Dell T7500 User Manual

Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
Working on Your Computer
Adding and Replacing Parts
Specifications
Diagnostics
About Memory
About Your System Board
System Setup
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of your computer.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates potential damage to hardware or loss of data if instructions are not followed.
WARNING: A WARNING indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury, or death.
If you purchased a Dell™ n Series computer, any references in this document to Microsoft® Windows® operating systems are not applicable.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. © 2009-2010 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of this material in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, and Dell Precision are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel and Xeon are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation; Bluetooth is a registered trademark owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc. and is used by Dell under license; Blu-ray Disc is a trademark of the Blu-ray Disc Association; Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, MS-DOS, Aero, Windows Vista. and the Windows Vista start button are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
Model DCDO
February 2010 |
Rev. A01 |

Working on Your Computer
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
 Before Working Inside Your Computer
Before Working Inside Your Computer
 Recommended Tools
Recommended Tools
 Turning Off Your Computer
Turning Off Your Computer
 After Working Inside Your Computer
After Working Inside Your Computer
Before Working Inside Your Computer
Use the following safety guidelines to help protect your computer from potential damage and to help to ensure your personal safety. Unless otherwise noted, each procedure included in this document assumes that the following conditions exist:
 You have performed the steps in Working on Your Computer.
You have performed the steps in Working on Your Computer.
 You have read the safety information that shipped with your computer.
You have read the safety information that shipped with your computer.
 A component can be replaced or—if purchased separately—installed by performing the removal procedure in reverse order.
A component can be replaced or—if purchased separately—installed by performing the removal procedure in reverse order.
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
CAUTION: Only a certified service technician should perform repairs on your computer. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered by your warranty.
CAUTION: To avoid electrostatic discharge, ground yourself by using a wrist grounding strap or by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface, such as a connector on the back of the computer.
CAUTION: Handle components and cards with care. Do not touch the components or contacts on a card. Hold a card by its edges or by its metal mounting bracket. Hold a component such as a processor by its edges, not by its pins.
CAUTION: When you disconnect a cable, pull on its connector or on its pull-tab, not on the cable itself. Some cables have connectors with locking tabs; if you are disconnecting this type of cable, press in on the locking tabs before you disconnect the cable. As you pull connectors apart, keep them evenly aligned to avoid bending any connector pins. Also, before you connect a cable, ensure that both connectors are correctly oriented and aligned.
NOTE: The color of your computer and certain components may appear differently than shown in this document.
To avoid damaging your computer, perform the following steps before you begin working inside the computer.
1.Ensure that your work surface is flat and clean to prevent the computer cover from being scratched.
2.Turn off your computer (see Turning Off Your Computer).
CAUTION: To disconnect a network cable, first unplug the cable from your computer and then unplug the cable from the network device.
3. Disconnect all network cables from the computer.
5.Disconnect your computer and all attached devices from their electrical outlets.
6.Press and hold the power button while the system is unplugged to ground the system board.
7.Remove the computer cover (see Removing and Replacing the Computer Cover).
CAUTION: Before touching anything inside your computer, ground yourself by touching an unpainted metal surface, such as the metal at the back of the computer. While you work, periodically touch an unpainted metal surface to dissipate static electricity, which could harm internal components.
Recommended Tools
The procedures in this document may require the following tools:
 Small flat-blade screwdriver
Small flat-blade screwdriver

Phillips screwdriver
Small plastic scribe
Flash BIOS update program CD (see the Dell Support website at support.dell.com)
Turning Off Your Computer
CAUTION: To avoid losing data, save and close all open files and exit all open programs before you turn off your computer.
1. Shut down the operating system:
In Windows Vista:
Click Start  , then click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as shown below, and then click Shut Down.
, then click the arrow in the lower-right corner of the Start menu as shown below, and then click Shut Down.
In Windows XP:
Click Start→ Turn Off Computer→ Turn Off.
The computer turns off after the operating system shutdown process is complete.
2.Ensure that the computer and all attached devices are turned off. If your computer and attached devices did not automatically turn off when you shut down your operating system, press and hold the power button for about 6 seconds to turn them off.
After Working Inside Your Computer
After you complete any replacement procedure, ensure you connect any external devices, cards, and cables before turning on your computer.
1.Replace the computer cover (see Removing and Replacing the Cover).
2.Connect any telephone or network cables to your computer.
CAUTION: To connect a network cable, first plug the cable into the network device and then plug it into the computer.
3.Connect your computer and all attached devices to their electrical outlets.
4.Turn on your computer.
5.Verify that the computer works correctly by running the Dell Diagnostics. See Dell Diagnostics.

Adding and Replacing Parts
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
Cover |
Chassis Intrusion Switch |
Battery |
Drives Bezel |
Hard Drive |
Hard-drive Fan |
Hard-drive Cage |
Optical Drive |
Front Fan Assembly |
Rear Fan |
Memory Shroud |
Memory |
Expansion Cards |
Heat Sink and Processor |
Processor Fan |
Dual Processor Riser (Optional) |
Dual Processor Riser Guide |
I/O Panel |
Power Supply |
System Board |
|
|

Specifications
Dell Precision™ T7500/T7500n Service Manual
Processors |
Drives |
System Information |
Connectors |
Memory |
Controls and Lights |
Video |
Power |
Audio |
Physical |
Expansion Bus |
Environmental |
NOTE: Offerings may vary by region. For more information regarding the configuration of
your Tablet-PC, click Start  (or Start in Windows XP)® Help and Support, and then select the option to view information about your Tablet-PC.
(or Start in Windows XP)® Help and Support, and then select the option to view information about your Tablet-PC.
Processor |
|
Processor types |
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5500 |
|
series |
|
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor |
|
5500 series |
System Information |
|
System chipset |
Intel 5500/5520 |
Data bus width |
64 bits |
Memory |
|
Memory module connectors |
Six |
|
Twelve with optional riser |
Memory module capacities |
1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB, 8 GB and 16 GB |
Memory type |
DDR3 1066 MHz SDRAM |
|
DDR3 1333 MHz SDRAM |
|
(DDR3 800 MHz capable) |
Minimum memory |
1 GB |
Maximum memory |
96 GB |
|
192 GB with optional riser |
Video |
|
Video type: |
|
Discrete |
PCI Express 2.0 x16 (2 slots) |
|
NOTE: Support for two full height, full |
|
length graphics cards using the PCIe x16 |
|
graphics card slot. |
Audio |
|
Audio type |
Analog Devices ADI1984A |

Expansion Bus |
|
|
Bus type |
|
PCI Express 2.0 |
|
||
|
|
PCI 2.3 |
|
|
PCI-X 2.0A |
|
|
SATA 1.0 and 2.0 |
|
|
eSATA 2.0 |
|
|
SAS |
|
|
USB 2.0 |
Bus speed
 Two PCI Express 2.0 x16 slots (video)
Two PCI Express 2.0 x16 slots (video)
Connector pins
 Connector data width (maximum)
Connector data width (maximum)
Two PCI Express 2.0 x8 slots (physical x16 connector)
 Connector pins
Connector pins
Connector data width (maximum)
One PCI Express 2.0 x4 slot (physical x16)
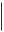 Connector pins
Connector pins
Connector data width (maximum)
 One PCI Slot
One PCI Slot
Connector pins
 Connector data width (maximum) One PCI-X Slot
Connector data width (maximum) One PCI-X Slot
133 MB/s (PCI)
x1-slot bidirectional speed - 500 MB/s (PCI Express)
x16-slot bidirectional speed - 8 GB/s (PCI Express)
1.5 Gbps and 3.0 Gbps (SATA)
480-Mbps high speed, 12-Mbps full speed, 1.2 Mbps
low speed (USB)
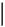 164 pins
164 pins
16 PCI Express lanes (each direction)
 164 pins
164 pins
8 PCI Express lanes (each direction)
 164 pins
164 pins
4 PCI Express lanes (each direction)
 120 pins 32 bits
120 pins 32 bits
Connector pins |
188 pins |
Connector data width (maximum) |
64 bits |
Drives |
|
Externally accessible |
Four 5.25 inch drive bays (can support |
|
3.5 inch flex bay) |
Internally accessible |
Four 3.5 inch drive bays |
Available devices |
Up to three of the following 5.25 inch |
|
devices: SATA DVD ROM, SATA DVD+/- |
|
RW super multi drive/Blu-ray™ drive |
|
One 3.5-inch USB media card reader or |
|
one 3.5 inch Floppy Disk Drive |
|
Up to five 3.5-inch SATA or four SAS |
|
hard drives |
Connectors |
|
External connectors: |
|
Video |
(Depending on video card) |
|
DVI connector |
|
Display port |

Network adapter |
RJ-45 connector |
USB |
USB 2.0 compliant |
|
Two internal connectors |
|
Two in the front |
|
Six in the back |
Serial |
One 9-pin connector; 16550C- |
|
compatible |
Parallel |
One 25-pin connector |
eSATA |
One 7-pin eSATA connector |
Audio |
Stereo support integrated (5.1 channel |
|
support) |
|
NOTE: 5.1 channel support comes from |
|
an add-in card only |
PS/2 |
Two 6-pin mini-DIN connectors |
System board connectors: |
|
Serial ATA |
Three 7-pin SATA connectors |
SAS |
Four 7-pin SAS connectors |
Internal USB device |
Two 10-pin connector (supports two |
|
USB ports) |
Fans: |
|
Hard Disk Drive fan |
One 5-pin connector |
Front fan |
One 7-pin connector |
Rear fan |
One 5-pin connector |
Card cage fan |
One 7-pin connector |
PCI |
One 120-pins connector |
PCI-X |
One 188-pins connector |
PCI Express x16 |
Two 164-pin connectors |
PCI Express x8 |
Two 164-pin connectors (physical x16 |
|
connector) |
PCI Express x4 |
One 164-pin connector |
Front panel control |
One 10-pin connector |
Front panel USB |
One 10-pin connector |
Front panel audio HDA header |
One 10-pin connector |
Processor |
One connector |
|
Second connector on optional riser |
Memory |
Six 240-pin connectors |
|
Six 240-pin connectors on optional riser |
Processor Power |
One 4-pin connector |
|
Second 4-pin connector on optional riser |
Power |
One 24-pin connector |
Controls and Lights |
|
Front of the computer |
|
Power button |
Push button |
Power light |
Amber light — Solid amber indicates a |
|
problem with an installed device; |
|
blinking amber indicates an internal |
|
power problem |
|
Green light — Blinking green in sleep |

Drive activity light
Network link light
 Back of the computer
Back of the computer
Link integrity light (on integrated network adapter)
Network activity light (on integrated network adapter)
 Power
Power
DC power supply:
Wattage
Voltage
 Coin-cell battery
Coin-cell battery
 Physical
Physical
Height
 Width
Width
Depth
 Weight
Weight
 Environmental
Environmental
Temperature range:
Operating
Storage
 Relative humidity (maximum): Maximum vibration
Relative humidity (maximum): Maximum vibration
Operating
Storage
 Maximum shock
Maximum shock
Operating
Storage
 Altitude (maximum):
Altitude (maximum):
 state; solid green for power-on state
state; solid green for power-on state
Green light — A blinking green light indicates the computer is reading data from or writing data to the hard drive or CD/DVD
Green light — Solid green indicates connection to an active network
Off (no light) — System is not connected to a network
Off — The computer is not detecting a physical connection to the network Green — A good connection at 10Mbs exists between the network and the computer
Orange — A good connection at 100Mbs exists between the network and the computer
Yellow — A good connection at 1000Mbs exists between the network and the computer
 Yellow blinking light
Yellow blinking light
 1100 W
1100 W
100–240 VAC, 50–60 Hz, 12.0 A  3V CR2032 lithium coin cell
3V CR2032 lithium coin cell
 56.50 cm (22.25 inches)
56.50 cm (22.25 inches)
21.60 cm (8.50 inches)
 55.30 cm (21.80 inches) at least 24.90 kg (55 lbs)
55.30 cm (21.80 inches) at least 24.90 kg (55 lbs)
 10° to 35°C (50° to 95°F)
10° to 35°C (50° to 95°F)  -40° to 65°C (-40° to 149°F)
-40° to 65°C (-40° to 149°F)  20% to 80% (noncondensing)
20% to 80% (noncondensing)
 5 to 350 Hz at 0.0002 G²/Hz 5 to 350 Hz at 0.0002 G²/Hz
5 to 350 Hz at 0.0002 G²/Hz 5 to 350 Hz at 0.0002 G²/Hz
40 G +/- 5% with pulse duration of 2 msec +/- 10% (equivalent to 51 cm/sec [20 in/sec])
105 G +/- 5% with pulse duration of 2 msec +/- 10% (equivalent to 127 cm/sec [50 in/sec])

Operating |
-15.2 to 3048 m (-50 to 10,000 ft) |
Storage |
-15.2 to 10,668 m (-50 to 35,000 ft) |
Airborne contaminant level |
G2 or lower as defined by ISA-S71.04- |
|
1985 |

Diagnostics
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
 Dell Diagnostics
Dell Diagnostics
 Power Button Light Codes
Power Button Light Codes
 Diagnostic Light Codes
Diagnostic Light Codes
 Pre-POST Diagnostic Light Patterns
Pre-POST Diagnostic Light Patterns
 POST Diagnostic Light Patterns
POST Diagnostic Light Patterns
 Beep Codes
Beep Codes
Dell Diagnostics
When to Use the Dell Diagnostics
It is recommended that you print these procedures before you begin.
NOTE: The Dell Diagnostics software works only on Dell computers.
NOTE: The Drivers and Utilities disc is optional and may not ship with your computer.
Enter system setup (see Entering System Setup), review your computer's configuration information, and ensure that the device you want to test displays in System Setup and is active.
Start the Dell Diagnostics from either your hard drive or from the Drivers and Utilities disc.
Starting the Dell Diagnostics From Your Hard Drive
1.Turn on (or restart) your computer.
2.When the DELL logo appears, press <F12> immediately.
NOTE: If you see a message stating that no diagnostics utility partition has been found, run the Dell Diagnostics from your Drivers and Utilities disc.
If you wait too long and the operating system logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Microsoft® Windows® desktop. Then shut down your computer (see Turning Off Your Computer), and try again.
3.When the boot device list appears, highlight Boot to Utility Partition and press <Enter>.
4.When the Dell Diagnostics Main Menu appears, select the test that you want to run.
Starting the Dell Diagnostics From the Drivers and Utilities Disc
1.Insert the Drivers and Utilities disc.
2.Shut down and restart the computer.
When the DELL logo appears, press <F12> immediately.
If you wait too long and the Windows logo appears, continue to wait until you see the Windows desktop. Then shut down your computer and try again.
NOTE: The next steps change the boot sequence for one time only. On the next startup, the computer boots according to the devices specified in the system setup program.
3.When the boot device list appears, highlight Onboard or USB CD-ROM Drive and press <Enter>.
4.Select the Boot from CD-ROM option from the menu that appears and press <Enter>.
5.Type 1 to start the menu and press <Enter> to proceed.

6.Select Run the 32 Bit Dell Diagnostics from the numbered list. If multiple versions are listed, select the version appropriate for your computer.
7.When the Dell Diagnostics Main Menu appears, select the test you want to run.
Dell Diagnostics Main Menu
1. After the Dell Diagnostics loads and the Main Menu screen appears, click the button for the option you want.
Option |
Function |
Express |
Performs a quick test of devices. This test typically takes 10 to 20 minutes and requires no interaction on |
Test |
your part. Run Express Test first to increase the possibility of tracing the problem quickly. |
Extended |
Performs a thorough check of devices. This test typically takes 1 hour or more and requires you to answer |
Test |
questions periodically. |
Custom |
Tests a specific device. You can customize the tests you want to run. |
Test |
|
Symptom |
Lists the most common symptoms encountered and allows you to select a test based on the symptom of the |
Tree |
problem you are having. |
2.If a problem is encountered during a test, a message appears with an error code and a description of the problem. Write down the error code and problem description and follow the instructions on the screen.
3.If you run a test from the Custom Test or Symptom Tree option, click the applicable tab described in the following table for more information.
Tab |
Function |
Results |
Displays the results of the test and any error conditions encountered. |
Errors |
Displays error conditions encountered, error codes, and the problem description. |
Help |
Describes the test and may indicate requirements for running the test. |
Configuration Displays your hardware configuration for the selected device.
The Dell Diagnostics obtains configuration information for all devices from system setup, memory, and various internal tests, and it displays the information in the device list in the left pane of the screen. The device list may not display the names of all the components installed on your computer or all devices attached to your computer.
Parameters |
Allows you to customize the test by changing the test settings. |
4.When the tests are completed, if you are running the Dell Diagnostics from the Drivers and Utilities disc, remove the disc.
5.Close the test screen to return to the Main Menu screen. To exit the Dell Diagnostics and restart the computer, close the Main Menu screen.
Power Button Light Codes
The diagnostic lights give much more information about the system state, but legacy power light states are also supported in your computer. The power light states are shown in following table.
Power
Light
State
Off
Blinking
Amber
Solid
Amber
Description
Power is off, light is blank.
Initial state of light at power up.
Indicates system has power, but the POWER_GOOD signal is not yet active.
If the Hard Drive light is off, it is probable that the power supply needs to be replaced.
If the Hard Drive light on, it is probable that an onboard regulator or VRM has failed. Look at the diagnostic lights for further information.
 Second state of the light at power up. Indicates the POWER_GOOD signal is active and it is probable that
Second state of the light at power up. Indicates the POWER_GOOD signal is active and it is probable that

|
the power supply is fine. Look at the diagnostic lights for further information. |
Blinking |
|
|
|
Green |
System is in a low power state, either S1 or S3. Look at the diagnostic lights to determine which state the |
|
system is in. |
Solid |
|
Green |
System is in S0 state, the normal power state of a functioning machine. |
|
The BIOS will turn the light to this state to indicate it has started fetching opcodes. |
Diagnostic Light Codes
Four (4) single color lights are incorporated on the front control panel to serve as a diagnostic aid for troubleshooting systems exhibiting No Post/No Video symptoms. The lights do NOT report runtime errors.
Each light has two possible states of OFF or ON. The most significant bit is labeled with the number 1, and the other three are labeled 2, 3, and 4, as you go down or across the LED stack. The normal operating condition after POST is for all four lights to be ON and then turn off as the BIOS hands over control to the operating system.
Pre-POST Diagnostic Light Patterns
 State
State 
Pb0a
Pb0b
Pb0c
Pb1
Pb2
Pb3
Pb4
Pb5
Light Pattern |
Light |
Power |
State |
( 1 2 3 4 ) |
Description |
Light |
Assignment |
|
1- Off |
|
System |
|
2- Off |
|
|
|
3- Off |
|
Unplugged |
|
4- Off |
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
ACPI S0; |
|
2- Off |
|
|
|
|
Normal |
|
|
3- Off |
|
|
|
|
Operation |
|
|
4- Off |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
|
|
2- Off |
|
ACPI S1 |
|
3- Off |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4- Off |
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
ACPI S4 or |
|
2- Off |
|
|
|
3- Off |
|
S5 |
|
4- Off |
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
|
|
2- Off |
- |
Reserved |
|
3- Solid |
||
|
|
|
|
|
4- Off |
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
|
|
2- Off |
|
ACPI S3 |
|
3- Solid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4- Solid |
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
|
|
2- Green |
- |
Reserved |
|
3- Off |
||
|
|
|
|
|
4- Off |
|
|
|
1- Off |
|
|
|
2- Green |
- |
Reserved |
|
3- Off |
||
|
|
|
|
|
4- Green |
|
|
State Description
System is not plugged into AC, PSU is not plugged into system board, or control panel not connected to system board.
System is on with no failures detected. This is actually a BIOS controlled state and is also S0e.
Windows Standby State.
Hibernate or Soft off. System plugged in, but either turned off or in Windows Hibernation State.
Reserved
Suspend to RAM Windows Standby State.
Reserved
Reserved

Pb6
Pb7
Pb8
Pb9
Pb10
Pb11
Pb12
Pb13
Pb14
Pb15
1- Off
2- Green
3- Green
4- Off
1- Off
2- Blink
3- Blink
4- Blink
1- Green
2- Off
3- Off
4- Off
1- Blink
2- Off
3- Off
4- Blink
1- Blink
2- Off
3- Blink
4- Off
1- Blink
2- Off
3- Blink
4- Blink
1- Blink
2- Blink
3- Off
4- Off
1- Blink
2- Blink
3- Off
4- Blink
1- Green
2- Green
3- Green
4- Off
1- Green
2- Green
3- Green
4- Green
-Reserved Reserved
ACPI S0, |
System on. BIOS not execution. This is the transition |
|
hand off to |
||
state to POST states. |
||
BIOS control |
-Reserved
Non-System board Regulator Failure
PSU Failure
PSU Cable
Failure
System board Regulator Failure
Mismatch
-Reserved
-Reserved
Reserved
A power failure has been detected on a plug-in component such as VRM, Video Riser, or Memory Riser.
PSU may be bad or PSU cable may be crimped creating a short on a main power rail. (PS_ON asserted, PS_PWRGOOD not asserted)
All PSU cables may not be properly connected to system board. (PS_ON asserted, missing a main power rail)
A power failure has been detected in one of the onboard system board regulators. This could be caused by a failed system board component or by a plug-in device creating a short on a regulated power rail. (PS_ON asserted, PS_PWRGOOD asserted, SYS_PWRGOOD de-asserted)
Hardware detected a population incompatibility with a critical system component such as CPU, VRM, PSU, or MEMORY RISER.
Reserved
Reserved
POST Diagnostic Light Patterns
All POST codes except S0 are accompanied by a Solid Green Power light state. If the power light is not green, see PrePOST Diagnostic Light Patterns.
State |
Light Pattern |
Light |
State |
State |
State Description |
|
( 1 2 3 4 ) |
Description Name Assignment |
|||||
|
|
|||||
1- Off
S0a 2- Off OFF OFF Power light Off. No power is supplied to the system. 3- Off
4- Off
S0e
S1
1- Off |
|
Normal |
|
2- Off |
|
||
ON |
Operation, |
||
3- Off |
|||
|
ACPI S0 |
||
4- Off |
|
||
|
|
||
1- Off |
|
System is in |
|
2- Off |
|
||
RCM |
Recovery |
||
3- Off |
|||
|
Mode |
||
4- Solid |
|
||
|
|
||
1- Off |
|
|
|
2- Off |
|
|
Power light Solid Green. System has successfully booted and is operating normally.
BIOS checksum failure was detected and the system is now in recovery mode.
 CPU configuration activity is in progress or a CPU
CPU configuration activity is in progress or a CPU

S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
S9
S10
S11
S12
S13
S14
S15
3- Solid
4- Off
1- Off
2- Off
3- Solid
4- Solid
1- Off
2- Solid
3- Off
4- Off
1- Off
2- Solid
3- Off
4- Solid
1- Off
2- Solid
3- Solid
4- Off
1- Off
2- Solid
3- Solid
4- Solid
1- Solid
2- Off
3- Off
4- Off
1- Solid
2- Off
3- Off
4- Solid
1- Solid
2- Off
3- Solid
4- Off
1- Solid
2- Off
3- Solid
4- Solid
1- Solid
2- Solid
3- Off
4- Off
1- Solid
2- Solid
3- Off
4- Solid
1- Solid
2- Solid
3- Solid
4- Off
1- Solid
2- Solid
3- Solid
4- Solid
CPU
MEM
PCI
VID
STO
USB
MEM
MBF
MEM
PRV
CFG
POV
STD
CPU
Memory
PCI device
Video Card
Storage
USB
Memory
System board
Memory
Other prevideo activity
Resource configuration
Reserved
Other postvideo activity
Boot hand off
failure was detected.
Memory subsystem configuration activity is in progress. Appropriate memory modules were detected but a memory failure has occurred.
PCI device configuration activity is in progress or PCI device failure was detected.
Video subsystem configuration activity in progress or video subsystem failure.
Storage device configuration in progress or storage subsystem failure.
USB subsystem configuration activity in progress or USB subsystem failure.
Memory subsystem configuration activity is in progress. No memory modules were detected.
Fatal system board failure detected.
Memory subsystem configuration activity is in progress. Memory modules have been detected but appear to be incompatible or in an invalid configuration.
Indicates routine system activity preceding video initialization.
System resource configuration in progress.
Reserved for future use. This pattern is being considered to indicate the Visual Off state on the Dimension systems.
Indicates routine system activity subsequent to video initialization.
Indicates End of POST process. Lights are normally in this state briefly as POST completes. Once the hand-off to the OS is done, the lights turn off and transition to S0e state.
Beep Codes
When errors occur during a boot routine that cannot be reported on the monitor, the computer may emit a beep code that identifies the problem. The beep code is a pattern of sounds: for example, one beep followed by a second beep, then followed by a burst of three beeps (code 1-1-3) means that the computer was unable to read the data in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM). If the system loses power and beeps constantly when you turn it back on, the BIOS is probably corrupted.

|
System Beep Codes |
|||
Beep |
Description |
Beep |
Description |
|
Code |
Code |
|||
|
|
|||
1-1-2 |
CPU register test in progress |
2-4-3 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit E |
||
1-1-3 CMOS read/write test in progress or failure |
2-4-4 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit F |
|||
1-1-4 BIOS ROM checksum in progress or failure |
3-1-1 Slave DMA register test in progress or failure |
|||
1-2-1 Timer Test in progress or failure |
3-1-2 Master DMA register test in progress or failure |
|||
1-2-2 |
DMA initialization in progress or failure |
3-1-3 |
Master IMR test in progress or failure |
|
1-2-3 |
DMA page register read/write test in progress |
3-1-4 |
Slave IMR test in progress or failure |
|
or failure |
||||
|
|
|
||
1-3-1 RAM refresh verification in progress or failure |
3-2-2 Interrupt vector loading in progress |
|||
1-3-2 |
1st 64 K RAM test in progress or failure |
3-2-4 |
Keyboard controller test in progress or failure |
|
1-3-3 |
1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure (multi |
3-3-1 |
CMOS power fail and checksum test in progress |
|
bit) |
||||
|
|
|
||
1-3-4 1st 64 K RAM odd/even logic failure |
3-3-2 CMOS Config info validation in progress |
|||
1-4-1 1st 64 K RAM address line failure |
3-3-3 |
RTC/Keyboard controller not found |
||
1-4-2 1st 64 K RAM parity test in progress or failure |
3-3-4 Screen memory test in progress or failure |
|||
1-4-3 Fail-safe timer test in progress |
3-4-1 Screen initialization test in progress or failure |
|||
1-4-4 |
Software NMI port test in progress |
3-4-2 Screen retrace tests test in progress or failure |
||
2-1-1 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 0 |
3-4-3 Search for video ROM in progress |
|||
2-1-2 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 1 |
4-2-1 Timer tick interrupt test in progress or failure |
|||
2-1-3 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 2 |
4-2-2 Shutdown test in progress or failure |
|||
2-1-4 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 3 |
4-2-3 |
Gate A20 failure |
||
2-2-1 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 4 |
4-2-4 |
Unexpected interrupt in Protected Mode |
||
2-2-2 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 5 |
4-3-1 |
RAM test in progress or failure above address |
||
0FFFFh |
||||
|
|
|
||
2-2-3 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 6 |
4-3-2 |
No memory in Bank 0 |
||
2-2-4 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 7 |
4-3-3 |
Interval Timer Channel 2 test in progress or |
||
failure |
||||
|
|
|
||
2-3-1 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 8 |
4-3-4 Time-Of-Day Clock test in progress or failure |
|||
2-3-2 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit 9 |
4-4-1 |
Super I/O chip failure |
||
2-3-3 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit A |
4-4-4 |
Cache test failure |
||
2-3-4 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit B |
|
|
||
2-4-1 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit C |
|
|
||
2-4-2 1st 64 K RAM chip or data line failure - bit D |
|
|
||

About Memory
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
 Memory Modules
Memory Modules
 Supported Memory Configurations
Supported Memory Configurations
 Memory Subsystem
Memory Subsystem
 Memory Slots
Memory Slots
 Memory Population Rules
Memory Population Rules
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Your computer uses 1066 MHz and 1333Mhz DDR3 unbuffered or registered ECC SDRAM memory. DDR3 SDRAM, or double-data- rate three synchronous dynamic random access memory, is a random access memory technology. It is a part of the SDRAM family of technologies, which is one of many DRAM (dynamic random access memory) implementations, and is an evolutionary improvement over its predecessor, DDR2 SDRAM.
The primary benefit of DDR3 SDRAM is its ability to run its I/O bus at four times the speed of the memory cells it contains, thus enabling faster bus speeds and higher peak throughputs than earlier technologies. This is achieved at the cost of higher latency. Also, the DDR3 standard allows for chip capacities of 512 megabit to 8 gigabit, effectively enabling memory modules of maximum 16 gigabyte in size.
DDR3 memory comes with a promise of a power consumption reduction of 30% compared to current commercial DDR2 modules due to DDR3’s 1.5 V supply voltage. This supply voltage works well with the 90 nm fabrication technology used for most DDR3 chips. Some manufacturers further propose to use "dual-gate" transistors to reduce leakage of current.
The main benefit of DDR3 comes from the higher bandwidth made possible by DDR3’s 8 bit deep prefetch buffer, whereas DDR2’s is 4 bits, and DDR’s is 2 bits deep.
Memory Modules
Standard |
Memory |
Cycle |
I/O Bus |
Data transfers per |
Module |
Peak transfer |
||
name |
|
clock |
time |
|
clock |
second |
name |
rate |
DDR3-1066 |
133 |
MHz |
7.5 ns |
533 |
MHz |
1066 Million |
PC3-8500 |
8533 MB/s |
DDR3-1333 |
166 |
MHz |
6 ns |
667 |
MHz |
1333 Million |
PC3-10600 |
10667 MB/s |
Supported Memory Configurations
Single Processor Memory Configurations
Size DIMM DIMM1 DIMM2 DIMM3 DIMM4 DIMM5 DIMM6
(GB) Ranks
3 |
SR |
1 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
4 |
SR |
1 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
4 |
MR |
2 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
6 |
SR |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
|
|
|
8 |
MR |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
12 |
SR |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
12 |
DR |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
|
|
|
24 |
DR |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
24 |
DR |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
|
|
|
32 |
MR |
8 GB |
8 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
48 |
DR |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
96 |
QR |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |

|
|
|
|
|
Dual Processor Memory Configurations |
|
|
|
|
||||
Size |
DIMM |
MB |
MB |
MB |
MB |
MB |
MB |
Riser |
Riser |
Riser |
Riser |
Riser |
Riser |
(GB) |
Ranks |
DIMM1 |
DIMM2 |
DIMM3 |
DIMM4 |
DIMM5 |
DIMM6 |
DIMM1 |
DIMM2 |
DIMM3 |
DIMM4 |
DIMM5 |
DIMM6 |
3 |
SR |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
|
1 GB |
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
SR |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
|
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
|
6 |
SR |
1 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
1 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
8 |
MR |
2 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
2 GB |
1 GB |
1 GB |
|
|
|
12 |
SR |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
|
|
|
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
|
|
|
24 |
DR |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
|
|
|
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
|
|
|
24 |
SR |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
2 GB |
48 |
DR |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
|
|
|
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
|
|
|
48 |
DR |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
4 GB |
96 |
DR |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
128 |
MR |
16 GB |
16 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
8 GB |
|
QR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
192 |
(RHEL |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
16 GB |
|
ONLY) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: If more than one Quad rank DIMM is installed within a channel (DIMM1 & DIMM4, DIMM2 & DIMM5, DIMM3 & DIMM6) then the maximum DDR3 speed is reduced to 800 MHz. Spreading Quad Rank memory modules accross multiple channels is recommended.
NOTE: DDR3 DIMMs have 240 pins, the same number as DDR2, and are the same size, but are electrically incompatible and have a different key notch location.
Memory Subsystem
The memory subsystem consists of three DDR3 memory channels attached to each processor. All single-processor configurations have six DIMM slots (two per channel) attached to the primary processor located on the system board. Dual-processor configurations require an optional riser card that contains the secondary processor and the DIMMs associated with the secondary processor. There are six DIMM slots on the riser, for a total of twelve DIMMs in the system.
DIMM slot configuration for a single processor or a second processor on the riser.
Memory Slots
There are six memory slots on the system board. The slots are numbered DIMM1 through DIMM6. DIMM1 is furthest from the processor.

In addition, the dual-processor riser features six additional memory slots. The slots are numbered DIMM1 through DIMM6. DIMM1 is furthest from the processor.
Memory Population Rules
Your computer requires DIMMs within a channel to be populated starting with the DIMMs farthest from the processor first. This means the DIMM slots 1, 2 and 3 must be populated before DIMM slots 4, 5 and 6. In addition, when populating a Quad-rank DIMM with a Singleor Dual-rank DIMM in the same channel, the Quad-rank DIMM must be populated farthest from the CPU.
To maximize available memory bandwidth, DIMMs within a configuration should generally be spread across as many channels as possible before populating multiple DIMMs per channel. The population guidelines below help to achieve this.
Single CPU configurations (6 DIMM slots on MB)
If configuration contains DIMMs of all the same size, populate in the following order: DIMM1, DIMM2, DIMM3, DIMM4, DIMM5, DIMM6
If configuration contains DIMMs of mixed sizes, populate the larger DIMMs first. For example, for a 4GB configuration consisting of one 2GB DIMM and two 1GB DIMMs, the population would be DIMM1=2GB, DIMM2=1GB, DIMM3=1GB, DIMM4=empty, DIMM5=empty, DIMM6=empty.
Dual CPU configurations (6 DIMM slots on MB plus 6 DIMM slots on Riser)
If configuration contains DIMMs of all the same size, populate in the following order: MB_DIMM1, Riser_DIMM1, MB_DIMM2, Riser_DIMM2, MB_DIMM3, Riser_DIMM3, MB_DIMM4, Riser_DIMM4, MB_DIMM5, Riser_DIMM5, MB_DIMM6, Riser_DIMM6. If configuration contains DIMMs of mixed sizes, populate the larger DIMMs in the dual-processor riser.

NOTE: If any DIMMs are >30mm tall (possible early 16GB DIMMs), they must be installed on the system board only.

About Your System Board
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
 System Board Schematic
System Board Schematic
 Clearing Forgotten Passwords
Clearing Forgotten Passwords
 Clearing CMOS Settings
Clearing CMOS Settings
System Board Schematic
1SATA Connectors (SATA0-3)
2 Main Power Connector (POWER1)
Main Power Connector (POWER1)
3 SAS Connectors (HDD0-3)
SAS Connectors (HDD0-3)
4Hard Drive Fan Connector (FAN_HDD)
18Front Panel Audio Connector (FP_AUDIO)
 19
19  Type A USB Port (INT_USB2)
Type A USB Port (INT_USB2)
20 Rear Fan Connector (FAN_REAR)
21 CPU Riser 2 (CPU2_RSR2)

5  Password Jumper (PSWD)
Password Jumper (PSWD)
6Hard Drive Fan Connector (FAN_HDD2)
7  Floppy Drive (DSKT)
Floppy Drive (DSKT)
8 Front Panel Connector (FRONTPANEL)
9Front Panel 1394 Connector (FP_1394)
10Chassis Intrusion Header (INTRUDER)
11PCI-X Card Slot (SLOT7)
12PCI Express 2.0 x16 Card Slot, wired as x4 (SLOT6)
 13
13  PCI Card Slot (SLOT5)
PCI Card Slot (SLOT5)
14PCI Express 2.0 x16 Card Slot (SLOT4)
15PCI Express 2.0 x16 Card Slot, wired as x8 (SLOT3)
16PCI Express 2.0 x16 Card Slot (SLOT2)
 22
22  CPU Riser 1 (CPU_RSR1)
CPU Riser 1 (CPU_RSR1)
23 Primary Processor Connector (CPU1)
 24
24  Power Connector (POWER_CPU1)
Power Connector (POWER_CPU1)
25 Front Fan Connector (FAN_FRONT)
26Card Cage Fan (FAN_CCAG)
27Memory Module Connectors (DIMM1-6)
28Optional Serial/PS2 Connector (SERIAL2)
29Auxiliary Hard-drive LED Connector (AUX_LED)
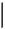 30
30  Battery Socket (BATTERY)
Battery Socket (BATTERY)
31Internal Speaker Connector (INT_SPKR)
32Flexbay USB (INT_USB)
33RTC Reset Jumper (RTCRST)
17PCI Express 2.0 x16 Card Slot, wired as x8 (SLOT1)
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Clearing Forgotten Passwords
1.Remove the computer cover.
2.Locate the 4-pin password connector (PSWD) on the system board.
3.Remove the 2-pin jumper plug from pins 3 and 4 and set the jumper plug aside.
4.Replace the computer cover.
5.Connect your keyboard and mouse, then connect your computer and monitor to electrical outlets and turn them on.
6.After the operating system loads, turn the computer off.
Ensure that the computer is off and not in a power management mode. If you cannot shut down the computer using the operating system, press and hold the power button for 4 seconds.
NOTE: Ensure that the computer is off and not in a power management mode. If you cannot shut down the computer using the operating system, press and hold the power button for 6 seconds.
7.Disconnect the keyboard and mouse, then disconnect the computer and monitor from their electrical outlets.
8.Press the power button on the computer to ground the system board.
9.Remove the computer cover.
10.Replace the 2-pin jumper plug onto pins 3 and 4 of the password connector (RTCRST_PSWD) on the system board.
NOTE: The password jumper plug must be reinstalled on the password jumper pins in order to enable the password feature.
11. Connect your computer and devices to electrical outlets, and then turn them on.
NOTE: In System Setup, both system and administrator password options appear as Not Set. The password feature is enabled, but a password is not assigned.
Clearing CMOS Settings

WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
NOTE: The computer must be disconnected from the electrical outlet to clear the CMOS setting.
1.Remove the computer cover.
2.Locate the 4-pin password connector (PSWD) on the system board.
3.Remove the 2-pin jumper plug from pins 3 and 4.
4.Locate the 4-pin CMOS jumper (RTCRST) on the system board.
5.Move the 2-pin jumper plug from the password jumper to pins 1 and 2 of the CMOS jumper.
6.Plug in AC power to the system and wait ten seconds for the CMOS to clear.
7.Move the 2-pin jumper plug back to pins 3 and 4 of the password jumper.
8.Replace the computer cover.
9.Connect your computer and devices to electrical outlets, and turn them on.
NOTE: You can use the RTCRST jumper procedure above to attempt recovery from a No POST, No Video situation.

System Setup
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
 POST Keystrokes
POST Keystrokes
 Boot Menu
Boot Menu
 Entering System Setup
Entering System Setup
 System Setup Navigation Keystrokes
System Setup Navigation Keystrokes
POST Keystrokes
Your computer has several keystroke options available during the POST process at the Dell™ Logo screen.
Keystroke |
Function |
Description |
< F2> |
Enter System |
|
Setup |
||
|
||
< F12> or |
Enter Boot Menu |
|
<Ctrl><Alt><F8> |
||
< F3> |
Network Boot |
Use System Setup to make changes to the user-definable settings.
One-time boot and diagnostics utility menu
 Bypass the BIOS boot sequence and boot directly to the network
Bypass the BIOS boot sequence and boot directly to the network
Boot Menu
As with previous Dell Precision™ workstation platforms, your computer includes a one-time boot menu. This feature offers a quick and convenient method with which to bypass the System Setup-defined boot device order and boot directly to a specific device (e.g., floppy, CD-ROM, or hard drive).
The boot menu enhancements introduced on previous platforms are as follows:
 Easier access—Although the <Ctrl><Alt><F8> keystroke still exists and can be used to call up the menu, you can also simply press <F12> during system boot to access the menu.
Easier access—Although the <Ctrl><Alt><F8> keystroke still exists and can be used to call up the menu, you can also simply press <F12> during system boot to access the menu.
 Diagnostics options—The boot menu includes two diagnostic options, IDE Drive Diagnostics (90/90 Hard Drive Diagnostics) and Boot to the Utility Partition.
Diagnostics options—The boot menu includes two diagnostic options, IDE Drive Diagnostics (90/90 Hard Drive Diagnostics) and Boot to the Utility Partition.
Entering System Setup
Press <F2> to enter System Setup and change the user-definable settings. If you have trouble entering System Setup using this key, press <F2> when the keyboard LEDs first flash.
Follow the on-screen instructions to view and/or change any settings. On each screen, the system setup options are listed at the left. To the right of each option is the setting or value for that option. You can change settings that appear as white type on the screen. Options or values that you cannot change (because they are determined by your Tablet-PC) appear less bright.
The upper-right corner of the screen displays help information for the currently highlighted option. The lower-right corner displays information about the computer. System setup key functions are listed across the bottom of the screen.

The system setup screens display the current setup information and settings for your computer, such as:
System configuration
Boot order
Boot (start-up) configuration
Basic device configuration settings
System security and hard drive password settings
System Setup Navigation Keystrokes
Use the following keystrokes to navigate the BIOS screens.
|
Navigation Keystrokes |
Action |
Keystroke |
Expand and collapse field |
<Enter>, leftand right-arrow keys, or +/– |
Expand or collapse all fields |
< > |
Exit BIOS |
<Esc>—Remain in Setup, Save/Exit, Discard/Exit |
Change a setting |
Leftand right-arrow keys |
Select field to change |
<Enter> |
Cancel a modification |
<Esc> |
Reset defaults |
<Alt><F> or Load Defaults menu option |
NOTE: Depending on your computer and any installed devices, the items listed in this section may or may not appear.

Cover
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Removing the Cover
1. Follow the procedures in Before Working Inside Your Computer.
2. Slide the cover release latch toward the back of the computer.

3. Pull the cover away from the computer.
4. Remove the cover from the computer.


Battery
Dell Precision™ T7500 Service Manual
WARNING: Before working inside your computer, read the safety information that shipped with your computer. For additional safety best practices information, see the Regulatory Compliance Homepage at www.dell.com/regulatory_compliance.
Removing the Battery
1.Follow the procedures in Before Working Inside Your Computer.
2.Remove the computer cover.
3.Remove the memory shroud.
4. Use a small screw driver or a scribe to press the coin-cell release tab.
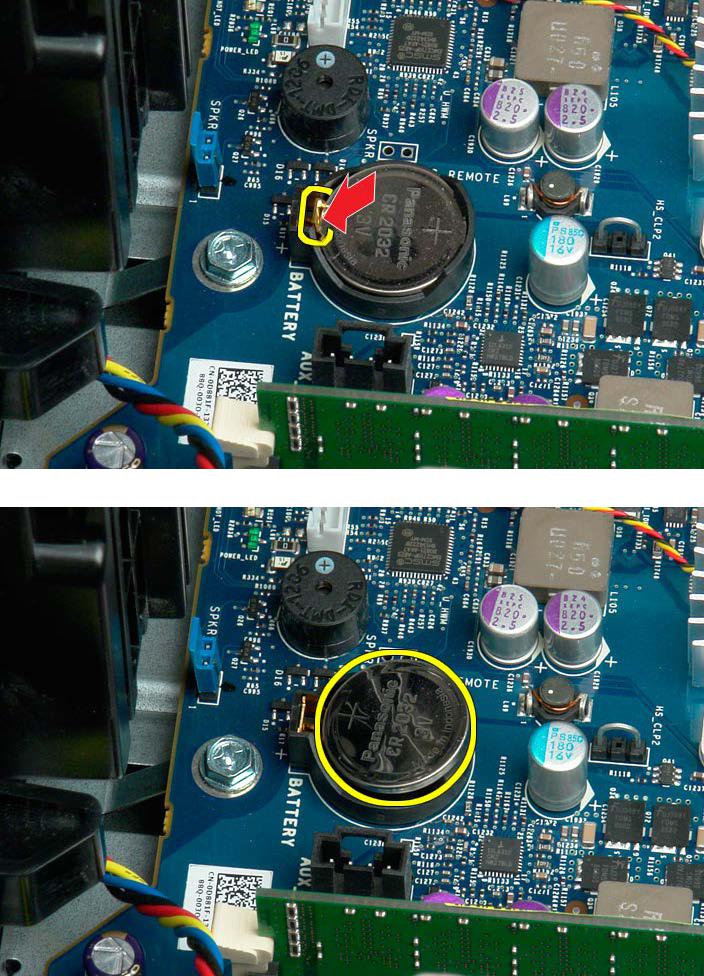
5. Remove the coin-cell battery from the computer.

 Loading...
Loading...