YOKOGAWA CX1006, CX1206 Guide
Model CX1006/CX1206
DAQSTATION CX1000
IM 04L31A01-03E
IM 04L31A01-03E
1st Edition

Thank you for purchasing the CX1000. This manual describes the functions (excluding the communications functions), installation and wiring procedures, operating procedures, and handling precautions of the CX1000. To ensure correct use, please read this manual thoroughly before beginning operation. The following four manuals are also provided in addition to this manual. Read them along with this manual.
Electronic Manuals Provided on the Accompanying CD-ROM
Manual Title |
Manual No. |
Description |
CX1000/CX2000 |
IM 04L31A01-17E |
Describes the communications functions of the |
Communications Interface |
|
CX1000/CX2000 using the Ethernet/serial |
interface. |
|
|
User’s Manual |
|
|
|
|
|
DAQSTANDARD for CX |
IM 04L31A01-61E |
Describes the functions and operating |
User’s Manual |
|
procedure of the software “DAQSTANDARD |
|
|
for CX” that comes with the package. |
|
|
|
Paper Manuals
Manual Title |
Manual No. |
Description |
CX1000 Installation and |
IM 04L31A01-73E |
Describes concisely the installation |
Connection Guide |
|
procedures and wiring procedures of the |
|
|
CX1000. |
|
|
|
Precautions on the Use of |
IM 04L31A01-72E |
Precautions regarding the use of the CX1000/ |
the CX1000/CX2000 |
|
CX2000. The same information is written on |
|
|
pages ii and iii of this user’s manual. |
|
|
|
Notes
•This manual describes the CX1000, style number “S1.”
•The contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice as a result of continuing improvements to the instrument’s performance and functions. Note that the program control operation described in this manual is not supported by this version of the CX1000. Therefore, the information regarding the program control operation may not be correct.
•Every effort has been made in the preparation of this manual to ensure the accuracy of its contents. However, should you have any questions or find any errors, please contact your nearest YOKOGAWA dealer as listed on the back cover of this manual.
•Copying or reproducing all or any part of the contents of this manual without the permission of Yokogawa Electric Corporation is strictly prohibited.
•The TCP/IP software of this product and the document concerning the TCP/IP software have been developed/created by YOKOGAWA based on the BSD Networking Software, Release 1 that has been licensed from the Regents of the University of California.
Trademarks
•Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
•Zip is either a registered trademark or trademark of Iomega Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
•Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe Systems incorporated.
•Company and product names that appear in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Revisions
1st Edition |
March, 2002 |
Disk No. RE36
1st Edition : March 2002 (YK)
All Rights Reserved, Copyright © 2002 Yokogawa Electric Corporation
IM 04L31A01-01E
i

 Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions
About This Manual
•This manual should be read by the end user.
•Read this manual thoroughly and have a clear understanding of the product before operation.
•This manual explains the functions of the product. YOKOGAWA does not guarantee that the product will suit a particular purpose of the user.
•Under absolutely no circumstances may the contents of this manual be transcribed or copied, in part or in whole, without permission.
•The contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice.
•Every effort has been made in the preparation of this manual to ensure the accuracy of its contents. However, should you have any questions or find any errors or omissions, please contact your nearest YOKOGAWA dealer.
Precautions Related to the Protection, Safety, and Alteration of the Product
• The following safety symbols are used on the product and in this manual.
“Handle with care.” (To avoid injury, death of personnel or damage to the instrument, the operator must refer to the explanation in the manual.)
Functional ground terminal. (Do not use this terminal as a protective ground terminal.)
Protective grounding terminal
Alternating current
•For the protection and safe use of the product and the system controlled by it, be sure to follow the instructions and precautions on safety that are stated in this manual whenever you handle the product. Take special note that if you handle the product in a manner that violate these instructions, the protection functionality of the product may be damaged or impaired. In such cases, YOKOGAWA does not guarantee the quality, performance, function, and safety of the product.
•When installing protection and/or safety circuits such as lightning protection devices and equipment for the product and control system or designing or installing separate protection and/or safety circuits for fool-proof design and fail-safe design of the processes and lines that use the product and the control system, the user should implement these using additional devices and equipment.
•If you are replacing parts or consumable items of the product, make sure to use parts specified by YOKOGAWA.
•This product is not designed or manufactured to be used in critical applications that directly affect or threaten human lives. Such applications include nuclear power equipment, devices using radioactivity, railway facilities, aviation equipment, air navigation facilities, aviation facilities, and medical equipment. If so used, it is the user’s responsibility to include in the system additional equipment and devices that ensure personnel safety.
•Do not modify this product.
ii
IM 04L31A01-03E

Safety Precautions
WARNING
Power Supply
Ensure that the source voltage matches the voltage of the power supply before turning ON the power.
Protective Grounding
Make sure to connect the protective grounding to prevent electric shock before turning ON the power.
Necessity of Protective Grounding
Never cut off the internal or external protective earth wire or disconnect the wiring of the protective earth terminal. Doing so invalidates the protective functions of the instrument and poses a potential shock hazard.
Defect of Protective Grounding
Do not operate the instrument if the protective earth or fuse might be defective. Make sure to check them before operation.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of flammable liquids or vapors. Operation in such environments constitutes a safety hazard.
Do Not Remove Covers
The cover should be removed by YOKOGAWA’s qualified personnel only. Opening the cover is dangerous, because some areas inside the instrument have high voltages.
External Connection
Connect the protective grounding before connecting to the item under measurement or to an external control unit.
Damage to the Protective Structure
Operating the CX1000 in a manner not described in this manual may damage its protective structure.
Exemption from Responsibility
•YOKOGAWA makes no warranties regarding the product except those stated in the WARRANTY that is provided separately.
•YOKOGAWA assumes no liability to any party for any loss or damage, direct or indirect, caused by the user or any unpredictable defect of the product.
Handling Precautions of the Software
•YOKOGAWA makes no warranties regarding the software accompanying this product except those stated in the WARRANTY that is provided separately.
•Use the software on a single PC.
•You must purchase another copy of the software, if you are to use the software on another PC.
•Copying the software for any purposes other than backup is strictly prohibited.
•Please store the original media containing the software in a safe place.
•Reverse engineering, such as decompiling of the software, is strictly prohibited.
•No portion of the software supplied by YOKOGAWA may be transferred, exchanged, sublet, or leased for use by any third party without prior permission by YOKOGAWA.
IM 04L31A01-01E |
iii |

 Checking the Contents of the Package
Checking the Contents of the Package
Unpack the box and check the contents before operating the instrument. If some of the contents are not correct or missing or if there is physical damage, contact the dealer from which you purchased them.
CX1000
When you open the operation cover on the front panel, a name plate is located on the back side of the cover. Check that the model name and suffix code given on the name plate on the rear panel match those on the order.
Open the operation  cover
cover 

MODEL and SUFFIX
MODEL STYLE
STYLE
SUFFIX NO
Model |
Suffix Code |
Optional Code |
Description |
|||
CX1006*1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of internal control loops: 0, number of inputs for measurement: 6 ch |
CX1206 |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of internal control loops: 2, number of inputs for measurement: 6 ch |
External |
–1 |
|
|
|
Floppy disk |
|
storage |
–2 |
|
|
|
Zip disk |
|
medium |
–3 |
|
|
|
ATA flash memory card |
|
Communication |
|
–0 |
|
Only Ethernet |
||
|
–1 |
|
Ethernet + RS-232 serial interface port*2 |
|||
interface |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
–2 |
|
Ethernet + RS-422A/485 serial interface port |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
Displayed language |
|
–1 |
|
Japanese |
||
|
–2 |
|
English |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Options |
|
|
|
|
/A6 |
6 measurement alarm outputs*3 |
|
|
|
|
/A6R |
6 measurement alarm output, 8 remote inputs*3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
/A4F |
4 measurement alarm outputs, 1 FAIL output, 1 memory end output*3 |
|
|
|
|
|
/A4FR |
4 measurement alarm outputs, 1 FAIL output, 1 memory end output, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 remote inputs*3 |
|
|
|
|
|
/M1 |
Computation function |
|
|
|
|
|
/N2 |
Three-wire isolated RTD (input for measurement) |
|
|
|
|
|
/P1 |
24-VDC/AC power supply driven |
|
|
|
|
|
/CM1 |
Green series communications*4 |
|
|
|
|
|
/CM2 |
Ladder communications*4 |
|
|
|
|
|
/PG1 |
Program control (number of program patterns: 4)*5 |
|
|
|
|
|
/PG2 |
Program control (number of program patterns: 30)*5 |
*1 Suffix Code –2 (Ethernet + RS-422A/485 serial interface port) must be selected for the communication interface and /CM1 (Green series communications) must be selected for the Optional Code.
*2 Includes the Modbus master/slave function. However, to use the Modbus master function, /M1 must be selected for the Optional Code.
*3 Only one of the options can be specified on the CX1006. Cannot be specified on the CX1206.
*4 Suffix Code –1 (with RS-232 serial interface port) or –2 (with RS422/485 interface port) must be selected for the communication interface. Either one can be specified on the CX1206. Ladder communication (/CM2) cannot be specified on the CX1006.
*5 Either one can be specified on the CX1206.
NO. (Instrument Number)
When contacting the dealer from which you purchased the instrument, please give them
the instrument number.
iv
IM 04L31A01-03E

Checking the Contents of the Package
Standard Accessories
The standard accessories below are supplied with the instrument. Check that all
contents are present and that they are undamaged.
|
|
|
|
|
|
or |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
No. |
Name |
|
Part Number/Model Q’ty |
Note |
|
|
1 |
Terminal screws |
|
|
5 |
M4 |
|
2 |
Mounting bracket |
|
B9900BX |
2 |
For panel mounting |
|
3 |
DAQSTANDARD |
|
CXA100-01 |
1 |
Software for setting the CX and |
|
|
for CX |
|
|
|
displaying data CD-ROM used to install |
|
|
|
|
|
|
“DAQSTANDARD for CX” |
|
4 |
CX1000/CX2000 |
|
B8700MA |
1 |
CD-ROM containing the PDF files of this |
|
|
electronic manual |
|
|
|
manual, the CX1000/CX2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Communication Interface User’s Manual, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DAQSTANDARD for CX User’s Manual, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
and other files. |
|
5 |
CX1000 Installation and |
IM 04L31A01-73E |
1 |
Abridged paper manual |
|
|
|
Connection Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Precautions on the Use |
IM 04L31A01-72E |
1 |
Paper stating the precautions. |
|
|
|
of the CX1000/CX2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
External storage medium A1053MP |
1 |
Zip disk (provided only when the external |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
storage medium suffix code is “-2”) |
|
|
|
|
B9968PK |
1 |
ATA flash memory card, provided only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
when the external storage medium suffix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
code is “-3” (the size and model may |
|
|
|
|
|
|
change in the future) |
|
Optional Accessories (Sold Separately)
The following optional accessories are available for purchase separately. When you receive the order, check that all contents are present and that they are undamaged. For information and ordering, contact your nearest YOKOGAWA dealer.
Part Name |
Part Number/Model |
Q’ty |
Note |
3.5" floppy disk |
7059 00 |
10 |
2HD |
|
|
|
|
Zip disk |
A1053MP |
1 |
100 MB |
|
|
|
|
ATA flash memory card |
B9968PK |
1 |
24 MB (The size and model may |
|
|
|
change in the future. Check with your |
|
|
|
YOKOGAWA dealer when ordering.) |
|
|
|
|
Shunt resistance |
4159 20 |
1 |
250 Ω±0.1% |
(for the screw terminal) |
4159 21 |
1 |
100 Ω±0.1% |
|
4159 22 |
1 |
10 Ω±0.1% |
Mounting bracket |
B9900BX |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
IM 04L31A01-01E |
v |

 How to Use This Manual
How to Use This Manual
Structure of the Manual
This user’s manual consists of the following sections. For details on the communications functions and the software “DAQSTANDARD for CX” provided with the package, see the respective manuals (IM 04L31A01-17E and IM 04L31A01-61E).
Chapter |
Title and Description |
1Explanation of Functions
Describes in detail the functions of the instrument. The chapters that explain the operation of the CX1000 only describe the operating procedures. For more detailed information about the functions, see this chapter.
2Installation and Wiring
Describes the installation and wiring procedures of the CX1000.
3Names of Parts, Display Modes, and Common Operations
Describes the names of the parts of the CX1000, the basic key operations, the basic operations carried out initially, and how to use the external storage medium drive.
4Control Function Related Setup Operations
Describes setup operations related to the control function that are carried out before starting control operations.
5Program Control Related Setup Operations (Only on Models with the Program
Control Option)
Describes the setup operations related to program control that are carried out before starting control operations on models with the program control option.
6Operations during Control Operation
Describes how to switch operation mode during control operation, how to change the setpoints of setting mode, how to tune the control parameters, and the operations on the program control screen (operations only on models with the option).
7Measurement Function Related Setup Operations
Describes how to set the PV input of the measurement function and alarms
(measurement alarms).
8Operations for Changing the Displayed Contents
Describes how to change the operating display of both the control function and the measurement function and the display format.
9Data Save/Load Operations
Describes how to write various data to the internal memory, how to save and load from the external storage medium, and the file operations on the external storage medium.
10Computation and Report Function Related Operations (Only on Models with the Computation Function Option)
Describes how to set and execute operations related to the computation function and report function of the computation function option.
11Operations of Other Functions
Describes the USER key, key lock, login/logout of key operation, log display, and remote input setting.
12Troubleshooting
Describes the error messages and the troubleshooting measures of the CX1000.
13Maintenance
Describes periodic inspection, calibration, and recommended replacement period for worn parts.
14Specifications
Describes the specifications of the CX1000.
Appendix Describes the acquisition function of measured data to the internal memory, additional information on the computation and report functions, the ASCII file format, and initial settings.
Index
Note
•This user’s manual covers information regarding CX1000s that have a suffix code for language “-2” (English).
•For details on setting the displayed language, see section 3.6.
vi
IM 04L31A01-03E

How to Use This Manual
Conventions Used in This Manual
Unit
K........ Denotes “1024.” Example: 768 KB (file size) k........ Denotes “1000.”
Safety Markings
The following markings are used in this manual.
WARNING
CAUTION
Danger. Refer to corresponding location on the instrument.
This symbol appears on dangerous locations on the instrument which require special instructions for proper handling or use. The same symbol appears in the corresponding place in the manual to identify those instructions.
Calls attention to actions or conditions that could cause serious injury or death to the user, and precautions that can be taken to prevent such occurences.
Calls attentions to actions or conditions that could cause damage to the instrument or user’s data, and precautions that can be taken to prevent such occurrences.
Note |
Calls attention to information that is important for proper operation |
|
of th instrument. |
Symbols Used on Pages Describing Operating Procedures
On pages that describe the operating procedures in Chapter 3 through 11, the following symbols are used to distinguish the procedures from their explanations.
[ ] ................ |
Indicates character strings that appear on the screen. |
|
|
Example: [Space] soft key, [Volt] |
|
|
This subsection contains the operating procedure used to carry out |
|
Procedure |
||
the function described in the current section. All procedures are |
||
|
||
|
written with inexperienced users in mind; experienced users may |
|
|
not need to carry out all the steps. |
|
|
Describes the details of the settings and the restrictions that exist with |
|
Setup Items |
||
the operating procedure. It does not give a detailed explanation of |
||
|
||
|
the function. For details on the function, see chapter 1. |
IM 04L31A01-01E |
vii |

 Contents
Contents
Safety Precautions .......................................................................................................................... |
ii |
Checking the Contents of the Package .......................................................................................... |
iv |
How to Use This Manual ................................................................................................................ |
vi |
Chapter 1 Explanation of Functions
1.1 |
CX1000 Overview ............................................................................................................ |
1-1 |
1.2 |
Control Function Overview ............................................................................................... |
1-2 |
1.3 |
Basic Settings of Control ................................................................................................ |
1-13 |
1.4 |
PV Input Related Settings .............................................................................................. |
1-18 |
1.5 |
Contact Input/Output Related Settings .......................................................................... |
1-22 |
1.6 |
Target Setpoint Related Settings ................................................................................... |
1-25 |
1.7 |
PID Parameter Settings ................................................................................................. |
1-27 |
1.8 |
Control Output Suppression Settings ............................................................................. |
1-31 |
1.9 |
Settings for ON/OFF Control .......................................................................................... |
1-33 |
1.10 |
Control Alarm Related Settings ...................................................................................... |
1-34 |
1.11 |
Program Control Related Settings ................................................................................. |
1-36 |
1.12 |
Tuning ............................................................................................................................ |
1-50 |
1.13 |
Measurement Function Overview .................................................................................. |
1-52 |
1.14 |
Measurement Function > Measurement Input Related Settings .................................... |
1-54 |
1.15 |
Measurement Function > Measurement Alarm Related Settings .................................. |
1-57 |
1.16 |
Display Function ............................................................................................................. |
1-62 |
1.17 |
Data Storage Function ................................................................................................... |
1-81 |
1.18 |
Computation and Report Functions (Option) ................................................................. |
1-86 |
1.19 |
Other Functions ............................................................................................................. |
1-90 |
Chapter 2 Installation and Wiring
2.1 |
Handling Precautions ....................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
2.2 |
Installation ........................................................................................................................ |
2-2 |
2.3 |
Wiring ............................................................................................................................... |
2-5 |
2.4 |
Connecting the Power Supply ........................................................................................ |
2-13 |
Chapter 3 Names of Parts, Display Modes, and Common Operations
3.1 |
Names and Functions of Sections ................................................................................... |
3-1 |
3.2 |
Basic Key Operations ....................................................................................................... |
3-4 |
3.3 |
Setting the Date and Time ............................................................................................. |
3-11 |
3.4 |
Setting the Brightness of the Display and the Backlight Saver Function ........................ |
3-13 |
3.5 |
Initializing the Setup Data and Clearing the Internal Memory ........................................ |
3-14 |
3.6 |
Changing the Displayed Language ................................................................................ |
3-15 |
3.7 |
Changing the Time Zone ................................................................................................ |
3-16 |
3.8 |
Inserting and Ejecting the External Storage Medium ..................................................... |
3-17 |
Chapter 4 Control Function Related Setup Operations
4.1 |
Control > Control action ................................................................................................... |
4-1 |
4.2 |
Control > Input setting (Burnout and RJC) ....................................................................... |
4-4 |
4.3 |
Control > Contact input-registration ................................................................................. |
4-6 |
4.4 |
Control > AUX (Remote setting, Alarm mode, SP No. selection source) ....................... |
4-11 |
4.5 |
Control > Output processing .......................................................................................... |
4-13 |
4.6 |
Control > Relay .............................................................................................................. |
4-15 |
4.7 |
Control > Tuning setting ................................................................................................. |
4-17 |
viii
IM 04L31A01-03E

|
|
Contents |
4.8 |
Control input range ........................................................................................................ |
4-19 |
4.9 |
Control alarm ................................................................................................................. |
4-23 |
4.10 |
Operation-related parameters/Zone PID ........................................................................ |
4-25 |
4.11 |
PID parameters .............................................................................................................. |
4-27 |
4.12 |
Control group setting ...................................................................................................... |
4-29 |
4.13 |
Ten-segment linearizer I/O ............................................................................................. |
4-31 |
4.14 |
Detailed setting (Control function/Hysteresis) ................................................................ |
4-33 |
Chapter 5 Program Control Related Setup Operations
5.1 |
Program Pattern Setup Procedure ................................................................................... |
5-1 |
5.2 |
Program parameter setting > Pattern initial setting .......................................................... |
5-2 |
5.3 |
Program parameter setting > Wait action setting ............................................................. |
5-4 |
5.4 |
Program parameter setting > Program start setting ......................................................... |
5-5 |
5.5 |
Program parameter setting > Program pattern setting ..................................................... |
5-6 |
5.6 |
Program parameter setting > Event setting ...................................................................... |
5-8 |
5.7 |
Program parameter setting > Repeat action setting ...................................................... |
5-10 |
5.8 |
Event output setting ....................................................................................................... |
5-11 |
5.9 |
AUX (Auto message, Display position) .......................................................................... |
5-12 |
Chapter 6 Operations during Control Operation
6.1Operations on the Control Group Display (Switching Displayed Information and
|
Control Operation Modes) ................................................................................................ |
6-1 |
6.2 |
Switching Displays on the Overview Display .................................................................... |
6-6 |
6.3 |
Tuning Operation .............................................................................................................. |
6-7 |
6.4Operations on the Program Control Display (Only on Models with the Program
Control Option) ............................................................................................................... |
6-10 |
Chapter 7 Measurement Function Related Setup Operations
7.1 |
Settings Related to Measurement Inputs ......................................................................... |
7-1 |
7.2 |
Settings Related to Measurement Alarms ....................................................................... |
7-6 |
7.3 |
Setting the Temperature Unit ......................................................................................... |
7-11 |
Chapter 8 Operations for Changing the Displayed Contents
8.1Using the Information Display (Alarm Summary, Message Summary, Memory
|
Summary, and Control Summary) .................................................................................... |
8-1 |
8.2 |
Measurement Function > Measurement Group Setup Operation .................................... |
8-2 |
8.3 |
Measurement Function > Settings Related to Tag Display for Channels ......................... |
8-4 |
8.4Measurement Function > Operations When Displaying Trend, Digital, and Bar
|
Graph Displays ................................................................................................................. |
8-6 |
8.5 |
Measurement Function > Operations When Displaying the Overview ............................. |
8-8 |
8.6 |
Measurement Function > Operations When Displaying the Historical Trend ................... |
8-9 |
8.7 |
Measurement Function > Changing the Display Update Rate of the Trend Display ...... |
8-10 |
8.8Measurement Function > Settings Related to Messages Displayed on the
|
Trend Display and Write Operation ................................................................................ |
8-11 |
8.9 |
Measurement Function > Changing the Trip Line of the Trend Display .......................... |
8-13 |
8.10 |
Measurement Function > Changing the Channel Display Color .................................... |
8-14 |
8.11 |
Measurement Function > Changing the Zone Display of the Trend Display .................. |
8-16 |
8.12Measurement Function > Setting the Scale Division, Bar Graph Base Position,
|
Scale Position of Trend Displays .................................................................................... |
8-17 |
8.13 |
Measurement Function > Setting the Partial Expanded Display on the Trend Display .. |
8-21 |
8.14 |
Measurement Function > Setting the Display Direction, Background Color, |
|
|
Waveform Line Width, Trip Line Width, Grid, and Scroll Time ........................................ |
8-23 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
App
Index
IM 04L31A01-01E |
ix |

Contents
Chapter 9 Data Save/Load Operations
9.1Acquiring Measurement Data to the Internal Memory and Saving Data to
|
the External Storage Medium .......................................................................................... |
9-1 |
9.2 |
Saving Measured/Computed Data at Arbitrary Times (Manual Sample) ......................... |
9-7 |
9.3 |
Saving and Loading Setup Data ...................................................................................... |
9-8 |
9.4 |
Loading the Stored Display/Event Data (Historical Trend) ............................................. |
9-10 |
9.5 |
Managing Files and Checking the Free Space on the External Storage Medium .......... |
9-11 |
9.6 |
Saving the Screen Image Data ...................................................................................... |
9-13 |
9.7 |
Clearing the Data in the Internal Memory ...................................................................... |
9-14 |
Chapter 10 Computation and Report Function Related Operations (Only on Models with the Computation Function Option)
10.1Assigning Computation Channels and Setting Computing Equations,
|
Constants and Tags ....................................................................................................... |
10-1 |
10.2 |
Starting, Stopping, and Resetting the Computation ....................................................... |
10-4 |
10.3 |
Setting Computation Channel Alarms ............................................................................ |
10-5 |
10.4 |
Setting TLOG Computations .......................................................................................... |
10-8 |
10.5 |
Setting the Rolling Average .......................................................................................... |
10-11 |
10.6 |
Creating Reports .......................................................................................................... |
10-12 |
10.7 |
Starting/Stopping the Report Function ......................................................................... |
10-14 |
Chapter 11 Operations of Other Functions
11.1 |
USER Key Assignment and Operation .......................................................................... |
11-1 |
11.2 |
Key Lock ......................................................................................................................... |
11-3 |
11.3 |
Key Operation Login/Logout .......................................................................................... |
11-5 |
11.4Displaying Logs (Checking Operations) and System Information Display
(Checking the System Specifications) ............................................................................ |
11-8 |
11.5 Setting the Measurement Remote Input (/A6R option or /A4FR option) ...................... |
11-11 |
Chapter 12 Troubleshooting
12.1 |
Messages ....................................................................................................................... |
12-1 |
12.2 |
Troubleshooting Flow Chart ......................................................................................... |
12-11 |
Chapter 13 Maintenance
13.1 |
Periodic Inspection ......................................................................................................... |
13-1 |
13.2 |
Calibration ...................................................................................................................... |
13-2 |
13.3 |
Replacement of Parts .................................................................................................... |
13-4 |
Chapter 14 Specifications
14.1 |
Input Section Specifications |
........................................................................................... 14-1 |
14.2 |
Control Function ............................................................................................................. |
14-3 |
14.3 |
Alarm Function ............................................................................................................... |
14-4 |
14.4 |
Display Function ............................................................................................................. |
14-5 |
14.5 |
Storage Function ............................................................................................................ |
14-7 |
14.6 |
Communication Functions ........................................................................................... |
14-10 |
14.7 |
Options ......................................................................................................................... |
14-11 |
14.8 |
General Specifications ................................................................................................. |
14-14 |
14.9 |
Dimensional Drawings ................................................................................................. |
14-18 |
x
IM 04L31A01-03E

|
Contents |
Appendix |
|
Appendix 1 Supplementary Explanation of the Acquisition of Display Data/Event Data |
|
to the Internal Memory ....................................................................................... |
App-1 |
Appendix 2 Supplementary Explanation of the Computation Function ................................ |
App-6 |
Appendix 3 Meaning and Syntax of Equations ..................................................................... |
App-9 |
Appendix 4 Additional Explanation of the Report Function ................................................ |
App-13 |
Appendix 5 Data Format of ASCII Files .............................................................................. |
App-16 |
Appendix 6 Initial Values ..................................................................................................... |
App-20 |
Appendix 7 Control Function Block Diagram ...................................................................... |
App-33 |
Appendix 8 Explanation of Engineering Units (EU and EUS) ............................................. |
App-39 |
Index |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
App
Index
IM 04L31A01-01E |
xi |
Chapter 1 Explanation of Functions
 1.1 CX1000 Overview
1.1 CX1000 Overview
The CX1000 consists of a control function and a measurement function. The control function executes control through PID control and ON/OFF control. The measurement function displays and acquires measured data and control-output data.
Control Function
The CX1000 supports thee control modes: single-loop control, cascade control, and loop control with PV switching. It can handle up to two loops of PID control. In addition, the UT Series controllers made by Yokogawa M&C Corporation can be connected and controlled simultaneously as external loops (four loops max.). You can check the control status on the controller style and faceplate style displays and the hybrid style display that is a mixture of the two styles. Furthermore, the overview display allows monitoring of all control loops including external loops. In addition, the CX1000 provides auto-tuning of PID constants as well as manual tuning, which enables you to adjust the control parameters such as PID constants while checking the control status.
Measurement Function
In addition to the measured data for the control function, the CX1000 can acquire up to six channels of measured data. The data can be displayed as waveforms, numeric values, and bar graphs. The measured data along with the control data can be stored to a floppy disk, Zip disk, or ATA flash memory card using the built-in drive.
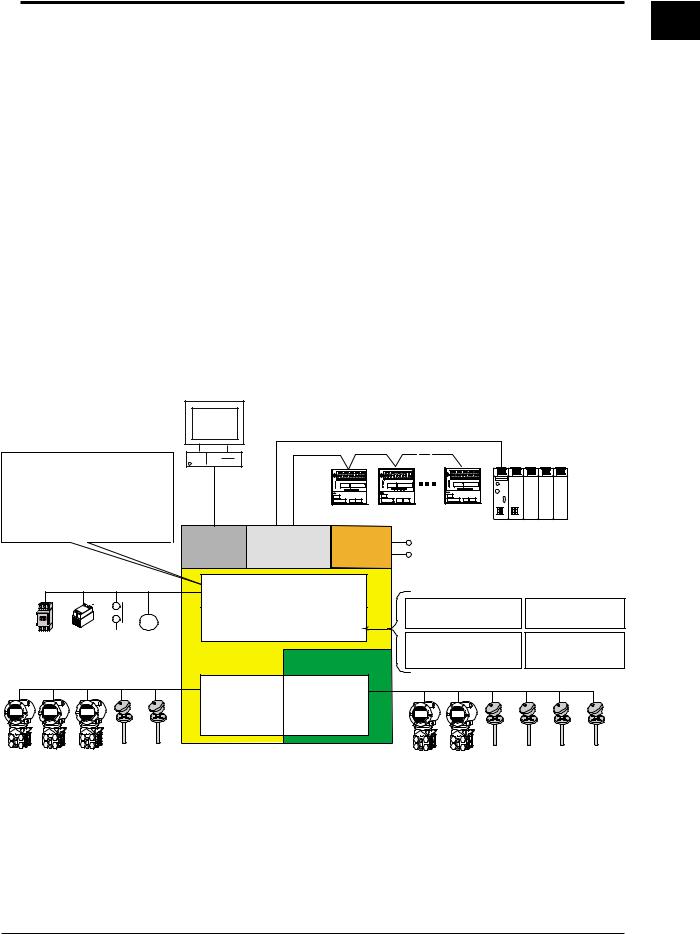
Conceptual Input/Output Diagram
PC
•Universal control output: for 2 loops Select current, voltage pulse, or relay output.
•Control contact input: 6 inputs
•Control contact input Relay output: 2 outputs
Transistor output: 4 outputs
LAN
(Ethernet)
CX1000
Serial interface Power
Ethernet port
RS-422/485/232 Supply
|
|
Control output terminal |
|
|
|
block (Loops 1 and 2) |
|
|
R1 |
Option terminal block |
|
|
(Can be installed in place of |
||
Magnet |
SSR Contact Contact |
the control output terminal block) |
|
|
|
||
switch |
input output |
Control loop |
Measurement input |
|
6 inputs 6 outputs |
section |
|
|
|
section |
|
|
|
(select 0 or 2 loops) |
|
5 universal measurement inputs |
Control/measurement input |
||
|
|
terminal block |
|
|
|
Control input |
Measurement input |
|
|
terminals |
terminals |
|
|
|
CH1 to CH6 |
Controllers (up to |
|
|
4 loops) |
PLC |
|
100 VAC to 240 VAC |
(such as the FA-M3 |
|
by YOKOGAWA) |
||
24 VDC/AC (/P1 option) |
|
|
Select one from the following option |
||
terminal blocks. |
|
|
Measurement alarm output |
Measurement alarm |
|
output + remote input/ |
||
(/A6 option) |
||
output (/A6R option) |
||
|
||
Measurement alarm output + |
Measurement alarm |
|
output + FAIL/memory |
||
FAIL/memory end output |
||
end output + remote |
||
(/A4F option) |
input/output (/A4FR option) |
|
6 universal measurement inputs
1
of Explanation
Functions
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-1 |

 1.2 Control Function Overview
1.2 Control Function Overview
Control Signal Input/Output
As shown in the following figure, the CX1000 can control up to two loops.
Control PV input (number of analog inputs: 5)
|
··· [Up to 2 loops] |
|
|
Control output |
|
|
• Relay |
|
|
• Voltage pulse |
|
CX |
• Current |
Controls |
|
|
and |
|
· |
switches |
|
· · |
|
|
DISP/ |
|
• TC
• RTD etc.
Object of
control
•SSR
•Magnet switch etc.
The UT Series controllers made by Yokogawa M&C Corporation can be connected via the serial interface and controlled simultaneously as external loops (four loops max.) (see the CX1000/CX2000 Communication Interface User’s Manual).
Analog Input for Loop Control
PV input and remote setpoint input (RSP) are available as control signal inputs. You can select thermocouple, resistance temperature detector, standard signal, or DC voltage for both PV input and RSP input. The RSP input is used as a terget setpoint (SP). There are five input terminals on the control/measurement input terminal block. The figure below shows their assignments according to the number of loops used and the control mode (see the next page).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement input terminals |
|
||||||||
[Control mode setting] |
LOOP2 |
|
LOOP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
During single-loop control |
2 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(RSP) |
PV |
|
(RSP) |
PV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
During cascade control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
PV |
|
(RSP) |
PV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
During loop control with |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PV2 |
PV1 |
(RSP) |
PV2 |
PV1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
PV switching |
PV, PV1, PV2: PV input, (RSP): RSP input |
|
|
|
(not used during program control), : unused terminal |
You can apply scale conversion, bias, input filter, ten-segment linearizer bias, tensegment linearizer approximation, and square-root computation on the control signal input. For thermocouple inputs, you can set reference junction compensation. In addition, ratio setting can be specified against RSP inputs.
Control Signal Output
The terminal provides universal output. Two loops can be controlled (except cascade control which uses two loops for one control). The following types of control output can be selected.
• PID control output |
|
• Time proportional PID |
Outputs ON/OFF signals with a pulse width that is proportional |
relay contact output: |
to the time as relay contact signals according to the computed |
|
PID value. |
• Time proportional PID |
Outputs ON/OFF signals with a pulse width that is proportional to |
voltage pulse output: |
the time as voltages according to the computed PID value. |
• Current output (continuous Continuously outputs a current (analog signal) that is |
|
PID control output): |
proportional to the computed PID value. |
• On/off control relay |
Outputs on/off control relay contact signals according to the |
contact output: |
polarity (positive/negative) of the deviation between the SP |
|
and the PV. |
1-2 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |

1.2 Control Function Overview
Control Methods
PID control and ON/OFF control are available. The following control modes can be selected for both PID control and ON/OFF control.
Control Mode
In PID control, the following three control modes are available in relation to the PV input selection.
•Single-loop control
Basic control consisting of a single system of controller CPU.
PV
SP 
 PID
PID
OUT
•Cascade control
Control consisting of two systems of controller CPUs that use the primary control
output as the secondary control SP.
|
|
|
PV1 |
|
PV2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SP |
|
|
PID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PID |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT
•Loop control with PV switching
Single-loop control that is switched between two PV inputs (PV1 and PV2) according to a specified condition.
PV1 PV2
SP 
 PID
PID
OUT
In PID control, you can also select the PID control mode.
PID Control Mode
Depending on the desired operation at the time the SP is changed, you can select the PID control mode from below. The selections between the PV derivative type and deviation derivative type as well as the presence or absence of the control output bumps are automatically made according to the PID control mode and operation mode (fixedpoint control or program control).
•Standard PID control
Controlled so that the control output reaches the new SP quickly after the SP is changed.
PV derivative type PID |
|
Deviation derivative type PID |
|
(with output bump) |
|
(with output bump) |
|
|
|
PV |
|
SP |
OUT |
SP |
OUT |
PV |
|||
•Fixed-point control
Select this mode if you wish to avoid the control OUT from reacting sensitively to the SP change causing a disturbance in the control such as in the case with a continuous
fixed-point control.
PV derivative type PID (without output bump) |
PV derivative type PID (with output bump) |
|
|
|
PV |
|
|
SP |
SP |
|
|
PV |
OUT |
OUT |
1
of Explanation
Functions
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-3 |

1.2 Control Function Overview
Control Parameters
The following control parameters are available. For each group, you can enter up to eight sets of SPs and PID parameters as underlined below.
SP, PID constant, control output limiter, ON/OFF of the shutdown function, manual reset value, relay hysteresis, control action direction, preset output, SP tracking, PV tracking, setpoint limiter, output velocity limiter, auto/manual switching of the over-integration prevention function (anti-reset windup), ON/OFF of the control output suppression function, and SP ramp-rate.
PID Selection Method
The following two methods are available.
•Target setpoint selection method
A group (up to 8 groups) consisting of a SP and PID parameters is registered to a PID number (SP number). By specifying the SP number using keys on the front panel, external contact input, or via communications, the SP and PID parameters are switched.
PV |
|
Rise according to the |
SP3 |
Fall according to the |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
(No.3PID) |
setpoint ramp-down |
SPn: Target setpoint number |
|||
|
|
setpoint ramp-up |
||||
|
|
|
setting |
SP2 |
||
|
|
setting |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
(No.2PID) |
|
|
|
SP1 |
|
SP1 |
Rise according to the |
|
|
|
(No.1PID) |
|
(No.1PID) |
setpoint ramp-up |
|
|
|
|
setting |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Switch from SP1 to SP3 |
Switch from SP3 to SP1 Switch from SP1 to SP2 |
|||
•Zone PID method
The measurement span is divided into a maximum of seven zones using reference points. The optimum PID constant is preassigned to each zone, and the PID constant (in actuality, other control parameters that are registered using the PID number are included) is automatically switched according to the PV. This method is suited for controlling equipment such as reactors in which the chemical reaction gain varies
depending on the temperature.
Maximum value of measurement span
Reference point 6
Reference point 5
Reference point 4
Reference point 3 Reference point 2
Reference point 1
Minimum value of measurement span
If the current PV is here, PID constant of PID No. 5 is used for control.
Change in the
PV.
No.7 PID
No.6 PID
No.5 PID
No.4 PID
No.3 PID
No.2 PID
No.1 PID
Note
•When performing program control operation on models with the program control option, you will select between segment PID method (zone PID selection OFF) and zone PID method.
•For a description on auto tuning, which automatically sets the optimum PID constant, see section 1.12, “Tuning.”
1-4 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |

1.2 Control Function Overview
Alarm Output
When the control action status matches the preset status (up to 4 points per loop), the CX1000 can output a relay contact signal from the control output terminal block or the DIO expansion terminal block or display the alarm occurrence status on the screen. In relay contact output, you can select and assign the type of alarm you wish to output at each output terminal of the control output terminal block or the control DIO extension terminal block.
Alarm Type
You can select the alarm type from below. For a detailed explanation on each alarm output, see section 1.10, “Control Alarm Related Settings.”
PV high-limit alarm, PV low-limit alarm, deviation high-limit alarm, deviation low-limit alarm, deviation high & low limit alarm, deviation within high & low limits alarm, SP highlimit alarm, SP low-limit alarm, output high-limit alarm, and output low-limit alarm.
Alarm Hysteresis
You can set a hysteresis to the setpoints used in the activation and releasing of the alarm.
Example of PV high limit alarm
ON
OFF
Alarm setpoint
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
PV
 Alarm ON
Alarm ON
 OFF
OFF
 ON
ON
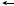 OFF
OFF
Time
Alarm Standby
You can put the alarm output on standby at the initial stage of control operation until the PV input reaches the SP.
PV |
Normal |
Normal |
Failure |
handling |
|
Alarm output ON |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Hysteresis |
|
|
|
Alarm low limit value |
 Alarm is not output during this period even if the PV is below the alarm low limit.
Alarm is not output during this period even if the PV is below the alarm low limit.

 Time Power up
Time Power up
Alarm Mode
You can set the condition for disabling the alarm output (such as when the operation is stopped).
FAIL Output/Self Diagnosis Output
In addition to the alarm output described above, the following relay contact signal for failure detection can be output from the control output terminal block.
•FAIL output
Output when a failure is detected in the CX1000 CPU. When a failure is detected, the CX1000 is put in the following condition.
Control: Stopped (preset output if in the middle of operation, control output is off or 0% when power is turned ON)
•Self diagnosis output
Output when an input burnout, A/D converter failure, or RJC failure occurs. If an input
burnout or A/D converter failure is detected, the control output is set to the preset output value. For RJC, PID control continues as though RJC is 0 °C.
1
of Explanation
Functions
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-5 |
1.2 Control Function Overview
Control Operation Mode
The following control operation switching is available. The control operation can be switched using keys on the CX1000 control group display (see page 1-12), using contact inputs, or via communications. For a description of the control operation modes on models with the program control option, see “Program Control” in the next section. The control function block diagram in the explanation below is a simplified one. For a detailed control function block diagram for each control mode, see appendix 7.
Switching between Remote (REM) and Local (LOC)
Select whether control is executed using the SPs set on the CX1000 or using the external analog signal (RSP) as the SP.
PV input |
RSP input (Analog signal) |
|
PV |
|
RSP |
SP |
|
|
Local |
|
Remote |
(LOC) |
|
(REM) |
Controller CPU |
|
|
Control output |
OUT |
|
Switching between Auto (AUT), Manual (MAN), and Cascade (CAS)
When set to auto, the control output value (OUT) is computed from the deviation between the PV input and the SP. When set to manual, the control output value (OUT) that is set manually is used rather than the computed control output value (OUT). Switching to “cascade (CAS)” is possible only when the control mode is set to “cascade control.” In cascade control, the primary PID control output is used as the SP of the secondary PID control.
Switching between Run (RUN) and Stop (STP)
When the operation is stopped, the control output value (OUT) is set to the preset value.
Single-loop control |
PV input |
|
|
|
PV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SP |
Manual operation |
Controller CPU |
|
Manual (MAN) |
Auto (AUT) |
|
|
||
Preset output |
Output limiter |
|
Stop (STP) |
|
Run (RUN) |
Control output OUT
Cascade control |
|
PV input 1 |
PV input 2 |
(Cascade primary) |
(Cascade secondary) |
PV1 |
|
PV2 |
|
SP1 |
|
||
Controller CPU 1 |
SP2 |
||
Cascade |
|
Auto/ |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Manual |
|
Manual operation Controller CPU 2 |
|||
Manual (MAN) |
Cascade/ |
||
Auto |
|||
|
|
||
|
|
(CAS/AUT) |
|
Preset output |
Output limiter |
||
Stop (STP) |
|
Run (RUN) |
|
Control output OUT
Enabling/Disabling Auto-Tuning
In PID control, the optimum PID constant is set automatically when auto-tuning (see page 1-52) is performed. Auto-tuning is possible only during auto operation.
Contact Input
Contact input can be used to carry out operations such as running/stopping operation, switching operation modes, changing SPs, switching PV inputs (during loop control with PV switching). For a description on the possible operations, see “Contact Input Information Registration” on page 1-23.
1-6 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |

1.2 Control Function Overview
Program Control (Optional Function)
|
This function is used to ramp-up or ramp-down the SP according to a program pattern. You can |
|
|
set multiple program patterns (up to 30) and switch among them according to the operating |
|
|
condition. A program pattern consists of multiple program segments. |
|
|
There are two methods in selecting the PID constant in program control. One is the |
|
|
“segment PID method” in which the PID constant is switched every segment according to |
|
|
the program pattern setting; the other is the “zone PID method” in which the PID |
|
This |
constant is automatically switched according to the PV. The “segment PID method” is |
|
used when a different PID constant is required in the same PV region when the |
||
|
||
|
temperature is rising and when the temperature is falling. |
The |
function |
|
|
|
Segment PID method |
|
|
The PID constant of PID No. 1 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
PV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
is used in the 5th segment (SEG5). |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
1000.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
infomation |
|
500.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
cannot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
given0.0 |
be |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
SEG1 SEG2 |
SEG3 |
SEG4 SEG5 |
SEG6 |
|
SEG7 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
here |
No.2 PID |
|
No.1 PID |
|
No.3 PID |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
used |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Setting the Operation for Program Control |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
on |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Settings include the number of repetitions of the program pattern (repeat function), delay |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
may |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
function (wait function) for the case when the PV cannot follow up the SP, and alarm |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
output/event output assignments (contact output assignments) according to the program |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
progression. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Operation Mode during Program Cont ol |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
change |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
The following 4 types of operation modes are available. |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
current |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
• |
|
Program operation mode |
in |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Condition in which control is carried out according to the program pattern. |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
• |
|
Hold operation mode |
|
the |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Condition in which program operation is paused. |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
• |
|
Reset mode |
|
|
|
|
|
version |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Condition in which program operation is stopped.futureAll vent |
utputs are cleared (off). |
||||||||||
|
|
|
• |
|
Local operation mode |
|
|
|
|
. |
|
the |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Mode in which fixed-point control is performed independently from the program |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
operation condition. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CX1000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Reset mode |
|
|
|
|
Local operation mode |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RUN |
|
RUN per |
|
|
|
|
|
. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
RESET |
|
loop |
|
|
|
LOC |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Release HOLD |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Program operation mode |
|
|
Hold operation mode |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HOLD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program operation |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Since the remote input cannot be used for the SP during program control, there is no |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
remote/local switching operation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
IM 04L31A01-03E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1-7 |
|
|
1
of Explanation
Functions

1.2 Control Function Overview
Flow of Setup Procedure
Below is a standard flow of setup procedure in executing control for the first time using
auto operation.
|
Power ON |
|
|
Operating condition |
|
|
Stop control |
|
|
Initial settings |
|
|
PID control or |
* |
|
ON/OFF control?* |
|
ON/OFF control |
PID control |
|
Set SP |
Set SP |
|
Section 1.10 |
|
|
Set relay hysteresis |
Set PID parameters |
|
Initial settings include the following parameters.
Initial settings
Basic control settings |
→ Section 1.3 |
||
|
→ Section 1.4 |
||
|
|
||
PV input related settings |
|||
Contact input/output |
→ Section 1.5 |
||
Set in |
related settings |
||
Control output |
|
||
"Control Output Type" |
|
||
of basic control settings |
suppression |
|
|
→ Section 1.6
→ Section 1.7
Set other control |
Set alarm-related |
||
parameters |
parameters |
||
Set alarm-related |
|
|
|
Start a test run |
|||
parameters |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Operating condition |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjust control |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Start actual operation |
||
|
|
|
|
→ Section 1.10
• Auto tuning
• Manual tuning → Section 1.12
•Other adjustments
(Parameters that cannot be changed during operation → section 6.1)
When using program control, set the items that include “Program control: On” in “Basic control settings” indicated above. Then, carry out the following settings in addition to
“Target setpoint/PID parameter settings.”
Settings for program control |
|
→ Section 1.11 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
Pattern initial setting: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
This |
|
|
Set the pattern numbers, pattern off/on, number of |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Pattern initial setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The |
function |
|
|
segments used, segment assignment method, and |
|||||
|
|
|
edit segment number. |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Wait operation setting: |
|
|
||||
Wait operation setting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
infomation |
|
|
Set wait zone off/on, wait zone settings, and timer. |
|||||
|
|
|
Pattern start setting: |
|
|
||||
|
cannot |
|
|
||||||
|
Set starting target setpoint and start code (operation |
||||||||
Pattern start setting |
|
|
|||||||
|
given |
be |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
start condition). |
|
|
|
||
Program pattern setting |
hereProgramused |
pattern setting: |
|
||||||
|
|
Set segment numbers, ramp/soak, final target setpoint, |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
on |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
may |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
segment time, ramp-rate-time unit, ramp-rate, segment |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
the |
|
|
|
|
Event setting |
|
|
PID group numbers, operation at the time of segment |
||||||
|
|
switching, wait operation type, and wait numbers. |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
change |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
current |
|
|
|
Event output setting |
|
|
Event setting:in |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Set event types, loop number/type/setpoint (only when |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PV event is selected), time event ON/OFF, and ON time/ |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
version |
||
|
|
|
|
OFF time (only when time event is selected). |
|||||
Repeat action setting |
|
|
|
|
future |
of |
|||
|
|
Event output setting: |
. |
the |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Set the event type, relay output ON/OFF, and relay |
|||||
Operation start time* |
|
|
output number. |
|
|
CX1000 |
|||
|
|
|
|
Repeat action setting: |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
Start segment number* |
|
|
Set the repeat function, number of repetitions, start |
||||||
|
|
segment number, and end segment number. |
|||||||
*The operation start time and start segment number is set using key operations on the operation screen.
1-8 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1.2 Control Function Overview
Switching Displays
Control-related settings are entered in basic setting mode and control setting mode. In addition, settings common to control and measurement are entered in the common and measurement setting mode.
Power ON |
Display Transition Diagram |
|
|
Operation mode |
|
|
|
|
[End] soft key -> DISP/ENTER key
(This operation saves the settings made
in the basic setting mode.)
Operation display
MENU key or ESC key
MENU key |
ESC key |
Control setting mode |
Common and measurement setting mode |
Basic setting |
[Setting mode (Control)] |
[Set mode] |
mode |
|
|
MENU key |
|
|
Press the FUNC |
|
|
Menu |
Press the FUNC |
|
Menu |
key for 3 s |
Menu |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
key for 3 s |
|
|
|
|
Soft keys |
MENU key or |
|
Soft keys |
MENU key or |
Soft keys |
ESC key |
ESC key |
|
ESC key |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Setup display |
|
|
Setup display |
Setup display |
|
|
(#1 to #7*) |
|
|
(#1 to #11) |
(#1 to #12**) |
|
* #1 to #8 when program control |
|
|
** #1 to #11: Basic common and |
|||
is ON. |
|
|
|
|
measurement settings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
#12: Basic control settings |
|
Basic Control Setup Items in Basic Setting Mode
#1 Control action
PID number, control period, zone PID, restart mode, restart mode (program) (only on models with the control option), initial PID, auto tuning, control mode, method (only during loop control with PV switching), program control ON/OFF (only on models with the program control option), and PID control mode.
#2 Input setting Burnout and RJC.
#3 Contact input-registration Contact input registration
#4 AUX
Remote setting, alarm mode, and SP number selection source. #5 Output processing
Control output, cycle time, and analog-output type #6 Relay
FAIL ON/OFF, self diagnosis ON/OFF, and relay action/behavior (energize/deenergize, hold/nonhold)
#7 Tuning setting Tuning item selection
#8 External loop setting (For details on the settings, see the CX1000/CX2000 Communication Interface User’s Manual.)
Setup Items in the Control Setting Mode
#1 Control input range
Input type, mode, type, range, span, scale, unit, square root, low-cut, bias, filter, and ratio. #2 Control alarm
Type, standby, relay output ON/OFF, and alarm value
1
of Explanation
Functions
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-9 |

1.2 Control Function Overview
#3 Operation-related parameters/Zone PID
Suppressing function, ramp-rate-time unit, SP ramp-down-rate/SP ramp-up-rate, tag, tag comment, reference point (when zone PID is selected), switching hysteresis (when zone PID is selected), and reference deviation (when zone PID is selected).
#4 PID parameters
SP, PID constant, output limit, shutdown ON/OFF, manual reset, relay hysteresis (only during ON/OFF control), reverse/direct, and preset output.
#5 Control group setting
Group name, kind (internal loop/external loop/measurement channel), and number. #6 Ten-segment linearizer I/O
Input type, mode, and biasing or approximation input/output values. #7 Program control (only when program control is ON)
#1 Program parameter setting
Pattern initial setting, wait action setting, program start setting, program pattern setting, event setting, and repeat action setting.
#2 Event output setting
Event kind, relay output ON/OFF, number, and program pattern end signal relay output ON/OFF.
#3 AUX (Auto message, Display position)
Auto message for program Run/Reset and Program display position. #8 Detailed setting (“#7” when program control is OFF)
#1 Control function
SP tracking, PV tracking, SP limiter, output velocity limiter, and anti-reset windup auto/manual.
#2 Hysteresis (Alarm and PV event)
Alarm hysteresis and PV event hysteresis
1-10 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |

1.2 Control Function Overview
Control Operation Display
In operation mode, the following control operation displays can be shown.
•Control group display
This display is used to monitor the control status of multiple loops simultaneously including external loops. You can select from three display styles as shown in the display example in the figure below. If you include the measurement channels for the measurement function in the group, you can also monitor the measured values on the measurement channels at the same time on this display.
•Tuning display
This display is used to optimize (tune) the control parameters such as PID constants.
•Overview display
This display is used to monitor the alarm status of all control loops.
•DI/DO status display
Displays the ON/OFF status of the current contact input (DI) and contact output (DO).
•Control action summary display
Displays a log of control actions such as operation run/stop and auto/manual operation switching.
On models with the program control function option, the following additional displays are available: 1) the program operation display, which can show the pattern and current PV accumulated on the screen during program operation and 2) the program event summary display, which shows a log of time events and PV events that occurred during program operation. Displays common with the measurement function include: 1) the alarm summary display, which shows a log of alarm occurrence status and 2) the memory summary display, which shows the file information of the internal memory. In addition, the values of PV, SP, and OUT can be assigned to channels, and the trends of these channels can be displayed along with the trends of measurement channels on the trend display of the measurement function.
Display Examples
• Control group display
1
of Explanation
Functions
Controller style |
Faceplate style |
Hybrid style |
• Tuning display |
• Overview display |
• DI/DO status display |
• Control operation summary display • Trend display
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-11 |

1.2 Control Function Overview
Saving Data
Acquisition to the Internal Memory
Along with the measurement data, the data of SPs, PVs and OUT, and event information for control are acquired to the internal memory.
Saving Data to the External Storage Medium
You can save the data acquired in the internal memory to an external storage medium (floppy disk, Zip disk, or ATA flash memory card).
Floppy disk
CX
Zip disk
• Control setup data |
ATA flash memory card |
|
•Measurement setup data
•Measured data
Communications
The following communications functions are available. For a description on the handling of the communications function and the software “DAQSTANDARD for CX” that comes with the package, see the respective manuals.
Communications with Controllers
The CX1000 can communicate with UT Series Controllers made by Yokogawa M&C Corporation to transmit/receive control parameters and receive PV data. Up to four external loops can be constructed.
CX
Controllers
Up to four units (four loops)
Communications with PLCs
The CX1000 can carry out ladder communications between PLCs (sequencers).
PLCs (such as the FA-M3 by YOKOGAWA)
CX |
CX |
Up to 32 units
Communications with PCs
The CX1000 can communicate with PCs.
|
|
• Modbus master/slave |
|
|
PC |
• Dedicated protocol communications |
|
CX |
with the PC (Command communications) |
||
|
|||
|
|
• Display settings/data of the CX using |
|
|
|
“DAQSTANDARD for CX” |
1-12 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |

1.2 Control Function Overview
 1.3 Basic Settings of Control
1.3 Basic Settings of Control
PID Group Number
You can set up to eight groups of control parameters (“PID parameters” on the setting display) that you wish to change collectively through control. You set the number of groups to be used from 1 to 8. For example, if you set a value of 4, the selectable PID numbers will be 1 through 4. The parameters that are included in a single control parameter group vary depending on the control method (“Control output” in the settings). During PID control: SP, PID constant, output lower/upper limit, shutdown ON/OFF
(only when outputting 4-20 mA of current), manual reset, reverse/ direct, and preset output
During ON/OFF control: SP, relay hysteresis, reverse/direct, and preset output
Control Period
The following control periods can be selected: 250 ms (initial value), 500 ms, and 1 s.
The control period is common to all loops. When the A/D integral time is set to 100 ms, the control period is fixed to 1 s.
The scan interval of control PV input is the same as the control period.
PID Selection Method (Zone PID ON/OFF)
Select either one from below. When program control is ON on models with the program control option, the selection is between the segment PID method (zone PID OFF) and the zone PID method.
•Target setpoint selection method (zone PID: OFF) (initial value)
In the target setpoint selection method, the operator can switch up to 8 SPs as necessary. There are two methods in switching the SPs. One method is to specify the SP number (SPs are registered to PID numbers (= SP numbers) along with PID constants and other parameters) using keys on the front panel. The other is to use external contact input or communications. The SP can be switched at any time. During switching, the setpoint ramp-up-rate or setpoint ramp-down-rate setting is activated. In addition, when a switch is made, control computation is performed using the PID constant group that corresponds to the SP at that point.
PV |
|
Rise according to |
SP3 |
|
|||
|
|
(No.3PID) |
|
|
|
the setpoint |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ramp-up setting |
|
|
|
SP1 |
|
|
|
(No.1PID) |
|
|
|
|
|
Fall according to the setpoint ramp-down setting
SP1
(No.1PID)
SPn: SP number
SP2
(No.2PID)
Rise according to the setpoint ramp-up setting
 Time
Time
Switch from SP1 to SP3 Switch from SP3 to SP1 Switch from SP1 to SP2
1
of Explanation
Functions
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-13 |

1.3Basic Settings of Control
•Zone PID method
In the zone PID method, the measurement span is divided into a maximum of seven zones using reference points. The optimum PID constant is preassigned to each zone, and the PID constant (in actuality, other control parameters that are registered using the PID number are included) is automatically switched according to the PV.
The number of reference points that can be specified is “PID group number – 2.” As shown in the figure below, if the PID group number is 7, the number of reference points is 5. If the number of reference points is 5, there are 6 zones. For example, if zones 1 through 6 correspond to PID numbers 1 through 6 and if the PV is within the zones of reference points 3 and 4, the control parameters of PID number 4 are selected. The control parameters of PID number 7, which cannot be assigned to a zone, are selected when the deviation between the
SP and PV becomes greater than the preset reference deviation.
Maximum value of measurement span
Reference point 5
Reference point 4
Reference point 3
Reference point 2
Reference point 1
Minimum value of measurement span
If the current PV here, control using thePID constant of No. 4.
Change in the
PV.
No.6 PID
No.5 PID
No.4 PID
No.3 PID
No.2 PID
No.1 PID
Restart and Restart for Program Control
Select how the CX1000 is to behave when an extended power failure occurs during control operation (power failure period of 5 s or more) and the power recovers.
•Continue (initial setting):
Continue the operation before the power failure occurred.
•Manual operation:
Start from the manual operation condition.
•Auto operation (only during fixed-point operation):
Auto operation by continuing the operation before the power failure occurred.
•Reset (only during program operation): Stop the program operation.
Note
If the duration of the power failure is less than or equal to 2 s (a short power disruption), the operation before the disruption continues. If the duration is between 2 to 5 s, the behavior for a short power disruption or an extended power failure is carried out depending on the condition.
Initial PID
Select whether the initial PID constant in PID parameter settings (see page 1-28) is optimized to temperature control, pressure control, or flow control. Below are the initial values of PID constants.
Initial values for temperature: P = 5.0%, I = 240 s, and D = 60 s.
Initial values for pressure/flow: P = 120.0%, I = 20 s, and D = 0 s.
Control Mode
The following three control modes are available. The mode is selected for each control loop.
•Single-loop control
Basic control consisting of a single system of controller CPU.
|
|
|
PV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SP |
|
|
PID |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
|
1-14 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |
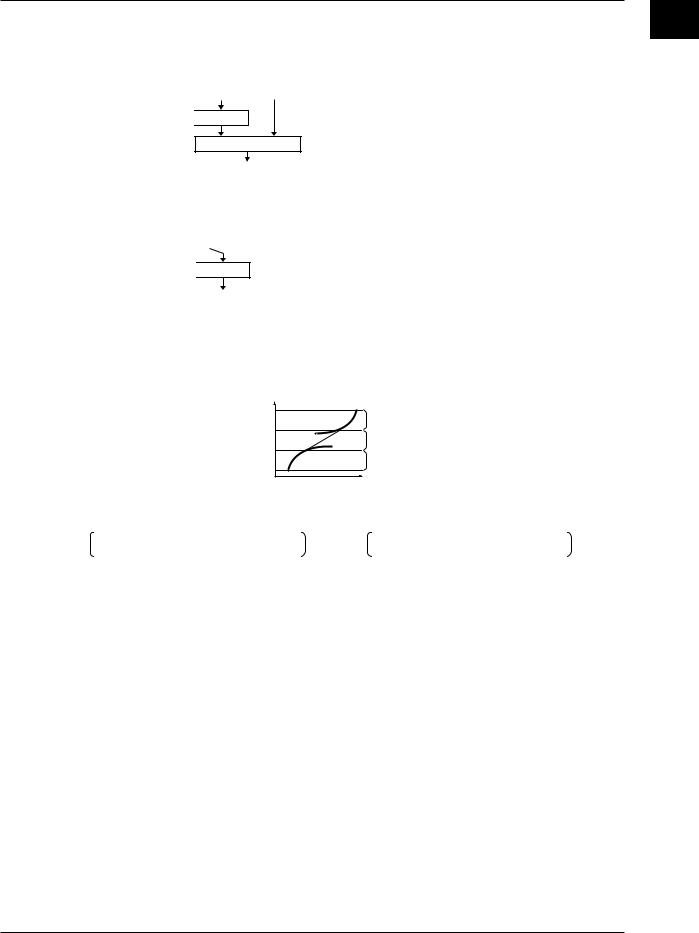
1.3 Basic Settings of Control
•Cascade control
Control consisting of two systems of controller CPUs that uses the primary control output as the secondary control SP. Continuous PID control is only possible for primary control.
PV1 PV2
SP
 PID
PID
PID
OUT
•Loop control with PV switching
Single-loop control that switches between two PV inputs (PV1 and PV2) according to the following conditions.
PV1 PV2
SP 
 PID
PID
OUT
Input Switching Condition ([Method] on the setting display)
•Auto switching according to the PV range ([Range] on the setting display) Switches PV inputs (PV1 and PV2) automatically according to the preset “PV switching low-limit” and “PV switching high-limit” as shown in the following figure.
However, PV1 must be less than PV2.
PV
PV range high limit
PV2
PV switching high limit
Process value according
PV switching low limit to the equation
PV1
PV range low limit
The PV value is computed using the following equation when “PV switching lower limit < PV1 ≤ PV switching upper limit” and “PV switching lower limit ≤ PV2 < PV switching upper limit.”
Process value = 1– |
PV input 1 – PV switching low limit |
× PV input 1+ |
PV input 1 – PV switching low limit |
× PV input 2 |
PV switching high limit – PV switching low limit |
PV switching high limit – PV switching low limit |
•Auto switching according to the PV switching upper limit ([PVHigh] on the setting display) The preset “PV switching upper limit” and PV1 are compared. Auto switching is performed according to the following conditions. The switching hysteresis is
approximately 0.5% of the PV range span.
When PV1 ≤ PV switching upper value: Switch to PV1 When PV1 > PV switching upper value: Switch to PV2
•Switching through control input ([Signal] on the setting display)
Input is switched using “PV switching (loops 1 and 2)” (see page 1-23) as follows:
Contact input is OFF: Switch to PV1. Contact input is ON: Switch to PV2.
Program Control ON/OFF (only on models with the program control option)
Select whether to use the program control function. For a description on the settings for program control, see section 1.11, “Program Control Related Settings.”
1
of Explanation
Functions
IM 04L31A01-03E |
1-15 |

1.3 Basic Settings of Control
PID Control Mode
There are two PID control modes: standard PID control mode and fixed-point control mode. To control the output so that the PV reaches the new SP quickly after the SP is changed, select
“standard PID control mode.” To perform a continuous fixed-point control, select “fixed-point control.” As shown in the figure below, the control behavior varies depending on the selected PID control mode. There are two control methods: PV derivative type PID control method and deviation derivative type PID control method. As shown in the figure below, the control method is automatically selected. In addition, the presence or absence of the control output bump at the point of change of the SP is automatically selected. When performing program control in standard PID control mode on models with the program control option, deviation derivative type PID control is used during operation (except during hold and soak) and on the secondary loop of cascade control. For all other cases, PV derivative type PID control is used.
Type of PID |
Control Method |
Description of the Control Operation |
||
Control Mode |
||||
|
|
|
||
|
PV derivative type PID |
Employs a PV derivative type PID so that the output reaches |
||
|
During operation in local |
the new SP quickly after the target setpoint is changed. In PV |
||
|
mode or auto mode |
derivative type PID, the proportional terms (P) that are |
||
|
(only the primary side |
proportional to the deviation that occurred due to the SP change |
||
|
during cascade control) |
are output immediately, forcing the process value to quickly reach |
||
|
|
the new SP. |
|
|
|
With bumps in the control |
|
|
|
|
output at the time the SP |
SP |
|
|
|
is changed |
|
||
Standard PID |
|
|
||
|
PV |
OUT |
||
control mode |
|
|||
(Initial value) |
Deviation derivative |
By applying the derivative term (D) against the deviation that |
||
|
type PID |
occurs due to minute changes in the program pattern, the process |
||
|
During operation in remote |
value quickly tracks the program pattern. |
|
|
|
mode (secondary side |
|
|
|
|
during cascade control) |
|
|
|
|
With bumps in the control |
|
|
|
|
output at the time the SP |
SP |
|
|
|
is changed |
PV |
OUT |
|
|
|
|||
|
PV derivative type PID |
Use this function on continuous fixed-point control, if you do not |
||
|
During operation in local |
wish to disturb the PV caused by the sensitive reaction of the |
||
|
mode or auto mode |
control output (OUT) at the time the SP is changed. |
||
|
(only the primary side |
In the case of "PV derivative type PID + no control output bumps, |
||
|
during cascade control) |
" the output value (OUT) does not drastically change at the time |
||
|
|
the SP is changed. The deviation is gradually eliminated using |
||
|
|
only the integral term (I) against the deviationthat occurs. |
||
|
Without bumps in the |
|
|
|
|
control output at the time |
|
|
|
|
the SP is changed |
|
|
|
|
|
SP |
|
|
Fixed-point |
|
PV |
OUT |
|
control mode |
|
|||
PV derivative type PID |
Use this function on the secondary loop of cascade control. |
|||
|
||||
|
During operation in remote |
A stable control output is achieved without sensitively reacting to |
||
|
mode (secondary side |
the output of the primary loop. |
|
|
|
during cascade control) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PV |
|
With bumps in the control
SP
output at the time the SP is changed
 OUT
OUT
1-16 |
IM 04L31A01-03E |
 Loading...
Loading...