Siemens FP210L100-22 Datasheet
Differential Magnetoresistive Sensor |
FP 210 L 100-22 |
Features
• High operating temperature
• High output voltage
• Robust cylindrical housing
• Biasing magnet build in
• Signal amplitude independent of speed
• Easily connectable
Typical applications
• Detection of speed
• Detection of position
• Detection of sense of rotation
• Angle encoder
• Linear position sensing
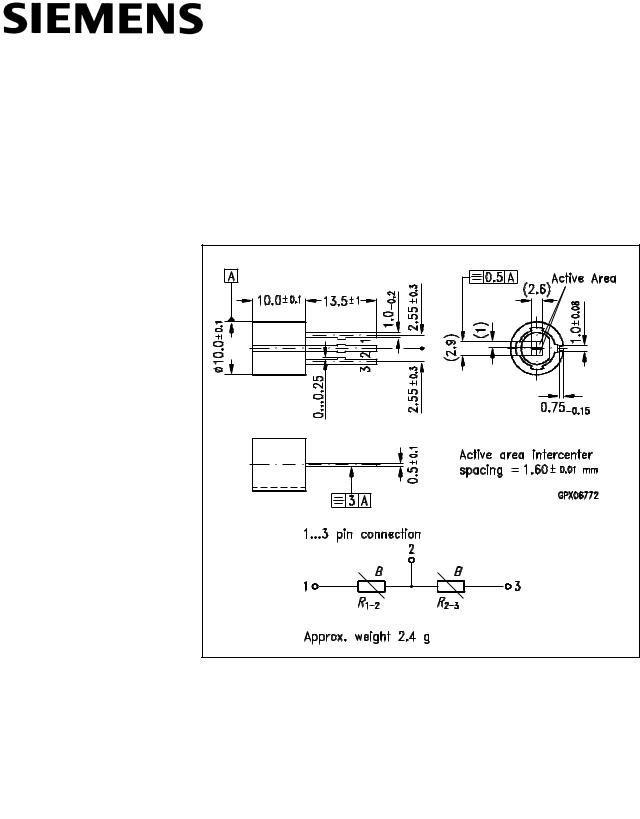
Dimensions in mm
Type |
Ordering Code |
|
|
FP 210 L 100-22 |
Q65210-L100-W4 |
|
|
The differential magnetoresistive sensor FP 210 L 100-22 consists of two series coupled L-type InSb/NiSb semiconductor resistors. The resistance value of the MRs, which are mounted onto an insulated ferrite substrate, can be magnetically controlled. The sensor is encapsulated in a plastic package with three in-line contacts extending from the base. The basic resistance of the total system in the unbiased state is 2×100 Ω. A permanent magnet which supplies a biasing magnetic field is built into the housing.
Semiconductor Group |
1 |
07.96 |

FP 210 L 100-22
Maximum ratings
Parameter |
Symbol |
Value |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
Operating temperature |
TA |
– 40/ +140 |
°C |
|
|
|
|
Storage temperature |
Tstg |
– 40/ +150 |
°C |
Power dissipation1) |
Ptot |
400 |
mW |
Supply voltage2) |
VIN |
7.5 |
V |
Insulation voltage between |
VI |
> 100 |
V |
terminals and casing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermal conductivity |
GthA |
³ 5 |
mW/K |
Characteristics (TA = 25 °C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nominal supply voltage |
VIN N |
5 |
V |
Total resistance, (d = ¥, I £ 1 mA) |
R1-3 |
220¼400 |
W |
Center symmetry3) (d = ¥) |
M |
£ 10 |
% |
Offset voltage4) |
V0 |
£ 130 |
mV |
(at VIN N and d = ¥) |
|
|
|
Open circuit output voltage5) |
Vout pp |
> 1000 |
mV |
(VIN N and d = 0.2 mm) |
|
|
|
Cut-off frequency |
fc |
> 20 |
kHz |
|
|
|
|
Measuring arrangements
By approaching a soft iron part close to the sensor a change in its resistance is obtained. The potential divider circuit of the magneto resistor causes a reduction in the temperature dependence of the output voltage VOUT.
1) |
Corresponding to diagram Ptot = f(TA) |
|
2) |
Corresponding to diagram VIN = f(TA) |
|
3) |
R1 –2 –R2 –3 |
> R2-3 |
|
M = ---------------------------- ´ 100% for R1-2 |
|
|
R1 –2 |
|
4) |
Corresponding to measuring circuit in Fig. 2 |
|
5) |
Corresponding to measuring circuit in Fig. 2 and arrangement as shown in Fig. 1 |
|
Semiconductor Group |
2 |
|
 Loading...
Loading...