fanuc 16C, 160C, 18C, 180-C Connection Manual
FANUC Series 16/18/160/180 - Model C
Connection Manual
(Hardware)
B-62753EN/01

•No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form.
•All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
The export of this product is subject to the authorization of the government of the country from where the product is exported.
In this manual we have tried as much as possible to describe all the various matters. However, we cannot describe all the matters which must not be done, or which cannot be done, because there are so many possibilities.
Therefore, matters which are not especially described as possible in this manual should be regarded as ”impossible”.
This manual contains the program names or device names of other companies, some of which are registered trademarks of respective owners. However, these names are not followed by or in the main body.

B±62753EN/01 |
Table of Contents |
1. PREFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
|
2. CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
|
3. INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
|
3.1 |
ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS OUTSIDE THE CABINET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
3.2 |
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS OF CNC AND SERVO UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
3.3 |
POWER CAPACITY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
3.4DESIGN AND INSTALLATION CONDITIONS OF THE MACHINE TOOL
|
MAGNETIC CABINET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 6 |
|
3.5 |
THERMAL DESIGN OF THE CABINET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
|
|
3.5.1 |
Temperature Rise within the Cabinet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
|
3.5.2 |
Cooling by Heat Exchanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
|
3.5.3 |
Heat Loss of Each Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
9 |
3.6 |
INSTALLING THE HEAT EXCHANGER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
|
|
3.6.1 |
Cooling Fin A/B/C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
|
3.6.2 |
Heat Exchanger for CRT/MDI Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
|
3.6.3 |
The Heat Pipe Type Heat Exchanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
18 |
|
3.6.3.1 |
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
18 |
3.7 |
ACTION AGAINST NOISE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
|
|
3.7.1 |
Separating Signal Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
|
3.7.2 |
Ground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
24 |
|
3.7.3 |
Connecting the Signal Ground (SG) of the Control Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
25 |
|
3.7.4 |
Noise Suppressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
26 |
|
3.7.5 |
Cable Clamp and Shield Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
27 |
3.8 |
CONTROL UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
30 |
|
|
3.8.1 |
Configuration and Installation of the Control Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
30 |
|
3.8.2 |
Battery for Memory Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
34 |
3.9 |
CABLE LEAD±IN DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
36 |
|
4. TOTAL CONNECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
49 |
||
5. POWER SUPPLY UNIT CONNECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
56 |
||
5.1 |
POWER SUPPLY UNIT PANEL LAYOUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
57 |
|
5.2 |
POWER SUPPLY UNIT CONNECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
59 |
|
5.3 |
24V INPUT POWER SOURCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
63 |
|
|
5.3.1 |
Power Supply for the Control Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
63 |
|
5.3.2 |
Procedure for Turning on the Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
65 |
|
5.3.3 |
Procedure for Turning off the Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
65 |
5.4 |
CABLE FOR POWER SUPPLY TO CONTROL UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
66 |
|
6. CONNECTION OF I/O UNITS TO MACHINE INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
67 |
||
6.1 |
GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
68 |
|
6.2 |
CONNECTION OF THE FANUC I/O Link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
69 |
|
|
6.2.1 |
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
69 |
c±1

O O S |
B±62753EN/01 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
6.2.2 |
Connection of FANUC I/O Link by Electric Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 70 |
|
6.2.3 |
Connection of FANUC I/O Link Optical Fiber Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 71 |
6.3 |
CONNECTION OF THE FANUC I/O Unit±MODEL A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 73 |
|
|
6.3.1 |
Structure of FANUC I/O Unit±MODEL A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 73 |
|
6.3.2 |
Outer Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 73 |
|
6.3.3 |
Mounting and Dismounting Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 74 |
|
6.3.4 |
Connection Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 75 |
|
6.3.5 |
Connecting Input Power Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 76 |
|
6.3.6 |
Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 76 |
|
6.3.7 |
Connecting Signal Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 77 |
|
6.3.8 |
Connecting with I/O Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 81 |
|
6.3.9 |
Digital Input/Output Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 82 |
|
6.3.10 |
Correspondence between I/O Signals and Addresses in a Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 84 |
|
6.3.11 |
Number of Points for I/O Unit±MODEL A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 85 |
6.4 |
CONNECTION OF MACHINE OPERATOR'S PANEL INTERFACE UNIT . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 86 |
|
|
6.4.1 |
Function Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 86 |
|
6.4.2 |
System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 88 |
|
6.4.3 |
Signal Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 89 |
|
6.4.4 |
Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . . 91 |
|
6.4.5 |
PMC Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . 101 |
|
6.4.6 |
Major Connection Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . 102 |
|
6.4.7 |
State of the LEDs on the Machine Operator's Panel Interface Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . 102 |
|
6.4.8 |
Connector (on the Cable Side) Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . . . . . . . 102 |
6.4.9Machine Operator's Panel Interface Unit Dimension Diagram
|
|
(Including Connector Locations) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
104 |
|
6.4.10 |
Machine Operator's Panel Interface Unit Mounting Dimension Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
105 |
|
6.4.11 |
Fuse Mounting Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
107 |
6.5 |
CONNECTION OF OPERATOR'S PANEL CONNECTION UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
108 |
|
|
6.5.1 |
Input Signal Regulations for Operator's Panel Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
109 |
|
6.5.2 |
Output Signal Regulations for Operator's Panel Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
110 |
|
6.5.3 |
Connector Layout for Operator's Panel Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
111 |
|
6.5.4 |
External View of Operator's Panel Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
113 |
6.6 |
CONNECTION OF SOURCE OUTPUT TYPE CONNECTION UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
114 |
|
|
6.6.1 |
Input Signal Specifications for Source Output Type Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
115 |
|
6.6.2 |
Output Signal Specifications for Source Output Type Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
116 |
|
6.6.3 |
Connector Pin Layout for Source Output Type Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
120 |
|
6.6.4 |
Dimensions of Source Output Type Connection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
122 |
6.7 |
CONNECTION OF FS0 OPERATOR'S PANEL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
124 |
|
6.8 |
I/O CARD CONNECTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
130 |
|
|
6.8.1 |
Input Signal Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
132 |
|
6.8.2 |
Specifications of the Output Signals of the I/O Card (Sink Type) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
134 |
|
6.8.3 |
Connector Layout for Sink Output Type I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
135 |
|
6.8.4 |
Input Signal Connector Pin Layout for Sink Output Type I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
137 |
|
6.8.5 |
Output Signal Connector Pin Layout for Sink Output Type I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
139 |
|
6.8.6 |
Address Mapping of I/O Card (Sink Type) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
140 |
6.9 |
SOURCE OUTPUT I/O CARD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
145 |
|
|
6.9.1 |
Input Signal Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
145 |
c±2

B±62753EN/01 O O S
6.9.2 |
Output Signal Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
145 |
|
6.9.3 |
Connector Layout for Source Output Type I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
147 |
|
6.9.4 |
Input Signal Connector Pin Layout for Source Output Type I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
149 |
|
6.9.5 |
Output Signal Connector Pin Layout for Source Output Type I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
151 |
|
6.9.6 |
Address map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
153 |
|
6.10 |
USE OF TWO I/O CARDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
159 |
|
6.10.1 |
Specifications of Input and Output Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
159 |
|
6.10.2 |
I/O Card Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
159 |
|
6.10.3 |
Addresses Assigned to Each I/O Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
159 |
|
7. CONNECTION TO CNC PERIPHERALS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
161 |
||
7.1 |
CRT/MDI UNIT INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
162 |
|
7.1.1 |
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
162 |
|
7.1.2 |
CRT, PDPor LCD Display Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
167 |
|
7.1.3 |
Adjusting the Flat Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
173 |
|
7.1.4 |
Contrast Adjustment for Monochrome LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
174 |
|
7.1.5 |
Keyboard Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
175 |
|
7.2 |
I/O DEVICE INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
176 |
|
7.2.1 |
RS±232±C Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
176 |
|
7.2.2 |
PPR Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
177 |
|
7.2.3 |
Portable Tape Reader Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
178 |
|
7.2.4 |
FANUC FLOPPY CASSETTE Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
179 |
|
7.2.5 |
Connection of Tape Reader without Reels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
180 |
|
7.2.6 |
Connection of Tape Reader with Reels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
181 |
|
7.3 |
MANUAL PULSE GENERATOR INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
182 |
|
7.3.1 |
Signal Specifications for Manual Pulse Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
184 |
|
7.4 |
REMOTE BUFFER INTERFACE (RS±232±C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
185 |
|
7.5 |
REMOTE BUFFER INTERFACE (RS±422) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
187 |
|
7.6 |
DNC1 INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
189 |
|
7.6.1 |
Multi±points Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
189 |
|
7.6.2 |
1 to 1 Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
190 |
|
7.7 |
DNC2 INTERFACE (RS±232±C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
191 |
|
7.8 |
HIGH SPEED DI SIGNAL INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
192 |
|
7.8.1 |
Receiver Input Signal Specifications for High±speed DI Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
193 |
|
7.9 |
SPINDLE INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
194 |
|
7.9.1 |
Serial Spindle Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
195 |
|
7.9.2 |
Analog Spindle Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
196 |
|
7.9.3 |
Series Spindle Amplifier Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
197 |
|
7.9.4 |
Position Coder Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
199 |
|
7.10 |
SERVO INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
200 |
|
7.10.1 |
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
200 |
|
7.10.2 |
Servo Amplifier Interface ( series servo amplifier) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
201 |
|
7.10.3 |
Serial Pulse Coder Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
202 |
|
7.10.4 |
Separate Type Detector Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
206 |
|
7.10.5 |
APC Battery Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
211 |
|
7.11 |
ANALOG SIGNAL INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
212 |
|
7.12 HIGH±SPEED SERIAL BUS (HSSB) INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
213 |
||
c±3

O O S |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
APPENDIX
A. EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS OF EACH UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
B. EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS OF EACH CONNECTOR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
C. 20±PIN INTERFACE CONNECTORS AND CABLES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
D. LIST OF UNIT FOR CE MARKING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
c±4

B±62753EN/01 |
1. PREFACE |
|
|
1
This manual describes the electrical and structural specifications required for connecting the CNC control unit to a machine tool. The manual outlines the components commonly used for FANUC CNC control units, as shown in the configuration diagram in Chapter 2, and supplies additional information on using these components. Refer to individual manuals for the detailed specifications of each component.
The models covered by this manual, and their abbreviations, are :
Product Name |
Abbreviations |
|
|
|
|
FANUC Series 16±TC |
16±TC |
Series 16 |
|
|
|
FANUC Series 16±MC |
16±MC |
|
|
|
|
FANUC Series 18±TC |
18±TC |
Series 18 |
|
|
|
FANUC Series 18±MC |
18±MC |
|
|
|
|
FANUC Series 160±TC |
160±TC |
Series 160 |
|
|
|
FANUC Series 160±MC |
160±MC |
|
|
|
|
FANUC Series 180±TC |
180±TC |
Series 180 |
|
|
|
FANUC Series 180±MC |
180±MC |
|
|
|
|
Related manuals |
The table below lists manuals related to MODEL C of Series 16, Series |
||
|
18, Series 160 and Series 180. |
|
|
|
In the table, this manual is marked with an asterisk(*). |
|
|
|
Table 1 Manuals Related |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manual name |
Specification |
|
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESCRIPTIONS |
B±62752EN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONNECTION MANUAL (HARDWARE) |
B±62753EN |
* |
|
|
|
|
|
CONNECTION MANUAL (FUNCTION) |
B±62753EN±1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATOR'S MANUAL (For LATHE) |
B±62754EN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATOR'S MANUAL (FOR MACHINING CENTER) |
B±62764EN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MAINTENANCE MANUAL |
B±62755EN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PARAMETER MANUAL |
B±62760EN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PROGRAMMING MANUAL |
B±61803E±1 |
|
|
(Macro Compiler / Macro Executer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FAPT MACRO COMPILER PROGRAMMING MANUAL |
B±66102E |
|
|
|
|
|
1

1. PREFACE |
B±62753EN/01 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1 Manuals Related |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manual name |
Specification |
|
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FANUC Super CAP T OPERATOR'S MANUAL |
B±62444E±1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
FANUC Super CAP M OPERATOR'S MANUAL |
B±62154E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
FANUC Super CAP M PROGRAMMING MANUAL |
B±62153E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONVERSATIONAL AUTOMATIC PROGRAMMING |
B±61804E±1 |
|
|
FUNCTION I FOR LATHE (Series 18±TB) |
|
|
|
OPERATOR'S MANUAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONVERSATIONAL AUTOMATIC PROGRAMMING |
B±61804E±2 |
|
|
FUNCTION FOR LATHE (Series 15±MODEL B, Series |
|
|
|
16 CAPII) OPERATOR'S MANUAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONVERSATIONAL AUTOMATIC PROGRAMMING |
B±61874E±1 |
|
|
FUNCTION I FOR MACHINING CENTER |
|
|
|
OPERATOR'S MANUAL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
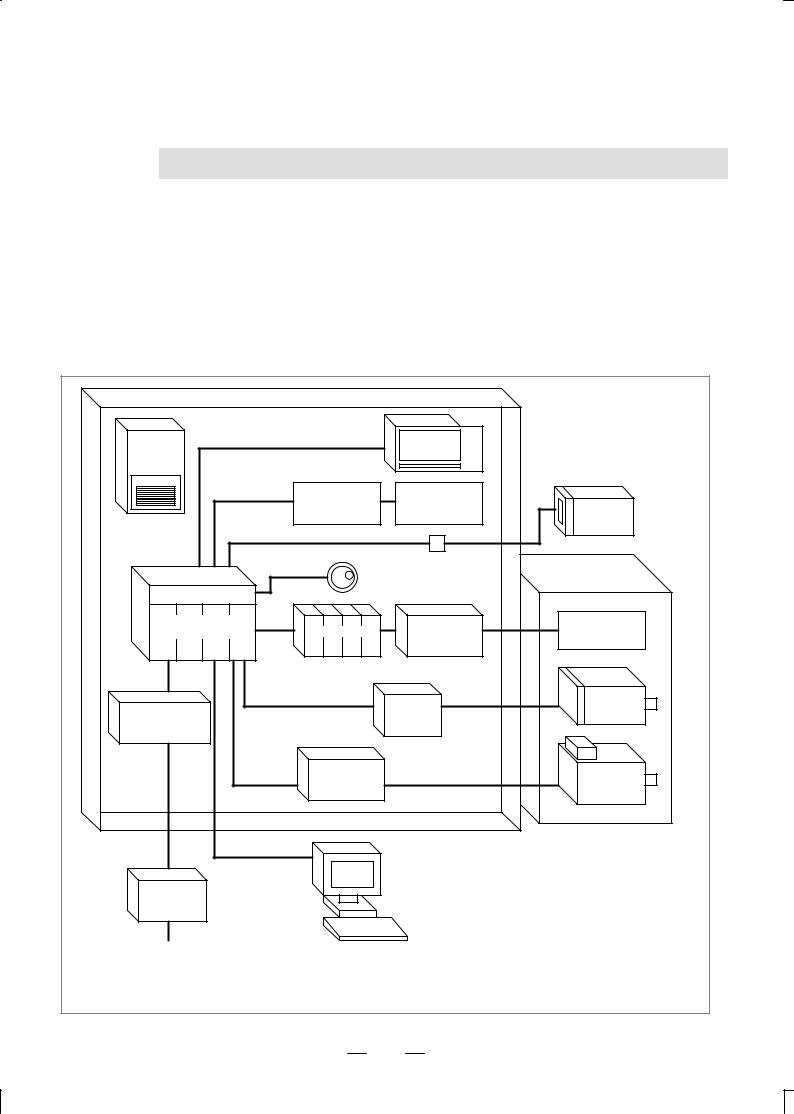
B±62753EN/01 |
2. CONFIGURATION |
|
|
2 CONFIGURATION
The following figure shows the configuration of the electrical system of the machine tool with which this control is used.
This manual describes how to connect the units illustrated in this diagram. The machine tool body, machine operator's panel, power magnetic circuit, and sensor/actuator are specific to the machine tool and are the builder's responsibility. This manual does not cover the internal connection of these units to the machine tool. The numbers in parentheses shown in the diagram are section references for this manual.
|
Machine tool magnetic cabinet |
|
|
|
|
Heat |
|
CRT/MDI |
|
|
|
exchanger |
|
unit |
|
|
|
(3.6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operator's |
Machine |
|
|
|
|
panel interface |
operator's |
I/O device |
||
|
(6.4, 6.5) |
panel |
|
||
|
|
Relay connector (7.2) |
|
||
|
Manual pulse generator |
|
|||
|
(7.3) |
|
|
|
|
Control unit |
Power |
|
Sensor / |
||
(3.8) |
I/O unit |
|
|||
magnetic |
actuator |
||||
|
|
||||
|
(Note1) |
circuit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(5) |
(6.2, 6.3, 6.7±6.9) |
|
|
|
|
Multi±tap |
|
Servo |
(Note 2) |
Servo |
|
|
|
motor |
|||
|
amplifier |
|
|||
transformer for |
|
|
|
||
|
(7.10) |
|
|
||
the control unit |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Spindle |
|
(Note 2) |
Spindle |
|
|
amplifier |
|
|||
|
(7.9) |
|
|
motor |
|
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
supply |
(7.4, 7.5, 7.6) |
Host computer |
|
||
|
|
||||
Distribution |
|
|
|
|
|
board |
|
|
|
|
|
Note 1 Refer to the ºFANUC I/O Unit Model A Connecting Maintenance Manual (B-61813E)º.
Note 2 Refer to the following manuals:
ªFANUC AC Servo Motorα Series Descriptions (B-65142E)º
ªFANUC AC Spindle Motorα Series Descriptions (B-65152E)º
ªFANUC CONTROL MOTOR AMPLIFIERα Series Descriptions (B±65162E)º
3

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
3 INSTALLATION
4

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
3.1
ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS OUTSIDE THE CABINET
3.2
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS OF CNC AND SERVO UNIT
3.3
POWER CAPACITY
The peripheral units, such as the control unit and CRT/MDI, have been designed on the assumption that they are housed in closed cabinets. In this manual ªcabinetº refers to the following:
Cabinet manufactured by the machine tool builder for housing the control unit or peripheral units;
Cabinet for housing the flexible turnkey system provided by FANUC;
Operation pendant, manufactured by the machine tool builder, for housing the CRT/MDI unit or operator's panel.
Equivalent to the above.
The environmental conditions when installing these cabinets shall conform to the following table. Section 3.4 describes the installation and design conditions of a cabinet satisfying these conditions.
Room temperature |
In operation |
|
0 to 45 |
|
|
|
|
||
In storage or transportation |
±20 to 60 |
|||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Change in |
1.1°C/minute max. |
|
|
|
temperature |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Relative humidity |
Normal |
|
75% or less |
|
|
|
|
||
Temporary (within 1 month) |
95% or less |
|||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Vibration |
In operation: |
0.5G or less |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Normal machine shop environment |
|||
Environment |
(The environment must be considered if the cabinets |
|||
are in a location where the density of dust, coolant, |
||||
|
||||
|
and/or organic solvent is relatively high.) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Room temperature |
In operation |
|
0°C to +55°C |
|
In storage or transportation |
±20°C to +60°C |
|||
|
||||
|
|
|
||
Relative humidity |
95% RH or less (no condensation) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Vibration |
0.5 G or less |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Environment |
The unit shall not be exposed direct to cutting oil, lu- |
|||
bricant or cutting chips. |
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
The power capacity of the CNC control unit, which in this section means the specification required for the power supply, is obtained by adding the power capacity of the control section and the power capacity of the servo section.
The power capacity of the control section includes the power capacity of the control unit, CRT/MDI, I/O unit, and operator's panel interface.
Power capacity of |
When power supply AI is used and AC out- |
0.3kVA |
the control section |
put terminals CP2 and CP3 are not used. |
|
|
|
|
|
When power supply AI is used and AC out- |
0.8kVA |
|
put terminals CP2 and CP3 are used. |
|
|
|
|
|
When power supply BI is used and AC out- |
0.5kVA |
|
put terminals CP2 and CP3 are not used. |
|
|
|
|
|
When power supply BI is used and AC out- |
1.0kVA |
|
put terminals CP2 and CP3 are used. |
|
|
|
|
Power capacity of |
Depends on servo motor type. |
|
the servo section |
|
|
|
|
|
5

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
3.4
DESIGN AND INSTALLATION CONDITIONS OF THE MACHINE TOOL MAGNETIC CABINET
When a cabinet is designed, it must satisfy the environmental conditions described in Section 3.1. In addition, the magnetic interference on the CRT screen, noise resistance, and maintenance requirements must be considered. The cabinet design must meet the following conditions :
DThe cabinet must be fully closed.
The cabinet must be designed to prevent the entry of airborne dust,coolant,and organic solvent.
Cabinets that let in air may be designed for the servo amplifier and servo transformer provided that they :
-Use an air filter on the air inlet ;
-Place the ventilating fan so that it does not blow air directly toward the unit;
-Control the air flow so that no dust or coolant enters the air outlet
DThe cabinet must be designed to maintain a difference in temperature of 10°C or less between the air in the cabinet and the outside air when the temperature in the cabinet increases.
See Section 3.5 for the details on thermal design of the cabinet.
DA closed cabinet must be equipped with a fan to circulate the air within.
The fan must be adjusted so that the air moves at 0.5 m/sec along the surface of each installed unit.
CAUTION : If the air blows directly from the fan to the unit, dust easily adheres to the unit. This may cause the unit to fail.
DFor the air to move easily, a clearance of 100 mm is required between each unit and the wall of the cabinet.
DPacking materials must be used for the cable port and the door in order to seal the cabinet.
Because the CRT unit uses a voltage of approximately 11 kV, airborne dust gathers easily. If the cabinet is insufficiently sealed, dust passes through the gap and adheres to the unit. This may cause the insulation of the unit to deteriorate.
DThe CRT/MDI unit must be installed in a location where coolant cannot be poured directly on it. The unit does have a dust±proof front panel.
DNoise must be minimized.
As the machine and the CNC unit are reduced in size, the parts that generate noise may be placed near noise±sensitive parts in the magnetics cabinet.
The CNC unit is built to protect it from external noise. Cabinet design to minimize noise generation and to prevent it from being transmitted to the CNC unit is necessary. See section 3.7 for details of noise elimination/management.
DThe units must be installed or arranged in the cabinet so that they are easy to inspect and maintain.
6

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
The CRT screen can be distorted by magnetic interference. Arranging magnetic sources must be done with care.
If magnetic sources (such as transformers, fan motors, electromagnetic contactors, solenoids, and relays) are located near the CRT display, they frequently distort the display screen. To prevent this, the CRT display and the magnetic sources generally must be kept 300 mm apart. If the CRT display and the magnetic sources are not 300 mm apart, the screen distortion may be suppressed by changing the direction in which the magnetic sources are installed.
The magnetic intensity is not constant, and it is often increased by magnetic interference from multiple magnetic sources interacting with each other. As a result, simply keeping the CRT and the magnetic sources 300 mm apart may not be enough to prevent the distortion. If they cannot be kept apart, or if the CRT screen remains distorted despite the distance, cover the screen with a magnetic shield.
The installation conditions of the I/O unit must be satisfied.
To obtain good ventilation in the module, the I/O unit must be installed in the direction shown in the following figure. Clearances of 100 mm or more both above and below the I/O unit are required for wiring and ventilation.
Equipment radiating too much heat must not be put below the I/O unit.
Top
I/O base unit
(No screws or protrusions shall extend from the bottom of this unit.)
Bottom
7

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
3.5
THERMAL DESIGN OF THE CABINET
The purpose of the thermal design of the cabinet is to limit the difference in temperature between the air in the cabinet and the outside air to 10°C or less when the temperature in the cabinet increases.
The internal air temperature of the cabinet increases when the units and parts installed in the cabinet generate heat. Since the generated heat is radiated from the surface of the cabinet, the temperature of the air in the cabinet and the outside air balance at certain heat levels. If the amount of heat generated is constant, the larger the surface area of the cabinet, the less the internal temperature rises. The thermal design of the cabinet refers to calculating the heat generated in the cabinet, evaluating the surface area of the cabinet, and enlarging that surface area by installing heat exchangers in the cabinet, if necessary. Such a design method is described in the following subsections.
3.5.1
e e e i e i i e i e
The cooling capacity of a cabinet made of sheet metal is generally 6 W/°C per 1m2 surface area, that is, when the 6W heat source is contained in a cabinet having a surface area of 1 m2, the temperature of the air in the cabinet rises by 1°C. In this case the surface area of the cabinet refers to the area useful in cooling , that is, the area obtained by subtracting the area of the cabinet touching the floor from the total surface area of the cabinet. There are two preconditions : The air in the cabinet must be circuited by the fun, and the temperature of the air in the cabinet must be almost constant.The following expression must then be satisfied to limit the difference in temperature between the air in the cabinet and the outside air to 10°C or less when the temperature in the cabinet rises:
Internal heat loss P [W]
6[W/m2 °C] ×surface area S[m2]×10[°C] of rise in temperature
For example, a cabinet having a surface area of 4m2 has a cooling capacity of 24W/°C. To limit the internal temperature increase to 10°C under these conditions, the internal heat must not exceed 240W. If the actual internal heat is 320W, however, the temperature in the cabinet rises by 13°C or more. When this happens, the cooling capacity of the cabinet must be improved using the heat exchanger described next.
3.5.2
i e c e
If the temperature rise cannot be limited to 10°C by the cooling capacity of the cabinet, a heat exchanger must be added. The heat exchanger forcibly applies the air from both the inside and outside of the cabinet to the cooling fin to obtain effective cooling. The heat exchanger enlarges the surface area. Section 3.7 explains five heat exchangers supplied by FANUC. Select one of these according to the application.
If cooling fin A is used for the cabinet, the total cooling capacity of a cabinet having a surface area of 4 m2 in the example above is improved as follows :
6W/m2 °C × 4m2 + 9.1W/°C= 33.1W/°C
The calculated value verifies that even if the internal heat is 320 W, the temperature rise can be limited to less than 10°C.
See Section 3.6 for installing the heat exchanger.
8

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
3.5.3
Heat Loss of Each Unit
|
|
Name |
Heat |
Remarks |
|
|
|
|
loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Basic unit (2 slots) |
60W |
Power supply AI |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Basic unit (4 slots) |
60W |
Power supply AI |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Basic unit (6 slots) |
80W |
Power supply BI |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Basic unit (8 slots) |
80W |
Power supply BI |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main CPU board |
20W |
|
|
|
Control unit |
|
|
|
|
|
Option 1 board |
15W |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Option 2 board |
15W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Option 3 board |
15W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O card (Sink type, Source type) |
15±20 |
*1 |
|
|
|
|
|
W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Robot control board |
15W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9″ |
monochrome CRT/MDI |
14W |
For small type |
|
|
|
|
|
CRT/MDI and stan- |
|
|
|
|
|
dard type CRT/MDI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9″ |
color CRT/MDI |
40W |
|
|
CRT/MDI |
|
|
|
|
|
9″ |
monochrome PDP/MDI |
20W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.4″ color LCD/MDI |
20W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.5″ color LCD/MDI |
20W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14″ color CRT/MDI |
70W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operator's |
Operator's panel connection unit |
30W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Machine operator's panel inter- |
24W |
|
|
||
panel |
|
|
|||
face unit |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O Unit |
AIF01A, AIF01B |
1.2W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
AID32A, AID32B |
1.2W + 0.23W |
number |
||
|
|
|
of ON points |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
AID16C, AID16D |
0.1W + 0.21W |
number |
||
|
|
|
of ON points |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
AID32E, AID32F |
0.1W + 0.23W |
number |
||
|
|
|
of ON points |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Refer to FANUC CONTROL MOTOR AMPLIFIER α Series Descriptions (B±65162E) for heat loss of servo amplifier.
*1 : 5W for 5V type ; 0.175W per pin that is turned on for 24V.
9

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
3.6
INSTALLING THE HEAT EXCHANGER
Table 3.6 lists the heat exchangers.Cooling fins A, B and C are not provided with a fan. Note that a fan motor is required for any of these cooling fins when it is used as a heat exchanger.
Table 3.6 List of Heat Exchangers
Name |
Ordering |
Cooling |
|
Size |
||
specification |
capacity |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cooling fin A |
A02B±0053±K303 |
9.1W/°C |
196 |
90 |
1000mm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cooling fin B |
A02B±0053±K304 |
10.1W/°C |
444 |
90 |
650mm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cooling fin C |
A02B±0053±K305 |
25.2W/°C |
560 |
90 |
970mm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heat pipe type |
A02B±0094±C901 |
9.0W/°C |
226 |
132 |
415mm |
|
heat exchanger |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heat exchanger for |
A02B±0060±K401 |
5.0W/°C |
590 |
86 |
480mm |
|
CRT/MDI unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.6.1
Cooling Fin A/B/C
The cooling fin is shown in Fig. 3.6.1 (a).
Viewed from cabinet mounting side |
Fig. 3.6.1(a) External view of cooling fin
10

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
It is installed in a cabinet made by the machine tool builder.
Cooling fin |
Cabinet |
|
|
Inside |
air |
flow |
|
Outside |
|
air flow |
|
Fig. 3.6.1(b) Internal view of cooling fin
The cooling fin can be installed in two ways, as shown in Fig.3.6.1(b). The following lists the general precautions to be observed when using the cooling fins :
DThe fans are not included with the cooling fin. They should be provided by the machine tool builder.
DBring in the outside air from the bottom and exhaust the hot air from the top.
DThe inside air may flow from top to bottom or bottom to top. However, generally decide the direction as follows :
-Bring in the air near high heat loss components.
-Exhaust the air toward the most important components to be cooled.
DFor the cooling fin to display the specified cooling capacity, the air inside the cooling fins must flow at a velocity of 2.5 m/sec or greater.
(velocity of air flow measurement)
Set the slit to the intake side and
 measure the velocity at the slit.
measure the velocity at the slit.
11

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
Generally, install the cooling fins to the door. But be sure that the door does not bend when installing the cooling fin. The cooling fins are equipped with packing.
|
|
196 |
|
100 |
136 |
|
70 |
|
4±M4 |
685 |
|
mounting |
|
screw for cooling fins
70
136
24.7
45
4±M4 5 mounting screw for fan mounting plate
PANEL CUT DRAWING
External dimensions
183
|
90 |
|
Terminal block for |
570 |
fan motor G±04 |
(Attached to the |
cooling fins. Its height is 20mm)
260
220
10
 24.7 5 150
24.7 5 150
|
168 |
|
|
C15 |
180188 |
|
|
|
570 |
|
770 |
260 |
|
70 |
|
|
Note1 |
|
164 |
45 |
|
Note2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note3 |
Fan mounting  plate
plate
1000
Fan motor
Door
Mounting metal for cooling fins (sheet metal about 3mm thick).
Cooling fins
Mounting metal for cooling fins
|
Mounting plate |
40 |
for fan motor |
|
Mounting diagram (example)
Fan motor, mounting plate for fan motor and mounting metal for cooling fins are not attached to the cooling fins.
So, prepare them at the machine tool builder. Use two fan motors with about 50W power. Weight : 6.5kg
Fig. 3.6.1(c) External dimension and mounting method of cooling fin A (02B±0053±K303)
12

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
External dimensions |
Mounting stud for cooling fins |
|
|
|
(2 studs are attached for the top and the bottom) |
|
|
444 |
90 |
|
|
Mounting plate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
72 |
|
for fan motor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
435 |
|
|
|
Fan motor |
Cooling fins |
650 |
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
||
|
|
124 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
116 |
72 |
|
25 |
|
|
Mounting |
|
|
14 |
|
|
6±6 dia |
|
|
|
350 |
1 |
432 |
6 |
Mounting hole |
Mounting plate |
||
hole for |
|
|||||||
|
370 |
02 10 |
|
|
|
|
||
fan motor |
1 |
4 |
6 |
|
|
|
for fan motor |
|
4±M4 |
20 |
418 |
|
Terminal block for fan motor G±04 |
r |
|
||
|
|
|
||||||
|
4 |
|
|
(Attached to the cooling fins. |
|
|
||
4±M4 |
|
370 |
|
|
||||
|
Its height is 20mm) |
|
Mounting diagram (example) |
|||||
(Mounting hole for |
350 |
|
|
|
||||
|
External shape |
|
|
|
|
|||
fan motor) |
|
|
Hole |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
116124 of cooling fins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
358 |
400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hole |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30060 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6±6 dia. hole or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
135 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
M5 stud bolt |
|
25 |
432 |
|
|
|
|
|
Stud hole |
5 dia |
(Make a hole 5 dia. for |
|
fan motor) |
|
l r i
Note1 Fan motor and mounting plate are not attached to the cooling fins. So, prepare them, at the machine tool builder.
Note2 Use four fan motors with about 20W power. Note3 Weight : 7.5kg
Fig. 3.6.1(d) External dimension and mounting method of cooling fin B (A02B±0053±K304)
13

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
External dimensions |
|
Mounting stud for cooling fins |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Attached to the cooling fins) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
560 |
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
Mounting plate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 for fan motor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
115 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
335 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
266 |
266 |
|
|
695 Terminal block |
|
315 |
Cooling fins |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
970 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
for fan motor |
|
Fan motor |
|
|
|
|
|
210 |
G±04 |
|
|
|
||||
6±M4 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
2878±6 dia. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
(Attached to the |
|
|
||||
Mounting |
|
233 |
37 |
|
|
|
cooling fins. Its |
|
610 mounting hole |
|
|
hole for fan |
213 |
6 |
35 |
10 height is 20mm) |
548 |
|
|||||
motor |
520 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
Mounting |
|
|
6 |
|
|
548 |
|
|
plat for |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
5M±4 |
|
|
|
|
440 |
|
|
|
fan motor |
||
(Mounting hole for |
|
|
|
|
|
Door |
40 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
fan motor) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
170 |
|
155 |
External shape of |
Mounting iagram ( xampl ) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
430 |
|
|
|||
|
|
335 |
|
|
|
5 DIA |
cooling fins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
(This hole |
|
|
|
|
||||
6±6 dia. hole or M5 |
315 |
combines |
775 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
mounting hole |
|
|
|
|||||||
stud bolt |
|
|
and stud hole.) |
|
|
|
|
||||
287 |
Note1 |
Fan motor and mounting plate for fan motor are |
60 |
|
not attached to the cooling fins. Prepare them at the |
514 |
|
machine tool builder. |
10 |
Note2 |
Use two fan motors with about 40W power. |
25 |
||
Panel cut drawing |
Note3 |
Weight : 13.5kg |
|
Fig. 3.6.1(e) External dimension and mounting method of cooling fin C (A02B±0053±K305)
14

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
3.6.2
Heat Exchanger for CRT/MDI Unit
External dimensions of |
External dimensions of |
finger guard |
external cooling fun |
|
|
+0.5 |
|
|
|
5"1 |
4.3±0 |
|
|
|
|
|
38+0.5 |
|
|
|
|
6+0.3 |
6+0.3 |
|
364 |
|
|
8±43 |
|
|
|
|
Hole |
|
|
|
+1.5 ±0.5 |
FLOW |
|
|
|
152.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
AIR |
|
|
|
|
Lot No. |
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
81 |
5 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Air inlet |
|
|
220 |
|
|
|
|
Packing |
|
|
|
|
480 |
|
Power terminal |
|
|
|
M4 screw |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200VAC 50Hz |
|
|
|
|
200/220VAC |
|
|
220 |
|
60Hz |
|
|
|
48W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
Air outlet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
378 |
|
|
|
6± 6 |
390 |
|
|
|
Connector for external cooling fan
119.5+0.5
104.8+0.3
+0.3 |
+0.5 |
104.8 |
119.5 |
Weight : 0.65kg
Cooling fin : About 6kg (Excluding attached parts)
Note ) External cooling fan and finger guard are attached beside cooling fin.
Fig. 3.6.2(a) External dimensions of external cooling fan and cooling unit for CRT/MDI (A02B±0060±K401 (Note))
15

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
220 20
480
Heat exchanger
|
Outside |
Inside |
|
|
Air outlet |
|
|
23 |
15=345 |
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
Air outlet |
|
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
|
|
Main body of |
|
10 |
(4) |
heat exchanger |
220 |
|
|
70 |
20 |
|
|
378 |
(1) |
390 |
Air inlet
(1)
(3) |
|
|
Prepare |
External cooling fan |
|
mounting |
||
(attached) |
||
screws and |
||
Finger guard |
||
mounting panel |
||
(attached) |
||
|
(1)Use M5 screws to mount the heat exchanger.
(2)Be careful with air flow when securing the external cooling fan.
(3)Prepare a mounting panel for external cooling fan and install the panel where it can be exchanged externally.
(4)Drill mounting holes for external cooling fan and air outlet on heat exchanger mounting panel.
Fig. 3.6.2(b) Mounting methods of heat exchanger for CRT/MDI
16

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
Horizontal type CRT/MDI only |
Horizontal type CRT/MDI and |
Vertical type CRT/MDI only |
|
machine operator's panel |
|||
|
|
Inside Outside
Side view
CRT/MDI |
Heat exchanger |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
370 |
|
Min |
|
|
370 |
Min |
|
|
370 |
Min |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Top view
Refer to these figures for allocation of CRT/MDI and heat exchanger
Fig. 3.6.2(c) Allocation of 14″ color CRT/MDI and heat exchanger
17

3. INSTALLATION B±62753EN/01
3.6.3
The Heat Pipe Type Heat Exchanger
3.6.3.1 |
The heat pipe type heat exchanger is used for cooling the airtight cabinet |
||||||
Installation |
of small sized electronic devices. It is a compact, lightweight, and |
||||||
heat±efficient unit. Because the fan is built±in, it is used simply by |
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
installing it, |
|
performing the ºpanel cut' operation. |
|
|||
Specifications |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Installation format |
Installation type in board |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fan |
|
|
Cooling ability (W/°C) |
9 (50Hz when operating) |
||
|
specifications |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Voltage (V) |
200VAC |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency (Hz) |
50 |
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rating current (A) |
0.28 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rating input (W) |
28 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weight (kg) |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Color |
|
|
|
Munsell signal N1.5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Order specifications Heat exchanger A02B±0094±C901
Remarks
A filter is installed on the outside air inhalation side.
The installation board thickness is the standard 1.6 t.
When a fan motor and filter are necessary for maintenance, prepare them separately.
Fan motor specifications A90L±0001±0219#A
Filter specifications A250±0689±X004
If the heat exchanger is installed near the CRT, screen distortion may occur due to magnetic flux leakage from the fan motor.
18

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
External dimensions
|
17.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power |
AIR |
|
|
|
|
source |
||
|
|
|
terminal M4 |
FLOW |
|
6±6 dia. |
190 |
|
|
Earth |
|
|
|
terminal |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M4 |
External |
|
|
|
|
|
|
415 |
|
|
|
|
fan unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
|
fan unit |
|
|
|
190 |
|
AIR |
|
|
|
|
FLOW |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
17.5 |
216 |
6 |
22.4 |
85 |
|
6 |
||||
|
|
226 |
|
|
22.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
(Installation board thickness) |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.5 |
|
|
|
199 |
|
|
|
19

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
Panel cut dimensions
190
190
180
HOLE |
6 |
175 |
3±5 dia. |
214
2.5
187.5
6±6 dia. or stud welder (M4)
20

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
Installation method |
Please install the heat exchanger by the following sequence: |
|
1 Take out the external fan unit from the heat exchanger main unit. (Fig. |
|
1) |
|
Detach the external fan unit installation screws A (2 pieces), take out |
|
the unit from the main unit by sliding it down, and detach the earth |
|
cable and the power cable to the fan. Also detach the installation screw |
|
B (1 piece). |
|
2 Install the heat exchanger main unit in the installation section which |
|
has been panel cut. (Fig. 2) |
|
When fastening down the heat exchanger main unit with the screws, |
|
first, temporarily secure the panel and the heat exchanger main unit |
|
with the installation screw B, which was taken out in 1). After that, |
|
secure the main unit by the installation screws. In this case, the |
|
external fan unit installation screw holes should be aligned with the |
|
main unit screw holes. (Please provide the installation screws for the |
|
heat exchanger main unit.) |
|
Because this product is composed of plastic, set the value shown |
|
below for the screw tightening torque. |
|
Heat exchanger main unit (M4 screw) : 11 kgf.cm |
|
External fan unit (M3 screw) : 5 kgf.cm |
|
3 Connect the power cable and the earth cable to the external fan unit (the |
|
unit detached in 1), and secure the installation screw A to the main unit |
|
from the outside. |
|
The installation is now complete. |
Heat exchanger main unit
Fan power cable (detach the connector)
External fan unit
Installation screw B (1) |
Installation screws A (2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earth cable (if the installation screw on the |
|
||
fan side is detached, it can be taken out.) |
Installation |
||
|
|
screw |
Installation screw B (1) |
|
|
|
Installation panel |
Fig. 1 Take out the external fan unit from the |
Fig. 2 |
Install the heat exchanger main unit and |
|
heat exchanger main unit |
|
|
the external fan unit |
21

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
3.7
ACTION AGAINST NOISE
The CNC has been steadily reduced in size using surface±mount and custom LSI technologies for electronic components. The CNC also is designed to be protected from external noise. However, it is difficult to measure the level and frequency of noise quantitatively, and noise has many uncertain factors. It is important to prevent both noise from being generated and generated noise from being introduced into the CNC. This precaution improves the stability of the CNC machine tool system.
The CNC component units are often installed close to the parts generating noise in the power magnetics cabinet. Possible noise sources into the CNC are capacitive coupling, electromagnetic induction, and ground loops.
When designing the power magnetics cabinet, guard against noise in the machine as described in the following section.
3.7.1
Separating Signal Lines
The cables used for the CNC machine tool are classified as listed in the following table:
Process the cables in each group as described in the action column.
Group |
Signal line |
Action |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Primary AC power line |
Bind the cables in group A sepa- |
|
|
|
rately (Note 1) from groups B |
|
|
Secondary AC power line |
||
|
and C, or cover group A with an |
||
|
|
||
|
AC/DC power lines (containing |
||
A |
electromagnetic shield (Note 2). |
||
the power lines for the servo and |
See Section 3.7.4 and connect |
||
|
spindle motors) |
||
|
spark killers or diodes with the |
||
|
|
||
|
AC/DC solenoid |
||
|
solenoid and relay. |
||
|
AC/DC relay |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DC solenoid (24VDC) |
Connect diodes with DC sole- |
|
|
|
noid and relay. |
|
|
|
Bind the cables in group B sepa- |
|
|
DC relay (24VDC) |
||
|
|
rately from group A, or cover |
|
|
|
group B with an electromagnetic |
|
B |
DI/DO cable between the CNC |
||
shield. |
|||
and power magnetics cabinet |
|||
|
|||
|
Separate group B as far from |
||
|
|
||
|
|
Group C as possible. |
|
|
DI/DO cable between the CNC |
||
|
It is more desirable to cover |
||
|
and machine |
||
|
|
group B with the shield. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cable between the CNC and ser- |
Bind the cables in group C sepa- |
|
|
vo amplifier |
rately from group A, or cover |
|
|
|
group C with an electromagnetic |
|
|
Cable for position and velocity |
||
|
shield. |
||
|
feedback |
||
|
Separate group C as far from |
||
|
|
||
|
Cable between the CNC and |
||
|
Group B as possible. |
||
|
spindle amplifier |
||
|
Be sure to perform shield pro- |
||
|
|
||
|
Cable for the position coder |
||
|
cessing in Section 3.7.5. |
||
|
|
||
C |
Cable for the manual pulse gen- |
||
|
|||
erator |
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Cable between the CNC and the |
|
|
|
CRT/MDI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RS±232±C and RS±422 interface |
|
|
|
cable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cable for the battery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other cables to be covered with |
|
|
|
the shield |
|
|
|
|
|
22

B±62753EN/01 |
3. INSTALLATION |
|
|
Notes
1.The groups must be 10 cm or more apart from one another when binding the cables in each group.
2.The electromagnetic shield refers to shielding between groups with grounded steel plates.
|
Cabinet |
|
|
Spindle |
Servo |
Control |
|
amp. |
amp. |
unit |
|
|
|
|
Cable of group B, C |
|
|
|
Duct |
|
|
|
To operator's |
|
|
|
panel, |
|
|
|
motor, etc. |
|
Cable of group A |
|
Section |
|
|
Group A |
Group B, C |
|
|
|
Cover |
23

3. INSTALLATION |
B±62753EN/01 |
|
|
3.7.2 |
The following ground systems are provided for the CNC machine tool: |
|
Ground |
|
Signal ground system (SG) |
|
|
The signal ground (SG) supplies the reference voltage (0V) of the |
|
|
electrical signal system. |
|
|
Frame ground system (FG) |
|
|
The frame ground system (FG) is used for safety, and suppressing |
|
|
external and internal noises. In the frame ground system, the frames, |
|
|
cases of the units, panels, and shields for the interface cables between |
|
|
the units are connected. |
|
|
System ground system |
|
|
The system ground system is used to connect the frame ground |
|
|
systems connected between devices or units with the ground. |
Power |
Servo |
CNC |
magnet- |
amplifier |
control |
ics |
|
unit |
unit |
|
|
Power |
|
|
magnetics |
|
|
cabinet |
|
|
Signal ground system
Frame ground system
System ground system
Operator's panel
Machine tool
Distribution board
Notes on connecting the ground systems
Connect the signal ground with the frame ground (FG) at only one place in the CNC control unit.
The grounding resistance of the system ground shall be 100 ohms or less (class 3 grounding).
The system ground cable must have enough cross±sectional area to safely carry the accidental current flow into the system ground when an accident such as a short circuit occurs.
(Generally, it must have the cross±sectional area of the AC power cable or more.)
Use the cable containing the AC power wire and the system ground wire so that power is supplied with the ground wire connected.
24
 Loading...
Loading...