Panasonic EW3003 User Manual
For questions or assistance with your blood pressure monitor, call us at 1-800-338-0552.
Panasonic Consumer Electronics Company
Division of Panasonic Corporation of
North America
One Panasonic Way 3D-1
Secaucus, NJ 07094
No.1 EN,SP |
|
© 2002 Matsushita Electric Works, Ltd. All Rights Reserved. |
Printed in China |
®
Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor
Monitor de Presión Arterial de Muñeca
Operating Instructions
Instrucciones de funcionamiento
Model No. EW3003
Modelo No. EW3003
Before operating this device, please read these instructions completely and save this manual for future use.
Antes de usar este dispositivo, lea completamente estas instrucciones y guarde este manual para utilizarlo como referencia en el futuro.

Panasonic Oscillometric Diagnostec™ Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor Model EW3003 is a device intended to measure systolic and diastolic blood pressure and pulse rate of an adult individual by using a pressurized cuff on the left wrist. The device is not intended for use on infants and children. The device is designed for home use only, not for ambulatory measurement.
Specification of this device including pulse rate (30 - 160 pulse/min. +/– 5%) are listed in page 20.
Blood pressure measurements determined with this device are equivalent to those obtained by a trained observer using the cuff/stethoscope auscultation method, within the limits prescribed by the American National Standard, Electronic or automated sphygmomanometers.
If you suffer from disorder of heart rhythm, known as arrhythmia only use this blood pressure monitor in consultation with your doctor. In certain cases oscillometric measurement method can produce incorrect readings.
Flash warning system for hypertensive readings are based on blood pressure values classified in the paper: “JNC 7 Express; The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES; National Institute of Health; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National High Blood Pressure Education Program; NIH Publication No. 03-5233; May 2003.” The display values are generally known, but not proven, to be an indicator of your blood pressure.
The EW3003 is not intended to be a diagnostic device. Contact your physician if prehypertensive or hypertensive values are indicated.
Table of Contents |
|
Introduction ...................................................................... |
3 |
Basics of Blood Pressure................................................. |
3 |
Important Instructions Before Use ................................... |
4 |
Precautions to Ensure Safe, Reliable Operation ............. |
6 |
Easily Check Your Blood Pressure Readings Against |
|
the JNC 7 Classification................................................... |
6 |
Name and Function of Each Product Part ....................... |
7 |
Inserting/Replacing Batteries........................................... |
8 |
When to Change Batteries............................................... |
8 |
Positioning the Pressure Cuff .......................................... |
9 |
Correct Position for Blood Pressure Measurement ......... |
10 |
Taking measurements while sitting down ...................... |
10 |
Measuring Your Blood Pressure...................................... |
13 |
Flash warning system for hypertensive readings........... |
14 |
Storing blood pressure readings.................................... |
15 |
Calling up readings from memory.................................. |
16 |
Care and Maintenance .................................................... |
17 |
Storing the Monitor .......................................................... |
17 |
Troubleshooting ............................................................... |
18 |
Specifications................................................................... |
20 |
1 |
2 |

Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Panasonic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor EW3003.
Measuring your own blood pressure is an important way of monitoring your health. High blood pressure (hypertension) is a major health problem which can be treated effectively once detected. Measuring your blood pressure between doctor visits on a regular basis in the comfort of your home, and keeping a record of the measurements, will help you monitor any significant changes in your blood pressure. Keeping an accurate record of your blood pressure will help your doctor diagnose and possibly prevent any health problems in the future.
Basics of Blood Pressure
Your heart acts like a pump, sending blood surging through your blood vessels each time it contracts. Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood pumped from the heart on the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the pressure exerted when the heart contracts and pumps blood into the arteries. Diastolic pressure is the pressure exerted when the heart expands, or relaxes. When you or your doctor take your blood pressure, both your systolic and diastolic pressures are measured. If your blood pressure measurement is 120 over 80 (120/80), for example, your systolic pressure is 120 while your diastolic pressure is 80.
3
Important Instructions Before Use
1.Do not confuse self-monitoring with self-diagnosis. Blood pressure measurements should only be interpreted by a health professional who is familiar with your medical history.
2.If you are taking medication, consult with your physician to determine the most appropriate time to measure your blood pressure. NEVER change a prescribed medication without first consulting with your physician.
3.For persons with irregular or unstable circulation resulting from diabetes, liver disease, arteriosclerosis or other medical conditions, there may be variations in blood pressure values measured at the wrist versus at the upper arm. Monitoring the trends in your blood pressure taken at either the arm or the wrist is nevertheless useful and important.
4.Blood pressure can vary based on many factors, including age, gender, weight and physical condition. In general, a person’s blood pressure is lower during sleep and higher when he or she is active. Blood pressure can change easily in response to physiological changes. The setting in which a person’s blood pressure is measured can also affect the results.
Having one’s blood pressure measured by a healthcare professional in a hospital or clinic can cause nervousness and may result in a temporarily elevated reading. Because blood pressure measurements taken in a clinical setting can vary considerably from those taken at home, a person’s blood pressure should be measured not only occasionally in the doctor’s office, but also on a regular basis at home. Also, if you find that your blood pressure is lower at home, this is not unusual. To accurately compare with your physician’s reading, take your Panasonic blood pressure monitor to your doctor’s office and compare readings in this setting.
5.People suffering from cardiac arrhythmia, vascular constriction, liver disorders or diabetes, people with cardiac pacemakers or a weak pulse, and women who are pregnant should consult their physician before measuring their blood pressure themselves. Different values may be obtained due to their condition.
6.Try to take your blood pressure measurements at the same time and under the same conditions every day.
•The ideal time to measure your blood pressure (to obtain your so-called “base blood pressure”) is in the morning just after waking up, before having breakfast and before any major activity or exercise. If this is not possible, however, try to take measurements at a specified time prior to breakfast, and before you have become active. You should relax for
4
about 5 minutes before taking the measurement.
•The following situations may cause substantial variations in blood pressure readings and should therefore be avoided at least 30 minutes prior to taking your blood pressure.
Blood pressure will be higher than usual:
-when you are excited or tense
-when you are taking a bath
-during exercising or soon after exercising
-when it is cold
-within one hour after eating
-after drinking coffee, tea or other beverages containing caffeine
-after smoking tobacco
-when your bladder is full
Blood pressure will be lower than usual:
-after taking a bath
-after drinking alcohol
7.Measurements may be impaired if this unit is used near a television, microwave oven, X-ray equipment or other devices with strong electrical fields. To prevent such interference, use the unit at a sufficient distance from such devices or turn the devices off.
8.This unit is designed for use by adults. Consult with your physician before using this unit on a child. Do not use on infants or toddlers.
9.This unit is not suitable for continuous monitoring during medical emergencies or operations.
10.Do not use the unit for any purpose other than measuring blood pressure. Do not use the unit together with other devices.
11.Improper handling of batteries may result in battery rupture or in corrosion from battery leakage. Please observe the following to ensure proper use of batteries.
a.Be sure to turn off the power after use.
b.Do not mix different types or sizes of batteries.
c.Change all batteries at the same time. Do not mix old and new batteries.
d.Be sure to insert batteries with correct polarity, as instructed.
e.Remove batteries when they are worn out, and dispose of them properly according to all applicable environmental regulations.
f.Do not disassemble batteries or throw them into a fire.
g.Do not short-circuit batteries.
h.Do not attempt to recharge the batteries included with the unit.
5
Precautions to Ensure Safe, Reliable Operation
1.Do not drop the unit. Protect it from sudden jars or shocks.
2.Do not insert foreign objects into any openings.
3.Do not attempt to disassemble the unit.
4.Do not crush the pressure cuff.
5.If the unit has been stored at temperatures below 0°C, leave it in a warm place for about 15 minutes before using it. Otherwise, the cuff may not inflate properly.
6.Do not store the unit in direct sunlight, high humidity or dust.
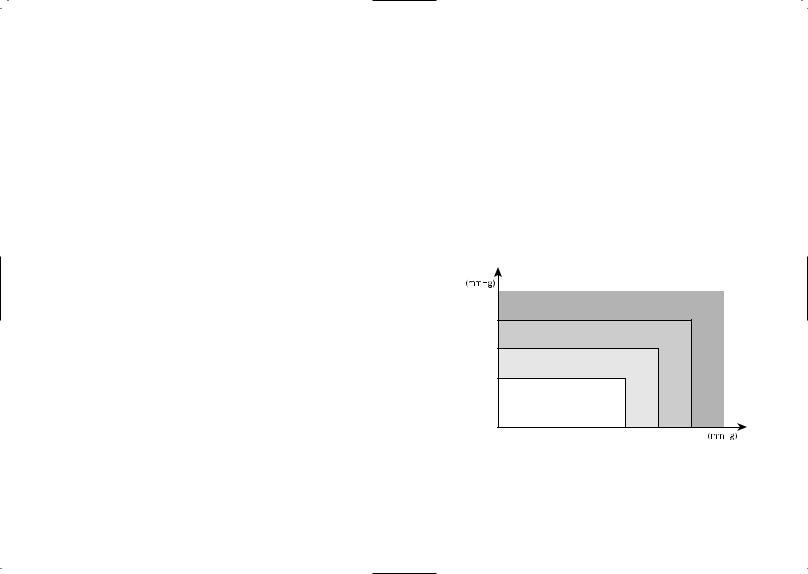
Easily Check Your Blood Pressure Readings Against the JNC 7* Classification
Blood Pressure Categories
(DBP) |
Stage 2 Hypertension |
e.g.: SBP 165 |
|
||
100 |
|
|
DBP 105 |
|
|
Pressure |
|
|
|
|
|
Stage 1 Hypertension |
e.g.: SBP 150 |
|
|||
90 |
|
|
DBP 95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prehypertension e.g.: SBP 130 |
|
||||
Blood |
|
||||
80 |
DBP |
85 |
|
||
e.g.: SBP 115 |
|
|
|
||
Normal |
|
|
|
||
Diastolic |
|
|
|
||
|
DBP 75 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120 |
140 |
160 |
Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP)
If your systolic pressure falls in one category but your diastolic pressure in another, your level is classified in the higher of the two categories.
*JNC 7: The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure
National Institute of Health (NIH) Publication; No. 03-5233, May 2003
6
 Loading...
Loading...