Motorola SN54LS196J, SN54LS197J, SN74LS196N, SN74LS197D, SN74LS197N Datasheet

SN54/74LS196
4-STAGE PRESETTABLE SN54/74LS197 RIPPLE COUNTERS
The SN54/74LS196 decade counter is partitioned into divide-by-two and di- vide-by-five sections which can be combined to count either in BCD (8, 4, 2, 1) sequence or in a bi-quinary mode producing a 50% duty cycle output. The SN54/74LS197 contains divide-by-two and divide-by-eight sections which can be combined to form a modulo-16 binary counter. Low Power Schottky technology is used to achieve typical count rates of 70 MHz and power dissipation of only 80 mW.
Both circuit types have a Master Reset (MR) input which overrides all other inputs and asynchronously forces all outputs LOW. A Parallel Load input (PL) overrides clocked operations and asynchronously loads the data on the Parallel Data inputs (Pn) into the flip-flops. This preset feature makes the circuits usable as programmable counters. The circuits can also be used as 4-bit latches, loading data from the Parallel Data inputs when PL is LOW and storing the data when PL is HIGH.
•Low Power Consumption Ð Typically 80 mW
•High Counting Rates Ð Typically 70 MHz
•Choice of Counting Modes Ð BCD, Bi-Quinary, Binary
•Asynchronous Presettable
•Asynchronous Master Reset
•Easy Multistage Cascading
•Input Clamp Diodes Limit High Speed Termination Effects
CONNECTION DIAGRAM DIP (TOP VIEW)
VCC |
|
MR |
|
Q3 |
|
P3 |
|
P1 |
|
Q1 |
|
CP0 |
||
|
14 |
|
13 |
|
12 |
|
11 |
|
10 |
|
9 |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE:
The Flatpak version has the same pinouts
(Connection Diagram) as the Dual In-Line Package.
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PL |
|
Q2 |
|
P2 |
|
P0 |
|
Q0 |
CP1 |
GND |
|||||
4-STAGE PRESETTABLE RIPPLE COUNTERS
LOW POWER SCHOTTKY
|
|
|
J SUFFIX |
|
|
|
CERAMIC |
|
|
|
CASE 632-08 |
14 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N SUFFIX |
|
|
|
PLASTIC |
14 |
|
|
CASE 646-06 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
D SUFFIX |
|
14 |
|
SOIC |
|
|
CASE 751A-02 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
ORDERING INFORMATION
SN54LSXXXJ Ceramic
SN74LSXXXN Plastic
SN74LSXXXD SOIC
PIN NAMES |
|
LOADING (Note a) |
|
|
|
|
LOGIC SYMBOL |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
HIGH |
LOW |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
4 |
10 |
3 |
11 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
CP0 |
Clock (Active LOW Going Edge) |
1.0 |
U.L. |
1.5 |
U.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
Input to Divide-by-Two Section |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
PL |
P0 |
P1 P2 P3 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
CP1 (LS196) |
Clock (Active LOW Going Edge) |
2.0 |
U.L. |
1.75 |
U.L. |
|
|
|
CP0 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Input to Divide-by-Five Section |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
CP1 MR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CP1 (LS197) |
Clock (Active LOW Going Edge) |
1.0 |
U.L. |
0.8 |
U.L. |
|
|
|
Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Input to Divide-by-Eight Section |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MR |
Master Reset (Active LOW) Input |
1.0 |
U.L. |
0.5 |
U.L. |
|
|
|
|
13 |
5 |
9 |
2 |
12 |
|
|||||||
PL |
Parallel Load (Active LOW) Input |
0.5 |
U.L. |
0.25 |
U.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
P0±P3 |
Data Inputs |
0.5 |
U.L. |
0.25 |
U.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
VCC = PIN 14 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
GND |
= |
PIN |
|
|
7 |
|
|
||||||||||
Q0±Q3 |
Outputs (Notes b, c) |
10 |
U.L. |
5 (2.5) |
U.L. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
NOTES:
a.1 TTL Unit Load (U.L.) = 40μA HIGH/1.6 mA LOW.
b.The Output LOW drive factor is 2.5 U.L. for Military (54) and 5 U.L. for Commercial (74)
b.Temperature Ranges.
c.In addition to loading shown, Q0 can also drive CP1.
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
5-372
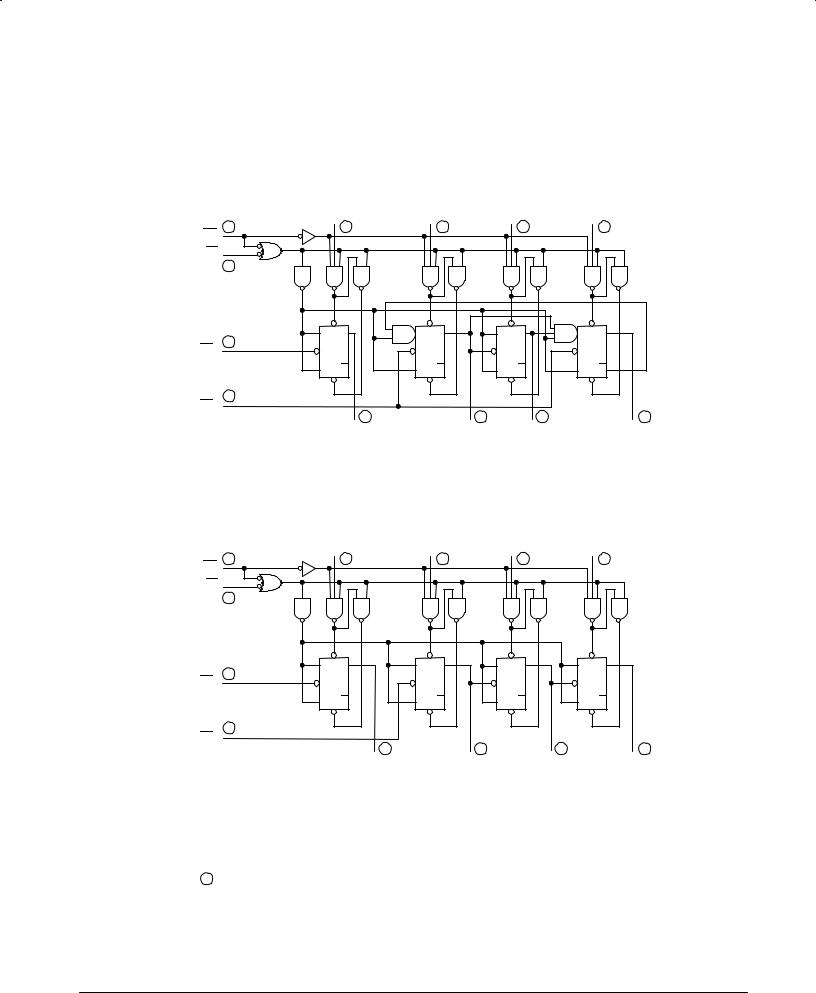
SN54/74LS196 •SN54/74LS197
LOGIC DIAGRAM
|
P0 |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
13 |
4 |
10 |
3 |
11 |
MR |
|
|
|
|
PL |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
J SD Q |
J SD Q |
J SD Q |
J SD Q |
CP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
KCD Q |
KCD Q |
KCD Q |
KCD Q |
6 |
|
|
|
|
CP1 |
5 |
9 |
|
2 |
Q0 |
Q1 |
Q2 |
LS196
|
P0 |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
13 |
4 |
10 |
3 |
11 |
MR |
|
|
|
|
PL |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
J SD Q |
J SD Q |
J SD Q |
J SD Q |
CP0 |
|
|
|
|
|
KCD Q |
KCD Q |
KCD Q |
KCD Q |
6 |
|
|
|
|
CP1 |
5 |
9 |
|
2 |
Q0 |
Q1 |
Q2 |
LS197
VCC = PIN 14
GND = PIN 7
= PIN NUMBERS
12 Q3
12 Q3
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
5-373

SN54/74LS196 •SN54/74LS197
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The LS196 and LS197 are asynchronously presettable decade and binary ripple counters. The LS196 Decade Counter is partitioned into divide-by-two and divide-by-five sections while the LS197 is partitioned into divide-by-two and divide- by-eight sections, with all sections having a separate Clock input. In the counting modes, state changes are initiated by the HIGH to LOW transition of the clock signals. State changes of the Q outputs, however, do not occur simultaneously because of the internal ripple delays. When using external logic to decode the Q outputs, designers should bear in mind that the unequal delays can lead to decoding spikes and thus a decoded signal should not be used as a clock or strobe. The CP0 input serves the Q0 flip-flop in both circuit types while the CP1 input serves the divide-by-five or divide-by-eight section. The Q0 output is designed and specified to drive the rated fan-out plus the CP1 input. With the input frequency connected to CP0 and Q0 driving CP1, the LS197 forms a straightforward module-16 counter, with Q0 the least significant output and Q3 the most
significant output.
The LS196 Decade Counter can be connected up to operate in two different count sequences, as indicated in the tables of Figure 2. With the input frequency connected to CP0 and with Q0 driving CP1, the circuit counts in the BCD (8, 4, 2, 1) sequence. With the input frequency connected to CP1 and Q3 driving CP0, Q0 becomes the low frequency output and has a 50% duty cycle waveform. Note that the maximum counting rate is reduced in the latter (bi-quinary) configuration because of the interstage gating delay within the divide-by-five section.
The LS196 and LS197 have an asynchronous active LOW Master Reset input (MR) which overrides all other inputs and forces all outputs LOW. The counters are also asynchronously presettable. A LOW on the Parallel Load input (PL) overrides the clock inputs and loads the data from Parallel Data (P0 ±P3) inputs into the flip-flops. While PL is LOW, the counters act as transparent latches and any change in the Pn inputs will be reflected in the outputs.
Figure 2. LS196 COUNT SEQUENCES
|
DECADE (NOTE 1) |
|
|
|
|
BI-QUINARY (NOTE 2) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COUNT |
Q3 |
Q2 |
Q1 |
Q0 |
COUNT |
Q0 |
Q3 |
Q2 |
Q1 |
0 |
L |
L |
L |
L |
0 |
L |
L |
L |
L |
1 |
L |
L |
L |
H |
1 |
L |
L |
L |
H |
2 |
L |
L |
H |
L |
2 |
L |
L |
H |
L |
3 |
L |
L |
H |
H |
3 |
L |
L |
H |
H |
4 |
L |
H |
L |
L |
4 |
L |
H |
L |
L |
5 |
L |
H |
L |
H |
5 |
H |
L |
L |
L |
6 |
L |
H |
H |
L |
6 |
H |
L |
L |
H |
7 |
L |
H |
H |
H |
7 |
H |
L |
H |
L |
8 |
H |
L |
L |
L |
8 |
H |
L |
H |
H |
9 |
H |
L |
L |
H |
9 |
H |
H |
L |
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES:
1.Signal applied to CP0, Q0 connected to CP1.
2.Signal applied to CP1, Q3 connected to CP0.
MODE SELECT TABLE
|
|
INPUTS |
|
|
|
RESPONSE |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MR |
PL |
|
|
CP |
|||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
Reset (Clear) |
|
|
H |
|
L |
|
|
|
X |
Parallel Load |
|
|
H |
|
H |
|
|
|
|
|
Count |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H = HIGH Voltage Level
L = LOW Voltage Level
X = Don't Care
= HIGH to Low Clock Transition
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
5-374
 Loading...
Loading...