Ivoclar Vivadent IPS e.max CAD-on User Manual

 CAD-On
CAD-On
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
all |
ceramic |
|
|
|||||
|
|
you |
need |
|
|
||||
|
all |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
instruc tions for use

Table of Contents
product |
information |
3 IPS e.max system – one system for every indication
 CAD-On 4 Product Information
CAD-On 4 Product Information
Description of the IPS e.max CAD-on Technique
Materials for the IPS e.max CAD-on Technique
Indications, Contraindications Composition
Shade Concept
Block Concept
13 Clinical Working Steps, Model Preparation
Overview of the Fabrication Process
Shade Determination – Tooth Shade, Shade of the Prepared Tooth Preparation Guidelines
Model Preparation
Layer Thicknesses
practical notes on processing
informa- tion
19 CAD/CAM Processing
CAD Process with Sirona inLab 3D Software CAM Process with Sirona inLab MC XL
24 Finishing of the Framework and Veneering Structure
Completing the IPS e.max ZirCAD Framework Completing the IPS e.max CAD Veneering Structure
32 Glass-ceramic Fusion Process
Preparation
Fusion Process
Cleaning, Checking
Fusion/Crystallization Firing
39 Glaze, Characterization
Characterization/Glaze Firing
Optional – Adjustments with IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Add-On
43 Seating and Follow-Up Care
Possibilities for Cementation
Preparing for Cementation
Care Notes
CAD-On 46 |
General Information |
Frequently Asked Questions
Materials Combination Table
Firing Parameters
2
IPS
e.max® System –
all you need
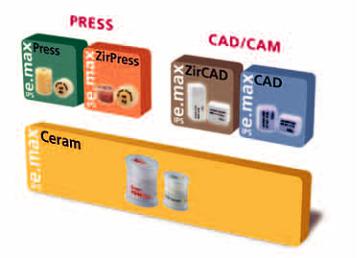
IPS e.max – one system for every indication
IPS e.max is an innovative all-ceramic system which covers the entire all-ceramic indication range – from thin veneers to 12-unit bridges.
The IPS e.max system delivers high-strength and highly esthetic materials for the Press and the CAD/CAM technologies. The system comprises lithium disilicate glass-ceramic used primarily for single-tooth restorations, high-strength zirconium oxide for long-span bridges and the veneering ceramic IPS e.max Ceram.
Every patient situation presents its own requirements and treatment objectives. IPS e.max meets these requirements, because due to the system components, you obtain exactly what you need in order to provide the optimum solution to every individual clinical case.
–The components of the Press technology include the highly esthetic IPS e.max Press lithium disilicate glass-ceramic ingots and the IPS e.max ZirPress fluorapatite glass-ceramic ingots for the fast and efficient press-on-zirconia technique.
–Depending on the case requirements, two types of materials are available for CAD/CAM techniques: the innovative IPS e.max CAD lithium disilicate blocks and the high-strength zirconium oxide IPS e.max ZirCAD.
–The nano-fluorapatite layering ceramic IPS e.max Ceram, which is used to characterize/veneer all IPS e.max components – glass or oxide ceramics –, completes the IPS e.max ystem.
IPS e.max CAD-on technique
The unique IPS e.max CAD lithium disilicate glass-ceramic (LS2) combines a high strength (360 MPa) and outstanding esthetic properties to provide durable all-ceramic restorations.
The CAD-on technique combines the advantages of IPS e.max CAD (LS2) with those of IPS e.max ZirCAD (ZrO2) in an innovative way and allows single crowns and up to 4-unit posterior bridges with outstanding strength to be fabricated.
With its outstanding final strength (>900 MPa), IPS e.max ZirCAD is the material of choice for the fabrication of bridge frameworks. The monolithic IPS e.max CAD HT veneering structure provides the excellent esthetic properties and contributes to the high strength of the completed IPS e.max CAD-on restoration.
The homogeneous glass-ceramic bond between the ZrO2 framework and the LS2 veneering structure is achieved by means of an innovative fusion glass-ceramic: IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect. The optimally coordinated system allows a convenient fusion of the IPS e.max ZirCAD framework and the IPS e.max CAD veneering structure.
3
IPS
e.max® CAD-on
Product Information
Description of the IPS e.max CAD-on technique
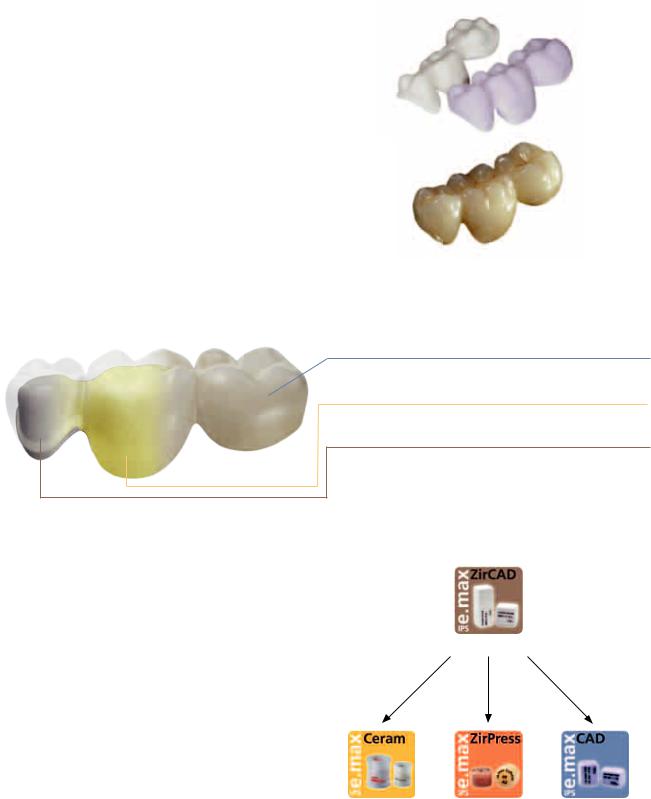
The IPS e.max CAD-on technique allows the lithium disilicate glassceramic (LS2) IPS e.max CAD to be used for the fabrication of highstrength zirconium oxide-based restorations.
The CAD/CAM-based fabrication technique IPS e.max CAD-on is characterized by the combination of the two materials: IPS e.max CAD and IPS e.max ZirCAD (zirconium oxide). The LS2 glass-ceramic is already being very successfully used for single-tooth restorations, e.g. monolithic crowns, and serves as veneering structure in the
IPS e.max CAD-on technique. The zirconium oxide material IPS e.max ZirCAD is used for the fabrication of a high-strength framework. Both components are designed in the software and milled to high precision in the milling unit. The IPS e.max ZirCAD framework is then sintered in the Programat® S1, for instance. The homogeneous allceramic fusion between the two separately milled parts is achieved with a specially developed innovative fusion glass-ceramic during the crystallization of the IPS e.max CAD material.
IPS e.max CAD veneering structure
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect fusion glass-ceramic
IPS e.max ZirCAD framework
Increasing speed and efficiency
The IPS e.max CAD-on technique increases the efficiency and productivity in the fabrication of toothor implant-borne posterior restorations. With this technique, zirconium oxide-supported IPS e.max CAD restorations which are unmatched in terms of strength and esthetics can be fabricated with little manual work in one workday. The IPS e.max CAD-on technique can be applied as an alternative to the layering or press-on technique.
Layering |
technique |
|
Zirconium oxide (ZrO2)
Press-on technique
CAD - on
technique
Nano-fluorapatite |
Fluorapatite |
Lithium disilicate (LS2) |
glass-ceramic |
glass-ceramic |
Glass-ceramic |
4

Materials for the IPS e.max CAD-on technique
IPS e.max CAD
IPS e.max CAD is a lithium disilicate glass-ceramic block for the CAD/CAM technique. It is manu factured using an innovative process which provides an impressive homogeneity of the material. The block can be processed very easily in a CAD/ CAM unit in this crystalline intermediate stage (metasilicate). The typical and striking colour of IPS e.max CAD ranges from whitish to blue and bluish-grey. This shade is a result of the composition and the microstructure of the glass-ceramic. The strength of the material in this processable intermediate phase is 130–150 MPa.
The crystallization takes places in a combined IPS e.max CAD-on Fusion/Crystallization firing in an Ivoclar Vivadent ceramic furnace (e.g. Programat® P700). This leads to a change in the microstructure in the IPS e.max CAD material,
during of which lithium disilicate crystals grow. The final physical properties, such as the flexural strength of 360 MPa, and the desired optical properties are achieved through the transformation of the microstructure.
IPS e.max ZirCAD
IPS e.max ZirCAD is a pre-sintered yttrium- stabilized zirconium oxide block for the CAD/CAM technique. The blocks are available both shaded and unshaded. IPS e.max ZirCAD can be processed very easily in a CAD/CAM unit in its partly sintered, "chalk-like" state. Milling is carried out with an enlargement of the framework of approximately 20–25%. Given the controlled manufacturing process of the blocks, combined with an coordinated sintering process in a high temperature furnace (e.g. Programat S1) the shrinkage of the enlarged milled frameworks can be controlled in such a way that excellent accuracy of fit can be achieved. During the sintering procedure, the final material-specific properties of IPS e.max ZirCAD are achieved. In the process, a structure that is densified to more than 99% is created, which features a high flexural strength (>900 MPa) combined with high fracture toughness (5.5 MPa m0.5) and thus fully meets the clinical requirements presented by masticatory forces – particularly in the posterior region.
CTE (100-400°C) [10-6 |
/K] |
10.2 |
CTE (100-500°C) [10-6 |
/K] |
10.5 |
Flexural strength (biaxial) [MPa]* |
360 |
|
Fracture toughness [MPa m0.5] |
2.25 |
|
Modulus of elasticity [GPa] |
95 |
|
Vickers hardness [MPa] |
|
5800 |
|
|
|
Chem. solubility [µg/cm2]* |
40 |
|
Crystallization temperature [°C] |
840 – 850 |
|
*according to ISO 6872 |
|
|
CTE (100-400°C) [10-6 |
/K] |
10.8 |
CTE (100-500°C) [10-6 |
/K] |
10.8 |
Flexural strength (biaxial) [MPa]* |
900 |
|
Fracture toughness [MPa m0.5] |
5.5 |
|
Vickers hardness [MPa] |
|
13000 |
Chem. solubility [µg/cm2]* |
1 |
|
Sinter temperature [°C] |
1500 |
|
|
|
|
*according to ISO 6872
5

IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect is a specially developed fusion glass-ceramic which is used to create a homogeneous bond between the IPS e. max ZirCAD framework and the IPS e.max CAD veneering structure during the IPS e.max CAD-on Fusion/Crystallization firing.
The shades of the fusion glass-ceramic are adjusted in such a way that the IPS e.max ZirCAD shades MO 0 to MO 4 combined with the IPS e.max CAD shades correspond to the shades of the IPS e.max shade concept. By combining the brighter
IPS e.max ZirCAD framework with the translucent IPS e.max CAD HT veneering structure and the harmonizing IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect material, restorations can be fabricated which exhibit outstanding esthetic properties.
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect is a pre-dosed, ready-to-use powder/liquid system available in single doses and nine shades.
The precisely adjusted powder/liquid mixture of IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect turns liquid when vibrated (with the Ivomix). This allows the material
to be mixed and the components to be joined on the Ivomix. Without mechanical influence (vibration) IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect turns stable again, which enables the joined restoration to be checked in the articulator. This special property is known as thixotropy.
1 µm
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect
CTE (100-400°C) [10-6 |
/K] |
9.5 |
CTE (100-500°C) [10-6 |
/K] |
9.2 |
Flexural strength (biaxial) [MPa]* |
160 |
|
Chem. solubility [µg/cm2]* |
10 |
|
Fusion temperature [°C] |
840 |
|
|
|
|
*according to ISO 6872
6

10 µm
After the IPS e.max CAD-on Fusion/Crystallization firing at 840°C / 1544 °F the sintered material exhibits a high strength of 160 MPa and forms a homogeneous bond both to the IPS e.max ZirCAD freamework and the IPS e.max CAD veneering structure. This homogeneous bond is clearly visible on both material interfaces in SEM images.
The sintering temperature of IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect has been adjusted to the crystallization temperature of IPS e.max CAD so that the fusion process and the crystallization of IPS e.max CAD can be conducted in one firing (Fusion/Crystallization firing).
The IPS e.max CAD crystallization program was used as a basis for the IPS e.max CAD-on Fusion/ Crystallization firing. The pre-drying of the restoration including the fusion area is an important partial step of the firing process. As the even drying of the fusion glass-ceramic takes place through the fusion gap, the fused restoration must be predried. The specific pre-drying takes place by means of a controlled process in a suitable ceramic furnace. An insufficient or too quick a drying might result in the veneering structure being completely or partially lifted off the framework. Furthermore, the heating rate and the holding time at 820 °C / 1508 °F have been adjusted so as to ensure an even heating of the entire restoration. At the end of the program cycle, the longterm cooling has been expanded to 600 °C / 1112 °F. Due to the complexity of the specially developed firing program, the ceramic furnace must meet strict requirements.
|
|
|
IPS e.max CAD |
100 µm |
|
|
|
|
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect
IPS e.max ZirCAD
IPS e.max CAD-on fusion area
10 µm
7

Uses
Indications
−Crowns
−Splinted crowns
−3- to 4-unit bridges
−Implant superstructure crown
−Implant superstructure splinted crown
−Implant superstructure 3- to 4-unit bridges
Contraindications
−Restorations with more than two connected bridge pontics
−Two bridge pontics as extension units
−Very deep sub-gingival preparations
−Patients with severely reduced residual dentition
−Patients suffering from bruxism
−Any other use not listed in the indications.
−Use of IPS e.max Ceram layering materials (layering technique, cut-back technique)
−Use of IPS e.max Ceram Glaze, Shades, Essences (staining technique)
Important note:
The fabrication of IPS e.max CAD HT bridges which are not supported by a zirconium oxide structure is contraindicated.
Important processing restrictions
Failure to observe the following restrictions may result in failure and defective restorations:
−Milling of IPS e.max CAD and IPS e.max ZirCAD with non- compatible CAD/CAM systems.
−Failure to observe the necessary minimum connector and restoration thicknesses
−Sintering of IPS e.max ZirCAD in a non-compatible high-temperature furnace
−Conducting the Fusion/Crystallization firing or the Characterization/Glaze firing in a ceramic furnace which has not been approved and which is not recommended
−Conducting the Fusion/Crystallization firing or the Characterization/Glaze firing with deviating parameters
−Conducting the Fusion/Crystallization firing or the Characterization/Glaze firing in a non-calibrated ceramic furnace
−Conducting the Fusion/Crystallization firing or the Characterization/Glaze firing in a high-temperatur furnace (e.g. Programat S1)
−Mixing of IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Glaze, Shades and Stains with other ceramic materials (e.g. IPS e.max Ceram Glaze, Stains and Essences).
−Wetting or rewetting the IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect (fusion glass-ceramic)
−Mixing of IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect with other ceramic materials in general
−Using a vibrator other than Ivomix
Side effects
If patients are known to be allergic to any of the components in the materials, IPS e.max restorations should not be used.
Composition
–IPS e.max CAD blocks
Components: SiO2
Additional components: Li2O, K2O, MgO, Al2O3, P2O5 and other oxides
–IPS e.max ZirCAD blocks
Components: ZrO2
Additional components: HfO2, A2O3, Y2O3 and other oxides
–IPS e.max ZirCAD Colouring Liquid
Components: Water, ethanol, colouring salts, additives
–IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect
Components: Oxides, water, butandiol and chloride
–IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Glaze, Shades and Stains
Components: Oxide, glycols
–IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Glaze Liquid
Components: Butandiol
–IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Add-On Incisal, Dentin, Connect
Components: Oxides
–IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Add-On Liquid allround
Components: Water, butandiol and chloride
–IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Add-On Liquid longlife
Components: Water, butandiol and chloride
–IPS Object Fix Putty / Flow
Components: Oxides, water, thickening agent
–IPS Contrast Spray Labside
Components: Pigment suspension in ethanol, propellant: Propane/butane mixture
Warning
–Do not inhale ceramic dust – use exhaust air discharge and mouth protection.
–IPS Contrast Spray Labside must not be used intraorally.
8

Scientific Data
Further scientific data (i.e. strength, wear, biocompatibility) are contained in the “Scientific Documentaion IPS e.max CAD-on”.
This Scientific Documentation can be obtained from Ivoclar Vivadent.
For further information about all-ceramics in general, please refer to the Ivoclar Vivadent Report No. 16 and 17.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scientific |
Documentation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9

Shade Concept
In the CAD-on technique, the desired restoration shade is the result of the combination of:
− the shade of the framework |
(IPS e.max ZirCAD MO) |
− the shade of the fusion glass-ceramic |
(IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect) |
− the shade of the veneering structure |
(IPS e.max CAD HT) |
− characterizations |
(IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Shades, Stains) |
The desired esthetic properties can be specifically achieved if the correct materials which correspond to the tooth shade are selected.
Note: If other combinations are selected (e.g. different zirconium oxide shades), the final shade may differ.
optional
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Desired tooth shade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BL1 |
BL2 |
|
BL3 |
BL4 |
A1 |
|
A2 |
A3 |
|
A3.5 |
A4 |
B1 |
|
B2 |
|
B3 |
|
B4 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
|
D2 |
D3 |
|
D4 |
IPS e.max ZirCAD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MO 0 |
|
MO 1 |
MO 2 |
– |
|
MO 1 |
|
– |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
shaded |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IPS e.max ZirCAD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
non-shaded |
|
|
|
|
|
MO 0 |
MO 0 |
|
MO 0 |
|
MO 0 |
|
|
|
|
MO 0 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
+ |
|
MO 0 |
|
|
+ |
|
+ |
|
+ |
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
IPS e.max ZirCAD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CL 1 |
|
CL 2 |
|
CL 1 |
|
CL 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
CL 4 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CL 4 |
|
|
|
|
CL 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Colouring Liquid * |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IPS e.max CAD |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
5 |
|
6 |
9 |
3 |
|
4 |
|
7 |
|
|
8 |
|
9 |
|
|
8 |
|
9 |
||||
Crystall./Connect |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IPS e.max CAD HT |
BL11 |
BL2 |
|
BL31 |
BL41 |
A1 |
|
A2 |
A3 |
|
A3.5 |
A41 |
B1 |
|
B2 |
|
B31 |
|
B41 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
|
C31 |
C41 |
|
D2 |
D31 |
|
D41 |
IPS e.max CAD |
|
|
SH 0 |
|
|
|
|
SH 1 |
|
|
|
|
SH 2 |
|
|
|
|
SH 3 |
|
|
|
SH 4 |
|
|
||||||
Crystall./Shade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IPS e.max CAD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crystall./Shade |
|
|
|
|
SH I1 |
|
|
|
|
|
SH I2 |
|
|
|
SH I1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SH I2 |
|
|
|
|
||||
Incisal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IPS e.max CAD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
white, creme, sunset, copper, olive, khaki, mahogany |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Crystall./Stains |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*The range of available products may vary from country to country.
1 IPS e.max CAD HT B40 blocks are available in 10 shades. To create the desired tooth shade, select the closest block shade in the respective shade group and determine the final tooth shade by means of Stains.
Note:
Do not use IPS e.max Ceram layering materials and Shades, Essences or Glaze materials
in conjunction with the IPS e.max CAD-on technique .
10
Translucency level
High
Translucency
Low
Translucency
Medium
Opacity
CR %
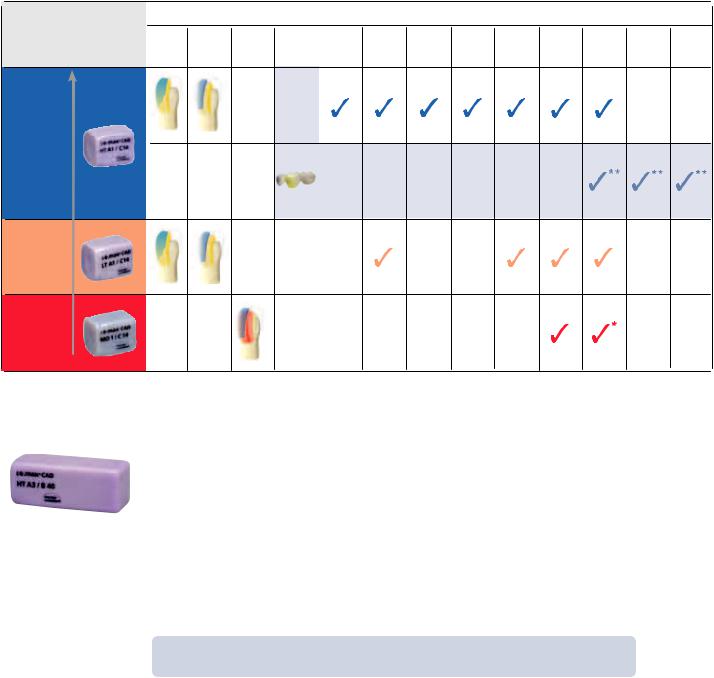
Block Concept
Block concept IPS e.max CAD
IPS e.max CAD is basically available in three levels of translucency (HT, LT, MO) and three block sizes (I12, C14, B40). Depending on the translucency level, different block sizes are available. For esthetic reasons, IPS e.max CAD HT blocks are used in the IPS e.max CAD-on technique.
|
Processing technique |
|
|
|
|
Indications |
|
|
|
|
||
Staining |
Cut-back |
Layering |
CAD-on |
Thin |
Veneers |
Inlays |
Onlays |
Partial |
Anterior |
Posterior |
Splinted |
3- to 4-unit |
technique |
technique |
technique |
technique |
veneers |
|
|
|
crowns |
crowns |
crowns |
crowns |
posterior |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bridges |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* up to the second premolar ** IPS e.max CAD-on technique in conjunction with IPS e.max ZirCAD
IPS e.max CAD HT (High Translucency)
IPS e.max CAD HT (High Translucency) B40 blocks are available in 9 A–D shades and 1 Bleach BL shade. For the fabrication of IPS CAD-on bridge restorations, only B40 blocks are used. Due to their translucency, IPS e.max CAD HT blocks are ideally suitable for the fabrication of IPS e.max CAD-on restorations in the staining technique. IPS e.max CAD-on restorations fabricated from HT blocks exhibit a lifelike brightness value and translucency. To characterize and glaze IPS e.max CAD-on restorations, only the IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Shades, Stains and Glaze are used.
The entire IPS e.max delivery program can be found at www.ivoclarvivadent.com.
11

IPS e.max ZirCAD block concept
IPS e.max ZirCAD is currently supplied in 9 block sizes (see table) and 3 shades
(MO 0, MO 1, MO 2). This provides utmost flexibility during block selection, with regard to both the shade and the block size.
The following IPS e.max ZirCAD blocks are available:
Block designation |
Length |
|
Dimensions in mm |
Width |
|
(width x length x height) |
||
|
||
|
Height |
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab C 13
13.2 x 13.2 x 14.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab C 15
14.5 x 15.5 x 18.5
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab C 15 L
15.4 x 19.0 x 20.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab B 40
14.2 x 15.5 x 40.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab B 40L
15.4 x 19.0 x 39.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab B 55
15.5 x 19.0 x 55.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab B 65
22.0 x 25.0 x 65.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab B 65 L-17
17.0 x 40.0 x 65.0
IPS e.max ZirCAD for inLab B 85 L-22
22.0 x 40.0 x 85.0
MO 0 |
MO 1 |
MO 2 |
|
|
|
The entire IPS e.max delivery program can be found at www.ivoclarvivadent.com.
12

|
e.max CAD-on |
IPS |
® |
|
Clinical Working Steps, Model Preparation
IPS e.max CAD-on technique
Working steps
Preparation, shade determination, impression-taking
|
Model fabrication |
|||
|
Scan and design (CAD) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
CAM |
process |
|
|
|
IPS e.max ZirCAD framework |
|
|
||
Pre-shaded block |
Shading with |
CAM process |
||
Colouring Liquids |
IPS e.max CAD |
|||
|
||||
|
|
veneering structure |
||
Drying |
|
|
||
Sintering |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
Finishing/checking |
|||
|
fit of framework and |
|||
|
veneering structure |
|||
|
Fusing framework and |
|||
|
veneering structure |
|||
Fusion/Crystallization firing
Characterization/Glaze firing
Preparing for cementation
Conditioning
Cementation
Check of articulation / occlusion + polishing
(after intraoral adjustment)
Recall
13
Ivoclar Vivadent Products
OptraGate®
IPS® Natural Die Material
Shade Guide
IPS® Contrast Spray Labside
IPS e.max ZirCAD MO
IPS e.max ZirCAD Colouring Liquids*
IPS e.max CAD HT
Programat® S1
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./Connect
Ivomix
IPS e.max CAD Crystall./
Shades, Stains, Glaze, Add-On
IPS e.max CAD Crystallization
Tray and Pins
IPS Object Fix Putty and Flow
Programat
P300, P500, P700, EP 5000
Monobond® Plus
Multilink® Automix
SpeedCEM
Vivaglass® CEM
bluephase®
OptraFine®
Proxyt®
*The range of available products may vary from country to country.
Clinical Working Steps, Model Fabrication

Shade Determination – Tooth Shade, Shade of the Prepared
Tooth
Optimum integration in the oral cavity of the patient is the prerequisite for a true-to-nature all-ceramic restoration. To achieve this, the dentist must observe the following guidelines and notes.
The overall esthetic result of an all-ceramic restoration is influenced by the following factors:
•Shade of prepared tooth (natural preparation, core build-up, abutment, implant)
•Shade of the restoration (framework shade, veneer, characterization)
•Shade of the cementation material
The optical effect of the preparation shade must not be underestimated during the fabrication of highly esthetic restorations. For that reason, the shade of the preparation should be determined together with the desired tooth shade in order to select the suitable block. Especially with severely discoloured preparations or non-tooth-shaded build-ups, this is of utmost importance. In order to achieve the desired esthetics, the shade of the prepared tooth must first be determined.
Preparation Shade |
Restoration Shade |
||
– Prepared natural tooth |
– Framework shade |
||
– |
Core build-up |
– |
Veneer |
– |
Implant, abutment |
– |
Characterization |
Desired tooth shade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cementation material |
|
|
Responsibility of the Dental Office |
Responsibility of the Laboratory |
|
Shade determination of the natural tooth |
|
|
After tooth cleaning, the tooth shade of the non-prepared tooth and/or the adjacent teeth is determined with the help of a shade guide. Individual characteristics have to be considered when determining the tooth shade. If a crown preparation is planned, for example, the cervical shade should also be determined. In order to achieve the best possible true-to-nature results, shade determination should be carried out at daylight. Furthermore, the patient should not wear clothes of intensive colours and/or lipstick.
Die shade selection
In order to facilitate the reproduction of the desired tooth shade, the shade of the preparation is determined with the help of the IPS Natural Die Material shade guide. This enables the technician to fabricate a model die similar to the preparation of the patient, on the basis
the correct shade and brightness values of the all-ceramic restorations may be selected.
14
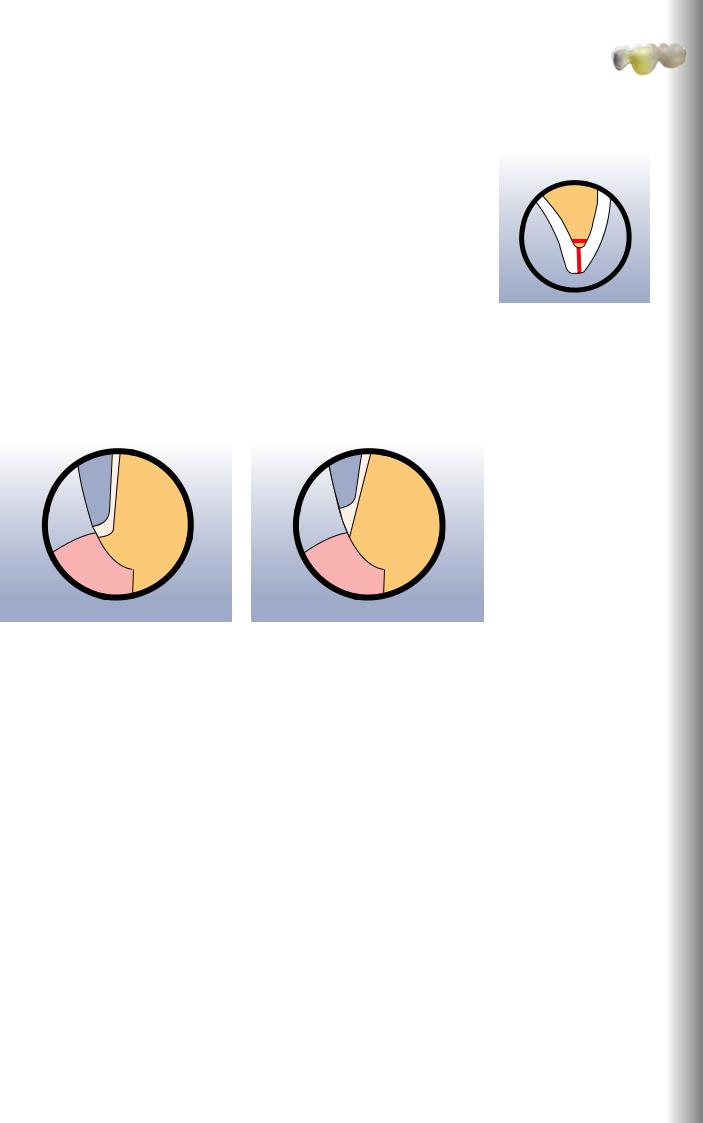
Preparation Guidelines
Basic preparation guidelines for all-ceramic restorations
–No angles or edges
–The incisal edge of the preparation, particularly for anterior teeth, should be at least 1.0 mm (milling tool geometry) in order to permit optimum milling during CAD/CAM processing.
The following notes should also be observed when using the IPS e.max CAD-on technique:
The zirconium oxide framework is designed in the software with a circumferential collar on abutment teeth / crown framework due to technical reasons. The height of this collar is mainly determined by the shape of preparation and the designed fully anatomical tooth shape.
–A very pronounced shoulder/chamfer results in a thin zirconium oxide collar.
–A minor shoulder/chamfer results in a wider zirconium oxide collar.
1.0
1.5
Clinical Working Steps, Model Fabrication
A very pronounced shoulder/chamfer results in a thin zirconium oxide collar.
A minor shoulder/chamfer results in a wider zirconium oxide collar.
15

Singe Crowns to 3-Unit Bridges
Anterior Crown
 1.0
1.0
1.0
1.5 1.0 1.5
1.5
−Reduce the anatomical shape and observe the stipulated minimum thickness. Prepare a circular shoulder with rounded inner edges or a chamfer at a degree of approximately 10°-30°. Width of the circular shoulder/ chamfer at least 1.0 mm.
−Reduce the incisal crown third by approx. 1.5 mm. Reduce the vestibular and/or oral area by approx. 1.5 mm.
−For conventional and/or self-adhesive cementation, the preparation must demonstrate retentive surfaces.
Posterior Crown
1.51.5
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
6° |
−Reduce the anatomical shape and observe the stipulated minimum thickness. Prepare a circular shoulder with rounded inner edges or a chamfer at a degree of approximately 10°-30°. Width of the circular shoulder/ chamfer at least 1.0 mm.
−Reduce the incisal crown third by approx. 1.5 mm. Reduce the vestibular and/or oral area by approx. 1.5 mm.
−For conventional and/or self-adhesive cementation, the preparation must demonstrate retentive surfaces.
4-Unit Bridges
|
|
1.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
|
|
1.5 |
1.5 |
|
|
|
||
1.5 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
6° |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
−Evenly reduce the anatomical shape and observe the stipulated minimum thickness. Prepare a circular shoulder with rounded inner edges or a chamfer with a width of at least 1.0 mm.
−Reduce the incisal crown third – incisal and/or occlusal - by approx. 1.5 mm.
−For anterior crowns, the reduction in the labial and/or palatal/lingual area is at least 1.5 mm. The incisal edge of the preparation should be at least 1.0 mm (milling tool geometry) in order to permit optimum milling of the incisal area during CAD/CAM processing.
−For posterior crowns, the reduction in the buccal and/or palatal/lingual area is at least 1.5 mm.
−For conventional and/or self-adhesive cementation, the preparation must demonstrate retentive surfaces
16
 Loading...
Loading...