HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers User Manual

HP PCIe IO Accelerator for ProLiant Servers User Guide
Part Number 607720-002
November 2010 (Second Edition)
© Copyright 2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows Server are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates. AMD is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Intended audience
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems. HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards in products with hazardous energy levels.

Contents |
|
About this guide ........................................................................................................................... |
7 |
Contents summary ..................................................................................................................................... |
7 |
Introduction.................................................................................................................................. |
8 |
Overview ................................................................................................................................................. |
8 |
Performance attributes................................................................................................................................ |
8 |
Packing list ............................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
Required operating environment.................................................................................................................. |
9 |
Supported firmware revisions .......................................................................................................... |
10 |
Supported hardware...................................................................................................................... |
10 |
Hardware installation.................................................................................................................. |
12 |
Installing the HP PCIe IO Accelerator ......................................................................................................... |
12 |
Installing a half-height bracket......................................................................................................... |
15 |
Installing the HP PCIe IO Accelerator Duo................................................................................................... |
18 |
Linux environments...................................................................................................................... |
21 |
Linux installation requirements................................................................................................................... |
21 |
Downloading and installing the driver and utilities using Linux ...................................................................... |
21 |
Installing the HP installer script ........................................................................................................ |
22 |
Loading the IO Accelerator driver using Linux ............................................................................................. |
23 |
Setting the driver options.......................................................................................................................... |
24 |
Module parameters ....................................................................................................................... |
24 |
One-time configuration................................................................................................................... |
25 |
Persistent configuration................................................................................................................... |
25 |
Controlling driver loading............................................................................................................... |
25 |
Upgrading firmware using Linux................................................................................................................ |
27 |
Uninstalling and upgrading the driver using Linux........................................................................................ |
28 |
Using the IO Accelerator as swap with Linux .............................................................................................. |
30 |
Using the Logical Volume Manager ........................................................................................................... |
30 |
Configuring RAID for Linux ....................................................................................................................... |
30 |
RAID0/Striped .............................................................................................................................. |
31 |
RAID1/Mirrored............................................................................................................................ |
31 |
RAID 10....................................................................................................................................... |
31 |
Setting up SNMP for Linux........................................................................................................................ |
32 |
SNMP details for Linux ................................................................................................................... |
32 |
SNMP master agent....................................................................................................................... |
32 |
Launching the SNMP master agent .................................................................................................. |
32 |
Configuring the SNMP master agent ................................................................................................ |
32 |
Running the SNMP master agent ..................................................................................................... |
33 |
SNMP agentx subagent.................................................................................................................. |
33 |
Troubleshooting SNMP................................................................................................................... |
37 |
SNMP MIB fields supporting Linux ................................................................................................... |
37 |
Windows Server environments ..................................................................................................... |
40 |
Uninstalling a previously-installed driver ..................................................................................................... |
40 |
Installing software on a Windows system ................................................................................................... |
40 |
Using the Setup Wizard ................................................................................................................. |
41 |
Contents |
3 |
Manual installation on Windows Server ..................................................................................................... |
45 |
Manual installation on Windows Server 2003 .................................................................................. |
46 |
Manual installation on Windows Server 2008 .................................................................................. |
47 |
Upgrading the device firmware using Windows .......................................................................................... |
47 |
Checking for outdated or old firmware ............................................................................................. |
47 |
Viewing the firmware version .......................................................................................................... |
48 |
Performing the upgrade.................................................................................................................. |
48 |
Upgrading driver software using Windows................................................................................................. |
49 |
Upgrading driver software using Windows in a non-RAID configuration ............................................... |
49 |
Upgrading driver software using Windows in a RAID configuration ..................................................... |
49 |
Defragmentation ..................................................................................................................................... |
50 |
IO Accelerator naming............................................................................................................................. |
50 |
Adding a file system, formatting, and performing multi-disk configuration ....................................................... |
51 |
Creating a RAID configuration .................................................................................................................. |
52 |
Using the IO Accelerator as swap with Windows operating system ............................................................... |
52 |
Setting up SNMP for Windows operating systems ....................................................................................... |
52 |
SNMP details for Windows operating systems................................................................................... |
52 |
Using test mode registry values........................................................................................................ |
53 |
SNMP MIB fields supporting Windows Server ................................................................................... |
54 |
Using installation logs .............................................................................................................................. |
56 |
Windows Installer logging options................................................................................................... |
57 |
Creating an installation log............................................................................................................. |
57 |
Creating an uninstall log ................................................................................................................ |
58 |
Creating a patch install log............................................................................................................. |
58 |
Automated logging with the Windows Installer Logging Policy ............................................................ |
58 |
Troubleshooting event log messages ................................................................................................ |
59 |
VMWare ESX environments ......................................................................................................... |
61 |
Creating the ESX IO Accelerator driver CD................................................................................................. |
61 |
Installing the driver as part of a new ESX installation.................................................................................... |
61 |
Installing the driver using vihostupdate ....................................................................................................... |
61 |
Installing the driver using esxupdate .......................................................................................................... |
62 |
Installing the IO Accelerator utilities using ESX ............................................................................................ |
62 |
Configuring the IO Accelerator using ESX................................................................................................... |
63 |
Upgrading the firmware using ESX ............................................................................................................ |
64 |
Working with IO Accelerator devices and PCI pass-through.......................................................................... |
64 |
Using IO Accelerator Duos with PCI pass-through .............................................................................. |
64 |
Using the IO Accelerator as swap with ESX ................................................................................................ |
65 |
Disabling the driver using ESX .................................................................................................................. |
65 |
Enabling the driver using ESX ................................................................................................................... |
65 |
Uninstalling the driver utilities using ESX ..................................................................................................... |
65 |
HP IO Accelerator Management Tool............................................................................................ |
66 |
Operating system support......................................................................................................................... |
66 |
Linux............................................................................................................................................ |
66 |
Windows ..................................................................................................................................... |
66 |
Software installation ................................................................................................................................ |
66 |
Installing software using Linux ......................................................................................................... |
66 |
IO Accelerator management ..................................................................................................................... |
67 |
Device report ................................................................................................................................ |
67 |
Performance report ........................................................................................................................ |
69 |
IO Accelerator Management Tool interface options............................................................................ |
69 |
Detached IO Accelerator after installation......................................................................................... |
70 |
Navigating the IO Accelerator Management Tool.............................................................................. |
70 |
Contents |
4 |
Device Tree ............................................................................................................................................ |
71 |
Drive status................................................................................................................................... |
72 |
Device Report panel ................................................................................................................................ |
75 |
Saving IO Accelerator information................................................................................................... |
77 |
Performance monitoring ........................................................................................................................... |
77 |
Operations............................................................................................................................................. |
78 |
Update firmware ........................................................................................................................... |
79 |
Firmware already updated.............................................................................................................. |
82 |
Attach Device ............................................................................................................................... |
83 |
Attaching mixed attached/detached devices..................................................................................... |
84 |
Detach Device............................................................................................................................... |
84 |
Detaching mixed attached/detached devices.................................................................................... |
85 |
Low level format ............................................................................................................................ |
85 |
IO Accelerator Management Tool Menu..................................................................................................... |
87 |
Maintenance .............................................................................................................................. |
89 |
Maintenance tools ................................................................................................................................... |
89 |
PCIe IO Accelerator LED indicators............................................................................................................ |
89 |
Common maintenance tasks ..................................................................................................................... |
90 |
Uninstalling the IO Accelerator driver package.................................................................................. |
90 |
Disabling auto attach ..................................................................................................................... |
90 |
Enabling auto attach...................................................................................................................... |
91 |
Unmanaged shutdown issues .......................................................................................................... |
92 |
Utilities ...................................................................................................................................... |
93 |
Utilities reference..................................................................................................................................... |
93 |
fio-attach................................................................................................................................................ |
94 |
fio-beacon.............................................................................................................................................. |
94 |
fio-bugreport........................................................................................................................................... |
95 |
fio-config (Windows only)......................................................................................................................... |
95 |
fio-config options........................................................................................................................... |
95 |
fio-detach ............................................................................................................................................... |
96 |
fio-format ............................................................................................................................................... |
96 |
fio-pci-check ........................................................................................................................................... |
97 |
fio-read-lebmap (Linux only) ...................................................................................................................... |
97 |
fio-snmp-agentx (Linux only) ...................................................................................................................... |
97 |
fio-status................................................................................................................................................. |
98 |
fio-trim-config........................................................................................................................................ |
100 |
fio-update-iodrive .................................................................................................................................. |
100 |
Monitoring IO Accelerator health ............................................................................................... |
102 |
NAND flash and component failure......................................................................................................... |
102 |
Health metrics....................................................................................................................................... |
102 |
Health monitoring techniques.................................................................................................................. |
102 |
Flashback substitution events................................................................................................................... |
103 |
Software RAID and health monitoring ...................................................................................................... |
103 |
Trim support (Windows only) ..................................................................................................... |
105 |
Introduction to Trim................................................................................................................................ |
105 |
Trim platforms....................................................................................................................................... |
105 |
Using Trim............................................................................................................................................ |
105 |
Starting and stopping Trim............................................................................................................ |
106 |
Enabling Trim.............................................................................................................................. |
106 |
Controlling Trim aggressiveness..................................................................................................... |
106 |
Trim configurations ................................................................................................................................ |
107 |
|
Contents 5 |
Using Windows page files with the IO Accelerator....................................................................... |
108 |
Introduction to Windows page files ......................................................................................................... |
108 |
Configuring IO Accelerator paging support .............................................................................................. |
108 |
RAM consumption ....................................................................................................................... |
108 |
Non-paged memory pool ............................................................................................................. |
109 |
Enabling and disabling paging support.......................................................................................... |
109 |
Windows page file management............................................................................................................. |
110 |
Setting up page files .................................................................................................................... |
110 |
System drive paging file configuration............................................................................................ |
111 |
Guaranteeing minimum commitable memory................................................................................... |
111 |
Verifying page file operation ........................................................................................................ |
112 |
Virtual Memory performance .................................................................................................................. |
112 |
Resources ................................................................................................................................ |
113 |
Subscription service ............................................................................................................................... |
113 |
For more information ............................................................................................................................. |
113 |
Documentation feedback........................................................................................................................ |
113 |
Technical support...................................................................................................................... |
114 |
Before you contact HP............................................................................................................................ |
114 |
HP contact information........................................................................................................................... |
114 |
Customer Self Repair ............................................................................................................................. |
114 |
Regulatory compliance notices ................................................................................................... |
122 |
Regulatory compliance identification numbers ........................................................................................... |
122 |
European Union regulatory notice ........................................................................................................... |
122 |
Disposal of waste equipment by users in private households in the European Union....................................... |
123 |
Taiwan battery recycling notice............................................................................................................... |
123 |
Acronyms and abbreviations...................................................................................................... |
124 |
Index....................................................................................................................................... |
128 |
Contents 6

About this guide
Contents summary
•Installing the IO Accelerator
•Downloading and installing the approved driver and utilities
•Maintaining the IO Accelerator
•Description of the following IO Accelerator models: o HP PCIe IO Accelerator
o HP PCIe IO Accelerator Duo
This user guide is intended for IO Accelerator software release 2.1 or later. For version 1.2.7.x, see the previous version of this user guide.
About this guide 7

Introduction
Overview
Designed around ioMemory, a revolutionary storage architecture, HP PCIe IO Accelerator is an advanced NAND flash storage device. With performance comparable to DRAM and storage capacity on par with hard disks, PCIe IO Accelerator increases performance so that every server can contain internal storage that exceeds the I/O performance of an enterprise SAN.
PCIe IO Accelerator is the first data accelerator designed specifically to improve the bandwidth for I/O- bound applications.
In addition to the hardware driver, the IO Accelerator also includes a VSL. This hybrid of the RAM virtualization subsystem and the disk I/O subsystem combines the best features of both systems. VSL functions as a disk to interface well with block-based applications and software while also running like RAM underneath to maximize performance. This produces the following benefits:
•Performance: The VSL offers direct and parallel access to multiple CPU cores, enabling near linear performance scaling, consistent performance across different read/write workloads, and low latency with minimal interruptions and context switching.
•Extensibility: The VSL enables flash-optimized software development, making each IO Accelerator module a flexible building block for creating a flash-optimized data center.
Performance attributes
IO Accelerator capacity |
160GB |
320GB |
|
|
|
NAND type |
Single level cell (SLC) |
Multi-level cell (MLC) |
|
|
|
Read bandwidth |
770 MB/s (64K packet size) |
735 MB/s (64K packet size) |
|
|
|
Write bandwidth |
750 MB/s (64K packet size) |
510 MB/s (64K packet size) |
|
|
|
IOPS* |
140,000 (512B read packet |
100,000 (512B read packet size) |
|
size) |
67,000 (75/25 r/w mix 512B |
|
123,000 (75/25 r/w mix |
packet size) |
|
512B |
|
|
packet size) |
|
|
|
|
Access latency |
26 μs (read) |
29 μs (read) |
|
|
|
IO Accelerator Duo |
320GB |
|
640GB |
|
capacity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
NAND type |
Single level cell (SLC) |
Multi-level cell (MLC) |
||
|
|
|
||
Read bandwidth |
1.5 GB/s (64K packet size) |
1.0 GB/s (64K packet size) |
||
|
|
|
||
Write bandwidth |
1.5 GB/s (64K packet size) |
1.5 GB/s (64K packet size) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
IOPS* |
261,000 |
(512B read packet |
196,000 |
(512B read packet size) |
|
size) |
|
138,000 |
(75/25 r/w mix 512B |
|
238,000 |
(75/25 r/w mix |
|
|
Introduction 8

IO Accelerator Duo |
320GB |
640GB |
capacity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
512B |
packet size) |
|
packet size) |
|
|
|
|
Access latency |
26 μs (read) |
29 μs (read) |
|
|
|
*Performance achieved using multiprocessor enterprise server
•Enterprise data integrity
•Field upgradeability
•Green footprint, 7.5 watts nominal per device
NOTE: MSI was disabled to obtain these statistics.
Packing list
•PCIe IO Accelerator Solid State Storage Device
•HP PCIe IO Accelerator for ProLiant Servers installation instructions
•PCIe IO Accelerator half-height bracket (used on low-profile systems)
Required operating environment
The HP PCIe IO Accelerator is supported for use in the following operating environments:
•Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (AMD64/EM64T)
•Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (AMD64/EM64T)
•Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 (AMD64/EM64T)
•SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 10 (AMD64/EM64T)
•SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 11 (AMD64/EM64T)
•Windows Server® 2003 (x86_64-bit only) SP2
•Windows Server® 2008 (x86_64-bit only) R1 with SP2 or higher
•Windows Server® 2008 (x86_64-bit only) R2
•VMWare ESX 4.0 Update 1
CAUTION: Version 2.2 of the driver software is not backward-compatible with any previous driver version. When you install version 2.2, you cannot revert to any previous version.
IMPORTANT: All operating systems must be 64-bit architecture.
NOTE: IO Accelerators cannot be used as hibernation devices.
Introduction 9

Supported firmware revisions
Release |
Firmware revision |
1.2.417350
1.2.736867 or 42014
1.2.8.443246
2.243674
Supported hardware
NOTE: ESX supports a maximum of five IO Accelerators or two IO Accelerator Duos per system.
HP PCIe IO Accelerator minimum requirements:
•An open PCI-Express slot—The accelerator requires a minimum of one half-length, half-height slot with an x4 physical connector. All four lanes must be connected for full performance. HP PCIe IO Accelerator Duo requires a minimum of a full-height, half-length slot with an x8 physical connection. If your system is using PCI 1.1, all x8 signaling lanes must be connected for full performance. If your system is using PCI 2.0, only x4 signaling lanes must be connected for full performance.
NOTE: For PCIe IO Accelerators, using PCIe slots greater than x4 does not improve performance.
•300 LFM of airflow at no greater than 50°C. To protect against thermal damage, the IO Accelerator also monitors the junction temperature of its controller. This is the internal temperature of the controller, and it is reported in fio-status. The IO Accelerator begins throttling write performance when the junction temperature reaches 78 degrees C. If the junction temperature continues to rise, the IO Accelerator shuts down when the temperature reaches 85 degrees C.
NOTE: If you experience write performance throttling due to high temperatures, see your computer documentation for details on increasing airflow, including fan speeds.
•Sufficient RAM to operate—The amount of RAM that the driver requires to manage the NAND flash varies according to the block size you select when formatting the device (filesystem format, not lowlevel format). The following table lists the amount of RAM required per 80GB of storage space, using various block sizes. The amount of RAM used in driver version 2.1 is significantly less than the amount used in version 1.2.x.
Average block |
RAM usage (Megabytes) |
RAM usage |
size(bytes) |
per 80GB of storage for |
(Megabytes) per |
|
version 2.x |
80GB of storage for |
|
|
version 1.2.x |
|
|
|
8,192 |
250 |
400 |
|
|
|
4,096 (most common) |
400 |
800 |
|
|
|
2,048 |
750 |
1,500 |
|
|
|
1,024 |
1,450 |
2,900 |
|
|
|
512 |
2,850 |
5,600 |
|
|
|
Introduction 10
* The fio-format utility automatically formats the device to this block size unless specified differently. You can reduce memory use by selecting a 4K sector size, forcing the average written block size to be 4K or greater. For most systems, even when formatted with 512 byte sectors, actual memory use typically tracks 4K or greater average I/O size.
The HP IO Accelerator Duo requires a PCIe Gen1 x8 slot or a PCIe Gen2 x4 slot. For maximum performance, HP recommends that an external power source be connected to the IO Accelerator Duo, through the Duo external power supply connector. If the external power supply connector is not used, the PCIe slot holding the Duo must be capable of providing a power requirement of at least 25 watts. The Duo power-throttles to an average of 25 watts to meet the 25-watt requirement of the PCIe slot when the external power connector is not used. This power throttling might cause slower performance with the Duo.
Introduction 11
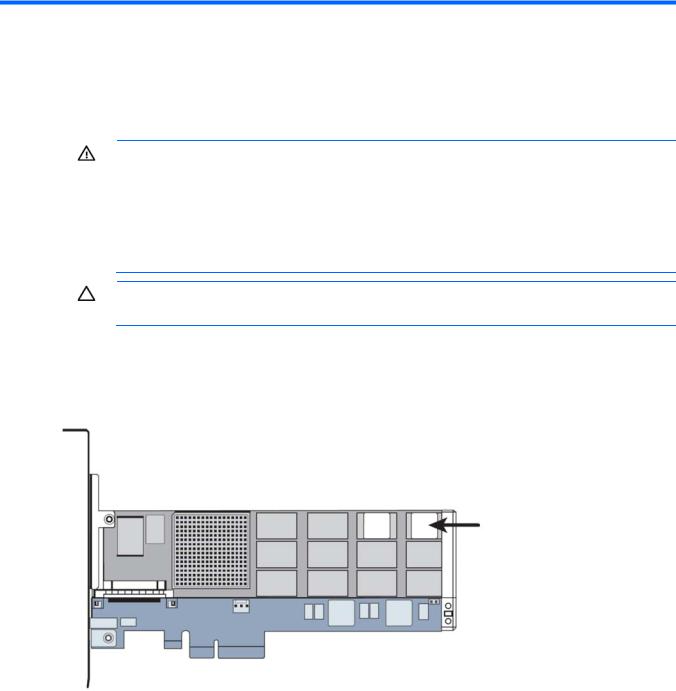
Hardware installation
Installing the HP PCIe IO Accelerator
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment, consult the safety information and user documentation provided with the server before attempting the installation.
Many servers are capable of providing energy levels that are considered hazardous and are intended to be serviced only by qualified personnel who have been trained to deal with these hazards. Do not remove enclosures or attempt to bypass any interlocks that may be provided for the purpose of removing these hazardous conditions.
CAUTION: Electrostatic discharge might damage electronic components. Be sure that you are properly grounded (earthed) before beginning any installation procedure.
To install the IO Accelerator:
1.If you are installing the PCIe IO Accelerator in a low-profile system, use the half-height bracket. See "Installing a half-height bracket (on page 15)."
2.Locate the serial number on your PCIe IO Accelerator and record it.
3.Power off the server, and then disconnect the power cable.
4.Remove the server access panel.
5.Locate an available PCIe slot. For details on removing the panel and identifying PCIe slots, see your server documentation.
Hardware installation 12
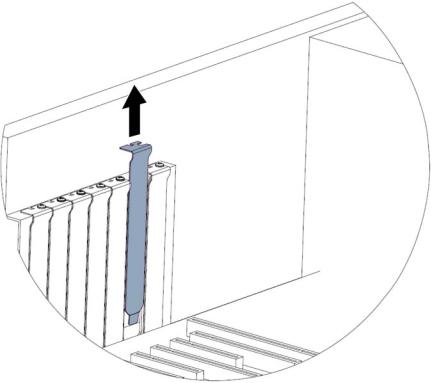
6.If applicable, remove the cover slot.
Hardware installation 13
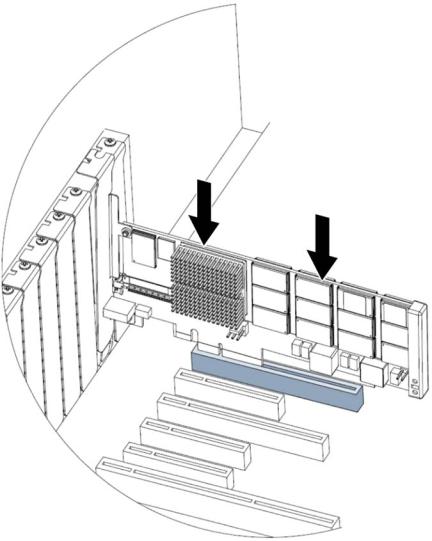
7.Grasp the PCIe IO Accelerator by the top edge and insert it gently, but firmly, into the available PCIe slot.
Hardware installation 14
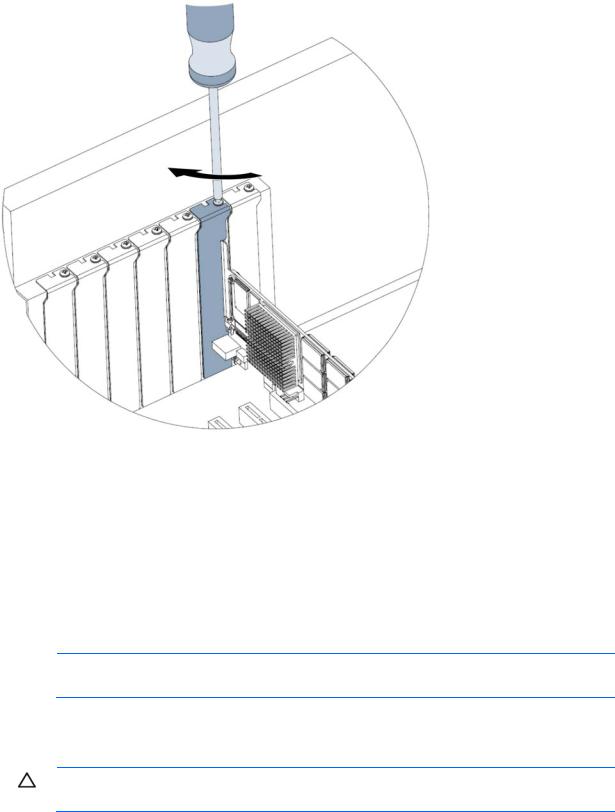
8.Secure the PCIe IO Accelerator retaining bracket using a screw or lever (depending on how your hardware is configured).
9.Replace the server access panel.
10.Plug in the power cable.
11.Power on the server.
If your operating system detects the PCIe IO Accelerator and prompts you to install a driver for the device, click Cancel.
12.Install the driver and utilities software. For instructions, see "Linux environments (on page 21)," "Windows Server environments (on page 40)," "Solaris environments," or "VMware ESX and ESXi environments ("VMWare ESX environments" on page 61)."
Installing a half-height bracket
NOTE: The PCIe IO Accelerator Duo is not compatible with the half-height bracket.
For half-height installation (such as in low-profile systems), replace the full-height retaining bracket with the included half-height bracket.
CAUTION: Electrostatic discharge might damage electronic components. Be sure that you are properly grounded (earthed) before beginning any installation procedure.
Hardware installation 15
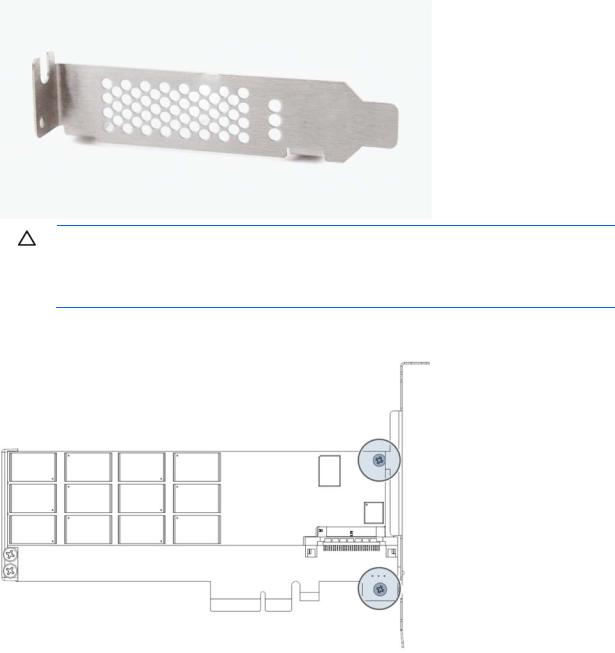
1.Locate the half-height bracket in your PCIe IO Accelerator package.
CAUTION: Use care when removing the retaining screws. Do not twist or pull on the bracket until both screws are out as this can cause damage to components.
To prevent damage to the PCIe IO Accelerator, use only a Philips #1 screwdriver.
2.Remove the two screws holding the full-height bracket to the PCIe IO Accelerator.
3.Remove the bracket carefully from the device.
Hardware installation 16
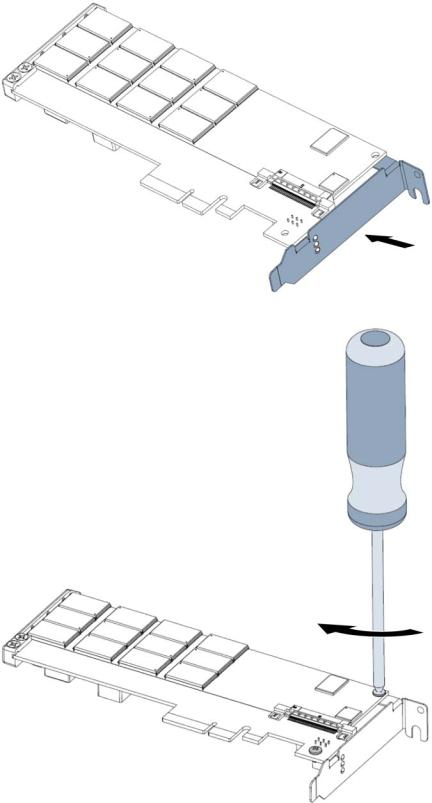
4.Align the LEDs on the PCIe IO Accelerator with the holes in the half-height bracket. Be sure the bracket tabs are on the heat sink side of the device.
5.Attach the half-height bracket using a Philips #1 screwdriver to tighten the two screws.
Hardware installation 17

CAUTION: Do not overly tighten screws. Overly tightening the screws might damage the device.
6.Return to "Installing the HP PCIe IO Accelerator (on page 12)" and begin with step 2.
Installing the HP PCIe IO Accelerator Duo
1.Locate the serial and informational numbers on each side of your ioDrive Duo and record them.
2.Power off the computer and disconnect the power cable.
3.Remove the computer access panel.
4.Locate an available Gen1 x8 or Gen2 x4 PCIe slot. For details on removing the panel and identifying PCIe slots, see your computer documentation.
NOTE: If you are not using an external power connection, choose a slot that provides ample power for the IO Accelerator Duo. For more information, see "Supported hardware (on page 10)."
5.If applicable, remove the cover slot.
Hardware installation 18
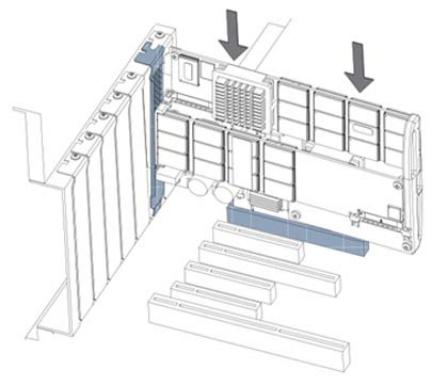
6.Grasp the Duo by the top edge and seat it in the available PCIe slot.
Hardware installation 19
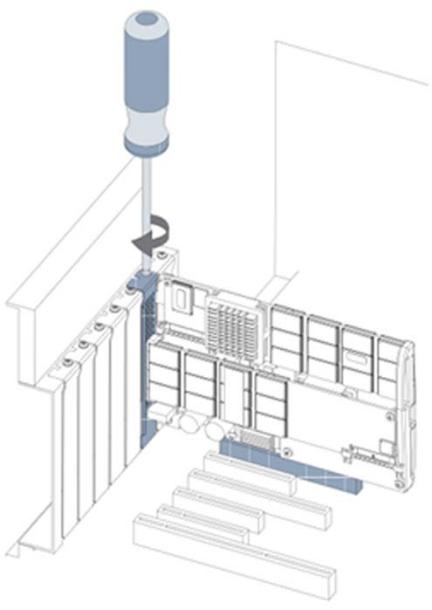
7.Secure the Duo retaining bracket using a screw or lever (depending on how your hardware is configured).
8.If you are connecting to an external power supply, plug one end of the supplied cable into the Duo power connection and the other into the external power source.
9.Replace the computer access panel.
10.Plug in the power cable and power on the computer.
11.Your operating system might detect the Duo and prompt you to install a driver for the device. If so, click Cancel.
Hardware installation 20

Linux environments
Linux installation requirements
The HP-provided Linux installers for the IO Accelerator do not contain binary driver modules. Instead, they build the binary driver RPMs specific to the active Linux kernel by using a source RPM for the driver and compiler or build tools. This action enables the use of customized kernels, but does place additional requirements on the system used for initial installation (also known as the build system). After performing an installation on the build system, the binary driver RPM can be deployed to other systems without having to rebuild it.
The following table summarizes the base modules required for the build system.
Distribution |
Requirements |
|
|
RHEL4 |
kernel (x86-64), kernel-devel (x86-64), rpm-build, rsync, |
|
redhat-lsb, gcc, dialog |
|
|
RHEL5, 6 |
kernel (x86-64), kernel-devel (x86-64), rpm-build, rsync, |
|
redhat-lsb, gcc, dialog |
|
|
SLES10 |
kernel-smp, kernel-source, rsync, lsb, gcc, dialog |
|
|
SLES11 |
kernel-smp, kernel-source, rsync, lsb, gcc, dialog |
|
|
These modules might have other dependencies that install automatically assuming you are using some type of package manager or installer. The kernel-level (for RHEL4, 5, and 6) and kernel-source (for SLES10 & SLES11) modules must match the kernel version in use.
To determine which kernel version is running on your system, enter the following command: $ uname -r
All commands require administrator privileges. Log in as root or use the sudo command to run the installation.
Downloading and installing the driver and utilities using Linux
CAUTION: Upgrading an IO Accelerator from Version 1.2.x to Version 2.x is a one-way process. New firmware is required that is not compatible with 1.2.x systems. Be sure all data is backed up before continuing with the upgrade.
The IO Accelerator software bundle includes the driver, firmware, utilities, and SNMP agent utilities. The 2.x software bundle also includes the Linux HP IO Accelerator Management Tool. You can download the SMH web templates separately from the same location.
For Linux, the two software packages to download, run, and manage the IO Accelerator are:
•HP IO Accelerator production installation software: hp_io_accelerator-{version}.run or a .tar file
Linux environments 21
•SMH webpage: hp_ioaccelerator_system_management_homepage_web_templates
To install the IO Accelerator software:
1.If you are upgrading your IO Accelerator, backup your data.
2.Install the hardware.
3.Download and install software version 2.2:
a.Go to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support).
b.Search for HP IO Accelerator, and navigate to the IO Accelerator product page.
c.Select the appropriate files for your operating environment.
d.Download the files.
4.Load the driver by running the following command: modprobe iomemory_vsl
5.To update the firmware (required on upgrades), open up the IO Accelerator Management Tool or run the following command:
fio—update-iodrive /usr/share/fio/firmware/ioaccelerator_43674.fff (or equivalent *.fff file)
6.Reboot the system.
7.If you plan to run SMH, install the SMH web templates.
Installing the HP installer script
You must uninstall any previous 1.2.x versions of the IO Accelerator software and RPMs, including the HP IO Accelerator Management Tool, before installing the HP installer script. For more information, see "Uninstalling and upgrading the driver using Linux (on page 28)." HP also recommends that you have net-snmp installed prior to installing the IO Accelerator software.
To install the HP installer script:
1.Download the IO Accelerator installation software package. ("Downloading and installing the driver and utilities using Linux" on page 21)
2.Insure that the system you are installing the HP installer script to has the necessary Linux components installed. ("Linux installation requirements" on page 21)
3.Change the directory to the location where you placed the downloaded package.
4.At the command line, enter the following command: gunzip -d <filename>.tar.gz
For example:
gunzip -d Linux_rhel-5.tar.gz
5.Enter the following command: tar -xvf <filename>.tar
This command creates a directory called <filename>.
6.Open the <filename> directory to locate the .sh or .run installer script.
7.Enter the following command to begin installation (the filename might change with the release): bash <filename>
where <filename> is the downloaded .sh or .run installer script.
Linux environments 22

Example: bash hp_io_accelerator-2.2.0.60.4-rhel5.run
8.If the dialog package is installed on your server, the installer script presents a menu to control the installer. If the dialog package is not installed, then the following message appears:
Performing standard install. For more advanced features of this installer please install the dialog package.
9.When the dialog is installed, you can choose which packages to install. HP recommends that you install the software RPMs. The SMI-S package is optional.
10.Once the software is installed and the system is rebooted, these are the RPM packages that are installed (revisions might vary):
a.IO Accelerator Driver (rpm –qa | grep iomemory) iomemory-vsl-source-2.2.0.82-1.0 iomemory-vsl-2.6.18-194.el5-2.2.0.82-1.0
b.Common utilities, firmware, SNMP, and SMI-S (rpm –qa | grep fio) fio-snmp-mib-hp-1.1.0.9-1.0
fio-smis-1.1.0.9-1.0 fio-common-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-util-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-firmware-ioaccelerator-43674-2-1.0 fio-snmp-agentx-1.1.0.9-1.0 libfio-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-sysvinit-2.2.0.82-1.0 libfusionjni-1.1.0.9-1.0
c.HP IO Accelerator Management Tool (rpm –qa | grep accelerator) hp_io_accelerator_management_tool-gui-2.3.0.1859-1.1 hp_io_accelerator_management_tool-jre-2.3.0.1859-1.1
NOTE: If you were unable to install the driver, see "Loading the driver."
Loading the IO Accelerator driver using Linux
1.Enter the following command:
o For 1.2.x systems: modprobe fio-driver
o For 2.x systems: $ modprobe iomemory-vsl
NOTE: If the IO Accelerator firmware is too outdated, a warning appears in the /var/log/messages file. For more information on updating the firmware, see Upgrading firmware using Linux (on page 27).
NOTE: The driver automatically loads at system boot. The IO Accelerator is now available to the operating system as /dev/fiox, where x is a letter.
2.To confirm that the IO Accelerator is attached, enter the command fio-status or fio-status -a.
Linux environments 23
The following is an example output showing that the system recognizes the IO Accelerator:
Found 1 ioDrive in this system Fusion-io driver version: 2.2.0 build 60
fct0 Attached as 'fioa' (block device)
HP 80GB IO Accelerator, Product Number:AJ876A SN:07644 Alt PN:507150-001
PCI:10:00.0
Firmware v5.0.5, rev 43674
80.47 GBytes block device size, 99 GBytes physical device size Sufficient power available: Unknown
Internal temperature: avg 56.1 degC, max 56.6 degC Media status: Healthy; Reserves: 100.00%, warn at 10.00%
Note: the Sufficient power available: Unknown is not supported on the mezzanine version of the IO Accelerator
Or use this one 1.2.x systems: Found 1 ioDrive in this system. Fusion-io driver version: 1.2.7.5
fct0 Attached as ’fioa’ (block device)
HP StorageWorks 80GB IO Accelerator, Product Number:AJ876A SN:7638 Firmware v36867
80 GBytes block device size, 99 GBytes physical device size capacity. PCI:48:00.0, Slot Number: Unavailable
Vendor:1aed, Device:1003, Sub vendor:103c, Sub device:324d Internal temperature: avg 37.4 degC, max 47.7 degC
Media status: Healthy. 99.46% blocks good.
Setting the driver options
This section explains how to set driver options.
Module parameters
The following table describes the module parameters you can set by editing the /usr/kernel/iomemory_vsl.conf file and changing the values. You must complete the edits before loading the driver, or they do not take effect.
Module parameter |
Default (min/max) |
Description |
|
|
|
auto_attach |
True |
Attach the device on startup. |
Linux environments 24
Module parameter |
Default (min/max) |
Description |
|
|
|
force_minimal_mode |
False |
Force minimal mode on the device. |
parallel_attach |
True |
Enable parallel attach of multiple drivers. |
preallocate_memory |
False |
For the selected device, pre-allocate all |
|
|
memory necessary to have the drive usable as |
|
|
swap space. |
|
|
|
tintr_hw_wait |
0 (0, 255) |
Interval (microseconds) to wait between |
|
|
hardware interrupts. |
use_workqueue |
3 (1 or 3) |
Linux only: 3 = Uses standard OS interfaces |
|
|
such as the page cache layer and I/O |
|
|
elevators; 0 = Bypasses these standard OS |
|
|
interfaces. |
|
|
|
One-time configuration
The IO Accelerator driver options can be set when the driver is installed on the command line of either insmod or modprobe. For example, to set the auto_attach driver option to 0, run the command:
$ modprobe iomemory_vsl auto-attach=0
This option takes effect only for this load of this driver. This option is not set for subsequent calls to modprobe or insmod.
Persistent configuration
To maintain a persistent setting for an option, add the option to the /etc/modprobe.d/iomemory_vsl.conf file or a similar file. To prevent the IO Accelerator from auto-attaching, add the following line to the iomemory_vsl.conf file:
options iomemory_vsl auto_attach=0
The driver option then takes effect for every subsequent driver load, as well as on autoload of the driver during boot time.
Controlling driver loading
You can control driver loading either through the init script or through udev.
In newer Linux distributions, users can rely on the udev device manager to automatically find and load drivers for their installed hardware at boot time. For older Linux distributions without this functionality, users must rely on a boot time init script to load needed drivers. HP provides an init script in /etc/init.d/iomemory-vsl to load the IO Accelerator driver in RHEL4 and SLES10 distributions.
Using the init scripts
The installation process places an init script in the /etc/init.d/iomemory-vsl file. This script uses the setting options found in the options file in /etc/sysconfig/iomemory-vsl. The options file contains documentation for the various settings. For more information on the mounts setting, see "Mounting filesystems (on page 26)." For more information on the kill_procs_on_unmount setting, see "Driver unloads (on page 26)."
Linux environments 25
On systems that use scripts to load drivers, you can enable or disable an init script with the standard init script utility, chkconfig. By default, the IO Accelerator init script loads the driver at boot time.
You can disable loading of the IO Accelerator driver with the following command: $ chkconfig --del iomemory-vsl
To re-enable the driver loading in the init script, use the following command: $ chkconfig --add iomemory-vsl
Mounting filesystems
Because the IO Accelerator driver is not loaded in the initrd, or built kernel, using the standard method for mounting filesystems (/etc/fstab) does not work. To set up auto-mounting of a filesystem hosted on an IO Accelerator:
1.Add the filesystem mounting command to /etc/fstab.
2.Add the noauto option to /etc/fstab. For example:
o /dev/fcta /mnt/fioa ext3 defaults,noauto 0 0
o /dev/fctb1 /mnt/iodrive ext3 defaults,noauto 0 0
To have the init script mount these drives after the driver is loaded, and unmount them before the driver is unloaded, add a list of mount points to the options file using the procedure documented there.
For the filesystem mounts shown in the previous example, the line in the options file appears similar to the following:
MOUNTS="/mnt/fioa /mnt/iodrive"
Driver unloads
Take special care when unloading drivers. By default, the init script searches for any processes holding open a mounted filesystem and kills them, thus enabling the filesystem to be unmounted. This behavior is controlled by the option KILL_PROCS_ON_UMOUNT in the options file. If these processes are not killed, the filesystem is not unmounted. Failure to unmount the filesystem might keep the driver from unloading cleanly, causing a significant delay on the subsequent boot.
To unload the IO Accelerator driver using Linux, enter the following commands: $ modprobe –r iomemory-vsl
$ modprobe -r fio-port
Uninstalling the IO Accelerator utilities using Linux
Enter the following command:
$ rpm –e fio-util fio-snmp-agentx
Using the udev script
On systems that rely on udev to load drivers, modify an IO Accelerator file to prevent udev from autoloading the IO Accelerator driver at boot time. To modify the file:
1.Locate and edit the /etc/modprobe.d/iodrive file, which already contains the following line:
# blacklist iomemory-vsl
2.To disable loading, remove the # symbol from the line, and then save the file.
Linux environments 26

3. With the blacklist command in place, reboot Linux. The IO Accelerator driver does not load. To restore driver auto-loading, replace the # symbol to comment out the line.
Disabling the driver
You can disable loading of the IO Accelerator driver at boot time on either udev or init script systems. This prevents the auto-attach process for diagnostic or troubleshooting purposes. Follow the steps in the "Disabling auto attach (on page 90)" section to disable or enable the auto attach functionality.
To disable the driver using Linux on either udev or init script systems:
1.To disable the driver auto-load, append the following parameter at the kernel command line of your boot loader:
o For 1.2.x systems: iodrive=0
o For 2.x systems: iomemory-vsl=0
2.Continue the Linux boot process.
The IO Accelerator driver does not load, so the device is not available to users. However, all other services and applications are now available.
NOTE: You can also uninstall the driver to keep it from loading, or move it out of the
/lib/modules/<kernel_version> directory.
3.If the issue is outdated firmware, set the driver to minimal mode. You can then use fio-update- iodrive to update the firmware.
4.Use the fio-attach utility to attach the device to the operating system.
To load the driver again, remove the iodrive=0 option from the kernel command line, and reboot the system.
Upgrading firmware using Linux
NOTE: For more information, see the Release Notes that came with your driver version.
NOTE: If your driver version is earlier than 1.2.4, you must upgrade to Version 1.2.4 before upgrading to Version 2.x.
To upgrade the firmware:
1.Open the HP IO Accelerator Management Tool or enter the following command (as root) to update the firmware:
fio-update-iodrive /usr/share/fio/firmware/ioaccelerator_xxxxx.fff
(where xxxxx is the version of the firmware release)
NOTE: If a driver is installed, the utility detects it and does not install the firmware. The error message Driver is not in a valid state to have firmware uploaded appears. If this error occurs, unmount the drive, run the rmmod iomemory_vsl command to unload the driver, and then attempt the update again.
2.When the update is complete, enter the following command to shut down the server:
Linux environments 27

shutdown -h now
IMPORTANT: For the firmware upgrade to write to the device properly, you must completely shut down the system, and then bring it all the way back up (not just perform a restart).
The following is an example of the screen display during a firmware update.
# fio-update-iodrive /usr/share/fio/firmware/ioaccelerator_43674.fff
Device ID 0 (48:00.0) Updating device firmware from 42014 to 43674
WARNING: DO NOT TURN OFF POWER WHILE THE FIRMWARE UPDATE IS IN PROGRESS.
Please wait (this may take a while)
Progress
-------------------------
/0: 13%
Uninstalling and upgrading the driver using Linux
NOTE: For more information, see the Release Notes that came with your driver version.
To upgrade the driver, you must uninstall the existing driver, and then install the new version. To uninstall the existing driver:
1.Log in to the system as root or use the su command to gain root access.
2.Ensure that there are no filesystems or RAID volumes using the IO Accelerator, and then unload the driver modules.
o To uninstall 1.2.x software:
i.Run the following command to uninstall the driver and upgrade from a system that has version 1.2.x installed:
modprobe -r fio-driver fio-port
If you have not unmounted any filesystems or RAID volumes that are using the IO Accelerator, this command might fail.
ii.Run the following commands, in order, to uninstall the driver: rpm -e iodrive-snmp
rpm -e iodrive-ini
rpm -e iodrive-firmware rpm -e iodrive-util rpm -e iodrive-driver
iii.Remove the IO Accelerator files left in the /usr/src/redhat/RPMS/x86_64/ directory on RHEL or the /usr/src/packages/RPMS/x86_64 directory on SLES. These files are usually named iodrive*.rpm.
Linux environments 28
iv. If the HP IO Accelerator Management Tool is installed, uninstall it.
oTo uninstall 2.x driver, run the following command: modprobe –r iomemory_vsl
If you have not unmounted any filesystems or RAID volumes that are using the IO Accelerator, this command might fail.
3.To uninstall the 2.2 packages, run the following commands in order.
oTo uninstall the HP IO Accelerator Management Tool:
# rpm -qa | grep accelerator
fio-firmware-ioaccelerator-43674.2-1.0 hp_io_accelerator_management_tool-gui-2.3.0.1859-1.1 hp_io_accelerator_management_tool-jre-2.3.0.1859-1.1
#rpm -e fio-firmware-ioaccelerator-43674.2-1.0
#rpm -e hp_io_accelerator_management_tool-jre-2.3.0.1859-1.1
#rpm –e hp_io_accelerator_management_tool-gui-2.3.0.1859-1.1
o To uninstall the Libfusion RPM packages:
# rpm -qa | grep libfusion libfusionjni-1.1.0.9-1.0
# rpm -e libfusionjni-1.1.0.9-1.0 o To uninstall the Fio driver RPM packages:
#rpm -qa | grep fio fio-util-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-smis-1.1.0.9-1.0 libfio-dev-1.1.0.9-1.0 fio-common-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-snmp-agentx-1.1.0.9-1.0 libfio-doc-1.1.0.9-1.0 fio-snmp-mib-hp-1.1.0.9-1.0 libfio-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-sysvinit-2.2.0.82-1.0
#rpm -e fio-util-2.2.0.82-1.0
#rpm -e fio-smis-1.1.0.9-1.0
#rpm -e libfio-dev-1.1.0.9-1.0 libfio-doc-1.1.0.9-1.0
#rpm -e fio-common-2.2.0.82-1.0 fio-snmp-agentx-1.1.0.9-1.0
#rpm -e fio-snmp-mib-hp-1.1.0.9-1.0
#rpm -e libfio-2.2.0.82-1.0
#rpm -e fio-sysvinit-2.2.0.82-1.0
oTo uninstall the iomemory RPM packages:
#rpm -qa | grep iomemory iomemory-vsl-source-2.2.0.82-1.0
iomemory-vsl-2.6.18-194.el5-2.2.0.82-1.0
#rpm -e iomemory-vsl-source-2.2.0.82-1.0
Linux environments 29

# rpm -e iomemory-vsl-2.6.18-194.el5-2.2.0.82-1.0
To install the new driver, see "Downloading and installing the driver and utilities using Linux (on page 21)."
NOTE: When upgrading from version 1.2.7.x to version 2.x, a firmware upgrade is required. For more information, see "Upgrading firmware using Linux (on page 27)."
Each new release includes instructions. Make sure you read the Release Notes and the installation instructions to ensure no loss of data.
Using the IO Accelerator as swap with Linux
To safely use the IO Accelerator as swap space, you must pass the swap_mode=1 kernel module parameter. To do this, add the following line to the /etc/modprobe.d/iomemory_vsl file:
options iomemory_vsl preallocate_memory=1072,4997,6710,10345
where 1072,4997,6710,10345 are serial numbers obtained from the fio-status utility. Be sure to use serial numbers for the IO Accelerator modules and not the adapter.
A 4K sector size format is required for swap. This reduces the driver memory footprint.
CAUTION: You must have 400MB of free RAM per 80GB of IO Accelerator capacity (formatted to 4KB block size) to enable the IO Accelerator with pre-allocation enabled for swap. Attaching an IO Accelerator with pre-allocation enabled and insufficient RAM might result in the loss of user processes and system instability.
Using the Logical Volume Manager
If you add the IO Accelerator as a supported type, the LVM volume group management application handles mass storage devices like the IO Accelerator. To use the LVM:
1.Locate the /etc/lvm/lvm.conf configuration file.
2.Edit the file to add an entry similar to the following: types = [ “fio”, 16 ]
The parameter “16” represents the maximum number of partitions supported by the drive. For the IO Accelerator, this can be any number from 1 upwards. Do not set this parameter to 0.
NOTE: For the IO Accelerator, HP recommends 16 for the partition setting.
Configuring RAID for Linux
You can configure two or more IO Accelerators into a RAID array using standard Linux procedures.
NOTE: If you are using RAID1 mirroring and one device fails, enter the fio-format command on the replacement device (not the existing good device) before rebuilding the RAID.
HP recommends that you do not use a RAID5 configuration.
Linux environments 30
 Loading...
Loading...