fanuc 0i-D Operators Manual
FANUC FAST Ethernet
FANUC FAST Data Server
For FANUC Series 0*-MODEL D
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
B-64414EN/01

•No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form.
•All specifications and designs are subject to change without notice.
The products in this manual are controlled based on Japan’s “Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law”. The export from Japan may be subject to an export license by the government of Japan.
Further, re-export to another country may be subject to the license of the government of the country from where the product is re-exported. Furthermore, the product may also be controlled by re-export regulations of the United States government.
Should you wish to export or re-export these products, please contact FANUC for advice.
In this manual we have tried as much as possible to describe all the various matters. However, we cannot describe all the matters which must not be done, or which cannot be done, because there are so many possibilities.
Therefore, matters which are not especially described as possible in this manual should be regarded as ”impossible”.
This manual contains the program names or device names of other companies, some of which are registered trademarks of respective owners. However, these names are not followed by or in the main body.

B-64414EN/01 |
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS |
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This section describes the safety precautions related to the use of CNC units, to ensure safe operation of machines fitted with FANUC CNC units. Read this section carefully before attempting to use any function described in this manual.
Users should also read the relevant descriptions in the User’s Manual of the CNC to become fully familiar with the functions to be used.
Contents |
|
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE ................ |
s-2 |
GENERAL WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS.................................... |
s-3 |
s-1

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS |
B-64414EN/01 |
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE
This manual includes safety precautions for protecting the user and preventing damage to the machine. Precautions are classified into Warnings and Cautions according to their bearing on safety. Also, supplementary information is described as Notes. Read the Warnings, Cautions, and Notes thoroughly before attempting to use the machine.
 WARNING
WARNING
Applied when there is a danger of the user being injured or when there is a danger of both the user being injured and the equipment being damaged if the approved procedure is not observed.
 CAUTION
CAUTION
Applied when there is a danger of the equipment being damaged, if the approved procedure is not observed.
NOTE
The Note is used to indicate supplementary information other than Warning and Caution.
•Read this manual carefully, and store it in a safe place.
s-2

B-64414EN/01 |
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS |
GENERAL WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
 WARNING
WARNING
1Before operating the machine, thoroughly check the entered data. Operating the machine with incorrectly specified data may result in the machine behaving unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the user.
2Never attempt to machine a workpiece without first checking the programmed value, compensation value, current position, and external signal settings. Also, never attempt to machine a workpiece without first checking the operation of the machine. Before starting a production run, ensure that the machine is operating correctly by performing a trial run using, for example, the single block, feedrate override, or machine lock function, or by operating the machine with neither a tool nor workpiece mounted. Failure to confirm the correct operation of the machine may result in the machine behaving unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the user.
3Ensure that the specified feedrate is appropriate for the intended operation. Generally, for each machine, there is a maximum allowable feedrate. The appropriate feedrate varies with the intended operation. Refer to the manual provided with the machine to determine the maximum allowable feedrate. If a machine is run at other than the correct speed, it may behave unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the user.
4When using a tool compensation function, thoroughly check the direction and amount of compensation. Operating the machine with incorrectly specified data may result in the machine behaving unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the user.
5The parameters for the CNC and PMC are factory-set.
Usually, there is no need to change them. When, however, there is no alternative other than to change a parameter, ensure that you fully Failure to set a parameter correctly may result in the machine behaving unexpectedly, possibly causing damage to the workpiece and/or machine itself, or injury to the user.
s-3

SAFETY PRECAUTIONS |
B-64414EN/01 |
 CAUTION
CAUTION
1Immediately after switching on the power, do not touch any of the keys on the MDI panel until the position display or alarm screen appears on the CNC unit.
Some of the keys on the MDI panel are dedicated to maintenance or other special operations. Pressing any of these keys may place the CNC unit in other than its normal state. Starting the machine in this state may cause it to behave unexpectedly.
2The operator's manual for FAST Ethernet / FAST Data Server describes all the basic functions of the CNC, including the optional functions. The selected optional functions vary with the machine. Some functions described in this manual may not, therefore, be supported by your machine. Check the machine specifications before using FAST Ethernet / FAST Data Server.
3Some machine operations and screen functions are implemented by the machine tool builder. For an explanation of their usage and related notes, refer to the manual provided by the machine tool builder.
For example:
•On some machines, executing a tool function causes the tool change unit to operate. When executing a tool function on such a machine, stand well clear of the tool change unit. Otherwise, there is a danger of injury to the operator.
•Many auxiliary functions trigger physical operations, such as rotation of the spindle. Before attempting to use an auxiliary function, therefore, ensure that you are fully aware of the operation to be triggered by that function.
NOTE
Command programs, parameters, and variables are stored in nonvolatile memory in the CNC. Generally, the contents of memory are not lost by a power on/off operation. However, the contents of memory may be erased by mistake, or important data in nonvolatile memory may have to be erased upon recovering from a failure.
To enable the restoration of data as soon as possible if such a situation arises, always make a backup of the data in advance.
s-4

B-64414EN/01 TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS............................................................................ |
s-1 |
||
|
DEFINITION OF WARNING, CAUTION, AND NOTE ............................................. |
s-2 |
|
|
GENERAL WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS............................................................... |
s-3 |
|
I. GENERAL |
|
||
1 |
GENERAL ............................................................................................... |
3 |
|
|
1.1 |
ORGANIZATION ........................................................................................... |
4 |
|
1.2 |
APPLICABLE MODELS................................................................................. |
5 |
|
1.3 |
RELATED MANUALS.................................................................................... |
6 |
II. SPECIFICATION |
|
||
1 |
PREFACE................................................................................................ |
9 |
|
2 |
DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS ............................................................... |
10 |
|
|
2.1 |
DATA SERVER FILE MANAGEMENT ........................................................ |
12 |
|
|
2.1.1 File Names of CNC File Management ................................................................... |
13 |
|
|
2.1.2 Files which can be Created on a Data Server ......................................................... |
14 |
|
|
2.1.3 Text Files and Binary Files .................................................................................... |
14 |
|
2.2 |
DATA SERVER MODES ............................................................................. |
15 |
|
2.3 |
OPERATION FROM A DATA SERVER ...................................................... |
17 |
|
2.4 |
NC PROGRAM FORMAT............................................................................ |
19 |
|
2.5 |
LIST FILE FORMAT .................................................................................... |
21 |
|
2.6 |
ISO CODE INPUT/OUTPUT FUNCTION .................................................... |
25 |
3 |
FOCAS2/Ethernet FUNCTIONS........................................................... |
28 |
|
4 |
DNS/DHCP FUNCTIONS ...................................................................... |
29 |
|
5 |
MACHINE REMOTE DIAGNOSIS FUNCTIONS................................... |
30 |
|
6 |
UNSOLICITED MESSAGING FUNCTION ............................................ |
31 |
|
7 |
FTP FILE TRANSFER FUNCTION ....................................................... |
34 |
|
III. SETTING |
|
||
1 |
SETTING THE COMMUNICATION FUNCTION ................................... |
37 |
|
2 |
SETTING THE DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS....................................... |
38 |
|
|
2.1 |
OPERATING THE DATA SERVER SETTING SCREEN............................. |
39 |
|
2.2 |
INPUT OF SPECIAL CHARACTERS .......................................................... |
49 |
c-1

TABLE OF CONTENTS |
B-64414EN/01 |
|
2.3 |
RELATED NC PARAMETERS .................................................................... |
50 |
2.4 |
EXAMPLE OF SETTING THE DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS ..................... |
54 |
3 SETTING THE FOCAS2/Ethernet FUNCTIONS .................................. |
55 |
|
3.1 |
OPERATING THE FOCAS2/Ethernet SETTING SCREEN ......................... |
56 |
3.2 |
RELATED NC PARAMETERS .................................................................... |
59 |
3.3 |
EXAMPLE OF SETTING THE FOCAS2/Ethernet FUNCTIONS.................. |
60 |
4ERROR MESSAGES DISPLAYED DURING PARAMETER SETTING 61
5BACKING UP OR RESTORING COMMUNICATION PARAMETERS .62
IV. OPERATION |
|
||
1 OPERATING THE DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS................................. |
67 |
||
1.1 |
DEVICE CHANGE ON THE PROGRAM DIRECTORY SCREEN ............... |
68 |
|
1.2 |
OPERATING THE DATA SERVER FILE LIST SCREEN ............................ |
69 |
|
|
1.2.1 Displaying and Operating the File List .................................................................. |
75 |
|
|
1.2.2 |
File Transfer Operation .......................................................................................... |
83 |
|
1.2.3 Preparations for File Operation and Editing........................................................... |
85 |
|
1.3 |
OPERATING THE DATA SERVER HOST FILE LIST SCREEN ................. |
87 |
|
|
1.3.1 Displaying and Operating the File List .................................................................. |
92 |
|
|
1.3.2 |
File Transfer Operation .......................................................................................... |
95 |
|
1.3.3 Preparations for File Operation .............................................................................. |
98 |
|
1.4 |
M198-BASED SUBPROGRAM CALL.......................................................... |
99 |
|
1.5 |
DNC OPERATION..................................................................................... |
100 |
|
1.6 |
NC PROGRAM INPUT .............................................................................. |
101 |
|
1.7 |
NC PROGRAM OUTPUT .......................................................................... |
103 |
|
1.8 |
FTP SERVER FUNCTIONS ...................................................................... |
105 |
|
1.9 |
INPUT OF SPECIAL CHARACTERS ........................................................ |
106 |
|
V. CONNECTION |
|
||
1 SETTING ............................................................................................. |
109 |
|
1.1 |
SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................................... |
110 |
1.2 |
INSTALLATION ......................................................................................... |
111 |
|
1.2.1 Installation on an Control Unit............................................................................. |
111 |
|
1.2.2 Total Connection Diagram ................................................................................... |
112 |
|
1.2.3 Installing a Memory Card..................................................................................... |
113 |
2 CABLE CONNECTION ....................................................................... |
115 |
2.1 CONNECTING TO Ethernet ...................................................................... |
116 |
c-2
B-64414EN/01 |
|
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
||
|
2.2 |
LEADING OUT THE Ethernet CABLE ....................................................... |
117 |
|
|
2.3 |
100BASE-TX CONNECTOR (CD38R) PIN ASSIGNMENTS .................... |
118 |
|
|
2.4 |
TWISTED-PAIR CABLE SPECIFICATION................................................ |
119 |
|
|
|
2.4.1 |
Cable Connection ................................................................................................. |
119 |
|
|
2.4.2 |
Cable Materials..................................................................................................... |
120 |
|
|
2.4.3 |
Connector Specification ....................................................................................... |
122 |
|
2.5 |
ELECTRICAL NOISE COUNTERMEASURES.......................................... |
123 |
|
|
|
2.5.1 |
Separating Signal Lines........................................................................................ |
123 |
|
|
2.5.2 Clamping and Shielding Cables ........................................................................... |
123 |
|
|
|
2.5.3 |
Grounding the Network........................................................................................ |
126 |
|
2.6 |
CHECK ITEMS AT INSTALLATION .......................................................... |
128 |
|
VI. MAINTENANCE |
|
|||
1 |
HARDWARE MAINTENANCE INFORMATION.................................. |
131 |
||
|
1.1 |
BOARD...................................................................................................... |
132 |
|
|
|
1.1.1 |
Component Layout............................................................................................... |
132 |
|
|
1.1.2 LED Indications and Meanings............................................................................ |
133 |
|
2 |
SOFTWARE MAINTENANCE INFORMATION................................... |
136 |
||
|
2.1 |
Ethernet LOG ............................................................................................ |
137 |
|
|
2.2 |
ETHERNET CONNECTION CONFIRMATION.......................................... |
143 |
|
|
2.3 |
COMMUNICATION STATE CONFIRMATION........................................... |
146 |
|
|
2.4 |
COMMUNICATION SOFTWARE CONFIRMATION.................................. |
148 |
|
APPENDIX |
|
|
||
A |
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................ |
155 |
||
|
A.1 |
CHECKING COMMUNICATION WITH A HUB.......................................... |
156 |
|
|
A.2 |
CHECKING CONNECTION WITH THE TRUNK ....................................... |
157 |
|
|
A.3 |
CHECKING SETTINGS............................................................................. |
158 |
|
|
A.4 |
CHECKING COMMUNICATION................................................................ |
159 |
|
|
A.5 |
TROUBLESHOOTING DATA SERVER FUNCTION PROBLEMS ............ |
162 |
|
|
|
A.5.1 DNC Operation or M198-Based Subprogram Calling ......................................... |
162 |
|
|
|
|
A.5.1.1 An alarm occurs when an NC program is performed long time ...................... |
162 |
|
|
A.5.2 M198-Based Subprogram Calling Fails for an NC Program ............................... |
164 |
|
|
|
A.5.3 Operating the DATA SERVER HOST FILE LIST Screen.................................. |
165 |
|
|
|
|
A.5.3.1 The list of files cannot be displayed ................................................................ |
165 |
|
|
|
A.5.3.2 Files cannot be transferred............................................................................... |
168 |
c-3

TABLE OF CONTENTS |
B-64414EN/01 |
|||
|
A.5.4 Operating the DATA SERVER FILE LIST Screen ............................................. |
|
170 |
|
|
|
A.5.4.1 A program cannot be selected as a main program ........................................... |
|
170 |
B EXAMPLE OF FTP SERVER SETUP ................................................. |
|
172 |
||
|
B.1 SETTING UP FTP SERVER OF Windows 2000 Professional |
|
|
|
|
(FOR INTERNET INFORMATION SERVICE) ........................................... |
|
173 |
|
|
B.2 SETTING UP FTP SERVER OF Windows XP Professional |
|
|
|
|
(FOR INTERNET INFORMATION SERVICE) ........................................... |
|
185 |
|
|
B.3 SETTING UP FTP SERVER OF Windows Vista |
|
|
|
|
(FOR INTERNET INFORMATION SERVICE) ........................................... |
|
209 |
|
C |
FTP CLIENT OPERATION.................................................................. |
|
228 |
|
|
C.1 OPERATION USING THE FTP COMMAND.............................................. |
|
229 |
|
|
C.2 SECURITY UNBLOCKING IN Windows.................................................... |
|
232 |
|
D |
DNS/DHCP FUNCTION....................................................................... |
|
234 |
|
|
D.1 SETTINGS ON THE COMMUNICATION BOARD SIDE ........................... |
|
235 |
|
|
D.1.1 Setting the DNS Client Function.......................................................................... |
|
235 |
|
|
D.1.2 Setting the DHCP Client Function ....................................................................... |
|
237 |
|
|
D.1.3 |
Related NC Parameters......................................................................................... |
|
241 |
|
D.2 SETTING UP THE DNS/DHCP SERVER OF Windows 2000 Server |
........ |
242 |
|
|
D.2.1 Example of Setting Up DHCP Server of Windows 2000 Server ......................... |
|
243 |
|
|
D.2.2 Example of Setting Up DNS Server of Windows 2000 Server............................ |
|
250 |
|
|
D.3 EXAMPLE OF SETTING DNS/DHCP........................................................ |
|
256 |
|
|
D.3.1 When DNS/DHCP is Used with the Data Server ................................................. |
|
256 |
|
|
D.3.2 When DHCP is Used with the FTP Server Function of the Data Server ............. |
|
258 |
|
|
D.3.3 When DHCP Function is Used with the FOCAS2/Ethernet Function ................. |
|
260 |
|
E MACHINE REMOTE DIAGNOSIS FUNCTIONS................................. |
|
262 |
||
|
E.1 SETTING THE MACHINE REMOTE DIAGNOSIS SETTING SCREEN .... |
263 |
||
|
E.1.1 |
Related NC Parameters......................................................................................... |
|
270 |
|
E.2 CONTROLLING THE MACHINE REMOTE DIAGNOSIS FUNCTIONS |
|
||
|
FROM THE PMC....................................................................................... |
|
271 |
|
|
E.2.1 |
Signals .................................................................................................................. |
|
271 |
|
E.2.2 |
Signal Timing Charts............................................................................................ |
|
274 |
|
|
E.2.2.1 When the start of machine remote diagnosis is accepted................................. |
|
274 |
|
|
E.2.2.2 When the start of machine remote diagnosis is rejected.................................. |
|
275 |
|
|
E.2.2.3 When machine remote diagnosis is forcibly terminated.................................. |
|
276 |
|
E.3 EXAMPLE OF SETTING THE MACHINE REMOTE DIAGNOSIS |
|
|
|
|
FUNCTIONS.............................................................................................. |
|
277 |
|
c-4

B-64414EN/01 |
|
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
||
|
E.4 |
OPERATING THE MACHINE REMOTE DIAGNOSIS SCREEN ............... |
278 |
|
|
|
E.4.1 |
Selecting an Inquiry Destination .......................................................................... |
280 |
|
|
E.4.2 |
Starting Diagnosis ................................................................................................ |
280 |
|
|
|
E.4.2.1 Diagnosis status ............................................................................................... |
280 |
|
|
|
E.4.2.2 Error numbers and error messages................................................................... |
281 |
|
|
E.4.3 |
Forcibly Terminating Diagnosis........................................................................... |
281 |
F |
UNSOLICITED MESSAGING FUNCTION .......................................... |
282 |
||
|
F.1 |
SETTING OF THE UNSOLICITED MESSAGING FUNCTION.................. |
283 |
|
|
|
F.1.1 |
Mode Selection..................................................................................................... |
287 |
|
|
F.1.2 |
Setting on the CNC Screen................................................................................... |
290 |
|
|
F.1.3 |
Setting on the personal computer ......................................................................... |
295 |
|
F.2 |
EXECUTING THE UNSOLICITED MESSAGING FUNCTION................... |
296 |
|
|
|
F.2.1 |
When a PMC Address for control is Used (Response Notification Method)....... |
297 |
|
|
F.2.2 |
When a PMC Address for Control is Used (Simplified Method)......................... |
300 |
|
|
F.2.3 |
When a Macro Variable for Control is Used (Simplified Method)...................... |
302 |
|
F.3 |
RELATED NC PARAMETERS .................................................................. |
304 |
|
G |
FTP TRANSFER FUNCTION.............................................................. |
305 |
||
|
G.1 SETTING OF THE FTP TRANSFER FUNCTION...................................... |
306 |
||
|
G.2 |
RELATED NC PARAMETERS .................................................................. |
311 |
|
|
G.3 Example of setting the FTP file transfer function ....................................... |
313 |
||
|
G.4 OPERATING THE FTP FILE TRANSFER FUNCTIONS ........................... |
314 |
||
|
|
G.4.1 |
Device Change on the Program Directory Screen................................................ |
315 |
|
|
G.4.2 |
FTP Transfer Host File List.................................................................................. |
316 |
|
|
|
G.4.2.1 Displaying and operating the file list............................................................... |
320 |
|
|
G.4.3 |
Program Transfer Operation................................................................................. |
323 |
|
G.5 Input of Special Characters ....................................................................... |
327 |
||
c-5
I. GENERAL

B-64414EN/01 |
GENERAL |
1.GENERAL |
1 GENERAL
This part explains the organization of this manual.
Chapter 1, "GENERAL", consists of the following sections:
1.1 |
ORGANIZATION ........................................................................ |
4 |
1.2 |
APPLICABLE MODELS ............................................................. |
5 |
1.3 |
RELATED MANUALS................................................................ |
6 |
- 3 -

1.GENERAL |
GENERAL |
B-64414EN/01 |
1.1 ORGANIZATION
This manual consists of the following parts:
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This section describes the precautions to be observed when reading this manual.
I. GENERAL
This part describes the chapter organization, applicable models, and related manuals.
II. SPECIFICATION
This part describes the specifications of the functions that operate on the FAST Ethernet/FAST Data Server.
III. SETTING
This part describes the method of setting.
IV. OPERATION
This part describes the method of operating the Data Server functions.
V. CONNECTION
This part describes the method of connection and provides notes.
VI. MAINTENANCE
This part provides an Ethernet board drawing number and describes the meanings of LED indications.
APPENDIX
These appendixes describe additional information such as that related to troubleshooting, the operation of the FTP client, and how to set up the FTP server.
- 4 -

B-64414EN/01 |
GENERAL |
1.GENERAL |
1.2 APPLICABLE MODELS
This Operator's Manual covers the following models.
The abbreviations in the following table are sometimes used in text descriptions.
Model name |
Abbreviation |
|
|
FANUC Series 0i-MODEL D |
Series 0i-D |
|
0i-D |
- 5 -

1.GENERAL |
GENERAL |
B-64414EN/01 |
1.3 RELATED MANUALS
The table below lists manuals related to this Operator's Manual.
Refer to these manuals when you use this Operator's Manual.
Related manuals of FANUC Series 0i-D
Manual name |
Specification |
|
number |
||
|
||
DESCRIPTIONS |
B-64302EN |
|
CONNECTION MANUAL (HARDWARE) |
B-64303EN |
|
CONNECTION MANUAL (FUNCTION) |
B-64303EN-1 |
|
USER’S MANUAL |
B-64304EN |
|
(Common to Lathe System/Machining Center System) |
||
|
||
USER’S MANUAL (For Lathe System) |
B-64304EN-1 |
|
USER’S MANUAL (For Machining Center System) |
B-64304EN-2 |
|
MAINTENANCE MANUAL |
B-64305EN |
|
PARAMETER MANUAL |
B-64310EN |
|
START-UP MANUAL |
B-64304EN-3 |
Related manuals of FANUC CIMPLICITY i CELL
Manual name |
Specification |
|
number |
||
|
||
OPERATOR’S MANUAL |
B-75074EN |
Related manuals of FANUC Machine Remote Diagnosis Package
Manual name |
Specification |
|
number |
||
|
||
OPERATOR’S MANUAL |
B-63734EN |
Related manuals of FANUC Program Transfer Tool
Manual name |
Specification |
|
number |
||
|
||
OPERATOR’S MANUAL |
B-64344EN |
- 6 -
II. SPECIFICATION

B-64414EN/01 |
SPECIFICATION |
1.PREFACE |
1 PREFACE
In this manual, a board that has an ATA Flash card or a Compact Flash Card (collectively called a memory card hereinafter) mounted to enable the use of the Data Server functions is referred to as a "FAST Data Server" (or simply as a "Data Server"). On the other hand, a board that does not have a memory card mounted is referred to as a "FAST Ethernet".
Board name |
|
Usable function |
|
|
- |
Data Server functions |
|
|
- |
FOCAS2/Ethernet functions |
|
FAST Data Server |
- CNC screen display functions |
||
- |
Machine remote diagnosis |
||
(or simply referred to as "Data Server") |
|||
|
functions |
||
|
|
||
|
- |
Unsolicited messaging |
|
|
|
function (FOCAS2/Ethernet) |
|
|
- |
FOCAS2/Ethernet functions |
|
|
- CNC screen display functions |
||
|
- |
Machine remote diagnosis |
|
FAST Ethernet |
|
functions |
|
|
- |
Unsolicited messaging |
|
|
|
function (FOCAS2/Ethernet) |
|
|
- FTP file transfer function |
||
NOTE
To use the Data Server functions, the Data Server function option is required.
To use the FOCAS2/Ethernet functions, CNC screen display functions, machine remote diagnosis functions, unsolicited messaging function, and FTP file transfer function, the
Ethernet function option is required.
- 9 -

2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
SPECIFICATION |
B-64414EN/01 |
2 DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS
The Data Server functions use a memory card built into a board for storing files and can transfer files and perform DNC operation using FTP.
A Data Server can operate on both FTP client and FTP server.
When you use a Data Server to transfer files, the Data Server operates as an FTP client and communicates with the FTP server on the host computer.
When you use the host computer to transfer files, the Data Server operates as an FTP server and communicates with the FTP client on the host computer.
NOTE
1When the host computer operates as an FTP server, FTP server software must be run on the host computer. When the host computer operates as an FTP client, FTP client software must be run on the host computer.
2The Program Transfer Tool (drawing number:
A08B-9510-J513 [Version 3 or later]) is available as a PC tool for transferring NC programs between the CNC and personal computer. This tool allows NC programs to be transferred between a personal computer and CNC memory or Data Server memory card through a simple operation on the personal computer side. The transfer of NC programs between a personal computer and CNC memory requires the FOCAS2/Ethernet functions, and that between a PC and Data Server memory card requires the Data Server functions.
Chapter 2, "DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS", consists of the following sections:
2.1 |
DATA SERVER FILE MANAGEMENT .................................. |
11 |
2.2 |
DATA SERVER MODES .......................................................... |
15 |
2.3 |
OPERATION FROM A DATA SERVER.................................. |
17 |
2.4 |
NC PROGRAM FORMAT......................................................... |
19 |
2.5 |
LIST FILE FORMAT ................................................................. |
21 |
2.6 |
ISO CODE INPUT/OUTPUT FUNCTION................................ |
25 |
- 10 -
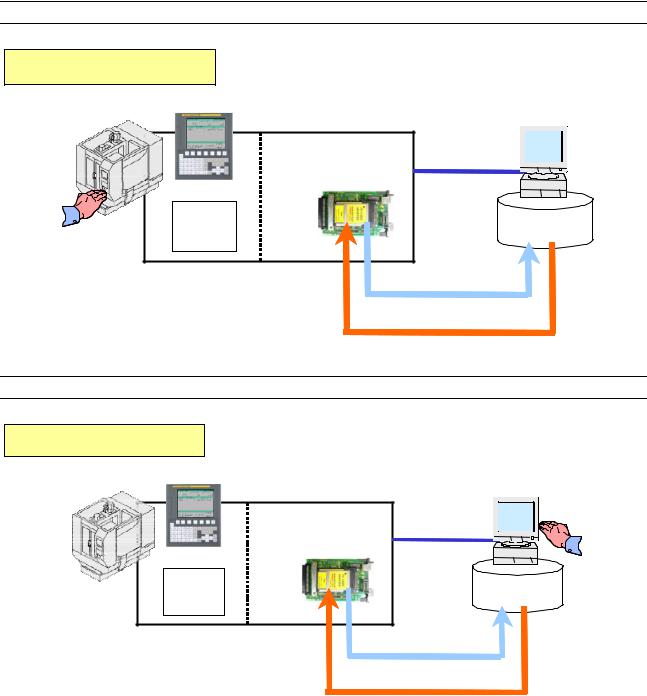
B-64414EN/01 |
SPECIFICATION |
2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
FTP client
FTP client
CNC |
FTP sever |
FAST Data Server
Ethernet
|
CNC |
Hard disk |
|
Operation |
memory |
||
|
|||
|
|
PUT
GET
FTP server
FTP server
CNC |
FTP client |
FAST Data Server |
Ethernet |
CNC |
Operation |
|
Hard disk |
||
memory |
||
|
GET
PUT
- 11 -

2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
SPECIFICATION |
B-64414EN/01 |
2.1 DATA SERVER FILE MANAGEMENT
With the Data Server functions, you can format the built-in memory card in the CNC file management mode to manage NC programs.
CNC file management
For NC programs managed in the CNC file management mode, memory operation such as custom macro commands and M98-based subprogram calling are available. Operate the NC programs using the PROGRAM FOLDER screen in the same way as for NC programs in the CNC memory.
As a CNC external input/output device, DNC operation and M198-based subprogram calling are available. In this case, operate NC programs using the DATA SERVER FILE LIST screen.
PROGRAM FOLDER screen |
Edit operation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CNC file management |
|
|
Memory operation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DATA SERVER FILE LIST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(DNC operation is also available.) |
||||
screen |
|
|
|
||||
File transfer operation |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE
1The Data Server for the Series 0i-D allows editing and memory operation of NC programs stored on the memory card, so the method of managing files on the memory card differs from the file management method of conventional Data Servers. Note that, therefore, the memory card of the Series 0i-D is not compatible with the memory cards of Data Server models for the Series 0i-C .
2For operation and details of the DATA SERVER
FILE LIST screen, refer to Chapter 1, "OPERATING THE DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS," in Part IV, "OPERATION."
- 12 -

B-64414EN/01 |
SPECIFICATION |
2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
2.1.1 File Names of CNC File Management
A file name of CNC file management may be an arbitrary file name of up to 32 characters.
•Up to 32 characters
•Alphabetic characters (in upper and lower cases), numeric characters, and four symbols (+, -, _, and .)
NOTE
1File names are case-sensitive.
2Any file name or folder name cannot begin with a period (.).
3It is impossible to assign the same name to a file and a folder.
File names and program numbers
When a file name assigned to a file consists of uppercase O and a numeric value, the file name is treated as a program number.
Values ranging from 1 to 9999 can be used.
A value beyond this range cannot be used for a file name in the program number format.
Example)
File names that can be used as program numbers
“O0123” |
Program number 123 |
“O0001” |
Program number 1 |
“O3000” |
Program number 3000 |
“O9999” |
Program number 9999 |
File names that cannot be used as program numbers |
|
“ABC” |
(Does not have the format "O plus a numeric value") |
“o123” |
(Does not begin with uppercase letter "O") |
“O123.4” (Uses a character other than numeric characters)
NOTE
1When files on a Data Server are managed by program number, their program numbers always consist of "O" plus a 4-digit number. So, even if there are files managed with different file names such as "O1" and "O01" on a personal computer, their program numbers are regarded as the same when these files are transferred to the Data Server.
2When a text file assigned an arbitrary file name other than a program number is input to the CNC memory, it is necessary to specify the program number set in the CNC memory.
- 13 -

2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
SPECIFICATION |
B-64414EN/01 |
2.1.2 Files which can be Created on a Data Server
In the initial status, the maximum number of files which can be created on a memory card on a Data Server is 2047 and the maximum file size is 512 MB. Each folder is counted as one file.
The maximum number of files and the maximum file size can be changed using NC parameter No. 930.
For details, see Section 2.3, "RELATED NC PARAMETERS," in Part III, "SETTING."
2.1.3 Text Files and Binary Files
You can store the following two types of files on a memory card on a Data Server: text files and binary files.
For a text file, memory operation and edit operation as well as DNC operation can be performed by selecting it as a main program.
On the other hand, memory and edit operations cannot be performed for a binary file.
If NC data other than an NC program is not handled as a binary file, it may not be able to be input or output correctly. NC data punched and stored on a memory card on a Data Server from the CNC is automatically handled as a binary file. A file to be transferred from a personal computer to a memory card on a Data Server must be specified explicitly as a binary file.
More specifically, for GET operation on a Data Server operation screen, you can use soft key [GET] or [BGET] to specify whether to handle the file as a text file or a binary file.
When the Data Server is used as an FTP server, you can execute an ASCII (text file) command or a BIN (binary file) command on your personal computer (FTP client) to specify whether to handle the file as a text file or a binary file.
NOTE
1An NC program stored as a text file is converted to an editable file format so that the file can be edited on the CNC. For this reason, when a text file is read from the host computer to the memory card on the Data Server, then the file is transferred to the host computer, binary compatibility can no longer be maintained.
2In the case of a text file, the file name and program name are identical. If a file having a program name different from the file name on the personal computer side is transferred as a text file, the program name is replaced by the file name.
Note, however, that only when the file is transferred through an operation on the CNC side, precedence can be given to the program name by setting bit 3 (DSF) of NC parameter No. 905.
- 14 -

B-64414EN/01 |
SPECIFICATION |
2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
2.2 DATA SERVER MODES
Each Data Server mode determines the input or output destination when a Data Server is operated as a CNC external input/output device. You can select one of the following two modes.
NOTE
Data Server modes are valid only when the Data
Server is operated as an external storage device of the CNC. In case of main program operation for editing and a memory operation and an M98-based subprogram call, programs on the memory card of the Data Server are selected regardless of the
Data Server mode.
Storage mode
The memory card built into the Data Server is selected as the external input/output device.
For example, when DNC operation or M198-based subprogram calling is executed, the relevant NC program is called from the memory card built into the Data Server.
When input operation is executed for the Data Server, the relevant NC program is read from the memory card built into the Data Server. Conversely, when NC program output operation is executed for the Data Server, the output NC program is written on the memory card built into the Data Server.
Data Server Memory card
Input |
CNC memory |
Output |
DNC operation |
FTP mode
The host computer connected to the Data Server is selected as the external input/output device.
For example, when DNC operation or M198-based subprogram calling is executed, the relevant NC program is called from the host computer.
When input operation is executed for the Data Server, the relevant NC program is read from the host computer connected to the Data Server. Conversely, when NC program output operation is executed for the Data Server, the output NC program is directly written on the host computer.
- 15 -

2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
SPECIFICATION |
B-64414EN/01 |
Data Server
Input
CNC memory
Host computer |
Output |
|
DNC operation
CAUTION
1In the FTP mode, an NC program is transferred from the host computer to the CNC. For this reason, if the line is disconnected during communication for some reason such as noise on the network, the disconnection directly affects the CNC operation as compared with the storage mode. Before DNC operation in the FTP mode, surely take measures to prevent noise and make sure that good communication conditions are present.
2When feed hold is performed during DNC operation in the FTP mode, communication with the host computer may be stopped. In this case, the host computer may disconnect the communication. Perform feed hold during a trial run and completely confirm that the communication with the host computer is not disconnected.
- 16 -

B-64414EN/01 |
SPECIFICATION |
2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
2.3 OPERATION FROM A DATA SERVER
Memory operation
You can perform memory operation for an NC program on the memory card built into a Data Server in the same way as for an NC program in the CNC memory.
You can also supply an NC program simultaneously for a multipath CNC system.
NOTE
1When memory operation is performed, a selected program on the Data Server must be a text file. It is impossible to use a binary file for memory operation.
2Memory and edit operations for the Data Server can be performed only for NC programs stored in the memory card built in the Data Server. Memory and edit operations cannot be performed directly for files on the host computer.
3When memory operation is performed using a program in the Data Server memory card as the main program, a subprogram in the same folder as the main program can be called by the M98 subprogram call.
M198 subprogram operation
In the storage mode, you can perform M198 calling from the memory card built into a Data Server. In the FTP mode, you can perform M198 calling form the host computer.
On the DATA SERVER FILE LIST screen, set an M198 folder in advance. When M198 calling is specified, the set M198 folder is searched for the target subprogram.
NOTE
M198 subprogram operation cannot be performed simultaneously for two paths.
- 17 -

2.DATA SERVER FUNCTIONS |
SPECIFICATION |
B-64414EN/01 |
DNC operation
In the storage mode, you can perform DNC operation from the memory card built into a Data Server. In the FTP, you can perform DNC operation from the host computer.
On the DATA SERVER FILE LIST screen, set the file name for DNC operation in advance. When DNC operation starts, the set DNC operation file is called.
NOTE
DNC operation cannot be performed for the second path.
- 18 -
 Loading...
Loading...