Siemens S7-200 User Manual

Preface, Contents
Product Overview
Getting Started
Installing the S7-200
SIMATIC
PLC Concepts
S7-200 Programmable Controller
System Manual
This manual has the order number:
6ES7298-8FA23-8BH0
Edition 05/2003
Programming Concepts,
Conventions and Features
S7-200 Instruction Set
Communicating over a Network
Hardware Troubleshooting Guide and Software Debugging Tools
Creating a Program for the Position Module
Creating a Program for the Modem Module
Using the USS Protocol Library to Control a MicroMaster Drive
Using the Modbus Protocol Library
Technical Specifications
Calculating a Power Budget
Error Codes
Special Memory (SM) Bits
S7-200 Order Numbers
Execution Times for STL
Instructions
S7-200 Quick Reference
Information
Index
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 A B C D E F G
A5E00212536-02

Contents
Safety Guidelines
This manual contains notices which you should observe to ensure your own personal safety, as well as to protect the product and connected equipment. These notices are highlighted in the manual by a warning triangle and are marked as follows according to the level of danger:
Danger
Danger indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Warning
Warning indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Caution
Caution used with the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
Caution
Caution used without the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in property damage.
Notice
Notice indicates a potential situation which, if not avoided, may result in an undesirable result or state.
Qualified Personnel
Only qualified personnel should be allowed to install and work on this equipment. Qualified persons are defined as persons who are authorized to commission, to ground, and to tag circuits, equipment, and systems in accordance with established safety practices and standards.
Correct Usage
Note the following:
Warning
This device and its components may only be used for the applications described in the catalog or the technical descriptions, and only in connection with devices or components from other manufacturers which have been approved or recommended by Siemens.
This product can only function correctly and safely if it is transported, stored, set up, and installed correctly, and operated and maintained as recommended.
Trademarks
SIMATICR, SIMATIC HMIR and SIMATIC NETR are registered trademarks of SIEMENS AG.
Some of other designations used in these documents are also registered trademarks; the owner’s rights may be violated if they are used by third parties for their own purposes.
Copyright Siemens AG 2003 All rights reserved
The reproduction, transmission or use of this document or its contents is not permitted without express written authority. Offenders will be liable for damages. All rights, including rights created by patent grant or registration of a utility model or design, are reserved.
Disclaimer of Liability
We have checked the contents of this manual for agreement with the hardware and software described. Since deviations cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full agreement. However, the data in this manual are reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections included in subsequent editions. Suggestions for improvement are welcomed.
Siemens AG |
|
Bereich Automation and Drives |
|
Geschaeftsgebiet Industrial Automation Systems |
E Siemens AG 2003 |
Postfach 4848, D- 90327 Nuernberg |
Technical data subject to change. |
ii |
|
Siemens Aktiengesellschaft |
6ES7298-8FA23-8BH0 |

Preface
The S7-200 series is a line of micro-programmable logic controllers (Micro PLCs) that can control a variety of automation applications. Compact design, low cost, and a powerful instruction set make the S7-200 a perfect solution for controlling small applications. The wide variety of S7-200 models and the Windows-based programming tool give you the flexibility you need to solve your automation problems.
Audience
This manual provides information about installing and programming the S7-200 Micro PLCs and is designed for engineers, programmers, installers, and electricians who have a general knowledge of programmable logic controllers.
Scope of the Manual
The information contained in this manual pertains in particular to the following products:
-S7-200 CPU models: CPU 221, CPU 222, CPU 224, CPU 226, and CPU 226XM
-S7-200 EM 22x expansion modules
-STEP 7--Micro/WIN, version 3.2, a 32-bit programming software package for the S7-200
-STEP 7--Micro/WIN Instruction Libraries and TP-Designer for TP070, Version 1.0, a set of software tools for customers who use an S7-200 with other components, such as the TP070 Touch Panel, Modbus, or a MicroMaster drive
Standards Compliance
The SIMATIC S7-200 series meets the following standards:
-European Community (CE) Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
EN 61131--2: Programmable Controllers -- Equipment requirements
-European Community (CE) EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
Electromagnetic emissions standard
EN 61000--6--3: residential, commercial, and light industry EN 61000--6--4: industrial environment
Electromagnetic immunity standards EN 61000--6--2: industrial environment
-Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.
UL 508 Listed (Industrial Control Equipment) |
Registration number E75310 |
-Canadian Standards Association: CSA C22.2 Number 142 (Process Control Equipment)
-Factory Mutual Research: FM Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, & D Hazardous Locations, T4A and Class I, Zone 2, IIC, T4
Refer to Appendix A for compliance information.
Tip
The SIMATIC S7-200 series meets the CSA standard.
The cULus logo indicates that the S7-200 has been examined and certified by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) to standards UL 508 and CSA 22.2 No. 142.
iii

Contents
Maritime Approvals
The S7-200 products are periodically submitted for special agency approvals related to specific markets and applications. This table identifies the agency and certificate number that the S7-200 products have been approved for. Not all S7-200 products in this manual have been approved for these special agency approvals. Consult your local Siemens representative if you need additional information related to the latest listing of exact approvals by part number.
Agency |
Certificate Number |
Lloyds Register of Shipping (LRS) |
99 / 20018(E1) |
|
|
American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) |
01--HG20020--PDA |
|
|
Germanischer Lloyd (GL) |
12 045 -- 98 HH |
|
|
Det Norske Veritas (DNV) |
A--8071 |
|
|
Bureau Veritas (BV) |
09051 / A2 BV |
|
|
Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (NK) |
A--534 |
|
|
How to Use This Manual
If you are a first-time (novice) user of S7-200 Micro PLCs, you should read the entire S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual. If you are an experienced user, refer to the table of contents or index to find specific information.
The S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual is organized according to the following topics:
-Chapter 1 (Product Overview) provides an overview of some of the features of the S7-200 family of Micro PLC products.
-Chapter 2 (Getting Started) provides a tutorial for creating and downloading a sample control program to an S7-200.
-Chapter 3 (Installing the S7-200) provides the dimensions and basic guidelines for installing the S7-200 CPU modules and expansion I/O modules.
-Chapter 4 (PLC Concepts) provides information about the operation of the S7-200.
-Chapter 5 (Programming Concepts, Conventions, and Features) provides information about the features of STEP 7--Micro/WIN, the program editors and types of instructions (IEC 1131-3 or SIMATIC), S7-200 data types, and guidelines for creating programs.
-Chapter 6 (S7-200 Instruction Set) provides descriptions and examples of programming instructions supported by the S7-200.
-Chapter 7 (Communicating over a Network) provides information for setting up the different network configurations supported by the S7-200.
-Chapter 8 (Hardware Troubleshooting Guide and Software Debugging Tools) provides information for troubleshooting problems with the S7-200 hardware and about the STEP 7--Micro/WIN features that help you debug your program.
-Chapter 9 (Creating a Program for the Position Module) provides information about the instructions and wizard used to create a program for the EM 253 Position module.
-Chapter 10 (Creating a Program for the Modem Module) provides information about the instructions and wizard used to create a program for the EM 241 Modem module.
-Chapter 11 (Using the USS Protocol Library to Control a MicroMaster Drive) provides information about the instructions used to create a control program for a MicroMaster drive. It also provides information about how to configure the MicroMaster 3 and MicroMaster 4 drives.
-Chapter 12 (Using the Modbus Protocol Library) provides information about the instructions used to create a program that uses the Modbus protocol for communications.
-Appendix A (Technical Specifications) provides the technical information and data sheets about the S7-200 hardware.
The other appendices provide additional reference information, such as descriptions of the error codes, descriptions of the Special Memory (SM) area, part numbers for ordering S7-200 equipment, and STL instruction execution times.
iv

Preface
Additional Information and Assistance
Information about the S7-200 and STEP 7-Micro/WIN
In addition to this manual, STEP 7--Micro/WIN provides extensive online help for getting started with programming the S7-200. Included with the purchase of the STEP 7--Micro/WIN software is a free documentation CD. On this CD you can find application tips, an electronic version of this manual and other information.
Online Help
Help is only a keystroke away! Pressing F1 accesses the extensive online help for STEP 7--Micro/WIN. The online help includes useful information about getting started with programming the S7-200, as well as many other topics.
Electronic Manual
An electronic version of this S7-200 System Manual is available on the documentation CD. You can install the electronic manual onto your computer so that you can easily access the information in the manual while you are working with the STEP 7--Micro/WIN software.
Programming Tips
The documentation CD includes Programming Tips, a set of application examples with sample programs. Reviewing or modifying these examples can help you find efficient or innovative solutions for your own application. You can also find the most current version of Programming Tips on the S7-200 Internet site.
Internet: www.siemens.com/S7--200
For additional information about Siemens products and services, technical support, frequently asked questions (FAQs), product updates, or application tips, refer to the following Internet addresses:
- www.ad.siemens.de for general Siemens information
This Siemens Automation & Drives Internet site includes information about the SIMATIC product line and other products available from Siemens.
-www.siemens.com/S7--200 for S7-200 product information
The S7-200 Internet site includes frequently asked questions (FAQs), Programming Tips (application examples and sample programs), information about newly released products, and product updates or downloads.
v

Contents
Technical Assistance and Purchasing S7-200 Products
Local Siemens Sales Office or Distributor
For assistance in answering any technical questions, for training on the S7-200 products, or for ordering S7-200 products, contact your Siemens distributor or sales office. Because your sales representatives are technically trained and have the most specific knowledge about your operations, process and industry, as well as about the individual Siemens products that you are using, they can provide the fastest and most efficient answers to any problems that you might encounter.
Technical Services
The highly trained staff of the S7-200 Technical Services center is also available to help you solve any problems that you might encounter. You can call on them 24 hours a day, 7 days a week:
-For calls originating from within the United States of America
Local time: |
Monday to Friday 0800 to 1900 Eastern time |
|
Telephone: |
+1 |
800 241--4453 |
Fax: |
+1 |
(0) 770 740--3699 |
E-Mail: |
drives.support@sea.siemens.com |
|
-For calls originating from the Americas outside of the USA
Local time: |
Monday to Friday 0800 to 1900 Eastern time |
Telephone: |
+1 (0) 770 740--3505 |
Fax: |
+1 (0) 770 740--3699 |
E-Mail: |
drives.support@sea.siemens.com |
-For calls originating from Europe and Africa
Local time (Nuremberg): Monday to Friday 0700 to 1700
Telephone: |
+49 (0) 180 5050--222 |
Fax: |
+49 (0) 180 5050--223 |
E-Mail: |
techsupport@ad.siemens.de |
-For calls originating from Asia and Australia
Local time (Singapore): |
Monday to Friday 0830 to 1730 |
|
Telephone: |
+65 (0) 740--7000 |
|
Fax: |
+65 (0) 740--7001 |
|
E-Mail: |
drives.support@sae.siemens.com.sg |
|
vi
Contents |
|
|
1 |
Product Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
1 |
|
S7-200 CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
2 |
|
S7-200 Expansion Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
|
STEP 7--Micro/WIN Programming Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
|
Communications Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
|
Display Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
2 |
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
|
Connecting the S7-200 CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
6 |
|
Creating a Sample Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
9 |
|
Downloading the Sample Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
|
Placing the S7-200 in RUN Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
3 |
Installing the S7-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
13 |
|
Guidelines for Installing S7-200 Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
14 |
|
Installing and Removing the S7-200 Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
|
Guidelines for Grounding and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
18 |
4 |
PLC Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
21 |
|
Understanding How the S7-200 Executes Your Control Logic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
|
Accessing the Data of the S7-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
24 |
|
Understanding How the S7-200 Saves and Restores Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
34 |
|
Storing Your Program on a Memory Cartridge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
36 |
|
Selecting the Operating Mode for the S7-200 CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
37 |
|
Using Your Program to Save V Memory to the EEPROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
38 |
|
Features of the S7-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
39 |
5 |
Programming Concepts, Conventions, and Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
47 |
|
Guidelines for Designing a Micro PLC System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
48 |
|
Basic Elements of a Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
49 |
|
Using STEP 7--Micro/WIN to Create Your Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
51 |
|
Choosing Between the SIMATIC and IEC 1131--3 Instruction Sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
53 |
|
Understanding the Conventions Used by the Program Editors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
|
Using Wizards To Help You Create Your Control Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
56 |
|
Handling Errors in the S7-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
56 |
|
Assigning Addresses and Initial Values in the Data Block Editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
58 |
|
Using the Symbol Table for Symbolic Addressing of Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
58 |
|
Using Local Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
59 |
|
Using the Status Chart to Monitor Your Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
59 |
|
Creating an Instruction Library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
60 |
|
Features for Debugging Your Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
60 |
vii

Contents |
|
|
6 |
S7-200 Instruction Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
61 |
|
Conventions Used to Describe the Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
63 |
|
S7-200 Memory Ranges and Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
64 |
|
Bit Logic Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
66 |
|
Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
66 |
|
Coils . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
69 |
|
Logic Stack Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
71 |
|
Set and Reset Dominant Bistable Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
73 |
|
Clock Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
74 |
|
Communications Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
75 |
|
Network Read and Network Write Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
75 |
|
Transmit and Receive Instructions (Freeport) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
80 |
|
Get Port Address and Set Port Address Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
89 |
|
Compare Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
90 |
|
Comparing Numerical Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
90 |
|
Compare String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
92 |
|
Conversion Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
93 |
|
Standard Conversion Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
93 |
|
ASCII Conversion Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
97 |
|
String Conversion Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
101 |
|
Encode and Decode Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
106 |
|
Counter Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
107 |
|
SIMATIC Counter Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
107 |
|
IEC Counter Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
110 |
|
High-Speed Counter Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
112 |
|
Pulse Output Instruction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
126 |
|
Math Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
141 |
|
Add, Subtract, Multiply, and Divide Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
141 |
|
Multiply Integer to Double Integer and Divide Integer with Remainder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
143 |
|
Numeric Functions Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
144 |
|
Increment and Decrement Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
145 |
|
Proportional/Integral/Derivative (PID) Loop Instruction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
146 |
|
Interrupt Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
156 |
|
Logical Operations Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
163 |
|
Invert Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
163 |
|
AND, OR, and Exclusive OR Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
164 |
|
Move Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
166 |
|
Move Byte, Word, Double Word, or Real . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
166 |
|
Move Byte Immediate (Read and Write) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
167 |
|
Block Move Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
168 |
|
Program Control Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
169 |
|
Conditional End . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
169 |
|
Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
169 |
|
Watchdog Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
169 |
|
For--Next Loop Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
171 |
|
Jump Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
173 |
|
Sequence Control Relay (SCR) Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
174 |
viii

Contents
Shift and Rotate Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Shift Right and Shift Left Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Rotate Right and Rotate Left Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Shift Register Bit Instruction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Swap Bytes Instruction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
String Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Table Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Add To Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
First-In-First-Out and Last-In-First-Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Memory Fill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Table Find . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Timer Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
SIMATIC Timer Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
IEC Timer Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Subroutine Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
7 |
Communicating over a Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
209 |
|
Understanding the Basics of S7-200 Network Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
210 |
|
Selecting the Communications Protocol for Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
214 |
|
Installing and Removing Communications Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
220 |
|
Building Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
222 |
|
Creating User-Defined Protocols with Freeport Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
227 |
|
Using Modems and STEP 7--Micro/WIN with Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
229 |
|
Advanced Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
235 |
|
Configuring the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master Cable for Remote Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
241 |
8 |
Hardware Troubleshooting Guide and Software Debugging Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
245 |
Features for Debugging Your Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246 Displaying the Program Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248 Using a Status Chart to Monitor and Modify the Data in the S7-200 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249 Forcing Specific Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250 Running Your Program for a Specified Number of Scans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250 Hardware Troubleshooting Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
9 |
Creating a Program for the Position Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
253 |
Features of the Position Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254 Configuring the Position Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256 Position Instructions Created by the Position Control Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267 Sample Programs for the Position Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279 Monitoring the Position Module with the EM 253 Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284 Error Codes for the Position Module and the Position Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286 Advanced Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
10 Creating a Program for the Modem Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
Features of the Modem Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298 Using the Modem Expansion Wizard to Configure the Modem Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304 Overview of Modem Instructions and Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 308 Instructions for the Modem Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 309
ix

Contents
Sample Program for the Modem Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313 S7-200 CPUs that Support Intelligent Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313 Special Memory Location for the Modem Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314 Advanced Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316 Messaging Telephone Number Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318 Text Message Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318 CPU Data Transfer Message Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
11 Using the USS Protocol Library to Control a MicroMaster Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
Requirements for Using the USS Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322 Calculating the Time Required for Communicating with the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323 Using the USS Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324 Instructions for the USS Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325 Sample Programs for the USS Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332 USS Execution Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333 Connecting and Setting Up the MicroMaster Series 3 Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334 Connecting and Setting Up the MicroMaster Series 4 Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 337
12 Using the Modbus Protocol Library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Requirements for Using the Modbus Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340 Initialization and Execution Time for the Modbus Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340 Modbus Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341 Using the Modbus Slave Protocol Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342 Instructions for the Modbus Slave Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
A |
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
347 |
|
General Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
348 |
|
CPU Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
351 |
|
Digital Expansion Modules Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
357 |
|
Analog Expansion Modules Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
363 |
|
Thermocouple and RTD Expansion Modules Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
373 |
|
EM 277 PROFIBUS--DP Module Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
385 |
|
EM 241 Modem Module Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
397 |
|
EM 253 Position Module Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
399 |
|
(CP 243--1) Ethernet Module Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
405 |
|
(CP 243--1 IT) Internet Module Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
407 |
|
(CP 243--2) AS--Interface Module Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
410 |
|
Optional Cartridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
412 |
|
I/O Expansion Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
412 |
|
RS-232/PPI Multi-Master Cable and USB/PPI Multi-Master Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
413 |
|
Input Simulators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
417 |
B |
Calculating a Power Budget . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
419 |
C |
Error Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
423 |
|
Fatal Error Codes and Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
424 |
|
Run-Time Programming Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
425 |
|
Compile Rule Violations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
426 |
x

Contents
D Special Memory (SM) Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
SMB0: Status Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428 SMB1: Status Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428 SMB2: Freeport Receive Character . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429 SMB3: Freeport Parity Error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429 SMB4: Queue Overflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429 SMB5: I/O Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430 SMB6: CPU ID Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430 SMB7: Reserved . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430 SMB8 to SMB21: I/O Module ID and Error Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431 SMW22 to SMW26: Scan Times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432 SMB28 and SMB29: Analog Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432 SMB30 and SMB130: Freeport Control Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432 SMB31 and SMW32: Permanent Memory (EEPROM) Write Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433 SMB34 and SMB35: Time Interval Registers for Timed Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433 SMB36 to SMB65: HSC0, HSC1, and HSC2 Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433 SMB66 to SMB85: PTO/PWM Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 435 SMB86 to SMB94, and SMB186 to SMB194: Receive Message Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 436 SMW98: Errors on the Expansion I/O Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437 SMB130: Freeport Control Register (see SMB30) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437 SMB131 to SMB165: HSC3, HSC4, and HSC5 Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437 SMB166 to SMB185: PTO0, PTO1 Profile Definition Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438 SMB186 to SMB194: Receive Message Control (see SMB86 to SMB94) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438 SMB200 to SMB549: Intelligent Module Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
E S7-200 Order Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441 F Execution Times for STL Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445 G S7-200 Quick Reference Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451 Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
xi

Contents
xii

Product Overview
The S7-200 series of micro-programmable logic controllers (Micro PLCs) can control a wide variety of devices to support your automation needs.
The S7-200 monitors inputs and changes outputs as controlled by the user program, which can include Boolean logic, counting, timing, complex math operations, and communications with other intelligent devices. The compact design, flexible configuration, and powerful instruction set combine to make the S7-200 a perfect solution for controlling a wide variety of applications.
In This Chapter |
|
S7-200 CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
2 |
S7-200 Expansion Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
STEP 7--Micro/WIN Programming Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
Communications Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
Display Panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
1
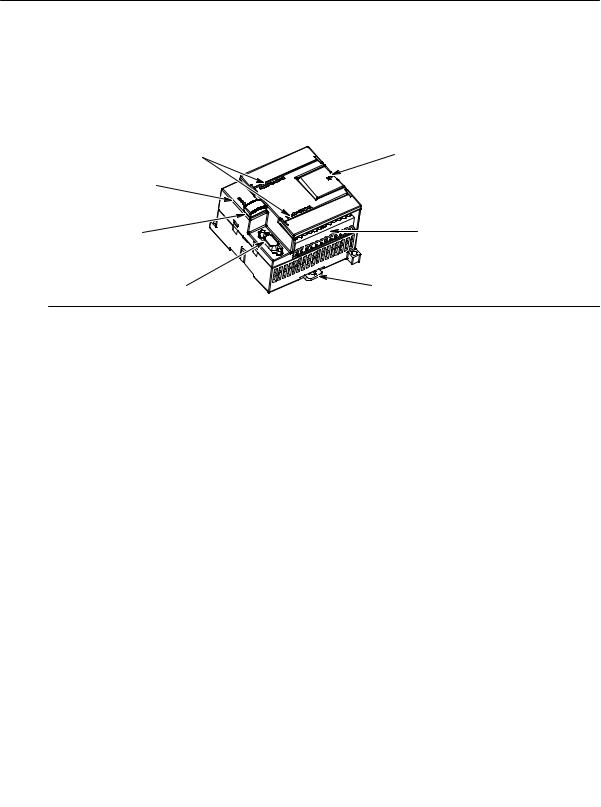
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
|
S7-200 CPU |
|
1 |
||
The S7-200 CPU combines a microprocessor, an integrated power supply, input circuits, and output |
||
|
||
|
circuits in a compact housing to create a powerful Micro PLC. See Figure 1-1. After you have |
|
|
||
|
downloaded your program, the S7-200 contains the logic required to monitor and control the input and |
|
|
output devices in your application. |
I/O LEDs
Status LEDs:
System Fault
RUN
STOP
Optional cartridge:
EEPROM
Real-time Clock
Battery
Communications port
Access door:
Mode selector switch (RUN/STOP) Analog adjustment potentiometer(s) Expansion port (for most CPUs)
Terminal connector
(removable on CPU 224, CPU 226 and CPU 226XM)
Clip for installation on a standard (DIN) rail
Figure 1-1 S7-200 Micro PLC
Siemens provides different S7-200 CPU models with a diversity of features and capabilities that help you create effective solutions for your varied applications. Table 1-1 briefly compares some of the features of the CPU. For detailed information about a specific CPU, see Appendix A.
Table 1-1 |
Comparison of the S7-200 CPU Models |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Feature |
|
CPU 221 |
CPU 222 |
CPU 224 |
CPU 226 |
CPU 226XM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Physical size (mm) |
90 x 80 x 62 |
90 x 80 x 62 |
120.5 x 80 x 62 |
190 x 80 x 62 |
190 x 80 x 62 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program memory |
4096 bytes |
4096 bytes |
8192 bytes |
8192 bytes |
16384 bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data memory |
2048 bytes |
2048 bytes |
5120 bytes |
5120 bytes |
10240 bytes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Memory backup |
50 hours typical |
50 hours typical |
190 hours typical |
190 hours typical |
190 hours typical |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Local on-board I/O |
6 In/4 Out |
8 In/6 Out |
14 In/10 Out |
24 In/16 Out |
24 In/16 Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expansion modules |
0 modules1 |
2 modules1 |
7 modules1 |
7 modules1 |
7 modules1 |
|
High-speed counters |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Single phase |
4 at 30 kHz |
4 at 30 kHz |
6 at 30 kHz |
6 at 30 kHz |
6 at 30 kHz |
|
Two phase |
2 at 20 kHz |
2 at 20 kHz |
4 at 20 kHz |
4 at 20 kHz |
4 at 20 kHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pulse outputs (DC) |
2 at 20 kHz |
2 at 20 kHz |
2 at 20 kHz |
2 at 20 kHz |
2 at 20 kHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analog adjustments |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Real-time clock |
Cartridge |
Cartridge |
Built-in |
Built-in |
Built-in |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Communications |
1 RS--485 |
1 RS--485 |
1 RS--485 |
2 RS--485 |
2 RS--485 |
|
ports |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Floating-point math |
Yes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Digital I/O image size |
256 (128 in, 128 out) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Boolean execution |
0.37 microseconds/instruction |
|
|
|
||
speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 You must calculate your power budget to determine how much power (or current) the S7-200 CPU can provide for your configuration. If the CPU power budget is exceeded, you may not be able to connect the maximum number of modules. See Appendix A for CPU and expansion module power requirements, and Appendix B to calculate your power budget.
2

Product Overview Chapter 1
S7-200 Expansion Modules |
|
|
1 |
||
To better solve your application requirements, the S7-200 family includes a wide variety of expansion |
||
|
||
modules. You can use these expansion modules to add additional functionality to the S7-200 CPU. |
|
|
|
||
Table 1-2 provides a list of the expansion modules that are currently available. For detailed information |
|
|
about a specific module, see Appendix A. |
|
Table 1-2 S7-200 Expansion Modules
Expansion Modules |
Types |
|
|
|
Discrete modules |
Input |
8 x DC In |
8 x AC In |
16 x DC In |
|
Output |
4 x DC |
4 x Relays |
|
|
|
8 x DC Out |
8 x AC Out |
8 x Relay |
|
Combination |
4 x DC In / 4 x DC Out |
8 x DC In / 8 x DC Out |
16 x DC In / 16 x DC Out |
|
|
4 x DC In / 4 x Relay |
8 x DC In / 8 x Relay |
16 x DC In / 16 x Relay |
|
|
|
|
|
Analog modules |
Input |
4 x Analog In |
4 x Thermocouple In |
2 x RTD In |
|
Output |
2 x Analog Out |
|
|
|
Combination |
4 x Analog In / 1 Analog Out |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intelligent modules |
Position |
Modem |
PROFIBUS-DP |
|
|
|
Ethernet |
Internet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other modules |
|
AS--Interface |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STEP 7-Micro/WIN Programming Package
The STEP 7--Micro/WIN programming package provides a user-friendly environment to develop, edit, and monitor the logic needed to control your application. STEP 7--Micro/WIN provides three program editors for convenience and efficiency in developing the control program for your application. To help you find the information you need, STEP 7--Micro/WIN provides an extensive online help system and a documentation CD that contains an electronic version of this manual, application tips, and other useful information.
Computer Requirements
STEP 7--Micro/WIN runs on either a personal computer or a Siemens programming device, such as a PG 760. Your computer or programming device should meet the following minimum requirements:
-Operating system: Windows 95, Windows 98,
Windows 2000, Windows Me (Millennium Edition), Windows NT 4.0 (or later version),
Windows XP Professional
-At least 100M bytes of free hard disk space
-Mouse (recommended)
Figure 1-2 STEP 7--Micro/WIN
3
|
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Installing STEP 7-Micro/WIN |
|
|
1 |
|
|||
|
Insert the STEP 7--Micro/WIN CD into the CD-ROM drive of your computer. The installation wizard starts |
|
||
|
|
automatically and prompts you through the installation process. Refer to the Readme file for more |
|
|
|
|
information about installing STEP 7--Micro/WIN. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tip |
|
|
|
|
To install STEP 7--Micro/WIN on a Windows NT, Windows 2000, or Windows XP Professional |
|
|
|
|
operating system, you must log in with Administrator privileges. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Communications Options
Siemens provides two programming options for connecting your computer to your S7-200: a direct connection with a PPI Multi-Master cable, or a Communications Processor (CP) card with an MPI cable.
The PPI Multi-Master programming cable is the most common and economical method of connecting your computer to the S7-200. This cable connects the communications port of the S7-200 to the serial communications of your computer. The PPI Multi-Master programming cable can also be used to connect other communications devices to the S7-200.
Display Panels
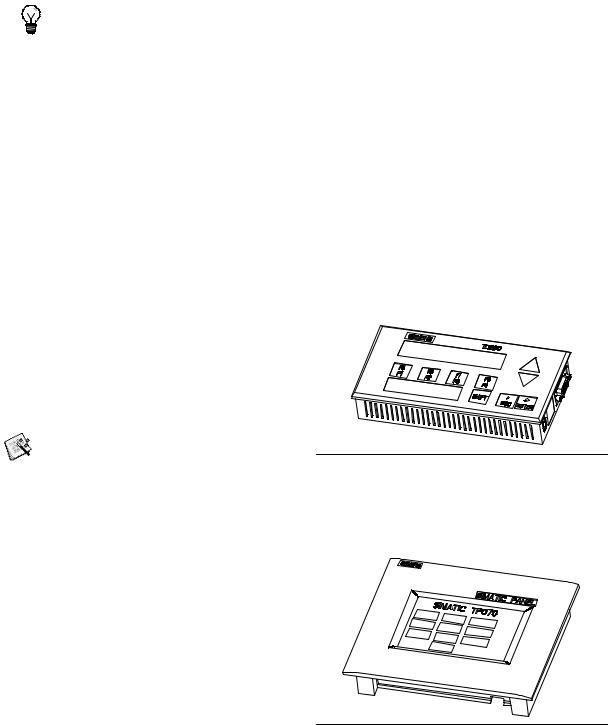
TD 200 Text Display Unit
The TD 200 is a 2-line, 20-character, text display device that can be connected to the S7-200. Using the TD 200 wizard, you can easily program your S7-200 to display text messages and other data pertaining to your application.
The TD 200 provides a low cost interface to your application by allowing you to view, monitor, and change the process variables pertaining to your application.
A separate manual describes the detailed functionality and specifications of the TD 200.
The TD 200 Configuration Wizard in
STEP 7--MicroWIN helps you configure TD 200 messages quickly and easily. To start the TD
TD 200 |
200 Wizard, select the Tools > TD 200 Wizard |
Figure 1-3 TD 200 Text Display Unit |
|
|
menu command.
TP070 Touch Panel Display
The TP070 is a touch panel display device that can be connected to the S7-200. This touch panel provides you with a means to customize your operator interface.
The TP070 can display custom graphics, slider bars, application variables, custom user buttons, and so forth, by means of a user-friendly touch panel.
The optional TP--Designer for TP070, Version 1.0 CD provides the TP Designer software, which is required for programming your TP070.
Figure 1-4 TP070 Touch Panel Unit
4

Getting Started
STEP 7--Micro/WIN makes it easy for you to program your S7-200. In just a few short steps using a simple example, you can learn how to connect, program, and run your S7-200.
All you need for this example is a PPI Multi-Master cable, an S7-200 CPU, and a programming device running the STEP 7--Micro/WIN programming software.
In This Chapter |
|
Connecting the S7-200 CPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
6 |
Creating a Sample Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
9 |
Downloading the Sample Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
Placing the S7-200 in RUN Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
12 |
5
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
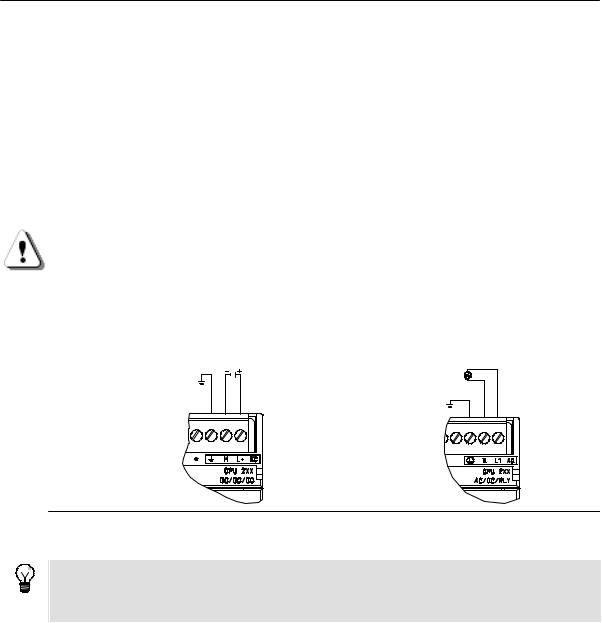
Connecting the S7-200 CPU
|
Connecting your S7-200 is easy. For this example, you only need to connect power to your S7-200 CPU |
|||
|
and then connect the communications cable between your programming device and the S7-200 CPU. |
|||
2 |
||||
Connecting Power to the S7-200 CPU |
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
The first step is to connect the S7-200 to a power source. Figure 2-1 shows the wiring connections for |
|||
|
either a DC or an AC model of the S7-200 CPU. |
|
||
|
Before you install or remove any electrical device, ensure that the power to that equipment has been |
|||
|
turned off. Always follow appropriate safety precautions and ensure that power to the S7-200 is disabled |
|||
|
before attempting to install or remove the S7-200. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
|
|
|
|
Attempts to install or wire the S7-200 or related equipment with power applied could cause electric |
||
|
|
shock or faulty operation of equipment. Failure to disable all power to the S7-200 and related |
||
|
|
equipment during installation or removal procedures could result in death or serious injury to |
||
|
|
personnel, and/or damage to equipment. |
|
|
|
|
Always follow appropriate safety precautions and ensure that power to the S7-200 is disabled before |
||
|
|
attempting to install or remove the S7-200 or related equipment. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 VDC |
85 to 265 VAC |
|
DC Installation AC Installation
Figure 2-1 Connecting Power to the S7-200 CPU
Tip
Examples in this manual use the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master cable. The RS-232/PPI Multi-Master cable replaces the previous PC/PPI cable. A USB/PPI Multi-Master cable is also available. Refer to Appendix E for order numbers.
6
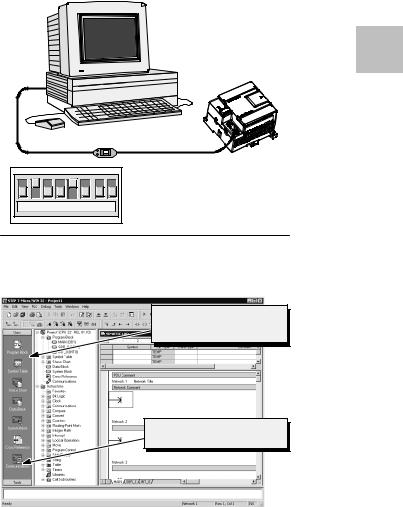
Getting Started |
Chapter 2 |
Connecting the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master Cable
Figure 2-2 shows an RS-232/PPI Multi-Master cable connecting the S7-200 to the programming device. To connect the cable:
1.Connect the RS-232 connector (marked “PC”) of the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master cable to the communications port of the programming device. (For this example, connect to COM 1.)
2.Connect the RS-485 connector (marked “PPI”) of the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master cable to Port 0 or Port 1 of the S7-200.
3.Ensure that the DIP switches of the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master cable are set as shown in Figure 2-2.
Programming
Device
2
S7-200
RS-232/PPI
Multi-Master Cable
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↑1 -- On |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
↓0 -- Off |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
Figure 2-2 Connecting the RS-232/PPI Multi-Master Cable
Starting STEP 7-Micro/WIN
Click on the STEP 7--Micro/WIN icon to open a new project. Figure 2-3 shows a new project.
Notice the navigation bar. You can use the icons on the navigation bar to open elements of the STEP 7--Micro/WIN project.
Click on the Communications icon in the navigation bar to display the Communications dialog box. You use this dialog box to set up the communications for STEP 7--Micro/WIN.
Navigation bar
Communications icon
Figure 2-3 New STEP 7--Micro/WIN Project
7
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
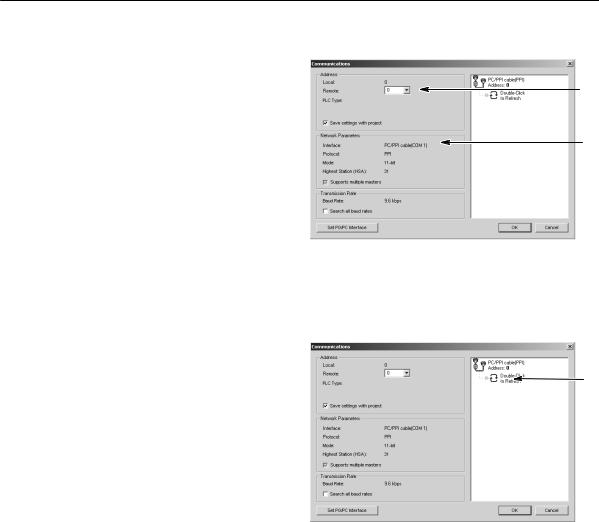
Verifying the Communications Parameters for STEP 7-Micro/WIN
|
The example project uses the default settings |
||
|
for STEP 7--Micro/WIN and the RS-232/PPI |
||
2 |
Multi-Master cable. To verify these settings: |
||
1. |
Verify that the address of the PC/PPI |
||
|
|||
|
|
cable in the Communications dialog box |
|
|
|
||
|
|
is set to 0. |
|
|
2. |
Verify that the interface for the network |
|
|
|
parameter is set for PC/PPI |
|
|
|
cable(COM1). |
|
|
3. |
Verify that the transmission rate is set to |
|
|
|
9.6 kbps. |
|
If you need to change your communications parameter settings, see Chapter 7.
1.
2.
 3.
3.
Figure 2-4 Verifying the Communications Parameters
Establishing Communications with the S7-200
Use the Communications dialog box to connect with your S7-200 CPU:
1. Double-click the refresh icon in the
Communications dialog box. |
|
|
STEP 7--Micro/WIN searches for the |
1. |
|
S7-200 station and displays a CPU icon |
|
|
for the connected S7-200 station. |
|
|
2. Select the S7-200 and click OK. |
|
|
If STEP 7--Micro/WIN does not find your |
|
|
S7-200 CPU, check the settings for the |
|
|
communications parameters and repeat these |
|
|
steps. |
|
|
After you have established communications |
|
|
with the S7-200, you are ready to create and |
Figure 2-5 Establishing Communications to the S7-200 |
|
download the example program. |
||
|
8
Getting Started Chapter 2
Creating a Sample Program
Entering this example of a control program will help you understand how easy it is to use |
|
|
STEP 7--Micro/WIN. This program uses six instructions in three networks to create a very simple, |
|
|
2 |
||
self-starting timer that resets itself. |
||
|
||
For this example, you use the Ladder (LAD) editor to enter the instructions for the program. The |
|
|
following example shows the complete program in both LAD and Statement List (STL). The network |
|
|
comments in the STL program explain the logic for each network. The timing diagram shows the |
|
|
operation of the program. |
|
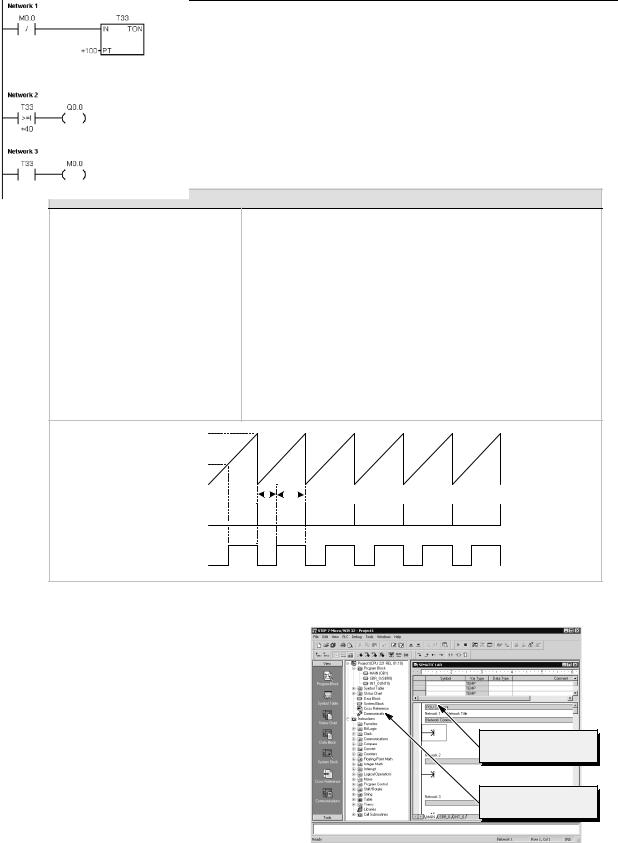
Example: Sample Program for getting started with STEP 7-Micro/WIN
Network 1 //10 ms timer T33 times out after (100 x 10 ms = 1 s) //M0.0 pulse is too fast to monitor with Status view.
LDN |
M0.0 |
TON |
T33, +100 |
Network 2 //Comparison becomes true at a rate that is visible with //Status view. Turn on Q0.0 after (40 x 10 ms = 0.4 s), //for a 40% OFF/60% ON waveform.
LDW>= T33, +40
=Q0.0
Network 3 //T33 (bit) pulse too fast to monitor with Status view. //Reset the timer through M0.0 after the
//(100 x 10 ms = 1 s) period.
LD T33
=M0.0
Timing Diagram |
current = 100 |
|
current = 40
T33 (current) |
0.4s 0.6s |
|
|
|
|
T33 (bit)
M0.0
Q0.0
Opening the Program Editor
Click on the Program Block icon to open the program editor. See Figure 2-6.
Notice the instruction tree and the program editor. You use the instruction tree to insert the LAD instructions into the networks of the program editor by dragging and dropping the instructions from the instruction tree to the networks.
The toolbar icons provide shortcuts to the menu commands.
After you enter and save the program, you can download the program to the S7-200.
Program editor
Instruction tree
Figure 2-6 STEP 7--Micro/WIN Window
9
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
Entering Network 1: Starting the Timer
When M0.0 is off (0), this contact turns on and provides power flow to start the timer. To enter the contact for M0.0:
2 |
1. |
Either double-click the Bit Logic icon or |
|
click on the plus sign (+) to display the bit |
|
|
|
logic instructions. |
|
|
|
|
2. |
Select the Normally Closed contact. |
|
3. |
Hold down the left mouse button and |
|
|
drag the contact onto the first network. |
|
4. |
Click on the “???” above the contact and |
|
|
enter the following address: M0.0 |
|
5. |
Press the Return key to enter the |
|
|
address for the contact. |
To enter the timer instruction for T33: |
Figure 2-7 Network 1 |
|
1.Double-click the Timers icon to display the timer instructions.
2.Select the TON (On-Delay Timer).
3.Hold down the left mouse button and drag the timer onto the first network.
4.Click on the “???” above the timer box and enter the following timer number: T33
5.Press the Return key to enter the timer number and to move the focus to the preset time (PT) parameter.
6.Enter the following value for the preset time: 100
7.Press the Return key to enter the value.
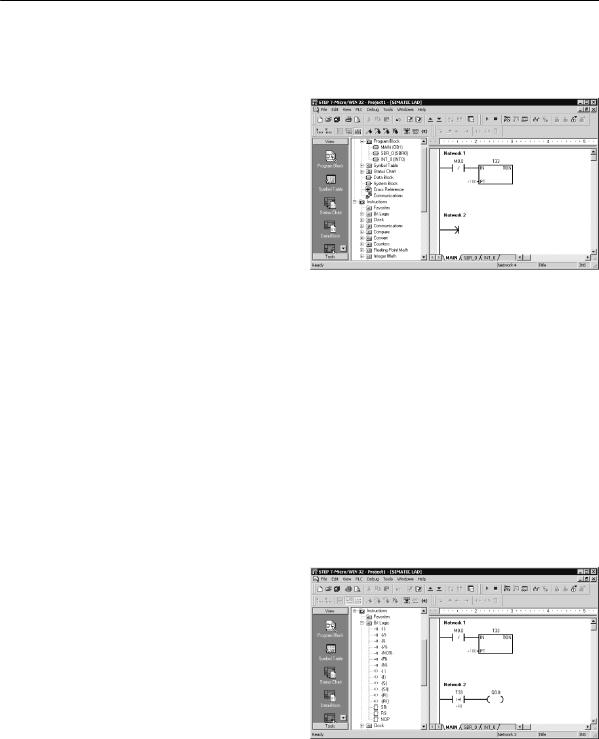
Entering Network 2: Turning the Output On
When the timer value for T33 is greater than or equal to 40 (40 times 10 milliseconds, or 0.4 seconds), the contact provides power flow to turn on output Q0.0 of the S7-200. To enter the Compare instruction:
1.Double-click the Compare icon to display the compare instructions. Select the >=I instruction (Greater-Than-Or-Equal-To-Integer ).
2.Hold down the left mouse button and drag the compare instruction onto the second network.
3.Click on the “???” above the contact and enter the address for the timer value: T33
4.Press the Return key to enter the timer number and to move the focus to the other value to be compared with the timer value.
5.Enter the following value to be compared with the timer value: 40
6. Press the Return key to enter the value. |
Figure 2-8 Network 2 |
|
To enter the instruction for turning on output Q0.0:
1.Double-click the Bit Logic icon to display the bit logic instructions and select the output coil.
2.Hold down the left mouse button and drag the coil onto the second network.
3.Click on the “???” above the coil and enter the following address: Q0.0
4.Press the Return key to enter the address for the coil.
10
Getting Started Chapter 2
Entering Network 3: Resetting the Timer
When the timer reaches the preset value (100) and turns the timer bit on, the contact for T33 turns on. |
|
|
Power flow from this contact turns on the M0.0 memory location. Because the timer is enabled by a |
|
|
Normally Closed contact for M0.0, changing the state of M0.0 from off (0) to on (1) resets the timer. |
2 |
|
To enter the contact for the timer bit of T33: |
||
1. |
Select the Normally Open contact from |
|
|
||
|
the bit logic instructions. |
|
2. |
Hold down the left mouse button and |
|
|
drag the contact onto the third network. |
|
3. |
Click on the “???” above the contact and |
|
|
enter the address of the timer bit: T33 |
|
4. |
Press the Return key to enter the |
|
|
address for the contact. |
|
To enter the coil for turning on M0.0:
1. Select the output coil from the bit logic
instructions. Figure 2-9 Network 3
2.Hold down the left mouse button and drag the output coil onto the third network.
3.Double-click the “???” above the coil and enter the following address: M0.0
4.Press the Return key to enter the address for the coil.
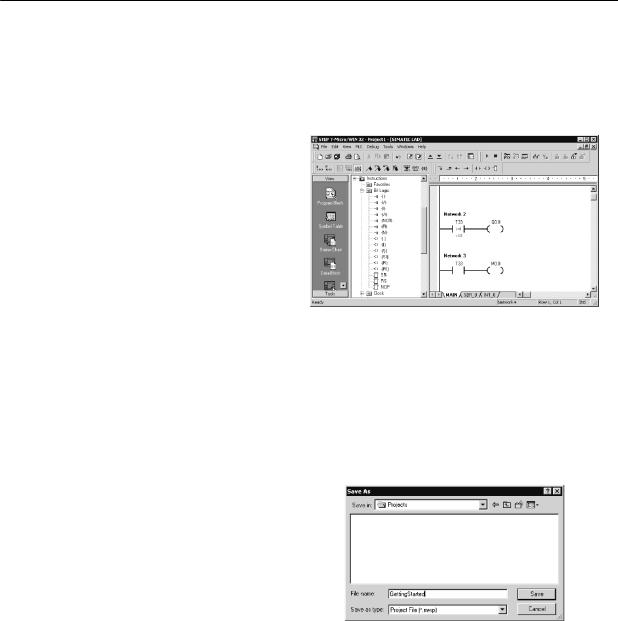
Saving the Sample Project
After entering the three networks of instructions, you have finished entering the program. When you save the program, you create a project that includes the S7-200 CPU type and other parameters. To save the project:
1.Select the File > Save As menu command from the menu bar.
2.Enter a name for the project in the Save As dialog box.
3.Click OK to save the project.
After saving the project, you can download the program to the S7-200.
Figure 2-10 Saving the Example Program
11
|
|
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Downloading the Sample Program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tip |
|
2 |
|
|
Each STEP 7--Micro/WIN project is associated with a CPU type (CPU 221, CPU 222, CPU 224, |
|
|
|
CPU 226, or CPU 226XM). If the project type does not match the CPU to which you are connected, |
|
|
|
|
|
STEP 7--Micro/WIN indicates a mismatch and prompts you to take an action. If this occurs, choose |
|
|
|
|
“Continue Download” for this example. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
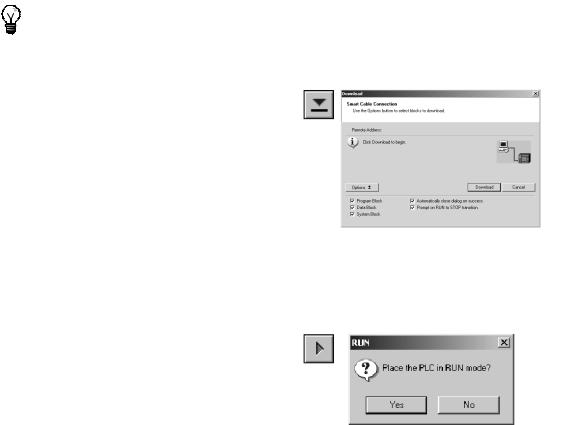
1.Click the Download icon on the toolbar or select the File > Download menu command to download the program. See Figure 2-11.
2.Click OK to download the elements of the program to the S7-200.
If your S7-200 is in RUN mode, a dialog box prompts you to place the S7-200 in STOP mode. Click Yes to place the S7-200 into STOP
mode. Figure 2-11 Downloading the Program
Placing the S7-200 in RUN Mode
For STEP 7--Micro/WIN to place the S7-200 CPU in RUN mode, the mode switch of the S7-200 must be set to TERM or RUN. When you place the S7-200 in RUN mode, the S7-200 executes the program:
1.Click the RUN icon on the toolbar or select the PLC > RUN menu command.
2.Click OK to change the operating mode of the S7-200.
When the S7-200 goes to RUN mode, the
output LED for Q0.0 turns on and off as the
S7-200 executes the program. Figure 2-12 Placing the S7-200 in RUN Mode
Congratulations! You have just completed your first S7-200 program.
You can monitor the program by selecting the Debug > Program Status menu command.
STEP 7--Micro/WIN displays the values for the instructions. To stop the program, place the S7-200 in
STOP mode by clicking the STOP icon or by selecting the PLC > STOP menu command.
12

Installing the S7-200
The S7-200 equipment is designed to be easy to install. You can use the mounting holes to attach the modules to a panel, or you can use the built-in clips to mount the modules onto a standard (DIN) rail. The small size of the S7-200 allows you to make efficient use of space.
This chapter provides guidelines for installing and wiring your S7-200 system.
In This Chapter |
|
Guidelines for Installing S7-200 Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
14 |
Installing and Removing the S7-200 Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
Guidelines for Grounding and Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
18 |
13
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
Guidelines for Installing S7-200 Devices
You can install an S7-200 either on a panel or on a standard rail, and you can orient the S7-200 either horizontally or vertically.
Separate the S7-200 Devices from Heat, High Voltage, and Electrical Noise
3 |
As a general rule for laying out the devices of your system, always separate the devices that generate |
|
high voltage and high electrical noise from the low-voltage, logic-type devices such as the S7-200. |
||
|
When configuring the layout of the S7-200 inside your panel, consider the heat-generating devices and locate the electronic-type devices in the cooler areas of your cabinet. Operating any electronic device in a high-temperature environment will reduce the time to failure.
Consider also the routing of the wiring for the devices in the panel. Avoid placing low voltage signal wires and communications cables in the same tray with AC power wiring and high-energy, rapidly-switched DC wiring.
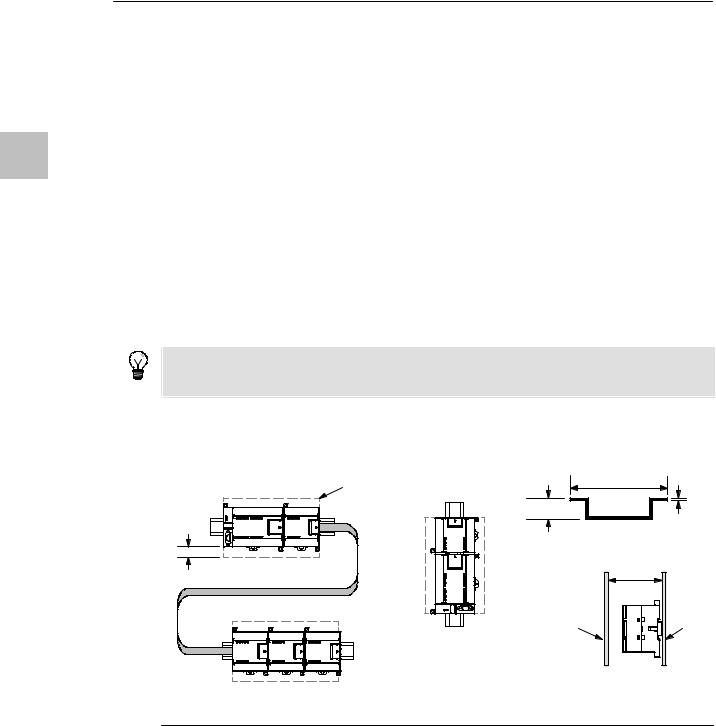
Provide Adequate Clearance for Cooling and Wiring
S7-200 devices are designed for natural convection cooling. For proper cooling, you must provide a clearance of at least 25 mm above and below the devices. Also, allow at least 75 mm of depth.
Tip
For vertical mounting, the maximum allowable ambient temperature is reduced by 10° C. Mount the S7-200 CPU below any expansion modules.
When planning your layout for the S7-200 system, allow enough clearance for the wiring and communications cable connections. For additional flexibility in configuring the layout of the S7-200 system, use the I/O expansion cable.
Clearance |
35 mm |
|
1 mm |
|
7.5 mm |
DIN Rail
25 mm
|
75 mm |
Front of the |
Mounting |
enclosure |
surface |
Vertical Panel Mounting |
|
Side View
Horizontal DIN Rail Mounting with Optional
Expansion Cable (limit one per system)
Figure 3-1 Mounting Methods, Orientation, and Clearance
14

Installing the S7-200 |
Chapter 3 |
Power Budget
All S7-200 CPUs have an internal power supply that provides power for the CPU, the expansion modules, and other 24 VDC user power requirements.
The S7-200 CPU provides the 5 VDC logic power needed for any expansion in your system. Pay careful attention to your system configuration to ensure that your CPU can supply the 5V power required by your selected expansion modules. If your configuration requires more power than the CPU can supply,
you must remove a module or select a CPU with more power capability. Refer to Appendix A for 3 information about the 5 VDC logic budget supplied by your S7-200 CPU and the 5 VDC power
requirements of the expansion modules. Use Appendix B as a guide for determining how much power (or current) the CPU can provide for your configuration.
All S7-200 CPUs also provide a 24 VDC sensor supply that can supply 24 VDC for input points, for relay coil power on the expansion modules, or for other requirements. If your power requirements exceed the budget of the sensor supply, then you must add an external 24 VDC power supply to your system. Refer to Appendix A for the 24 VDC sensor supply power budget for your particular S7-200 CPU.
If you require an external 24 VDC power supply, ensure that the power supply is not connected in parallel with the sensor supply of the S7-200 CPU. For improved electrical noise protection, it is recommended that the commons (M) of the different power supplies be connected.
Warning
Connecting an external 24 VDC power supply in parallel with the S7-200 24 VDC sensor supply can result in a conflict between the two supplies as each seeks to establish its own preferred output voltage level.
The result of this conflict can be shortened lifetime or immediate failure of one or both power supplies, with consequent unpredictable operation of the PLC system. Unpredictable operation could result in death or serious injury to personnel, and/or damage to equipment.
The S7-200 DC sensor supply and any external power supply should provide power to different points.
Installing and Removing the S7-200 Modules
The S7-200 can be easily installed on a standard DIN rail or on a panel.
Prerequisites
Before you install or remove any electrical device, ensure that the power to that equipment has been turned off. Also, ensure that the power to any related equipment has been turned off.
Warning
Attempts to install or remove S7-200 or related equipment with the power applied could cause electric shock or faulty operation of equipment.
Failure to disable all power to the S7-200 and related equipment during installation or removal procedures could result in death or serious injury to personnel, and/or damage to equipment.
Always follow appropriate safety precautions and ensure that power to the S7-200 is disabled before attempting to install or remove S7-200 CPUs or related equipment.
Always ensure that whenever you replace or install an S7-200 device you use the correct module or equivalent device.
Warning
If you install an incorrect module, the program in the S7-200 could function unpredictably.
Failure to replace an S7-200 device with the same model, orientation, or order could result in death or serious injury to personnel, and/or damage to equipment.
Replace an S7-200 device with the same model, and be sure to orient and position it correctly.
15
S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
Mounting Dimensions
The S7-200 CPUs and expansion modules include mounting holes to facilitate installation on panels. Refer to Table 3-1 for the mounting dimensions.
Table 3-1 Mounting Dimensions
3 |
|
9.5 mm* |
* Minimum spacing |
|
A |
between modules when |
|
4 mm |
hard-mounted |
||
B |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mounting holes |
|
|
|
(M4 or No. 8) |
96 mm |
88 mm |
80 mm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
4 mm |
|
|
|
4 mm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
S7-200 Module |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Width A |
Width B |
|
|||
CPU 221 and CPU 222 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 mm |
82 mm |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
CPU 224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120.5 mm |
112.5 mm |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
CPU 226 and CPU 226XM |
|
|
196 mm |
188 mm |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Expansion modules: |
4- and 8-point DC and Relay I/O (8I, 4Q, 8Q, 4I/4Q) |
|
|
|
46 mm |
38 mm |
||||||||||
|
|
and Analog Out (2 AQ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Expansion modules: |
16-point digital I/O (16I, 8I/8Q), Analog I/O (4AI, 4AI/1AQ), |
|
71.2 mm |
63.2 mm |
||||||||||||
|
|
RTD, Thermocouple, PROFIBUS, Ethernet, Internet, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
AS-Interface, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
8-point AC (8I and 8Q), Position, and Modem |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Expansion modules: |
32-point digital I/O (16I/16Q) |
|
137.3 mm |
129.3 mm |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Installing a CPU or Expansion Module
Installing the S7-200 is easy! Just follow these steps.
Panel Mounting
1.Locate, drill, and tap the mounting holes (M4 or American Standard number 8), using the dimensions in Table 3-1.
2.Secure the module(s) to the panel, using the appropriate screws.
3.If you are using an expansion module, connect the expansion module ribbon cable into the expansion port connector under the access door.
DIN Rail Mounting
1.Secure the rail to the mounting panel every 75 mm.
2.Snap open the DIN clip (located on the bottom of the module) and hook the back of the module onto the DIN rail.
3.If you are using an expansion module, connect the expansion module ribbon cable into the expansion port connector under the access door.
4.Rotate the module down to the DIN rail and snap the clip closed. Carefully check that the clip has fastened the module securely onto the rail. To avoid damage to the module, press on the tab of the mounting hole instead of pressing directly on the front of the module.
16
Installing the S7-200 Chapter 3
Tip
Using DIN rail stops could be helpful if your S7-200 is in an environment with high vibration potential or if the S7-200 has been installed vertically.
If your system is in a high-vibration environment, then panel-mounting the S7-200 will provide a greater level of vibration protection.
Removing a CPU or Expansion Module |
3 |
|
To remove an S7-200 CPU or expansion module, follow these steps: |
||
|
||
|
|
1.Remove power from the S7-200.
2.Disconnect all the wiring and cabling that is attached to the module. Most S7-200 CPU and expansion modules have removable connectors to make this job easier.
3.If you have expansion modules connected to the unit that you are removing, open the access cover door and disconnect the expansion module ribbon cable from the adjacent modules.
4.Unscrew the mounting screws or snap open the DIN clip.
5.Remove the module.
Removing and Reinstalling the Terminal Block Connector
Most S7-200 modules have removable connectors to make installing and replacing the module easy. Refer to Appendix A to determine whether your S7-200 module has removable connectors. You can order an optional fan-out connector for modules that do not have removable connectors. See Appendix E for order numbers.
To Remove the Connector
1.Open the connector door to gain access to the connector.
2.Insert a small screwdriver in the notch in the middle of the connector.
3.Remove the terminal connector by prying the screwdriver away from the S7-200 housing. See Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Removing the Connector
To Reinstall the Connector
1.Open the connector door.
2.Align the connector with the pins on the unit and align the wiring edge of the connector inside the rim of the connector base.
3.Press down firmly to rotate the connector until it snaps into place. Check carefully to ensure that the connector is properly aligned and fully engaged.
17

S7-200 Programmable Controller System Manual
Guidelines for Grounding and Wiring
Proper grounding and wiring of all electrical equipment is important to help ensure the optimum operation of your system and to provide additional electrical noise protection for your application and the S7-200.
|
Prerequisites |
||
3 |
|||
Before you ground or install wiring to any electrical device, ensure that the power to that equipment has |
|||
|
|||
|
been turned off. Also, ensure that the power to any related equipment has been turned off. |
||
|
Ensure that you follow all applicable electrical codes when wiring the S7-200 and related equipment. |
||
|
Install and operate all equipment according to all applicable national and local standards. Contact your |
||
|
local authorities to determine which codes and standards apply to your specific case. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
|
|
|
Attempts to install or wire the S7-200 or related equipment with power applied could cause electric |
|
|
|
shock or faulty operation of equipment. Failure to disable all power to the S7-200 and related |
|
|
|
equipment during installation or removal procedures could result in death or serious injury to |
|
|
|
personnel, and/or damage to equipment. |
|
|
|
Always follow appropriate safety precautions and ensure that power to the S7-200 is disabled before |
|
|
|
attempting to install or remove the S7-200 or related equipment. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Always take safety into consideration as you design the grounding and wiring of your S7-200 system. |
||
|
Electronic control devices, such as the S7-200, can fail and can cause unexpected operation of the |
||
|
equipment that is being controlled or monitored. For this reason, you should implement safeguards that |
||
|
are independent of the S7-200 to protect against possible personal injury or equipment damage. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
|
|
|
Control devices can fail in an unsafe condition, resulting in unexpected operation of controlled |
|
|
|
equipment. Such unexpected operations could result in death or serious injury to personnel, and/or |
|
|
|
damage to equipment. |
|
|
|
Use an emergency stop function, electromechanical overrides, or other redundant safeguards that are |
|
|
|
independent of the S7-200. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guidelines for Isolation |
||
|
S7-200 AC power supply boundaries and I/O boundaries to AC circuits are rated 1500 VAC. These |
||
|
isolation boundaries have been examined and approved as providing safe separation between AC line |
||
|
and low voltage circuits. |
||
|
All low voltage circuits connected to an S7-200, such as 24V power, must be supplied from an approved |
||
|
source that provides safe isolation from AC line and other high voltages. Such sources include double |
||
|
insulation as defined in international electrical safety standards and have outputs that are rated as SELV, |
||
|
PELV, Class 2, or Limited Voltage according to various standards. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warning |
|
|
|
Use of non-isolated or single insulation supplies to supply low voltage circuits from an AC line can |
|
|
|
result in hazardous voltages appearing on circuits that are expected to be touch safe, such as |
|
|
|
communications circuits and low voltage sensor wiring. |
|
|
|
Such unexpected high voltages could result in death or serious injury to personnel, and/or damage to |
|
|
|
equipment. |
|
|
|
Only use high voltage to low voltage power converters that are approved as sources of touch safe, |
|
|
|
limited voltage circuits. |
|
|
|
|
|
18
 Loading...
Loading...