chassis may not be a suitable grounding source if it is unplugged.
Preparation
This section includes subsections on hardware configuration that may need to be performed immediately before and after board installation. It includes a brief reminder on setting bits in control registers, setting jumpers for the appropriate configuration, and other VME data considerations.
Hardware Configuration
To produce the desired board configuration and to ensure proper operation of the MVME5100, it may be necessary to perform certain modifications before and after installation. The following paragraphs discuss the preparation of the MVME5100 hardware components prior to installing them into a chassis and connecting them.
The MVME5100 provides software control over most of its options by setting bits in control registers. After installing it in a system, you can modify its configuration. For additional information on the board’s control registers, refer to the MVME5100 Single Board Computer Programmer's Reference Guide listed in Appendix C, Related Documentation.
http://www.motorola.com/computer/literature |
1-3 |

1 |
Hardware Preparation and Installation
It is important to note that some options are not software-programmable. These specific options are controlled through manual installation or removal of jumpers, and in some cases, the addition of other interface modules on the MVME5100. The following table lists the manually configured jumpers on the MVME5100, and their default settings.
If you are resetting the board jumpers from their default settings, it is important to verify that all settings are reset properly. For example, the SBC mode requires setting jumpers 4, 10 and 17 for rear Ethernet functions, but it also requires resetting jumpers J6 and J20.
Neglecting to reset J6 and J20 could damage or destroy subsequent PMCs or PrPMCs installed on the base board at power-up.
Table 1-1. Manually Configured Headers/Jumpers
Jumper |
Description |
Setting |
Default |
|
|
|
|
J1 |
RISCWatch Header |
None (Factory Use Only) |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
J2 |
PAL Programming Header |
None (Lab Use Only) |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
J4 |
Ethernet Port 2 Selection |
For P2 Ethernet Port 2: |
|
|
(see also J10/J17) |
Pins 1,2; 3,4; 5,6; 7,8 (set when in SBC |
No |
|
|
mode, also called 761 mode) |
Jumper |
|
|
|
Installed |
|
|
For Front Panel Ethernet Port 2: |
|
|
|
(front |
|
|
|
No Jumpers Installed |
|
|
|
panel) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J6, J20 |
Operation Mode |
Pins 1, 2 for PMC Mode |
PMC |
|
(Set Both Jumpers) |
|
Mode |
|
Pins 2, 3 for SBC Mode* |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J7 |
Flash Memory Selection |
Pins 1, 2 for Soldered Bank A |
Socketed |
|
|
|
Bank B |
|
|
Pins 2, 3 for Socketed Bank B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J10, J17 |
Ethernet Port 2 Selection |
For Front Panel Ethernet Port 2: |
Front |
|
(see also J4) |
Pins 1, 3 and 2,4 on Both Jumpers |
Panel |
|
|
|
Ethernet |
|
|
For P2 Ethernet Port 2: |
|
|
|
Port 2 |
|
|
|
Pins 3, 5 and 4, 6 on Both Jumpers (set |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for SBC mode) |
|
|
|
|
|
1-4 |
Computer Group Literature Center Web Site |

Preparation
1
Table 1-1. Manually Configured Headers/Jumpers (Continued)
Jumper |
Description |
Setting |
Default |
|
|
|
|
J15 |
System Controller (VME) |
Pins 1, 2 for No SCON |
|
|
|
|
Auto |
|
|
Pins 2, 3 for Auto SCON |
|
|
|
|
SCON |
|
|
No Jumper for ALWAYS SCON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J16 |
Soldered Flash Protection |
Pins 1, 2 Enables Programming of |
Flash |
|
|
Flash |
Prog. |
|
|
|
Enabled1 |
|
|
Pins 2, 3 Disables Programming of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
upper 64KB of Flash |
|
|
|
|
|
Refer to the section titled Jumper Settings on the next page for additional information.
Note 1. Write protects only outer two 8K boot sectors. Refer to Flash
Memory on page 4-5 for an complete explanation.
Jumper Settings
Prior to performing the installation instructions, you must ensure that the jumpers are set properly for your particular configuration. For example, if you are using an IPMC761/MVME761 or IPMC712/MVME712 combination in conjunction with the MVME5100, you must reset the jumpers for the SBC mode (jumpers J4, J6, J10, J17 and J20). These are factory configured for the PMC mode. Verify all settings according to the previous table and follow the instructions below if applicable.
http://www.motorola.com/computer/literature |
1-5 |

1 |
Hardware Preparation and Installation
|
|
PMC I/O Mode |
|
|
SBC I/O Mode |
||||||||||||
2 |
4 |
6 |
|
2 |
4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
J10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
J10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1 |
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
6 |
|
2 |
|
4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
J17 |
|
|
|
|
|
J17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
J4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
|
|||||||||
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For rear panel LAN, jumper |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
entire 8 pin header on J4 |
||||||||||
PMC/SBC (761/IPMC) Mode Selection
There are five headers associated with the selection of the PMC or SBC mode: J4, J6 J10, J17 and J20. Three of these headers are responsible for secondary Ethernet I/O (J4, J10 and J17) to either the front panel (PMC mode), or to the P2 connector via J4 (SBC mode). The other two headers (J6 and J20) ensure proper routing of +/- 12V signal routing. The MVME5100 is set at the factory for front panel I/O: PMC mode (see Table 1-1). The SBC mode should only be selected when using one of the IPMC7xx modules in conjunction with the corresponding MVME7xx transition module.
Installation Considerations
The MVME5100 draws power from the VMEbus backplane connectors P1 and P2. Connector P2 is also used for the upper 16 bits of data in 32-bit transfers, and for the upper 8 address lines in extended addressing mode. The MVME5100 will not function properly without its main board connected to VMEbus backplane connectors P1 and P2.
1-6 |
Computer Group Literature Center Web Site |

Preparation
1
Whether the MVME5100 operates as a VMEbus master or as a VMEbus slave, it is configured for 32 bits of address and 32 bits of data (A32/D32). However, it handles A16 or A24 devices in the appropriate address ranges. D8 and/or D16 devices in the system must be handled by the processor software.
If the MVME5100 tries to access off-board resources in a nonexistent location and if the system does not have a global bus time-out, the MVME5100 waits indefinately for the VMEbus cycle to complete. This will cause the system to lock up. There is only one situation in which the system might lack this global bus time-out; that is when the MVME5100 is not the system controller and there is no global bus time-out elsewhere in the system.
Note Software can also disable the bus timer by setting the appropriate bits in the Universe II VMEbus interface.
Multiple MVME5100 boards may be installed in a single VME chassis; however, each must have a unique VMEbus address. Other MPUs on the VMEbus can interrupt, disable, communicate with, and determine the operational status of the processor(s).
http://www.motorola.com/computer/literature |
1-7 |

1 |
Hardware Preparation and Installation |
|
Installation
This section discusses the installation of PMCs onto the MVME5100, installation of PMCspan modules onto the MVME5100, and the installation of the MVME5100 into a VME chassis.
Note If you have ordered one or more of the optional RAM500 memory mezzanine boards for the MVME5100, ensure that they are installed on the board prior to proceeding. If they have not been installed by the factory, and you are installing them yourself, please refer to Appendix D, RAM500 Memory Expansion Module, for installation instructions. It is recommended that the memory mezzainine modules be installed prior to installing other board accessories, such as PMCs, IPMCs, or transition modules.
1-8 |
Computer Group Literature Center Web Site |
1
Installation
2788 0700
|
|
P1 |
|
|
|
P2 |
2788 0700 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J4 |
J5 |
|
|
J3 |
|
||
J6 |
J20 |
||
|
|
|
J22 |
|
|
|
|
|
J24 |
|
|
|
|
J12 |
|
|
|
|
|
J14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J21 |
J23 |
J11 |
J13 |
|
|
Layout |
|
S1 |
|
|
|
J25 |
|
|
|
|
J8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XU1 |
XU2 |
|
|
|
MVME5100 |
L1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HAWK |
J7 |
|
|
|
|
|
ASIC |
|
|
|
-11. |
|
|
|
J15 |
|
|
|
|
L2 |
|
J16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
J1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Figure |
|
|
|
|
J10 J17 |
|
LAN 2 |
LAN 1 |
|
|
BFL CPU |
|
PCI MEZZANINE CARD |
PCI MEZZANINE CARD |
ABT/RST10/100 BASE T10/100 BASE T |
DEBUG |
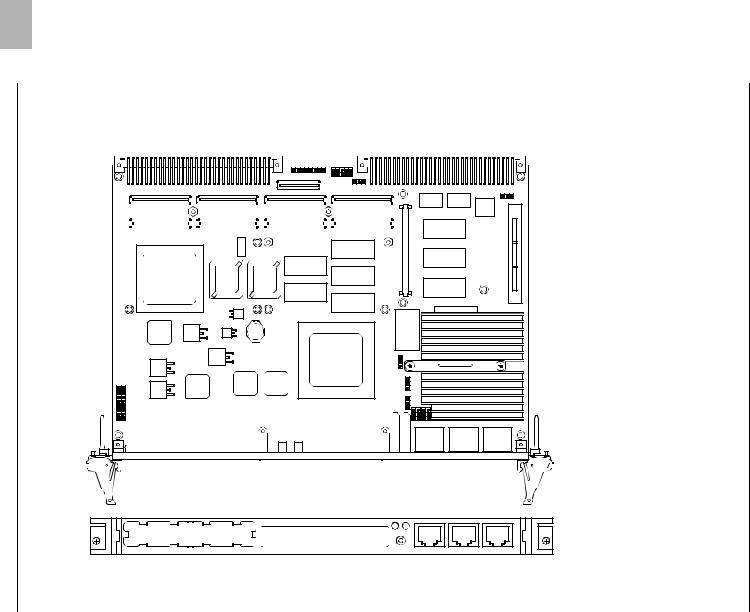
1-9
http://www.motorola.com/computer/literature

1 |
Hardware Preparation and Installation |
|
PMC Modules
Warning
Caution
PMC modules mount on top of the MVME5100. Perform the following steps to install a PMC module on your MVME5100.
Dangerous voltages, capable of causing death, are present in this equipment. Use extreme caution when handling, testing, and adjusting.
Inserting or removing modules with power applied may result in damage to module components. Avoid touching areas of integrated circuitry, static discharge can damage these circuits.
Note This procedure assumes that you have read the user’s manual that came with your PMCs.
1.Attach an ESD strap to your wrist. Attach the other end of the ESD strap to an electrical ground. Note that the system chassis may not be grounded if it is unplugged. The ESD strap must be secured to your wrist and to ground throughout the procedure.
2.Perform an operating system shutdown. Turn the AC or DC power off and remove the AC cord or DC power lines from the system. Remove chassis or system cover(s) as necessary for access to the VME modules.
3.If the MVME5100 has already been installed in a VMEbus card slot, carefully remove it as shown in Figure 1-2 and place it with connectors P1and P2 facing you.
4.Remove the filler plate(s) from the front panel of the MVME5100.
5.Align the PMC module’s mating connectors to the MVME5100’s mating connectors and press firmly into place.
6.Insert the appropriate number of Phillips screws (typically 4) from the bottom of the MVME5100 into the standoffs on the PMC module and tighten the screws (refer to Figure 1-3).
1-10 |
Computer Group Literature Center Web Site |
 Loading...
Loading...