MOTOROLA LM2575TV-ADJ, LM2575TV-3.3, LM2575TV-015, LM2575TV-012, LM2575T-ADJ Datasheet
...
|
|
|
|
|
|
Order this document by LM2575/D |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
LM2575 |
||
Easy |
Switcher |
1.0 |
A |
|
|
|
||
Step-Down |
Voltage |
Regulator |
EASY SWITCHER |
|||||
The LM2575 series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits ideally |
1.0 A STEP±DOWN |
|||||||
VOLTAGE REGULATOR |
||||||||
suited for easy and convenient design of a step±down switching regulator |
||||||||
(buck converter). All circuits of this series are capable of driving a 1.0 A load |
|
SEMICONDUCTOR |
||||||
with excellent line and load regulation. These devices are available in fixed |
|
|||||||
output voltages of 3.3 V, 5.0 V, 12 V, 15 V, and an adjustable output version. |
|
TECHNICAL DATA |
||||||
These regulators were designed to minimize the number of external |
|
|
|
|||||
components to simplify the power supply design. Standard series of |
|
|
|
|||||
inductors optimised for use with the LM2575 are offered by several different |
|
|
|
|||||
inductor manufacturers. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Since the LM2575 converter is a switch±mode power supply, its efficiency |
T SUFFIX |
|
||||||
is significantly |
higher in comparison |
with popular |
three±terminal linear |
|
||||
PLASTIC PACKAGE |
|
|||||||
regulators, especially with higher input voltages. In many cases, the power |
|
|||||||
CASE 314D |
1 |
|||||||
dissipated by the LM2575 regulator is so low, that no heatsink is required or |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
its size could be reduced dramatically. |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
The LM2575 features include a guaranteed ±4% tolerance on output |
Pin 1. |
Vin |
|
|||||
voltage within specified input voltages and output load conditions, and ±10% |
2. |
Output |
|
|||||
on the oscillator frequency (±2% over 0°C to 125°C). External shutdown is |
3. |
Ground |
|
|||||
4. |
Feedback |
|
||||||
included, featuring 80 μA typical standby current. The output switch includes |
|
|||||||
5. ON/OFF |
|
|||||||
cycle±by±cycle current limiting, as well as thermal shutdown for full |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
||||||
protection under fault conditions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Features |
|
|
|
|
TV SUFFIX |
|
||
• 3.3 V, 5.0 V, 12 V, 15 V, and Adjustable Output Versions |
1 |
|||||||
PLASTIC PACKAGE |
|
|||||||
• Adjustable Version Output Voltage Range of 1.23 V to 37 V ±4% |
CASE 314B |
5 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||
Maximum Over Line and Load Conditions |
|
Heatsink surface |
|
|||||
• Guaranteed 1.0 A Output Current |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
connected to Pin 3. |
|
|||||
•Wide Input Voltage Range: 4.75 V to 40 V
•Requires Only 4 External Components
• 52 kHz Fixed Frequency Internal Oscillator |
D2T SUFFIX |
|
||
PLASTIC PACKAGE |
|
|||
• TTL Shutdown Capability, Low Power Standby Mode |
1 |
|||
CASE 936A |
||||
• High Efficiency |
(D2PAK) |
5 |
||
|
|
|
||
• Uses Readily Available Standard Inductors |
|
|
|
|
• Thermal Shutdown and Current Limit Protection |
Heatsink surface (shown as terminal 6 in case outline |
|||
Applications |
drawing) is connected to Pin 3. |
|||
|
|
|
||
• Simple and High±Efficiency Step±Down (Buck) Regulators |
DEVICE TYPE/NOMINAL OUTPUT VOLTAGE |
|||
• Efficient Pre±Regulator for Linear Regulators |
||||
LM2575±3.3 |
|
3.3 V |
||
• On±Card Switching Regulators |
|
|||
LM2575±5 |
|
5.0 V |
||
• Positive to Negative Converters (Buck±Boost) |
LM2575±12 |
|
12 V |
|
• Negative Step±Up Converters |
LM2575±15 |
|
15 V |
|
LM2575±Adj |
|
1.23 V to 37 V |
||
• Power Supply for Battery Chargers |
|
|||
|
|
|
||
|
ORDERING INFORMATION |
|||
|
|
Operating |
|
|
|
Device |
Temperature Range Package |
||
|
LM2575T±** |
|
Straight Lead |
|
|
LM2575TV±** |
TJ = ±40° to +125°C Vertical Mount |
||
|
LM2575D2T±** |
|
Surface Mount |
|
|
** = Voltage Option, ie. 3.3, 5.0, 12, 15 V and |
|||
|
Adjustable Output. |
|
||
|
Motorola, Inc. 1999 |
Rev 2, 07/1999 |
||
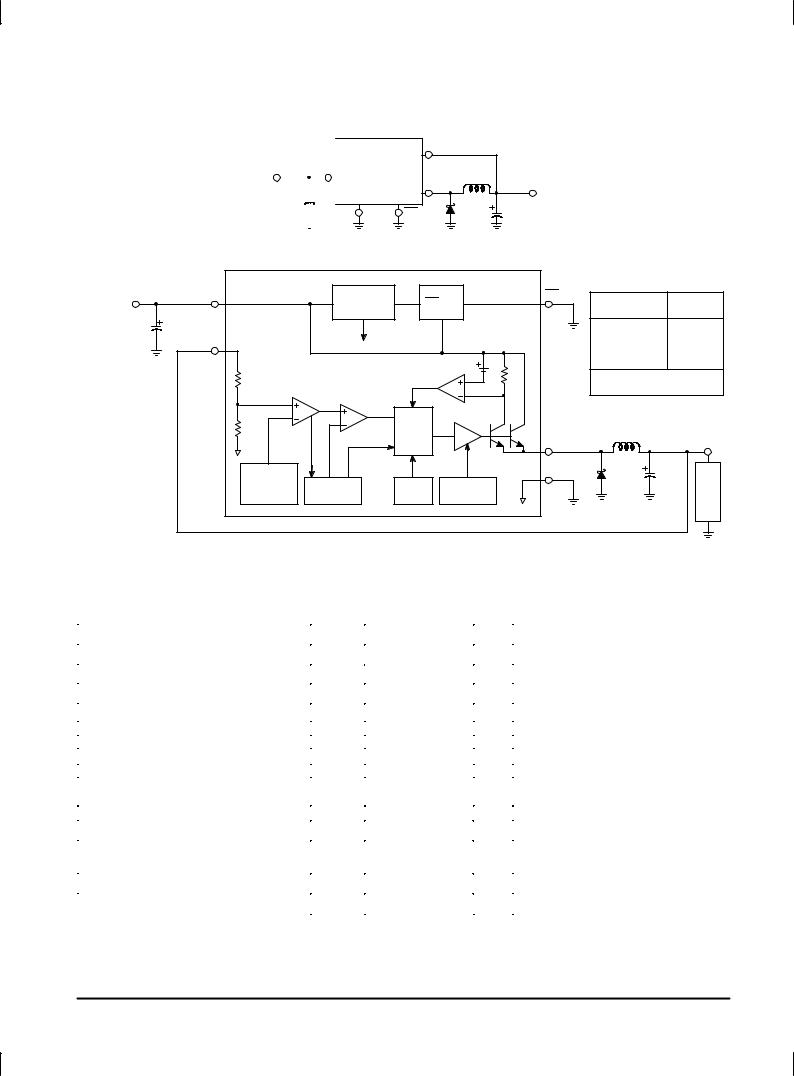
LM2575
Figure 1. Block Diagram and Typical Application
Typical Application (Fixed Output Voltage Versions)
7.0 V ± 40 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+Vin |
||
Unregulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DC Input |
|
1 |
|||||||
|
|
Cin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
100 μF |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback |
|
|
|
LM2575 |
4 |
L1 |
|
|
|
|
330 μH |
|
||
|
|
|
Output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
D1 |
Cout |
3 |
Gnd |
5 |
ON/OFF |
1N5819 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
330 μF |
5.0 V Regulated
Output 1.0 A Load
Representative Block Diagram and Typical Application
Unregulated |
+Vin |
|
3.1 V Internal |
ON/OFF |
ON/OFF |
Output |
|
R2 |
|
DC Input |
1 |
|
Regulator |
|
Voltage Versions |
(Ω) |
|||
|
|
|
5 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.7 k |
||
|
Cin |
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 V |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 V |
|
3.1 k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 V |
|
8.84 k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Feedback |
|
|
Current |
|
|
15 V |
|
11.3 k |
|
|
|
|
|
|
For adjustable version |
|
||
|
R2 |
Fixed Gain |
|
Limit |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Error Amplifier Comparator |
|
|
|
R1 = open, R2 = 0 Ω |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
R1 |
|
|
|
Driver |
|
|
|
Regulated |
|
Freq |
|
Latch |
|
|
|
|
Output |
|
|
1.0 k |
|
|
|
L1 |
|
|||
|
Shift |
|
|
|
Output |
|
Vout |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
18 kHz |
|
|
1.0 Amp |
2 |
|
|
|
|
1.235 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
52 kHz |
|
Switch |
Gnd |
D1 |
Cout |
|
||
|
Band±Gap |
Reset |
Thermal |
3 |
|
|
Load |
||
|
Reference |
Oscillator |
Shutdown |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
This device contains 162 active transistors.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur.)
|
|
Rating |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Supply Voltage |
Vin |
45 |
V |
|
|
|
|
± |
±0.3 V ≤ V ≤ +Vin |
V |
|
ON/OFF Pin Input Voltage |
||||
|
Output Voltage to Ground (Steady±State) |
± |
±1.0 |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Power Dissipation |
|
|
|
|
|
Case 314B and 314D (TO±220, 5±Lead) |
PD |
Internally Limited |
W |
|
|
Thermal Resistance, Junction±to±Ambient |
RθJA |
65 |
°C/W |
|
|
Thermal Resistance, Junction±to±Case |
RθJC |
5.0 |
°C/W |
|
|
Case 936A (D2PAK) |
PD |
Internally Limited |
W |
|
|
Thermal Resistance, Junction±to±Ambient |
RθJA |
70 |
°C/W |
|
|
(Figure 34) |
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal Resistance, Junction±to±Case |
RθJC |
5.0 |
°C/W |
|
|
Storage Temperature Range |
Tstg |
±65 to +150 |
°C |
|
|
Minimum ESD Rating (Human Body Model: C |
± |
3.0 |
kV |
|
|
= 100 pF, R = 1.5 kΩ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 s) |
± |
260 |
°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum Junction Temperature |
TJ |
150 |
°C |
|
NOTE: ESD data available upon request.
2 |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |

LM2575
OPERATING RATINGS (Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.)
Rating |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
Operating Junction Temperature Range |
TJ |
±40 to +125 |
°C |
Supply Voltage |
Vin |
40 |
V |
SYSTEM PARAMETERS ([Note 1] Test Circuit Figure 14)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Unless otherwise specified, Vin = 12 V for the 3.3 V, 5.0 V, and Adjustable version, Vin = 25 V for
the 12 V version, and Vin = 30 V for the 15 V version. ILoad = 200 mA. For typical values TJ = 25°C, for min/max values TJ is the operating junction temperature range that applies [Note 2], unless otherwise noted.)
Characteristics |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LM2575±3.3 ([Note 1] Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage (Vin = 12 V, ILoad = 0.2 A, TJ = 25°C) |
Vout |
3.234 |
3.3 |
3.366 |
V |
Output Voltage (4.75 V ≤ Vin ≤ 40 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILoad ≤ 1.0 A) |
Vout |
|
|
|
V |
TJ = 25°C |
|
3.168 |
3.3 |
3.432 |
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
3.135 |
± |
3.465 |
|
Efficiency (Vin = 12 V, ILoad = 1.0 A) |
η |
± |
75 |
± |
% |
LM2575±5 ([Note 1] Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage (Vin = 12 V, ILoad = 0.2 A, TJ = 25°C) |
Vout |
4.9 |
5.0 |
5.1 |
V |
Output Voltage (8.0 V ≤ Vin ≤ 40 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILoad ≤ 1.0 A) |
Vout |
|
|
|
V |
TJ = 25°C |
|
4.8 |
5.0 |
5.2 |
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
4.75 |
± |
5.25 |
|
Efficiency (Vin = 12 V, ILoad = 1.0 A) |
η |
± |
77 |
± |
% |
LM2575±12 ([Note 1] Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage (Vin = 25 V, ILoad = 0.2 A, TJ = 25°C) |
Vout |
11.76 |
12 |
12.24 |
V |
Output Voltage (15 V ≤ Vin ≤ 40 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILoad ≤ 1.0 A) |
Vout |
|
|
|
V |
TJ = 25°C |
|
11.52 |
12 |
12.48 |
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
11.4 |
± |
12.6 |
|
Efficiency (Vin = 15V, ILoad = 1.0 A) |
η |
± |
88 |
± |
% |
LM2575±15 ([Note 1] Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Output Voltage (Vin = 30 V, ILoad = 0.2 A, TJ = 25°C) |
Vout |
14.7 |
15 |
15.3 |
V |
Output Voltage (18 V ≤ Vin ≤ 40 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILoad ≤ 1.0 A) |
Vout |
|
|
|
V |
TJ = 25°C |
|
14.4 |
15 |
15.6 |
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
14.25 |
± |
15.75 |
|
Efficiency (Vin = 18 V, ILoad = 1.0 A) |
η |
± |
88 |
± |
% |
LM2575 ADJUSTABLE VERSION ([Note 1] Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback Voltage (Vin = 12 V, ILoad = 0.2 A, Vout = 5.0 V, TJ = 25°C) |
VFB |
1.217 |
1.23 |
1.243 |
V |
Feedback Voltage (8.0 V ≤ Vin ≤ 40 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILoad ≤ 1.0 A, Vout = 5.0 V) |
VFB |
|
|
|
V |
TJ = 25°C |
|
1.193 |
1.23 |
1.267 |
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
1.18 |
± |
1.28 |
|
Efficiency (Vin = 12 V, ILoad = 1.0 A, Vout = 5.0 V) |
η |
± |
77 |
± |
% |
NOTES: 1. External components such as the catch diode, inductor, input and output capacitors can affect switching regulator system performance. When the LM2575 is used as shown in the Figure 14 test circuit, system performance will be as shown in system parameters section.
2. Tested junction temperature range for the LM2575: |
Tlow = ±40°C |
Thigh = +125°C |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
3 |
|

LM2575
DEVICE PARAMETERS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Unless otherwise specified, Vin = 12 V for the 3.3 V, 5.0 V, and Adjustable version, Vin = 25 V for
the 12 V version, and Vin = 30 V for the 15 V version. ILoad = 200 mA. For typical values TJ = 25°C, for min/max values TJ is the operating junction temperature range that applies [Note 2], unless otherwise noted.)
|
|
|
|
Characteristics |
Symbol |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALL OUTPUT VOLTAGE VERSIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback Bias Current (Vout = 5.0 V [Adjustable Version Only]) |
Ib |
|
|
|
nA |
|||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
± |
25 |
100 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
± |
± |
200 |
|
||||
|
Oscillator Frequency [Note 3] |
fosc |
|
|
|
kHz |
|||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
± |
52 |
± |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = 0 to +125°C |
|
47 |
± |
58 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
42 |
± |
63 |
|
||||
|
Saturation Voltage (Iout = 1.0 A [Note 4]) |
Vsat |
|
|
|
V |
|||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
± |
1.0 |
1.2 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
± |
± |
1.3 |
|
||||
|
Max Duty Cycle (ªonº) [Note 5] |
DC |
94 |
98 |
± |
% |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current Limit (Peak Current [Notes 4 and 3]) |
ICL |
|
|
|
A |
|||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
1.7 |
2.3 |
3.0 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
1.4 |
± |
3.2 |
|
||||
|
Output Leakage Current [Notes 6 and 7], TJ = 25°C |
IL |
|
|
|
mA |
|||||
|
|
Output = 0 V |
|
± |
0.8 |
2.0 |
|
||||
|
|
Output = ±1.0 V |
|
± |
6.0 |
20 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quiescent Current [Note 6] |
IQ |
|
|
|
mA |
|||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
± |
5.0 |
9.0 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
± |
± |
11 |
|
||||
|
Standby Quiescent Current |
|
|
Istby |
|
|
|
μA |
|||
(ON/OFF Pin = 5.0 V (ªoffº)) |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
± |
80 |
200 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
± |
± |
400 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V |
|
ON/OFF Pin Logic Input Level (Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Vout = 0 V |
VIH |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
2.2 |
1.4 |
± |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
2.4 |
± |
± |
|
||||
|
|
Vout = Nominal Output Voltage |
VIL |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
TJ = 25°C |
|
± |
1.2 |
1.0 |
|
||||
|
|
TJ = ±40 to +125°C |
|
± |
± |
0.8 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
μA |
|
ON/OFF Pin Input Current (Test Circuit Figure 14) |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
I |
± |
15 |
30 |
|
|||
|
|
ON/OFF Pin = 5.0 V (ªoffº), T = 25°C |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
J |
IH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ON/OFF Pin = 0 V (ªonº), T = 25°C |
I |
± |
0 |
5.0 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
J |
IL |
|
|
|
|
||
NOTES: 3. The oscillator frequency reduces to approximately 18 kHz in the event of an output short or an overload which causes the regulated output voltage to drop approximately 40% from the nominal output voltage. This self protection feature lowers the average dissipation of the IC by lowering the minimum duty cycle from 5% down to approximately 2%.
4.Output (Pin 2) sourcing current. No diode, inductor or capacitor connected to output pin.
5.Feedback (Pin 4) removed from output and connected to 0 V.
6.Feedback (Pin 4) removed from output and connected to +12 V for the Adjustable, 3.3 V, and 5.0 V versions, and +25 V for the 12 V and 15 V versions, to force the output transistor ªoffº.
7.Vin = 40 V.
4 |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |

LM2575
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS (Circuit of Figure 14)
Figure 2. Normalized Output Voltage |
Figure 3. Line Regulation |
Vout, OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHANGE (%)
0.6
Vin = 20 V
ILoad = 200 mA 0.4 Normalized at
TJ = 25°C
0.2
0
±0.2
±0.4
±0.6 |
±25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
±50 |
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C)
Vout, OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHANGE (%)
1.0
ILoad = 200 mA
0.8TJ = 25°C
0.63.3 V, 5.0 V and Adj
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
12 V and 15 V |
|
|
|
±0.20 |
5.0 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
|
|
|
Vin, INPUT VOLTAGE (V) |
|
|
|
||
Vsat , SATURATION VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 4. Switch Saturation Voltage
1.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
125°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
SWITCH CURRENT (A)
IO, OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
Figure 5. Current Limit
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
Vin = 25 V
0
±50 |
±25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
|
|
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C) |
|
|
|||
Figure 6. Dropout Voltage |
Figure 7. Quiescent Current |
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DIFFERENTIAL(V) |
1.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
Vout = 5% |
CURRENTQUIESCENT(mA) |
ILoad = 1.0 A |
|
|
|
Rind = 0.2 Ω |
||||
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INPUT±OUTPUT |
1.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
ILoad = 200 mA |
|
|
|
|
I |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
±25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
|
±50 |
|||||||
|
|
|
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C) |
|
||||
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vout = |
5.0 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measured at |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ground Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
° |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ = 25 C |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ILoad |
= 1.0 A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ILoad |
= 200 mA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
8.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
|||||||||
0 |
|||||||||||||||||
Vin, INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
5 |
|
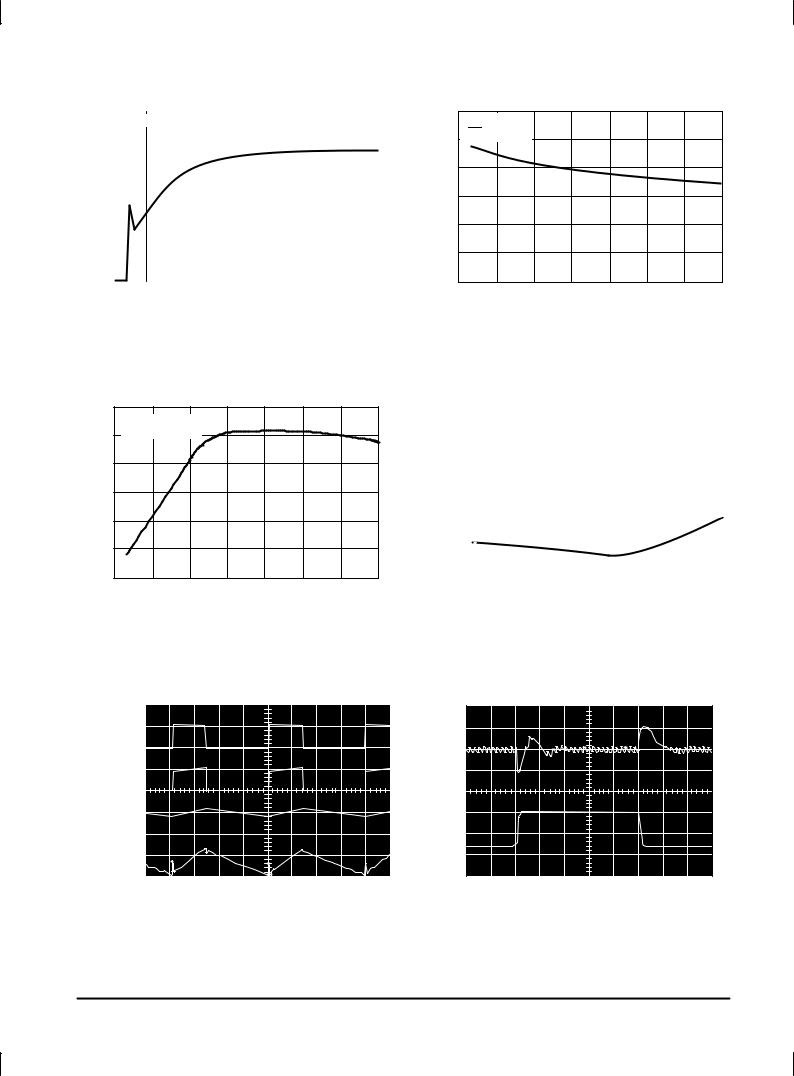
LM2575
Istby, STANDBY QUIESCENT CURRENT (μ A)
|
|
Figure 8. Standby Quiescent Current |
|
|
|||||||||||||
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TJ = 25 |
°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
5.0 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
|||||||||
Vin, INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Istby, STANDBY QUIESCENT CURRENT (μA)
Figure 9. Standby Quiescent Current
120
Vin = 12 V
VON/OFF = 5.0 V
100
80
60
40
20
0 |
±25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
±50 |
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 10. Oscillator Frequency
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(%) |
|
Vin = 12 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
Normalized at 25°C |
|
|
|
|
|
||
FREQUENCY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±4.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NORMALIZED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±8.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±10 |
±25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
|
±50 |
|||||||
|
|
|
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C) |
|
|
|||
Figure 12. Switching Waveforms
OUTPUT |
10 V |
VOLTAGE |
0 |
(PIN 2) |
|
OUTPUT |
1.0 A |
CURRENT |
|
(PIN 2) |
0 |
INDUCTOR 1.0 A |
|
CURRENT 0.5 A |
|
OUTPUT |
20 mV |
RIPPLE |
/DIV |
VOLTAGE |
|
|
5.0 μs/DIV |
Figure 11. Feedback Pin Current
(nA) |
40 |
Adjustable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Version |
Only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
CURRENTPIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FEEDBACK, |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
FB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±25 |
0 |
25 |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
||||||||
|
±50 |
|||||||||||||||
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUTPUTVOLTAGE |
Figure 13. Load Transient Response |
|
100 |
||
0 |
||
(mV)CHANGE |
||
, |
±100 |
|
out |
||
|
||
V |
|
|
(A) |
|
|
CURRENT |
1.0 |
|
0.5 |
||
|
||
, LOAD |
0 |
|
|
||
Load |
100 μs/DIV |
|
I |
||
|
6 |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
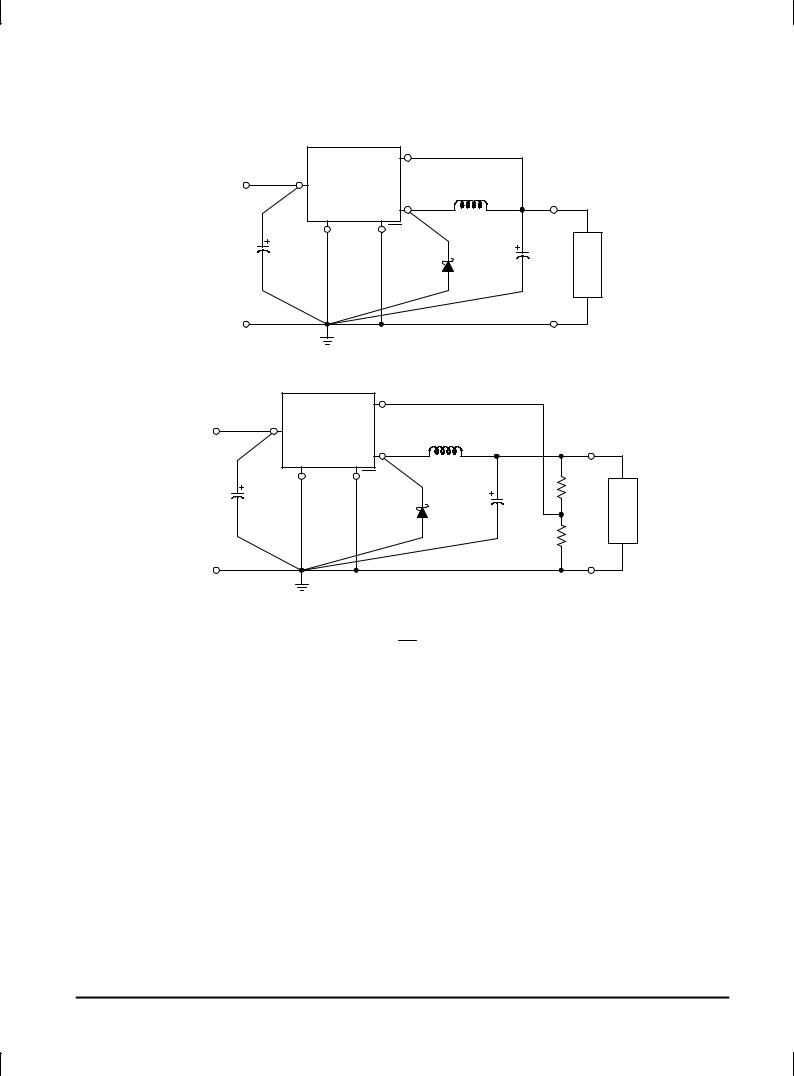
LM2575
Figure 14. Typical Test Circuit
5.0 Output Voltage Versions
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback |
|
|
|
|
|
Vin |
|
|
4 |
|
|
Vout |
|
|
LM2575±5 |
L1 |
|
|
|||
+ |
|
1 |
330 μH |
|
|
Regulated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
|
|
Output |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
Vin |
|
3 |
Gnd |
5 |
ON/OFF |
|
|
|
Unregulated |
Cin |
μF/50 V |
|
|
D1 |
Cout |
|
|
DC Input |
100 |
|
|
330 |
μF |
Load |
||
8.0 V ± 40 V |
|
|
|
|
1N5819 |
/16 V |
||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjustable Output Voltage Versions
|
|
|
|
|
Feedback |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Vin |
LM2575 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vout |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L1 |
|
||||
|
+ |
1 |
Adjustable |
|
|
|
|
330 μH |
|
Regulated |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
|
|
|
Output |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unregulated |
|
3 |
Gnd |
5 |
ON/OFF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cout |
R2 |
|
DC Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
100 |
μF/50 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D1 |
330 μF |
|
|
8.0 V ± 40 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Load |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1N5819 |
/16 V |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1 |
|
± |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vout + V |
ref |
1 ) |
R2 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
R1 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
R2 + R1 |
Vout |
± 1 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Vref |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Where Vref = 1.23 V, R1 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
between 1.0 kΩ and 5.0 kΩ |
|
|
|||||
PCB LAYOUT GUIDELINES
As in any switching regulator, the layout of the printed circuit board is very important. Rapidly switching currents associated with wiring inductance, stray capacitance and parasitic inductance of the printed circuit board traces can generate voltage transients which can generate electromagnetic interferences (EMI) and affect the desired operation. As indicated in the Figure 14, to minimize inductance and ground loops, the length of the leads indicated by heavy lines should be kept as short as possible. For best results, single±point grounding (as indicated) or ground plane construction should be used.
On the other hand, the PCB area connected to the Pin 2 (emitter of the internal switch) of the LM2575 should be kept to a minimum in order to minimize coupling to sensitive circuitry.
Another sensitive part of the circuit is the feedback. It is important to keep the sensitive feedback wiring short. To assure this, physically locate the programming resistors near to the regulator, when using the adjustable version of the LM2575 regulator.
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
7 |
|

|
|
|
|
LM2575 |
|
|
|
|
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION |
|
|
|
|
|
Pin |
|
|
Symbol |
Description (Refer to Figure 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Vin |
This pin is the positive input supply for the LM2575 step±down switching regulator. In order to minimize |
||
|
|
|
|
voltage transients and to supply the switching currents needed by the regulator, a suitable input bypass |
|
|
|
|
capacitor must be present (Cin in Figure 1). |
2 |
Output |
This is the emitter of the internal switch. The saturation voltage Vsat of this output switch is typically 1.0 V. |
||
|
|
|
|
It should be kept in mind that the PCB area connected to this pin should be kept to a minimum in order to |
|
|
|
|
minimize coupling to sensitive circuitry. |
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Gnd |
Circuit ground pin. See the information about the printed circuit board layout. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Feedback |
This pin senses regulated output voltage to complete the feedback loop. The signal is divided by the |
||
|
|
|
|
internal resistor divider network R2, R1 and applied to the non±inverting input of the internal error amplifier. |
|
|
|
|
In the Adjustable version of the LM2575 switching regulator this pin is the direct input of the error amplifier |
|
|
|
|
and the resistor network R2, R1 is connected externally to allow programming of the output voltage. |
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
It allows the switching regulator circuit to be shut down using logic level signals, thus dropping the total |
ON/OFF |
||||
|
|
|
|
input supply current to approximately 80 μA. The input threshold voltage is typically 1.4 V. Applying a |
|
|
|
|
voltage above this value (up to +Vin) shuts the regulator off. If the voltage applied to this pin is lower than |
|
|
|
|
1.4 V or if this pin is connected to ground, the regulator will be in the ªonº condition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESIGN PROCEDURE |
Buck Converter Basics
The LM2575 is a ªBuckº or Step±Down Converter which is the most elementary forward±mode converter. Its basic schematic can be seen in Figure 15.
The operation of this regulator topology has two distinct time periods. The first one occurs when the series switch is on, the input voltage is connected to the input of the inductor.
The output of the inductor is the output voltage, and the rectifier (or catch diode) is reverse biased. During this period, since there is a constant voltage source connected across the inductor, the inductor current begins to linearly ramp upwards, as described by the following equation:
IL(on) + |
Vin ± Vout ton |
|
L |
|
|
During this ªonº period, energy is stored within the core material in the form of magnetic flux. If the inductor is properly designed, there is sufficient energy stored to carry the requirements of the load during the ªoffº period.
IL(off) + |
Vout ± VD toff |
L |
This period ends when the power switch is once again turned on. Regulation of the converter is accomplished by varying the duty cycle of the power switch. It is possible to describe the duty cycle as follows:
d + tonT , where T is the period of switching.
For the buck converter with ideal components, the duty cycle can also be described as:
d + Vout Vin
Figure 16 shows the buck converter idealized waveforms of the catch diode voltage and the inductor current.
Figure 16. Buck Converter Idealized Waveforms
Von(SW)
|
Figure 15. Basic Buck Converter |
|
|
|
Power |
L |
|
|
Switch |
Vout |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
V |
D1 |
Cout |
RLoad |
in |
|
|
|
The next period is the ªoffº period of the power switch. When the power switch turns off, the voltage across the inductor reverses its polarity and is clamped at one diode voltage drop below ground by catch dioded. Current now flows through the catch diode thus maintaining the load current loop. This removes the stored energy from the inductor. The inductor current during this time is:
Voltage |
Power |
|
Power |
Power |
|
Switch |
Power |
Switch |
Switch |
||
Off |
Off |
On |
|||
Diode |
|||||
|
Switch |
|
|
||
|
On |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Time |
Current |
VD(FWD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ipk |
ILoad(AV) |
||
Inductor |
|
|
|
||
Imin |
Power |
|
Power |
||
Diode |
Switch |
Diode |
Switch |
||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Time |
8 |
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |

LM2575
Procedure (Fixed Output Voltage Version) In order to simplify the switching regulator design, a step±by±step design procedure and example is provided.
|
Procedure |
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Given Parameters: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Given Parameters: |
|||
|
Vout = Regulated Output Voltage (3.3 V, 5.0 V, 12 V or 15 V) |
|
Vout = 5.0 V |
||||||||||
|
Vin(max) = Maximum DC Input Voltage |
|
|
|
Vin(max) = 20 V |
||||||||
|
ILoad(max) = Maximum Load Current |
|
|
|
ILoad(max) = 0.8 A |
||||||||
1. |
Controller IC Selection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Controller IC Selection |
|
|
According to the required input voltage, output voltage and |
|
According to the required input voltage, output voltage, current |
||||||||||
|
current, select the appropriate type of the controller IC output |
|
polarity and current value, use the LM2575±5 controller IC |
||||||||||
|
voltage version. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2. Input Capacitor Selection (Cin) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Input Capacitor Selection (Cin) |
|||||
|
To prevent large voltage transients from appearing at the input |
|
A 47 μF, 25 V aluminium electrolytic capacitor located near to |
||||||||||
|
and for stable operation of the converter, an aluminium or |
|
the input and ground pins provides sufficient bypassing. |
||||||||||
|
tantalum electrolytic bypass capacitor is needed between the |
|
|
||||||||||
|
input pin +Vin and ground pin Gnd. This capacitor should be |
|
|
||||||||||
|
located close to the IC using short leads. This capacitor should |
|
|
||||||||||
|
have a low ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) value. |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Catch Diode Selection (D1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Catch Diode Selection (D1) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A. For this example the current rating of the diode is 1.0 A. |
|||
|
A. Since the diode maximum peak current exceeds the |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
regulator maximum load current the catch diode current |
|
|
||||||||||
|
rating must be at least 1.2 times greater than the maximum |
|
|
||||||||||
|
load current. For a robust design the diode should have a |
|
|
||||||||||
|
current rating equal to the maximum current limit of the |
|
|
||||||||||
|
LM2575 to be able to withstand a continuous output short |
|
B. Use a 30 V 1N5818 Schottky diode, or any of the suggested |
||||||||||
|
B. The reverse voltage rating of the diode should be at least |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
fast recovery diodes shown in the Table 4. |
|||||||||||
|
1.25 times the maximum input voltage. |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Inductor Selection (L1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
Inductor Selection (L1) |
|
|
A. According to the required working conditions, select the |
|
A. Use the inductor selection guide shown in Figures 17 to 21. |
||||||||||
|
correct inductor value using the selection guide from |
|
|
||||||||||
|
Figures 17 to 21. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B. From the appropriate inductor selection guide, identify the |
|
B. From the selection guide, the inductance area intersected |
||||||||||
|
inductance region intersected by the Maximum Input |
|
by the 20 V line and 0.8 A line is L330. |
||||||||||
|
Voltage line and the Maximum Load Current line. Each |
|
|
||||||||||
|
region is identified by an inductance value and an inductor |
|
|
||||||||||
|
code. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C. Select an appropriate inductor from the several different |
|
C. Inductor value required is 330 μH. From the Table 1 or |
||||||||||
|
manufacturers part numbers listed in Table 1 or Table 2. |
|
Table 2, choose an inductor from any of the listed |
||||||||||
|
When using Table 2 for selecting the right inductor the |
|
manufacturers. |
||||||||||
|
designer must realize that the inductor current rating must |
|
|
||||||||||
|
be higher than the maximum peak current flowing through |
|
|
||||||||||
|
the inductor. This maximum peak current can be calculated |
|
|
||||||||||
|
as follows: |
|
|
|
V ±V |
ton |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Ip(max) + ILoad(max) ) |
|
|
in |
out |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
2L |
|
|
|
||||||
|
where ton is the ªonº time of the power switch and |
|
|
||||||||||
|
ton + |
Vout |
x |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
V |
in |
|
|
f |
osc |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
For additional information about the inductor, see the |
|
|
||||||||||
|
inductor section in the ªExternal Componentsº section of |
|
|
||||||||||
|
this data sheet. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA |
9 |
|
 Loading...
Loading...